Segluromet prior authorization resources
Most recent state uniform prior authorization forms
Dosage & administration
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- Assess renal function prior to initiation and as clinically indicated. (2.1 )
- Correct volume depletion before initiation. (2.1 )
- Individualize the starting dosage based on the patient's current regimen. (2.2 )
- Maximum recommended dosage is 7.5 mg ertugliflozin/1,000 mg metformin orally twice daily. (2.2 )
- Take orally twice daily with meals, with gradual dose escalation. (2.2 )
- Do not use in patients with an estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) below 30 mL/minute/1.73 m 2 .
- Use is not recommended in patients with an eGFR less than 45 mL/min/1.73 m 2 . (2.2 )
- Use is contraindicated in patients with severe renal impairment (eGFR less than 30 mL/min/1.73 m 2 ), end stage-renal disease (ESRD), or on dialysis. (2.2 )
- SEGLUROMET may need to be discontinued at time of, or prior to, iodinated contrast imaging procedures. (2.3 )
- Withhold SEGLUROMET for at least 4 days, if possible, prior to surgery or procedures associated with prolonged fasting. (2.4 )
Prior to Initiation of SEGLUROMET
- Assess renal function before initiating SEGLUROMET and as clinically indicated [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) ] .
- Assess volume status. In patients with volume depletion, correct this condition before initiating SEGLUROMET [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4) and Use in Specific Populations (8.5 , 8.6) ].
Recommended Dosage
- Individualize the starting dosage of SEGLUROMET, ertugliflozin and metformin hydrochloride (HCI), based on the patient’s current regimen, while not exceeding the maximum recommended oral daily dosage of 15 mg ertugliflozin and 2,000 mg metformin HCl:
- In patients on metformin HCI, switch to SEGLUROMET tablets containing 2.5 mg ertugliflozin, with a similar total oral daily dosage of metformin HCl.
- In patients on ertugliflozin, switch to SEGLUROMET tablets containing 500 mg metformin HCl, with a similar total oral daily dosage of ertugliflozin.
- In patients already treated with ertugliflozin and metformin HCl, switch to SEGLUROMET tablets containing the same total oral daily dosage of ertugliflozin and a similar daily dosage of metformin HCI.
- Take SEGLUROMET orally twice daily with meals, with gradual dosage escalation for those initiating metformin HCl to reduce the gastrointestinal side effects due to metformin [see Adverse Reactions (6.1) ].
- Dosing may be adjusted based on effectiveness and tolerability.
- Use of SEGLUROMET is not recommended in patients with an estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) less than 45 mL/min/1.73 m 2 .
- Use of SEGLUROMET is contraindicated in patients with severe renal impairment (eGFR less than 30 mL/min/1.73 m 2 ), end stage-renal disease (ESRD), or on dialysis [see Contraindications (4) ] .
Discontinuation for Iodinated Contrast Imaging Procedures
Discontinue SEGLUROMET at the time of, or prior to, an iodinated contrast imaging procedure in patients with an eGFR less than 60 mL/min/1.73 m 2 ; in patients with a history of liver disease, alcoholism or heart failure; or in patients who will be administered intra-arterial iodinated contrast. Re-evaluate eGFR 48 hours after the imaging procedure; restart SEGLUROMET if renal function is stable [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) ] .
2.4 Temporary Interruption for Surgery
Withhold SEGLUROMET for at least 4 days, if possible, prior to surgery or procedures associated with prolonged fasting. Resume SEGLUROMET when the patient is clinically stable and has resumed oral intake [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.2) ].

By using PrescriberAI, you agree to the AI Terms of Use.
Segluromet prescribing information
WARNING: LACTIC ACIDOSIS
Postmarketing cases of metformin-associated lactic acidosis have resulted in death, hypothermia, hypotension, and resistant bradyarrhythmias. The onset of metformin-associated lactic acidosis is often subtle, accompanied only by nonspecific symptoms such as malaise, myalgias, respiratory distress, somnolence, and abdominal pain. Metformin-associated lactic acidosis was characterized by elevated blood lactate levels (>5 mmol/Liter), anion gap acidosis (without evidence of ketonuria or ketonemia), an increased lactate/pyruvate ratio, and metformin plasma levels generally >5 mcg/mL [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) ] .
Risk factors for metformin-associated lactic acidosis include renal impairment, concomitant use of certain drugs (e.g., carbonic anhydrase inhibitors such as topiramate), age 65 years old or greater, having a radiological study with contrast, surgery and other procedures, hypoxic states (e.g., acute congestive heart failure), excessive alcohol intake, and hepatic impairment.
Steps to reduce the risk of and manage metformin-associated lactic acidosis in these high risk groups are provided in the Full Prescribing Information [see Dosage and Administration (2.2) , Contraindications (4) , Warnings and Precautions (5.1) , Drug Interactions (7) , and Use in Specific Populations (8.6 , 8.7 )] .
If metformin-associated lactic acidosis is suspected, immediately discontinue SEGLUROMET and institute general supportive measures in a hospital setting. Prompt hemodialysis is recommended [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) ] .
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
SEGLUROMET ® is indicated as an adjunct to diet and exercise to improve glycemic control in adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Limitations of Use
Not recommended for use to improve glycemic control in patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) ].
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- Assess renal function prior to initiation and as clinically indicated. (2.1 )
- Correct volume depletion before initiation. (2.1 )
- Individualize the starting dosage based on the patient's current regimen. (2.2 )
- Maximum recommended dosage is 7.5 mg ertugliflozin/1,000 mg metformin orally twice daily. (2.2 )
- Take orally twice daily with meals, with gradual dose escalation. (2.2 )
- Do not use in patients with an estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) below 30 mL/minute/1.73 m 2 .
- Use is not recommended in patients with an eGFR less than 45 mL/min/1.73 m 2 . (2.2 )
- Use is contraindicated in patients with severe renal impairment (eGFR less than 30 mL/min/1.73 m 2 ), end stage-renal disease (ESRD), or on dialysis. (2.2 )
- SEGLUROMET may need to be discontinued at time of, or prior to, iodinated contrast imaging procedures. (2.3 )
- Withhold SEGLUROMET for at least 4 days, if possible, prior to surgery or procedures associated with prolonged fasting. (2.4 )
Prior to Initiation of SEGLUROMET
- Assess renal function before initiating SEGLUROMET and as clinically indicated [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) ] .
- Assess volume status. In patients with volume depletion, correct this condition before initiating SEGLUROMET [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4) and Use in Specific Populations (8.5 , 8.6) ].
Recommended Dosage
- Individualize the starting dosage of SEGLUROMET, ertugliflozin and metformin hydrochloride (HCI), based on the patient’s current regimen, while not exceeding the maximum recommended oral daily dosage of 15 mg ertugliflozin and 2,000 mg metformin HCl:
- In patients on metformin HCI, switch to SEGLUROMET tablets containing 2.5 mg ertugliflozin, with a similar total oral daily dosage of metformin HCl.
- In patients on ertugliflozin, switch to SEGLUROMET tablets containing 500 mg metformin HCl, with a similar total oral daily dosage of ertugliflozin.
- In patients already treated with ertugliflozin and metformin HCl, switch to SEGLUROMET tablets containing the same total oral daily dosage of ertugliflozin and a similar daily dosage of metformin HCI.
- Take SEGLUROMET orally twice daily with meals, with gradual dosage escalation for those initiating metformin HCl to reduce the gastrointestinal side effects due to metformin [see Adverse Reactions (6.1) ].
- Dosing may be adjusted based on effectiveness and tolerability.
- Use of SEGLUROMET is not recommended in patients with an estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) less than 45 mL/min/1.73 m 2 .
- Use of SEGLUROMET is contraindicated in patients with severe renal impairment (eGFR less than 30 mL/min/1.73 m 2 ), end stage-renal disease (ESRD), or on dialysis [see Contraindications (4) ] .
Discontinuation for Iodinated Contrast Imaging Procedures
Discontinue SEGLUROMET at the time of, or prior to, an iodinated contrast imaging procedure in patients with an eGFR less than 60 mL/min/1.73 m 2 ; in patients with a history of liver disease, alcoholism or heart failure; or in patients who will be administered intra-arterial iodinated contrast. Re-evaluate eGFR 48 hours after the imaging procedure; restart SEGLUROMET if renal function is stable [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) ] .
2.4 Temporary Interruption for Surgery
Withhold SEGLUROMET for at least 4 days, if possible, prior to surgery or procedures associated with prolonged fasting. Resume SEGLUROMET when the patient is clinically stable and has resumed oral intake [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.2) ].
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
- Tablets: ertugliflozin 2.5 mg and metformin HCl 500 mg, pink, oval, debossed with "2.5/500" on one side and plain on the other side.
- Tablets: ertugliflozin 2.5 mg and metformin HCl 1,000 mg, pink, oval, debossed with "2.5/1000" on one side and plain on the other side.
- Tablets: ertugliflozin 7.5 mg and metformin HCl 500 mg, red, oval, debossed with "7.5/500" on one side and plain on the other side.
- Tablets: ertugliflozin 7.5 mg and metformin HCl 1,000 mg, red, oval, debossed with "7.5/1000" on one side and plain on the other side.
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
- Pregnancy: Advise females of the potential risk to a fetus, especially during the second and third trimesters. (8.1 )
- Lactation: Breastfeeding not recommended. (8.2 )
- Females and Males of Reproductive Potential: Advise premenopausal females of the potential for an unintended pregnancy. (8.3 )
- Geriatrics: Higher incidence of adverse reactions related to reduced intravascular volume. (8.5 )
- Renal impairment: Higher incidence of adverse reactions related to reduced intravascular volume and renal function. (8.6 )
- Hepatic impairment : Avoid use in patients with hepatic impairment. (8.7 )
Pregnancy
Risk Summary
Based on animal data showing adverse renal effects, from ertugliflozin, SEGLUROMET is not recommended during the second and third trimesters of pregnancy. Published studies with metformin use during pregnancy have not reported a clear association with metformin and major birth defect or miscarriage risk (see Data ) .
The limited available data with SEGLUROMET in pregnant women are not sufficient to determine a drug-associated risk for major birth defects or miscarriage. There are risks to the mother and fetus associated with poorly controlled diabetes in pregnancy (see Clinical Considerations ) .
In animal studies, adverse renal changes were observed in rats when ertugliflozin was administered during a period of renal development corresponding to the late second and third trimesters of human pregnancy. Doses approximately 13 times the maximum clinical dose caused renal pelvic and tubule dilatations and renal mineralization that were not fully reversible. There was no evidence of fetal harm in rats or rabbits at exposures of ertugliflozin approximately 300 times higher than the maximal clinical dose of 15 mg/day when administered during organogenesis (see Data ) .
The estimated background risk of major birth defects is 6-10% in women with pre-gestational diabetes with a HbA1c >7 and has been reported to be as high as 20-25% in women with HbA1c >10. The estimated background risk of miscarriage for the indicated population is unknown. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2-4% and 15-20%, respectively.
Clinical Considerations
Disease-Associated Maternal and/or Embryo/Fetal Risk
Poorly controlled diabetes in pregnancy increases the maternal risk for diabetic ketoacidosis, pre-eclampsia, spontaneous abortions, preterm delivery, and delivery complications. Poorly controlled diabetes increases the fetal risk for major birth defects, stillbirth, and macrosomia related morbidity.
Data
Human Data
Published data from postmarketing studies have not reported a clear association with metformin and major birth defects, miscarriage, or adverse maternal or fetal outcomes when metformin was used during pregnancy. However, these studies cannot definitely establish the absence of any metformin-associated risk because of methodological limitations, including small sample size and inconsistent comparator groups.
Animal Data
Ertugliflozin
When ertugliflozin was orally administered to juvenile rats from PND 21 to PND 90, increased kidney weight, renal tubule and renal pelvis dilatation, and renal mineralization occurred at doses greater than or equal to 5 mg/kg (13-fold human exposures, based on AUC). These effects occurred with drug exposure during periods of renal development in rats that correspond to the late second and third trimester of human renal development, and did not fully reverse within a 1-month recovery period.
In embryo-fetal development studies, ertugliflozin (50, 100 and 250 mg/kg/day) was administered orally to rats on gestation days 6 to 17 and to rabbits on gestation days 7 to 19. Ertugliflozin did not adversely affect developmental outcomes in rats and rabbits at maternal exposures that were approximately 300 times the human exposure at the maximum clinical dose of 15 mg/day, based on AUC. A maternally toxic dose (250 mg/kg/day) in rats (707 times the clinical dose) was associated with reduced fetal viability and a higher incidence of a visceral malformation (membranous ventricular septal defect). In the pre- and post-natal development study in pregnant rats, ertugliflozin was administered to the dams from gestation day 6 through lactation day 21 (weaning). Decreased post-natal growth (weight gain) was observed at maternal doses ≥100 mg/kg/day (greater than or equal to 331 times the human exposure at the maximum clinical dose of 15 mg/day, based on AUC).
Metformin HCl
Metformin did not adversely affect development outcomes when administered to rats and rabbits at doses up to 600 mg/kg/day. This represents an exposure of about 2 and 6 times the maximum recommended human dose of 2,000 mg based on body surface area comparisons for rats and rabbits, respectively. Determination of fetal concentrations demonstrated a partial placental barrier to metformin.
Lactation
Risk Summary
There is no information regarding the presence of SEGLUROMET or ertugliflozin in human milk, the effects on the breastfed infant, or the effects on milk production. Limited published studies report that metformin is present in human milk (see Data ) . However, there is insufficient information on the effects of metformin on the breastfed infant and no available information on the effects of metformin on milk production. Ertugliflozin (see Data ) and metformin are present in the milk of lactating rats. Since human kidney maturation occurs in utero and during the first 2 years of life when lactational exposure may occur, there may be risk to the developing human kidney, based on data with ertugliflozin. Because of the potential for serious adverse reactions in a breastfed infant, advise women that the use of SEGLUROMET is not recommended while breastfeeding.
Data
The lacteal excretion of radiolabeled ertugliflozin in lactating rats was evaluated 10 to 12 days after parturition. Ertugliflozin derived radioactivity exposure in milk and plasma were similar, with a milk/plasma ratio of 1.07, based on AUC. Juvenile rats directly exposed to ertugliflozin during a developmental period corresponding to human kidney maturation were associated with a risk to the developing kidney (persistent increased organ weight, renal mineralization, and renal pelvic and tubular dilatations).
Published clinical lactation studies report that metformin is present in human milk, which resulted in infant doses approximately 0.11% to 1% of the maternal weight-adjusted dosage and a milk/plasma ratio ranging between 0.13 and 1. However, the studies were not designed to definitely establish the risk of use of metformin during lactation because of small sample size and limited adverse event data collected in infants.
Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
Discuss the potential for unintended pregnancy with premenopausal women as therapy with metformin may result in ovulation in some anovulatory women.
Pediatric Use
Safety and effectiveness of SEGLUROMET in pediatric patients under 18 years of age have not been established.
Geriatric Use
SEGLUROMET
No dosage adjustment of SEGLUROMET is recommended based on age. Elderly patients are more likely to have decreased renal function. Because renal function abnormalities can occur after initiating ertugliflozin, and metformin is known to be substantially excreted by the kidneys, care should be taken in dose selection in the elderly. Assess renal function in elderly patients prior to initiating dosing and periodically thereafter [see Dosage and Administration (2.1) and Warnings and Precautions (5.1 , 5.4) ] .
Ertugliflozin
In ertugliflozin clinical trials, a total of 876 (25.7%) patients treated with ertugliflozin were 65 years and older, and 152 (4.5%) patients treated with ertugliflozin were 75 years and older. Patients 65 years and older had a higher incidence of adverse reactions related to volume depletion compared to younger patients; events were reported in 1.1%, 2.2%, and 2.6% of patients treated with comparator, ertugliflozin 5 mg, and ertugliflozin 15 mg, respectively [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4) and Adverse Reactions (6.1) ] .
In VERTIS CV, a total of 2780 (50.5%) patients treated with ertugliflozin were 65 years and older, and 595 (10.8%) patients treated with ertugliflozin were 75 years and older. Safety and efficacy were generally similar for patients age 65 years and older compared to patients younger than 65.
Metformin HCl
Controlled clinical studies of metformin did not include sufficient numbers of elderly patients to determine whether they respond differently from younger patients, although other reported clinical experience has not identified differences in responses between the elderly and young patients. In general, dose selection for an elderly patient should be cautious, usually starting at the low end of the dosing range, reflecting the greater frequency of decreased hepatic, renal, or cardiac function, and of concomitant disease or other drug therapy and the higher risk of lactic acidosis. Assess renal function more frequently in elderly patients [see Contraindications (4) , Warnings and Precautions (5.1) , and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ] .
Renal Impairment
A 26-week placebo-controlled study of 313 patients with Stage 3 Chronic Kidney Disease (eGFR ≥30 to less than 60 mL/min/1.73 m 2 ) treated with ertugliflozin did not have improvement in glycemic control.
In the VERTIS CV study, there were 1370 patients (25%) with an eGFR ≥90 mL/min/1.73 m 2 , 2929 patients (53%) with an eGFR of ≥60 to less than 90 mL/min/1.73 m 2 , 879 patients (16%) with an eGFR of ≥45 to less than 60 mL/min/1.73 m 2 , and 299 patients (5%) with eGFR of 30 to <45 mL/min/1.73 m 2 treated with ertugliflozin. Similar effects on glycemic control at Week 18 were observed in patients treated with ertugliflozin in each eGFR subgroup and also in the overall patient population.
SEGLUROMET is contraindicated in patients with severe renal impairment (eGFR less than 30 mL/min/1.73 m 2 ), ESRD, or on dialysis [see Contraindications (4) ].
No dosage adjustment is needed in patients with eGFR ≥45 mL/min/1.73 m 2 .
Metformin is substantially excreted by the kidney, and the risk of metformin accumulation and lactic acidosis increases with the degree of renal impairment.
Hepatic Impairment
Use of metformin in patients with hepatic impairment has been associated with some cases of lactic acidosis. SEGLUROMET is not recommended in patients with hepatic impairment [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) ] .
CONTRAINDICATIONS
SEGLUROMET is contraindicated in patients with:
- Hypersensitivity to ertugliflozin, metformin, or any excipient in SEGLUROMET. Reactions such as angioedema or anaphylaxis have occurred [see Adverse Reactions (6.2) ].
- Severe renal impairment (eGFR less than 30 mL/min/1.73 m 2 ), end stage-renal disease (ESRD), or on dialysis [see Use in Specific Populations (8.6) ] .
- Acute or chronic metabolic acidosis, including diabetic ketoacidosis, with or without coma.
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- Lactic Acidosis: See boxed warning . (5.1 )
- Diabetic Ketoacidosis in Patients with Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus and Other Ketoacidosis: Consider ketone monitoring in patients at risk for ketoacidosis, as indicated. Assess for ketoacidosis regardless of presenting blood glucose levels and discontinue SEGLUROMET if ketoacidosis is suspected. Monitor patients for resolution of ketoacidosis before restarting. (5.2 )
- Lower Limb Amputation: Monitor patients for infections or ulcers of lower limbs, and discontinue if these occur. (5.3 )
- Volume Depletion: May result in acute kidney injury. Before initiating, assess and correct volume status in patients with renal impairment, low systolic blood pressure, elderly patients, or patients on diuretics. Monitor for signs and symptoms during therapy. (5.4 )
- Urosepsis and Pyelonephritis: Evaluate patients for signs and symptoms of urinary tract infections and treat promptly, if indicated. (5.5 )
- Hypoglycemia: Consider a lower dose of insulin or insulin secretagogue to reduce risk of hypoglycemia when used in combination. (5.6 )
- Necrotizing Fasciitis of the Perineum (Fournier's Gangrene): Serious, life-threatening cases have occurred in both females and males. Assess patients presenting with pain or tenderness, erythema, or swelling in the genital or perineal area, along with fever or malaise. If suspected, institute prompt treatment. (5.7 )
- Genital Mycotic Infections: Monitor and treat if indicated. (5.8 )
- Vitamin B 12 Deficiency: Metformin may lower vitamin B 12 levels. Measure hematological parameters annually. (5.9 )
Lactic Acidosis
There have been postmarketing cases of metformin-associated lactic acidosis, including fatal cases. These cases had a subtle onset and were accompanied by nonspecific symptoms such as malaise, myalgias, abdominal pain, respiratory distress, or increased somnolence; however, hypothermia, hypotension and resistant bradyarrhythmias have occurred with severe acidosis. Metformin-associated lactic acidosis was characterized by elevated blood lactate concentrations (>5 mmol/Liter), anion gap acidosis (without evidence of ketonuria or ketonemia), and an increased lactate: pyruvate ratio; metformin plasma levels were generally >5 mcg/mL. Metformin decreases liver uptake of lactate increasing lactate blood levels which may increase the risk of lactic acidosis, especially in patients at risk.
If metformin-associated lactic acidosis is suspected, general supportive measures should be instituted promptly in a hospital setting, along with immediate discontinuation of SEGLUROMET. In SEGLUROMET-treated patients with a diagnosis or strong suspicion of lactic acidosis, prompt hemodialysis is recommended to correct the acidosis and remove accumulated metformin (metformin hydrochloride is dialyzable, with a clearance of up to 170 mL/minute under good hemodynamic conditions). Hemodialysis has often resulted in reversal of symptoms and recovery.
Educate patients and their families about the symptoms of lactic acidosis and if these symptoms occur instruct them to discontinue SEGLUROMET and report these symptoms to their healthcare provider.
For each of the known and possible risk factors for metformin-associated lactic acidosis, recommendations to reduce the risk of and manage metformin-associated lactic acidosis are provided below:
Renal Impairment: The postmarketing metformin-associated lactic acidosis cases primarily occurred in patients with significant renal impairment. The risk of metformin accumulation and metformin-associated lactic acidosis increases with the severity of renal impairment because metformin is substantially excreted by the kidney [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ] .
- Before initiating SEGLUROMET, obtain an eGFR.
- Use of SEGLUROMET is not recommended in patients with an eGFR less than 45 mL/min/1.73 m 2 .
- SEGLUROMET is contraindicated in patients with severe renal impairment (an eGFR less than 30 mL/min/1.73 m 2 ), end stage-renal disease (ESRD), or on dialysis.
- Obtain an eGFR at least annually in all patients taking SEGLUROMET. In patients at increased risk for the development of renal impairment (e.g., the elderly), renal function should be assessed more frequently.
Drug Interactions:The concomitant use of SEGLUROMET with specific drugs may increase the risk of metformin-associated lactic acidosis: those that impair renal function, result in significant hemodynamic change, interfere with acid-base balance or increase metformin accumulation (e.g., cationic drugs) [see Drug Interactions (7) ] . Therefore, consider more frequent monitoring of patients.
Age 65 or Greater:The risk of metformin-associated lactic acidosis increases with the patient's age because elderly patients have a greater likelihood of having hepatic, renal, or cardiac impairment than younger patients. Assess renal function more frequently in elderly patients [see Use in Specific Populations (8.5) ] .
Radiological Studies with Contrast:Administration of intravascular iodinated contrast agents in metformin-treated patients has led to an acute decrease in renal function and the occurrence of lactic acidosis. Stop SEGLUROMET at the time of, or prior to, an iodinated contrast imaging procedure in patients with an eGFR less than 60 mL/min/1.73 m 2 ; in patients with a history of hepatic impairment, alcoholism, or heart failure; or in patients who will be administered intra-arterial iodinated contrast. Re-evaluate eGFR 48 hours after the imaging procedure, and restart SEGLUROMET if renal function is stable.
Surgery and Other Procedures:Withholding of food and fluids during surgical or other procedures may increase the risk for volume depletion, hypotension and renal impairment. SEGLUROMET should be temporarily discontinued while patients have restricted food and fluid intake.
Hypoxic States:Several of the postmarketing cases of metformin-associated lactic acidosis occurred in the setting of acute congestive heart failure (particularly when accompanied by hypoperfusion and hypoxemia). Cardiovascular collapse (shock), acute myocardial infarction, sepsis, and other conditions associated with hypoxemia have been associated with lactic acidosis and may also cause pre-renal azotemia. When such events occur, discontinue SEGLUROMET.
Excessive Alcohol Intake:Alcohol potentiates the effect of metformin on lactate metabolism and this may increase the risk of metformin-associated lactic acidosis. Warn patients against excessive alcohol intake while receiving SEGLUROMET.
Hepatic Impairment:Patients with hepatic impairment have developed metformin-associated lactic acidosis. This may be due to impaired lactate clearance resulting in higher lactate blood levels. Therefore, avoid use of SEGLUROMET in patients with clinical or laboratory evidence of hepatic disease.
Diabetic Ketoacidosis in Patients with Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus and Other Ketoacidosis
In patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus, SEGLUROMET significantly increases the risk of diabetic ketoacidosis, a life-threatening event, beyond the background rate. In placebo-controlled trials of patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus, the risk of ketoacidosis was markedly increased in patients who received sodium glucose transporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors compared to patients who received placebo; this risk may be greater with higher doses. SEGLUROMET is not indicated for glycemic control in patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus.
Type 2 diabetes mellitus and pancreatic disorders (e.g., history of pancreatitis or pancreatic surgery) are also risk factors for ketoacidosis. There have been postmarketing reports of fatal events of ketoacidosis in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus using SGLT2 inhibitors.
Precipitating conditions for diabetic ketoacidosis or other ketoacidosis include under-insulinization due to insulin dose reduction or missed insulin doses, acute febrile illness, reduced caloric intake, ketogenic diet, surgery, volume depletion, and alcohol abuse.
Signs and symptoms are consistent with dehydration and severe metabolic acidosis and include nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, generalized malaise, and shortness of breath. Blood glucose levels at presentation may be below those typically expected for diabetic ketoacidosis (e.g., less than 250 mg/dL). Ketoacidosis and glucosuria may persist longer than typically expected. Urinary glucose excretion persists for 4 days after discontinuing SEGLUROMET [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.2) ]; however, there have been postmarketing reports of ketoacidosis and/or glucosuria lasting greater than 6 days and some up to 2 weeks after discontinuation of SGLT2 inhibitors.
Consider ketone monitoring in patients at risk for ketoacidosis if indicated by the clinical situation. Assess for ketoacidosis regardless of presenting blood glucose levels in patients who present with signs and symptoms consistent with severe metabolic acidosis. If ketoacidosis is suspected, discontinue SEGLUROMET, promptly evaluate, and treat ketoacidosis, if confirmed. Monitor patients for resolution of ketoacidosis before restarting SEGLUROMET.
Withhold SEGLUROMET, if possible, in temporary clinical situations that could predispose patients to ketoacidosis. Resume SEGLUROMET when the patient is clinically stable and has resumed oral intake [see Dosage and Administration (2.4) ].
Educate all patients on the signs and symptoms of ketoacidosis and instruct patients to discontinue SEGLUROMET and seek medical attention immediately if signs and symptoms occur.
5.3 Lower Limb Amputation
In a long-term cardiovascular outcomes study [see Clinical Studies (14.2) ] , in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and established cardiovascular disease, the occurrence of non-traumatic lower limb amputations was reported with event rates of 4.7, 5.7, and 6.0 events per 1,000 patient-years in the placebo, ertugliflozin 5 mg, and ertugliflozin 15 mg treatment arms, respectively.
Amputation of the toe and foot were most frequent (81 out of 109 patients with lower limb amputations). Some patients had multiple amputations, some involving both lower limbs.
Lower limb infections, gangrene, and diabetic foot ulcers were the most common precipitating medical events leading to the need for an amputation. Patients with amputations were more likely to be male, have higher A1C (%) at baseline, have a history of peripheral arterial disease, amputation or peripheral revascularization procedure, diabetic foot, and to have been taking diuretics or insulin.
Across seven ertugliflozin clinical trials, non-traumatic lower limb amputations were reported in 1 (0.1%) patient in the comparator group, 3 (0.2%) patients in the ertugliflozin 5 mg group, and 8 (0.5%) patients in the ertugliflozin 15 mg group.
Monitor patients receiving SEGLUROMET for signs and symptoms of infection (including osteomyelitis), new pain or tenderness, sores or ulcers involving the lower limbs, and discontinue SEGLUROMET if these complications occur.
Volume Depletion
SEGLUROMET can cause intravascular volume contraction which may sometimes manifest as symptomatic hypotension or acute transient changes in creatinine [see Adverse Reactions (6.1) ] . There have been postmarketing reports of acute kidney injury, some requiring hospitalization and dialysis, in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus receiving SGLT2 inhibitors, including SEGLUROMET. Patients with impaired renal function (eGFR less than 60 mL/min/1.73 m 2 ) [see Use in Specific Populations (8.6) ] , elderly patients, patients with low systolic blood pressure, or patients on loop diuretics may be at increased risk for volume depletion or hypotension. Before initiating SEGLUROMET in patients with one or more of these characteristics, assess volume status and renal function. In patients with volume depletion, correct this condition before initiating SEGLUROMET. Monitor for signs and symptoms of volume depletion, and renal function after initiating therapy.
Urosepsis and Pyelonephritis
There have been postmarketing reports of serious urinary tract infections, including urosepsis and pyelonephritis, requiring hospitalization in patients receiving medicines containing SGLT2 inhibitors. Treatment with medicines containing SGLT2 inhibitors increases the risk for urinary tract infections. Evaluate patients for signs and symptoms of urinary tract infections and treat promptly, if indicated [see Adverse Reactions (6) ] .
5.6 Hypoglycemia with Concomitant Use with Insulin or Insulin Secretagogues
Insulin and insulin secretagogues (e.g., sulfonylurea) are known to cause hypoglycemia. SEGLUROMET may increase the risk of hypoglycemia when used in combination with insulin or an insulin secretagogue [see Adverse Reactions (6.1) ] . The risk of hypoglycemia may be lowered by a reduction in the dose of insulin or sulfonylurea (or other concomitantly administered insulin secretagogues). Inform patients using these medications concomitantly of this risk and educate them on the signs and symptoms of hypoglycemia.
Necrotizing Fasciitis of the Perineum (Fournier's Gangrene)
Reports of necrotizing fasciitis of the perineum (Fournier’s Gangrene), a rare but serious and life-threatening necrotizing infection requiring urgent surgical intervention, have been identified in postmarketing surveillance in patients with diabetes mellitus receiving SGLT2 inhibitors, including ertugliflozin. Cases have been reported in females and males. Serious outcomes have included hospitalization, multiple surgeries, and death.
Patients treated with SEGLUROMET presenting with pain or tenderness, erythema, or swelling in the genital or perineal area, along with fever or malaise, should be assessed for necrotizing fasciitis. If suspected, start treatment immediately with broad-spectrum antibiotics and, if necessary, surgical debridement. Discontinue SEGLUROMET, closely monitor blood glucose levels, and provide appropriate alternative therapy for glycemic control.
Genital Mycotic Infections
Ertugliflozin increases the risk of genital mycotic infections. Patients who have a history of genital mycotic infections or who are uncircumcised are more likely to develop genital mycotic infections [see Adverse Reactions (6.1) ] . Monitor and treat appropriately.
Vitamin B 12 Deficiency
In metformin clinical trials of 29-week duration, a decrease to subnormal levels of previously normal serum vitamin B 12 levels was observed in approximately 7% of patients. Such decrease, possibly due to interference with B 12 absorption from the B 12 -intrinsic factor complex, may be associated with anemia but appears to be rapidly reversible with discontinuation of metformin or vitamin B 12 supplementation. Certain individuals (those with inadequate vitamin B 12 or calcium intake or absorption) appear to be predisposed to developing subnormal vitamin B 12 levels. Measure hematologic parameters on an annual basis and vitamin B 12 at 2 to 3 year intervals in patients on metformin and manage any abnormalities [see Adverse Reactions (6.1) ].
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following important adverse reactions are described elsewhere in the labeling:
- Lactic Acidosis [see Boxed Warning and Warnings and Precautions (5.1) ]
- Diabetic Ketoacidosis in Patients with Type 1 Diabetes and Other Ketoacidosis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) ]
- Lower Limb Amputation [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3) ]
- Volume Depletion [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4) ]
- Urosepsis and Pyelonephritis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5) ]
- Hypoglycemia with Concomitant Use with Insulin or Insulin Secretagogues [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6) ]
- Necrotizing Fasciitis of the Perineum (Fournier's Gangrene) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7) ]
- Genital Mycotic Infections [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8) ]
- Vitamin B 12 Deficiency [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9) ]
Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
Ertugliflozin and Metformin Hydrochloride
The incidence and type of adverse reactions in the two 26-week, placebo-controlled trials of ertugliflozin 5 mg and 15 mg added to metformin HCl, representing a majority of data from the three 26-week, placebo-controlled trials, were similar to the adverse reactions described in Table 1 .
Ertugliflozin
Pool of Placebo-Controlled Trials
The data in Table 1 are derived from a pool of three 26-week, placebo-controlled trials. Ertugliflozin was used as monotherapy in one trial and as add-on therapy in two trials [see Clinical Studies (14) ] . These data reflect exposure of 1,029 patients to ertugliflozin with a mean exposure duration of approximately 25 weeks. Patients received ertugliflozin 5 mg (N=519), ertugliflozin 15 mg (N=510), or placebo (N=515) once daily. The mean age of the population was 57 years and 2% were older than 75 years of age. Fifty-three percent (53%) of the population was male and 73% were White, 15% were Asian, and 7% were Black or African American. At baseline the population had diabetes for an average of 7.5 years, had a mean HbA1c of 8.1%, and 19.4% had established microvascular complications of diabetes. Baseline renal function (mean eGFR 88.9 mL/min/1.73 m 2 ) was normal or mildly impaired in 97% of patients and moderately impaired in 3% of patients.
Table 1 shows common adverse reactions associated with the use of ertugliflozin. These adverse reactions were not present at baseline, occurred more commonly on ertugliflozin than on placebo, and occurred in at least 2% of patients treated with either ertugliflozin 5 mg or ertugliflozin 15 mg.
| Number (%) of Patients | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Placebo N = 515 | Ertugliflozin 5 mg N = 519 | Ertugliflozin 15 mg N = 510 | |
| Female genital mycotic infections Includes: genital candidiasis, genital infection fungal, vaginal infection, vulvitis, vulvovaginal candidiasis, vulvovaginal mycotic infection, and vulvovaginitis. Percentages calculated with the number of female patients in each group as denominator: placebo (N=235), ertugliflozin 5 mg (N=252), ertugliflozin 15 mg (N=245). | 3.0% | 9.1% | 12.2% |
| Male genital mycotic infections Includes: balanitis candida, balanoposthitis, genital infection, and genital infection fungal. Percentages calculated with the number of male patients in each group as denominator: placebo (N=280), ertugliflozin 5 mg (N=267), ertugliflozin 15 mg (N=265). | 0.4% | 3.7% | 4.2% |
| Urinary tract infections Includes: cystitis, dysuria, streptococcal urinary tract infection, urethritis, urinary tract infection. | 3.9% | 4.0% | 4.1% |
| Headache | 2.3% | 3.5% | 2.9% |
| Vaginal pruritus Includes: vulvovaginal pruritus and pruritus genital. Percentages calculated with the number of female patients in each group as denominator: placebo (N=235), ertugliflozin 5 mg (N=252), ertugliflozin 15 mg (N=245). | 0.4% | 2.8% | 2.4% |
| Increased urination Includes: pollakiuria, micturition urgency, polyuria, urine output increased, and nocturia. | 1.0% | 2.7% | 2.4% |
| Nasopharyngitis | 2.3% | 2.5% | 2.0% |
| Back pain | 2.3% | 1.7% | 2.5% |
| Weight decreased | 1.0% | 1.2% | 2.4% |
| Thirst Includes: thirst, dry mouth, polydipsia, and dry throat. | 0.6% | 2.7% | 1.4% |
Volume Depletion
Ertugliflozin causes an osmotic diuresis, which may lead to intravascular volume contraction and adverse reactions related to volume depletion, particularly in patients with impaired renal function (eGFR less than 60 mL/min/1.73 m 2 ). In patients with moderate renal impairment, adverse reactions related to volume depletion (e.g., dehydration, dizziness postural, presyncope, syncope, hypotension, and orthostatic hypotension) were reported in 0%, 4.4%, and 1.9% of patients treated with placebo, ertugliflozin 5 mg, and ertugliflozin 15 mg, respectively. Ertugliflozin may also increase the risk of hypotension in other patients at risk for volume contraction [see Use in Specific Populations (8.5 , 8.6) ] .
Hypoglycemia
The incidence of hypoglycemia by study is shown in Table 2 .
| Add-on Combination Therapy with Metformin HCl (26 weeks) | Placebo (N = 209) | Ertugliflozin 5 mg (N = 207) | Ertugliflozin 15 mg (N = 205) |
| Overall [N (%)] | 9 (4.3) | 15 (7.2) | 16 (7.8) |
| Severe [N (%)] | 1 (0.5) | 1 (0.5) | 0 (0.0) |
| Add-on Combination Therapy with Metformin HCl and Sitagliptin (26 weeks) | Placebo (N = 153) | Ertugliflozin 5 mg (N = 156) | Ertugliflozin 15 mg (N = 153) |
| Overall [N (%)] | 5 (3.3) | 7 (4.5) | 3 (2.0) |
| Severe [N (%)] | 1 (0.7) | 1 (0.6) | 0 (0.0) |
| Add-on Combination with Insulin with or without Metformin HCl (18 weeks) | Placebo (N = 347) | Ertugliflozin 5 mg (N = 348) | Ertugliflozin 15 mg (N = 370) |
| Overall [N (%)] | 130 (37.5) | 137 (39.4) | 144 (38.9) |
| Severe [N (%)] | 12 (3.5) | 13 (3.7) | 19 (5.1) |
| Add-on Combination with Metformin HCl and a Sulfonylurea (18 weeks) | Placebo (N = 117) | Ertugliflozin 5 mg (N = 100) | Ertugliflozin 15 mg (N = 113) |
| Overall [N (%)] | 17 (14.5) | 20 (20.0) | 30 (26.5) |
| Severe [N (%)] | 1 (0.9) | 2 (2.0) | 2 (1.8) |
Lower Limb Amputation
In a long-term cardiovascular outcomes study [see Clinical Studies (14.2) ] , in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and established cardiovascular disease, the occurrence of non-traumatic lower limb amputations was reported with event rates of 4.7, 5.7, and 6.0 events per 1,000 patient-years in the placebo, ertugliflozin 5 mg, and ertugliflozin 15 mg treatment arms, respectively.
Across seven ertugliflozin clinical trials, non-traumatic lower limb amputations were reported in 1 (0.1%) patient in the comparator group, 3 (0.2%) patients in the ertugliflozin 5 mg group, and 8 (0.5%) patients in the ertugliflozin 15 mg group.
Genital Mycotic Infections
In the pool of three placebo-controlled clinical trials, the incidence of female genital mycotic infections (e.g., genital candidiasis, genital infection fungal, vaginal infection, vulvitis, vulvovaginal candidiasis, vulvovaginal mycotic infection, vulvovaginitis) occurred in 3%, 9.1%, and 12.2%, of females treated with placebo, ertugliflozin 5 mg, and ertugliflozin 15 mg, respectively (see Table 1 ). In females, discontinuation due to genital mycotic infections occurred in 0% and 0.6% of patients treated with placebo and ertugliflozin, respectively.
In the same pool, male genital mycotic infections (e.g., balanitis candida, balanoposthitis, genital infection, genital infection fungal) occurred in 0.4%, 3.7%, and 4.2% of males treated with placebo, ertugliflozin 5 mg, and ertugliflozin 15 mg, respectively. Male genital mycotic infections occurred more commonly in uncircumcised males. In males, discontinuations due to genital mycotic infections occurred in 0% and 0.2% of patients treated with placebo and ertugliflozin, respectively. Phimosis was reported in 8 of 1,729 (0.5%) male ertugliflozin-treated patients, of which four required circumcision.
Urinary Tract Infections
In VERTIS CV urinary tract infections (e.g., urinary tract infection, cystitis, dysuria) occurred in 10.2%, 12.2% and 12.0% of patients treated with placebo, ertugliflozin 5 mg and ertugliflozin 15 mg, respectively. The incidences of serious urinary tract infections were 0.8%, 0.9% and 0.4% with placebo, ertugliflozin 5 mg and ertugliflozin 15 mg, respectively.
Metformin HCl
The most common (5% or greater incidence) established adverse reactions due to initiation of metformin HCl therapy are diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, flatulence, abdominal discomfort, indigestion, asthenia, and headache.
In controlled clinical trials of metformin HCl of 29 weeks duration, a decrease to subnormal levels of previously normal serum vitamin B 12 levels was observed in approximately 7% of patients.
Laboratory Tests
Ertugliflozin
Changes in Serum Creatinine and eGFR
Initiation of ertugliflozin causes an increase in serum creatinine and decrease in eGFR within weeks of starting therapy and then these changes stabilize. In a study of patients with moderate renal impairment, larger mean changes were observed. In a long-term cardiovascular outcomes trial, an initial increase in serum creatinine and a decrease in eGFR within weeks of starting therapy was observed (at Week 6 eGFR changes of -2.7, -3.8 and -0.4 mL/min/1.73 m 2 in the ertugliflozin 5 mg, ertugliflozin 15 mg and placebo arms, respectively). The initial decline was followed by a recovery toward baseline to Week 52 (eGFR change from baseline of - 0.4, - 1.1 and - 0.2 mL/min/1.73 m 2 in ertugliflozin 5 mg, ertugliflozin 15 mg, and placebo arms, respectively). Acute hemodynamic changes may play a role in the early renal function changes observed with ertugliflozin since they are reversed after treatment discontinuation.
Increases in Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol (LDL-C)
In the pool of three placebo-controlled trials, dose-related increases in LDL-C were observed in patients treated with ertugliflozin. Mean percent changes from baseline to Week 26 in LDL-C relative to placebo were 2.6% and 5.4% with ertugliflozin 5 mg and ertugliflozin 15 mg, respectively. The range of mean baseline LDL-C was 96.6 to 97.7 mg/dL across treatment groups.
Increases in Hemoglobin
In the pool of three placebo-controlled trials, mean changes (percent changes) from baseline to Week 26 in hemoglobin were -0.21 g/dL (-1.4%) with placebo, 0.46 g/dL (3.5%) with ertugliflozin 5 mg, and 0.48 g/dL (3.5%) with ertugliflozin 15 mg. The range of mean baseline hemoglobin was 13.90 to 14.00 g/dL across treatment groups. At the end of treatment, 0.0%, 0.2%, and 0.4% of patients treated with placebo, ertugliflozin 5 mg, and ertugliflozin 15 mg, respectively, had a hemoglobin increase greater than 2 g/dL and above the upper limit of normal.
Increases in Serum Phosphate
In the pool of three placebo-controlled trials, mean changes (percent changes) from baseline in serum phosphate were 0.04 mg/dL (1.9%) with placebo, 0.21 mg/dL (6.8%) with ertugliflozin 5 mg, and 0.26 mg/dL (8.5%) with ertugliflozin 15 mg. The range of mean baseline serum phosphate was 3.53 to 3.54 mg/dL across treatment groups. In a clinical trial of patients with moderate renal impairment, mean changes (mean percent changes) from baseline at Week 26 in serum phosphate were -0.01 mg/dL (0.8%) with placebo, 0.29 mg/dL (9.7%) with ertugliflozin 5 mg, and 0.24 mg/dL (7.8%) with ertugliflozin 15 mg.
Postmarketing Experience
Additional adverse reactions have been identified during post approval use of ertugliflozin, metformin HCl, both components of SEGLUROMET. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is generally not possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Ertugliflozin
- Infections: necrotizing fasciitis of the perineum (Fournier’s Gangrene)
- Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue Disorders: angioedema, rash
Metformin HCl
- Hepatobiliary Disorders: cholestatic, hepatocellular, and mixed hepatocellular liver injury
DRUG INTERACTIONS
| Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors | |
|---|---|
| Clinical Impact: | The risk of lactic acidosis may increase due to concomitant use of Topiramate or other carbonic anhydrase inhibitors (e.g., zonisamide, acetazolamide or dichlorphenamide) with metformin. These drugs frequently cause a decrease in serum bicarbonate and induce non-anion gap, hyperchloremic metabolic acidosis. |
| Intervention: | more frequent monitoring of these patients. |
| Drugs that Reduce Metformin Clearance | |
| Clinical Impact: | The risk of lactic acidosis may increase due to concomitant use of drugs that interfere with common renal tubular transport systems involved in the renal elimination of metformin (e.g., organic cationic transporter-2 [OCT2] / multidrug and toxin extrusion [MATE] inhibitors such as ranolazine, vandetanib, dolutegravir, and cimetidine) which increase systemic exposure to metformin |
| Intervention | Consider the benefits and risks of concomitant use. |
| Alcohol | |
| Clinical Impact: | Potentiate the effect of metformin on lactate metabolism. |
| Intervention: | Warn patients against excessive alcohol intake while receiving SEGLUROMET. |
| Insulin or Insulin Secretagogues | |
| Clinical Impact: | The risk of hypoglycemia is increased when ertugliflozin is used in combination with insulin or an insulin secretagogue. |
| Intervention: | A lower dose of insulin or insulin secretagogue may be required to minimize the risk of hypoglycemia when used in combination with SEGLUROMET. |
| Drugs that Affect Glycemic Control | |
| Clinical Impact: | Certain drugs tend to produce hyperglycemia and may lead to loss of glycemic control. These drugs include the thiazides and other diuretics, corticosteroids, phenothiazines, thyroid products, estrogens, oral contraceptives, phenytoin, nicotinic acid, sympathomimetics, calcium channel blocking drugs, and isoniazid. |
| Intervention: | When a patient is receiving SEGLUROMET along with such drugs, the patient should be closely observed to maintain adequate glycemic control. |
| Lithium | |
| Clinical Impact: | Concomitant use of an SGLT2 inhibitor with lithium may decrease serum lithium concentrations. |
| Intervention: | Monitor serum lithium concentration more frequently during SEGLUROMET initiation and dosage changes. |
| Positive Urine Glucose Test | |
| Clinical Impact: | SGLT2 inhibitors increase urinary glucose excretion and will lead to positive urine glucose tests. |
| Intervention: | Monitoring glycemic control with urine glucose tests is not recommended in patients taking SEGLUROMET. Use alternative methods to monitor glycemic control. |
| Interference with 1,5-anhydroglucitol (1,5-AG) Assay | |
| Clinical Impact: | Measurements of 1,5-AG are unreliable in assessing glycemic control in patients taking SGLT2 inhibitors. |
| Intervention: | Monitoring glycemic control with 1,5-AG assay is not recommended. Use alternative methods to monitor glycemic control. |
DESCRIPTION
SEGLUROMET (ertugliflozin and metformin hydrochloride) tablet for oral use contains ertugliflozin L-pyroglutamic acid, a SGLT2 inhibitor, and metformin HCl, a member of the biguanide class.
Ertugliflozin
The chemical name of ertugliflozin L-pyroglutamic acid is (1 S ,2 S ,3 S ,4 R ,5 S )-5-(4-chloro-3-(4-ethoxybenzyl)phenyl)-1-(hydroxymethyl)-6,8-dioxabicyclo[3.2.1]octane-2,3,4-triol, compound with (2 S )-5-oxopyrrolidine-2-carboxylic acid. The molecular formula is C 27 H 32 ClNO 10 and the molecular weight is 566.00.
The chemical structure is:
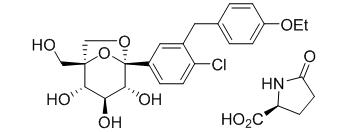
Ertugliflozin L-pyroglutamic acid is a white to off-white powder that is soluble in ethyl alcohol and acetone, slightly soluble in ethyl acetate and acetonitrile and very slightly soluble in water.
Metformin HCl
Metformin hydrochloride ( N , N -dimethylimidodicarbonimidic diamide hydrochloride) is not chemically or pharmacologically related to any other classes of oral antihyperglycemic agents. The structural formula is as shown:
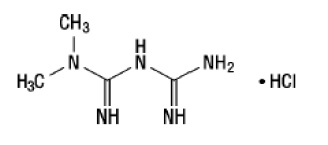
Metformin HCl is a white to off-white crystalline compound with a molecular formula of C 4 H 11 N 5 ∙HCl and a molecular weight of 165.63. Metformin hydrochloride is freely soluble in water and is practically insoluble in acetone, ether and chloroform. The pK a of metformin is 12.4. The pH of a 1% aqueous solution of metformin hydrochloride is 6.68.
SEGLUROMET is available as film-coated tablets containing:
- 3.24 mg ertugliflozin L-pyroglutamic acid equivalent to 2.5 mg of ertugliflozin and 500 mg metformin HCl (SEGLUROMET 2.5/500)
- 3.24 mg ertugliflozin L-pyroglutamic acid equivalent to 2.5 mg of ertugliflozin and 1,000 mg metformin HCl (SEGLUROMET 2.5/1000)
- 9.71 mg ertugliflozin L-pyroglutamic acid equivalent to 7.5 mg of ertugliflozin and 500 mg metformin HCl (SEGLUROMET 7.5/500)
- 9.71 mg ertugliflozin L-pyroglutamic acid equivalent to 7.5 mg of ertugliflozin and 1,000 mg metformin HCl (SEGLUROMET 7.5/1000)
Inactive ingredients are povidone, microcrystalline cellulose, crospovidone, sodium lauryl sulfate, and magnesium stearate.
The film coating contains: hypromellose, hydroxypropyl cellulose, titanium dioxide, iron oxide red, and carnauba wax.
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Mechanism of Action
SEGLUROMET
SEGLUROMET combines two antihyperglycemic agents with complementary mechanisms of action to improve glycemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: ertugliflozin, a SGLT2 inhibitor, and metformin hydrochloride, a member of the biguanide class.
Ertugliflozin
SGLT2 is the predominant transporter responsible for reabsorption of glucose from the glomerular filtrate back into the circulation. Ertugliflozin is an inhibitor of SGLT2. By inhibiting SGLT2, ertugliflozin reduces renal reabsorption of filtered glucose and lowers the renal threshold for glucose, and thereby increases urinary glucose excretion.
Metformin HCl
Metformin is an antihyperglycemic agent which improves glucose tolerance in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus, lowering both basal and postprandial plasma glucose. Its pharmacologic mechanisms of action are different from other classes of oral antihyperglycemic agents. Metformin decreases hepatic glucose production, decreases intestinal absorption of glucose, and improves insulin sensitivity by increasing peripheral glucose uptake and utilization. Metformin does not produce hypoglycemia in either patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus or normal subjects (except in special circumstances) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5) ] and does not cause hyperinsulinemia. With metformin therapy, insulin secretion remains unchanged while fasting insulin levels and day-long plasma insulin response may actually decrease.
Pharmacodynamics
Ertugliflozin
Urinary Glucose Excretion and Urinary Volume
Dose-dependent increases in the amount of glucose excreted in urine were observed in healthy subjects and in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus following single- and multiple-dose administration of ertugliflozin. Dose-response modeling indicates that ertugliflozin 5 mg and 15 mg result in near maximal urinary glucose excretion (UGE). Enhanced UGE is maintained after multiple-dose administration. UGE with ertugliflozin also results in increases in urinary volume.
Cardiac Electrophysiology
The effect of ertugliflozin on QTc interval was evaluated in a Phase 1 randomized, placebo- and positive-controlled 3-period crossover study in 42 healthy subjects. At 6.7 times the therapeutic exposures with maximum recommended dose, ertugliflozin does not prolong QTc to any clinically relevant extent.
Pharmacokinetics
General Introduction
Ertugliflozin
The pharmacokinetics of ertugliflozin are similar in healthy subjects and patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. The steady state mean plasma AUC and C max were 398 ng∙hr/mL and 81.3 ng/mL, respectively, with 5 mg ertugliflozin once-daily treatment, and 1,193 ng∙hr/mL and 268 ng/mL, respectively, with 15 mg ertugliflozin once-daily treatment. Steady-state is reached after 4 to 6 days of once-daily dosing with ertugliflozin. Ertugliflozin does not exhibit time-dependent pharmacokinetics and accumulates in plasma up to 10-40% following multiple dosing.
Absorption
SEGLUROMET
The effects of a high-fat meal on the pharmacokinetics of ertugliflozin and metformin when administered as SEGLUROMET tablets are comparable to those reported for the individual tablets. Food had no meaningful effect on AUC inf of ertugliflozin and metformin, but reduced mean ertugliflozin C max by approximately 41% and metformin C max by approximately 29% compared to the fasted condition.
Ertugliflozin
Following single-dose oral administration of 5 mg and 15 mg of ertugliflozin, peak plasma concentrations of ertugliflozin occur at 1 hour postdose (median T max ) under fasted conditions. Plasma C max and AUC of ertugliflozin increase in a dose-proportional manner following single doses from 0.5 mg (0.1 times the lowest recommended dose) to 300 mg (20 times the highest recommended dose) and following multiple doses from 1 mg (0.2 times the lowest recommended dose) to 100 mg (6.7 times the highest recommended dose). The absolute oral bioavailability of ertugliflozin following administration of a 15 mg dose is approximately 100%.
Effect of Food
Administration of ertugliflozin with a high-fat and high-calorie meal decreases ertugliflozin C max by 29% and prolongs T max by 1 hour, but does not alter AUC as compared with the fasted state. The observed effect of food on ertugliflozin pharmacokinetics is not considered clinically relevant, and ertugliflozin may be administered with or without food. In Phase 3 clinical trials, ertugliflozin was administered without regard to meals.
Metformin hydrochloride
The absolute bioavailability of a metformin HCl 500-mg tablet given under fasting conditions is approximately 50-60%. Studies using single oral doses of metformin hydrochloride tablets 500 mg to 1,500 mg, and 850 mg to 2,550 mg (approximately 1.3 times the maximum recommended daily dosage), indicate that there is a lack of dose proportionality with increasing doses, which is due to decreased absorption rather than an alternation in elimination. Food decreases the extent of and slightly delays the absorption of metformin, as shown by approximately a 40% lower mean peak plasma concentration (C max ), a 25% lower area under the plasma concentration versus time curve (AUC), and a 35-minute prolongation of time to peak plasma concentration (T max ) following administration of a single 850-mg tablet of metformin with food, compared to the same tablet strength administered fasting. The clinical relevance of these decreases is unknown.
Distribution
Ertugliflozin
The mean steady-state volume of distribution of ertugliflozin following an intravenous dose is 85.5 L. Plasma protein binding of ertugliflozin is 93.6% and is independent of ertugliflozin plasma concentrations. Plasma protein binding is not meaningfully altered in patients with renal or hepatic impairment. The blood-to-plasma concentration ratio of ertugliflozin is 0.66.
Metformin
The apparent volume of distribution (V/F) of metformin following single oral doses of metformin hydrochloride tablets 850 mg averaged 654 ± 358 L. Metformin is negligibly bound to plasma proteins, in contrast to sulfonylureas, which are more than 90% protein bound. Metformin partitions into erythrocytes, most likely as a function of time. At usual clinical doses and dosing schedules of metformin hydrochloride tablets, steady-state plasma concentrations of metformin are reached within 24-48 hours and are generally <1 mcg/mL. During controlled clinical trials of metformin, maximum metformin plasma levels did not exceed 5 mcg/mL, even at maximum doses.
Elimination
Metabolism
Ertugliflozin
Metabolism is the primary clearance mechanism for ertugliflozin. The major metabolic pathway for ertugliflozin is UGT1A9 and UGT2B7-mediated O-glucuronidation to two glucuronides that are pharmacologically inactive at clinically relevant concentrations. CYP-mediated (oxidative) metabolism of ertugliflozin is minimal (12%).
Metformin
Intravenous single-dose studies in normal subjects demonstrate that metformin is excreted unchanged in the urine and does not undergo hepatic metabolism (no metabolites have been identified in humans) nor biliary excretion.
Excretion
Ertugliflozin
The mean systemic plasma clearance following an intravenous 100 µg dose was 11.2 L/hr. The mean elimination half-life in type 2 diabetic patients with normal renal function was estimated to be 16.6 hours based on the population pharmacokinetic analysis. Following administration of an oral [ 14 C]-ertugliflozin solution to healthy subjects, approximately 40.9% and 50.2% of the drug-related radioactivity was eliminated in feces and urine, respectively. Only 1.5% of the administered dose was excreted as unchanged ertugliflozin in urine and 33.8% as unchanged ertugliflozin in feces, which is likely due to biliary excretion of glucuronide metabolites and subsequent hydrolysis to parent.
Metformin
Renal clearance is approximately 3.5 times greater than creatinine clearance, which indicates that tubular secretion is the major route of metformin elimination. Following oral administration, approximately 90% of the absorbed drug is eliminated via the renal route within the first 24 hours, with a plasma elimination half-life of approximately 6.2 hours. In blood, the elimination half-life is approximately 17.6 hours, suggesting that the erythrocyte mass may be a compartment of distribution.
Specific Populations
Patients with Renal Impairment
SEGLUROMET
Studies characterizing the pharmacokinetics of ertugliflozin and metformin after administration of SEGLUROMET in renally impaired patients have not been performed [see Dosage and Administration (2.2) ].
Ertugliflozin
In a clinical pharmacology study in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and mild, moderate, or severe renal impairment (as determined by eGFR), following a single-dose administration of 15 mg ertugliflozin, the mean increases in AUC of ertugliflozin were 1.6-, 1.7-, and 1.6-fold, respectively, for mild, moderate, and severe renally-impaired patients compared to subjects with normal renal function. These increases in ertugliflozin AUC are not considered clinically meaningful. The 24-hour urinary glucose excretion declined with increasing severity of renal impairment [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) and Use in Specific Populations (8.6) ] . The plasma protein binding of ertugliflozin was unaffected in patients with renal impairment.
Metformin
In patients with decreased renal function, the plasma and blood half-life of metformin is prolonged and the renal clearance is decreased [see Contraindications (4) and Warnings and Precautions (5.1) ] .
Patients with Hepatic Impairment
Ertugliflozin
Moderate hepatic impairment (based on the Child-Pugh classification) did not result in an increase in exposure of ertugliflozin. The AUC of ertugliflozin decreased by approximately 13%, and C max decreased by approximately 21% compared to subjects with normal hepatic function. This decrease in ertugliflozin exposure is not considered clinically meaningful. There is no clinical experience in patients with Child-Pugh class C (severe) hepatic impairment. The plasma protein binding of ertugliflozin was unaffected in patients with moderate hepatic impairment [see Use in Specific Populations (8.7) ] .
Metformin
No pharmacokinetic studies of metformin have been conducted in patients with hepatic impairment [see Use in Specific Populations (8.7) ] .
Effects of Age, Body Weight, Gender, and Race
Ertugliflozin
Based on a population pharmacokinetic analysis, age, body weight, gender, and race do not have a clinically meaningful effect on the pharmacokinetics of ertugliflozin.
Metformin
Limited data from controlled pharmacokinetic studies of metformin in healthy elderly subjects suggest that total plasma clearance of metformin is decreased, the half-life is prolonged, and C max is increased, compared to healthy young subjects. From these data, it appears that the change in metformin pharmacokinetics with aging is primarily accounted for by a change in renal function.
Metformin pharmacokinetic parameters did not differ significantly between normal subjects and patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus when analyzed according to gender. Similarly, in controlled clinical studies in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus, the antihyperglycemic effect of metformin was comparable in males and females.
No studies of metformin pharmacokinetic parameters according to race have been performed. In controlled clinical studies of metformin in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus, the antihyperglycemic effect was comparable in Whites (n=249), Blacks (n=51), and Hispanics (n=24).
Drug Interaction Studies
SEGLUROMET
Coadministration of single dose of ertugliflozin (15 mg) and metformin (1,000 mg) did not meaningfully alter the pharmacokinetics of either ertugliflozin or metformin in healthy subjects.
Pharmacokinetic drug interaction studies with SEGLUROMET have not been performed; however, such studies have been conducted with ertugliflozin and metformin, the individual components of SEGLUROMET.
Ertugliflozin
In Vitro Assessment of Drug Interactions
In in vitro studies, ertugliflozin and ertugliflozin glucuronides did not inhibit CYP450 isoenzymes (CYPs) 1A2, 2C9, 2C19, 2C8, 2B6, 2D6, or 3A4, and did not induce CYPs 1A2, 2B6, or 3A4. Ertugliflozin was not a time-dependent inhibitor of CYP3A in vitro . Ertugliflozin did not inhibit UGT1A6, 1A9, or 2B7 in vitro and was a weak inhibitor (IC 50 >39 µM) of UGT1A1 and 1A4. Ertugliflozin glucuronides did not inhibit UGT1A1, 1A4, 1A6, 1A9, or 2B7 in vitro . Overall, ertugliflozin is unlikely to affect the pharmacokinetics of drugs eliminated by these enzymes. Ertugliflozin is a substrate of P-glycoprotein (P-gp) and breast cancer resistance protein (BCRP) transporters and is not a substrate of organic anion transporters (OAT1, OAT3), organic cation transporters (OCT1, OCT2), or organic anion transporting polypeptides (OATP1B1, OATP1B3). Ertugliflozin or ertugliflozin glucuronides do not meaningfully inhibit P-gp, OCT2, OAT1, or OAT3 transporters, or transporting polypeptides OATP1B1 and OATP1B3, at clinically relevant concentrations. Overall, ertugliflozin is unlikely to affect the pharmacokinetics of concurrently administered medications that are substrates of these transporters.
In Vivo Assessment of Drug Interactions
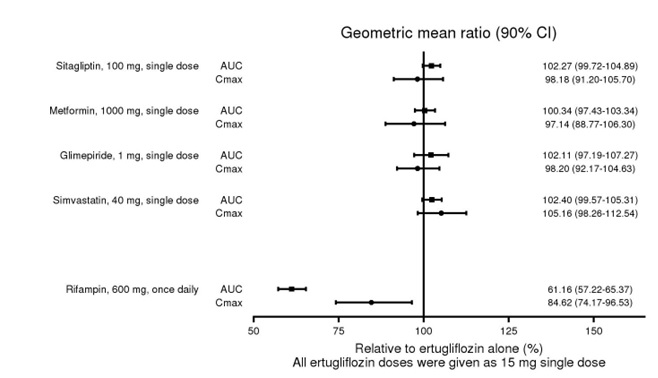
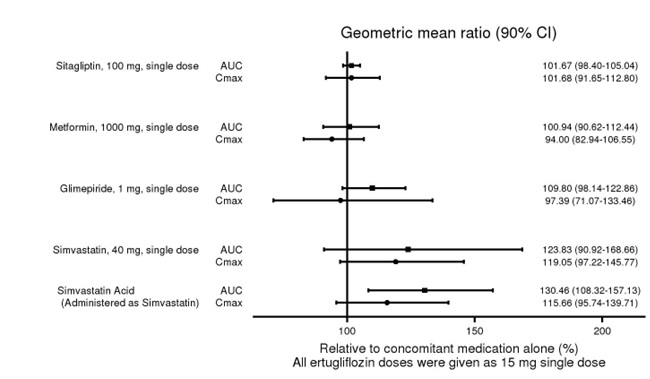
No dose adjustment of SEGLUROMET is recommended when coadministered with commonly prescribed medicinal products. Ertugliflozin pharmacokinetics were similar with and without coadministration of metformin, glimepiride, sitagliptin, and simvastatin in healthy subjects (see Figure 1 ). Coadministration of ertugliflozin with multiple doses of 600 mg once-daily rifampin (an inducer of UGT and CYP enzymes) resulted in approximately 39% and 15% mean reductions in ertugliflozin AUC and C max , respectively, relative to ertugliflozin administered alone. These changes in exposure are not considered clinically relevant. Ertugliflozin had no clinically relevant effect on the pharmacokinetics of metformin, glimepiride, sitagliptin, and simvastatin when coadministered in healthy subjects (see Figure 2 ). Physiologically-based PK (PBPK) modeling suggests that coadministration of mefenamic acid (UGT inhibitor) may increase the AUC and C max of ertugliflozin by 1.51- and 1.19-fold, respectively. These predicted changes in exposure are not considered clinically relevant.
 |
 |
Metformin hydrochloride
| Coadministered Drug | Dose of Coadministered Drug All doses administered as single dose unless otherwise specified. | Dose of Metformin HCl | Geometric Mean Ratio (ratio with/without metformin) No Effect = 1.00 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AUC AUC is reported as AUC 0-∞ unless otherwise specified. | C max | ||||
| No dosing adjustments required for the following: | |||||
| Cimetidine | 400 mg | 850 mg | Cimetidine | 0.95 AUC 0-24hr . | 1.01 |
| Glyburide | 5 mg | 500 mg Metformin HCl extended-release tablets 500 mg. | Glyburide | 0.78 Ratio of arithmetic means, p value of difference <0.05. | 0.63 |
| Furosemide | 40 mg | 850 mg | Furosemide | 0.87 | 0.69 |
| Nifedipine | 10 mg | 850 mg | Nifedipine | 1.10 | 1.08 |
| Propranolol | 40 mg | 850 mg | Propranolol | 1.01 | 0.94 |
| Ibuprofen | 400 mg | 850 mg | Ibuprofen | 0.97 Ratio of arithmetic means. | 1.01 |
| Coadministered Drug | Dose of Coadministered Drug All doses administered as single dose unless otherwise specified. | Dose of Metformin HCl | Geometric Mean Ratio (ratio with/without coadministered drug) No Effect = 1.00 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AUC AUC is reported as AUC 0-∞ unless otherwise specified. | C max | ||||
| No dosing adjustments required for the following: | |||||
| Glyburide | 5 mg | 500 mg Metformin hydrochloride extended-release tablets 500 mg. | Metformin | 0.98 Ratio of arithmetic means. | 0.99 |
| Furosemide | 40 mg | 850 mg | Metformin | 1.09 | 1.22 |
| Nifedipine | 10 mg | 850 mg | Metformin | 1.16 | 1.21 |
| Propranolol | 40 mg | 850 mg | Metformin | 0.90 | 0.94 |
| Ibuprofen | 400 mg | 850 mg | Metformin | 1.05 | 1.07 |
| Drugs that are eliminated by renal tubular secretion may increase the accumulation of metformin [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) and Drug Interactions (7.2) ]. | |||||
| Cimetidine | 400 mg | 850 mg | Metformin | 1.40 | 1.61 |
| Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors may cause metabolic acidosis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) and Drug Interactions (7.2) ]. | |||||
| Topiramate | 100 mg Steady-state 100 mg topiramate every 12 hr + metformin 500 mg every 12 hr AUC = AUC 0-12hr . | 500 mg | Metformin | 1.25 | 1.17 |
NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenesis
Ertugliflozin
Carcinogenicity was evaluated in CD-1 mice and Sprague-Dawley rats. In the mouse study, ertugliflozin was administered by oral gavage at doses of 5, 15, and 40 mg/kg/day for up to 97 weeks in males and 102 weeks in females. There were no ertugliflozin-related neoplastic findings at doses up to 40 mg/kg/day (approximately 50 times human exposure at the maximum recommended human dose [MRHD] of 15 mg/day based on AUC). In the rat study, ertugliflozin was administered by oral gavage at doses of 1.5, 5, and 15 mg/kg/day for up to 92 weeks in females and 104 weeks in males. Ertugliflozin-related neoplastic findings included an increased incidence of adrenal medullary pheochromocytoma (PCC) in male rats at 15 mg/kg/day. Although the molecular mechanism remains unknown, this finding may be related to carbohydrate malabsorption leading to altered calcium homeostasis, which has been associated with PCC development in rats and has unclear relevancy to human risk. The no-observed-effect level (NOEL) for neoplasia was 5 mg/kg/day (approximately 16 times human exposure at the MRHD of 15 mg/day, based on AUC).
Metformin HCl
Long-term carcinogenicity studies have been performed in rats (dosing duration of 104 weeks) and mice (dosing duration of 91 weeks) at doses up to and including 900 mg/kg/day and 1,500 mg/kg/day, respectively. These doses are both approximately four times the maximum recommended human daily dose of 2,000 mg based on body surface area comparisons. No evidence of carcinogenicity with metformin was found in either male or female mice. Similarly, there was no tumorigenic potential observed with metformin in male rats. There was, however, an increased incidence of benign stromal uterine polyps in female rats treated with 900 mg/kg/day.
Mutagenesis
Ertugliflozin
Ertugliflozin was not mutagenic or clastogenic with or without metabolic activation in the microbial reverse mutation, in vitro cytogenetic (human lymphocytes), and in vivo rat micronucleus assays.
Metformin
There was no evidence of a mutagenic potential of metformin in the following in vitro tests: Ames test ( S. typhimurium ), gene mutation test (mouse lymphoma cells), or chromosomal aberrations test (human lymphocytes). Results in the in vivo mouse micronucleus test were also negative.
Impairment of Fertility
Ertugliflozin
In the rat fertility and embryonic development study, male and female rats were administered ertugliflozin at 5, 25, and 250 mg/kg/day. No effects on fertility were observed at 250 mg/kg/day (approximately 480 and 570 times male and female human exposures, respectively, at the MRHD of 15 mg/day based on AUC comparison).
Metformin HCl
Fertility of male or female rats was unaffected by metformin when administered at doses as high as 600 mg/kg/day, which is approximately three times the maximum recommended human daily dose based on body surface area comparisons.
CLINICAL STUDIES
Glycemic Control Trials in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
The efficacy and safety of ertugliflozin in combination with metformin HCl have been studied in 4 multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo- and active comparator-controlled, clinical studies involving 3,643 patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. These studies included White, Hispanic or Latino, Black or African American, Asian, and other racial and ethnic groups, and patients with an age range of 21 to 86 years.
In VERTIS CV, ertugliflozin has been studied as add on to insulin (with or without metformin HCl) and as add on to metformin HCl plus a sulfonylurea in substudies.
In patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus, treatment with ertugliflozin in combination with metformin HCl reduced hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) compared to placebo.
In patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus treated with ertugliflozin in combination with metformin HCl, the reduction in HbA1c was generally similar across subgroups defined by age, sex, race, geographic region, baseline body mass index (BMI), and duration of type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Ertugliflozin as Add-on Combination Therapy with Metformin HCl
A total of 621 patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus inadequately controlled (HbA1c between 7% and 10.5%) on metformin HCl monotherapy (≥1,500 mg/day for ≥8 weeks) participated in a randomized, double-blind, multi-center, 26-week, placebo-controlled study (NCT02033889) to evaluate the efficacy and safety of ertugliflozin in combination with metformin HCl. Patients entered a 2-week, single-blind, placebo run-in, and were randomized to placebo, ertugliflozin 5 mg, or ertugliflozin 15 mg administered orally once daily in addition to continuation of background metformin HCl therapy.
At Week 26, statistically significant reductions in HbA1c were observed in the ertugliflozin 5 mg and 15 mg groups compared to placebo. Ertugliflozin also resulted in a greater proportion of patients achieving an HbA1c <7% compared to placebo (see Table 6 and Figure 3 ).
| Placebo | Ertugliflozin 5 mg | Ertugliflozin 15 mg | |
|---|---|---|---|
| HbA1c (%) | N = 207 | N = 205 | N = 201 |
| Baseline (mean) | 8.2 | 8.1 | 8.1 |
| Change from baseline (LS mean Intent-to-treat analysis using ANCOVA adjusted for baseline value, prior antihyperglycemic medication, menopausal status and baseline eGFR. ) | -0.2 | -0.7 | -0.9 |
| Difference from placebo (LS mean, 95% CI) | -0.5 p<0.001 compared to placebo. (-0.7, -0.4) | -0.7(-0.9, -0.5) | |
| Patients [N (%)] with HbA1c <7% | 38 (18.4) | 74 (36.3) | 87 (43.3) |
| FPG (mg/dL) | N = 202 | N = 199 | N = 201 |
| Baseline (mean) | 169.1 | 168.1 | 167.9 |
| Change from baseline (LS mean) | -8.7 | -30.3 | -40.9 |
| Difference from placebo (LS mean, 95% CI) | -21.6(-27.8, -15.5) | -32.3(-38.5, -26.0) |
The mean baseline body weight was 84.5 kg, 84.9 kg, and 85.3 kg in the placebo, ertugliflozin 5 mg, and ertugliflozin 15 mg groups, respectively. The mean changes from baseline to Week 26 were - 1.4 kg, -3.2 kg, and -3.0 kg in the placebo, ertugliflozin 5 mg, and ertugliflozin 15 mg groups, respectively. The difference from placebo (95% CI) for ertugliflozin 5 mg was -1.8 kg (-2.4, -1.2) and for ertugliflozin 15 mg was -1.7 kg (-2.2, -1.1).
The mean baseline systolic blood pressure was 129.3 mmHg, 130.5 mmHg, and 130.2 mmHg in the placebo, ertugliflozin 5 mg, and ertugliflozin 15 mg groups, respectively. The mean changes from baseline to Week 26 were -1.8 mmHg, -5.1 mmHg, and -5.7 mmHg in the placebo, ertugliflozin 5 mg, and ertugliflozin 15 mg groups, respectively. The difference from placebo (95% CI) for ertugliflozin 5 mg was -3.3 mmHg (-5.6, -1.1) and for ertugliflozin 15 mg was -3.8 mmHg (-6.1, -1.5).
| Figure 3: HbA1c (%) Change over Time in a 26-Week Placebo-Controlled Study for Ertugliflozin Used in Combination with Metformin HCl in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Data to the left of the vertical line are observed means (non-model-based) excluding values occurring post glycemic rescue. Data to the right of the vertical line represent the final Week 26 data, including all values regardless of use of glycemic rescue medication and use of study drug, with missing Week 26 values imputed using multiple imputation (26-MI) with a mean equal to the baseline value of the patient (see Table 6 ). |
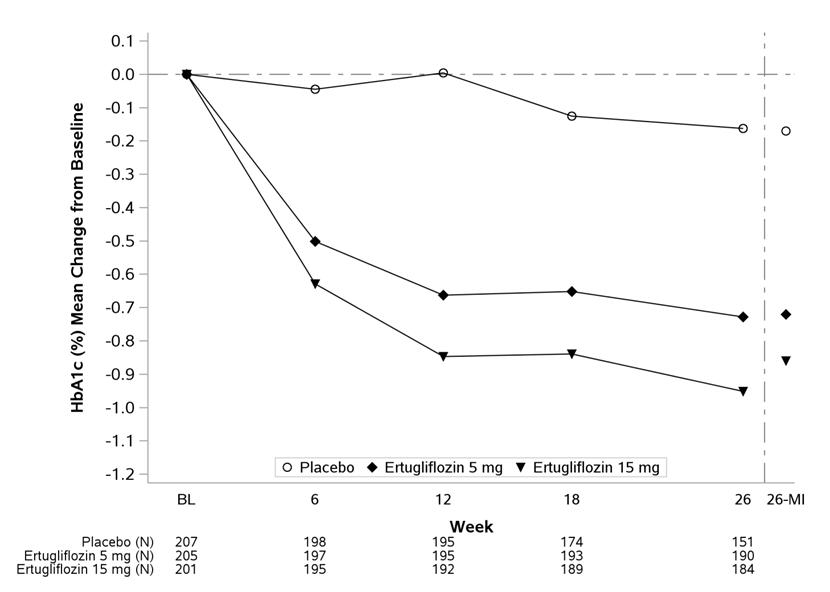 |
In Combination with Sitagliptin versus Ertugliflozin Alone and Sitagliptin Alone, as Add-on to Metformin HCl
A total of 1,233 patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus with inadequate glycemic control (HbA1c between 7.5% and 11%) on metformin HCl monotherapy (≥1,500 mg/day for ≥8 weeks) participated in a randomized, double-blind, 26-week, active controlled study (NCT02099110) to evaluate the efficacy and safety of ertugliflozin 5 mg or 15 mg administered orally in combination with sitagliptin 100 mg compared to the individual components. Patients were randomized to one of five treatment arms: ertugliflozin 5 mg, ertugliflozin 15 mg, sitagliptin 100 mg, ertugliflozin 5 mg + sitagliptin 100 mg, or ertugliflozin 15 mg + sitagliptin 100 mg.
At Week 26, ertugliflozin 5 mg or 15 mg + sitagliptin 100 mg provided statistically significantly greater reductions in HbA1c compared to ertugliflozin (5 mg or 15 mg) alone or sitagliptin 100 mg alone. The mean change from baseline in HbA1c was -1.4% for ertugliflozin 5 mg or 15 mg + sitagliptin 100 mg versus -1.0%, for ertugliflozin 5 mg, ertugliflozin 15 mg, or sitagliptin 100 mg, respectively. More patients receiving ertugliflozin 5 mg or 15 mg + sitagliptin 100 mg achieved an HbA1c <7% (53.3% and 50.9%, for ertugliflozin 5 mg or 15 mg, respectively, + sitagliptin 100 mg) compared to the individual components (29.3%, 33.7%, and 38.5% for ertugliflozin 5 mg, ertugliflozin 15 mg, or sitagliptin 100 mg, respectively).
Ertugliflozin as Add-on Combination Therapy with Metformin HCl and Sitagliptin
A total of 463 patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus inadequately controlled (HbA1c between 7% and 10.5%) on metformin HCl (≥1,500 mg/day for ≥8 weeks) and sitagliptin 100 mg orally once daily participated in a randomized, double-blind, multi-center, 26-week, placebo-controlled study (NCT02036515) to evaluate the efficacy and safety of ertugliflozin. Patients entered a 2-week, single-blind, placebo run-in period and were randomized to placebo, ertugliflozin 5 mg, or ertugliflozin 15 mg.
At Week 26, treatment with ertugliflozin at 5 mg or 15 mg daily provided statistically significant reductions in HbA1c. Ertugliflozin also resulted in a higher proportion of patients achieving an HbA1c <7% compared to placebo (see Table 7 ).
| Placebo | Ertugliflozin 5 mg | Ertugliflozin 15 mg | |
|---|---|---|---|
| HbA1c (%) | N = 152 | N = 155 | N = 152 |
| Baseline (mean) | 8.0 | 8.1 | 8.0 |
| Change from baseline (LS mean Intent-to-treat analysis using ANCOVA adjusted for baseline value, prior antihyperglycemic medication and baseline eGFR. ) | -0.2 | -0.7 | -0.8 |
| Difference from placebo (LS mean, 95% CI) | -0.5 p<0.001 compared to placebo. (-0.7, -0.3) | -0.6(-0.8, -0.4) | |
| Patients [N (%)] with HbA1c <7% | 31 (20.2) | 54 (34.6) | 64 (42.3) |
| FPG (mg/dL) | N = 152 | N = 156 | N = 152 |
| Baseline (mean) | 169.6 | 167.7 | 171.7 |
| Change from baseline (LS mean) | -6.5 | -25.7 | -32.1 |
| Difference from placebo (LS mean, 95% CI) | -19.2(-26.8, -11.6) | -25.6(-33.2, -18.0) |
The mean baseline body weight was 86.5 kg, 87.6 kg, and 86.6 kg in the placebo, ertugliflozin 5 mg, and ertugliflozin 15 mg groups, respectively. The mean changes from baseline to Week 26 were -1.0 kg, -3.0 kg, and -2.8 kg in the placebo, ertugliflozin 5 mg, and ertugliflozin 15 mg groups, respectively. The difference from placebo (95% CI) for ertugliflozin 5 mg was -1.9 kg (-2.6, -1.3) and for ertugliflozin 15 mg was -1.8 kg (-2.4, -1.2).
The mean baseline systolic blood pressure was 130.2 mmHg, 132.1 mmHg, and 131.6 mmHg in the placebo, ertugliflozin 5 mg, and ertugliflozin 15 mg groups, respectively. The mean changes from baseline to Week 26 were -0.2 mmHg, -3.8 mmHg, and -4.5 mmHg in the placebo, ertugliflozin 5 mg, and ertugliflozin 15 mg groups, respectively. The difference from placebo (95% CI) for ertugliflozin 5 mg was -3.7 mmHg (-6.1, -1.2) and for ertugliflozin 15 mg was -4.3 mmHg (-6.7, -1.9).
Active Controlled Study of Ertugliflozin Versus Glimepiride as Add-on Combination Therapy with Metformin HCl
A total of 1,326 patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus inadequately controlled (HbA1c between 7% and 9%) on metformin HCl monotherapy participated in a randomized, double-blind, multi-center, 52-week, active comparator-controlled study (NCT01999218) to evaluate the efficacy and safety of ertugliflozin in combination with metformin HCl. These patients, who were receiving metformin HCl monotherapy (≥1,500 mg/day for ≥8 weeks), entered a 2-week, single-blind, placebo run-in period and were randomized to glimepiride, ertugliflozin 5 mg, or ertugliflozin 15 mg, administered orally once daily in addition to continuation of background metformin HCl therapy. Glimepiride was initiated at 1 mg/day and titrated up to a maximum dose of 6 or 8 mg/day (depending on maximum approved dose in each country) or a maximum tolerated dose or down-titrated to avoid or manage hypoglycemia. The mean daily dose of glimepiride was 3.0 mg.
Ertugliflozin 15 mg was non-inferior to glimepiride after 52 weeks of treatment. (See Table 8 .)
| Glimepiride | Ertugliflozin 5 mg | Ertugliflozin 15 mg | |
|---|---|---|---|
| HbA1c (%) | N = 437 | N = 447 | N = 440 |
| Baseline (mean) | 7.8 | 7.8 | 7.8 |
| Change from baseline (LS mean Intent-to-treat analysis using ANCOVA adjusted for baseline value, prior antihyperglycemic medication and baseline eGFR. ) | -0.6 | -0.5 | -0.5 |
| Difference from glimepiride (LS mean, 95% CI) | 0.2 Non-inferiority is declared when the upper bound of the two-sided 95% confidence interval (CI) for the mean difference is less than 0.3%. (0.0, 0.3) | 0.1(-0.0, 0.2) | |
| Patients [N (%)] with HbA1c <7% | 208 (47.7) | 177 (39.5) | 186 (42.2) |
The mean baseline body weight was 86.8 kg, 87.9 kg, and 85.6 kg in the glimepiride, ertugliflozin 5 mg, and ertugliflozin 15 mg groups, respectively. The mean changes from baseline to Week 52 were 0.6 kg, -2.6 kg, and -3.0 kg in the glimepiride, ertugliflozin 5 mg, and ertugliflozin 15 mg groups, respectively. The difference from glimepiride (95% CI) for ertugliflozin 5 mg was -3.2 kg (-3.7, -2.7) and for ertugliflozin 15 mg was -3.6 kg (-4.1, -3.1).
Ertugliflozin as Add-on Combination Therapy with Insulin (With or Without Metformin HCl)
In an 18-week randomized, double-blind, multi-center, placebo-controlled, glycemic sub-study of VERTIS CV (NCT01986881, study details see 14.2 ), a total of 1,065 patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and established atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease with inadequate glycemic control (HbA1c between 7% and 10.5%) on background therapy of insulin ≥20 units/day (59% also on metformin HCl ≥1,500 mg/day) were randomized to placebo, ertugliflozin 5 mg or ertugliflozin 15 mg oral once daily treatment.
At Week 18, treatment with ertugliflozin at 5 mg or 15 mg daily provided statistically significant reductions in HbA1c compared to placebo (see Table 9 ).
| Placebo | Ertugliflozin 5 mg | Ertugliflozin 15 mg | |
|---|---|---|---|
| SE: standard error. | |||
| HbA1c (%) | N = 346 | N = 346 | N = 367 |
| Baseline (mean) | 8.4 | 8.4 | 8.4 |
| Change from baseline (LS mean Intent-to-treat analysis using ANCOVA adjusted for baseline value, insulin stratum, and baseline eGFR. , SE) | -0.2 (0.05) | -0.7 (0.05) | -0.7 (0.05) |
| Difference from placebo (LS mean, 95% CI) | -0.5 p<0.001 compared to placebo. (-0.6, -0.4) | -0.5(-0.7, -0.4) | |
| Patients [N (%)] with HbA1c <7% Missing values imputed as not meeting the <7% criterion. | 37 (10.7) | 79 (22.8) | 81 (22.1) |
| FPG (mg/dL) | N = 343 | N = 346 | N = 368 |
| Baseline (mean) | 167.4 | 173.8 | 175.4 |
| Change from baseline (LS mean, SE) | -6.3 (2.91) | -25.6 (2.90) | -29.8 (2.86) |
| Difference from placebo (LS mean, 95% CI) | -19.2(-26.8, -11.6) | -23.4(-30.9, -16.0) | |
The mean baseline body weights were 93.3 kg, 93.8 kg, and 92.1 kg in the placebo, ertugliflozin 5 mg, and ertugliflozin 15 mg groups, respectively. The mean changes from baseline to Week 18 were -0.2 kg, - 1.6 kg, and -1.9 kg in the placebo, ertugliflozin 5 mg, and ertugliflozin 15 mg groups, respectively. The differences from placebo (95% CI) for ertugliflozin 5 mg were - 1.4 kg (- 1.9, - 0.9) and for ertugliflozin 15 mg was -1.6 kg (-2.1, -1.1).
The mean baseline systolic blood pressures were 134.0 mmHg, 135.6 mmHg, and 133.7 mmHg in the placebo, ertugliflozin 5 mg, and ertugliflozin 15 mg groups, respectively. The mean changes from baseline to Week 18 were 0.7 mmHg, -2.2 mmHg, and -1.7 mmHg in the placebo, ertugliflozin 5 mg, and ertugliflozin 15 mg groups, respectively. The differences from placebo (95% CI) for ertugliflozin 5 mg was – 2.9 mmHg (-4.9, -1.0) and for ertugliflozin 15 mg were -2.5 mmHg (- 4.4, - 0.5).
Add-on Combination Therapy with Metformin HCl and Sulfonylurea
In an 18-week randomized, double-blind, multi-center, placebo-controlled, glycemic sub-study of VERTIS CV (NCT01986881, study details see 14.2 ), a total of 330 patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and established atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease with inadequate glycemic control (HbA1c between 7% and 10.5%) with background therapy of metformin HCl ≥1,500 mg/day and a sulfonylurea (SU) were randomized to placebo, ertugliflozin 5 mg or ertugliflozin 15 mg oral once daily treatment.
At Week 18, treatment with ertugliflozin at 5 mg or 15 mg daily provided statistically significant reductions in HbA1c compared to placebo (see Table 10 ).
| Placebo | Ertugliflozin 5 mg | Ertugliflozin 15 mg | |
|---|---|---|---|
| SE: standard error | |||
| HbA1c (%) | N = 116 | N = 99 | N = 113 |
| Baseline (mean) | 8.3 | 8.4 | 8.3 |
| Change from baseline (LS mean Intent-to-treat analysis using ANCOVA adjusted for baseline value and baseline eGFR. , SE) | -0.3 (0.08) | -0.8 (0.09) | -0.9 (0.08) |
| Difference from placebo (LS mean, 95% CI) | -0.6 p<0.001 compared to placebo. (-0.8, -0.3) | -0.7(-0.9, -0.4) | |
| Patients [N (%)] with HbA1c <7% Missing values imputed as not meeting the <7% criterion. | 17 (14.7) | 39 (39.4) | 38 (33.6) |
| FPG (mg/dL) | N = 117 | N = 99 | N = 113 |
| Baseline (mean) | 177.3 | 183.5 | 174.0 |
| Change from baseline (LS mean, SE) | -3.5 (3.65) | -31.3 (3.87) | -33.0 (3.67) |
| Difference from placebo (LS mean, 95% CI) | -27.9(-37.8, -17.9) | -29.5(-39.0, -19.9) | |
The mean baseline body weights were 90.5 kg, 92.1 kg, and 92.9 kg in the placebo, ertugliflozin 5 mg, and ertugliflozin 15 mg groups, respectively. The mean changes from baseline to Week 18 were - 0.6 kg, -2.0 kg, and - 2.2 kg in the placebo, ertugliflozin 5 mg, and ertugliflozin 15 mg groups, respectively. The differences from placebo (95% CI) for ertugliflozin 5 mg were - 1.4 kg (- 2.2, - 0.7) and for ertugliflozin 15 mg was - 1.6 kg (- 2.3, - 0.9).
Ertugliflozin Cardiovascular Outcomes in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes and Established Cardiovascular Disease
The effect of ertugliflozin on cardiovascular risk in adult patients with type 2 diabetes and established atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease was evaluated in the VERTIS CV study (NCT 01986881), a multicenter, multi-national, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, event-driven trial. The study compared the risk of experiencing a major adverse cardiovascular event (MACE) between ertugliflozin and placebo when these were added to and used concomitantly with standard of care treatments for diabetes and atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease.
A total of 8,246 patients were randomized to placebo (N=2,747), oral once daily ertugliflozin 5 mg (N=2,752), or oral once daily ertugliflozin 15 mg (N=2,747) and followed for a median of 3 years. Approximately 88% of the study population was White, 6% Asian, and 3% Black or African American. The mean age was 64 years and approximately 70% were male.
All patients in the study had inadequately controlled type 2 diabetes mellitus at baseline (HbA1c greater than or equal to 7%). The mean duration of type 2 diabetes mellitus was 13 years, the mean HbA1c at baseline was 8.2% and the mean eGFR was 76 mL/min/1.73 m 2 . At baseline, patients were treated with one (32%) or more (67%) antidiabetic medications including biguanides (metformin HCl) (76%), insulin (47%), sulfonylureas (41%), DPP-4 inhibitors (11%) and GLP-1 receptor agonists (3%).
Almost all patients (99%) had established atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease at baseline including: a documented history of coronary artery disease (76%), cerebrovascular disease (23%) or peripheral artery disease (19%). Approximately 24% patients had a history of heart failure (HF). At baseline, the mean systolic blood pressure was 133 mmHg, the mean diastolic blood pressure was 77 mmHg, the mean LDL was 89 mg/dL, and the mean HDL was 44 mg/dL. At baseline, approximately 81% of patients were treated with renin angiotensin system inhibitors, 69% with beta-blockers, 43% with diuretics, 82% with statins, 4% ezetimibe, and 89% with antiplatelet agents.
The primary endpoint in VERTIS CV was the time to first occurrence of a Major Adverse Cardiac Event (MACE). A major adverse cardiovascular event was defined as occurrence of either a cardiovascular death or a nonfatal myocardial infarction (MI) or a nonfatal stroke. The statistical analysis plan pre-specified that the 5 and 15 mg doses would be combined for the analysis. A Cox proportional hazards model was used to test for non-inferiority against the pre-specified risk margin of 1.3 for the hazard ratio of MACE. Type-1 error was controlled across multiple tests using a hierarchical testing strategy.
The incidence rate of MACE was similar between the ertugliflozin-treated and placebo-treated patients. The estimated hazard ratio of MACE associated with ertugliflozin relative to placebo was 0.97 with 95.6% confidence interval (0.85, 1.11). The upper bound of this confidence interval excluded a risk larger than 1.3 (Table 11 ). Results for the 5 mg and 15 mg doses were consistent with results for the combined dose group.
| Endpoint MACE was evaluated in subjects who took at least one dose of study medication and, for subjects who discontinued study medication prior to the end of the study, censored events that occurred more than 365 days after the last dose of study medication. Other endpoints were evaluated using all randomized subjects and events that occurred any time after the first dose of study medication until the last contact date. The total number of first events was analyzed for each endpoint. | Placebo (N=2747) | ertugliflozin (N=5499) | Hazard Ratio vs Placebo (CI) HR and CI are based on Cox proportional hazards regression model, stratified by cohorts. For MACE a 95.6% CI is presented, for other endpoints a 95% CI is presented. | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N (%) | Event Rate (per 100 person-years) | N (%) | Event Rate (per 100 person-years) | ||
| N=Number of patients, CI=Confidence interval, CV=Cardiovascular, MI=Myocardial infarction. | |||||
| MACE (CV death, non-fatal MI, or non-fatal stroke) Composite | 327 (11.9) | 4.0 | 653 (11.9) | 3.9 | 0.97 (0.85, 1.11) |
| Components of Composite Endpoint | |||||
| Non-fatal MI | 148 (5.4) | 1.6 | 310 (5.6) | 1.7 | 1.04 (0.86, 1.27) |
| Non-fatal Stroke | 78 (2.8) | 0.8 | 157 (2.9) | 0.8 | 1.00 (0.76, 1.32) |
| CV death | 184 (6.7) | 1.9 | 341 (6.2) | 1.8 | 0.92 (0.77, 1.11) |
HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
SEGLUROMET (ertugliflozin and metformin hydrochloride) tablets are available as follows:
| Strength | Description | How Supplied | NDC |
|---|---|---|---|
| ertugliflozin 2.5 mg and metformin hydrochloride 500 mg tablets | pink, oval, debossed with “2.5/500” on one side and plain on the other side | unit-of-use bottles of 60 | 0006-5369-03 |
| unit-of-use bottles of 180 | 0006-5369-06 | ||
| ertugliflozin 2.5 mg and metformin hydrochloride 1,000 mg tablets | pink, oval, debossed with “2.5/1000” on one side and plain on the other side | unit-of-use bottles of 60 | 0006-5373-03 |
| unit-of-use bottles of 180 | 0006-5373-06 | ||
| ertugliflozin 7.5 mg and metformin hydrochloride 500 mg tablets | red, oval, debossed with “7.5/500” on one side and plain on the other side | unit-of-use bottles of 60 | 0006-5370-03 |
| unit-of-use bottles of 180 | 0006-5370-06 | ||
| ertugliflozin 7.5 mg and metformin hydrochloride 1,000 mg tablets | red, oval, debossed with “7.5/1000” on one side and plain on the other side | unit-of-use bottles of 60 | 0006-5374-03 |
| unit-of-use bottles of 180 | 0006-5374-06 |
Store at 20°C-25°C (68°F-77°F), excursions permitted between 15°C-30°C (between 59°F-86°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature]. Protect from moisture. Store in a dry place.
Mechanism of Action
SEGLUROMET
SEGLUROMET combines two antihyperglycemic agents with complementary mechanisms of action to improve glycemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: ertugliflozin, a SGLT2 inhibitor, and metformin hydrochloride, a member of the biguanide class.
Ertugliflozin
SGLT2 is the predominant transporter responsible for reabsorption of glucose from the glomerular filtrate back into the circulation. Ertugliflozin is an inhibitor of SGLT2. By inhibiting SGLT2, ertugliflozin reduces renal reabsorption of filtered glucose and lowers the renal threshold for glucose, and thereby increases urinary glucose excretion.
Metformin HCl
Metformin is an antihyperglycemic agent which improves glucose tolerance in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus, lowering both basal and postprandial plasma glucose. Its pharmacologic mechanisms of action are different from other classes of oral antihyperglycemic agents. Metformin decreases hepatic glucose production, decreases intestinal absorption of glucose, and improves insulin sensitivity by increasing peripheral glucose uptake and utilization. Metformin does not produce hypoglycemia in either patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus or normal subjects (except in special circumstances) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5) ] and does not cause hyperinsulinemia. With metformin therapy, insulin secretion remains unchanged while fasting insulin levels and day-long plasma insulin response may actually decrease.