Targretin Capsules patient education
Patient toolkit
Dosage & administration
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
The recommended initial dose of TARGRETIN is 300 mg/m 2 /day (see Table 1). TARGRETIN should be taken as a single oral daily dose with a meal. For precautions to prevent pregnancy and birth defects in women of child-bearing potential [ see Use in Specific Populations (8.1) ].
Initial Dose Level (300 mg/m 2 /day) | Number of 75 mg | |
Body Surface Area (m 2 ) | Total Daily Dose (mg/day) | |
0.88 – 1.12 | 300 | 4 |
1.13 – 1.37 | 375 | 5 |
1.38 – 1.62 | 450 | 6 |
1.63 – 1.87 | 525 | 7 |
1.88 – 2.12 | 600 | 8 |
2.13 – 2.37 | 675 | 9 |
2.38 – 2.62 | 750 | 10 |
Dose Modification Guidelines: The 300 mg/m 2 /day dose level of TARGRETIN may be adjusted to 200 mg/m 2 /day then to 100 mg/m 2 /day, or temporarily suspended, if necessitated by toxicity. When toxicity is controlled, doses may be carefully readjusted upward. If there is no tumor response after 8 weeks of treatment and if the initial dose of 300 mg/m 2 /day is well tolerated, the dose may be escalated to 400 mg/m 2 /day with careful monitoring.
Duration of Therapy: In clinical trials in CTCL, TARGRETIN was administered for up to 97 weeks.
TARGRETIN should be continued as long as the patient is deriving benefit.

By using PrescriberAI, you agree to the AI Terms of Use.
Targretin Capsules prescribing information
WARNING: BIRTH DEFECTS
TARGRETIN is a member of the retinoid class of drugs that is associated with birth defects in humans. Bexarotene also caused birth defects when administered orally to pregnant rats. TARGRETIN must not be administered to a pregnant woman. (8.1 )
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
TARGRETIN ® (bexarotene) Capsules are indicated for the treatment of cutaneous manifestations of cutaneous T-cell lymphoma in patients who are refractory to at least one prior systemic therapy.
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
The recommended initial dose of TARGRETIN is 300 mg/m 2 /day (see Table 1). TARGRETIN should be taken as a single oral daily dose with a meal. For precautions to prevent pregnancy and birth defects in women of child-bearing potential [ see Use in Specific Populations (8.1) ].
Initial Dose Level (300 mg/m 2 /day) | Number of 75 mg TARGRETIN Capsules | |
Body Surface Area (m 2 ) | Total Daily Dose (mg/day) | |
0.88 – 1.12 | 300 | 4 |
1.13 – 1.37 | 375 | 5 |
1.38 – 1.62 | 450 | 6 |
1.63 – 1.87 | 525 | 7 |
1.88 – 2.12 | 600 | 8 |
2.13 – 2.37 | 675 | 9 |
2.38 – 2.62 | 750 | 10 |
Dose Modification Guidelines: The 300 mg/m 2 /day dose level of TARGRETIN may be adjusted to 200 mg/m 2 /day then to 100 mg/m 2 /day, or temporarily suspended, if necessitated by toxicity. When toxicity is controlled, doses may be carefully readjusted upward. If there is no tumor response after 8 weeks of treatment and if the initial dose of 300 mg/m 2 /day is well tolerated, the dose may be escalated to 400 mg/m 2 /day with careful monitoring.
Duration of Therapy: In clinical trials in CTCL, TARGRETIN was administered for up to 97 weeks.
TARGRETIN should be continued as long as the patient is deriving benefit.
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Capsules: 75 mg, off-white, oblong soft gelatin capsules, imprinted with black ink “Targretin”.
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
Pregnancy
Risk Summary
TARGRETIN, a retinoid, can cause fetal harm based on findings from animal studies when administered to a pregnant female and is contraindicated during pregnancy. Bexarotene was teratogenic and caused developmental mortality in rats following oral administration during organogenesis [see Data] . TARGRETIN must not be given to a pregnant female or a female who intends to become pregnant. If pregnancy does occur during treatment with TARGRETIN, immediately discontinue the drug and advise the pregnant female of the potential risk to a fetus.
The background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated populations is unknown. However, the background risk in the U.S. general population of major birth defects is 2-4% and of miscarriage is 15-20% of clinically recognized pregnancies.
Data
Animal Data
Bexarotene caused malformations when administered orally to pregnant rats during days 7-17 of gestation. Developmental abnormalities included incomplete ossification at 4 mg/kg/day and cleft palate, depressed eye bulge/microphthalmia, and small ears at 16 mg/kg/day. The plasma AUC of bexarotene in rats at 4 mg/kg/day is approximately one third the AUC in humans at the recommended daily dose. At doses greater than 10 mg/kg/day, bexarotene caused developmental mortality. The no effect dose for fetal effects in rats was 1 mg/kg/day (producing an AUC approximately one sixth of the AUC at the recommended human daily dose).
Lactation
Risk Summary
There is no information regarding the presence of TARGRETIN in human milk, the effects on the breast fed infant, or the effects on milk production. Because many drugs are excreted in human milk and because of the potential for serious adverse reactions in nursing infants from TARGRETIN, discontinue breastfeeding during treatment with TARGRETIN.
Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
Pregnancy Testing
Obtain a negative serum pregnancy test (e.g., serum beta-human chorionic gonadotropin [beta-HCG]) with a sensitivity of at least 50 mIU/L within 1 week prior to TARGRETIN therapy. Obtain another pregnancy test at monthly intervals while the patient remains on TARGRETIN.
Contraception
Females
TARGRETIN can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant female [ see Use in Specific Populations (8.1) ]. Females of reproductive potential should be advised to avoid becoming pregnant when TARGRETIN is used. Effective contraception must be used for 1 month prior to the initiation of therapy, during therapy and for at least 1 month following discontinuation of therapy; it is recommended that two reliable forms of contraception be used simultaneously unless abstinence is the chosen method. Bexarotene can potentially induce metabolic enzymes and thereby theoretically reduce the plasma concentrations of oral or other systemic hormonal contraceptives [ see Drug Interactions (7) ]. Thus, if treatment with TARGRETIN is intended in a female with reproductive potential, it is strongly recommended that one of the two reliable forms of contraception should be non-hormonal. TARGRETIN therapy should be initiated on the second or third day of a normal menstrual period. No more than a 1-month supply of TARGRETIN should be given to the patient so that the results of pregnancy testing can be assessed and counseling regarding avoidance of pregnancy and birth defects can be reinforced.
Males
Male patients with sexual partners who are pregnant, possibly pregnant, or who could become pregnant must use condoms during sexual intercourse while taking TARGRETIN and for at least 1 month after the last dose of drug.
Pediatric Use
Safety and effectiveness of TARGRETIN in pediatric patients have not been established.
Geriatric Use
Of the total patients with CTCL in clinical trials of TARGRETIN, 64% were 60 years or older, while 33% were 70 years or older. No overall differences in safety were observed between patients 70 years or older and younger patients, but greater sensitivity of some older individuals to TARGRETIN cannot be ruled out. Responses to TARGRETIN were observed across all age group decades, without preference for any individual age group decade.
Hepatic Impairment
No specific studies have been conducted with TARGRETIN in subjects with hepatic impairment. Hepatic impairment is expected to lead to decreased clearance [ see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ]. If TARGRETIN is used in patients with hepatic impairment, monitor for signs of toxicity that may be due to increased exposure.
CONTRAINDICATIONS
Pregnancy
TARGRETIN can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant female. TARGRETIN is a member of the retinoid class of drugs that is associated with birth defects in humans and is contraindicated in females who are pregnant. Bexarotene was also teratogenic and caused developmental mortality when administered orally to pregnant rats. If this drug is used during pregnancy or if the patient becomes pregnant while taking this drug, the patient should be advised of the potential risk to a fetus.
Hypersensitivity
TARGRETIN Capsules are contraindicated in patients with a known serious hypersensitivity to bexarotene or other components of the product.
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- Hyperlipidemia: TARGRETIN causes elevations in blood lipids. Obtain baseline values, monitor, and manage elevations during therapy by dose reduction, interruption, discontinuation and/or lipid lowering therapy. (5.1 , 5.11 )
- Pancreatitis: Interrupt TARGRETIN and evaluate if suspected. (5.2 )
- Hepatotoxicity, Cholestasis, and Hepatic Failure: Interrupt or discontinue TARGRETIN and evaluate if liver chemistry tests exceed three times the upper limit of normal values. (5.3 )
- Hypothyroidism: TARGRETIN therapy can cause hypothyroidism. Monitor and replace thyroid hormone if needed. (5.5 )
- Neutropenia: Monitor for neutropenia. Reduce TARGRETIN dose or interrupt as indicated. (5.6 )
- Photosensitivity: Minimize exposure to sunlight and artificial ultraviolet light during treatment. (5.10 )
Hyperlipidemia
TARGRETIN induces substantial elevations in lipids in most patients. About 70% of patients with CTCL who received an initial dose of > 300 mg/m 2 /day of TARGRETIN had fasting triglyceride levels greater than 2.5 times the upper limit of normal. About 55% had values over 800 mg/dL with a median of about 1200 mg/dL in those patients. Cholesterol elevations above 300 mg/dL occurred in approximately 60% and 75% of patients with CTCL who received an initial dose of 300 mg/m 2 /day or greater than 300 mg/m 2 /day, respectively. Decreases in high density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol to less than 25 mg/dL were seen in about 55% and 90% of patients receiving an initial dose of 300 mg/m 2 /day or greater than 300 mg/m 2 /day, respectively, of TARGRETIN. Monitor lipid changes and treat abnormalities during therapy. The effects on triglycerides, HDL cholesterol, and total cholesterol were reversible with cessation of therapy, and could generally be mitigated by dose reduction and/or concomitant antilipemic therapy.
Perform fasting blood lipid determinations before TARGRETIN therapy is initiated and weekly until the lipid response to TARGRETIN is established, which usually occurs within 2 to 4 weeks, and monitor at 8-week intervals thereafter. Fasting triglycerides should be normal or normalized with appropriate intervention prior to initiating TARGRETIN therapy. Maintain triglyceride levels below 400 mg/dL to reduce the risk of clinical sequelae [ see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) ]. If fasting triglycerides are elevated or become elevated during treatment, institute antilipemic therapy, and if necessary, reduce or interrupt the dose of TARGRETIN. In the 300 mg/m 2 /day initial dose group, 60% of patients were given lipid lowering drugs. Atorvastatin was used in 48% (73/152) of patients with CTCL. Because of a potential drug-drug interaction, avoid gemfibrozil use with TARGRETIN [ see Drug Interactions (7) ].
Pancreatitis
Acute pancreatitis, including a fatal case, has been reported in four patients with CTCL and in six patients with non-CTCL cancers treated with TARGRETIN; the cases were associated with marked elevations of fasting serum triglycerides, the lowest being 770 mg/dL in one patient. One patient with advanced non-CTCL cancer died of pancreatitis. Interrupt TARGRETIN and evaluate if pancreatitis is suspected. Patients with CTCL who have risk factors for pancreatitis (e.g., prior pancreatitis, uncontrolled hyperlipidemia, excessive alcohol consumption, uncontrolled diabetes mellitus, biliary tract disease, and medications known to increase triglyceride levels or to be associated with pancreatic toxicity) may be at greater risk for pancreatitis associated with TARGRETIN [ see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) ].
Hepatotoxicity, Cholestasis, and Hepatic Failure
TARGRETIN caused elevations in liver chemistry tests (LFTs) in 5% (AST), 2% (ALT), and 0% (bilirubin) in patients with CTCL receiving an initial dose of 300 mg/m 2 /day. In contrast, with an initial dose greater than 300 mg/m 2 /day of TARGRETIN, the incidence of LFT elevations was higher at 7% (SGOT/AST), 9% (SGPT/ALT), and 6% (bilirubin). Two patients developed cholestasis, including one patient who died of liver failure. In clinical trials, elevated LFTs resolved within 1 month in 80% of patients following a decrease in dose or discontinuation of therapy. Obtain baseline LFTs and monitor LFTs after 1, 2, and 4 weeks of treatment initiation, and if stable, at least every 8 weeks thereafter during treatment. Interrupt or discontinue TARGRETIN if test results exceed three times the upper limit of normal values for AST, ALT, or bilirubin.
Hypothyroidism
TARGRETIN induces hypothyroidism in about half of all patients treated by causing a reversible reduction in levels of thyroid hormone (total thyroxine [total T4]) and thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH). The incidence of decreases in TSH and total T4 were about 60% and 45%, respectively, in patients with CTCL receiving an initial dose of 300 mg/m 2 /day. Hypothyroidism was reported as an adverse event in 29% of patients. Consider treatment with thyroid hormone supplementation in patients with hypothyroidism. In the 300 mg/m 2 /day initial dose group, 37% of patients were treated with thyroid hormone replacement. Obtain baseline thyroid function tests and patients monitor during treatment.
Neutropenia
Leukopenia in the range of 1000 to <3000 WBC x 10 6 /L occurred in 18% of patients with CTCL receiving an initial dose of 300 mg/m 2 /day of TARGRETIN. Patients receiving an initial dose greater than 300 mg/m 2 /day of TARGRETIN had an incidence of leukopenia of 43%. No patient with CTCL treated with TARGRETIN developed leukopenia of less than 1000 WBC x 10 6 /L. The usual time to onset of leukopenia was 4 to 8 weeks after initiating TARGRETIN. The leukopenia observed in most patients was predominantly neutropenia. In the 300 mg/m 2 /day initial dose group, the incidence of NCI Grade 3 and Grade 4 neutropenia, respectively, was 12% and 4%. The leukopenia and neutropenia experienced during TARGRETIN therapy resolved after dose reduction or discontinuation of treatment, on average within 30 days in 93% of the patients with CTCL and 82% of patients with non-CTCL cancers. Leukopenia and neutropenia were rarely associated with severe sequelae or serious adverse events. Obtain complete blood counts (CBC) at baseline and periodically during treatment.
Cataracts
Posterior subcapsular cataracts occurred in preclinical toxicity studies in rats and dogs administered bexarotene daily for 6 months. New cataracts or worsening of previous cataracts occurred in 15 of 79 patients who were monitored with serial slit lamp examinations. Because of the high prevalence and rate of cataract formation in older patient populations, the relationship of TARGRETIN and cataracts cannot be determined in the absence of an appropriate control group. Patients treated with TARGRETIN who experience visual difficulties should have an appropriate ophthalmologic evaluation.
Vitamin A Supplementation Hazard
In clinical studies, patients were advised to limit vitamin A intake to ≤15,000 IU/day. Because of the relationship of bexarotene to vitamin A, patients should be advised to limit vitamin A supplements to avoid potential additive toxic effects.
Hypoglycemia Risk in Patients with Diabetes Mellitus
In patients using insulin, agents enhancing insulin secretion (e.g., sulfonylureas), or insulin sensitizers (e.g., thiazolidinedione class), based on the mechanism of action, TARGRETIN could enhance the action of these agents, resulting in hypoglycemia. Hypoglycemia has not been associated with the use of TARGRETIN as monotherapy.
Photosensitivity
Retinoids as a class have been associated with photosensitivity. In vitro assays indicate that bexarotene is a potential photosensitizing agent. Phototoxicity manifested as sunburn and skin sensitivity to sunlight occurred in patients who were exposed to direct sunlight while receiving TARGRETIN. Advise patients to minimize exposure to sunlight and artificial ultraviolet light while receiving TARGRETIN.
Laboratory Tests
Before initiating TARGRETIN therapy, obtain a CBC, fasting lipid profile, liver function tests, and a thyroid profile. Fasting triglycerides should be normal or normalized with appropriate intervention prior to therapy. Monitor lab tests during TARGRETIN therapy as described above.
Hyperlipidemia usually occurs within the initial 2 to 4 weeks. Therefore, weekly lipid determinations are recommended during this interval. Subsequently, in patients not hyperlipidemic, determinations can be performed less frequently [ see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) ].
A white blood cell count with differential should be obtained at baseline and periodically during treatment. Baseline liver function tests should be obtained and should be carefully monitored after 1, 2, and 4 weeks of treatment initiation, and if stable, periodically thereafter during treatment. Baseline thyroid function tests should be obtained and then monitored during treatment as indicated [ see Warnings and Precautions (5.3 , 5.4 , 5.5 , 5.6 )] .
Drug/Laboratory Test Interactions
CA125 assay values in patients with ovarian cancer may be increased by TARGRETIN therapy.
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following serious adverse reactions are discussed in greater detail in other sections of the prescribing information:
- Hyperlipidemia [ see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) ]
- Pancreatitis [ see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) ]
- Hepatotoxicity, Cholestasis, and Hepatic Failure [ see Warnings and Precautions (5.3) ]
- Hypothyroidism [ see Warnings and Precautions (5.4) ]
- Neutropenia [ see Warnings and Precautions (5.5) ]
- Cataracts [ see Warnings and Precautions (5.6) ]
- Vitamin A Supplementation Hazard [ see Warnings and Precautions (5.7) ]
- Hypoglycemia Risk in Patients with Diabetes Mellitus [ see Warnings and Precautions (5.8) ]
- Photosensitivity [ see Warnings and Precautions (5.9) ]
- Laboratory Tests [ see Warnings and Precautions (5.10) ]
- Drug/Laboratory Test Interactions [ see Warnings and Precautions (5.11) ]
Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
The safety of TARGRETIN has been evaluated in two clinical trials of 152 patients with CTCL who received TARGRETIN for up to 97 weeks and in 352 patients in other trials. The mean duration of therapy for the 152 patients with CTCL was 166 days. The most common adverse events reported with an incidence of at least 10% in patients with CTCL treated at an initial dose of 300 mg/m 2 /day of TARGRETIN are shown in Table 2. The events at least possibly related to treatment are lipid abnormalities (elevated triglycerides, elevated total and LDL cholesterol and decreased HDL cholesterol), hypothyroidism, headache, asthenia, rash, leukopenia, anemia, nausea, infection, peripheral edema, abdominal pain, and dry skin. Most adverse events occurred at a greater incidence in patients treated at starting doses of greater than 300 mg/m 2 /day (see Table 2).
Adverse reactions leading to TARGRETIN dose reduction or discontinuation in at least two patients were hyperlipemia, neutropenia/leukopenia, diarrhea, fatigue/lethargy, hypothyroidism, headache, liver function test abnormalities, rash, pancreatitis, nausea, anemia, allergic reaction, muscle spasm, pneumonia, and confusion.
The NCI Grade 3 and NCI Grade 4 adverse reactions reported in two or more patients with CTCL treated at an initial dose of 300 mg/m 2 /day of TARGRETIN (see Table 3) were hypertriglyceridemia, pruritus, headache, peripheral edema, leukopenia, rash, and hypercholesteremia. Most of these moderately severe or severe adverse events occurred at a higher rate in patients treated at starting doses of greater than 300 mg/m 2 /day than in patients treated at a starting dose of 300 mg/m 2 /day.
In patients with CTCL receiving an initial dose of 300 mg/m 2 /day, the incidence of NCI Grade 3 or 4 elevations in triglycerides and total cholesterol was 28% and 25%, respectively (Table 4). In contrast, in patients with CTCL receiving greater than 300 mg/m 2 /day, the incidence of NCI Grade 3 or 4 elevated triglycerides and total cholesterol was 45% and 45%, respectively. Other Grade 3 and 4 laboratory abnormalities are shown in Table 3.
In addition to the 152 patients enrolled in the two CTCL trials, 352 patients received TARGRETIN as monotherapy for various advanced malignancies at doses from 5 mg/m 2 /day to 1000 mg/m 2 /day. The common adverse reactions (incidence greater than 10%) were similar to those seen in patients with CTCL.
In the 504 patients (CTCL and non-CTCL) who received TARGRETIN as monotherapy, drug-related serious adverse reactions that were fatal, in one patient each, were acute pancreatitis, subdural hematoma, and liver failure.
In the patients with CTCL receiving an initial dose of 300 mg/m 2 /day of TARGRETIN, adverse reactions reported at an incidence of less than 10% and not included in Tables 2 through 4 or discussed in other parts of labeling and possibly related to treatment were as follows:
Body as a Whole: chills, cellulitis, chest pain, breast pain, sepsis, and monilia infection.
Cardiovascular: hemorrhage, hypertension, angina pectoris, right heart failure, syncope, and tachycardia.
Digestive: constipation, dry mouth, flatulence, colitis, dyspepsia, cheilitis, gastroenteritis, gingivitis, liver failure, and melena.
Hemic and Lymphatic: eosinophilia, thrombocythemia, coagulation time increased, lymphocytosis, and thrombocytopenia.
Metabolic and Nutritional: LDH increased, creatinine increased, hypoproteinemia, hyperglycemia, weight decreased, weight increased, and amylase increased.
Musculoskeletal: arthralgia, myalgia, bone pain, myasthenia, and arthrosis.
Nervous: depression, agitation, ataxia, cerebrovascular accident, confusion, dizziness, hyperesthesia, hypesthesia, and neuropathy.
Respiratory: pharyngitis, rhinitis, dyspnea, pleural effusion, bronchitis, cough increased, lung edema, hemoptysis, and hypoxia.
Skin and Appendages: skin ulcer, acne, alopecia, skin nodule, macular papular rash, pustular rash, serous drainage, and vesicular bullous rash.
Special Senses: dry eyes, conjunctivitis, ear pain, blepharitis, corneal lesion, keratitis, otitis externa, and visual field defect.
Urogenital: albuminuria, hematuria, urinary incontinence, urinary tract infection, urinary urgency, dysuria, and kidney function abnormal.
Initial Assigned Dose Group (mg/m 2 /day) | ||
300 | >300 | |
Body System | N=84 | N=53 |
Adverse Event (AE) Preferred English term coded according to Ligand-modified COSTART 5 Dictionary. , Patients are counted at most once in each AE category. | N (%) | N (%) |
METABOLIC AND NUTRITIONAL DISORDERS | ||
Hyperlipemia | 66 (79) | 42 (79) |
Hypercholesteremia | 27 (32) | 33 (62) |
Lactic dehydrogenase increased | 6 (7) | 7 (13) |
BODY AS A WHOLE | ||
Headache | 25 (30) | 22 (42) |
Asthenia | 17 (20) | 24 (45) |
Infection | 11 (13) | 12 (23) |
Abdominal pain | 9 (11) | 2 (4) |
Chills | 8 (10) | 7 (13) |
Fever | 4 (5) | 9 (17) |
Flu syndrome | 3 (4) | 7 (13) |
Back pain | 2 (2) | 6 (11) |
Infection bacterial | 1 (1) | 7 (13) |
ENDOCRINE | ||
Hypothyroidism | 24 (29) | 28 (53) |
SKIN AND APPENDAGES | ||
Rash | 14 (17) | 12 (23) |
Dry skin | 9 (17) | 5 (9) |
Exfoliative dermatitis | 8 (10) | 15 (28) |
Alopecia | 3 (4) | 6 (11) |
HEMIC AND LYMPHATIC SYSTEM | ||
Leukopenia | 14 (17) | 25 (47) |
Anemia | 5 (6) | 13 (25) |
Hypochromic anemia | 3 (4) | 7 (13) |
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM | ||
Nausea | 13 (16) | 4 (8) |
Diarrhea | 6 (7) | 22 (42) |
Vomiting | 3 (4) | 7 (13) |
Anorexia | 2 (2) | 12 (23) |
CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM | ||
Peripheral edema | 11 (13) | 6 (11) |
NERVOUS SYSTEM | ||
Insomnia | 4 (5) | 6 (11) |
Table 3 : Incidence of Moderately Severe and Severe Adverse Events
Reported in at Least Two Patients (CTCL Trials)
Initial Assigned Dose Group (mg/m 2 /day) | ||||
300 (N=84) | >300 (N=53) | |||
Mod Sev | Severe | Mod Sev | Severe | |
Body System | ||||
Adverse Event (AE) Preferred English term coded according to Ligand-modified COSTART 5 Dictionary. , Patients are counted at most once in each AE category. Patients are classified by the highest severity within each row. | N (%) | N (%) | N (%) | N (%) |
BODY AS A WHOLE | ||||
Asthenia | 1 (1) | 0 (0) | 11 (21) | 0 (0) |
Headache | 3 (4) | 0 (0) | 5 (9) | 1 (2) |
Infection bacterial | 1 (1) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 2 (4) |
CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM | ||||
Peripheral edema | 2 (2) | 1 (1) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) |
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM | ||||
Anorexia | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 3 (6) | 0 (0) |
Diarrhea | 1 (1) | 1 (1) | 2 (4) | 1 (2) |
Pancreatitis | 1 (1) | 0 (0) | 3 (6) | 0 (0) |
Vomiting | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 2 (4) | 0 (0) |
ENDOCRINE | ||||
Hypothyroidism | 1 (1) | 1 (1) | 2 (4) | 0 (0) |
HEMIC AND LYMPHATIC SYSTEM | ||||
Leukopenia | 3 (4) | 0 (0) | 6 (11) | 1 (2) |
METABOLIC AND NUTRITIONAL DISORDERS | ||||
Bilirubinemia | 0 (0) | 1 (1) | 2 (4) | 0 (0) |
Hypercholesteremia | 2 (2) | 0 (0) | 5 (9) | 0 (0) |
Hyperlipemia | 16 (19) | 6 (7) | 17 (32) | 5 (9) |
SGOT/AST increased | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 2 (4) | 0 (0) |
SGPT/ALT increased | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 2 (4) | 0 (0) |
RESPIRATORY SYSTEM | ||||
Pneumonia | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 2 (4) | 2 (4) |
SKIN AND APPENDAGES | ||||
Exfoliative dermatitis | 0 (0) | 1 (1) | 3 (6) | 1 (2) |
Rash | 1 (1) | 2 (2) | 1 (2) | 0 (0) |
Table 4 : Treatment-Emergent Abnormal Laboratory Values in CTCL Trials
Initial Assigned Dose (mg/m 2 /day) | ||||
300 | >300 | |||
N=83 Number of patients with at least one analyte value post-baseline. | N=53 | |||
Analyte | Grade 3 Adapted from NCI Common Toxicity Criteria, Grade 3 and 4, Version 2.0. Patients are considered to have had a Grade 3 or 4 value if either of the following occurred: a) Value becomes Grade 3 or 4 during the study; b) Value is abnormal at baseline and worsens to Grade 3 or 4 on study, including all values beyond study drug discontinuation, as defined in data handling conventions. (%) | Grade 4 (%) | Grade 3 (%) | Grade 4 (%) |
Triglycerides The denominator used to calculate the incidence rates for fasting Total Cholesterol and Triglycerides were N=75 for the 300 mg/m 2 /day initial dose group and N=44 for the >300 mg/m 2 /day initial dose group. | 21 | 7 | 32 | 14 |
Total cholesterol | 19 | 7 | 16 | 30 |
Alkaline phosphatase | 1 | 0 | 0 | 2 |
Hyperglycemia | 1 | 0 | 6 | 0 |
Hypocalcemia | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
Hyponatremia | 1 | 0 | 9 | 0 |
SGPT/ALT | 1 | 0 | 2 | 2 |
Hyperkalemia | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 |
Hypernatremia | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
SGOT/AST | 0 | 0 | 2 | 2 |
Total bilirubin | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 |
ANC decreased | 12 | 4 | 19 | 8 |
ALC decreased | 7 | 0 | 15 | 0 |
WBC decreased | 4 | 0 | 11 | 0 |
Hemoglobin decreased | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 |
The safety profile from the one post-approval trial with 59 subjects was generally comparable to that of the pivotal trials with the exception of serious adverse events hypertriglyceridemia, neutropenia and bone marrow failure which were observed more frequently in the TARGRETIN 300 mg/m 2 /day group than in the TARGRETIN 150 mg/m 2 /day group.
Severe hypertriglyceridemia (≥800 mg/dL) was not seen in any subject in the lower dosage arm.
The most common AEs by preferred term in either the TARGRETIN 300 or 150 mg/m 2 /day treatment group were as follows: hypertriglyceridemia (18 subjects [62.1%] and 17 subjects [56.7%], respectively); hypothyroidism (15 subjects [51.7%] and 13 subjects [43.3%], respectively); headache (9 subjects [31.0%] and 7 subjects [23.3%], respectively); hypercholesterolemia (8 subjects [27.6%] and 7 subjects [23.3%], respectively); neutropenia (7 subjects [24.1%] and 2 subjects [6.7%], respectively); and skin exfoliation (5 subjects [17.2%] and 5 subjects [16.7%], respectively).
Higher percentage of subjects in the TARGRETIN 300 mg/m 2 /day group than in the TARGRETIN 150 mg/m 2 /day group experienced SAEs (13 subjects [44.8%] vs 11 subjects [36.7%], respectively.
Of the SAEs of special interest, there were more events in the TARGRETIN 300 mg/m 2 /day group than in TARGRETIN 150 mg/m 2 /day group of bone marrow failure (3 [10.3%] vs 1 [3.3%, respectively]), neutropenia (3 [10.3%] vs 0 [0%], respectively), and hypertriglyceridemia (9 [31%] vs 2 [6.7%], respectively).
DRUG INTERACTIONS
Effect of Other Drugs on TARGRETIN
Gemfibrozil: Concomitant administration of TARGRETIN and gemfibrozil resulted in increases in plasma concentrations of bexarotene. Concomitant administration of gemfibrozil with TARGRETIN is not recommended.
Effect of TARGRETIN on Other Drugs
TARGRETIN may be an inducer for the CYP3A4 enzymes, and may reduce plasma concentrations of other substrates metabolized by CYP3A4. Drug products which may be affected include oral or other systemic hormonal contraceptives. Thus, if treatment with TARGRETIN is intended for a female with reproductive potential, it is strongly recommended that a non-hormonal contraception be considered. [ see Use in Specific Populations (8.3) , Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ].
Laboratory Test Interference
CA125 assay values in patients with ovarian cancer may be increased by TARGRETIN therapy.
DESCRIPTION
TARGRETIN ® (bexarotene) Capsules contain bexarotene, a member of a subclass of retinoids that selectively activate retinoid X receptors (RXRs). These retinoid receptors have biologic activity distinct from that of retinoic acid receptors (RARs).
The chemical name of bexarotene is 4-[1-(5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-3,5,5,8,8-pentamethyl-2-naphthalenyl)ethenyl]benzoic acid, and the structural formula is as follows:
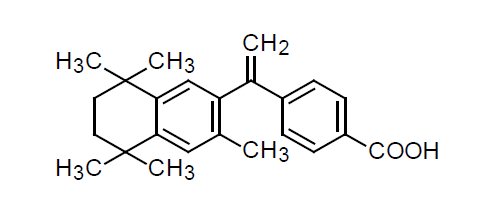
Bexarotene is an off-white to white powder with a molecular weight of 348.48 and a molecular formula of C 24 H 28 O 2 . It is insoluble in water and slightly soluble in vegetable oils and ethanol, USP.
Each TARGRETIN capsule contains 75 mg of bexarotene for oral administration. It also contains the following inactive ingredients: butylated hydroxyanisole, NF, polyethylene glycol 400, NF, polysorbate 20, NF, and povidone, USP. The capsule shell contains gelatin, NF, sorbitol special glycerin blend, and titanium dioxide, USP.
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Mechanism of Action
Bexarotene selectively binds and activates retinoid X receptor subtypes (RXRα, RXRß, RXRγ). RXRs can form heterodimers with various receptor partners such as retinoic acid receptors (RARs), vitamin D receptor, thyroid receptor, and peroxisome proliferator activator receptors (PPARs). Once activated, these receptors function as transcription factors that regulate the expression of genes that control cellular differentiation and proliferation. Bexarotene inhibits the growth in vitro of some tumor cell lines of hematopoietic and squamous cell origin. It also induces tumor regression in vivo in some animal models. The exact mechanism of action of bexarotene in the treatment of cutaneous T-cell lymphoma (CTCL) is unknown.
Pharmacokinetics
Terminal half-life of bexarotene is approximately 7 hours. Studies in patients with advanced malignancies show approximate single dose linearity within the therapeutic range.
Absorption
After oral administration of TARGRETIN, bexarotene is absorbed with a T max of about 2 hours. Plasma bexarotene AUC and C max values resulting from a 75 to 300 mg dose were 35% and 48% higher, respectively, after a fat-containing meal than after a glucose solution.
Distribution
Bexarotene is highly bound (>99%) to plasma proteins. The plasma proteins to which bexarotene binds have not been elucidated, and the ability of bexarotene to displace drugs bound to plasma proteins and the ability of drugs to displace bexarotene binding have not been studied.
Elimination
Metabolism
Four bexarotene metabolites have been identified in plasma: 6- and 7-hydroxy-bexarotene and 6- and 7-oxo-bexarotene. In vitro studies suggest that cytochrome P450 3A4 is the major cytochrome P450 responsible for formation of the oxidative metabolites and that the oxidative metabolites may be glucuronidated. The oxidative metabolites are active in in vitro assays of retinoid receptor activation, but the relative contribution of the parent and any metabolites to the efficacy and safety of TARGRETIN is unknown.
Excretion
The renal elimination of bexarotene and its metabolites was examined in patients with Type 2 diabetes mellitus. Urinary elimination of bexarotene and its known metabolites is a minor excretory pathway (<1% of administered dose).
Pharmacokinetics in Specific Populations
Age: Based on the population pharmacokinetic analysis of data for 232 patients aged ≥65 years and 343 patients aged <65 years, age has no statistically significant effect on bexarotene pharmacokinetics.
Body Weight and Gender: Based on the population pharmacokinetics analysis of data for 614 patients with a weight range of 26 to 145 kg, the bexarotene apparent clearance increases with increasing body weight. Gender has no statistically significant effect on bexarotene pharmacokinetics.
Race: Based on the population pharmacokinetic analysis of data for 540 Caucasian and 44 Black patients, bexarotene pharmacokinetics are similar in Blacks and Caucasians. There are insufficient data to evaluate potential differences in the pharmacokinetics of bexarotene for other races.
Renal Impairment: No formal studies have been conducted with TARGRETIN in patients with renal impairment. Urinary elimination of bexarotene and its known metabolites is a minor excretory pathway (<1% of administered dose), but because renal impairment can result in significant protein binding changes, pharmacokinetics may be altered in patients with renal impairment.
Hepatic Impairment: No specific studies have been conducted with TARGRETIN in patients with hepatic impairment. Because less than 1% of the dose is excreted in the urine unchanged and there is in vitro evidence of extensive hepatic contribution to bexarotene elimination, hepatic impairment would be expected to lead to greatly decreased clearance.
Drug Interactions
Effect of Other Drugs on TARGRETIN
CYP3A4 Inhibitors/Inducers: In a clinical study, concomitant administration of multiple doses of ketoconazole with TARGRETIN did not alter bexarotene plasma concentrations. This suggests that bexarotene elimination is not dependent on CYP3A4 metabolism.
Paclitaxel plus Carboplatin: The co-administration of paclitaxel (200 mg/m 2 IV dose over 3 hours) plus carboplatin (at a dose expected to achieve an AUC of 6 mg●min/mL) with TARGRETIN (400 mg/m 2 orally once daily) increased the exposure to bexarotene (AUC 0-24 and C max ) by 2-fold compared to TARGRETIN alone.
Atorvastatin: Bexarotene concentrations were not affected by concomitant atorvastatin administration.
Effect of TARGRETIN on Other Drugs
Bexarotene did not significantly inhibit the following enzymes in human liver microsomes: CYP1A2, CYP2A6, CYP2C9, CYP2C19, CYP2D6, CYP2E1 and CYP3A4. In vitro data suggested a potential for bexarotene to inhibit CYP2C8 and induce CYP3A4.
Atorvastatin: The exposure (AUC) to atorvastatin (a substrate for CYP3A4) decreased by half when atorvastatin was co-administered with TARGRETIN (400 mg/m 2 orally once daily).
Tamoxifen: Based on interim data, concomitant administration of TARGRETIN and tamoxifen resulted in approximately a 35% decrease in plasma concentrations of tamoxifen, possibly through induction of CYP3A4 by bexarotene.
Paclitaxel: The exposure (AUC) to paclitaxel (a substrate for CYP3A4 and CYP2C8) decreased by 19% when paclitaxel (200 mg/m 2 IV dose over 3 hours) was co-administered with TARGRETIN (400 mg/m 2 orally once daily).
Carboplatin: The co-administration of TARGRETIN (400 mg/m 2 orally once daily) had no effect on the exposure to free or total carboplatin.
NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Long-term studies in animals to assess the carcinogenic potential of bexarotene have not been conducted. Bexarotene is not mutagenic to bacteria (Ames assay) or mammalian cells (mouse lymphoma assay). Bexarotene was not clastogenic in vivo (micronucleus test in mice).
No formal fertility studies were conducted with bexarotene. Bexarotene caused testicular degeneration when oral doses of 1.5 mg/kg/day were given to dogs for 91 days (producing an AUC of approximately one fifth the AUC at the recommended human daily dose).
CLINICAL STUDIES
TARGRETIN was evaluated in two clinical trials in 152 patients with advanced and early stage cutaneous T-cell lymphoma (CTCL) in two multicenter, open-label, historically controlled clinical trials conducted in the U.S., Canada, Europe, and Australia.
The advanced disease patients had disease refractory to at least one prior systemic therapy (median of two, range 1 to 6 prior systemic therapies) and had been treated with a median of five (range 1 to 11) prior systemic, irradiation, and/or topical therapies. Early disease patients were intolerant to, had disease that was refractory to, or had reached a response plateau of 6 months on, at least two prior therapies. The patients entered had been treated with a median of 3.5 (range 2 to 12) therapies (systemic, irradiation, and/or topical).
The two clinical trials enrolled a total of 152 patients, 102 of whom had disease refractory to at least one prior systemic therapy, 90 with advanced disease and 12 with early disease. This is the patient population for whom TARGRETIN is indicated.
Patients were initially treated with a starting dose of 650 mg/m 2 /day with a subsequent reduction of starting dose to 500 mg/m 2 /day. Neither of these starting doses was tolerated, and the starting dose was then reduced to 300 mg/m 2 /day. If, however, a patient on 300 mg/m 2 /day of TARGRETIN showed no response after 8 or more weeks of therapy, the dose could be increased to 400 mg/m 2 /day.
Tumor response was assessed in both trials by observation of up to five baseline-defined index lesions using a Composite Assessment of Index Lesion Disease Severity (CA). This endpoint was based on a summation of the grades, for all index lesions, of erythema, scaling, plaque elevation, hypopigmentation or hyperpigmentation, and area of involvement. Also considered in response assessment was the presence or absence of cutaneous tumors and extracutaneous disease manifestations.
All tumor responses required confirmation over at least two assessments separated by at least 4 weeks. A partial response was defined as an improvement of at least 50% in the index lesions without worsening, or development of new cutaneous tumors or non-cutaneous manifestations. A complete clinical response required complete disappearance of all manifestations of disease, but did not require confirmation by biopsy.
At the initial dose of 300 mg/m 2 /day, 1/62 (1.6%) of patients had a complete clinical tumor response and 19/62 (30%) of patients had a partial tumor response. The rate of relapse (25% increase in CA or worsening of other aspects of disease) in the 20 patients who had a tumor response was 6/20 (30%) over a median duration of observation of 21 weeks, and the median duration of tumor response had not been reached. Responses were seen as early as 4 weeks and new responses continued to be seen at later visits.
In one post-approval clinical trial with a total of 59 subjects (29 in 300 mg/m 2 /day dose group and 30 in the 150 mg/m 2 /day dose), the objective response rate was higher in the TARGRETIN 300 mg/m 2 /day group than in the TARGRETIN 150 mg/m 2 /day group with respect to the CA (34.5% vs 23.3%), Physicians Global Assessment (PGA) (37.9% vs 20.0%), and percent BSA involvement (34.5% vs 23.3%).
The median duration of response in the TARGRETIN 300 mg/m 2 /day group based on the CA, PGA, and percent BSA involvement was 86.5 days, 72.0 days and 60.0 days, respectively. While in the TARGRETIN 150 mg/m 2 /day group the median duration of response based on the CA, PGA, and percent BSA involvement was 55 days, 119.0 days and 118.0 days, respectively.
The median time to cutaneous tumor response (the time to cutaneous tumor response for a given subject is defined as the time interval from the first day of TARGRETIN treatment to the time of the first observation when the subject with subsequent confirmation of response meets criteria for CR, CCR or PR) in the TARGRETIN 300 mg/m 2 /day group based on the CA, PGA, and percent BSA involvement was 85 days, 98 days and 117.5 days, respectively. While in the TARGRETIN 150 mg/m 2 /day group the median time to cutaneous tumor response based on the CA, PGA, and percent BSA involvement was 87 days, 57 days and 57 days, respectively. In the TARGRETIN 300 mg/m 2 /day group, the median time to cutaneous tumor progression based on the CA, PGA, and percent BSA involvement was 77.5, 115.5, and 88.0 days, respectively. In the TARGRETIN 150 mg/m 2 /day group, the median time to cutaneous tumor progression was 203.0 days based on the CA and 86.0 days based on percent BSA involvement; no subject in this treatment group had cutaneous tumor progression based on the PGA.
HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
TARGRETIN ® (bexarotene) Capsules are supplied as 75 mg off-white, oblong soft gelatin capsules, imprinted with “Targretin”, in high density polyethylene bottles with child-resistant closures.
Bottles of 100 capsules: NDC 0187-5526-75
Store at 2° to 25°C (36° to 77°F). Avoid exposing to high temperatures and humidity after the bottle is opened. Protect from light.
Mechanism of Action
Bexarotene selectively binds and activates retinoid X receptor subtypes (RXRα, RXRß, RXRγ). RXRs can form heterodimers with various receptor partners such as retinoic acid receptors (RARs), vitamin D receptor, thyroid receptor, and peroxisome proliferator activator receptors (PPARs). Once activated, these receptors function as transcription factors that regulate the expression of genes that control cellular differentiation and proliferation. Bexarotene inhibits the growth in vitro of some tumor cell lines of hematopoietic and squamous cell origin. It also induces tumor regression in vivo in some animal models. The exact mechanism of action of bexarotene in the treatment of cutaneous T-cell lymphoma (CTCL) is unknown.