Xeljanz prior authorization resources
Most recent state uniform prior authorization forms
Brand Resources
Xeljanz patient education
Patient toolkit
Dosage & administration
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Recommended Evaluations and Immunization Prior to Treatment Initiation
- Prior to initiating XELJANZ/XELJANZ XR, consider performing an active and latent TB evaluation, viral hepatitis screening, a complete blood count, and updating immunizations. Avoid XELJANZ or XELJANZ XR initiation if absolute lymphocyte count <500 cells/mm 3 , an absolute neutrophil count (ANC) <1000 cells/mm 3 or hemoglobin <9 g/dL. (2.1 )
Important Administration Instructions
- XELJANZ XR (extended-release tablets) is not substitutable with XELJANZ (tablets and oral solution). (2.2)
- Switching between XELJANZ and XELJANZ XR should be made by the healthcare provider. (2.2 )
Recommended Dosage
Adult Patients with RA, PsA or AS
- XELJANZ tablets 5 mg twice daily or XELJANZ XR (extended-release tablets) 11 mg once daily. (2.3 )
Pediatric Patients 2 Years of Age and Older with PsA or pcJIA Who Weigh At Least 10 kg
- XELJANZ (tablets or oral solution) 5 mg twice daily for those ≥40 kg or weight-based equivalent twice daily for those <40 kg. (2.4 )
Adult Patients with UC
- Induction: XELJANZ tablets 10 mg twice daily or XELJANZ XR 22 mg once daily for 8 weeks; evaluate patients and transition to maintenance therapy depending on therapeutic response. If needed, continue XELJANZ tablets 10 mg twice daily or XELJANZ XR 22 mg once daily for a maximum of 16 weeks. Discontinue XELJANZ tablets 10 mg twice daily or XELJANZ XR 22 mg once daily after 16 weeks if adequate therapeutic response is not achieved. (2.5 )
- Maintenance: XELJANZ tablets 5 mg twice daily or XELJANZ XR 11 mg once daily. For patients with loss of response during maintenance treatment, XELJANZ tablets 10 mg twice daily or XELJANZ XR 22 mg once daily may be considered and limited to the shortest duration, with careful consideration of the benefits and risks for the individual patient. Use the lowest effective dose needed to maintain response. (2.5 )
Dosage in Patients with Renal Impairment or Hepatic Impairment
- Use of XELJANZ (tablets and oral solution) or XELJANZ XR in patients with severe HI is not recommended. (2.3 , 2.4 , 2.5 , 8.7 )
- See full prescribing information (FPI) for recommended dosage in patients with moderate or severe RI or moderate HI. (2.3 , 2.4 , 2.5 , 8.6 , 8.7 )
Dosage Modification
See the full prescribing information for dosage modification by indication for patients who concomitantly use CYP2C19 and/or CYP3A4 inhibitors and patients with lymphopenia, neutropenia, or anemia. (2.3 , 2.4 , 2.5 , 7 )
Recommended Evaluations and Immunization Prior to Treatment Initiation
Prior to initiating XELJANZ (tablets and oral solution) or XELJANZ XR (extended-release tablets), consider performing the following:
- Active and latent tuberculosis (TB) infection evaluation: If the patient has latent TB, treat for TB prior to XELJANZ/XELJANZ XR treatment [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) ] .
- Viral hepatitis screening in accordance with clinical guidelines [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) ] .
- A complete blood count: Avoid initiation of XELJANZ/XELJANZ XR treatment in patients with a lymphocyte count less than 500 cells/mm 3 , absolute neutrophil count less than 1000 cells/mm 3 , or hemoglobin level less than 9 g/dL [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8) ] .
- Baseline hepatic function evaluation: XELJANZ/XELJANZ XR is not recommended for patients with severe hepatic impairment [see Use in Specific Populations (8.7) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ] .
- Update immunizations according to current immunization guidelines. The interval between live vaccinations and initiation of XELJANZ/XELJANZ XR should be in accordance with current vaccination guidelines regarding immunosuppressive agents [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9) ] .
Important Administration Instructions
- XELJANZ XR (extended-release tablets) is not substitutable with XELJANZ (tablets and oral solution). Switching between XELJANZ and XELJANZ XR should be made by the healthcare provider.
- Dose interruption is recommended for management of lymphopenia, neutropenia, and anemia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8) and Adverse Reactions (6.1) ] .
- Interrupt use of XELJANZ/XELJANZ XR if a patient develops a serious infection until the infection is controlled [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) ] .
- Take XELJANZ/XELJANZ XR with or without food [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ] .
- Swallow XELJANZ XR whole and intact. Do not crush, split, or chew the extended-release tablets [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ] .
Recommended Dosage in Adults with Rheumatoid Arthritis, Psoriatic Arthritis, and Ankylosing Spondylitis
Table 1 displays the recommended dosage of XELJANZ tablets and XELJANZ XR (extended-release tablets) for adults with RA, PsA, and AS [see Indication and Usage (1.1 , 1.2 , 1.3) ] with and without renal impairment (including those who are undergoing hemodialysis) or hepatic impairment [see Use in Specific Populations (8.6 , 8.7 )] . The table also displays the recommended dosage modifications for patients concomitantly using CYP2C19 and/or CYP3A4 inhibitors [see Drug Interactions (7) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ] , and patients with lymphopenia, neutropenia, or anemia.
Adults | XELJANZ Tablets | XELJANZ XR (extended-release tablets) |
Patients with Normal Renal and Hepatic Function Excludes patients who concomitantly use XELJANZ tablets/XELJANZ XR with strong CYP3A4 inhibitor(s) or moderate CYP3A4 inhibitor(s) and strong CYP2C19 inhibitor(s), as well as patients with lymphocyte count less than 500 cells/mm 3 , ANC <1000 cells/mm 3 , or hemoglobin less than 8 g/dL or a decrease of more than 2 g/dL. | 5 mg twice daily | 11 mg once daily |
Recommended Dosage in Patients with Renal Impairment (RI) Tofacitinib PK was evaluated in subjects with varying degrees of renal impairment, where the severity of renal impairment was defined based on creatinine clearance (CLcr) estimated using the Cockcroft‑Gault equation: CLcr >80 mL/min (normal renal function); >50 and ≤80 mL/min (mild renal impairment); ≥30 and ≤50 mL/min (moderate renal impairment); <30 mL/min (severe renal impairment). | ||
Mild RI (CLcr >50 and ≤80 mL/min) | 5 mg twice daily | 11 mg once daily |
Moderate RI (CLcr ≥30 and ≤50 mL/min) | 5 mg once daily | XELJANZ tablets 5 mg once daily |
Severe RI (CLcr <30 mL/min) | 5 mg once daily | XELJANZ tablets 5 mg once daily |
For patients undergoing hemodialysis, administer the dose after the dialysis session on dialysis days. If a dose was taken before the dialysis procedure, supplemental doses are not recommended after dialysis. | ||
Recommended Dosage in Patients with Hepatic Impairment (HI) | ||
Mild HI (Child-Pugh A) | 5 mg twice daily | 11 mg once daily |
Moderate HI (Child-Pugh B) | 5 mg once daily | XELJANZ tablets 5 mg once daily |
Severe HI (Child-Pugh C) | Use of XELJANZ tablets/XELJANZ XR is not recommended. | |
Dosage Modifications with Concomitant Use of CYP3A4 and/or CYP2C19 Inhibitor(s) | ||
Strong CYP2C19 inhibitor(s) | 5 mg twice daily | 11 mg once daily |
Moderate CYP2C19 inhibitor(s) | ||
Moderate CYP3A4 inhibitor(s) | ||
Moderate CYP3A4 inhibitor(s) with strong CYP2C19 inhibitor(s) (e.g., fluconazole) | 5 mg once daily | XELJANZ tablets 5 mg once daily |
Strong CYP3A4 inhibitor(s) | ||
Dosage Modifications for Lymphopenia, Neutropenia, or Anemia | ||
Patients with lymphocyte count less than 500 cells/mm 3 , confirmed by repeat testing | Discontinue dosing. | |
Patients with ANC less than 500 cells/mm 3 | Discontinue dosing. | |
Patients with ANC 500 to 1000 cells/mm 3 | Interrupt dosing. When ANC is greater than 1000, resume 5 mg twice daily. | Interrupt dosing. When ANC is greater than 1000, resume 11 mg once daily. |
Patients with hemoglobin less than 8 g/dL or a decrease of more than 2 g/dL | Interrupt dosing until hemoglobin values have normalized. | |
Switching from XELJANZ Tablets to XELJANZ XR Extended-Release Tablets
Patients treated with XELJANZ tablets 5 mg twice daily may be switched to XELJANZ XR extended-release tablets 11 mg once daily the day following the last dose of XELJANZ tablets 5 mg.
Recommended Dosage in Pediatric Patients 2 Years of Age and Older with Psoriatic Arthritis or Polyarticular Course Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis
Table 2 displays the recommended body weight-based dosages for XELJANZ tablets and XELJANZ oral solution in pediatric patients 2 years of age and older with PsA or pcJIA [see Indication and Usage (1.2 , 1.4) ] with and without renal impairment (including those who are undergoing hemodialysis) or hepatic impairment [see Use in Specific Populations (8.6 , 8.7) ] . The table also includes recommended dosage modification for pediatric patients concomitantly using CYP2C19 and/or CYP3A4 inhibitors [see Drug Interactions (7) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ] , and pediatric patients with lymphopenia, neutropenia, or anemia.
Administer XELJANZ oral solution using the included press-in bottle adapter and oral dosing syringe [see Instructions for Use ] .
| Pediatric Patients 2 Years of Age and Older | XELJANZ tablets and XELJANZ oral solution |
|---|---|
Patients with Normal Renal and Hepatic Function Excludes patients who concomitantly use XELJANZ (tablets and oral solution) with strong CYP3A4 inhibitor(s) or moderate CYP3A4 inhibitor(s) and strong CYP2C19 inhibitor(s), as well as patients with lymphocyte count less than 500 cells/mm 3 , ANC <1000 cells/mm 3 , or hemoglobin less than 8 g/dL or a decrease of more than 2 g/dL. |
|
Recommended Dosage in Patients with Renal Impairment (RI) | |
Mild RI | Same as patients with normal renal function. |
Moderate RI |
|
Severe RI |
|
For patients undergoing hemodialysis, administer the dose after the dialysis session on dialysis days. If a dose was taken before the dialysis procedure, supplemental doses are not recommended after dialysis. | |
Recommended Dosage in Patients with Hepatic Impairment (HI) | |
Mild HI | Same as patients with normal hepatic function. |
Moderate HI |
|
Severe HI | Use of XELJANZ tablets/XELJANZ oral solution is not recommended. |
Dosage Modifications with Concomitant Use of CYP3A4 and/or CYP2C19 Inhibitor(s) | |
Strong CYP2C19 inhibitor(s) | No dosage modification is recommended. |
Moderate CYP2C19 inhibitor(s) | |
Moderate CYP3A4 inhibitor(s) | |
Moderate CYP3A4 inhibitor(s) with strong CYP2C19 inhibitor(s) (e.g., fluconazole) |
|
Strong CYP3A4 inhibitor(s) | |
Dosage Modifications for Lymphopenia, Neutropenia, or Anemia | |
Patients with lymphocyte count less than 500 cells/mm 3 , confirmed by repeat testing | Discontinue dosing. |
Patients with ANC less than 500 cells/mm 3 | Discontinue dosing. |
Patients with ANC 500 to 1000 cells/mm 3 | Interrupt dosing until ANC is greater than 1000 cells/mm 3 . |
Patients with hemoglobin less than 8 g/dL or a decrease of more than 2 g/dL | Interrupt dosing until hemoglobin values have normalized. |
Recommended Dosage in Adults with Ulcerative Colitis
Table 3 displays the recommended dosage of XELJANZ tablets and XELJANZ XR (extended-release tablets) in adult patients with ulcerative colitis (UC) [see Indications and Usage (1.5) ] with and without renal impairment (including those who are undergoing hemodialysis) or hepatic impairment [see Use in Specific Populations (8.6 , 8.7) ] . Table 4 displays the recommended dosage modification for patients concomitantly using CYP2C19 and/or CYP3A4 inhibitors [see Drug Interactions (7) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ] , and patients with lymphopenia, neutropenia, or anemia.
| Adults | XELJANZ tablets | XELJANZ XR (extended-release tablets) |
|---|---|---|
Patients with Normal Renal and Hepatic Function Excludes patients who concomitantly use XELJANZ tablets/XELJANZ XR with strong CYP3A4 inhibitor(s) or moderate CYP3A4 inhibitor(s) and strong CYP2C19 inhibitor(s), as well as patients with lymphocyte count less than 500 cells/mm 3 , ANC <1000 cells/mm 3 , or hemoglobin less than 8 g/dL or a decrease of more than 2 g/dL. | Induction: 10 mg twice daily for at least 8 weeks [see Clinical Studies (14.5) ] ; evaluate patients and transition to maintenance therapy depending on therapeutic response. If needed continue 10 mg twice daily for a maximum of 16 weeks. Discontinue 10 mg twice daily after 16 weeks if adequate therapeutic response is not achieved. | Induction: 22 mg once daily for at least 8 weeks; evaluate patients and transition to maintenance therapy depending on therapeutic response. If needed continue 22 mg once daily for a maximum of 16 weeks. Discontinue 22 mg once daily after 16 weeks if adequate therapeutic response is not achieved. |
Maintenance: 5 mg twice daily. For patients with loss of response during maintenance treatment, may consider a dosage of 10 mg twice daily (limited to the shortest duration), with careful consideration of the benefits and risks for the individual patient. Use the lowest effective dosage needed to maintain response. | Maintenance: 11 mg once daily. For patients with loss of response during maintenance treatment, may consider a dosage of 22 mg once daily (limited to the shortest duration), with careful consideration of the benefits and risks for the individual patient. Use the lowest effective dose needed to maintain response. | |
Recommended Dosage in Patients with Renal Impairment (RI) Tofacitinib PK was evaluated in subjects with varying degrees of renal impairment, where the severity of renal impairment was defined based on creatinine clearance (CLcr) estimated using the Cockcroft‑Gault equation: CLcr >80 mL/min (normal renal function); CLcr >50 and ≤80 mL/min (mild renal impairment); ≥30 and ≤50 mL/min (moderate renal impairment); <30 mL/min (severe renal impairment). | ||
Mild RI | Same as patients with normal renal function. | |
Moderate RI | Induction: 5 mg twice daily for at least 8 weeks [see Clinical Studies (14.5) ] ; evaluate patients and transition to maintenance therapy depending on therapeutic response. If needed continue 5 mg twice daily for a maximum of 16 weeks. Discontinue 5 mg twice daily after 16 weeks if adequate therapeutic response is not achieved. | Induction: 11 mg once daily for at least 8 weeks; evaluate patients and transition to maintenance therapy depending on therapeutic response. If needed continue 11 mg once daily for a maximum of 16 weeks. Discontinue 11 mg once daily after 16 weeks if adequate therapeutic response is not achieved. |
Severe RI | Maintenance: 5 mg once daily.
| Maintenance: XELJANZ XR is not recommended. See Maintenance Dosage for XELJANZ tablets for Moderate or Severe RI.
|
Recommended Dosage in Patients with Hepatic Impairment (HI) | ||
Mild HI | Same as patients with normal hepatic function. | |
Moderate HI | Induction: 5 mg twice daily for at least 8 weeks [see Clinical Studies (14.5) ] ; evaluate patients and transition to maintenance therapy depending on therapeutic response. If needed continue 5 mg twice daily for a maximum of 16 weeks. Discontinue 5 mg twice daily after 16 weeks if adequate therapeutic response is not achieved. | Induction: 11 mg once daily for at least 8 weeks; evaluate patients and transition to maintenance therapy depending on therapeutic response. If needed continue 11 mg once daily for a maximum of 16 weeks. Discontinue 11 mg once daily after 16 weeks if adequate therapeutic response is not achieved. |
Maintenance: 5 mg once daily. For patients with loss of response during maintenance treatment, may consider a dosage of 5 mg twice daily (limited to the shortest duration), with careful consideration of the benefits and risks for the individual patient. Use the lowest effective dosage needed to maintain response. | Maintenance: XELJANZ XR is not recommended. See Maintenance Dosage for XELJANZ tablets for Moderate HI. | |
Severe HI | Use of XELJANZ tablets/XELJANZ XR is not recommended. | |
| Adults | XELJANZ Tablets | XELJANZ XR (extended-release tablets) |
|---|---|---|
Dosage Modifications with Concomitant Use of CYP3A4 and/or CYP2C19 Inhibitor(s) | ||
Strong CYP2C19 inhibitor(s) | No dosage modification is recommended. | |
Moderate CYP2C19 inhibitor(s) | ||
Moderate CYP3A4 inhibitor(s) | ||
Moderate CYP3A4 inhibitor(s) with strong CYP2C19 inhibitor(s) (e.g., fluconazole) | Induction: 5 mg twice daily for at least 8 weeks [see Clinical Studies (14.5) ] ; evaluate patients and transition to maintenance therapy depending on therapeutic response. If needed continue 5 mg twice daily for a maximum of 16 weeks. Discontinue 5 mg twice daily after 16 weeks if adequate therapeutic response is not achieved. | Induction: 11 mg once daily for at least 8 weeks; evaluate patients and transition to maintenance therapy depending on therapeutic response. If needed continue 11 mg once daily for a maximum of 16 weeks. Discontinue 11 mg once daily after 16 weeks if adequate therapeutic response is not achieved. |
Strong CYP3A4 inhibitor(s) | ||
Maintenance: 5 mg once daily. For patients with loss of response during maintenance treatment, may consider a dosage of 5 mg twice daily (limited to the shortest duration), with careful consideration of the benefits and risks for the individual patient. Use the lowest effective dosage needed to maintain response. | Maintenance: XELJANZ XR is not recommended. see Maintenance Dosage for XELJANZ tablets for Strong CYP3A4 inhibitors. | |
Dosage Modifications for Lymphopenia, Neutropenia, or Anemia | ||
Lymphocyte count less than 500 cells/mm 3 , confirmed by repeat testing | Discontinue dosing. | |
ANC less than 500 cells/mm 3 | Discontinue dosing. | |
ANC 500 to 1000 cells/mm 3 | If taking:
| If taking:
|
Hemoglobin less than 8 g/dL or a decrease of more than 2 g/dL | Interrupt dosing until hemoglobin values have normalized. | |
Switching from XELJANZ Tablets to XELJANZ XR Extended-Release Tablets
Patients treated with XELJANZ tablets:
- 5 mg twice daily may be switched to XELJANZ XR extended-release tablets 11 mg once daily the day following the last dose of XELJANZ tablets 5 mg.
- 10 mg twice daily may be switched to XELJANZ XR extended-release tablets 22 mg once daily the day following the last dose of XELJANZ tablets 10 mg.

Xeljanz prescribing information
WARNING: SERIOUS INFECTIONS, MORTALITY, MALIGNANCY, MAJOR ADVERSE CARDIOVASCULAR EVENTS, and THROMBOSIS
SERIOUS INFECTIONS
Patients treated with XELJANZ (tablets and oral solution) or XELJANZ XR (extended-release tablets) are at increased risk for developing serious bacterial, fungal, viral, and opportunistic infections, including tuberculosis (TB), that may lead to hospitalization or death [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) and Adverse Reactions (6.1) ] . Most patients who developed these infections were taking concomitant immunosuppressants such as methotrexate or corticosteroids. Reported infections included:
- Active TB, which may present with pulmonary or extrapulmonary disease. Patients should be tested for latent TB before XELJANZ/XELJANZ XR use and during therapy. Treatment for latent infection should be initiated prior to XELJANZ/XELJANZ XR use.
- Invasive fungal infections, including cryptococcosis and pneumocystosis. Patients with invasive fungal infections may present with disseminated, rather than localized, disease.
- Bacterial, viral, including herpes zoster, and other infections due to opportunistic pathogens.
The risks and benefits of XELJANZ/XELJANZ XR treatment should be carefully considered prior to initiating therapy in patients with chronic or recurrent infection.
Patients should be closely monitored for the development of signs and symptoms of infection during and after XELJANZ/XELJANZ XR treatment, including the possible development of TB in patients who tested negative for latent TB infection prior to initiating therapy. If a serious infection develops, interrupt XELJANZ/XELJANZ XR until the infection is controlled [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) ] .
MORTALITY
In a large, randomized, postmarketing safety study in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients 50 years of age and older with at least one cardiovascular (CV) risk factor comparing XELJANZ tablets 5 mg or 10 mg twice a day to tumor necrosis factor (TNF) blockers, a higher rate of all-cause mortality, including sudden CV death, was observed with XELJANZ tablets 5 mg or 10 mg twice a day [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) ] . XELJANZ 10 mg twice daily and XELJANZ XR 22 mg once daily dosages are not recommended for the treatment of RA, psoriatic arthritis (PsA), ankylosing spondylitis (AS), or polyarticular course juvenile idiopathic arthritis (pcJIA) [see Dosage and Administration (2.3, 2.4) ] .
MALIGNANCIES
Malignancies, including lymphomas and solid tumors, have occurred in patients treated with XELJANZ and other Janus kinase inhibitors used to treat inflammatory conditions. In RA patients, a higher rate of malignancies (excluding non-melanoma skin cancer (NMSC)) was observed in patients treated with XELJANZ tablets 5 mg or 10 mg twice a day compared with TNF blockers [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3) ] .
Lymphomas and lung cancers were observed at a higher rate in patients treated with XELJANZ tablets 5 mg or 10 mg twice a day in RA patients compared to those treated with TNF blockers. Patients who are current or past smokers are at additional increased risk.
MAJOR ADVERSE CARDIOVASCULAR EVENTS
RA patients 50 years of age and older with at least one cardiovascular risk factor, treated with XELJANZ tablets 5 mg or 10 mg twice daily, had a higher rate of major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) (defined as cardiovascular death, myocardial infarction, and stroke), compared to those treated with TNF blockers. Patients who are current or past smokers are at additional increased risk. Discontinue XELJANZ/XELJANZ XR in patients that have experienced a myocardial infarction or stroke [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4) ] .
THROMBOSIS
Thrombosis, including pulmonary embolism, deep venous thrombosis, and arterial thrombosis have occurred in patients treated with XELJANZ and other Janus kinase inhibitors used to treat inflammatory conditions. Many of these events were serious and some resulted in death. RA patients 50 years of age and older with at least one cardiovascular risk factor treated with XELJANZ tablets 5 mg or 10 mg twice daily compared to TNF blockers had an observed increase in incidence of these events. Avoid XELJANZ/XELJANZ XR in patients at risk. Discontinue XELJANZ/XELJANZ XR and promptly evaluate patients with symptoms of thrombosis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5) ] .
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
XELJANZ (tablets and oral solution) and XELJANZ XR (extended-release tablets) are Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors.
XELJANZ tablets and XELJANZ XR are indicated for the treatment of adult patients with:
- Moderately to severely active rheumatoid arthritis (RA), who have had an inadequate response or intolerance to one or more TNF blockers.
- Active psoriatic arthritis (PsA), who have had an inadequate response or intolerance to one or more TNF blockers.
- Active ankylosing spondylitis (AS), who have had an inadequate response or intolerance to one or more TNF blockers.
- Moderately to severely active ulcerative colitis (UC), who have had an inadequate response or intolerance to one or more TNF blockers.
XELJANZ (tablets and oral solution) are indicated for the treatment of pediatric patients 2 years of age and older with:
- Active PsA, who have had an inadequate response or intolerance to one or more TNF blockers.
- Active polyarticular course juvenile idiopathic arthritis (pcJIA), who have had an inadequate response or intolerance to one or more TNF blockers.
Limitations of Use :
- Use of XELJANZ/XELJANZ XR for RA, AS, PsA, or pcJIA in combination with biologic DMARDs or potent immunosuppressants such as azathioprine and cyclosporine is not recommended. (1.1 , 1.2 , 1.3 , 1.4 )
- Use of XELJANZ tablets and XELJANZ XR for UC in combination with biological therapies for UC or with potent immunosuppressants such as azathioprine and cyclosporine is not recommended. (1.5 )
Rheumatoid Arthritis
XELJANZ tablets and XELJANZ XR (extended-release tablets) are indicated for the treatment of adult patients with moderately to severely active rheumatoid arthritis (RA), who have had an inadequate response or intolerance to one or more TNF blockers.
Limitations of Use
Use of XELJANZ tablets or XELJANZ XR in combination with biologic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) or with potent immunosuppressants such as azathioprine and cyclosporine is not recommended.
1.2 Psoriatic Arthritis
XELJANZ (tablets and oral solution) is indicated for the treatment of adult and pediatric patients 2 years of age and older with active psoriatic arthritis (PsA), who have had an inadequate response or intolerance to one or more TNF blockers.
XELJANZ XR (extended-release tablets) is indicated for the treatment of adults with active PsA who have had an inadequate response or intolerance to one or more TNF blockers.
Limitations of Use
Use of XELJANZ or XELJANZ XR in combination with biologic DMARDs or with potent immunosuppressants such as azathioprine and cyclosporine is not recommended.
Ankylosing Spondylitis
XELJANZ tablets and XELJANZ XR (extended-release tablets) are indicated for the treatment of adult patients with active ankylosing spondylitis (AS), who have had an inadequate response or intolerance to one or more TNF blockers.
Limitations of Use
Use of XELJANZ tablets or XELJANZ XR in combination with biologic DMARDs or potent immunosuppressants such as azathioprine and cyclosporine is not recommended.
Polyarticular Course Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis
XELJANZ (tablets and oral solution) are indicated for the treatment of pediatric patients 2 years of age and older with of active polyarticular course juvenile idiopathic arthritis (pcJIA), who have had an inadequate response or intolerance to one or more TNF blockers.
Limitations of Use
Use of XELJANZ in combination with biologic DMARDs or with potent immunosuppressants such as azathioprine and cyclosporine is not recommended.
Ulcerative Colitis
XELJANZ tablets and XELJANZ XR (extended-release tablets) are indicated for the treatment of adult patients with moderately to severely active ulcerative colitis (UC), who have an inadequate response or intolerance to one or more TNF blockers.
Limitations of Use
Use of XELJANZ tablets or XELJANZ XR in combination with biological therapies for UC or with potent immunosuppressants such as azathioprine and cyclosporine is not recommended.
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Recommended Evaluations and Immunization Prior to Treatment Initiation
- Prior to initiating XELJANZ/XELJANZ XR, consider performing an active and latent TB evaluation, viral hepatitis screening, a complete blood count, and updating immunizations. Avoid XELJANZ or XELJANZ XR initiation if absolute lymphocyte count <500 cells/mm 3 , an absolute neutrophil count (ANC) <1000 cells/mm 3 or hemoglobin <9 g/dL. (2.1 )
Important Administration Instructions
- XELJANZ XR (extended-release tablets) is not substitutable with XELJANZ (tablets and oral solution). (2.2)
- Switching between XELJANZ and XELJANZ XR should be made by the healthcare provider. (2.2 )
Recommended Dosage
Adult Patients with RA, PsA or AS
- XELJANZ tablets 5 mg twice daily or XELJANZ XR (extended-release tablets) 11 mg once daily. (2.3 )
Pediatric Patients 2 Years of Age and Older with PsA or pcJIA Who Weigh At Least 10 kg
- XELJANZ (tablets or oral solution) 5 mg twice daily for those ≥40 kg or weight-based equivalent twice daily for those <40 kg. (2.4 )
Adult Patients with UC
- Induction: XELJANZ tablets 10 mg twice daily or XELJANZ XR 22 mg once daily for 8 weeks; evaluate patients and transition to maintenance therapy depending on therapeutic response. If needed, continue XELJANZ tablets 10 mg twice daily or XELJANZ XR 22 mg once daily for a maximum of 16 weeks. Discontinue XELJANZ tablets 10 mg twice daily or XELJANZ XR 22 mg once daily after 16 weeks if adequate therapeutic response is not achieved. (2.5 )
- Maintenance: XELJANZ tablets 5 mg twice daily or XELJANZ XR 11 mg once daily. For patients with loss of response during maintenance treatment, XELJANZ tablets 10 mg twice daily or XELJANZ XR 22 mg once daily may be considered and limited to the shortest duration, with careful consideration of the benefits and risks for the individual patient. Use the lowest effective dose needed to maintain response. (2.5 )
Dosage in Patients with Renal Impairment or Hepatic Impairment
- Use of XELJANZ (tablets and oral solution) or XELJANZ XR in patients with severe HI is not recommended. (2.3 , 2.4 , 2.5 , 8.7 )
- See full prescribing information (FPI) for recommended dosage in patients with moderate or severe RI or moderate HI. (2.3 , 2.4 , 2.5 , 8.6 , 8.7 )
Dosage Modification
See the full prescribing information for dosage modification by indication for patients who concomitantly use CYP2C19 and/or CYP3A4 inhibitors and patients with lymphopenia, neutropenia, or anemia. (2.3 , 2.4 , 2.5 , 7 )
Recommended Evaluations and Immunization Prior to Treatment Initiation
Prior to initiating XELJANZ (tablets and oral solution) or XELJANZ XR (extended-release tablets), consider performing the following:
- Active and latent tuberculosis (TB) infection evaluation: If the patient has latent TB, treat for TB prior to XELJANZ/XELJANZ XR treatment [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) ] .
- Viral hepatitis screening in accordance with clinical guidelines [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) ] .
- A complete blood count: Avoid initiation of XELJANZ/XELJANZ XR treatment in patients with a lymphocyte count less than 500 cells/mm 3 , absolute neutrophil count less than 1000 cells/mm 3 , or hemoglobin level less than 9 g/dL [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8) ] .
- Baseline hepatic function evaluation: XELJANZ/XELJANZ XR is not recommended for patients with severe hepatic impairment [see Use in Specific Populations (8.7) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ] .
- Update immunizations according to current immunization guidelines. The interval between live vaccinations and initiation of XELJANZ/XELJANZ XR should be in accordance with current vaccination guidelines regarding immunosuppressive agents [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9) ] .
Important Administration Instructions
- XELJANZ XR (extended-release tablets) is not substitutable with XELJANZ (tablets and oral solution). Switching between XELJANZ and XELJANZ XR should be made by the healthcare provider.
- Dose interruption is recommended for management of lymphopenia, neutropenia, and anemia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8) and Adverse Reactions (6.1) ] .
- Interrupt use of XELJANZ/XELJANZ XR if a patient develops a serious infection until the infection is controlled [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) ] .
- Take XELJANZ/XELJANZ XR with or without food [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ] .
- Swallow XELJANZ XR whole and intact. Do not crush, split, or chew the extended-release tablets [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ] .
Recommended Dosage in Adults with Rheumatoid Arthritis, Psoriatic Arthritis, and Ankylosing Spondylitis
Table 1 displays the recommended dosage of XELJANZ tablets and XELJANZ XR (extended-release tablets) for adults with RA, PsA, and AS [see Indication and Usage (1.1 , 1.2 , 1.3) ] with and without renal impairment (including those who are undergoing hemodialysis) or hepatic impairment [see Use in Specific Populations (8.6 , 8.7 )] . The table also displays the recommended dosage modifications for patients concomitantly using CYP2C19 and/or CYP3A4 inhibitors [see Drug Interactions (7) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ] , and patients with lymphopenia, neutropenia, or anemia.
Adults | XELJANZ Tablets | XELJANZ XR (extended-release tablets) |
Patients with Normal Renal and Hepatic Function Excludes patients who concomitantly use XELJANZ tablets/XELJANZ XR with strong CYP3A4 inhibitor(s) or moderate CYP3A4 inhibitor(s) and strong CYP2C19 inhibitor(s), as well as patients with lymphocyte count less than 500 cells/mm 3 , ANC <1000 cells/mm 3 , or hemoglobin less than 8 g/dL or a decrease of more than 2 g/dL. | 5 mg twice daily | 11 mg once daily |
Recommended Dosage in Patients with Renal Impairment (RI) Tofacitinib PK was evaluated in subjects with varying degrees of renal impairment, where the severity of renal impairment was defined based on creatinine clearance (CLcr) estimated using the Cockcroft‑Gault equation: CLcr >80 mL/min (normal renal function); >50 and ≤80 mL/min (mild renal impairment); ≥30 and ≤50 mL/min (moderate renal impairment); <30 mL/min (severe renal impairment). | ||
Mild RI (CLcr >50 and ≤80 mL/min) | 5 mg twice daily | 11 mg once daily |
Moderate RI (CLcr ≥30 and ≤50 mL/min) | 5 mg once daily | XELJANZ tablets 5 mg once daily |
Severe RI (CLcr <30 mL/min) | 5 mg once daily | XELJANZ tablets 5 mg once daily |
For patients undergoing hemodialysis, administer the dose after the dialysis session on dialysis days. If a dose was taken before the dialysis procedure, supplemental doses are not recommended after dialysis. | ||
Recommended Dosage in Patients with Hepatic Impairment (HI) | ||
Mild HI (Child-Pugh A) | 5 mg twice daily | 11 mg once daily |
Moderate HI (Child-Pugh B) | 5 mg once daily | XELJANZ tablets 5 mg once daily |
Severe HI (Child-Pugh C) | Use of XELJANZ tablets/XELJANZ XR is not recommended. | |
Dosage Modifications with Concomitant Use of CYP3A4 and/or CYP2C19 Inhibitor(s) | ||
Strong CYP2C19 inhibitor(s) | 5 mg twice daily | 11 mg once daily |
Moderate CYP2C19 inhibitor(s) | ||
Moderate CYP3A4 inhibitor(s) | ||
Moderate CYP3A4 inhibitor(s) with strong CYP2C19 inhibitor(s) (e.g., fluconazole) | 5 mg once daily | XELJANZ tablets 5 mg once daily |
Strong CYP3A4 inhibitor(s) | ||
Dosage Modifications for Lymphopenia, Neutropenia, or Anemia | ||
Patients with lymphocyte count less than 500 cells/mm 3 , confirmed by repeat testing | Discontinue dosing. | |
Patients with ANC less than 500 cells/mm 3 | Discontinue dosing. | |
Patients with ANC 500 to 1000 cells/mm 3 | Interrupt dosing. When ANC is greater than 1000, resume 5 mg twice daily. | Interrupt dosing. When ANC is greater than 1000, resume 11 mg once daily. |
Patients with hemoglobin less than 8 g/dL or a decrease of more than 2 g/dL | Interrupt dosing until hemoglobin values have normalized. | |
Switching from XELJANZ Tablets to XELJANZ XR Extended-Release Tablets
Patients treated with XELJANZ tablets 5 mg twice daily may be switched to XELJANZ XR extended-release tablets 11 mg once daily the day following the last dose of XELJANZ tablets 5 mg.
Recommended Dosage in Pediatric Patients 2 Years of Age and Older with Psoriatic Arthritis or Polyarticular Course Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis
Table 2 displays the recommended body weight-based dosages for XELJANZ tablets and XELJANZ oral solution in pediatric patients 2 years of age and older with PsA or pcJIA [see Indication and Usage (1.2 , 1.4) ] with and without renal impairment (including those who are undergoing hemodialysis) or hepatic impairment [see Use in Specific Populations (8.6 , 8.7) ] . The table also includes recommended dosage modification for pediatric patients concomitantly using CYP2C19 and/or CYP3A4 inhibitors [see Drug Interactions (7) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ] , and pediatric patients with lymphopenia, neutropenia, or anemia.
Administer XELJANZ oral solution using the included press-in bottle adapter and oral dosing syringe [see Instructions for Use ] .
| Pediatric Patients 2 Years of Age and Older | XELJANZ tablets and XELJANZ oral solution |
|---|---|
Patients with Normal Renal and Hepatic Function Excludes patients who concomitantly use XELJANZ (tablets and oral solution) with strong CYP3A4 inhibitor(s) or moderate CYP3A4 inhibitor(s) and strong CYP2C19 inhibitor(s), as well as patients with lymphocyte count less than 500 cells/mm 3 , ANC <1000 cells/mm 3 , or hemoglobin less than 8 g/dL or a decrease of more than 2 g/dL. |
|
Recommended Dosage in Patients with Renal Impairment (RI) | |
Mild RI | Same as patients with normal renal function. |
Moderate RI |
|
Severe RI |
|
For patients undergoing hemodialysis, administer the dose after the dialysis session on dialysis days. If a dose was taken before the dialysis procedure, supplemental doses are not recommended after dialysis. | |
Recommended Dosage in Patients with Hepatic Impairment (HI) | |
Mild HI | Same as patients with normal hepatic function. |
Moderate HI |
|
Severe HI | Use of XELJANZ tablets/XELJANZ oral solution is not recommended. |
Dosage Modifications with Concomitant Use of CYP3A4 and/or CYP2C19 Inhibitor(s) | |
Strong CYP2C19 inhibitor(s) | No dosage modification is recommended. |
Moderate CYP2C19 inhibitor(s) | |
Moderate CYP3A4 inhibitor(s) | |
Moderate CYP3A4 inhibitor(s) with strong CYP2C19 inhibitor(s) (e.g., fluconazole) |
|
Strong CYP3A4 inhibitor(s) | |
Dosage Modifications for Lymphopenia, Neutropenia, or Anemia | |
Patients with lymphocyte count less than 500 cells/mm 3 , confirmed by repeat testing | Discontinue dosing. |
Patients with ANC less than 500 cells/mm 3 | Discontinue dosing. |
Patients with ANC 500 to 1000 cells/mm 3 | Interrupt dosing until ANC is greater than 1000 cells/mm 3 . |
Patients with hemoglobin less than 8 g/dL or a decrease of more than 2 g/dL | Interrupt dosing until hemoglobin values have normalized. |
Recommended Dosage in Adults with Ulcerative Colitis
Table 3 displays the recommended dosage of XELJANZ tablets and XELJANZ XR (extended-release tablets) in adult patients with ulcerative colitis (UC) [see Indications and Usage (1.5) ] with and without renal impairment (including those who are undergoing hemodialysis) or hepatic impairment [see Use in Specific Populations (8.6 , 8.7) ] . Table 4 displays the recommended dosage modification for patients concomitantly using CYP2C19 and/or CYP3A4 inhibitors [see Drug Interactions (7) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ] , and patients with lymphopenia, neutropenia, or anemia.
| Adults | XELJANZ tablets | XELJANZ XR (extended-release tablets) |
|---|---|---|
Patients with Normal Renal and Hepatic Function Excludes patients who concomitantly use XELJANZ tablets/XELJANZ XR with strong CYP3A4 inhibitor(s) or moderate CYP3A4 inhibitor(s) and strong CYP2C19 inhibitor(s), as well as patients with lymphocyte count less than 500 cells/mm 3 , ANC <1000 cells/mm 3 , or hemoglobin less than 8 g/dL or a decrease of more than 2 g/dL. | Induction: 10 mg twice daily for at least 8 weeks [see Clinical Studies (14.5) ] ; evaluate patients and transition to maintenance therapy depending on therapeutic response. If needed continue 10 mg twice daily for a maximum of 16 weeks. Discontinue 10 mg twice daily after 16 weeks if adequate therapeutic response is not achieved. | Induction: 22 mg once daily for at least 8 weeks; evaluate patients and transition to maintenance therapy depending on therapeutic response. If needed continue 22 mg once daily for a maximum of 16 weeks. Discontinue 22 mg once daily after 16 weeks if adequate therapeutic response is not achieved. |
Maintenance: 5 mg twice daily. For patients with loss of response during maintenance treatment, may consider a dosage of 10 mg twice daily (limited to the shortest duration), with careful consideration of the benefits and risks for the individual patient. Use the lowest effective dosage needed to maintain response. | Maintenance: 11 mg once daily. For patients with loss of response during maintenance treatment, may consider a dosage of 22 mg once daily (limited to the shortest duration), with careful consideration of the benefits and risks for the individual patient. Use the lowest effective dose needed to maintain response. | |
Recommended Dosage in Patients with Renal Impairment (RI) Tofacitinib PK was evaluated in subjects with varying degrees of renal impairment, where the severity of renal impairment was defined based on creatinine clearance (CLcr) estimated using the Cockcroft‑Gault equation: CLcr >80 mL/min (normal renal function); CLcr >50 and ≤80 mL/min (mild renal impairment); ≥30 and ≤50 mL/min (moderate renal impairment); <30 mL/min (severe renal impairment). | ||
Mild RI (CLcr >50 and ≤80 mL/min) | Same as patients with normal renal function. | |
Moderate RI (CLcr ≥30 and ≤50 mL/min) | Induction: 5 mg twice daily for at least 8 weeks [see Clinical Studies (14.5) ] ; evaluate patients and transition to maintenance therapy depending on therapeutic response. If needed continue 5 mg twice daily for a maximum of 16 weeks. Discontinue 5 mg twice daily after 16 weeks if adequate therapeutic response is not achieved. | Induction: 11 mg once daily for at least 8 weeks; evaluate patients and transition to maintenance therapy depending on therapeutic response. If needed continue 11 mg once daily for a maximum of 16 weeks. Discontinue 11 mg once daily after 16 weeks if adequate therapeutic response is not achieved. |
Severe RI (CLcr <30 mL/min) | Maintenance: 5 mg once daily. For patients with loss of response during maintenance treatment, may consider a dosage of 5 mg twice daily (limited to the shortest duration), with careful consideration of the benefits and risks for the individual patient. Use the lowest effective dosage needed to maintain response. For patients undergoing hemodialysis, administer the dose after the dialysis session on dialysis days. If a dose was taken before the dialysis procedure, supplemental doses are not recommended after dialysis. | Maintenance: XELJANZ XR is not recommended. See Maintenance Dosage for XELJANZ tablets for Moderate or Severe RI. For patients undergoing hemodialysis, administer the dose after the dialysis session on dialysis days. If a dose was taken before the dialysis procedure, supplemental doses are not recommended after dialysis. |
Recommended Dosage in Patients with Hepatic Impairment (HI) | ||
Mild HI (Child-Pugh A) | Same as patients with normal hepatic function. | |
Moderate HI (Child-Pugh B) | Induction: 5 mg twice daily for at least 8 weeks [see Clinical Studies (14.5) ] ; evaluate patients and transition to maintenance therapy depending on therapeutic response. If needed continue 5 mg twice daily for a maximum of 16 weeks. Discontinue 5 mg twice daily after 16 weeks if adequate therapeutic response is not achieved. | Induction: 11 mg once daily for at least 8 weeks; evaluate patients and transition to maintenance therapy depending on therapeutic response. If needed continue 11 mg once daily for a maximum of 16 weeks. Discontinue 11 mg once daily after 16 weeks if adequate therapeutic response is not achieved. |
Maintenance: 5 mg once daily. For patients with loss of response during maintenance treatment, may consider a dosage of 5 mg twice daily (limited to the shortest duration), with careful consideration of the benefits and risks for the individual patient. Use the lowest effective dosage needed to maintain response. | Maintenance: XELJANZ XR is not recommended. See Maintenance Dosage for XELJANZ tablets for Moderate HI. | |
Severe HI (Child-Pugh C) | Use of XELJANZ tablets/XELJANZ XR is not recommended. | |
| Adults | XELJANZ Tablets | XELJANZ XR (extended-release tablets) |
|---|---|---|
Dosage Modifications with Concomitant Use of CYP3A4 and/or CYP2C19 Inhibitor(s) | ||
Strong CYP2C19 inhibitor(s) | No dosage modification is recommended. | |
Moderate CYP2C19 inhibitor(s) | ||
Moderate CYP3A4 inhibitor(s) | ||
Moderate CYP3A4 inhibitor(s) with strong CYP2C19 inhibitor(s) (e.g., fluconazole) | Induction: 5 mg twice daily for at least 8 weeks [see Clinical Studies (14.5) ] ; evaluate patients and transition to maintenance therapy depending on therapeutic response. If needed continue 5 mg twice daily for a maximum of 16 weeks. Discontinue 5 mg twice daily after 16 weeks if adequate therapeutic response is not achieved. | Induction: 11 mg once daily for at least 8 weeks; evaluate patients and transition to maintenance therapy depending on therapeutic response. If needed continue 11 mg once daily for a maximum of 16 weeks. Discontinue 11 mg once daily after 16 weeks if adequate therapeutic response is not achieved. |
Strong CYP3A4 inhibitor(s) | ||
Maintenance: 5 mg once daily. For patients with loss of response during maintenance treatment, may consider a dosage of 5 mg twice daily (limited to the shortest duration), with careful consideration of the benefits and risks for the individual patient. Use the lowest effective dosage needed to maintain response. | Maintenance: XELJANZ XR is not recommended. see Maintenance Dosage for XELJANZ tablets for Strong CYP3A4 inhibitors. | |
Dosage Modifications for Lymphopenia, Neutropenia, or Anemia | ||
Lymphocyte count less than 500 cells/mm 3 , confirmed by repeat testing | Discontinue dosing. | |
ANC less than 500 cells/mm 3 | Discontinue dosing. | |
ANC 500 to 1000 cells/mm 3 | If taking:
| If taking:
|
Hemoglobin less than 8 g/dL or a decrease of more than 2 g/dL | Interrupt dosing until hemoglobin values have normalized. | |
Switching from XELJANZ Tablets to XELJANZ XR Extended-Release Tablets
Patients treated with XELJANZ tablets:
- 5 mg twice daily may be switched to XELJANZ XR extended-release tablets 11 mg once daily the day following the last dose of XELJANZ tablets 5 mg.
- 10 mg twice daily may be switched to XELJANZ XR extended-release tablets 22 mg once daily the day following the last dose of XELJANZ tablets 10 mg.
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
XELJANZ tablets:
- 5 mg of tofacitinib: White, round, immediate-release film-coated tablets, debossed with “Pfizer” on one side, and “JKI 5” on the other side.
- 10 mg of tofacitinib: Blue, round, immediate-release film-coated tablets, debossed with “Pfizer” on one side, and “JKI 10” on the other side.
XELJANZ XR extended-release tablets:
- 11 mg of tofacitinib: Pink, oval, extended-release film-coated tablets with a drilled hole at one end of the tablet band and “JKI 11” printed on one side of the tablet.
- 22 mg of tofacitinib: Beige, oval, extended-release film-coated tablets with a drilled hole at one end of the tablet band and “JKI 22” printed on one side of the tablet.
XELJANZ oral solution:
1 mg/mL of tofacitinib: Clear, colorless oral solution.
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
Lactation : Advise not to breastfeed. (8.2 )
Pregnancy
Risk Summary
The available data with XELJANZ (tablets and oral solution) and XELJANZ XR (extended-release tablets) from a pregnancy exposure registry that enrolled 11 exposed pregnant females, pharmacovigilance, and published literature are insufficient to draw conclusions about a drug‑associated risk of major birth defects, miscarriage, or other adverse maternal or fetal outcomes. There are risks to the mother and the fetus associated with RA and UC in pregnancy (see Clinical Considerations ) . In animal reproduction studies, fetocidal and teratogenic effects were noted when pregnant rats and rabbits received tofacitinib during the period of organogenesis at exposures multiples of 73-times and 6.3-times the maximum recommended dose of 10 mg twice daily, respectively. Further, in a peri- and post-natal study in rats, tofacitinib resulted in reductions in live litter size, postnatal survival, and pup body weights at exposure multiples of approximately 73-times the recommended dosage of 5 mg twice daily and approximately 36 times the maximum recommended dosage of 10 mg twice daily, respectively (see Data ) .
The background risks of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated populations are unknown. All pregnancies have a background risk of birth defect, loss, or other adverse outcomes. The background risks in the U.S. general population of major birth defects and miscarriages are 2 to 4% and 15 to 20% of clinically recognized pregnancies, respectively.
Clinical Considerations
Disease-Associated Maternal and/or Embryo/Fetal Risk: Published data suggest that increased disease activity is associated with the risk of developing adverse pregnancy outcomes in women with RA or UC. Adverse pregnancy outcomes include preterm delivery (before 37 weeks of gestation), low birth weight (less than 2500 grams) infants, and small for gestational age at birth.
Data
Animal Data: In a rat embryofetal developmental study, in which pregnant rats received tofacitinib during organogenesis, tofacitinib was teratogenic at exposure levels approximately 146 times the recommended dose of 5 mg twice daily, and approximately 73 times the maximum recommended dose of 10 mg twice daily (on an AUC basis at oral doses of 100 mg/kg/day in rats). Teratogenic effects consisted of external and soft tissue malformations of anasarca and membranous ventricular septal defects, respectively; and skeletal malformations or variations (absent cervical arch; bent femur, fibula, humerus, radius, scapula, tibia, and ulna; sternoschisis; absent rib; misshapen femur; branched rib; fused rib; fused sternebra; and hemicentric thoracic centrum). In addition, there was an increase in post-implantation loss, consisting of early and late resorptions, resulting in a reduced number of viable fetuses. Mean fetal body weight was reduced. No developmental toxicity was observed in rats at exposure levels approximately 58 times the recommended dose of 5 mg twice daily, and approximately 29 times the maximum recommended dose of 10 mg twice daily (on an AUC basis at oral doses of 30 mg/kg/day in pregnant rats).
In a rabbit embryofetal developmental study in which pregnant rabbits received tofacitinib during the period of organogenesis, tofacitinib was teratogenic at exposure levels approximately 13 times the recommended dose of 5 mg twice daily, and approximately 6.3 times the maximum recommended dose of 10 mg twice daily (on an AUC basis at oral doses of 30 mg/kg/day in rabbits) in the absence of signs of maternal toxicity. Teratogenic effects included thoracogastroschisis, omphalocele, membranous ventricular septal defects, and cranial/skeletal malformations (microstomia, microphthalmia), mid-line and tail defects. In addition, there was an increase in post-implantation loss associated with late resorptions. No developmental toxicity was observed in rabbits at exposure levels approximately 3 times the recommended dose of 5 mg twice daily, and approximately 1.5 times the maximum recommended dose of 10 mg twice daily (on an AUC basis at oral doses of 10 mg/kg/day in pregnant rabbits).
In a peri- and postnatal development study in pregnant rats that received tofacitinib from gestation day 6 through day 20 of lactation, there were reductions in live litter size, postnatal survival, and pup body weights at exposure levels approximately 73 times the recommended dose of 5 mg twice daily, and approximately 36 times the maximum recommended dose of 10 mg twice daily (on an AUC basis at oral doses of 50 mg/kg/day in rats). There was no effect on behavioral and learning assessments, sexual maturation or the ability of the F1 generation rats to mate and produce viable F2 generation fetuses in rats at exposure levels approximately 17 times the recommended dose of 5 mg twice daily, and approximately 8.3 times the maximum recommended dose of 10 mg twice daily (on an AUC basis at oral doses of 10 mg/kg/day in rats).
Lactation
Risk Summary
Based on published data, tofacitinib is present in human milk. Data on the effects of tofacitinib on the breastfed infant is limited to a small number of cases with no reported adverse effects. There are no data on the effects on milk production. Given the serious adverse reactions seen in patients treated with XELJANZ (tablets and oral solution) and XELJANZ XR (extended-release tablets), such as increased risk of serious infections, advise patients that breastfeeding is not recommended during treatment and for at least 18 hours after the last dose of XELJANZ or 36 hours after the last dose of XELJANZ XR (approximately 6 elimination half-lives).
Data
Following administration of tofacitinib to lactating rats, concentrations of tofacitinib in milk over time paralleled those in serum and were approximately 2 times higher in milk relative to maternal serum at all time points measured.
Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
Contraception
Females
In an animal reproduction study, tofacitinib at AUC multiples of 13 times the recommended dosage of 5 mg twice daily and 6.3 times the maximum recommended dosage of 10 mg twice daily demonstrated adverse embryo-fetal findings [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1) ] . However, there is uncertainty as to how these animal findings relate to females of reproductive potential treated with the recommended clinical dosage. Consider pregnancy planning and prevention for females of reproductive potential.
Infertility
Females
Based on findings in rats, treatment with XELJANZ (tablets and oral solution) and XELJANZ XR (extended-release tablets) may result in reduced fertility in females of reproductive potential. It is not known if this effect is reversible [see Nonclinical Toxicology (13.1) ] .
Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of XELJANZ (tablets and oral solution) in pediatric patients for indications, other than in patients with active pcJIA and PsA, have not been established.
The safety and effectiveness of XELJANZ have not been established in pediatric patients less than 2 years of age.
The safety and effectiveness of XELJANZ XR (extended-release tablets) in pediatric patients have not been established.
Polyarticular Course Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis (pcJIA)
The safety and effectiveness of XELJANZ (tablets and oral solution) for the treatment of active pcJIA have been established in pediatric patients 2 years of age and older who have had an inadequate response or intolerance to one or more TNF blockers.
Use of XELJANZ for this indication is supported by evidence from adequate and well-controlled studies of XELJANZ tablets in adults with RA, pharmacokinetic (PK) data from adult patients with RA, and with additional safety, efficacy, and PK data from a clinical trial of XELJANZ in pediatric patients 2 years and older with active pcJIA (Study pcJIA-I) [see Adverse Reactions (6.1) , Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) , and Clinical Studies (14.1 , 14.4) ] .
Adverse reactions observed in pediatric patients with pcJIA who received XELJANZ were consistent with those reported in adults with RA [see Adverse Reactions (6.1) ] .
Psoriatic Arthritis
The safety and effectiveness of XELJANZ (tablets and oral solution) for the treatment of active PsA have been established in pediatric patients 2 years of age and older who have had an inadequate response or intolerance to one or more TNF blockers.
Use of XELJANZ for this indication is supported by evidence from well-controlled studies of XELJANZ tablets in adults with PsA, PK data from adults with PsA, and PK data from a clinical trial of XELJANZ in 225 pediatric patients with JIA, and safety data from 280 pediatric patients 2 years of age and older with JIA [see Adverse Reactions (6.1) , Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) , and Clinical Studies (14.2) ] . Following administration of the recommended XELJANZ dosage in pediatric patients 2 years of age and older with PsA, tofacitinib plasma exposures are predicted to be comparable to those observed in adults with PsA based on population PK modeling and simulation [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ] .
Systemic Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis
The safety and effectiveness of XELJANZ for the treatment of pediatric patients with systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis (sJIA) have not been established.
The results from a two-part study (an open-label, run-in phase, followed by a double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomized event-driven withdrawal phase) in 100 patients 2 years to 17 years of age with sJIA with active systemic features did not demonstrate that XELJANZ (dosed at 5 mg twice daily or body weight-based equivalent twice daily) was efficacious in the treatment of sJIA with active systemic features.
Of the 100 patients enrolled in the open-label run-in phase, 59 (59%) patients achieved a clinical response and were eligible for the double-blind withdrawal phase. There were 28 patients randomized to XELJANZ and 31 patients to placebo. The study data were insufficient to demonstrate efficacy and, therefore, XELJANZ is not recommended for the treatment of sJIA.
Adverse reactions observed in pediatric patients with sJIA receiving XELJANZ/XELJANZ oral solution were consistent with those reported in pcJIA and RA patients [see Adverse Reactions (6.1) ] .
Geriatric Use
Of the 3315 adults who were enrolled in clinical trials with RA (Studies RA-I to V), a total of 505 patients were 65 years of age and older, including 71 patients 75 years and older. The frequency of serious infection among XELJANZ tablets-treated patients 65 years of age and older was higher than among those adults under the age of 65.
Of the 1156 XELJANZ tablet-treated patients in clinical trials of patients with UC, a total of 77 patients (7%) were 65 years of age or older. Clinical studies of XELJANZ in patients with UC did not include sufficient numbers of patients aged 65 years and older to determine whether they respond differently from younger adult patients.
Of the 783 XELJANZ tablet-treated patients in clinical trials of patients with PsA, a total of 72 (9.2%) patients were 65 years of age and older, including 2 (0.3%) patients 75 years and older. These clinical studies did not include sufficient numbers of patients aged 65 years and older with PsA to determine if they respond differently from younger adult patients.
Of the 420 XELJANZ tablet-treated patients in clinical trials of patients with AS, a total of 12 (2.9%) patients were 65 years of age and older, including 1 (0.2%) patient 75 years and older. These clinical studies did not include sufficient numbers of patients aged 65 years and older with AS to determine if they respond differently from younger adult patients.
Renal Impairment
Moderate and Severe Renal Impairment
XELJANZ-treated patients with moderate renal impairment (RI) (CLcr ≥30 and ≤50 mL/minute) or severe RI (<30 mL/minute) had greater tofacitinib blood concentrations than XELJANZ-treated patients with normal renal function (CLcr >80 mL/minute). The recommended dosage of XELJANZ (tablets and oral solution) and XELJANZ XR (extended-release tablets) in patients with moderate or severe RI (including those with severe RI who are undergoing hemodialysis) is lower than the recommended dosage in patients with normal renal function [see Dosage and Administration (2.3 , 2.4 , 2.5) ] .
Mild Renal Impairment
The recommended dosage in patients with mild RI (CLcr >50 and ≤80 mL/minute) is the same as patients with normal renal function.
Hepatic Impairment
Severe Hepatic Impairment
XELJANZ (tablets and oral solution) and XELJANZ XR (extended-release tablets) has not been studied in patients with severe hepatic impairment (HI) (Child-Pugh C); therefore, use of XELJANZ/XELJANZ XR in patients with severe HI is not recommended.
Moderate Hepatic Impairment
XELJANZ-treated patients with moderate hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh B) had greater tofacitinib blood concentration than XELJANZ-treated patients with normal hepatic function [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ] . Higher blood concentrations may increase the risk of some adverse reactions. The recommended XELJANZ (tablets and oral solution) and XELJANZ XR (extended-release tablets) dosage in patients with moderate HI is lower than the recommended dosage in patients with normal hepatic function [see Dosage and Administration (2.3 , 2.4 , 2.5 )] .
Mild Hepatic Impairment
The recommended dosage of XELJANZ/XELJANZ XR in patients with mild hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh A) is the same as patients with normal hepatic function.
Hepatitis B or C Serology
The safety and efficacy of XELJANZ/XELJANZ XR have not been studied in patients with positive hepatitis B virus or hepatitis C virus serology.
CONTRAINDICATIONS
None.
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- Serious Infections : Avoid use of XELJANZ (tablets and oral solution) and XELJANZ XR (extended-release tablets) during an active serious infection, including localized infections. (5.1 )
- Gastrointestinal Perforations : Promptly evaluate patients at increased risk for gastrointestinal perforation who present with new onset abdominal symptoms. (5.6 )
- Laboratory Monitoring : Recommended due to potential changes in lymphocytes, neutrophils, hemoglobin, liver enzymes and lipids. (5.8 )
- Vaccinations : Avoid use of live vaccines concurrently with XELJANZ or XELJANZ XR. (5.9 )
Serious Infections
Serious and sometimes fatal infections may occur with XELJANZ (tablets and oral solution) and XELJANZ XR (extended-release tablets). Serious and sometimes fatal infections due to bacterial, mycobacterial, invasive fungal, viral, or other opportunistic pathogens have been reported in patients receiving XELJANZ. The most common serious infections reported with XELJANZ included pneumonia, cellulitis, herpes zoster, urinary tract infection, diverticulitis, and appendicitis. Among opportunistic infections, tuberculosis and other mycobacterial infections, cryptococcosis, histoplasmosis, esophageal candidiasis, pneumocystosis, multi-dermatomal herpes zoster, cytomegalovirus infections, BK virus infection, and listeriosis were reported with XELJANZ. Some patients have presented with disseminated rather than localized disease, and were often taking concomitant immunomodulating agents such as methotrexate or corticosteroids.
In the UC population, treatment with XELJANZ tablets 10 mg twice daily was associated with greater risk of serious infections compared to 5 mg twice daily. Additionally, opportunistic herpes zoster infections (including meningoencephalitis, ophthalmologic, and disseminated cutaneous) were seen in patients who were treated with XELJANZ tablets 10 mg twice daily.
Other serious infections that were not reported in clinical studies may also occur (e.g., coccidioidomycosis).
Avoid use of XELJANZ/XELJANZ XR in patients with an active, serious infection, including localized infections. The risks and benefits of treatment should be considered prior to initiating XELJANZ/XELJANZ XR in patients:
- with chronic or recurrent infection
- who have been exposed to tuberculosis
- with a history of a serious or an opportunistic infection
- who have resided or traveled in areas of endemic tuberculosis or endemic mycoses; or
- with underlying conditions that may predispose them to infection.
Closely monitor patients for the development of signs and symptoms of infection during and after treatment with XELJANZ/XELJANZ XR. Interrupt XELJANZ/XELJANZ XR if a patient develops a serious infection, an opportunistic infection, or sepsis. In patients who develop a new infection during treatment with XELJANZ/XELJANZ XR, promptly complete diagnostic testing appropriate for an immunocompromised patient; initiate appropriate antimicrobial therapy, and monitor the patients closely.
Caution is also recommended in patients with a history of chronic lung disease, or in those who develop interstitial lung disease, as they may be more prone to infections.
Risk of infection may be higher with increasing degrees of lymphopenia and consideration should be given to lymphocyte counts when assessing individual patient risk of infection. Discontinuation and monitoring criteria for lymphopenia are recommended [see Dosage and Administration (2.3 , 2.4 , 2.5) ].
Tuberculosis
Evaluate and test patients for latent or active tuberculosis (TB) infection prior to and per applicable guidelines during administration of XELJANZ/XELJANZ XR.
Consider anti-TB therapy prior to administration of XELJANZ/XELJANZ XR in patients with a past history of latent or active TB in whom an adequate course of treatment cannot be confirmed, and for patients with a negative test for latent TB but who have risk factors for TB infection. Consultation with a physician with expertise in the treatment of TB is recommended to aid in the decision about whether initiating anti-TB therapy is appropriate for an individual patient.
Monitor patients closely for the development of signs and symptoms of TB, including patients who tested negative for latent TB infection prior to initiating therapy.
Treat patients with latent TB with standard antimycobacterial therapy before administering XELJANZ/XELJANZ XR.
Viral Reactivation
Viral reactivation, including cases of herpes virus reactivation (e.g., herpes zoster), were observed in clinical studies with XELJANZ. Postmarketing cases of hepatitis B reactivation have been reported in patients treated with XELJANZ. The impact of XELJANZ/XELJANZ XR on chronic viral hepatitis reactivation is unknown. Patients who screened positive for hepatitis B or C were excluded from clinical trials. Perform screening for viral hepatitis in accordance with clinical guidelines before starting therapy with XELJANZ/XELJANZ XR. The risk of herpes zoster is increased in patients treated with XELJANZ/XELJANZ XR and appears to be higher in patients treated with XELJANZ in Japan and Korea.
Increased Risk of Mortality
Increased risk of mortality may occur with XELJANZ (tablets and oral solution) and XELJANZ XR (extended-release tablets). Adult patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA), 50 years of age and older, with at least one cardiovascular risk factor treated with XELJANZ tablets 5 mg or 10 mg twice a day had a higher observed rate of all-cause mortality, including sudden cardiovascular death, compared to those treated with TNF blockers in a large, randomized, postmarketing safety study (RA Safety Study 1). The incidence rate of all-cause mortality per 100 patient-years was 1.23 for XELJANZ tablets 10 mg twice a day, 0.88 for XELJANZ tablets 5 mg twice a day, and 0.69 for TNF blockers [see Clinical Studies (14.6) ] . Consider the benefits and risks for the individual patient prior to initiating or continuing therapy with XELJANZ/XELJANZ XR.
XELJANZ 10 mg twice daily (or XELJANZ XR 22 mg once daily) dosages are not recommended for the treatment of RA, PsA, AS, or pcJIA [see Dosage and Administration (2.3 , 2.4) ] .
For the treatment of UC, use XELJANZ/XELJANZ XR at the lowest effective dose and for the shortest duration needed to achieve/maintain therapeutic response [see Dosage and Administration (2.5) ] .
Malignancy and Lymphoproliferative Disorders
Malignancies and lymphoproliferative disorders may occur with XELJANZ (tablets and oral solution) and XELJANZ XR (extended-release tablets). Malignancies, including lymphomas and solid cancers, were observed in clinical studies of XELJANZ [see Adverse Reactions (6.1) ].
Other malignancies were observed in XELJANZ clinical studies and the postmarketing setting, including, but not limited to, lung cancer, breast cancer, melanoma, prostate cancer, and pancreatic cancer.
In RA Safety Study 1, a higher rate of malignancies (excluding non-melanoma skin cancer (NMSC)) was observed in patients treated with XELJANZ tablets 5 mg or 10 mg twice a day compared with TNF blockers. The incidence rate of malignancies (excluding NMSC) per 100 patient-years was 1.13 for XELJANZ tablets 10 mg twice a day, 1.13 for XELJANZ tablets 5 mg twice a day, and 0.77 for TNF blockers. Patients who are current or past smokers are at additional increased risk [see Clinical Studies (14.6) ].
Lymphomas and lung cancers, which are a subset of all malignancies in RA Safety Study 1, were observed at a higher rate in patients treated with XELJANZ tablets 5 mg twice a day and XELJANZ tablets 10 mg twice a day compared to those treated with TNF blockers. The incidence rate of lymphomas per 100 patient-years was 0.11 for XELJANZ tablets 10 mg twice a day, 0.07 for XELJANZ tablets 5 mg twice a day, and 0.02 for TNF blockers. The incidence rate of lung cancers per 100 patient-years among current and past smokers was 0.59 for XELJANZ tablets 10 mg twice a day, 0.48 for XELJANZ tablets 5 mg twice a day, and 0.27 for TNF blockers [see Clinical Studies (14.6) ] .
Consider the benefits and risks for the individual patient prior to initiating or continuing therapy with XELJANZ/XELJANZ XR, particularly in patients with a known malignancy (other than a successfully treated NMSC), patients who develop a malignancy while on treatment, and patients who are current or past smokers. XELJANZ 10 mg twice daily (or XELJANZ XR 22 mg once daily) dosages are not recommended for the treatment of RA, PsA, AS, or pcJIA [see Dosage and Administration (2.3 , 2.4) ] .
Non-Melanoma Skin Cancer
Non-melanoma skin cancers (NMSCs) have been reported in patients treated with XELJANZ tablets. Periodic skin examination is recommended for patients who are at increased risk for skin cancer. In the UC population, treatment with XELJANZ tablets 10 mg twice daily was associated with greater risk of NMSC than treatment with placebo.
Major Adverse Cardiovascular Events
Major adverse cardiovascular events may occur with XELJANZ (tablets and oral solution) and XELJANZ XR (extended-release tablets). In RA Safety Study 1, patients with RA who were 50 years of age and older with at least one cardiovascular risk factor and treated with XELJANZ tablets 5 mg or 10 mg twice daily had a higher rate of major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) defined as cardiovascular death, non-fatal myocardial infarction (MI), and non-fatal stroke, compared to those treated with TNF blockers. The incidence rate of MACE per 100 patient-years was 1.11 for XELJANZ tablets 10 mg twice a day, 0.91 for XELJANZ tablets 5 mg twice a day, and 0.79 for TNF blockers. The incidence rate of fatal or non-fatal myocardial infarction per 100 patient-years was 0.39 for XELJANZ tablets 10 mg twice a day, 0.36 for XELJANZ tablets 5 mg twice a day, and 0.2 for TNF blockers [see Clinical Studies (14.6) ] . Patients who are current or past smokers are at additional increased risk.
Consider the benefits and risks for the individual patient prior to initiating or continuing therapy with XELJANZ/XELJANZ XR, particularly in patients who are current or past smokers and patients with other cardiovascular risk factors. Inform patients about the symptoms of serious cardiovascular events and the steps to take if they occur. Discontinue XELJANZ/XELJANZ XR in patients that have experienced a MI or stroke. XELJANZ 10 mg twice daily (or XELJANZ XR 22 mg once daily) dosages are not recommended for the treatment of RA, PsA, AS, or pcJIA [see Dosage and Administration (2.3 , 2.4) ] .
Thrombosis
Thrombosis may occur with XELJANZ (tablets and oral solution) and XELJANZ XR (extended-release tablets). Thrombosis, including pulmonary embolism (PE), deep venous thrombosis (DVT), and arterial thrombosis, have occurred in patients treated with XELJANZ and other Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors used to treat inflammatory conditions. Many of these events were serious and some resulted in death [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) ] .
Patients with RA 50 years of age and older with at least one cardiovascular risk factor treated with XELJANZ tablets 5 mg or 10 mg twice daily compared to TNF blockers in RA Safety Study 1 had an observed increase in incidence of these thrombotic events. The incidence rate of DVT per 100 patient-years was 0.28 for XELJANZ tablets 10 mg twice a day, 0.22 for XELJANZ tablets 5 mg twice a day, and 0.16 for TNF blockers. The incidence rate of PE per 100 patient-years was 0.49 for XELJANZ tablets 10 mg twice a day, 0.18 for XELJANZ tablets 5 mg twice a day, and 0.05 for TNF blockers [see Clinical Studies (14.6) ] .
XELJANZ 10 mg twice daily (or XELJANZ XR 22 mg once daily) dosages are not recommended for the treatment of RA, PsA, AS, or pcJIA [see Dosage and Administration (2.3 , 2.4) ] .
In a long-term extension study in patients with UC, five cases of pulmonary embolism were reported in patients taking XELJANZ 10 mg twice daily, including one death in a patient with advanced cancer.
Promptly evaluate patients with symptoms of thrombosis and discontinue XELJANZ/XELJANZ XR in patients with symptoms of thrombosis.
Avoid XELJANZ/XELJANZ XR in patients that may be at increased risk of thrombosis. For the treatment of UC, use XELJANZ tablets or XELJANZ XR at the lowest effective dose and for the shortest duration needed to achieve/maintain therapeutic response [see Dosage and Administration (2.5) ] .
Gastrointestinal Perforations
Gastrointestinal perforations may occur with XELJANZ (tablets and oral solution) and XELJANZ XR (extended-release tablets). Events of gastrointestinal perforation have been reported in clinical studies with XELJANZ tablets, although the role of JAK inhibition in these events is not known. In these studies, many patients with RA received background therapy with nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs).
There was no discernable difference in frequency of gastrointestinal perforation between the placebo and the XELJANZ tablets treatment groups in clinical trials of patients with UC, and many of them were receiving background corticosteroids.
Promptly evaluate patients treated with XELJANZ/XELJANZ XR who may be at increased risk for gastrointestinal perforation (e.g., patients with a history of diverticulitis or taking NSAIDs) and who present with new onset abdominal symptoms for early identification of gastrointestinal perforation [see Adverse Reactions (6.1) ] .
Hypersensitivity Reactions
Hypersensitivity reactions may occur with XELJANZ (tablets and oral solution) and XELJANZ XR (extended-release tablets). Reactions such as angioedema and urticaria that may reflect drug hypersensitivity have been observed in patients receiving XELJANZ/XELJANZ XR. Some events were serious. If a serious hypersensitivity reaction occurs, promptly discontinue XELJANZ/XELJANZ XR while evaluating the potential cause or causes of the reaction [see Adverse Reactions (6.2) ] .
Laboratory Abnormalities
Laboratory abnormalities may occur with XELJANZ (tablets and oral solution) and XELJANZ XR (extended-release tablets).
Lymphocyte Abnormalities
Treatment with XELJANZ tablets was associated with initial lymphocytosis at one month of XELJANZ tablets treatment followed by a gradual decrease in mean absolute lymphocyte counts below the baseline of approximately 10% during 12 months of therapy. Lymphocyte counts less than 500 cells/mm 3 in these patients were associated with an increased incidence of treated and serious infections.
- Monitor lymphocyte counts at baseline and every 3 months thereafter.
- Avoid initiation of XELJANZ/XELJANZ XR treatment in patients with a low lymphocyte count (i.e., less than 500 cells/mm 3 ). In patients who develop a confirmed absolute lymphocyte count less than 500 cells/mm 3 , treatment with XELJANZ/XELJANZ XR is not recommended.
Neutropenia
Treatment with XELJANZ tablets was associated with an increased incidence of neutropenia (less than 2000 cells/mm 3 ) compared to treatment with placebo.
- Monitor neutrophil counts at baseline and after 4-8 weeks of treatment and every 3 months thereafter.
- Avoid initiation of XELJANZ/XELJANZ XR treatment in patients with a low neutrophil count (i.e., ANC less than 1000 cells/mm 3 ). For patients who develop a persistent ANC of 500 to 1000 cells/mm 3 , interrupt dosing until ANC is greater than or equal to 1000 cells/mm 3 . In patients who develop an ANC less than 500 cells/mm 3 , treatment with XELJANZ/XELJANZ XR is not recommended.
Anemia
- Monitor hemoglobin at baseline and after 4-8 weeks of treatment and every 3 months thereafter.
- Avoid initiation of XELJANZ/XELJANZ XR treatment in patients with a low hemoglobin level (i.e., less than 9 g/dL). Interrupt treatment with XELJANZ/XELJANZ XR in patients who develop hemoglobin levels less than 8 g/dL or whose hemoglobin level drops greater than 2 g/dL on treatment until hemoglobin values have normalized.
Liver Enzyme Elevations
Treatment with XELJANZ tablets was associated with an increased incidence of liver enzyme elevation compared to treatment with placebo. Most of these abnormalities occurred in studies with background DMARD therapy (primarily methotrexate).
- Routine monitoring of liver tests and prompt investigation of the causes of liver enzyme elevations is recommended to identify potential cases of drug-induced liver injury.
- If drug-induced liver injury is suspected, interrupt the administration of XELJANZ/XELJANZ XR until this diagnosis has been excluded.
Lipid Elevations
Treatment with XELJANZ tablets was associated with dose-dependent increases in lipid parameters including total cholesterol, low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol, and high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol. Maximum changes in these lipid parameters were generally observed within 6 weeks. There were no clinically relevant changes in LDL/HDL cholesterol ratios. The effect of these lipid parameter elevations on cardiovascular morbidity and mortality has not been determined.
- Perform assessment of lipid parameters approximately 4-8 weeks following initiation of XELJANZ/XELJANZ XR therapy.
- Manage patients according to clinical guidelines [e.g., National Cholesterol Educational Program (NCEP)] for the management of hyperlipidemia.
Vaccinations
Avoid use of live vaccines concurrently with XELJANZ (tablets and oral solution) or XELJANZ XR (extended-release tablets). Prior to initiating XELJANZ/XELJANZ XR therapy, update immunizations in agreement with current immunization guidelines. The interval between live vaccinations and initiation of XELJANZ/XELJANZ XR therapy should be in accordance with current vaccination guidelines regarding immunosuppressive agents.
Risk of Gastrointestinal Obstruction with XELJANZ XR - A Non-Deformable Extended-Release Formulation
Gastrointestinal obstruction may occur with XELJANZ XR (extended-release tablets). Avoid use of XELJANZ XR in patients with pre-existing severe gastrointestinal narrowing (pathologic or iatrogenic). There have been rare reports of obstructive symptoms in patients with known strictures in association with the ingestion of other drugs utilizing a non-deformable extended-release formulation.
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following clinically significant adverse reactions are described elsewhere in the labeling:
- Serious Infections [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) ]
- Increased Risk of Mortality [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) ]
- Malignancy and Lymphoproliferative Disorders [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3) ]
- Major Adverse Cardiovascular Events [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4) ]
- Thrombosis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5) ]
- Gastrointestinal Perforations [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6) ]
- Hypersensitivity Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7) ]
- Laboratory Abnormalities [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8) ]
Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical studies are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical studies of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical studies of another drug and may not predict the rates observed in a broader patient population in clinical practice.
The clinical studies described in this subsection were conducted using XELJANZ tablets (referred to as “XELJANZ” in this subsection of labeling) and/or XELJANZ oral solution.
Adverse Reactions in Adults with Rheumatoid Arthritis
In RA Safety Study 1, 1,455 adults were treated with XELJANZ 5 mg twice daily, 1,456 adults were treated with 10 mg twice daily, and 1,451 adults were treated with a TNF blocker for a median of 4 years [see Clinical Studies (14.6) ] . A dosage of XELJANZ 10 mg twice daily is not recommended for the treatment of RA because of increased risks [see Dosage and Administration (2.3) and Warnings and Precautions (5) ] . For the treatment of adults with moderately to severely active RA [see Indications and Usage (1.1) ] , the recommended dosage of XELJANZ is 5 mg twice daily and the recommended dosage for XELJANZ XR is 11 mg once daily.
The safety of XELJANZ was also evaluated in two Phase 2 and five Phase 3 double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicenter trials in patients with RA. In these trials, adults were randomized to receive:
- XELJANZ (monotherapy) 5 mg twice daily (292 patients) or 10 mg twice daily (306 patients),
- In combination with DMARDs (including methotrexate), XELJANZ 5 mg twice daily (1044 patients) or 10 mg twice daily (1043 patients and
- Placebo (809 patients).
All seven trials included provisions for patients taking placebo to receive treatment with XELJANZ at Month 3 or Month 6 either by patient response (based on uncontrolled disease activity) or by design, so that adverse events cannot always be unambiguously attributed to a given treatment. Therefore, some analyses that follow include patients who changed treatment by design or by patient response from placebo to XELJANZ in both the placebo and XELJANZ group of a given interval. Comparisons between placebo and XELJANZ groups were based on the first 3 months of exposure, and comparisons between XELJANZ 5 mg twice daily and XELJANZ 10 mg twice daily were based on the first 12 months of exposure.
The long-term safety population includes all adults with RA who participated in a double-blind, placebo-controlled trial (including earlier development phase studies) and then participated in one of two long-term safety studies. The design of the long-term safety studies allowed for modification of XELJANZ doses according to clinical judgment. This limits the interpretation of the long-term safety data with respect to dose.
The most common serious adverse reactions were serious infections [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) ] .
The proportion of patients who discontinued treatment due to any adverse reaction during the 0 to 3 months exposure in the double-blind, placebo-controlled trials was 4% for XELJANZ-treated patients and 3% for placebo-treated patients.
Overall Infections
In the seven placebo-controlled trials in patients with RA, during the 0 to 3 months exposure, the overall frequency of infections was 20% and 22% in the XELJANZ 5 mg twice daily and XELJANZ 10 mg twice daily groups, respectively, and 18% in the placebo group.
The most commonly reported infections with XELJANZ were upper respiratory tract infections, nasopharyngitis, and urinary tract infections (4%, 3%, and 2% of patients, respectively).
Serious Infections: In the seven placebo-controlled trials in patients with RA, during the 0 to 3 months exposure, serious infections were reported in 1 patient (0.5 events per 100 patient-years) who received placebo and 11 patients (1.7 events per 100 patient-years) who received XELJANZ 5 mg or 10 mg twice daily. The rate difference between treatment groups (and the corresponding 95% confidence interval) was 1.1 (-0.4, 2.5) events per 100 patient-years for the combined XELJANZ 5 mg twice daily and 10 mg twice daily group minus placebo.
In the seven placebo-controlled trials, during the 0 to 12 months exposure, serious infections were reported in 34 patients (2.7 events per 100 patient-years) who received XELJANZ 5 mg twice daily and 33 patients (2.7 events per 100 patient-years) who received XELJANZ 10 mg twice daily. The rate difference between XELJANZ doses (and the corresponding 95% confidence interval) was -0.1 (-1.3, 1.2) events per 100 patient-years for XELJANZ 10 mg twice daily minus XELJANZ 5 mg twice daily.
The most common serious infections included pneumonia, cellulitis, herpes zoster, and urinary tract infection [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) ] .
Tuberculosis: In the seven placebo-controlled trials in patients with RA, during the 0 to 3 months exposure, tuberculosis (TB) was not reported in patients who received placebo, XELJANZ 5 mg twice daily, or XELJANZ 10 mg twice daily.
In the seven placebo-controlled trials, during the 0 to 12 months exposure, TB was reported in 0 patients who received XELJANZ 5 mg twice daily and 6 patients (0.5 events per 100 patient-years) who received XELJANZ 10 mg twice daily. The rate difference between XELJANZ doses (and the corresponding 95% confidence interval) was 0.5 (0.1, 0.9) events per 100 patient-years for XELJANZ 10 mg twice daily minus XELJANZ 5 mg twice daily.
Cases of disseminated TB were also reported. The median XELJANZ exposure prior to diagnosis of TB was 10 months (range from 152 to 960 days) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) ].
Opportunistic Infections (excluding tuberculosis): In the seven placebo-controlled trials in patients with RA, during the 0 to 3 months exposure, opportunistic infections were not reported in patients who received placebo, XELJANZ 5 mg twice daily, or XELJANZ 10 mg twice daily.
In the seven placebo-controlled trials, during the 0 to 12 months exposure, opportunistic infections were reported in 4 patients (0.3 events per 100 patient-years) who received XELJANZ 5 mg twice daily and 4 patients (0.3 events per 100 patient-years) who received XELJANZ 10 mg twice daily. The rate difference between XELJANZ doses (and the corresponding 95% confidence interval) was 0 (-0.5, 0.5) events per 100 patient-years for XELJANZ 10 mg twice daily minus XELJANZ 5 mg twice daily.
The median XELJANZ exposure prior to diagnosis of an opportunistic infection was 8 months (range from 41 to 698 days) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) ].
Malignancies
In the seven placebo-controlled trials in patients with RA, during the 0 to 3 months exposure, malignancies excluding NMSC were reported in 0 patients who received placebo and 2 patients (0.3 events per 100 patient-years) who received either XELJANZ 5 mg or 10 mg twice daily. The rate difference between treatment groups (and the corresponding 95% confidence interval) was 0.3 (-0.1, 0.7) events per 100 patient-years for the combined XELJANZ 5 mg and 10 mg twice daily group minus placebo.
In the seven placebo-controlled trials, during the 0 to 12 months exposure, malignancies excluding NMSC were reported in 5 patients (0.4 events per 100 patient-years) who received XELJANZ 5 mg twice daily and 7 patients (0.6 events per 100 patient-years) who received XELJANZ 10 mg twice daily. The rate difference between XELJANZ doses (and the corresponding 95% confidence interval) was 0.2 (-0.4, 0.7) events per 100 patient-years for XELJANZ 10 mg twice daily minus XELJANZ 5 mg twice daily. One of these malignancies was a case of lymphoma that occurred during the 0-to-12-month period in a patient treated with XELJANZ 10 mg twice daily.
The most common types of malignancy, including malignancies observed during the long-term extension in XELJANZ-treated patients, were lung and breast cancer, followed by gastric, colorectal, renal cell, prostate cancer, lymphoma, and malignant melanoma [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3) ].
Laboratory Abnormalities
Lymphopenia: In the placebo-controlled clinical trials in patients with RA, confirmed decreases in absolute lymphocyte counts below 500 cells/mm 3 occurred in 0.04% of patients for the XELJANZ 5 mg twice daily and 10 mg twice daily groups combined during the first 3 months of exposure.
Confirmed lymphocyte counts less than 500 cells/mm 3 were associated with an increased incidence of treated and serious infections [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8) ].
Neutropenia: In the placebo-controlled clinical trials in patients with RA, confirmed decreases in ANC below 1,000 cells/mm 3 occurred in 0.07% of patients for the XELJANZ 5 mg twice daily and 10 mg twice daily groups combined during the first 3 months of exposure.
There were no confirmed decreases in ANC below 500 cells/mm 3 observed in any treatment group. There was no clear relationship between neutropenia and the occurrence of serious infections.
In the long-term safety population, the pattern and incidence of confirmed decreases in ANC remained consistent with what was seen in the placebo-controlled clinical trials [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8) ].
Liver Enzyme Elevations: Confirmed increases in liver enzymes greater than 3 times the upper limit of normal (3× ULN) were observed in patients with RA treated with XELJANZ. In patients experiencing liver enzyme elevation, modification of treatment regimen, such as reduction in the dose of concomitant DMARD, interruption of XELJANZ, or reduction in XELJANZ dosage, resulted in decrease or normalization of liver enzymes.
In the placebo-controlled monotherapy trials (0–3 months), no differences in the incidence of ALT or AST elevations were observed between the placebo, and XELJANZ 5 mg, and 10 mg twice daily groups.
In the placebo-controlled background DMARD trials (0–3 months), ALT elevations greater than 3× ULN were observed in 1.0%, 1.3% and 1.2% of patients who received placebo, XELJANZ 5 mg, and 10 mg twice daily, respectively. In these trials, AST elevations greater than 3× ULN were observed in 0.6%, 0.5% and 0.4% of patients who received placebo, XELJANZ 5 mg, and 10 mg twice daily, respectively.
One case of drug-induced liver injury was reported in a patient treated with XELJANZ 10 mg twice daily for approximately 2.5 months. The patient developed symptomatic elevations of AST and ALT greater than 3× ULN and bilirubin elevations greater than 2× ULN, which required hospitalizations and a liver biopsy.
Lipid Elevations: In the placebo-controlled clinical trials in patients with RA, dose-related elevations in lipid parameters (total cholesterol, LDL cholesterol, HDL cholesterol, triglycerides) were observed at one month of exposure and remained stable thereafter. Changes in lipid parameters during the first 3 months of exposure in the placebo-controlled clinical trials are summarized below:
- Mean LDL cholesterol increased by 15% in the XELJANZ 5 mg twice daily arm and 19% in the XELJANZ 10 mg twice daily arm.
- Mean HDL cholesterol increased by 10% in the XELJANZ 5 mg twice daily arm and 12% in the XELJANZ 10 mg twice daily arm.
- Mean LDL/HDL ratios were essentially unchanged in XELJANZ-treated patients.
In a placebo-controlled clinical trial, elevations in LDL cholesterol and ApoB decreased to pretreatment levels in response to statin therapy.
In the long-term safety population, elevations in lipid parameters remained consistent with what was seen in the placebo-controlled clinical trials.
Serum Creatinine Elevations: In the placebo-controlled clinical trials in patients with RA, dose-related elevations in serum creatinine were observed with XELJANZ treatment. The mean increase in serum creatinine was <0.1 mg/dL in the 12-month pooled safety analysis; however, with increasing duration of exposure in the long-term extensions, up to 2% of patients were discontinued from XELJANZ treatment due to the protocol-specified discontinuation criterion of an increase in creatinine by more than 50% of baseline. The clinical significance of the observed serum creatinine elevations is unknown.
Common Adverse Reactions
Table 5 displays adverse reactions that occurred in 2% or more of patients on XELJANZ 5 mg or 10 mg twice daily and at least 1% greater than in XELJANZ-treated patients that observed in placebo-treated patients with or without DMARD in the RA trials.
| Preferred Term | Placebo | XELJANZ 5 mg Twice Daily | XELJANZ 10 mg Twice Daily The recommended dose of XELJANZ for the treatment of RA is 5 mg twice daily [see Dosage and Administration (2) ] . |
|---|---|---|---|
| N = 809 (%) | N = 1336 (%) | N = 1349 (%) | |
| N reflects randomized and treated patients from the seven placebo-controlled clinical trials. | |||
Upper respiratory tract infection | 3 | 4 | 4 |
Nasopharyngitis | 3 | 4 | 3 |
Diarrhea | 2 | 4 | 3 |
Headache | 2 | 4 | 3 |
Hypertension | 1 | 2 | 2 |
Other adverse reactions that occurred in placebo-controlled and open-label extension studies in patients with RA included:
Blood and lymphatic system disorders: Anemia
Infections and infestations: Diverticulitis
Metabolism and nutrition disorders: Dehydration
Psychiatric disorders: Insomnia
Nervous system disorders: Paresthesia
Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders: Dyspnea, cough, sinus congestion, interstitial lung disease (cases were limited to patients with RA and some were fatal)
Gastrointestinal disorders: Abdominal pain, dyspepsia, vomiting, gastritis, nausea
Hepatobiliary disorders: Hepatic steatosis
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders: Rash, erythema, pruritus
Musculoskeletal, connective tissue and bone disorders: Musculoskeletal pain, arthralgia, tendonitis, joint swelling
Neoplasms benign, malignant and unspecified (including cysts and polyps): Non-melanoma skin cancers
General disorders and administration site conditions: Pyrexia, fatigue, peripheral edema
Clinical Experience in Methotrexate-Naïve Patients
Study RA-VI was an active-controlled clinical trial in methotrexate-naïve patients [see Clinical Studies (14) ] . The safety experience in these patients was consistent with Studies RA-I through V.
Adverse Reactions in Adults with Psoriatic Arthritis
The safety of XELJANZ was evaluated in 2 double-blind Phase 3 clinical trials in adults with active psoriatic arthritis (PsA):
- Study PsA-I (NCT01877668) had a duration of 12 months and enrolled adults who had an inadequate response to a nonbiologic DMARD and who were naïve to treatment with a TNF blocker. Study PsA-I included a 3-month placebo-controlled period and also included adalimumab 40 mg subcutaneously once every 2 weeks for 12 months.
- Study PsA-II (NCT01882439) had a duration of 6 months and enrolled adults who had an inadequate response to at least one approved TNF blocker. This clinical trial included a 3-month placebo-controlled period.
In these combined Phase 3 clinical trials, 238 patients were randomized and treated with XELJANZ 5 mg twice daily and 236 patients were randomized and treated with XELJANZ 10 mg twice daily. A dosage of XELJANZ 10 mg twice daily is not recommended for the treatment of PsA. For the treatment of adults with active PsA [see Indications and Usage (1.2) ] , the recommended dosage of XELJANZ is 5 mg twice daily and the recommended dosage for XELJANZ XR is 11 mg once daily [see Dosage and Administration (2.3) ].
All patients in the clinical trials in patients with PsA were required to receive treatment with a stable dose of a nonbiologic DMARD [the majority (79%) received methotrexate]. The study population randomized and treated with XELJANZ (474 patients) included 45 (10%) patients aged 65 years or older and 66 (14%) patients with diabetes at baseline.
During the 2 PsA controlled clinical trials, there were:
- 3 malignancies (excluding NMSC) in 474 patients who received XELJANZ plus non-biologic DMARD (6 to 12 months exposure)
- 0 malignancies in 236 patients who received placebo plus non-biologic DMARD group (3 months exposure) and
- 0 malignancies in 106 patients in patients who received adalimumab plus non-biologic DMARD group (12 months exposure).
No lymphomas were reported. Malignancies have also been observed in the long-term extension study in patients with PsA treated with XELJANZ.
The safety profile observed in adults with active PsA treated with XELJANZ was consistent with the safety profile observed in adults with RA.
Adverse Reactions in Adults with Ankylosing Spondylitis
The safety of XELJANZ was evaluated in adults with active ankylosing spondylitis (AS) in a double-blind placebo-controlled Phase 3 clinical trial (Study AS-I) and in a dose-ranging Phase 2 clinical trial (Study AS-II).
- Study AS-I (NCT03502616) had a duration of 48 weeks and enrolled adults who had an inadequate response to at least 2 NSAIDs. Study AS-I included a 16-week double-blind period in which patients received XELJANZ 5 mg or placebo twice daily and a 32-week open-label treatment period in which all patients received XELJANZ 5 mg twice daily.
- Study AS-II (NCT01786668) had a duration of 16 weeks and enrolled adults who had an inadequate response to at least 2 NSAIDs. This clinical trial included a 12-week treatment period in which patients received either XELJANZ 2 mg (40% of the recommended dose), 5 mg, 10 mg, or placebo twice daily. A dosage of XELJANZ 10 mg twice daily is not recommended for the treatment of AS. For the treatment of adults with active AS [see Indications and Usage (1.3) ] , the recommended dosage of XELJANZ is 5 mg twice daily and the recommended dosage for XELJANZ XR is 11 mg once daily [see Dosage and Administration (2.3) ] .
In the combined Phase 2 and Phase 3 clinical trials, a total of 420 patients were treated with either XELJANZ 2 mg, 5 mg, or 10 mg twice daily. Of these, 316 patients were treated with XELJANZ 5 mg twice daily for up to 48 weeks. In the combined double-blind period, 185 patients were randomized to and treated with XELJANZ 5 mg twice daily and 187 to placebo for up to 16 weeks. Concomitant treatment with stable doses of nonbiologic DMARDs, NSAIDs, or corticosteroids (≤10 mg/day) was permitted. The study population randomized and treated with XELJANZ included 13 (3%) patients aged 65 years or older and 18 (4%) patients with diabetes at baseline.
The safety profile observed in adults with AS treated with XELJANZ was consistent with the safety profile observed in adults with RA and PsA.
Adverse Reactions in Pediatric Patients 2 Years of Age and Older with Polyarticular Course Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis
XELJANZ tablets and XELJANZ oral solution 5 mg twice daily or weight-based equivalent twice daily was studied in 225 pediatric patients from 2 years to 17 years of age in Study pcJIA-I [see Clinical Studies (14.4) ] and one open-label extension study (Study A3921145). The total patient exposure (defined as patients who received at least one dose of XELJANZ tablets or XELJANZ oral solution) was 105.6 patient-years in Study pcJIA-I and 777.5 patient-years in Study A3921145.
In general, the types of adverse reactions in pediatric patients 2 years of age and older with pcJIA, were consistent with those seen in adults with RA and PsA (see Adverse Reactions in Adults with Rheumatoid Arthritis and Adverse Reactions in Adults with Psoriatic Arthritis ) .
Adverse Reactions in Adults with Ulcerative Colitis
The safety of XELJANZ has been evaluated in adults with moderately to severely active UC in 4 randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trials (UC-I, UC-II, UC-III, and dose-ranging UC-V) and an open-label long-term extension study (UC-IV) [see Clinical Studies (14.5) ] .
Adverse reactions reported in ≥5% of patients treated with either XELJANZ 5 mg or 10 mg twice daily and ≥1% greater than reported in patients receiving placebo in either the induction or maintenance clinical trials of patients with UC were: nasopharyngitis, elevated cholesterol levels, headache, upper respiratory tract infection, increased blood creatine phosphokinase, rash, diarrhea, and herpes zoster.
Induction Trials in Adults with UC
Common adverse reactions reported in ≥2% of patients treated with XELJANZ 10 mg twice daily and ≥1% greater in XELJANZ-treated patients than placebo-treated patients in the 3 induction trials of patients with UC (Studies UC-I, UC-II, and UC-V) were: headache, nasopharyngitis, elevated cholesterol levels, acne, increased blood creatine phosphokinase, and pyrexia.
Maintenance Trial in Adults with UC
Common adverse reactions reported in ≥4% of patients treated with either dosage of XELJANZ and ≥1% greater than reported in patients treated with placebo in the maintenance trial of patients with UC (Study UC-III) are shown in Table 6.
Preferred Term | Placebo | XELJANZ 5 mg Twice Daily | XELJANZ 10 mg Twice Daily |
N = 198 (%) | N = 198 (%) | N = 196 (%) | |
Nasopharyngitis | 6 | 10 | 14 |
Elevated cholesterol levels Includes hypercholesterolemia, hyperlipidemia, blood cholesterol increased, dyslipidemia, blood triglycerides increased, low-density lipoprotein increased, low-density lipoprotein abnormal, or lipids increased. | 1 | 5 | 9 |
Headache | 6 | 9 | 3 |
Upper respiratory tract infection | 4 | 7 | 6 |
Increased blood creatine phosphokinase | 2 | 3 | 7 |
Rash | 4 | 3 | 6 |
Diarrhea | 3 | 2 | 5 |
Herpes zoster | 1 | 1 | 5 |
Gastroenteritis | 3 | 3 | 4 |
Anemia | 2 | 4 | 2 |
Nausea | 3 | 1 | 4 |
Dose-dependent adverse reactions seen in patients treated with XELJANZ 10 mg twice daily, in comparison to 5 mg twice daily, include the following: herpes zoster infections, serious infections, and NMSC [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1 , 5.3) ] .
During the UC controlled clinical studies (8-week induction and 52-week maintenance studies), which included 1,220 patients, 0 cases of solid cancer or lymphoma were observed in XELJANZ-treated patients.
In the long-term extension study, malignancies (including solid cancers, lymphomas and NMSC) were observed in patients treated with XELJANZ 5 mg and 10 mg twice daily [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3) ] . Five cases of pulmonary embolism were reported in patients taking XELJANZ 10 mg twice daily, including one fatality in a patient with advanced cancer [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5) ] .
Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during post-approval use of XELJANZ (tablets and oral solution) and XELJANZ XR (extended-release tablets). Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Immune system disorders: Drug hypersensitivity (events such as angioedema and urticaria have been observed)
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders: Acne
DRUG INTERACTIONS
Table 7 includes drugs with clinically significant drug interactions when concomitantly used with XELJANZ (tablets and oral solution) and XELJANZ XR (extended-release tablets) and instructions for preventing or managing them.
Strong CYP3A4 Inhibitors (e.g., ketoconazole) | |
Clinical Impact | Increased exposure to tofacitinib |
Intervention | Dosage modification of XELJANZ/XELJANZ XR is recommended [see Dosage and Administration (2) , Clinical Pharmacology, Figure 3 (12.3) ] |
Moderate CYP3A4 Inhibitors Concomitantly Used with Strong CYP2C19 Inhibitors (e.g., fluconazole) | |
Clinical Impact | Increased exposure to tofacitinib |
Intervention | Dosage modification of XELJANZ/XELJANZ XR is recommended [see Dosage and Administration (2) , Clinical Pharmacology, Figure 3 (12.3) ] |
Strong CYP3A4 Inducers (e.g., rifampin) | |
Clinical Impact | Decreased exposure to tofacitinib and may result in loss of or reduced clinical response |
Intervention | Concomitant use with XELJANZ/XELJANZ XR is not recommended [see Clinical Pharmacology, Figure 3 (12.3) ] |
Immunosuppressive Drugs (e.g., azathioprine, tacrolimus, cyclosporine) | |
Clinical Impact | Risk of added immunosuppression; concomitant use of XELJANZ/XELJANZ XR with biologic DMARDs or potent immunosuppressants has not been studied in patients with RA, PsA, AS, UC, or pcJIA. |
Intervention | Concomitant use with XELJANZ/XELJANZ XR is not recommended [see Indications and Usage (1) , Clinical Pharmacology, Figure 3 (12.3) ] |
DESCRIPTION
XELJANZ (tofacitinib) tablets, XELJANZ XR (tofacitinib) extended-release tablets and XELJANZ (tofacitinib) oral solution are formulated with the citrate salt of tofacitinib, a JAK inhibitor.
Tofacitinib citrate is a white to off-white powder with the following chemical name: (3R,4R)-4-methyl-3-(methyl-7H-pyrrolo [2,3-d]pyrimidin-4-ylamino)-ß-oxo-1-piperidinepropanenitrile, 2-hydroxy-1,2,3-propanetricarboxylate (1:1).
The solubility of tofacitinib citrate in water is 2.9 mg/mL.
Tofacitinib citrate has a molecular weight of 504.5 Daltons (or 312.4 Daltons as the tofacitinib free base) and a molecular formula of C 16 H 20 N 6 O•C 6 H 8 O 7 . The chemical structure of tofacitinib citrate is:
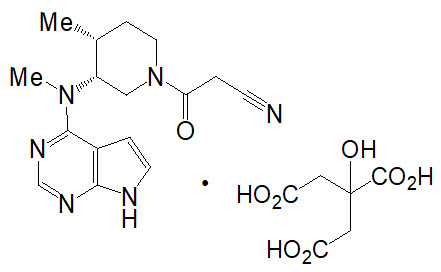
XELJANZ tablets is supplied for oral administration as a:
- 5 mg white round, immediate-release film-coated tablet. Each tablet contains 5 mg of tofacitinib (equivalent to 8.08 mg of tofacitinib citrate) and the following inactive ingredients: croscarmellose sodium, HPMC 2910/Hypromellose 6cP, lactose monohydrate, macrogol/PEG3350, magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose, titanium dioxide, and triacetin.
- 10 mg blue round, immediate-release film-coated tablet. Each tablet contains 10 mg of tofacitinib (equivalent to 16.16 mg of tofacitinib citrate) and the following inactive ingredients: croscarmellose sodium, FD&C Blue #1/Brilliant Blue FCF Aluminum Lake, FD&C Blue #2/Indigo Carmine Aluminum Lake, HPMC 2910/Hypromellose 6cP, lactose monohydrate, macrogol/PEG3350, magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose, titanium dioxide, and triacetin.
XELJANZ XR is supplied for oral administration as a:
- 11 mg pink, oval, extended-release film-coated tablet with a drilled hole at one end of the tablet band. Each tablet contains 11 mg of tofacitinib (equivalent to 17.77 mg tofacitinib citrate) and the following inactive ingredients: cellulose acetate, copovidone, hydroxyethyl cellulose, hydroxypropyl cellulose, HPMC 2910/Hypromellose, magnesium stearate, red iron oxide, sorbitol, titanium dioxide and triacetin. Printing ink contains, ammonium hydroxide, ferrosoferric oxide/black iron oxide, propylene glycol, and shellac glaze.
- 22 mg beige, oval, extended-release film-coated tablet with a drilled hole at one end of the tablet band. Each tablet contains 22 mg of tofacitinib (equivalent to 35.54 mg tofacitinib citrate) and the following inactive ingredients: cellulose acetate, copovidone, FD&C Blue #2 Aluminum Lake, hydroxyethyl cellulose, hydroxypropyl cellulose, HPMC 2910/Hypromellose, magnesium stearate, red iron oxide, sorbitol, titanium dioxide, triacetin, and yellow iron oxide. Printing ink contains ammonium hydroxide, ferrosoferric oxide/black iron oxide, propylene glycol, and shellac glaze.
XELJANZ oral solution is supplied for oral administration as a 1 mg/mL clear, colorless solution. Each 1 mL contains 1 mg of tofacitinib (equivalent to 1.62 mg of tofacitinib citrate) and the following inactive ingredients: grape flavor (natural), hydrochloric acid, lactic acid, purified water, sodium benzoate, sucralose, and xylitol.
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Mechanism of Action
Tofacitinib is a Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitor. JAKs are intracellular enzymes which transmit signals arising from cytokine or growth factor-receptor interactions on the cellular membrane to influence cellular processes of hematopoiesis and immune cell function. Within the signaling pathway, JAKs phosphorylate and activate Signal Transducers and Activators of Transcription (STATs) which modulate intracellular activity including gene expression. Tofacitinib modulates the signaling pathway at the point of JAKs, preventing the phosphorylation and activation of STATs. JAK enzymes transmit cytokine signaling through pairing of JAKs (e.g., JAK1/JAK3, JAK1/JAK2, JAK1/TyK2, JAK2/JAK2). Tofacitinib inhibited the in vitro activities of JAK1/JAK2, JAK1/JAK3, and JAK2/JAK2 combinations with IC 50 of 406, 56, and 1377 nM, respectively. However, the relevance of specific JAK combinations to therapeutic effectiveness is not known.
Pharmacodynamics
Treatment with XELJANZ was associated with dose-dependent reductions of circulating CD16/56+ natural killer cells, with estimated maximum reductions occurring at approximately 8-10 weeks after initiation of therapy. These changes generally resolved within 2-6 weeks after discontinuation of treatment. Treatment with XELJANZ was associated with dose-dependent increases in B cell counts. Changes in circulating T-lymphocyte counts and T-lymphocyte subsets (CD3+, CD4+ and CD8+) were small and inconsistent. The clinical significance of these changes is unknown.
Total serum IgG, IgM, and IgA levels after 6-month dosing in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) were lower than in patients who received placebo; however, changes were small and not dose-dependent.
After treatment with XELJANZ in patients with RA, rapid decreases in serum C-reactive protein (CRP) were observed and maintained throughout dosing. Changes in CRP observed with XELJANZ treatment do not reverse fully within 2 weeks after discontinuation, indicating a longer duration of pharmacodynamic activity compared to the pharmacokinetic half-life.
Similar changes in T cells, B cells, and serum CRP have been observed in patients with active psoriatic arthritis (PsA) although reversibility was not assessed. Total serum immunoglobulins were not assessed in patients with active PsA.
Pharmacokinetics
Following oral administration of XELJANZ (tablets and oral solution), peak plasma concentrations were reached within 0.5 hour - 1 hour, elimination half-life was about 3 hours and a dose-proportional increase in systemic exposure was observed in the therapeutic dosage range. Steady state concentrations were achieved in 24-48 hours with negligible accumulation after twice daily administration.
Following oral administration of XELJANZ XR (extended-release tablets), peak plasma concentrations were reached at 4 hours and half-life was about 6 to 8 hours. Steady state concentrations were achieved within 48 hours with negligible accumulation after once daily administration.
Table 8 describes the pharmacokinetic parameters of XELJANZ and XELJANZ XR.
| PK Parameters Values represent the geometric mean, except T max , for which is the median (range) is shown. (CV%) | XELJANZ | XELJANZ XR | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dosing Regimen | 5 mg Twice Daily | 10 mg Twice Daily | 11 mg Once Daily | 22 mg Once Daily |
| Abbreviations: AUC 24 = area under the concentration time profile from time 0 to 24 hours; C max = maximum plasma concentration; C min = minimum plasma concentration; T max = time to C max ; CV = Coefficient of variation. | ||||
AUC 24 (ng.hr/mL) | 263.4 (15) | 539.6 (22) | 269.0 (18) | 596.6 (19) |
C max (ng/mL) | 42.7 (26) | 84.7 (18) | 38.2 (15) | 83.8 (25) |
C min (ng/mL) | 1.41 (40) | 3.10 (54) | 1.07 (69) | 3.11 (43) |
T max (hours) | 1.0 (0.5 to14.0 Values beyond 12 hours were after the evening dose which was administered 12 hours after the morning dose of twice-daily XELJANZ. ) | 0.8 (0.5 to 14.0) | 4.0 (3.0 to 4.0) | 4.0 (2.0 to 4.0) |
Absorption
XELJANZ
The absolute oral bioavailability of XELJANZ is 74%. Coadministration of XELJANZ with a high-fat meal resulted in no changes in AUC while C max was reduced by 32%. In clinical trials, XELJANZ was administered without regard to meals [see Dosage and Administration (2.2) ] .
XELJANZ XR
Coadministration of XELJANZ XR 11 and 22 mg with a high-fat meal resulted in no changes in AUC while C max was increased by 27% and 19% respectively. T max was extended by approximately 1 hour for both XELJANZ XR 11 and 22 mg.
Distribution
After intravenous administration, the volume of distribution was 87 L. The protein binding of tofacitinib is approximately 40%. Tofacitinib binds predominantly to albumin and does not appear to bind to α1-acid glycoprotein. Tofacitinib distributes equally between red blood cells and plasma.
Metabolism and Excretion
Clearance mechanisms for tofacitinib are approximately 70% hepatic metabolism and 30% renal excretion of the parent drug. The metabolism of tofacitinib is primarily mediated by CYP3A4 with minor contribution from CYP2C19. In a human radiolabeled study, more than 65% of the total circulating radioactivity was accounted for by unchanged tofacitinib, with the remaining 35% attributed to 8 metabolites, each accounting for less than 8% of total radioactivity. The pharmacologic activity of tofacitinib is attributed to the parent molecule.
Pharmacokinetics in Patients with RA, PsA, AS, and UC
Population pharmacokinetic (PK) analyses indicated that PK characteristics were similar between patients with RA, PsA, ankylosing spondylitis, and UC. The coefficient of variation (%) in AUC of tofacitinib were generally similar across different disease patients, ranging from 22% to 34% (Table 9).
| Pharmacokinetic Parameters Pharmacokinetic parameters estimated based on population pharmacokinetic analysis. Geometric Mean (CV%) | XELJANZ 5 mg Twice Daily | XELJANZ 10 mg Twice Daily | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rheumatoid Arthritis | Psoriatic Arthritis | Ankylosing Spondylitis | Ulcerative Colitis | Ulcerative Colitis | |
| Abbreviations: AUC 0–24,ss = area under the plasma concentration-time curve over 24 hours at steady state; CV = coefficient of variation. | |||||
AUC 0–24 , ss (ng∙h/mL) | 504 (22.0%) | 419 (34.1%) | 381 (25.4%) | 423 (22.6%) | 807 (24.6%) |
Specific Populations
Covariate evaluation as part of population PK analyses in adult patient populations indicated no clinically relevant change in tofacitinib exposure, after accounting for differences in renal function (i.e., creatinine clearance) between patients, based on age, weight, biological sex and race (Figure 1). An approximately linear relationship between body weight and volume of distribution was observed, resulting in higher peak (C max ) and lower trough (C min ) concentrations in lighter patients. However, this difference is not considered to be clinically relevant.
Covariate evaluation as part of population PK analyses in pediatric patients with pcJIA, including PsA, identified body weight significantly impacting tofacitinib exposure, which supports weight-based dosing in this population. There were no identified clinically significant differences in tofacitinib exposure with different age, biological sex, racial, or pcJIA or PsA disease severity groups.
The effect of renal and hepatic impairment and other intrinsic factors on the PK of tofacitinib is shown in Figure 1.
Figure 1: Impact of Intrinsic Factors on Tofacitinib Pharmacokinetics

Note: Reference values for weight, age, biological sex, and race comparisons are 70 kg, 55 years, male, and white, respectively; reference groups for renal and hepatic impairment data are patients with normal renal and hepatic function. Renal function was estimated using creatinine clearance by Cockcroft-Gault method and hepatic function was estimated using Child-Pugh scoring method.
In patients with end-stage renal disease maintained on hemodialysis, mean AUC was approximately 40% higher compared with historical healthy subject data, consistent with approximately 30% contribution of renal clearance to the total clearance of tofacitinib [see Dosage and Administration (2.3 , 2.4 , 2.5) and Use in Specific Populations (8.6) ] .
Drug Interaction Studies
Potential for XELJANZ/XELJANZ XR to Influence the PK of Other Drugs
In vitro studies indicate that tofacitinib does not significantly inhibit or induce the activity of the major human drug-metabolizing CYPs (CYP1A2, CYP2B6, CYP2C8, CYP2C9, CYP2C19, CYP2D6, and CYP3A4) at concentrations corresponding to the steady state C max of a 10 mg twice daily dose. These in vitro results were confirmed by a human drug interaction study showing no changes in the pharmacokinetics of midazolam, a highly sensitive CYP3A4 substrate, when concomitantly administered with XELJANZ.
In vitro studies indicate that tofacitinib does not significantly inhibit the activity of the major human drug-metabolizing uridine 5'-diphospho-glucuronosyltransferases (UGTs) [UGT1A1, UGT1A4, UGT1A6, UGT1A9, and UGT2B7] at concentrations exceeding 250 times the steady state C max of a 10 mg twice daily dose.
In patients with RA, the oral clearance of tofacitinib does not vary with time, indicating that tofacitinib does not normalize CYP enzyme activity in patients with RA. Therefore, concomitant use with XELJANZ/XELJANZ XR is not expected to result in clinically relevant increases in the metabolism of CYP substrates in patients with RA.
In vitro data indicate that the potential for tofacitinib to inhibit transporters such as P-glycoprotein, organic anionic or cationic transporters at therapeutic concentrations is low.
The impact of tofacitinib on the PK of other drugs for the concomitant drugs are shown in Figure 2.
Figure 2: Impact of Tofacitinib on the Pharmacokinetics of Other Drugs

Note: Reference group is administration of concomitant medication alone; OCT = Organic Cationic Transporter; MATE = Multidrug and Toxic Compound Extrusion.
Potential for Other Drugs to Influence the Pharmacokinetics of Tofacitinib
Since tofacitinib is metabolized by CYP3A4, interaction with drugs that inhibit or induce CYP3A4 is likely. Inhibitors of CYP2C19 alone or P-glycoprotein are unlikely to substantially alter the pharmacokinetics of tofacitinib (see Figure 3 ).
Figure 3: Impact of Other Drugs on the Pharmacokinetics of Tofacitinib

Note: Reference group is administration of XELJANZ alone.
NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
In a 39-week toxicology study in monkeys, tofacitinib at exposure levels approximately 6 times the recommended dose of 5 mg twice daily, and approximately 3 times the 10 mg twice daily dose (on an AUC basis at oral doses of 5 mg/kg twice daily) produced lymphomas. No lymphomas were observed in this study at exposure levels 1 times the recommended dose of 5 mg twice daily, and approximately 0.5 times the 10 mg twice daily dose (on an AUC basis at oral doses of 1 mg/kg twice daily).
The carcinogenic potential of tofacitinib was assessed in 6-month rasH2 transgenic mouse carcinogenicity and 2-year rat carcinogenicity studies. Tofacitinib, at exposure levels approximately 34 times the recommended dose of 5 mg twice daily, and approximately 17 times the 10 mg twice daily dose (on an AUC basis at oral doses of 200 mg/kg/day) was not carcinogenic in mice.
In the 24-month oral carcinogenicity study in Sprague-Dawley rats, tofacitinib caused benign Leydig cell tumors, hibernomas (malignancy of brown adipose tissue), and benign thymomas at doses greater than or equal to 30 mg/kg/day (approximately 42 times the exposure levels at the recommended dose of 5 mg twice daily, and approximately 21 times the 10 mg twice daily dose on an AUC basis). The relevance of benign Leydig cell tumors to human risk is not known.
Tofacitinib was not mutagenic in the bacterial reverse mutation assay. It was positive for clastogenicity in the in vitro chromosome aberration assay with human lymphocytes in the presence of metabolic enzymes, but negative in the absence of metabolic enzymes. Tofacitinib was negative in the in vivo rat micronucleus assay and in the in vitro CHO-HGPRT assay and the in vivo rat hepatocyte unscheduled DNA synthesis assay.
In rats, tofacitinib at exposure levels approximately 17 times the recommended dose of 5 mg twice daily, and approximately 8.3 times the 10 mg twice daily dose (on an AUC basis at oral doses of 10 mg/kg/day) reduced female fertility due to increased post-implantation loss. There was no impairment of female rat fertility at exposure levels of tofacitinib equal to the recommended dose of 5 mg twice daily, and approximately 0.5 times the 10 mg twice daily dose (on an AUC basis at oral doses of 1 mg/kg/day). Tofacitinib exposure levels at approximately 133 times the recommended dose of 5 mg twice daily, and approximately 67 times the 10 mg twice daily dose (on an AUC basis at oral doses of 100 mg/kg/day) had no effect on male fertility, sperm motility, or sperm concentration.
CLINICAL STUDIES
Clinical Studies in Rheumatoid Arthritis
The rheumatoid arthritis (RA) clinical development program with XELJANZ tablets (referred to as “XELJANZ” in this subsection of labeling) included six randomized controlled trials in adults with moderate to severe active RA.
Trial Design
- Study RA-I (NCT00814307) was a 6-month monotherapy trial in which 610 patients with moderate to severe active RA who had an inadequate response to a DMARD (nonbiologic or biologic) received XELJANZ 5 mg or 10 mg twice daily or placebo added to their background DMARD. At the Month 3 visit, all patients randomized to placebo treatment were switched in a blinded fashion to a second predetermined treatment of XELJANZ 5 mg or 10 mg twice daily. The primary endpoints at Month 3 were the proportion of patients who achieved an ACR20 response, changes in Health Assessment Questionnaire – Disability Index (HAQ-DI), and rates of Disease Activity Score DAS28-4(ESR) less than 2.6.
- Study RA-II (NCT00856544) was a 12-month trial in which 792 patients with moderate to severe active RA who had an inadequate response to a nonbiologic DMARD received XELJANZ 5 mg or 10 mg twice daily or placebo added to background DMARD treatment (excluding potent immunosuppressive treatments such as azathioprine or cyclosporine). At the Month 3 visit, nonresponding patients were switched in a blinded fashion to a second predetermined treatment of XELJANZ 5 mg or 10 mg twice daily. At the end of Month 6, all patients treated with placebo were switched to their second predetermined XELJANZ treatment in a blinded fashion. The primary endpoints were the proportion of patients who achieved an ACR20 response at Month 6, changes in HAQ-DI at Month 3, and rates of DAS28-4(ESR) less than 2.6 at Month 6.
- Study RA-III (NCT00853385) was a 12-month trial in 717 patients with moderate to severe active RA who had an inadequate response to methotrexate (MTX). Patients received XELJANZ 5 mg or 10 mg orally twice daily, adalimumab 40 mg subcutaneously every other week, or placebo added to background MTX. Patients treated with placebo were switched as in Study RA-II. The primary endpoints were the proportion of patients who achieved an ACR20 response at Month 6, HAQ-DI at Month 3, and DAS28-4(ESR) less than 2.6 at Month 6.
- Study RA-IV (NCT00847613) was a 2-year trial with a planned analysis at 1 year in which 797 patients with moderate to severe active RA who had an inadequate response to MTX received XELJANZ 5 mg or 10 mg twice daily or placebo added to background MTX. Patients treated with placebo were switched as in Study RA-II. The primary endpoints were the proportion of patients who achieved an ACR20 response at Month 6, mean change from baseline in van der Heijde-modified total Sharp Score (mTSS) at Month 6, HAQ-DI at Month 3, and DAS28-4(ESR) less than 2.6 at Month 6.
- Study RA-V (NCT00960440) was a 6-month trial in which 399 patients with moderate to severe active RA who had an inadequate response to at least one approved TNF blocking biological product received XELJANZ 5 mg or 10 mg twice daily or placebo added to background MTX. At the Month 3 visit, all patients randomized to placebo treatment were switched in a blinded fashion to a second predetermined treatment of XELJANZ 5 or 10 mg twice daily. The primary endpoints at Month 3 were the proportion of patients who achieved an ACR20 response, HAQ-DI, and DAS28-4(ESR) less than 2.6.
- Study RA-VI (NCT01039688) was a 2-year monotherapy trial with a planned analysis at 1 year in which 952 MTX-naïve patients with moderate to severe active RA received XELJANZ 5 or 10 mg twice daily or MTX dose-titrated over 8 weeks to 20 mg weekly. The primary endpoints were mean change from baseline in van der Heijde-modified Total Sharp Score (mTSS) at Month 6 and the proportion of patients who achieved an ACR70 response at Month 6.
Although other dosages have been studied, the recommended dosage of XELJANZ is 5 mg twice daily. XELJANZ 10 mg twice daily is not recommended for the treatment of RA [see Dosage and Administration (2.3) ] .
Clinical Response
The percentages of XELJANZ-treated patients who achieved ACR20, ACR50, and ACR70 responses in Studies RA-I, IV, and V are shown in Table 10. Similar results were observed with Studies RA-II and III. In trials RA-I through V, patients treated with 5 mg twice daily XELJANZ had higher ACR20, ACR50, and ACR70 response rates versus patients treated with placebo, with or without background DMARD treatment, at Month 3 and Month 6. Higher ACR20 response rates were observed within 2 weeks compared to placebo. In the 12-month trials, ACR response rates in XELJANZ-treated patients were consistent at 6 and 12 months.
Monotherapy in Nonbiologic or Biologic DMARD Inadequate Responders Inadequate response to at least one DMARD (biologic or nonbiologic) due to lack of efficacy or toxicity. | MTX Inadequate Responders Inadequate response to MTX defined as the presence of sufficient residual disease activity to meet the entry criteria. | TNF Blocker Inadequate Responders Inadequate response to a least one TNF blocker due to lack of efficacy and/or intolerance. | ||||
Study RA-I | Study RA-IV | Study RA-V | ||||
N N is number of randomized and treated patients. | Placebo + background DMARD | XELJANZ 5 mg Twice Daily + background DMARD | Placebo + background MTX | XELJANZ 5 mg Twice Daily + background MTX | Placebo + background MTX | XELJANZ 5 mg Twice Daily + background MTX |
122 | 243 | 160 | 321 | 132 | 133 | |
ACR20 Month 3 Month 6 | 26% NA NA (not applicable), as data for placebo treatment is not available beyond 3 months in Studies RA-I and RA-V due to placebo advancement. | 59% 69% | 27% 25% | 55% 50% | 24% NA | 41% 51% |
ACR50 Month 3 Month 6 | 12% NA | 31% 42% | 8% 9% | 29% 32% | 8% NA | 26% 37% |
ACR70 Month 3 Month 6 | 6% NA | 15% 22% | 3% 1% | 11% 14% | 2% NA | 14% 16% |
In Study RA-IV, a greater proportion of patients treated with XELJANZ 5 mg twice daily plus MTX achieved a low level of disease activity as measured by a DAS28-4(ESR) less than 2.6 at 6 months compared to those treated with MTX alone (Table 11).
Study RA-IV | ||
DAS28-4(ESR) Less Than 2.6 | Placebo + MTX 160 | XELJANZ 5 mg Twice Daily + MTX 321 |
Proportion of responders at Month 6 (n) | 1% (2) | 6% (19) |
Of responders, proportion with 0 active joints (n) | 50% (1) | 42% (8) |
Of responders, proportion with 1 active joint (n) | 0 | 5% (1) |
Of responders, proportion with 2 active joints (n) | 0 | 32% (6) |
Of responders, proportion with 3 or more active joints (n) | 50% (1) | 21% (4) |
The results of the components of the ACR response criteria for Study RA-IV are shown in Table 12. Similar results were observed for XELJANZ in Studies RA-I, II, III, V, and VI.
Study RA-IV | ||||
Placebo + MTX N=160 | XELJANZ 5 mg Twice Daily + MTX N=321 | |||
Component (mean) Data shown is mean (Standard Deviation) at Month 3. | Baseline | Month 3 | Baseline | Month 3 |
Number of tender joints (0-68) | 23 (13) | 18 (14) | 24 (14) | 13 (14) |
Number of swollen joints (0-66) | 14 (9) | 10 (9) | 14 (8) | 6 (8) |
Pain Visual analog scale: 0 = best, 100 = worst. | 55 (24) | 47 (24) | 58 (23) | 34 (23) |
Patient global assessment | 54 (23) | 47 (24) | 58 (24) | 35 (23) |
Disability index (HAQ-DI) Health Assessment Questionnaire Disability Index: 0 = best, 3 = worst; 20 questions; categories: dressing and grooming, arising, eating, walking, hygiene, reach, grip, and activities. | 1.32 (0.67) | 1.19 (0.68) | 1.41 (0.68) | 0.99 (0.65) |
Physician global assessment | 56 (18) | 43 (22) | 59 (16) | 30 (19) |
CRP (mg/L) | 13.7 (14.9) | 14.6 (18.7) | 15.3 (19.0) | 7.1 (19.1) |
The percent of ACR20 responders by visit for Study RA-IV is shown in Figure 4. Similar responses were observed for XELJANZ in Studies RA-I, II, III, V, and VI.
Figure 4: Percentage of ACR20 Responders by Visit Through Month 6 in Study RA-IV

Radiographic Response
Two studies were conducted to evaluate the effect of XELJANZ on structural joint damage. In Study RA-IV and Study RA-VI, progression of structural joint damage was assessed radiographically and expressed as change from baseline in mTSS and its components, the erosion score and joint space narrowing score, at Months 6 and 12. The proportion of patients with no radiographic progression (mTSS change less than or equal to 0) was also assessed.
In Study RA-IV, XELJANZ 5 mg twice daily reduced the mean progression of structural damage (not statistically significant) as shown in Table 13. Analyses of erosion and joint space narrowing scores were consistent with the overall results.
In the placebo plus MTX group, 74% of patients experienced no radiographic progression at Month 6 compared to 84% of patients treated with XELJANZ plus MTX 5 mg twice daily.
In Study RA-VI, XELJANZ monotherapy inhibited the progression of structural damage compared to MTX at Months 6 and 12 as shown in Table 13. Analyses of erosion and joint space narrowing scores were consistent with the overall results.
In the MTX group, 55% of patients experienced no radiographic progression at Month 6 compared to 73% of patients treated with XELJANZ 5 mg twice daily.
Study RA-IV | |||
Placebo N=139 Mean (SD) SD = Standard Deviation | XELJANZ 5 mg Twice Daily N=277 Mean (SD) | XELJANZ 5 mg Twice Daily Mean Difference from Placebo Difference between least squares means XELJANZ minus placebo or MTX (95% CI = 95% confidence interval) (CI) | |
mTSS Month 6 and Month 12 data are mean change from baseline. | |||
Baseline | 33 (42) | 31 (48) | |
Month 6 | 0.5 (2.0) | 0.1 (1.7) | -0.3 (-0.7, 0.0) |
Study RA-VI | |||
MTX N=166 Mean (SD) | XELJANZ 5 mg Twice Daily N=346 Mean (SD) | XELJANZ 5 mg Twice Daily Mean Difference from MTX (CI) | |
mTSS | |||
Baseline | 17 (29) | 20 (40) | |
Month 6 | 0.8 (2.7) | 0.2 (2.3) | -0.7 (-1.0, -0.3) |
Month 12 | 1.3 (3.7) | 0.4 (3.0) | -0.9 (-1.4, -0.4) |
Physical Function Response
Improvement in physical functioning was measured by the HAQ-DI. Patients who received XELJANZ 5 mg twice daily demonstrated greater improvement from baseline in physical functioning compared to patients who received placebo at Month 3.
The mean (95% CI) difference from placebo in HAQ-DI improvement from baseline at Month 3 in Study RA-III was -0.22 (-0.35, -0.10) in patients who received 5 mg XELJANZ twice daily. Similar results were obtained in Studies RA-I, II, IV and V. In the 12-month trials, HAQ-DI results in XELJANZ-treated patients were consistent at 6 and 12 months.
Other Health-Related Outcomes
General health status was assessed by the Short Form health survey (SF-36). In Studies RA-I, IV, and V, patients who received XELJANZ 5 mg twice daily demonstrated greater improvement from baseline compared to placebo in physical component summary (PCS), mental component summary (MCS) scores and in all 8 domains of the SF-36 at Month 3.
Clinical Studies in Psoriatic Arthritis
The psoriatic arthritis (PsA) clinical development program with XELJANZ tablets (referred to as “XELJANZ” in this subsection of labeling) included 2 multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trials in 816 adults with active PsA (Studies PsA-I and PsA-II).
Trial Designs and Population
All patients had active PsA for at least 6 months based upon the Classification Criteria for Psoriatic Arthritis (CASPAR), at least 3 tender/painful joints and at least 3 swollen joints, and active plaque psoriasis. Patients randomized and treated across the 2 clinical trials represented different PsA subtypes at screening, including <5 joints or asymmetric involvement (21%), ≥5 joints involved (90%), distal interphalangeal (DIP) joint involvement (61%), arthritis mutilans (8%), and spondylitis (19%). Patients in these clinical trials had a diagnosis of PsA for a mean (SD) of 7.7 (7.2) years. At baseline, 80% and 53% of patients had enthesitis and dactylitis, respectively. At baseline, all patients were required to receive treatment with a stable dose of a nonbiologic DMARD (79% received methotrexate, 13% received sulfasalazine, 7% received leflunomide, 1% received other nonbiologic DMARDs). In both clinical trials, the primary endpoints were the ACR20 response and the change from baseline in HAQ-DI at Month 3.
- Study PsA-I was a 12-month clinical trial in 422 patients who had an inadequate response to a nonbiologic DMARD (67% and 33% were inadequate responders to 1 nonbiologic DMARD and ≥2 nonbiologic DMARDs, respectively) and who were naïve to treatment with a TNF blocker. Although Study PsA-1 included patients who are TNF blocker-naïve, XELJANZ and XELJANZ XR are not approved for use in TNF blocker-naïve patients [see Indications and Usage (1.2) ] . Patients were randomized in a 2:2:2:1:1 ratio to receive XELJANZ 5 mg twice daily, XELJANZ 10 mg twice daily, adalimumab 40 mg subcutaneously once every 2 weeks, placebo to XELJANZ 5 mg twice daily treatment sequence, or placebo to XELJANZ 10 mg twice daily treatment sequence, respectively; study drug was added to background nonbiologic DMARD treatment. At the Month 3 visit, all patients randomized to placebo treatment were switched in a blinded fashion to a predetermined XELJANZ dosage of 5 mg or 10 mg twice daily. Study PsA-I was not designed to demonstrate noninferiority or superiority to adalimumab.
- Study PsA-II was a 6-month clinical trial in 394 patients who had an inadequate response to at least 1 approved TNF blocker (66%, 19%, and 15% were inadequate responders to 1 TNF blocker, 2 TNF blockers and ≥3 TNF blockers, respectively). Patients were randomized in a 2:2:1:1 ratio to receive XELJANZ 5 mg twice daily, XELJANZ 10 mg twice daily, placebo to XELJANZ 5 mg twice daily treatment sequence, or placebo to XELJANZ 10 mg twice daily treatment sequence, respectively; study drug was added to background nonbiologic DMARD treatment. At the Month 3 visit, placebo patients were switched in a blinded fashion to a predetermined XELJANZ dosage of 5 mg or 10 mg twice daily as in Study PsA-I.
Although other dosages have been studied, the recommended dosage of XELJANZ is 5 mg twice daily. XELJANZ 10 mg twice daily is not recommended for treatment of PsA [see Dosage and Administration (2.3) ] .
Clinical Response
At Month 3, patients treated with XELJANZ 5 mg twice daily had higher (p≤0.05) response rates versus placebo for ACR20, ACR50, and ACR70 in Study PsA-I and for ACR20 and ACR50 in Study PsA-II; ACR70 response rates were also higher for XELJANZ 5 mg twice daily versus placebo in Study PsA-II, although the differences versus placebo were not statistically significant (p>0.05) (Tables 14 and 15).
| Treatment Group | Placebo | XELJANZ 5 mg Twice Daily + Background Nonbiologic DMARD | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Patients with missing data were treated as non-responders. | |||
N N is number of randomized and treated patients. | 105 | 107 | |
Response Rate | Response Rate | Difference (%) 95% CI from Placebo | |
Month 3 | |||
ACR20 | 33% | 50% | 17.1 (4.1, 30.2) |
ACR50 | 10% | 28% | 18.5 (8.3, 28.7) |
ACR70 | 5% | 17% | 12.1 (3.9, 20.2) |
| Treatment Group | Placebo | XELJANZ 5 mg Twice Daily | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Patients with missing data were treated as non-responders. | |||
N N is number of randomized and treated patients. | 131 | 131 | |
Response Rate | Response Rate | Difference (%) 95% CI from Placebo | |
Month 3 | |||
ACR20 | 24% | 50% | 26.0 (14.7, 37.2) |
ACR50 | 15% | 30% | 15.3 (5.4, 25.2) |
ACR70 | 10% | 17% | 6.9 (-1.3, 15.1) |
Improvements from baseline in the ACR response criteria components for both studies are shown in Table 16.
| Nonbiologic DMARD Inadequate Responders (TNF Blocker-Naïve) | TNF Blocker Inadequate Responders | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Study PsA-I Patients received one concomitant nonbiologic DMARD. , XELJANZ and XELJANZ XR are not approved for use in TNF blocker-naïve patients [see Indications and Usage (1.2) ] . | Study PsA-II | |||
Treatment Group | Placebo | XELJANZ 5 mg Twice Daily | Placebo | XELJANZ 5 mg Twice Daily |
N at Baseline | 105 | 107 | 131 | 131 |
ACR Component Data shown are mean value at baseline and at Month 3. | ||||
Number of tender/painful joints (0–68) | ||||
Baseline | 20.6 | 20.5 | 19.8 | 20.5 |
Month 3 | 14.6 | 12.2 | 15.1 | 11.5 |
Number of swollen joints (0–66) | ||||
Baseline | 11.5 | 12.9 | 10.5 | 12.1 |
Month 3 | 7.1 | 6.3 | 7.7 | 4.8 |
Patient assessment of arthritis pain Visual analog scale (VAS): 0 = best, 100 = worst. | ||||
Baseline | 53.2 | 55.7 | 54.9 | 56.4 |
Month 3 | 44.7 | 34.7 | 48.0 | 36.1 |
Patient global assessment of arthritis | ||||
Baseline | 53.9 | 54.7 | 55.8 | 57.4 |
Month 3 | 44.4 | 35.5 | 49.2 | 36.9 |
HAQ-DI HAQ-DI = Health Assessment Questionnaire – Disability Index: 0 = best, 3 = worst; 20 questions; categories: dressing and grooming, arising, eating, walking, hygiene, reach, grip, and activities. | ||||
Baseline | 1.11 | 1.16 | 1.25 | 1.26 |
Month 3 | 0.95 | 0.81 | 1.09 | 0.88 |
Physician's Global Assessment of Arthritis | ||||
Baseline | 53.8 | 54.6 | 53.7 | 53.5 |
Month 3 | 35.4 | 29.5 | 36.4 | 27.0 |
CRP (mg/L) | ||||
Baseline | 10.4 | 10.5 | 12.1 | 13.8 |
Month 3 | 8.6 | 4.0 | 11.4 | 7.7 |
The percentage of ACR20 responders by visit for Study PsA-I is shown in Figure 5. Similar responses were observed in Study PsA-II. In both studies, improvement in ACR20 response on XELJANZ was observed at the first visit after baseline (Week 2).
| BID = twice daily; SE = standard error. |
| Patients with missing data were treated as non-responders. |
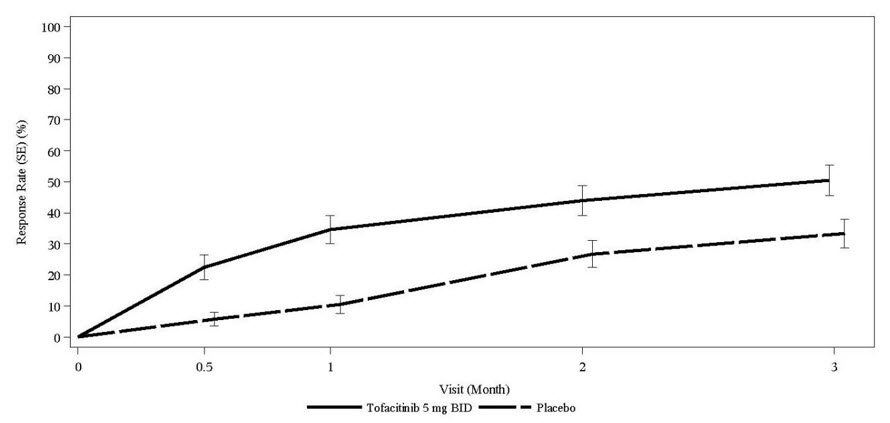 |
In patients with active PsA evidence of benefit in enthesitis and dactylitis was observed with XELJANZ treatment.
Physical Function
Improvement in physical functioning was measured by the HAQ-DI. Patients receiving XELJANZ 5 mg twice daily demonstrated significantly greater improvement (p ≤0.05) from baseline in physical functioning compared to placebo at Month 3 (Table 17).
| Least Squares Mean Change from Baseline In HAQ-DI at Month 3 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nonbiologic DMARD Inadequate Responders Inadequate response to at least one nonbiologic DMARD due to lack of efficacy and/or intolerability. (TNF Blocker-Naïve) | TNF Blocker Inadequate Responders Inadequate response to at least one TNF blocker due to lack of efficacy and/or intolerability. | |||
| Study PsA-I Patients received one concomitant nonbiologic DMARD. , XELJANZ and XELJANZ XR are not approved for use in TNF blocker-naïve patients [see Indications and Usage (1.2) ] . | Study PsA-II | |||
Treatment Group | Placebo | XELJANZ 5 mg Twice Daily | Placebo | XELJANZ 5 mg Twice Daily |
N N is the total number of patients in the statistical analysis. | 104 | 107 | 131 | 129 |
LSM Change from Baseline | -0.18 | -0.35 | -0.14 | -0.39 |
Difference from Placebo (95% CI) | -0.17 (-0.29, -0.05) | -0.25 (-0.38, -0.13) | ||
In Study PsA-I, the HAQ-DI responder rate (response defined as having improvement from baseline of ≥0.35) at Month 3 was 53% in patients receiving XELJANZ 5 mg twice daily and 31% in patients receiving placebo. Similar responses were observed in Study PsA-II.
Other Health-Related Outcomes
General health status was assessed by the Short Form health survey (SF-36). In Studies PsA-I and PsA-II, patients receiving XELJANZ 5 mg twice daily had greater improvement from baseline compared to placebo in Physical Component Summary (PCS) score, but not in Mental Component Summary (MCS) score at Month 3. Patients receiving XELJANZ 5 mg twice daily reported consistently greater improvement relative to placebo in the domains of Physical Functioning, Bodily Pain, Vitality, and Social Functioning, but not in Role-Physical, General Health, Role-Emotional, or Mental Health.
Radiographic Response
Treatment effect on inhibition of radiographic progression in PsA could not be established from the results of Study PsA-I.
Clinical Studies in Ankylosing Spondylitis
The ankylosing spondylitis (AS) clinical development program with XELJANZ tablets (referred to as “XELJANZ” in this subsection of labeling) included one placebo-controlled trial (Study AS-I) in adults with active AS. Patients had active disease as defined by both Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Index (BASDAI) and back pain score (BASDAI question 2) of greater or equal to 4 despite non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID), corticosteroid or disease modifying anti-rheumatic drug (DMARD) therapy.
Trial Design
Study AS-I was a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, 48-week clinical trial in 269 adult patients who had an inadequate response (inadequate clinical response or intolerance) to at least 2 NSAIDs. Although Study AS-I included some patients who are TNF blocker-naïve, XELJANZ and XELJANZ XR are not approved for use in TNF blocker-naïve patients [see Indications and Usage (1.3) ] . Patients were randomized and treated with XELJANZ 5 mg twice daily or placebo for 16 weeks of blinded treatment and then all received treatment of XELJANZ 5 mg twice daily for additional 32 weeks. The primary endpoint was to evaluate the proportion of patients who achieved an ASAS20 response at Week 16.
Approximately 7% and 21% of patients used concomitant methotrexate or sulfasalazine, respectively from baseline to Week 16. Twenty-two percent of patients had an inadequate response to 1 or 2 TNF blockers.
Clinical Response
Patients treated with XELJANZ 5 mg twice daily achieved greater improvements in ASAS20 and ASAS40 responses compared to patients treated with placebo at Week 16 (Table 18). Consistent results were observed in the subgroup of patients who had an inadequate response to TNF blockers for both the ASAS20 (primary endpoint) and ASAS40 (secondary endpoint) at Week 16 (Table 18).
| Placebo | XELJANZ 5 mg Twice Daily | Difference from Placebo (95% CI) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Abbreviations: CI = confidence interval; TNFi-IR = tumor necrosis factor inhibitor inadequate response. | |||
All patients (N) | N=136 | N=133 | |
ASAS20 response type I error-controlled. , % | 29 | 56 | 27 (16, 38) p-value <0.0001. |
ASAS40 response, % | 13 | 41 | 28 (18, 38) |
TNFi-IR patients (N) | N=30 | N=29 | |
ASAS20 response, % | 17 | 41 | 25 (2, 47) |
ASAS40 response, % | 7 | 28 | 21 (2, 39) |
The improvements in the components of the ASAS response and other measures of disease activity were greater in the XELJANZ 5 mg twice daily group compared to the placebo group as shown in Table 19.
| Placebo (N=136) | XELJANZ 5 mg Twice Daily (N=133) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline (mean) | Week 16 (LSM change from Baseline) Estimates are generated based on a mixed model for repeated measures using both on-treatment and off-treatment data. | Baseline (mean) | Week 16 (LSM change from Baseline) | Difference from Placebo (95% CI) | |
| LSM = least squares mean. | |||||
ASAS Components | |||||
| 7.0 | -1.0 | 6.9 | -2.5 | -1.5 (-2.00, -0.97) p < 0.0001. |
| 6.9 | -1.1 | 6.9 | -2.6 | -1.5 (-2.00, -1.03) |
| 5.9 | -0.8 | 5.8 | -2.0 | -1.2 (-1.64, -0.79) |
| 6.8 | -1.1 | 6.6 | -2.8 | -1.7 (-2.13, -1.18) |
BASDAI Score BASDAI total score. | 6.5 | -1.2 | 6.4 | -2.6 | -1.4 (-1.86, -0.98) |
BASMI Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Metrology Index. , | 4.4 | -0.1 | 4.5 | -0.6 | -0.5 (-0.66, -0.36) |
hsCRP High sensitivity C-reactive protein. , (mg/dL) | 1.8 | -0.1 | 1.6 | -1.1 | -0.9 (-1.17, -0.69) |
The percentage of patients with active AS who achieved ASAS20 response by visit is shown in Figure 6.
Figure 6: Percentage of ASAS20 Responders Over Time Up to Week 16 in Patients with Active AS in Study AS-I

SE = standard error. Patients with missing data were treated as non-responders.
Other Health-Related Outcomes
Patients treated with XELJANZ 5 mg twice daily achieved greater improvements from baseline in Ankylosing Spondylitis Quality of Life (ASQoL) (-4.0 vs -2.0) compared to patients treated with placebo at Week 16.
Clinical Studies in Polyarticular Course Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis
The efficacy of XELJANZ (tablets and oral solution) for pcJIA was assessed in Study pcJIA-I (NCT02592434). This was a 44-week, two-part study (that consisted of an 18-week, open-label, run-in phase, followed by a 26-week double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomized withdrawal phase) in pediatric patients 2 years to 17 years of age with active rheumatoid factor (RF) negative polyarthritis, RF positive polyarthritis, extended oligoarthritis, and systemic JIA without systemic manifestations who had an inadequate response or intolerance to at least one DMARD which could have included MTX or biologic agents. This study also included patients ages 2 years to 17 years of age with active juvenile psoriatic arthritis (jPsA) and enthesitis-related arthritis (ERA) who had an inadequate response to NSAIDs. Although the clinical studies included some patients who are TNF blocker-naïve, XELJANZ is not approved for use in TNF blocker-naïve patients [see Indications and Usage (1.4) ] .
Patients received XELJANZ (dosed at 5 mg twice daily or body weight-based equivalent twice daily) for 18 weeks (run-in phase) followed by randomization to either XELJANZ (dosed at 5 mg twice daily or body weight-based equivalent twice daily) or placebo for 26 weeks (double-blind phase). Only patients who achieved at least a JIA ACR30 response at the end of the run-in phase were randomized (1:1) to the double-blind phase. Treatment with a stable dose of MTX was permitted but was not required during the study. Concurrent use of biologics or DMARDs other than MTX was not permitted in the study.
Baseline Disease Characteristics
A total of 225 pediatric patients with JIA (56 male and 169 female) with active polyarthritis were enrolled in the run-in phase including RF negative (104), RF positive (39), extended oligoarthritis (28), systemic JIA without systemic manifestations (13), jPsA (20), and ERA (21). Patients had a mean (SD) disease duration of 3.8 ± 3.5 years, and a mean (SD) number of active joints of 12.2 ± 8.1.
Efficacy Results
Of the 225 patients, 173 (77%) patients achieved JIA ACR30 response at Week 18 and were randomized into the double-blind phase to either XELJANZ (n=88) or placebo (n=85). At the conclusion of the 18-week, open-label, run-in phase, pediatric ACR 30/50/70 responses were 77%, 70%, and 49%, respectively.
In both the run-in and double-blind phases, approximately one-third of the patients were taking concomitant oral corticosteroids, and approximately two-thirds were taking concomitant MTX.
The primary endpoint was the occurrence of disease flare at Week 44 relative to the double-blind phase baseline at Week 18. Disease flare was defined (according to Pediatric Rheumatology Collaborative Study Group (PRCSG)/Pediatric Rheumatology International Trials Organization (PRINTO) Disease Flare criteria) as worsening of ≥30% in 3 or more of the 6 JIA core response variables with no more than 1 of the remaining JIA core response variables improving by ≥30%.
XELJANZ-treated patients experienced significantly fewer disease flares at Week 44 compared to placebo-treated patients (31% [27/88] vs. 55% [47/85]; difference in proportions -25% [95% CI: -39%, -10%]; p=0.0007). The occurrence of disease flare by visit in Study pcJIA-I is shown in Figure 7.
| BID = twice daily; SE = standard error; N = total number of patients. |
| The 26-week double-blind phase is from Week 18 through Week 44 on and after randomization day. |
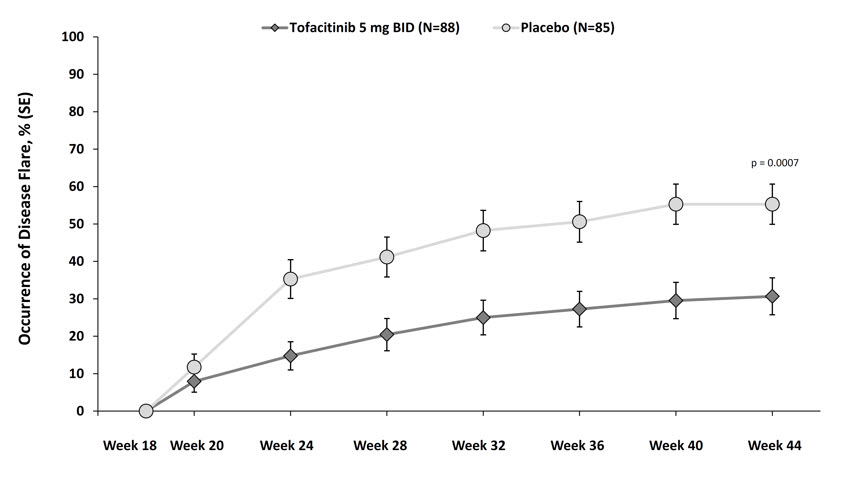 |
Clinical Studies in Ulcerative Colitis
The efficacy of XELJANZ tablets (referred to as “XELJANZ” in this subsection of labeling) was evaluated in two 12-week induction studies (UC-I and UC-II), a 52-week maintenance study (UC-III), and a long-term extension study (UC-IV).
Induction Trials (Study UC-I [NCT01465763] and Study UC-II [NCT01458951])
In two identical induction trials (UC-I and UC-II), 1139 adult patients were randomized (598 and 541 patients, respectively) to XELJANZ 10 mg twice daily or placebo with a 4:1 treatment allocation ratio. These trials included adult patients with moderately to severely active UC (total Mayo score of 6 to 12, with an endoscopy subscore of at least 2, and rectal bleeding subscore of at least 1) and who had failed or were intolerant to at least 1 of the following treatments: oral or intravenous corticosteroids, azathioprine, 6-MP or TNF blocker. XELJANZ and XELJANZ XR are indicated only for use in patients who have had inadequate response or intolerance to one or more TNF blockers [see Indications and Usage (1.5) ] .
The disease activity was assessed by Mayo scoring index (0 to 12) which consists of four subscores (0 to 3 for each subscore): stool frequency, rectal bleeding, findings on endoscopy, and physician global assessment. An endoscopy subscore of 2 was defined by marked erythema, absent vascular pattern, any friability, and erosions; an endoscopy subscore of 3 was defined by spontaneous bleeding and ulceration.
Patients were permitted to use stable doses of oral aminosalicylates and corticosteroids (prednisone daily dose up to 25 mg equivalent). Concomitant immunosuppressants (oral immunomodulators or biologic therapies) were not permitted for UC patients during these studies.
A total of 52%, 73% and 72% of patients had previously failed or were intolerant to TNF blockers (51% in Study UC-1 and 52% in Study UC-II), corticosteroids (75% in Study UC-I and 71% in Study UC-II), and/or immunosuppressants (74% in Study UC-I and 70% in Study UC-II), respectively.
Oral corticosteroids were received as concomitant treatment for UC by 47% of patients (45% in Study UC-I and 48% in Study UC-II) and 71% received concomitant aminosalicylates as treatment for UC (71% in Study UC-I, and 72% in Study UC-II). The baseline clinical characteristics were generally similar between the XELJANZ-treated patients and placebo-treated patients.
The primary endpoint of Study UC-I and Study UC-II was the proportion of patients in remission at Week 8, and the key secondary endpoint was the proportion of patients with improvement of endoscopic appearance of the mucosa at Week 8.
The efficacy results of Study UC-I and Study UC-II based on the centrally read endoscopy results are shown in Table 20.
| CI = Confidence interval; N = number of patients in the analysis set; TNF = tumor necrosis factor | |||
Study UC‑I | |||
Endpoint | Placebo | XELJANZ 10 mg Twice Daily | Treatment Difference versus Placebo (95% CI) |
Remission at Week 8 Remission was defined as clinical remission (a Mayo score ≤2 with no individual subscore >1) and rectal bleeding subscore of 0. | |||
Total Population | N=122 8% | N=476 18% | 10% p-value <0.01. (4.3, 16.3) |
With Prior TNF Blocker Failure Prior TNF blocker failure was defined in this program as inadequate response, loss of response, or intolerance to TNF blocker therapy. | N=64 2% | N=243 11% | |
Without Prior TNF Blocker Failure Patients in this group had failed one or more conventional therapies (corticosteroid, azathioprine, 6 mercaptopurine) but did not have history of prior failure of TNF blocker therapy. , XELJANZ and XELJANZ XR are indicated only for use in patients who have had inadequate response or intolerance to one or more TNF blockers [see Indications and Usage (1.5) ] . | N=58 16% | N=233 26% | |
Improvement of Endoscopic Appearance of the Mucosa at Week 8 Improvement of endoscopic appearance of the mucosa was defined as Mayo endoscopy subscore of 0 (normal or inactive disease) or 1 (erythema, decreased vascular pattern). | |||
Total Population | N=122 16% | N=476 31% | 16% p-value <0.001. (8.1, 23.4) |
With Prior TNF Blocker Failure | N=64 6% | N=243 23% | |
Without Prior TNF Blocker Failure , | N=58 26% | N=233 40% | |
Study UC-II | |||
Endpoint | Placebo | XELJANZ 10 mg Twice Daily | Treatment Difference (95% CI) |
Remission at Week 8 | |||
Total Population | N=112 4% | N=429 17% | 13% (8.1, 17.9) |
With Prior TNF Blocker Failure | N=60 0% | N=222 12% | |
Without Prior TNF Blocker Failure , | N=52 8% | N=207 22% | |
Improvement of Endoscopic Appearance of the Mucosa at Week 8 | |||
Total Population | N=112 12% | N=429 28% | 17% (9.5, 24.1) |
With Prior TNF Blocker Failure | N=60 7% | N=222 22% | |
Without Prior TNF Blocker Failure , | N=52 17% | N=207 36% | |
Clinical Response at Week 8
Clinical response was defined as a decrease from baseline in Mayo score of ≥3 points and ≥30%, with an accompanying decrease in the subscore for rectal bleeding of ≥1 point or absolute subscore for rectal bleeding of 0 or 1.
Clinical response was observed in 60% of patients treated with XELJANZ 10 mg twice daily compared to 33% of patients treated with placebo in Study UC-I and 55% compared to 29% in Study UC-II.
Normalization of the Endoscopic Appearance of the Mucosa at Week 8
Normalization of endoscopic appearance of the mucosa was defined as a Mayo endoscopic subscore of 0 and was observed in 7% of patients treated with XELJANZ 10 mg twice daily compared to 2% of treated with placebo in both Studies UC-I and UC-II.
Rectal Bleeding and Stool Frequency
Decreases in rectal bleeding and stool frequency subscores were observed as early as Week 2 in patients treated with XELJANZ.
Maintenance Trial (Study UC-III [NCT01458574])
A total of 593 adult patients who completed the induction trials (UC-I or UC-II) and achieved clinical response were re-randomized with 1:1:1 treatment allocation ratio to XELJANZ 5 mg twice daily, XELJANZ 10 mg twice daily, or placebo for 52 weeks in Study UC-III. XELJANZ 5 mg twice daily is the recommended dosage for maintenance therapy; limit use of XELJANZ 10 mg twice daily beyond induction to those with loss of response and should be used for the shortest duration [see Dosage and Administration (2.5) ]. As in the induction trials, patients were permitted to use stable doses of oral aminosalicylates; however, corticosteroid tapering was required upon entrance into this study for patients who were receiving corticosteroids at baseline. Concomitant immunosuppressants (oral immunomodulators or biologic therapies) were not permitted.
At baseline of Study UC-III:
- 179 (30%) patients were in remission
- 289 (49%) patients were receiving oral corticosteroids
- 265 (45%), 445 (75%), and 413 (70%) patients had previously failed or were intolerant to TNF blocker therapy, corticosteroids, and immunosuppressants, respectively. XELJANZ and XELJANZ XR are indicated only for use in patients who have had inadequate response or intolerance to one or more TNF blockers [see Indications and Usage (1.5) ] .
In Study UC-III, the primary endpoint was the proportion of patients in remission at Week 52. There were two key secondary endpoints: the proportion of patients with improvement of endoscopic appearance at Week 52, and the proportion of patients with sustained corticosteroid-free remission at both Week 24 and Week 52 among patients in remission at baseline of Study UC-III.
The efficacy results of Study UC-III based on the centrally read endoscopy results are summarized in Table 21.
| Treatment Difference versus Placebo (95% CI) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Endpoint | Placebo | XELJANZ 5 mg Twice Daily | XELJANZ 10 mg Twice Daily | XELJANZ 5 mg Twice Daily | XELJANZ 10 mg Twice Daily |
| CI = Confidence interval; N = number of patients in the analysis set; TNF = tumor necrosis factor. | |||||
Remission at Week 52 Remission was defined as clinical remission (a Mayo score ≤2 with no individual subscore >1) and rectal bleeding subscore of 0. | |||||
Total Population | N=198 | N=198 | N=197 | 23% p-value <0.0001. (15.3, 31.2) | 30% (21.4, 37.6) |
11% | 34% | 41% | |||
With Prior TNF Blocker Failure Prior TNF blocker failure was defined in this program as inadequate response, loss of response, or intolerance to TNF blocker therapy. | N=89 | N=83 | N=93 | ||
11% | 24% | 37% | |||
Without Prior TNF Blocker Failure Patients in this group had failed one or more conventional therapies (corticosteroid, azathioprine, 6-mercaptopurine) but did not have history of prior failure of TNF blocker therapy. XELJANZ and XELJANZ XR are indicated only for use in patients who have had inadequate response or intolerance to one or more TNF blockers [see Indications and Usage (1.5) ] . | N=109 | N=115 | N=104 | ||
11% | 42% | 44% | |||
Improvement of endoscopic appearance of the mucosa at Week 52 Improvement of endoscopic appearance of the mucosa was defined as Mayo endoscopy subscore of 0 (normal or inactive disease) or 1 (erythema, decreased vascular pattern). | |||||
Total Population | N=198 | N=198 | N=197 | 24% (16.0, 32.5) | 33% (24.2, 41.0) |
13% | 37% | 46% | |||
With Prior TNF Blocker Failure | N=89 | N=83 | N=93 | ||
12% | 30% | 40% | |||
Without Prior TNF Blocker Failure | N=109 | N=115 | N=104 | ||
14% | 43% | 51% | |||
Sustained corticosteroid-free remission at both Week 24 and Week 52 among patients in remission at baseline Sustained corticosteroid-free remission was defined as being in remission and not taking corticosteroids for at least 4 weeks prior to the visit at both Week 24 and Week 52. | |||||
Total Population | N=59 | N=65 | N=55 | 30% (17.4, 43.2) | 42% (27.9, 56.5) |
5% | 35% | 47% | |||
With Prior TNF Blocker Failure | N=21 | N=18 | N=18 | ||
5% | 22% | 39% | |||
Without Prior TNF Blocker Failure | N=38 | N=47 | N=37 | ||
5% | 40% | 51% | |||
Maintenance of Clinical Response
Maintenance of clinical response was defined as the proportion of patients who met the definition of clinical response (defined as a decrease from the induction study (UC-I, UC-II) baseline Mayo score of ≥3 points and ≥30%, with an accompanying decrease in the rectal bleeding subscore of ≥1 point or rectal bleeding subscore of 0 or 1) at both Baseline and Week 52 of Study UC-III.
Maintenance of clinical response was observed in 20% in the placebo group, 52% in the XELJANZ 5 mg twice daily group, and 62% in the XELJANZ 10 mg twice daily group.
Maintenance of Remission (Among Patients in Remission at Baseline)
In the 179 patients who were in remission at baseline of Study UC-III (N = 59 for placebo, N = 65 for XELJANZ 5 mg twice daily, N = 55 for XELJANZ 10 mg twice daily), 10% in the placebo group, 46% in the XELJANZ 5 mg twice daily group and 56% in the XELJANZ 10 mg twice daily group maintained remission at Week 52.
Normalization of the Endoscopic Appearance of the Mucosa
Normalization of endoscopic appearance of the mucosa was defined as a Mayo endoscopic subscore of 0 and was observed at Week 52 in 15% of patients in the XELJANZ 5 mg twice daily group and 17% of patients in the XELJANZ 10 mg twice daily group compared to 4% of placebo patients.
Open-label Extension Study (Study UC-IV [NCT01470612])
In Study UC-IV, 914 patients were treated of which 156 received XELJANZ 5 mg twice daily and 758 received XELJANZ 10 mg twice daily.
Of the 905 patients who were assigned to XELJANZ 10 mg twice daily in the 8-week induction studies (Study UC-I or Study UC-II), 322 patients completed the induction studies but did not achieve clinical response. Of these 322 patients, 291 continued to receive XELJANZ 10 mg twice daily (unblinded) and had available data after an additional 8 weeks in Study UC-IV. After 8 additional weeks (a total of 16 weeks treatment), 148 patients achieved clinical response, and 25 patients achieved remission (based on central endoscopy read). Among those 143 patients who achieved clinical response by 16 weeks and had available data at Week 52, 66 patients achieved remission (based on local endoscopy read) after continued treatment with XELJANZ 10 mg twice daily for 52 weeks.
Safety Study in Adults with Rheumatoid Arthritis (XELJANZ Versus TNF-blocker)
A randomized open-label trial (RA Safety Study 1; NCT02092467) was conducted to evaluate safety with XELJANZ tablets (referred to as “XELJANZ” in this subsection of labeling) at two doses, 5 mg twice daily (N=1455) and 10 mg twice daily (N=1456), versus the TNF-blocker control (N=1451) in RA patients 50 years of age and older with at least one cardiovascular risk factor. The co-primary endpoints were adjudicated MACE (defined as cardiovascular death, non-fatal MI, and non-fatal stroke) and adjudicated malignancy (excluding non-melanoma skin cancer). The study was designed to exclude a prespecified risk margin of 1.8 for the hazard ratio of combined XELJANZ regimens versus the TNF-blocker control for each co-primary endpoint. An independent committee conducted a blinded evaluation of the co-primary endpoints according to predefined criteria (adjudication). The study was event-driven and patients were followed until a sufficient number of primary outcome events accrued. Other endpoints included mortality, serious infections, and thromboembolic events. The median on-study follow-up time was 4 years.
The mean age of the population was 61 years (range: 50 to 88 years). Most patients were female (78%) and Caucasian (77%). Patients had a diagnosis of RA for a mean of 10 years, and a median swollen and tender joint count of 11 and 15 respectively. Cardiovascular risk factors included cigarette smoking (current or past) (48%), hypertension (66%), high density lipoprotein <40 mg/dL (12%), diabetes mellitus (17%), family history of premature coronary heart disease (15%), extra-articular disease associated with RA (37%), and history of coronary artery disease (11%).
The non-inferiority criterion was not met for the primary comparison of the combined XELJANZ dosages to TNF blockers since the upper limit of the 95% CI exceeded the pre-specified non-inferiority criterion of 1.8 (for MACE, the upper limit of the 95% CI was 1.94; for malignancies excluding NMSC, the upper limit of the 95% CI was 2.09).
Table 22 shows the study results for each of the co-primary endpoints, and other endpoints. There was an increased risk of death, MACE, malignancies, serious infections, and thromboembolic events associated with both dosages of XELJANZ.
| Endpoint | TNF Blocker N=1451 PY=5468 | XELJANZ 5 mg Twice Daily N=1455 PY=5490 | XELJANZ 10 mg Twice Daily N=1456 PY=5298 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Note: XELJANZ 10 mg twice daily was discontinued by the Data Monitoring Committee due to safety concerns, and ongoing patients switched from XELJANZ 10 mg to XELJANZ 5 mg. The column “XELJANZ 10 mg Twice Daily” includes all events and follow-up for patients randomized to XELJANZ 10 mg twice daily. A XELJANZ (refers to tablets and oral solution) 10 mg twice daily (or a XELJANZ XR 22 mg once daily) dosage is not recommended for the treatment of RA, PsA, AS, or pcJIA [see Dosage and Administration (2.3) ] . N indicates number of patients; n indicates number of patients with events. IR indicates incidence rate per 100 person-year (PY). NMSC: Non-melanoma Skin Cancer; MACE: Major Adverse Cardiac Events; HR: Hazard Ratio; DVT: Deep Vein Thrombosis; PE: Pulmonary Embolism; VTE: Venous Thromboembolism, first occurrence of a VTE, defined as the composite of adjudicated DVT and adjudicated PE; ATE: Arterial Thromboembolism; TE: Thromboembolism, first occurrence of a TE, defined as the composite of adjudicated VTE and unadjudicated ATE. | |||
MACE, n [IR] | 43 [0.79] | 50 [0.91] | 59 [1.11] |
HR (95% CI) HR (95%) CI for XELJANZ vs. TNF Blocker (Univariate Cox Proportional Hazard Model). | 1.16 (0.77, 1.74) | 1.41 (0.95, 2.10) | |
MI, MI and Stroke include fatal and non-fatal events. n [IR] | 11 [0.20] | 20 [0.36] | 21 [0.39] |
HR (95% CI) | 1.81 (0.87, 3.79) | 1.97 (0.95, 4.09) | |
Stroke,n [IR] | 20 [0.36] | 18 [0.33] | 21 [0.39] |
HR (95% CI) | 0.89 (0.47, 1.69) | 1.08 (0.59, 2.00) | |
Cardiovascular Death, n [IR] | 15 [0.27] | 18 [0.32] | 25 [0.47] |
HR (95% CI) | 1.20 (0.60, 2.37) | 1.71 (0.90, 3.24) | |
Malignancies Excl. NMSC, n [IR] | 42 [0.77] | 62 [1.13] | 60 [1.13] |
HR (95% CI) | 1.47 (1.00, 2.18) | 1.48 (1.00, 2.19) | |
Malignancies Excl. NMSC (among current and past smokers) Data and analyses for Malignancies excluding NMSC for current and ex-smokers are included. There were 720 current and ex-smokers randomized to XELJANZ 5 mg, 704 to XELJANZ 10 mg, and 679 to TNF blockers. | 25 [0.99] | 41 [1.53] | 48 [1.91] |
HR (95% CI) | 1.55 (0.94, 2.55) | 1.94 (1.19, 3.14) | |
All Death | 38 [0.69] | 49 [0.88] | 66 [1.23] |
HR (95% CI) | 1.29 (0.84, 1.96) | 1.79 (1.20, 2.66) | |
Serious Infections | 133 [2.52] | 155 [2.95] | 184 [3.65] |
HR (95% CI) | 1.17 (0.93, 1.47) | 1.44 (1.15, 1.80) | |
DVT | 9 [0.16] | 12 [0.22] | 15 [0.28] |
HR (95% CI) | 1.33 (0.56, 3.15) | 1.72 (0.75, 3.92) | |
PE | 3 [0.05] | 10 [0.18] | 26 [0.49] |
HR (95% CI) | 3.32 (0.91, 12.08) | 8.95 (2.71, 29.56) | |
VTE | 12 [0.22] | 18 [0.33] | 36 [0.68] |
HR (95% CI) | 1.50 (0.72, 3.10) | 3.10 (1.61, 5.96) | |
ATE | 45 [0.83] | 51 [0.93] | 55 [1.04] |
HR (95% CI) | 1.13 (0.76, 1.69) | 1.26 (0.85, 1.87) | |
TE | 56 [1.03] | 67 [1.23] | 86 [1.65] |
HR (95% CI) | 1.19 (0.84, 1.70) | 1.60 (1.14, 2.23) | |
Lymphomas and lung cancers, which are a subset of all malignancies in RA Safety Study 1, were observed at a higher rate in patients treated with XELJANZ 5 mg twice a day and XELJANZ 10 mg twice a day compared to those treated with TNF blockers. Lymphoma was reported for 4 patients who received XELJANZ 5 mg twice a day, 6 patients who received XELJANZ 10 mg twice a day, and 1 patient who received TNF blockers (Incidence Rate [IR] of 0.07, 0.11, and 0.02 per 100 patient-years, respectively). Among current and past smokers, lung cancer was reported for 13 patients who received XELJANZ 5 mg twice a day, 15 patients who received XELJANZ 10 mg twice a day, and 7 patients who received TNF blockers (IR of 0.48, 0.59, and 0.27 per 100 patient-years, respectively).
Given these increased risks, XELJANZ (tablets and oral solution) 10 mg twice daily (or XELJANZ XR (extended-release tablets) 22 mg once daily) dosages are not recommended for the treatment of RA, PsA, AS or pcJIA [see Dosage and Administration (2.3 , 2.4) ] .
HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
How Supplied Information for XELJANZ Tablets and XELJANZ XR
How supplied information for XELJANZ tablets and XELJANZ XR (extended-release tablets) is shown in Table 23.
| Dosage Form, Strength, and Description | Bottle Size (number of tablets) | NDC Number |
|---|---|---|
XELJANZ (tofacitinib) tablets, 5 mg White, round, immediate-release film-coated tablets, debossed with “Pfizer” on one side, and “JKI 5” on the other side | 60 | NDC 0069-1001-01 |
XELJANZ (tofacitinib) tablets, 10 mg Blue, round, immediate-release film-coated tablets, debossed with “Pfizer” on one side, and “JKI 10” on the other side | 60 | NDC 0069-1002-01 |
XELJANZ XR (tofacitinib) extended-release tablets, 11 mg Pink, oval, extended-release film-coated tablets with a drilled hole at one end of the tablet band and “JKI 11” printed on one side of the tablet | 30 | NDC 0069-0501-30 |
XELJANZ XR (tofacitinib) extended-release tablets, 22 mg Beige, oval, extended-release film-coated tablets with a drilled hole at one end of the tablet band and “JKI 22” printed on one side of the tablet | 30 | NDC 0069-0502-30 |
How Supplied Information for XELJANZ Oral Solution
XELJANZ (tofacitinib) oral solution, 1 mg/mL is supplied in bottles (240 mL fill volume) (NDC 0069-1029-02) and is a clear, colorless solution that contains 1 mg of tofacitinib. Each high-density polyethylene (HDPE) bottle contains one press-in bottle adapter and one 5 mL oral dosing syringe with 3.2 mL, 4 mL, and 5 mL gradations. The press-in bottle adapter and oral dosing syringe are not made with natural rubber latex.
Storage and Handling for XELJANZ Tablets/XELJANZ XR
Store XELJANZ tablets and XELJANZ XR at 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F). [See USP Controlled Room Temperature].
Do not repackage.
Storage and Handling for XELJANZ Oral Solution
Store at 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F), excursions permitted between 15°C and 30°C (between 59°F and 86°F). [See USP Controlled Room Temperature].
Store in the original bottle and carton to protect from light.
Use contents of bottle within 60 days of opening.
Discard unused oral solution after 60 days.
INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE
XELJANZ ® (ZEL' JANS') (tofacitinib) oral solution
Read this Instructions for Use before you start taking XELJANZ oral solution and each time you get a refill. There may be new information. This leaflet does not take the place of talking to your healthcare provider about your medical condition or treatment.
Important information about measuring XELJANZ oral solution:
Always use the oral dosing syringe that comes with XELJANZ oral solution to measure and take your prescribed dose. Ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist to show you how to measure your prescribed dose if you are not sure.
How should I store XELJANZ?
- Store XELJANZ oral solution at room temperature between 68°F to 77°F (20°C to 25°C).
- Always store XELJANZ oral solution in the original bottle and carton to protect from light.
Keep XELJANZ and all medicines out of the reach of children.
Use XELJANZ oral solution within 60 days of opening the bottle. Throw away (discard) remaining XELJANZ oral solution after 60 days.
To help you remember when to throw away your bottle of XELJANZ oral solution, you can write the date when you first start to use it on the carton and below:
Date of first use ____ / ____ / ____.
Before each use:
Wash your hands with soap and water and place the items from the carton on a clean, flat surface.
Each carton of XELJANZ oral solution contains:
- 1 press-in bottle adapter
- 1 bottle of XELJANZ oral solution
- 1 oral dosing syringe

Step 1. Remove bottle from carton
Open the carton and remove the bottle of XELJANZ oral solution.
Step 2. Open bottle
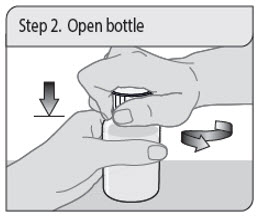
Open the bottle by pushing down on the child-resistant cap and turning it to the left (counter-clockwise) as shown. Remove the seal off the top of the bottle (first time only) .
Do not throw away the child-resistant cap.
Note: The bottle does not need to be shaken before use.
Step 3. Insert press-in bottle adapter (first time only)

Remove the press-in bottle adapter and oral dosing syringe from the plastic overwrap. With the bottle on a flat surface, push the ribbed end of the press-in bottle adapter all the way into the neck of the bottle with your thumbs while holding the bottle firmly.
Note: Do not remove the press-in bottle adapter from the bottle after it is inserted.
Step 4. Remove air from oral dosing syringe

Push the oral dosing syringe plunger all the way down to the tip of the syringe barrel to remove excess air.
Step 5. Insert the oral dosing syringe
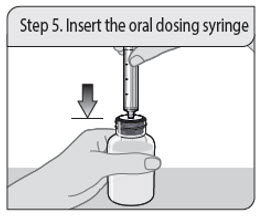
Insert the oral dosing syringe tip into the upright bottle through the opening of the press-in bottle adapter until it is firmly in place.
Step 6. Withdraw dose from bottle
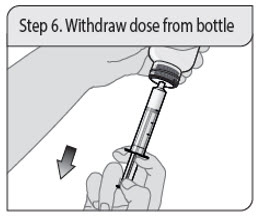
With the oral dosing syringe in place, turn the bottle upside down. Pull down on the plunger until the bottom of the plunger is even with the markings on the oral dosing syringe for your prescribed dose of oral solution.
If you see air bubbles in the oral dosing syringe, fully push the plunger in so that the oral solution flows back into the bottle. Then withdraw your prescribed dose of oral solution.
Step 7. Remove oral dosing syringe
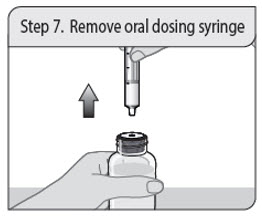
Turn the bottle upright and place the bottle on a flat surface. Remove the oral dosing syringe from the press-in bottle adapter and bottle by pulling straight up on the oral dosing syringe barrel.
Step 8. Check the dose
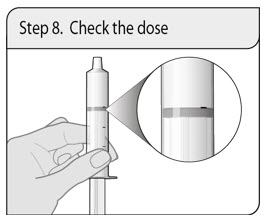
Check that the correct dose was drawn up into the oral dosing syringe.
If the dose is not correct, insert the oral dosing syringe tip firmly into the press-in bottle adapter. Fully push in the plunger so that the oral solution flows back into the bottle. Repeat Step 6 and Step 7.
Step 9. Take the dose of XELJANZ
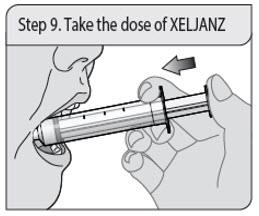
Place the tip of the oral dosing syringe into the inside of the cheek.
Slowly push the plunger all the way down to give all of the medicine in the oral dosing syringe. Make sure there is time to swallow the medicine.
Step 10. Close the bottle
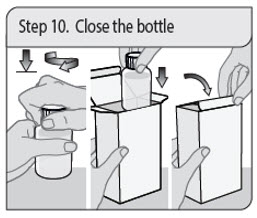
Close the bottle tightly by turning the child-resistant cap to the right (clockwise), leaving the press-in bottle adapter in place.
Place the bottle back into the carton.
Close the carton to protect XELJANZ oral solution from light.
Step 11. Clean oral dosing syringe
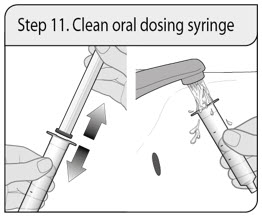
Remove the plunger from the barrel by pulling the plunger and the barrel away from each other.
Rinse both with water after each use.
Allow to air dry. When the barrel and plunger are dry, put the oral dosing syringe back together by inserting the plunger into the barrel.
Store the oral dosing syringe with the XELJANZ oral solution.
Do not throw away the oral dosing syringe.

LAB-1422-3.0
This Instructions for Use has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Approved: October 2025
This Instructions for Use may have been updated. For the most recent Instructions for Use, please visit www.pfizer.com .
Mechanism of Action
Tofacitinib is a Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitor. JAKs are intracellular enzymes which transmit signals arising from cytokine or growth factor-receptor interactions on the cellular membrane to influence cellular processes of hematopoiesis and immune cell function. Within the signaling pathway, JAKs phosphorylate and activate Signal Transducers and Activators of Transcription (STATs) which modulate intracellular activity including gene expression. Tofacitinib modulates the signaling pathway at the point of JAKs, preventing the phosphorylation and activation of STATs. JAK enzymes transmit cytokine signaling through pairing of JAKs (e.g., JAK1/JAK3, JAK1/JAK2, JAK1/TyK2, JAK2/JAK2). Tofacitinib inhibited the in vitro activities of JAK1/JAK2, JAK1/JAK3, and JAK2/JAK2 combinations with IC 50 of 406, 56, and 1377 nM, respectively. However, the relevance of specific JAK combinations to therapeutic effectiveness is not known.