Absorica prior authorization resources
Most recent state uniform prior authorization forms
Dosage & administration
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- ABSORICA is not substitutable with ABSORICA LD because of different bioavailability and recommended dosage. (2.1 , 5.3 )
- Recommended dosage for:
o ABSORICA is 0.5 to 1 mg/kg/day given in two divided doses without regard to meals for 15 to 20 weeks (2.1 )
o ABSORICA LD is 0.4 to 0.8 mg/kg/day given in two divided doses without regard to meals for 15 to 20 weeks (2.1 )
- Adult patients with very severe disease (scarring, trunk involvement) may increase dosage to 2 mg/kg/day of ABSORICA (1.6 mg/kg/day of ABSORICA LD) in divided doses. (2.1 )
- Once daily dosing is not recommended. (2.1 )
- If a dose of ABSORICA/ABSORICA LD is missed, just skip that dose. Do not take two doses of ABSORICA/ABSORICA LD at the same time. (2.1 )
- Perform pregnancy tests prior to prescribing, each month during therapy, end of therapy, and one month after discontinuation. (2.3 , 8.3 )
- Prior to prescribing, perform fasting lipid profile and liver function tests. (2.3 )
Recommended Dosage
ABSORICA is not substitutable with ABSORICA LD [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3) ] . The recommended dosage of:
- ABSORICA is 0.5 to 1 mg/kg/day given in two divided doses with or without meals for 15 to 20 weeks (see Table 1).
- ABSORICA LD is 0.4 to 0.8 mg/kg/day given in two divided doses with or without meals for 15 to 20 weeks (see Table 2).
To decrease the risk of esophageal irritation, instruct patients to swallow the capsules with a full glass of liquid. During treatment, the dosage may be adjusted according to response of the disease and/or adverse reactions, some of which may be dose-related. Adult patients whose disease is very severe with scarring or is primarily manifested on the trunk may require dosage adjustments up to 2 mg/kg/day for ABSORICA (1.6 mg/kg/day for ABSORICA LD) in divided doses, as tolerated.
The safety and effectiveness of once daily dosing with ABSORICA/ABSORICA LD has not been established and is not recommended.
If a dose of ABSORICA/ABSORICA LD is missed, just skip that dose. Do not take two doses of ABSORICA/ ABSORICA LD at the same time.
Body Weight | Total Daily Dosage (mg) 1 | ||
0.5 mg/kg | 1 mg/kg | 2 mg/kg | |
40 kg | 20 | 40 | 80 |
50 kg | 25 | 50 | 100 |
60 kg | 30 | 60 | 120 |
70 kg | 35 | 70 | 140 |
80 kg | 40 | 80 | 160 |
90 kg | 45 | 90 | 180 |
100 kg | 50 | 100 | 200 |
1 Administer in two divided doses with or without meals
Table 2: ABSORICA LD Daily Dosage by Body Weight 1
Body Weight | Total Daily Dosage (mg) 1 | ||
0.4 mg/kg | 0.8 mg/kg | 1.6 mg/kg | |
40 kg | 16 | 32 | 64 |
50 kg | 20 | 40 | 80 |
60 kg | 24 | 48 | 96 |
70 kg | 28 | 56 | 112 |
80 kg | 32 | 64 | 128 |
90 kg | 36 | 72 | 144 |
100 kg | 40 | 80 | 160 |
1 Administer in two divided doses with or without meals
Duration of Use
A normal course of treatment is 15 to 20 weeks. If the total nodule count has been reduced by more than 70% prior to completing 15 to 20 weeks of treatment, may discontinue ABSORICA/ABSORICA LD.
After a period of 2 months or more off therapy, and if warranted by persistent or recurring severe nodular acne, may initiate a second course of ABSORICA/ABSORICA LD in patients who have completed skeletal growth. The use of another course of ABSORICA/ABSORICA LD therapy is not recommended before a two-month waiting period because the patient’s acne may continue to improve after a 15 to 20-week course of therapy. The optimal interval before retreatment has not been defined for patients who have not completed skeletal growth.
Long-term use of ABSORICA/ABSORICA LD, even in low dosages, has not been studied, and is not recommended. The effect of long-term use of ABSORICA/ABSORICA LD on bone loss is unknown [see Warnings and Precautions (5.12) ] .
Laboratory Testing Prior to Administration
The following laboratory testing must be completed prior to ABSORICA/ABSORICA LD use:
- Pregnancy testing: Ensure patient is not pregnant prior to administering ABSORICA/ABSORICA LD [see Contraindications (4) and Use in Specific Populations (8.1 , 8.3) ]
- A fasting lipid profile including triglycerides [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8 , 5.15) ] .
- Liver function tests [see Warnings and Precautions (5.10 , 5.15) ] .

By using PrescriberAI, you agree to the AI Terms of Use.
Absorica prescribing information
WARNING: EMBRYO-FETAL TOXICITY – CONTRAINDICATED IN PREGNANCY
ABSORICA/ABSORICA LD can cause life-threatening birth defects and is contraindicated in pregnancy.
There is an extremely high risk that life-threatening birth defects will result if pregnancy occurs while taking any amount of ABSORICA/ABSORICA LD even for short periods of time. Potentially any fetus exposed during pregnancy can be affected. There are no accurate means of determining prenatally whether an exposed fetus has been affected. If pregnancy occurs, discontinue ABSORICA/ABSORICA LD immediately and refer the patient to an Obstetrician- Gynecologist experienced in reproductive toxicity for further evaluation and counseling [see Contraindications (4) , Warnings and Precautions (5.1) , and Use in Specific Populations (8.1) ].
Because of the risk of embryo-fetal toxicity, ABSORICA and ABSORICA LD are available only through a restricted program under a Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy (REMS) called the iPLEDGE REMS [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) ] .
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
ABSORICA and ABSORICA LD are indicated for the treatment of severe recalcitrant nodular acne in non-pregnant patients 12 years of age and older with multiple inflammatory nodules with a diameter of 5 mm or greater. Because of significant adverse reactions associated with its use, ABSORICA and ABSORICA LD are reserved for patients with severe nodular acne who are unresponsive to conventional therapy, including systemic antibiotics.
Limitations of Use :
If a second course of ABSORICA/ABSORICA LD therapy is needed, it is not recommended before a two-month waiting period because the patient’s acne may continue to improve following a 15 to 20-week course of therapy [see Dosage and Administration (2.2) ].
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- ABSORICA is not substitutable with ABSORICA LD because of different bioavailability and recommended dosage. (2.1 , 5.3 )
- Recommended dosage for:
o ABSORICA is 0.5 to 1 mg/kg/day given in two divided doses without regard to meals for 15 to 20 weeks (2.1 )
o ABSORICA LD is 0.4 to 0.8 mg/kg/day given in two divided doses without regard to meals for 15 to 20 weeks (2.1 )
- Adult patients with very severe disease (scarring, trunk involvement) may increase dosage to 2 mg/kg/day of ABSORICA (1.6 mg/kg/day of ABSORICA LD) in divided doses. (2.1 )
- Once daily dosing is not recommended. (2.1 )
- If a dose of ABSORICA/ABSORICA LD is missed, just skip that dose. Do not take two doses of ABSORICA/ABSORICA LD at the same time. (2.1 )
- Perform pregnancy tests prior to prescribing, each month during therapy, end of therapy, and one month after discontinuation. (2.3 , 8.3 )
- Prior to prescribing, perform fasting lipid profile and liver function tests. (2.3 )
Recommended Dosage
ABSORICA is not substitutable with ABSORICA LD [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3) ] . The recommended dosage of:
- ABSORICA is 0.5 to 1 mg/kg/day given in two divided doses with or without meals for 15 to 20 weeks (see Table 1).
- ABSORICA LD is 0.4 to 0.8 mg/kg/day given in two divided doses with or without meals for 15 to 20 weeks (see Table 2).
To decrease the risk of esophageal irritation, instruct patients to swallow the capsules with a full glass of liquid. During treatment, the dosage may be adjusted according to response of the disease and/or adverse reactions, some of which may be dose-related. Adult patients whose disease is very severe with scarring or is primarily manifested on the trunk may require dosage adjustments up to 2 mg/kg/day for ABSORICA (1.6 mg/kg/day for ABSORICA LD) in divided doses, as tolerated.
The safety and effectiveness of once daily dosing with ABSORICA/ABSORICA LD has not been established and is not recommended.
If a dose of ABSORICA/ABSORICA LD is missed, just skip that dose. Do not take two doses of ABSORICA/ ABSORICA LD at the same time.
Body Weight | Total Daily Dosage (mg) 1 | ||
0.5 mg/kg | 1 mg/kg | 2 mg/kg | |
40 kg | 20 | 40 | 80 |
50 kg | 25 | 50 | 100 |
60 kg | 30 | 60 | 120 |
70 kg | 35 | 70 | 140 |
80 kg | 40 | 80 | 160 |
90 kg | 45 | 90 | 180 |
100 kg | 50 | 100 | 200 |
1 Administer in two divided doses with or without meals
Table 2: ABSORICA LD Daily Dosage by Body Weight 1
Body Weight | Total Daily Dosage (mg) 1 | ||
0.4 mg/kg | 0.8 mg/kg | 1.6 mg/kg | |
40 kg | 16 | 32 | 64 |
50 kg | 20 | 40 | 80 |
60 kg | 24 | 48 | 96 |
70 kg | 28 | 56 | 112 |
80 kg | 32 | 64 | 128 |
90 kg | 36 | 72 | 144 |
100 kg | 40 | 80 | 160 |
1 Administer in two divided doses with or without meals
Duration of Use
A normal course of treatment is 15 to 20 weeks. If the total nodule count has been reduced by more than 70% prior to completing 15 to 20 weeks of treatment, may discontinue ABSORICA/ABSORICA LD.
After a period of 2 months or more off therapy, and if warranted by persistent or recurring severe nodular acne, may initiate a second course of ABSORICA/ABSORICA LD in patients who have completed skeletal growth. The use of another course of ABSORICA/ABSORICA LD therapy is not recommended before a two-month waiting period because the patient’s acne may continue to improve after a 15 to 20-week course of therapy. The optimal interval before retreatment has not been defined for patients who have not completed skeletal growth.
Long-term use of ABSORICA/ABSORICA LD, even in low dosages, has not been studied, and is not recommended. The effect of long-term use of ABSORICA/ABSORICA LD on bone loss is unknown [see Warnings and Precautions (5.12) ] .
Laboratory Testing Prior to Administration
The following laboratory testing must be completed prior to ABSORICA/ABSORICA LD use:
- Pregnancy testing: Ensure patient is not pregnant prior to administering ABSORICA/ABSORICA LD [see Contraindications (4) and Use in Specific Populations (8.1 , 8.3) ]
- A fasting lipid profile including triglycerides [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8 , 5.15) ] .
- Liver function tests [see Warnings and Precautions (5.10 , 5.15) ] .
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
ABSORICA and ABSORICA LD have different dosage regimens [see Dosage and Administration (2.1) ] . Although ABSORICA and ABSORICA LD have a 20 mg strength, these strengths have different bioavailability and are not substitutable.
ABSORICA is available in 10 mg, 20 mg, 25 mg, 30 mg, 35 mg and 40 mg capsules.
- 10 mg: Dark yellow, opaque, capsule imprinted with black ink “ G 240 ” on cap and “ 10 ” on the body
- 20 mg: Red, opaque, capsule imprinted with black ink “ G 241 ” on cap and “ 20 ” on the body
- 25 mg: Green, opaque, capsule imprinted with white ink “ G 342 ” on cap and “ 25 ” on the body
- 30 mg: Brown, opaque, capsule imprinted with white ink “ G 242 ” on cap and “ 30 ” on the body
- 35 mg: Dark blue, opaque, capsule imprinted with white ink “ G 343 ” on cap and “ 35 ” on the body
- 40 mg: Brown and red, capsule imprinted with white ink “ G 325 ” on cap and “ 40 ” on the body
ABSORICA LD is available in 8 mg, 16 mg, 20 mg, 24 mg, 28 mg and 32 mg opaque-printed, hard-gelatin capsules.
- 8 mg: A size 3, light green with a colorless band (the cap is printed in white with “RL29” and the body is printed in white with “ RL29 ”).
- 16 mg : A size 2, dark blue with a colorless band (the cap is printed in white with “RL30” and the body is printed in white with “ RL30 ”).
- 20 mg : A size 1, dark pink with a colorless band (the cap is printed in black with “RL33”and the body is printed in black with “ RL33 ”).
- 24 mg : A size 1, yellow with a colorless band (the cap is printed in white with “RL31” and the body is printed in white with “ RL31 ”).
- 28 mg : A size 0, light blue, with a colorless band (the cap is printed in black with “RL34” and the body is printed in black with “ RL34 ”).
- 32 mg : A size 0, caramel with a colorless band (the cap is printed in white with “RL32” and the body is printed in white with “ RL32 ”).
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
Lactation: Breastfeeding not recommended (8.2) .
Pregnancy
Pregnancy Exposure Registry
There is a pregnancy exposure registry that monitors pregnancy outcomes in patients exposed to isotretinoin during pregnancy. Report any suspected fetal exposure during or 1 month after ABSORICA/ABSORICA LD therapy immediately to the FDA via the MedWatch telephone number 1-800-FDA-1088 and also to the iPLEDGE pregnancy registry at 1-866-495-0654 or via the internet (www.ipledgeprogram.com ).
Risk Summary
ABSORICA/ABSORICA LD are contraindicated during pregnancy because isotretinoin can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant patient. There is an increased risk of major congenital malformations, spontaneous abortions, and premature births following isotretinoin exposure during pregnancy in humans. If ABSORICA/ABSORICA LD is used during pregnancy, or if the patient becomes pregnant while taking ABSORICA/ABSORICA LD, the patient should be apprised of the potential hazard to a fetus. If pregnancy occurs during treatment of a patient who is taking ABSORICA/ABSORICA LD, ABSORICA/ABSORICA LD must be discontinued immediately and the patient should be referred to an Obstetrician-Gynecologist experienced in reproductive toxicity for further evaluation and counseling.
Data
Human Data
Major congenital malformations that have been documented following isotretinoin exposure include malformations of the face, eyes, ears, skull, central nervous system, cardiovascular system, and thymus and parathyroid glands. External malformations include: skull; ear (including anotia, micropinna, small or absent external auditory canals); eye (including microphthalmia); facial dysmorphia and cleft palate. Internal abnormalities include: CNS (including cerebral and cerebellar malformations, hydrocephalus, microcephaly, cranial nerve deficit); cardiovascular; thymus gland; parathyroid hormone deficiency. In some cases, death has occurred as a result of the malformations.
Cases of IQ scores less than 85 with or without other abnormalities have been reported in children exposed in utero to isotretinoin. An increased risk of spontaneous abortion and premature births have been reported with isotretinoin exposure during pregnancy.
Lactation
Risk Summary
There are no data on the presence of isotretinoin in either animal or human milk, the effects on the breastfed infant, or the effects on milk production. Because of the potential for serious adverse reactions in nursing infants from isotretinoin, advise patients that breastfeeding is not recommended during treatment with ABSORICA/ABSORICA LD, and for at least 8 days after the last dose of ABSORICA/ABSORICA LD.
Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
All patients who can become pregnant must comply with the iPLEDGE program requirements [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) ].
Pregnancy Testing
ABSORICA/ABSORICA LD must only be prescribed to patients who are known not to be pregnant as confirmed by a negative CLIA-certified laboratory conducted pregnancy test. Patients who can become pregnant must have had two negative urine or serum pregnancy tests with a sensitivity of at least 25 mIU/mL before receiving the initial ABSORICA/ABSORICA LD prescription (the interval between the two tests must be at least 19 days).
- The first test (a screening test) is obtained by the prescriber when the decision is made to prescribe ABSORICA/ABSORICA LD therapy.
- The second pregnancy test (a confirmation test) is performed after the patient has used 2 forms of contraception for 1 month and during the first 5 days of the menstrual period immediately preceding the beginning of ABSORICA/ABSORICA LD therapy (for patients with regular menstrual cycles) or immediately preceding the beginning of ABSORICA/ABSORICA LD therapy (for patients with amenorrhea, irregular cycles, or using a contraceptive method that precludes withdrawal bleeding).
A pregnancy test must be repeated each month, in a CLIA-certified laboratory prior to the patient receiving each prescription. A pregnancy test must also be completed at the end of the entire course of ABSORICA/ABSORICA LD therapy and 1 month after the discontinuation of ABSORICA/ABSORICA LD.
Contraception
Patients who can become pregnant must use 2 forms of contraception simultaneously, at least 1 of which must be a primary form, for at least 1 month prior to initiation of ABSORICA/ABSORICA LD therapy, during ABSORICA/ABSORICA LD therapy, and for 1 month after discontinuing ABSORICA/ABSORICA LD therapy. However, 2 forms of contraception is not required if the patient commits to continuous abstinence from not having any sexual contact with a partner which may result in pregnancy, has undergone a hysterectomy or bilateral oophorectomy, or has been medically confirmed to be post-menopausal. Micro-dosed progesterone preparations (“minipills” that do not contain an estrogen) are an inadequate method of contraception during ABSORICA/ABSORICA LD therapy.
Primary forms | Secondary forms |
•Tubal sterilization | Barrier: |
•Male vasectomy | •male latex condom with or without spermicide |
•Intrauterine device | •diaphragm with spermicide |
•Hormonal (combination oral contraceptives, vaginal systems, vaginal inserts, transdermal systems, injections, or implants) | •cervical cap with spermicide |
Other: •Vaginal sponge (contains spermicide) |
Any birth control method can fail. There have been reports of pregnancy from patients who have used combination oral contraceptives, as well as contraceptive vaginal systems, vaginal inserts, transdermal systems, and injections; these pregnancies occurred while taking isotretinoin. These reports are more frequent for patients who use only a single method of contraception. Therefore, it is critically important that patients who can become pregnant use 2 methods of contraception simultaneously.
A clinical drug interaction study did not show any clinically significant interaction between isotretinoin and norethindrone and ethinyl estradiol; however, it is not known if there is an interaction between isotretinoin with other progestins [see
Drug Interactions (7.5) ]. Prescribers are advised to consult the prescribing information of any medication administered concomitantly with hormonal contraceptives, since some medications may decrease the effectiveness of these birth control products.
Patients who can become pregnant should be prospectively cautioned not to self-medicate with the herbal supplement St. John’s Wort because of a possible interaction with hormonal contraceptives based on reports of breakthrough bleeding on oral contraceptives shortly after starting St. John’s Wort. Pregnancies have been reported by users of combined hormonal contraceptives who also used some form of St. John’s Wort.
If the patient has unprotected sexual contact with a partner that could result in pregnancy at any time 1 month before, during, or 1 month after therapy, the patient must:
- Stop taking ABSORICA/ABSORICA LD immediately, if on therapy
- Have a pregnancy test at least 19 days after the last act of unprotected sexual contact with a partner that could result in pregnancy
- Start using 2 forms of contraception simultaneously again for 1 month before resuming ABSORICA/ABSORICA LD therapy
- Have a second pregnancy test after using 2 forms of contraception for 1 month.
Infertility
In a trial of female acne patients (n = 79) receiving another isotretinoin capsule product, the mean total ovarian volume, the total antral follicle count and mean anti-Mullerian hormone decreased at the end of the treatment (sixth month). However, the values returned to normal at the 18 th month (12 months after the end of treatment). There were no statistically significant changes in terms of follicle-stimulating hormone and luteinizing hormone, both at the end of the treatment and 12 months after the end of treatment. Although the results suggest that possible deteriorative effects of isotretinoin on ovarian reserve may be reversible, the study has important methodological limitations, including a small sample size, lack of a control group, and lack of generalizability.
Sperm Study
In trials of 66 men, 30 of whom were patients with nodular acne under treatment with oral isotretinoin, no significant changes were noted in the count or motility of spermatozoa in the ejaculate. In a study of 50 men (ages 17 to 32 years) receiving isotretinoin therapy for nodular acne, no significant effects were seen on ejaculate volume, sperm count, total sperm motility, morphology or seminal plasma fructose.
Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of ABSORICA/ABSORICA LD for the treatment of severe recalcitrant nodular acne have been established in pediatric subjects ages 12 to 17 years. Use of ABSORICA/ABSORICA LD in this age group for this indication is supported by evidence from a clinical trial (Study 1) that compared the use ABSORICA to another isotretinoin capsule product in 397 pediatric subjects (12 to 17 years) [see Clinical Studies (14) ] and pharmacokinetic data in pediatric subjects [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ] .
The safety and effectiveness of ABSORICA/ABSORICA LD in pediatric patients less than 12 years of age have not been established.
Adverse Reactions in Pediatric Subjects
In trials with isotretinoin capsules, adverse reactions reported in pediatric subjects aged 12 to 17 years old were similar to those described in adults except for the increased incidence of back pain and arthralgia (both of which were sometimes severe) and myalgia in pediatric subjects. In a trial of pediatric subjects aged 12 to 17 years old treated with isotretinoin capsules, approximately 29% (104/358) developed back pain. Back pain was severe in 14% (14/104) of the cases and occurred at a higher frequency in female subjects than male subjects. Arthralgias were experienced in 22% (79/358) of pediatric subjects including severe arthralgias in 8% (6/79) of subjects. Appropriate evaluation of the musculoskeletal system should be done in adolescents who present with these symptoms during or after a course of ABSORICA/ABSORICA LD. Consider discontinuing ABSORICA/ABSORICA LD if any significant abnormality is found.
Effects on Bone Mineral Density in Pediatric Subjects
The effect on bone mineral density (BMD) of a 20-week course of therapy with ABSORICA or another isotretinoin capsule product was evaluated in a double-blind, randomized clinical trial involving 396 adolescents with severe recalcitrant nodular acne (mean age 15.4 years old, range 12 to 17 years old, 80% males). Given that there were no statistically significant differences between the two isotretinoin capsule groups following 20 weeks of treatment, the results are presented for the pooled treatment groups. The mean changes in BMD from baseline for the overall trial population were 1.8% for lumbar spine, -0.1% for total hip and -0.3% for femoral neck. Mean BMD Z-scores declined from baseline at each of these sites (-0.053, -0.109 and -0.104 respectively). Out of 306 adolescents, 27 (9%) had clinically significant BMD declines defined as ≥4% lumbar spine or total hip, or ≥5% femoral neck, including 2 subjects for lumbar spine, 17 for total hip and 20 for femoral neck. Repeat DXA scans within 2 to 3 months after the post treatment scan showed no recovery of BMD. Long-term follow-up at 4 to 11 months showed that 3 out of 7 subjects had total hip and femoral neck BMD below pre-treatment baseline, and 2 others did not show the increase in BMD above baseline expected in this adolescent population. The significance of these changes in regard to long-term bone health and future fracture risk is unknown [see Warnings and Precautions (5.12) ] .
In an open-label clinical trial (N=217) of a single course of therapy with isotretinoin capsules for adolescents with severe recalcitrant nodular acne, BMD at several skeletal sites were not significantly decreased (lumbar spine change >-4% and total hip change >-5%) or were increased in the majority of subjects. One patient had a decrease in lumbar spine BMD >4% based on unadjusted data. Sixteen (8%) subjects had decreases in lumbar spine BMD >4%, and all the other subjects (92%) did not have significant decreases or had increases (adjusted for body mass index). Nine subjects (5%) had a decrease in total hip BMD >5% based on unadjusted data. Twenty-one (11%) subjects had decreases in total hip BMD >5%, and all the other subjects (89%) did not have significant decreases or had increases (adjusted for body mass index). Follow-up trials performed in 8 of the subjects with decreased BMD for up to 11 months thereafter demonstrated increasing BMD in 5 subjects at the lumbar spine, while the other 3 subjects had lumbar spine BMD measurements below baseline values. Total hip BMD remained below baseline (range −1.6% to −7.6%) in 5 of 8 subjects (63%).
In a separate open-label extension trial of 10 subjects including those ages 13 to 17 years, who started a second course of isotretinoin capsules 4 months after the first course, two subjects showed a decrease in mean lumbar spine BMD up to 3.3%.
Epiphyseal Closure
There are reports of premature epiphyseal closure in acne patients who used isotretinoin at recommended doses. The effect of multiple courses of isotretinoin on epiphyseal closure is unknown. In a 20-week clinical trial that included 289 adolescents who had hand radiographs taken to assess bone age, a total of 9 subjects had bone age changes that were clinically significant and for which an isotretinoin-related effect cannot be excluded [see Warnings and Precautions (5.12) ] .
Geriatric Use
Clinical studies of ABSORICA/ABSORICA LD did not include sufficient numbers of geriatric subjects (subjects aged 65 years of age and older) to determine whether they respond differently from younger adults. Although reported clinical experience has not identified differences in responses between geriatric and younger adults, effects of aging may increase some risks associated with ABSORICA/ABSORICA LD therapy.
CONTRAINDICATIONS
Pregnancy
Hypersensitivity
ABSORICA/ABSORICA LD is contraindicated in patients with hypersensitivity to isotretinoin (or Vitamin A, given the chemical similarity to isotretinoin) or to any of its components (anaphylaxis and other allergic reactions have occurred) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.14) ] .
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- Psychiatric Disorders (depression, psychosis, suicidal thoughts and behavior, and aggressive and/or violent behaviors): Prior to and during therapy assess for these conditions; stop if these conditions occur on therapy (5.4)
- Intracranial Hypertension (Pseudotumor Cerebri) : Avoid use with concomitant tetracyclines (5.5)
- Serious Skin Reactions : Monitor for Stevens-Johnson syndrome (SJS), toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN), and other serious skin reactions (5.6)
- Acute Pancreatitis : If occurs, discontinue treatment (5.7)
- Lipid Abnormalities (hypertriglyceridemia, low HDL, and elevation of cholesterol): Monitor lipid levels at regular intervals; stop if hypertriglyceridemia cannot be controlled (5.8)
- Hearing Impairment : Discontinue and refer to specialized care (5.9)
- Hepatotoxicity : Monitor liver function tests prior to and during therapy (5.10 , 5.15)
- Inflammatory Bowel Disease : Discontinue for abdominal pain, rectal bleeding, or severe diarrhea (5.11)
- Musculoskeletal Abnormalities : Arthralgias, back pain, decreases in bone mineral density and premature epiphyseal closure (5.12)
- Ocular Abnormalities e.g., corneal opacities, decreased night vision: If visual symptoms occur, discontinue and refer for an ophthalmological exam (5.13)
Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
ABSORICA/ABSORICA LD is contraindicated in pregnancy [see Contraindications (4.1) ] . Based on human data, ABSORICA/ABSORICA LD can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant patient. There is an extremely high risk that life-threatening birth defects will result if pregnancy occurs while taking any amount of ABSORICA/ABSORICA LD even for short periods of time. Potentially any fetus exposed during pregnancy can be affected. There are no accurate means of determining prenatally whether an exposed fetus has been affected. Major congenital malformations, spontaneous abortions, and premature births have been documented following exposure to isotretinoin during pregnancy [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1) ] .
If a pregnancy occurs during ABSORICA/ABSORICA LD treatment, discontinue ABSORICA/ABSORICA LD immediately and refer the patient to an obstetrician/gynecologist experienced in reproductive toxicity for further evaluation and counseling. Any suspected fetal exposure during or 1 month after ABSORICA/ABSORICA LD therapy must be reported immediately to the FDA via the MedWatch telephone number 1-800-FDA-1088, and also to the iPLEDGE pregnancy registry at 1-866-495-0654 or via the internet (www.ipledgeprogram.com).
Patients must be informed not to donate blood during ABSORICA/ABSORICA LD therapy and for 1 month following discontinuation because the blood might be given to a pregnant patient whose fetus must not be exposed to isotretinoin.
ABSORICA/ABSORICA LD is available only through a restricted program under a REMS [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) ].
iPLEDGE Program
ABSORICA/ABSORICA LD are available only through a restricted program under a REMS called the iPLEDGE REMS because of the risk of embryo-fetal toxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) ] . Notable requirements of the iPLEDGE REMS include the following:
- Prescribers must be certified with the program and comply with the following requirements: Determine reproductive status of all patients prior to initiating treatment
- Provide contraception counseling to patients who can get pregnant prior to and during treatment, or refer patients who can get pregnant to an expert for such counseling
- Provide scheduled pregnancy testing, and verify and document the negative pregnancy test result prior to writing each prescription, for no more than a 30-day supply
- Patients who can become pregnant must be enrolled by signing an informed consent form and must comply with the following requirements
- Comply with the pregnancy testing and contraception requirements [see Use in Specific Populations (8.3)]
- Demonstrate comprehension of the safe-use conditions of the program every month
- Obtain the prescription within 7 days of the pregnancy test collection
- Patients who cannot become pregnant must be enrolled by signing an informed consent form and must obtain the prescription within 30 days of the office visit
- Pharmacies that dispense ABSORICA/ABSORICA LD must be certified by being registered and activated in the program, must only dispense to patients who are authorized to receive ABSORICA/ABSORICA LD, and comply with the following requirements: o Only dispense a maximum of a 30-day supply with a Medication Guide. o Do not dispense refills. Dispense only with a new prescription and a new authorization from the program. o Return ABSORICA/ABSORICA LD to inventory if patients do not obtain the prescription by the “Do Not Dispense To After” date
- Wholesalers and distributors must be registered with the program and must only distribute to certified pharmacies.
Further information, including a list of qualified pharmacies and distributors, is available at www.ipledgeprogram.com or 1-866-495-0654.
ABSORICA and ABSORICA LD are Not Substitutable
Given that the bioavailability and the recommended dosage of ABSORICA and ABSORICA LD are different, ABSORICA and ABSORICA LD are not substitutable. For example, ABSORICA and ABSORICA LD have a 20 mg strength; however, these strengths have different bioavailability and are not substitutable.
Psychiatric Disorders
ABSORICA/ABSORICA LD may cause depression, psychosis and, rarely, suicidal ideation, suicide attempts, suicide, and aggressive and/or violent behaviors [see Adverse Reactions (6) ] .
Healthcare providers should be alert to the warning signs of psychiatric disorders to help ensure patients receive the help they need (Prescribers should read the brochure, Recognizing Psychiatric Disorders in Adolescents and Young Adults: A Guide for Prescribers of Isotretinoin ). Prior to initiation of ABSORICA/ABSORICA LD therapy, patients and family members should be asked about any history of psychiatric disorder, and at each visit during therapy patients should be assessed for symptoms of depression, mood disturbance, psychosis, or aggression to determine if further evaluation is necessary.
Patients should immediately stop ABSORICA/ABSORICA LD and the patient (or caregiver) should promptly contact their prescriber if the patient develops depression, mood disturbance, psychosis, or aggression. Discontinuation of ABSORICA/ABSORICA LD may be insufficient; further evaluation may be necessary such as a referral to a mental healthcare professional.
Intracranial Hypertension (Pseudotumor Cerebri)
Isotretinoin use has been associated with cases of intracranial hypertension (pseudotumor cerebri), some of which involved concomitant use of tetracyclines. Concomitant treatment with tetracyclines should therefore be avoided with ABSORICA/ABSORICA LD use. Early signs and symptoms of intracranial hypertension include papilledema, headache, nausea and vomiting, and visual disturbances. Patients with these symptoms should be screened for papilledema and, if present, they should be told to discontinue ABSORICA/ABSORICA LD immediately and be referred to a neurologist for further diagnosis and care [see Adverse Reactions (6 )] .
Serious Skin Reactions
There have been postmarketing reports of erythema multiforme and severe skin reactions [e.g., Stevens-Johnson syndrome (SJS), toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN)] associated with isotretinoin use. These reactions may be serious and result in death, life-threatening events, hospitalization, or disability. Patients should be monitored closely for severe skin reactions, and ABSORICA/ABSORICA LD should be discontinued if they occur.
Pancreatitis
Acute pancreatitis has been reported with isotretinoin use in patients with either elevated or normal serum triglyceride levels. In rare instances, fatal hemorrhagic pancreatitis has been reported. If symptoms of pancreatitis occur, discontinue ABSORICA/ABSORICA LD and seek medical attention.
Lipid Abnormalities
Elevations of serum triglycerides above 800 mg/dL have been reported with isotretinoin use. In clinical trials, marked elevations of serum triglycerides, decreases in high-density lipoproteins (HDL), and increases in cholesterol levels were reported in 25%, 15%, and 7% of patients treated with isotretinoin capsules, respectively. These lipid changes were reversible upon isotretinoin capsule cessation. Some patients have been able to reverse triglyceride elevation by reduction in weight and restriction of dietary fat and alcohol while continuing isotretinoin or through dosage reduction. The cardiovascular consequences of hypertriglyceridemia associated with isotretinoin are unknown.
Fasting lipid tests should be performed before ABSORICA/ABSORICA LD treatment and then at intervals until the lipid response to ABSORICA/ABSORICA LD is known, which usually occurs within 4 weeks. Careful consideration should be given to risk/benefit of ABSORICA/ABSORICA LD in patients who are at higher risk of hypertriglyceridemia (e.g., patients with diabetes, obesity, increased alcohol intake, lipid metabolism disorder or familial history of lipid metabolism disorder). If ABSORICA/ABSORICA LD therapy is instituted in such patients, more frequent checks of serum values for lipids are recommended [see Warnings and Precautions (5.15) ] . ABSORICA/ABSORICA LD should be stopped if hypertriglyceridemia cannot be controlled.
Hearing Impairment
Impaired hearing has been reported in patients taking isotretinoin; in some cases, the hearing impairment has been reported to persist after therapy has been discontinued. Mechanism(s) and causality for this reaction have not been established. Patients who experience tinnitus or hearing impairment should discontinue ABSORICA/ABSORICA LD treatment and be referred for specialized care for further evaluation.
Hepatotoxicity
Clinical hepatitis has been reported with isotretinoin use. Additionally, mild to moderate elevations of liver enzymes have been observed in approximately 15% of individuals treated during clinical trials with isotretinoin capsules, some of which normalized with dosage reduction or continued administration of the drug. If normalization does not readily occur or if hepatitis is suspected during treatment, ABSORICA/ABSORICA LD should be discontinued.
Inflammatory Bowel Disease
Isotretinoin has been associated with inflammatory bowel disease (including regional ileitis) in patients without a prior history of intestinal disorders. In some instances, symptoms have been reported to persist after isotretinoin treatment has been stopped. Patients experiencing abdominal pain, rectal bleeding or severe diarrhea should discontinue ABSORICA/ABSORICA LD immediately [see Adverse Reactions (6) ] .
Musculoskeletal Abnormalities
Bone Mineral Density Changes, Osteoporosis, and Fractures
Isotretinoin may have a negative effect on bone mineral density (BMD) in some patients. In a clinical trial of ABSORICA and another isotretinoin capsule product, 27/306 (9%) of adolescents had BMD declines, defined as ≥ 4% lumbar spine or total hip, or ≥ 5% femoral neck, during the 20-week treatment period. Repeat scans conducted within 2 to 3 months after the post-treatment scan showed no recovery of BMD. Long-term data at 4 to 11 months showed that 3 out of 7 patients had total hip and femoral neck BMD below pre-treatment baseline, and 2 others did not show the increase in BMD above baseline expected in this adolescent population. Therefore, healthcare providers should use caution when prescribing ABSORICA/ABSORICA LD to patients with a history of childhood osteoporosis conditions, osteomalacia, or other disorders of bone metabolism. This would include patients diagnosed with anorexia nervosa and those who are on chronic drug therapy that causes drug-induced osteoporosis/osteomalacia and/or affects vitamin D metabolism, such as systemic corticosteroids and any anticonvulsant [see Use in Specific Populations (8.4) ] .
There have been spontaneous reports of osteoporosis, osteopenia, fractures and/or delayed healing of fractures in patients while on therapy with isotretinoin or following cessation of therapy with isotretinoin.
Patients in early and late adolescence who participate in sports with repetitive impact may be at an increased risk of spondylolisthesis with and without pars fractures, and hip growth plate injuries have been reported.
Musculoskeletal Abnormalities
Approximately 16% of patients treated with isotretinoin capsules in a clinical trial developed musculoskeletal symptoms (including arthralgia) during treatment. In general, these symptoms were mild to moderate, but occasionally required discontinuation of isotretinoin.
In a trial of pediatric patients treated with isotretinoin capsules, approximately 29% (104/358) developed back pain. Back pain was severe in 14% (14/104) of the cases and occurred at a higher frequency in female patients than male patients.
Arthralgias were experienced in 22% (79/358) of pediatric patients. Arthralgias were severe in 8% (6/79) of patients. Appropriate evaluation of the musculoskeletal system should be done in patients who present with these symptoms during or after a course of ABSORICA/ABSORICA LD. Consider discontinuing ABSORICA/ABSORICA LD if any significant abnormality is found.
Effects of multiple courses of isotretinoin on the developing musculoskeletal system are unknown. There is some evidence that long-term, high-dose, or multiple courses of therapy with isotretinoin have more of an effect than a single course of therapy on the musculoskeletal system. It is important that ABSORICA/ABSORICA LD be given at the recommended dose for no longer than the recommended duration.
Hyperostosis
A high prevalence of skeletal hyperostosis was noted in clinical trials for disorders of keratinization with a mean dose of 2.24 mg/kg/day of isotretinoin capsules (approximately 1.1 times the maximum recommended daily dosage). Additionally, skeletal hyperostosis was noted in 6 of 8 patients in a prospective trial of disorders of keratinization. Minimal skeletal hyperostosis and calcification of ligaments and tendons have also been observed by x-ray in prospective trials of nodular acne patients treated with a single course of therapy at recommended doses. The skeletal effects of multiple isotretinoin treatment courses for acne are unknown.
In a clinical trial of 217 pediatric patients (12 to 17 years) with severe recalcitrant nodular acne, hyperostosis was not observed after 16 to 20 weeks of treatment with approximately 1 mg/kg/day of isotretinoin capsules given in two divided doses. Hyperostosis may require a longer time frame to appear. The clinical course and significance remain unknown.
Premature Epiphyseal Closure
There are spontaneous literature reports of premature epiphyseal closure in acne patients receiving recommended doses of isotretinoin capsules. The effect of multiple courses of isotretinoin on epiphyseal closure is unknown.
In a 20-week clinical trial that included 289 adolescents on ABSORICA or another isotretinoin capsule product who had hand radiographs taken to assess bone age, a total of 9 (3%) patients had bone age changes that were clinically significant and for which a drug-related effect cannot be excluded.
Ocular Abnormalities
Visual problems should be carefully monitored. If visual difficulties occur, discontinue ABSORICA/ABSORICA LD treatment and obtain an ophthalmological examination [see Adverse Reactions (6) ].
Corneal Opacities
Corneal opacities have occurred in patients receiving isotretinoin capsules and more frequently when higher drug dosages were used in patients with disorders of keratinization. The corneal opacities that have been observed in clinical trial patients treated with isotretinoin capsules have either completely resolved or were resolving at follow-up 6 to 7 weeks after discontinuation of isotretinoin [see Adverse Reactions (6) ].
Decreased Night Vision
Decreased night vision has been reported during isotretinoin use and in some instances the event has persisted after therapy was discontinued. Because the onset in some patients was sudden, patients should be advised of this potential problem and warned to be cautious when driving or operating any vehicle at night.
Dry Eyes
Dry eyes has been reported in patients during isotretinoin use. Patients who wear contact lenses may have trouble wearing them while on ABSORICA/ABSORICA LD treatment and afterwards.
Hypersensitivity Reactions
Anaphylactic reactions and other allergic reactions have been reported with isotretinoin use. Cutaneous allergic reactions and serious cases of allergic vasculitis, often with purpura (bruises and red patches) of the extremities and extracutaneous involvement (including renal) have been reported. Severe allergic reaction necessitates discontinuation of therapy and appropriate medical management.
Allergic Reactions Due to the Inactive Ingredient (FD&C Yellow No. 5) in the 25 mg ABSORICA Capsule
The 25 mg ABSORICA capsule contains FD&C Yellow No. 5 (tartrazine) which may cause allergic-type reactions (including bronchial asthma) in certain susceptible persons. Although the overall incidence of tartrazine sensitivity in the general population is low, it is frequently seen in patients who also have aspirin hypersensitivity. The 10 mg, 20 mg, 30 mg, 35 mg, and 40 mg ABSORICA capsules do not contain FD&C Yellow No. 5 and all of the ABSORICA LD capsules do not contain FD&C Yellow No. 5. Thus, in patients with allergic reactions to tartrazine, avoid using the 25 mg ABSORICA capsules.
Laboratory Abnormalities and Laboratory Monitoring for Adverse Reactions
Laboratory Monitoring
Pregnancy Testing
A pregnancy test must be obtained prior to obtaining a prescription , repeated each month, at the end of the entire course of ABSORICA/ABSORICA LD therapy and 1 month after the discontinuation of ABSORICA/ABSORICA LD [see Use in Specific Populations (8.3) ].
Lipid Tests
Pretreatment and follow-up fasting lipid tests should be obtained under fasting conditions. After consumption of alcohol, at least 36 hours should elapse before testing is performed. It is recommended that these tests be performed periodically until the lipid response to ABSORICA/ABSORICA LD is known. The incidence of hypertriglyceridemia is 25% in patients treated with isotretinoin capsules [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8) ] .
Liver Function Tests
As elevations of liver enzymes have been observed during clinical trials, and hepatitis has been reported in patients on isotretinoin capsules, pretreatment and follow-up liver function tests should be performed periodically until the response to ABSORICA/ABSORICA LD is known [see Warnings and Precautions (5.10) ].
Additional Laboratory Abnormalities
Glucose
With isotretinoin use, some patients have experienced problems in the control of their blood sugar. In addition, new cases of diabetes have been diagnosed during isotretinoin use.
CPK
Some patients undergoing vigorous physical activity while taking isotretinoin have experienced elevated CPK levels; however, the clinical significance is unknown. There have been rare postmarketing reports of rhabdomyolysis with isotretinoin use, some associated with strenuous physical activity. In a clinical trial of 924 patients, marked elevations in CPK (≥350 U/L) were observed in approximately 24% of patients treated with isotretinoin capsules.
In another clinical trial of 217 pediatric patients (12 to 17 years old) elevations in CPK were observed in 12% of patients, including those undergoing strenuous physical activity in association with reported musculoskeletal adverse events such as back pain, arthralgia, limb injury, or muscle sprain. In these patients, approximately half of the CPK elevations returned to normal within 2 weeks and half returned to normal within 4 weeks. No cases of rhabdomyolysis were reported in this clinical trial.
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following adverse reactions with ABSORICA/ABSORICA LD or other isotretinoin capsule products are described in more detail in other sections of the labeling:
- Embryo-Fetal Toxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1 )]
- Psychiatric Disorders [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4 )]
- Intracranial Hypertension (Pseudotumor Cerebri) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5 )]
- Serious Skin Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6 )]
- Pancreatitis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7 )]
- Lipid Abnormalities [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8 )]
- Hearing Impairment [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9 )]
- Hepatotoxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.10 )]
- Inflammatory Bowel Disease [see Warnings and Precautions (5.11 )]
- Musculoskeletal Abnormalities [see Warnings and Precautions (5.12 )]
- Ocular Abnormalities [see Warnings and Precautions (5.13 )]
- Hypersensitivity Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.14 )]
The following adverse reactions associated with the use of isotretinoin capsules were identified in clinical studies or postmarketing reports. Because some of these reactions were reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Dose Relationship
Cheilitis and hypertriglyceridemia were dose related.
Body as a Whole
Fatigue, irritability, pain, allergic reactions, systemic hypersensitivity, edema, lymphadenopathy, weight loss.
Cardiovascular
Vascular thrombotic disease, stroke, palpitation, tachycardia.
Endocrine/Metabolism and Nutritional
Decreased appetite, weight fluctuation, alterations in blood sugar.
Gastrointestinal
Dry lips, chapped lips, cheilitis, nausea, constipation, diarrhea, abdominal pain, vomiting, inflammatory bowel disease,
hepatitis, pancreatitis, bleeding and inflammation of the gums, colitis, esophagitis, esophageal ulceration, ileitis.
Hematologic
Anemia and decreased RBC parameters, thrombocytopenia, increased platelet counts, decreased WBC counts, severe neutropenia, rare reports of agranulocytosis.
Infections and Infestations
Nasopharyngitis, hordeolum, infections (including disseminated herpes simplex and upper respiratory tract infection).
Laboratory Abnormalities
The following lab tests were increased: creatine phosphokinase (CPK), triglycerides, alanine aminotransferase (SGPT), aspartate aminotransferase (SGOT), gamma-glutamyltransferase (GGTP), cholesterol, low density lipoprotein (LDL), alkaline phosphatase, bilirubin, LDH, fasting blood glucose, uric acid, and sedimentation rate. However, high density lipoprotein (HDL) was decreased. Urine findings included increased white cells, proteinuria, microscopic or gross hematuria.
Musculoskeletal and Connective Tissue
Decreases in bone mineral density, musculoskeletal symptoms (sometimes severe) including back pain, arthralgia, musculoskeletal pain, neck pain, extremity pain, myalgia, musculoskeletal stiffness [see Warnings and Precautions (5.12)] , skeletal hyperostosis, calcification of tendons and ligaments, premature epiphyseal closure, tendonitis, arthritis, transient chest pain, and rare reports of rhabdomyolysis.
Neurological
Headache, syncope, intracranial hypertension (pseudotumor cerebri), dizziness, drowsiness, lethargy, malaise, nervousness, paresthesia, seizures, stroke, weakness.
Psychiatric
Suicidal ideation, insomnia, anxiety, depression, irritability, panic attack, anger, euphoria, violent behaviors, emotional instability, suicide attempts, suicide, aggression, psychosis and auditory hallucinations. Of the patients reporting depression, some reported that the depression subsided with discontinuation of therapy and recurred with reinstitution of therapy.
Reproductive System
Abnormal menses, sexual dysfunction, including erectile dysfunction, decreased libido, decreased vaginal lubrication, and vaginal dryness.
Respiratory
Epistaxis, nasal dryness, bronchospasm (with or without a history of asthma), respiratory infection, voice alteration.
Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue
Dry skin, dermatitis, eczema, rash, contact dermatitis, alopecia, pruritus, sunburn, erythema, acne fulminans, alopecia(which in some cases persisted), bruising, dry nose, eruptive xanthomas, erythema multiforme, flushing, skin fragility, hair abnormalities, hirsutism, hyperpigmentation and hypopigmentation, nail dystrophy, paronychia, peeling of palms and soles, photoallergic/photosensitizing reactions, pruritus, pyogenic granuloma, rash (including facial erythema, seborrhea, and eczema), Stevens-Johnson syndrome, increased sunburn susceptibility, sweating, toxic epidermal necrolysis, urticaria,vasculitis (including granulomatosis with polyangiitis), abnormal wound healing (delayed healing or exuberant granulation tissue with crusting).
Senses
Hearing: tinnitus and hearing impairment.
Ocular : dry eyes, reduced visual acuity, blurred vision, eye pruritis, eye irritation, asthenopia, decreased night vision, ocular hyperemia, increased lacrimation, conjunctivitis, corneal opacities, decreased night vision which may persist, cataracts, color vision disorder, conjunctivitis, eyelid inflammation, keratitis, optic neuritis, photobia, visual disturbances.
Renal and Urinary
Glomerulonephritis.
DRUG INTERACTIONS
Vitamin A
ABSORICA/ABSORICA LD is closely related to vitamin A. Therefore, the use of both vitamin A and ABSORICA/ABSORICA LD at the same time may lead to vitamin A related adverse reactions. Patients treated with ABSORICA/ABSORICA LD should be advised against taking supplements containing Vitamin A to avoid additive toxic effects.
Tetracyclines
Concomitant treatment with ABSORICA/ABSORICA LD and tetracyclines should be avoided because isotretinoin use has been associated with a number of cases of intracranial hypertension (pseudotumor cerebri), some of which involved concomitant use of tetracyclines [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5) ] .
Phenytoin
Phenytoin is known to cause osteomalacia. No formal clinical trials have been conducted to assess if there is an interactive effect on bone loss between phenytoin and isotretinoin. Therefore, caution should be exercised when using these drugs together.
Systemic Corticosteroids
Systemic corticosteroids are known to cause osteoporosis. No formal clinical trials have been conducted to assess if there is an interactive effect on bone loss with concomitant use of systemic corticosteroids and isotretinoin. Therefore, caution should be exercised when using these drugs together.
Norethindrone/ethinyl estradiol
In a trial of 31 premenopausal female patients with severe recalcitrant nodular acne receiving norethindrone and ethinyl estradiol as an oral contraceptive agent, isotretinoin capsules within the recommended dosage, did not induce clinically relevant changes in the pharmacokinetics of ethinyl estradiol and norethindrone and in the serum levels of progesterone, follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH). Although this study did not show any clinically significant interaction between isotretinoin and norethindrone, it is not known if there is an interaction between isotretinoin with other progestins.
DESCRIPTION
ABSORICA
ABSORICA (isotretinoin) Capsules contain 10 mg, 20 mg, 25 mg, 30 mg, 35 mg or 40 mg of isotretinoin (a retinoid) in hard gelatin capsules for oral administration. In addition to the active ingredient, isotretinoin, each capsule contains the following inactive ingredients: propyl gallate, sorbitan monooleate, soybean oil and stearoyl polyoxylglycerides. The gelatin capsules contain the following dye systems:
•10 mg – iron oxide (yellow) and titanium dioxide;
•20 mg – iron oxide (red), and titanium dioxide;
•25 mg – FD&C Blue #1, FD&C Yellow #5 [see Warnings and Precautions (5.14) ] , FD&C Yellow #6 and titanium dioxide;
•30 mg – iron oxide (black, red and yellow) and titanium dioxide;
•35 mg – FD&C Blue #2, iron oxide (black, red and yellow) and titanium dioxide;
•40 mg – iron oxide (black, red and yellow) and titanium dioxide.
ABSORICA LD
ABSORICA LD (isotretinoin) Capsules contain 8 mg, 16 mg, 20 mg, 24 mg, 28 mg and 32 mg of micronized isotretinoin (a retinoid) in suspension filled in hard gelatin capsules for oral administration. In addition to the active ingredient, isotretinoin, USP each capsule contains the following inactive ingredients: butylated hydroxy anisole, gelatin, hard gelatin capsule shell, polysorbate 80 and soybean oil. The gelatin capsules contain the following dye systems:
•8 mg – D&C Yellow #10, FD&C Blue #1, FD&C Red #40 and titanium dioxide
•16 mg – FD&C Blue #1, FD&C Red #40, and titanium dioxide
•20 mg – FD&C Blue #1, FD&C Red #40, and titanium dioxide
•24 mg – D&C Yellow #10, FD&C Yellow #6 and titanium dioxide
•28 mg – FD&C Blue #1, FD&C Red #40, and titanium dioxide
•32 mg – ferrosoferric oxide, ferric oxide (red and yellow) and titanium dioxide
The imprinting ink of 8 mg, 16 mg, 24 mg and 32 mg capsules contain the following ingredients: potassium hydroxide, propylene glycol, shellac and titanium dioxide.
The imprinting ink of 20 mg and 28 mg capsules contain the following ingredients: ferrosoferric oxide, propylene glycol and shellac glaze.
Isotretinoin
Chemically, isotretinoin is 13- cis -retinoic acid and is related to both retinoic acid and retinol (vitamin A). It is a yellow to orange crystalline powder with a molecular weight of 300.44. It is practically insoluble in water, soluble in chloroform and sparingly soluble in alcohol and in isopropyl alcohol. The structural formula is:
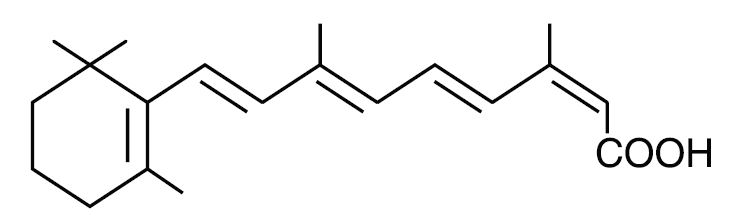
ABSORICA meets USP Dissolution Test 3.
For ABSORICA LD, FDA approved dissolution test differs from the USP.
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Mechanism of Action
ABSORICA/ABSORICA LD is a retinoid, which when administered at the recommended dosage [see Dosage and Administration (2.1) ] , inhibits sebaceous gland function and keratinization. Clinical improvement in nodular acne patients occurs in association with a reduction in sebum secretion. The decrease in sebum secretion is temporary and is related to the dose and duration of treatment with isotretinoin capsules and reflects a reduction in sebaceous gland size and an inhibition of sebaceous gland differentiation. The exact mechanism of action of ABSORICA/ABSORICA LD in the treatment of severe recalcitrant nodular acne is unknown.
Pharmacodynamics
The pharmacodynamics of ABSORICA/ABSORICA LD are unknown.
Pharmacokinetics
No clinically significant differences in the pharmacokinetics of isotretinoin between patients with nodular acne and healthy subjects without acne were reported in published literature.
Absorption Following ABSORICA Administration
The ABSORICA mean T max was 6.4 hours under fed conditions and 2.9 hours under fasting conditions following administration of a single 40 mg dose.
Effect on Food
No clinically significant differences in ABSORICA pharmacokinetics were observed following administration with a modified high-fat, high-calorie meal (123.2 calories from protein, 265.6 calories from carbohydrates, and 468 calories from fat; total calories 857 calories) with reduced vitamin A content. The mean AUC 0-t and C max of isotretinoin were 6095 ng•hr/mL and 369 ng/mL, respectively, following administration of a single 40 mg ABSORICA dose under fed conditions; which were approximately 50% and 26% higher, respectively, compared to fasting conditions. However, ABSORICA may be given with or without meals [see Dosage and Administration (2.1) ].
Absorption Following ABSORICA LD Administration
The ABSORICA LD median T max was 5 hours under fed conditions and 3.5 hours under fasting conditions following administration of a single 32 mg dose.
Effect on Food
No clinically significant differences in ABSORICA LD pharmacokinetics were observed following administration with a high-fat, high-calorie meal (150 calories from protein, 250 calories from carbohydrates, and 500 calories from fat; total calories 900 calories). The mean AUC 0-t and C max of isotretinoin were 10209 ng•hr/mL and 646 ng/mL, respectively, following administration of a single 32 mg ABSORICA LD dose under fed conditions; which were approximately 20% and 6% higher, respectively, compared to fasting conditions. However, ABSORICA LD may be given with or without meals [see Dosage and Administration (2.1) ] .
Distribution
Isotretinoin is more than 99.9% bound to plasma proteins, primarily albumin.
Elimination
The mean elimination half-lives of isotretinoin and its 4-oxo-isotretinoin metabolite were:
•18 hours and 38 hours, respectively, after a single oral ABSORICA 40 mg dose.
•Approximately 24 hours and 38 hours, respectively, after a single oral ABSORICA LD 32 mg dose.
Metabolism : Isotretinoin is primarily metabolized by CYP2C8, 2C9, 3A4, and 2B6 in vitro. Isotretinoin and its metabolites are further metabolized into conjugates.
Following oral administration of isotretinoin capsules, at least three metabolites (4-oxo-isotretinoin, retinoic acid (tretinoin), and 4-oxo-retinoic acid (4-oxo-tretinoin)) have been identified in human plasma. The extent of formation of all metabolites was higher under fed conditions. All of these metabolites possess retinoid activity in vitro. The clinical significance is unknown.
Excretion : Following oral administration of an 80 mg dose of radiolabeled-isotretinoin as a liquid suspension, the metabolites of isotretinoin were excreted in feces and urine in relatively equal amounts (total of 65% to 83%).
Specific Populations
Pediatric Patients: No clinically significant differences in the pharmacokinetics of isotretinoin were observed based on age (12 to 15 years (n=38), and ≥18 years (n=19)). In both age groups, 4-oxo-isotretinoin was the major metabolite; tretinoin and 4-oxo-tretinoin were also observed [see Use in Specific Populations (8.4) ] .
Drug Interaction Studies
No clinically significant differences in the pharmacokinetics of phenytoin (CYP2C9 substrate) were observed when used concomitantly with isotretinoin.
NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis and Impairment of Fertility
In male and female Fischer 344 rats given oral isotretinoin at dosages of 8 or 32 mg/kg/day (1.3 or 5.3 times the recommended clinical ABSORICA dosage of 1 mg/kg/day or the recommended clinical ABSORICA LD dosage of 0.8 mg/kg/day, respectively, after normalization for total body surface area) for greater than 18 months, there was a dose-related increased incidence of pheochromocytoma relative to controls. The incidence of adrenal medullary hyperplasia was also increased at the higher dosage in both sexes. The relatively high level of spontaneous pheochromocytomas occurring in the male Fischer 344 rat makes it an equivocal model for study of this tumor; therefore, the relevance of this tumor to humans is uncertain.
The Ames test was conducted with isotretinoin in two laboratories. The results of the tests in one laboratory were negative, while in the second laboratory, a weakly positive response (less than 1.6 times background) was noted in S. typhimurium TA100 when the assay was conducted with metabolic activation. No dose response effect was seen, and all other strains were negative. Additionally, other tests designed to assess genotoxicity (Chinese hamster cell assay, mouse micronucleus test, S. cerevisiae D7 assay, in vitro clastogenesis assay with human-derived lymphocytes, and unscheduled DNA synthesis assay) were all negative.
In rats, no adverse effects on gonadal function, fertility, conception rate, gestation or parturition were observed at oral dosages of isotretinoin of 2, 8, or 32 mg/kg/day (0.3, 1.3, or 5.3 times the recommended clinical ABSORICA dosage of 1 mg/kg/day or the recommended clinical ABSORICA LD dosage of 0.8 mg/kg/day, respectively, after normalization for total body surface area).
In dogs, testicular atrophy was noted after treatment with oral isotretinoin for approximately 30 weeks at dosages of 20 or 60 mg/kg/day (10 or 30 times the recommended clinical ABSORICA dosage of 1 mg/kg/day or the recommended clinical ABSORICA LD dosage of 0.8 mg/kg/day, respectively, after normalization for total body surface area). In general, there was microscopic evidence for appreciable depression of spermatogenesis, but some sperm were observed in all testes examined, and in no instance were completely atrophic tubules seen.
Animal Toxicology
In rats given 8 or 32 mg/kg/day of isotretinoin (1.3 or 5.3 times the recommended clinical ABSORICA dosage of 1 mg/kg/day or the recommended clinical ABSORICA LD dosage of 0.8 mg/kg/day, respectively, after normalization for total body surface area) for 18 months or longer, the incidences of focal calcification, fibrosis and inflammation of the myocardium, calcification of coronary, pulmonary and mesenteric arteries, and metastatic calcification of the gastric mucosa were greater than in control rats of similar age. Focal endocardial and myocardial calcifications associated with calcification of the coronary arteries were observed in two dogs after approximately 6 to 7 months of treatment with isotretinoin at a dosage of 60 to 120 mg/kg/day (30 to 60 times the recommended clinical ABSORICA dosage of 1 mg/kg/day or the recommended clinical ABSORICA LD dosage of 0.8 mg/kg/day, respectively, after normalization for total body surface area).
CLINICAL STUDIES
The effectiveness of ABSORICA/ABSORICA LD for the treatment of severe recalcitrant nodular acne in patients 12 years of age and older has been established and is based on a double-blind, randomized, parallel group trial (Study 1) in subjects with severe recalcitrant nodular acne who received ABSORICA or another isotretinoin capsule product under fed conditions. A total of 925 subjects were randomized 1:1 to receive ABSORICA or another isotretinoin capsule product. Study subjects ranged from 12 to 54 years of age (including 397 pediatric subjects 12 to 17 years old); 60% were male, 40% were female; and the racial groups included 87% White, 4% Black, 6% Asian, and 3% Other. Enrolled subjects had a weight of 40 to 110 kg and had at least 10 nodular lesions on the face and/or trunk. Subjects were treated with an initial dose of 0.5 mg/kg/day in two divided doses for the first 4 weeks, followed by 1 mg/kg/day in two divided doses for the following 16 weeks.
Change from baseline to Week 20 in total nodular lesion count and proportion of subjects with at least a 90% reduction in total nodular lesion count from baseline to Week 20 are presented in Table 3. Total nodular lesion counts by visit are presented in Figure 1. A single course of ABSORICA and another isotretinoin capsule product therapy for 15 to 20 weeks has been shown to result in complete and prolonged remission of acne in many patients.
Table 3: Efficacy Results in Subjects with Severe Recalcitrant Nodular Acne at Week 20 (Study 1)
ABSORICA N=464 | Another Isotretinoin Capsule Product• N=461 | |
Nodular Lesions Mean Baseline Count Mean Reduction | 18.4 -15.68 | 17.7 -15.62 |
Subjects Achieving 90% Reduction, n (%) | 324 (70%) | 344 (75%) |
Figure 1: Total Nodular (Facial and Truncal) Lesion Count in Subjects with Severe Recalcitrant Nodular Acne by Visit in Study 1
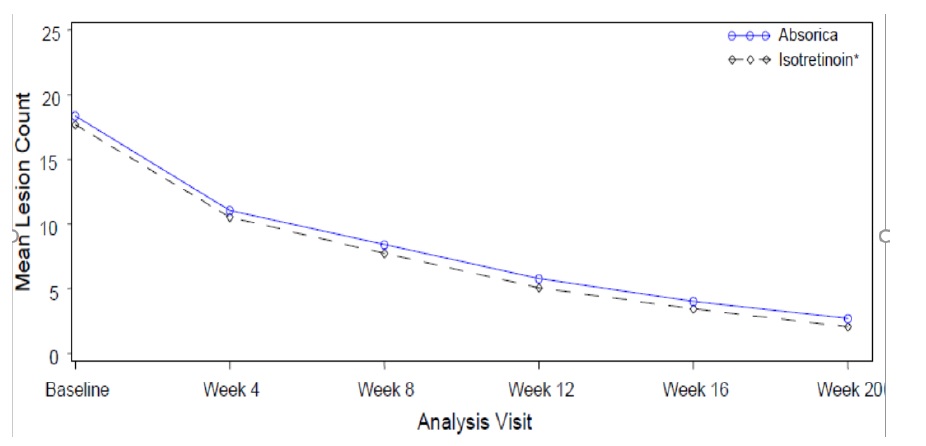
• Another isotretinoin capsule product.
HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
ABSORICA and ABSORICA LD have different dosage regimens. Although ABSORICA and ABSORICA LD have a 20 mg strength, these strengths have different bioavailability and are not substitutable [see Dosage and Administration (2.1) ] .
ABSORICA
ABSORICA (isotretinoin) Capsules (opaque) are supplied as follows:
- 10 mg : Dark yellow, capsule imprinted with black ink “G 240” on cap and “10” on the body
- Box of 30 capsules (3 x 10 Prescription Packs): NDC 10631-115-31
- 20 mg : Red, capsule imprinted with black ink “G 241” on cap and “20” on the body
- Box of 30 capsules (3 x 10 Prescription Packs): NDC 10631-116-31
- 25 mg : Green, capsule imprinted with white ink “G 342” on cap and “25” on the bodyBox of 30 capsules (3 x 10 Prescription Packs): NDC 10631-133-31
- 30 mg : Brown, capsule imprinted with white ink “G 242” on cap and “30” on the bodyBox of 30 capsules (3 x 10 Prescription Packs): NDC 10631-117-31
- 35 mg : Dark blue, capsule imprinted with white ink “G 343” on cap and “35” on the bodyBox of 30 capsules (3 x 10 Prescription Packs): NDC 10631-134-31
- 40 mg : Brown and red, capsule imprinted with white ink “G 325” on cap and “40” on the bodyBox of 30 capsules (3 x 10 Prescription Packs): NDC 10631-118-31
ABSORICA LD
ABSORICA LD (isotretinoin) Capsules (opaque-printed, hard-gelatin) are supplied as follows:
- 8 mg: A size 3, light green, capsules banded with a colorless band. The cap is printed in white with “RL29” and the body is printed in white with “RL29”.
Box of 30 capsules (3 x 10 Prescription Packs) NDC 10631-002-31
- 16 mg: A size 2, dark blue, capsules banded with a colorless band. The cap is printed in white with “RL30” and the body is printed in white with “RL30”.
Box of 30 capsules (3 x 10 Prescription Packs) NDC 10631-003-31
- 20 mg: A size 1, dark pink, capsules banded with a colorless band. The cap is printed in black with “RL33”and the body is printed in black with “RL33”.
Box of 30 capsules (3 x 10 Prescription Packs) NDC 10631-004-31
- 24 mg: A size 1, yellow, capsules banded with a colorless band. The cap is printed in white with “RL31” and the body is printed in white with “RL31”.
Box of 30 capsules (3 x 10 Prescription Packs) NDC 10631-005-31
- 28 mg: A size 0, light blue, capsules banded with a colorless band. The cap is printed in black with “RL34” and the body is printed in black with “RL34”.
Box of 30 capsules (3 x 10 Prescription Packs) NDC 10631-006-31
- 32 mg: A size 0, caramel, capsules banded with a colorless band. The cap is printed in white with “RL32” and the body is printed in white with “RL32”.
Box of 30 capsules (3 x 10 Prescription Packs): NDC 10631-007-31
Storage and Handling of ABSORICA and ABSORICA LD
Store at 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F), excursions permitted between 15°C to 30°C (59°F to 86°F) [see USP controlled room temperature]. Protect from light.
Mechanism of Action
ABSORICA/ABSORICA LD is a retinoid, which when administered at the recommended dosage [see Dosage and Administration (2.1) ] , inhibits sebaceous gland function and keratinization. Clinical improvement in nodular acne patients occurs in association with a reduction in sebum secretion. The decrease in sebum secretion is temporary and is related to the dose and duration of treatment with isotretinoin capsules and reflects a reduction in sebaceous gland size and an inhibition of sebaceous gland differentiation. The exact mechanism of action of ABSORICA/ABSORICA LD in the treatment of severe recalcitrant nodular acne is unknown.