Get your patient on Ajovy (Fremanezumab-Vfrm)
Ajovy prior authorization resources
Most recent state uniform prior authorization forms
Brand Resources
Patient education
Patient education materials
Clinical information
Insurance resources
Prior authorization & coverage support
Financial assistance & copay programs
Other resources
Dosage & administration
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Recommended Dosage
Adults
The recommended dosage in adults for the preventive treatment of migraine is administered by subcutaneous injection as one of the following options:
- 225 mg monthly, or
- 675 mg every 3 months (quarterly), which is administered as three consecutive subcutaneous injections of 225 mg each.
When switching dosage options, administer the first dose of the new regimen on the next scheduled date of administration.
Pediatric Patients who are 6 to 17 Years of Age and who Weigh 45 kg or More:
The recommended dosage for the preventive treatment of episodic migraine in pediatric patients who are 6 to 17 years of age and who weigh 45 kg or more is administered by subcutaneous injection as follows:
- 225 mg monthly.
AJOVY is not approved in pediatric patients weighing less than 45 kg because of the lack of an appropriate strength presentation [see Clinical Studies (14) and How Supplied/Storage and Handling (16.1)] .
Missed Dose
If a dose of AJOVY is missed, administer as soon as possible. Thereafter, AJOVY can be scheduled from the date of the last dose.
Important Administration Instructions
AJOVY is for subcutaneous use only.
AJOVY may be administered by healthcare providers, patients 13 years of age and older, and/or caregivers. In pediatric patients 6 to 12 years of age, AJOVY must be administered by a healthcare provider or adult caregiver. Prior to use, provide proper training to patients and/or caregivers on the preparation and administration of AJOVY prefilled syringe, including aseptic technique [see Instructions for Use ] :
- Remove AJOVY from the refrigerator. Prior to use, allow AJOVY to sit at room temperature for 30 minutes protected from direct sunlight. Do not warm by using a heat source such as hot water or a microwave. Do not use AJOVY if it has been at room temperature for 7 days or longer [see How Supplied/Storage and Handling (16.2 )].
- Follow aseptic injection technique every time AJOVY is administered.
- Inspect AJOVY for particles or discoloration prior to administration [see Dosage Forms and Strengths (3 )] . Do not use if the solution is cloudy, discolored, or contains particles.
- Administer AJOVY by subcutaneous injection into areas of the abdomen, thigh, or upper arm that are not tender, bruised, red, or indurated. For multiple injections, you may use the same body site, but not the exact location of the previous injection.
- Do not co-administer AJOVY with other injectable drugs at the same injection site.

By using PrescriberAI, you agree to the AI Terms of Use.
Ajovy prescribing information
RECENT MAJOR CHANGES
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
AJOVY is indicated for:
- the preventive treatment of migraine in adults, and
- the preventive treatment of episodic migraine in pediatric patients who are 6 to 17 years of age and who weigh 45 kg or more.
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Recommended Dosage
Adults
The recommended dosage in adults for the preventive treatment of migraine is administered by subcutaneous injection as one of the following options:
- 225 mg monthly, or
- 675 mg every 3 months (quarterly), which is administered as three consecutive subcutaneous injections of 225 mg each.
When switching dosage options, administer the first dose of the new regimen on the next scheduled date of administration.
Pediatric Patients who are 6 to 17 Years of Age and who Weigh 45 kg or More:
The recommended dosage for the preventive treatment of episodic migraine in pediatric patients who are 6 to 17 years of age and who weigh 45 kg or more is administered by subcutaneous injection as follows:
- 225 mg monthly.
AJOVY is not approved in pediatric patients weighing less than 45 kg because of the lack of an appropriate strength presentation [see Clinical Studies (14) and How Supplied/Storage and Handling (16.1)] .
Missed Dose
If a dose of AJOVY is missed, administer as soon as possible. Thereafter, AJOVY can be scheduled from the date of the last dose.
Important Administration Instructions
AJOVY is for subcutaneous use only.
AJOVY may be administered by healthcare providers, patients 13 years of age and older, and/or caregivers. In pediatric patients 6 to 12 years of age, AJOVY must be administered by a healthcare provider or adult caregiver. Prior to use, provide proper training to patients and/or caregivers on the preparation and administration of AJOVY prefilled syringe, including aseptic technique [see Instructions for Use ] :
- Remove AJOVY from the refrigerator. Prior to use, allow AJOVY to sit at room temperature for 30 minutes protected from direct sunlight. Do not warm by using a heat source such as hot water or a microwave. Do not use AJOVY if it has been at room temperature for 7 days or longer [see How Supplied/Storage and Handling (16.2 )].
- Follow aseptic injection technique every time AJOVY is administered.
- Inspect AJOVY for particles or discoloration prior to administration [see Dosage Forms and Strengths (3 )] . Do not use if the solution is cloudy, discolored, or contains particles.
- Administer AJOVY by subcutaneous injection into areas of the abdomen, thigh, or upper arm that are not tender, bruised, red, or indurated. For multiple injections, you may use the same body site, but not the exact location of the previous injection.
- Do not co-administer AJOVY with other injectable drugs at the same injection site.
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
AJOVY is a sterile, clear to opalescent, colorless to slightly yellow solution, available as follows:
- Injection: 225 mg/1.5 mL single-dose prefilled autoinjector
- Injection: 225 mg/1.5 mL single-dose prefilled syringe
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
Pregnancy
Pregnancy Exposure Registry
There is a pregnancy exposure registry that monitors pregnancy outcomes in women exposed to AJOVY during pregnancy. Healthcare providers are encouraged to register pregnant patients, or pregnant women may enroll themselves in the registry by calling 1-833-927-2605 or visiting www.tevamigrainepregnancyregistry.com.
Risk Summary
There are no adequate data on the developmental risk associated with the use of AJOVY in pregnant women. AJOVY has a long half-life [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3 )] . This should be taken into consideration for women who are pregnant or plan to become pregnant while using AJOVY. Administration of fremanezumab-vfrm to rats and rabbits during the period of organogenesis or to rats throughout pregnancy and lactation at doses resulting in plasma levels greater than those expected clinically did not result in adverse effects on development [see Animal Data] . In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2-4% and 15-20%, respectively. The estimated rate of major birth defects (2.2-2.9%) and miscarriage (17%) among deliveries to women with migraine are similar to rates reported in women without migraine.
Clinical Considerations
Disease-Associated Maternal and/or Embryo/Fetal Risk
Published data have suggested that women with migraine may be at increased risk of preeclampsia and gestational hypertension during pregnancy.
Data
Animal Data
When fremanezumab-vfrm (0, 50, 100, or 200 mg/kg) was administered to male and female rats by weekly subcutaneous injection prior to and during mating and continuing in females throughout organogenesis, no adverse embryofetal effects were observed. The highest dose tested was associated with plasma exposures (AUC) approximately 2 times that in humans at a dose of 675 mg.
Administration of fremanezumab-vfrm (0, 10, 50, or 100 mg/kg) weekly by subcutaneous injection to pregnant rabbits throughout the period of organogenesis produced no adverse effects on embryofetal development. The highest dose tested was associated with plasma AUC approximately 3 times that in humans (675 mg).
Administration of fremanezumab-vfrm (0, 50, 100, or 200 mg/kg) weekly by subcutaneous injection to female rats throughout pregnancy and lactation resulted in no adverse effects on pre- and postnatal development. The highest dose tested was associated with plasma AUC approximately 2 times that in humans (675 mg).
Lactation
Risk Summary
There are no data on the presence of fremanezumab-vfrm in human milk, the effects on the breastfed infant, or the effects on milk production. The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother’s clinical need for AJOVY and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed infant from AJOVY or from the underlying maternal condition.
Pediatric Use
Episodic Migraine
The safety and effectiveness of AJOVY have been established in an adequate and well-controlled study for the preventive treatment of episodic migraine in pediatric patients who are 6 to 17 years of age and who weigh 45 kg or more (Study 3). The safety and efficacy profile of AJOVY in these patients was similar to the safety and efficacy profile seen in clinical trials in adults with migraine [see Adverse Reactions (6.1 ), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3 ), and Clinical Studies (14 )].
AJOVY is not approved in pediatric patients weighing less than 45 kg because of the lack of an appropriate strength presentation.
The safety and effectiveness of AJOVY for the preventive treatment of episodic migraine in pediatric patients younger than 6 years of age have not been established.
Chronic Migraine
The safety and effectiveness of AJOVY for the preventive treatment of chronic migraine in pediatric patients have not been established.
Juvenile Animal Toxicity Data
Subcutaneous administration of fremanezumab-vfrm (0, 50, 150, or 450 mg/kg) to juvenile rats once weekly from postnatal day (PND) 28 to PND 63 resulted in no adverse effects on growth, sexual maturation, or neurobehavioral or reproductive function. The highest dose tested was associated with plasma drug exposures (AUC) approximately 58 times that in pediatric patients at the recommended human dose (225 mg), when calculated on a monthly basis.
Geriatric Use
Clinical studies of AJOVY did not include sufficient numbers of subjects aged 65 and over to determine whether they respond differently from younger subjects.
CONTRAINDICATIONS
AJOVY is contraindicated in patients with serious hypersensitivity to fremanezumab-vfrm or to any of the excipients. Reactions have included anaphylaxis and angioedema [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1 )].
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Hypersensitivity Reactions
Hypersensitivity reactions, including rash, pruritus, drug hypersensitivity, and urticaria, were reported with AJOVY in clinical trials. Most reactions were mild to moderate, but some led to discontinuation or required corticosteroid treatment. Most reactions were reported from within hours to one month after administration. Cases of anaphylaxis and angioedema have been reported in the postmarketing setting.
If a hypersensitivity reaction occurs, consider discontinuing AJOVY, and institute appropriate therapy [see Contraindications (4 )] .
5.2 Hypertension
Development of hypertension and worsening of pre-existing hypertension have been reported following the use of CGRP antagonists, including AJOVY, in the postmarketing setting. Some of the patients who developed new-onset hypertension had risk factors for hypertension. There were cases requiring initiation of pharmacological treatment for hypertension and, in some cases, hospitalization. Hypertension may occur at any time during treatment, but was most frequently reported within 7 days of therapy initiation. AJOVY was discontinued in many of the reported cases.
Monitor patients treated with AJOVY for new-onset hypertension or worsening of pre-existing hypertension, and consider whether discontinuation of AJOVY is warranted if evaluation fails to establish an alternative etiology or blood pressure is inadequately controlled.
5.3 Raynaud's Phenomenon
Development of Raynaud’s phenomenon and recurrence or worsening of pre-existing Raynaud’s phenomenon have been reported in the postmarketing setting following the use of CGRP antagonists, including AJOVY. In reported cases with monoclonal antibody CGRP antagonists, symptom onset occurred a median of 71 days following dosing. Many of the cases reported serious outcomes, including hospitalizations and disability, generally related to debilitating pain.
In most reported cases, discontinuation of the CGRP antagonist resulted in resolution of symptoms.
AJOVY should be discontinued if signs or symptoms of Raynaud’s phenomenon develop and patients should be evaluated by a healthcare provider if symptoms do not resolve. Patients with a history of Raynaud’s phenomenon should be monitored for, and informed about the possibility of, worsening or recurrence of signs and symptoms.
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following clinically significant adverse reactions are discussed in greater detail in other sections of the labeling:
Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug, and may not reflect the rates observed in clinical practice.
Adults
The safety of AJOVY was evaluated in 2512 patients with migraine who received at least 1 dose of AJOVY, representing 1279 patient-years of exposure. Of these, 1730 patients were exposed to AJOVY 225 mg monthly or AJOVY 675 mg quarterly for at least 6 months, 775 patients for at least 12 months, and 138 patients for at least 15 months. In placebo-controlled clinical trials (Studies 1 and 2), 662 patients received AJOVY 225 mg monthly for 12 weeks (with or without a loading dose of 675 mg), and 663 patients received AJOVY 675 mg quarterly for 12 weeks [see Clinical Studies (14 )] . In the controlled trials, 87% of patients were female, 80% were White, and the mean age was 41 years.
The most common adverse reactions in the clinical trials for the preventive treatment of migraine (incidence at least 5% and greater than placebo) were injection site reactions. The adverse reactions that most commonly led to discontinuations were injection site reactions (1%). Table 1 summarizes adverse reactions reported in the 3-month placebo-controlled studies (Study 1 and Study 2), and the 1-month follow-up period after those studies.
| Adverse Reaction | AJOVY 225 mg Monthly (n=290) % | AJOVY 675 mg Quarterly (n=667) % | Placebo Monthly (n=668) % |
|---|---|---|---|
Injection site reactions a | 43 | 45 | 38 |
a Injection site reactions include multiple related adverse event terms, such as injection site pain, induration, and erythema.
Pediatric Patients 6 to 17 Years of Age
The safety of AJOVY was evaluated in 225 pediatric patients 6 to 17 years of age with episodic migraine who received at least one dose of AJOVY. Of these patients, 209 received AJOVY monthly for at least 6 months and 100 received AJOVY for at least 12 months. In the placebo-controlled trial (Study 3), 123 pediatric patients with episodic migraine were treated with AJOVY [see Clinical Studies (14)] . The most common adverse reactions of AJOVY observed in Study 3 were injection site reactions. Hypersensitivity reactions were also observed. Overall, the safety profile in pediatric patients is similar to the known safety profile in adults.
Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during postapproval use of AJOVY. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Immune System Disorders : Anaphylactic reactions and angioedema [see Contraindications (4 ) and Warnings and Precautions (5.1 )]
Vascular Disorders : Hypertension [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2 )] , Raynaud’s phenomenon [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3 )]
DESCRIPTION
Fremanezumab-vfrm is a humanized IgG2Δa/kappa monoclonal antibody specific for calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) ligand. Fremanezumab-vfrm is produced by recombinant DNA technology in Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) cells. The antibody consists of 1324 amino acids and has a molecular weight of approximately 148 kDa.
AJOVY (fremanezumab-vfrm) injection is a sterile, preservative-free, clear to opalescent, colorless to slightly yellow solution for subcutaneous injection, supplied in a single-dose 225 mg/1.5 mL prefilled autoinjector and a single-dose 225 mg/1.5 mL prefilled syringe.
Each prefilled autoinjector or prefilled syringe delivers 1.5 mL of solution containing 225 mg fremanezumab-vfrm, disodium ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid dihydrate (EDTA) (0.204 mg), L-histidine (0.815 mg), L-histidine hydrochloride monohydrate (3.93 mg), polysorbate-80 (0.3 mg), sucrose (99 mg), and Water for Injection, and has a pH of 5.5.
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Mechanism of Action
Fremanezumab-vfrm is a humanized monoclonal antibody that binds to calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) ligand and blocks its binding to the receptor.
Pharmacodynamics
The relationship between the pharmacodynamic activity and the mechanism(s) by which fremanezumab-vfrm exerts its clinical effects is unknown.
Pharmacokinetics
Absorption
After single subcutaneous (SC) administrations of 225 mg, 675 mg, and 900 mg fremanezumab-vfrm, median time to maximum concentrations (t max ) was 5 to 7 days. Dose-proportionality, based on population PK, was observed between 225 mg to 900 mg. The geometric mean (%CV) for fremanezumab-vfrm maximum concentration (C max ) was 29.7 (13.7%) µg/mL and total systemic exposure (AUC 0-inf ) was 42.5 (17.5%) h•mg/mL following administration of 225 mg fremanezumab-vfrm. The geometric mean (%CV) for fremanezumab-vfrm maximum concentration (C max ) was 104.8 (28.8%) µg/mL and total systemic exposure (AUC 0-inf ) was 132.8 (31.7%) h•mg/mL following administration of 675 mg fremanezumab-vfrm. Steady state was achieved by approximately 168 days (approximately 6 months) following 225 mg SC monthly and 675 mg SC quarterly dosing regimens. Median accumulation ratio, based on once-monthly and once-quarterly dosing regimens, is approximately 2.3 and 1.2, respectively.
Distribution
Fremanezumab-vfrm has an apparent volume of distribution of approximately 6 liters, suggesting minimal distribution to the extravascular tissues.
Metabolism
Similar to other monoclonal antibodies, fremanezumab-vfrm is degraded by enzymatic proteolysis into small peptides and amino acids.
Elimination
Fremanezumab-vfrm apparent clearance was approximately 0.141 L/day. Fremanezumab-vfrm was estimated to have a half-life of approximately 31 days.
Specific Populations
No clinically significant differences in fremanezumab-vfrm pharmacokinetics were predicted based on race (White, Black, Asian, and other races), sex, mild hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh Class A), and moderate hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh Class B). The effect of severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh Class C) on fremanezumab-vfrm pharmacokinetics is unknown.
Pediatric Patients
Following subcutaneous administration of 225 mg AJOVY monthly in the pediatric population weighing 45 kg or more, the predicted steady state fremanezumab-vfrm exposures (maximum plasma concentration [C max ], area under the plasma concentration-time curve [AUC]) are similar to those of adults.
Drug Interactions
Fremanezumab is not metabolized by cytochrome P450 enzymes; therefore, interactions with concomitant medications that are substrates, inducers, or inhibitors of cytochrome P450 enzymes are unlikely. Additionally, the effects of medications for the acute treatment (specifically analgesics, ergots, and triptans) and preventive treatment of migraine were evaluated in a population PK model, and found not to influence fremanezumab exposure.
12.6 Immunogenicity
The observed incidence of anti-drug antibodies is highly dependent on the sensitivity and specificity of the assay. Differences in assay methods preclude meaningful comparisons of the incidence of anti-drug antibodies in the studies described below with the incidence of anti-drug antibodies in other studies, including those of fremanezumab-vfrm or of other fremanezumab products.
In 3-month, placebo-controlled studies in adult patients, treatment-emergent anti-drug antibodies were observed in 0.4% (6 out of 1701) AJOVY-treated patients. One of the 6 patients developed anti-AJOVY neutralizing antibodies at Day 84. In the long-term, open-label study, anti-drug antibodies were detected in 1.6% of patients (30 out of 1888). Out of 30 anti-drug antibody-positive patients, 17 had a neutralizing activity in their post-dose samples. Although these data do not demonstrate an impact of anti-fremanezumab-vfrm antibody development on efficacy or safety of AJOVY in these patients, available data are too limited to make definitive conclusions.
In the 3-month, placebo-controlled study in pediatric patients with episodic migraine, treatment-emergent anti-drug antibody responses were observed in 2 out of 123 (1.6%) AJOVY-treated patients. One of the 2 patients developed anti-fremanezumab-vfrm neutralizing antibodies at Day 84. The available data are too limited to make definitive conclusions about the impact of the development of anti-fremanezumab-vfrm antibodies on the pharmacokinetics, efficacy, or safety of AJOVY in pediatric patients.
NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenesis
Carcinogenicity studies of fremanezumab-vfrm were not conducted.
Mutagenesis
Genetic toxicology studies of fremanezumab-vfrm were not conducted.
Impairment of Fertility
When fremanezumab-vfrm (0, 50, 100, or 200 mg/kg) was administered to male and female rats by weekly subcutaneous injection prior to and during mating and continuing in females throughout organogenesis, no adverse effects on male or female fertility were observed. The highest dose tested was associated with plasma exposures (AUC) approximately 2 times that in humans at a dose of 675 mg.
CLINICAL STUDIES
Adults
The efficacy of AJOVY was evaluated as a preventive treatment of episodic or chronic migraine in adult patients in two multicenter, randomized, 3-month, double-blind, placebo-controlled studies (Study 1 and Study 2, respectively).
Episodic Migraine
Study 1 (NCT 02629861) included adults with a history of episodic migraine (patients with <15 headache days per month). All patients were randomized (1:1:1) to receive subcutaneous injections of either AJOVY 675 mg every three months (quarterly), AJOVY 225 mg monthly, or placebo monthly, over a 3-month treatment period. Patients were allowed to use acute headache treatments during the study. A subset of patients (21%) was allowed to use one additional concomitant preventive medication.
The study excluded patients with a history of significant cardiovascular disease, vascular ischemia, or thrombotic events, such as cerebrovascular accident, transient ischemic attacks, deep vein thrombosis, or pulmonary embolism.
The primary efficacy endpoint was the mean change from baseline in the monthly average number of migraine days during the 3-month treatment period. Secondary endpoints included the proportion of patients reaching at least a 50% reduction in monthly average number of migraine days during the 3-month treatment period, the mean change from baseline in the monthly average number of days of use of any acute headache medication during the 3-month treatment period, and the mean change from baseline in the number of migraine days during the first month of the treatment period.
In Study 1, a total of 875 patients (742 females, 133 males), ranging in age from 18 to 70 years, were randomized. A total of 791 patients completed the 3-month double-blind phase. The mean migraine frequency at baseline was approximately 9 migraine days per month, and was similar across treatment groups.
Both monthly and quarterly dosing regimens of AJOVY demonstrated statistically significant improvements for efficacy endpoints compared to placebo over the 3-month period, as summarized in Table 3.
| Study 1 Efficacy Endpoint | AJOVY 225 mg Monthly (N=287) | AJOVY 675 mg Quarterly (N=288) | Placebo (N=290) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Monthly migraine days (MMD) | |||
| Baseline migraine days | 8.9 | 9.2 | 9.1 |
Change from baseline | -3.7 | -3.4 | -2.2 |
| Difference from placebo | -1.5 | -1.2 | |
| p-value | <0.001 | <0.001 | |
| ≥50% MMD responders | |||
% responders | 47.7% | 44.4% | 27.9% |
| Difference from placebo | 19.8% | 16.5% | |
| p-value | <0.001 | <0.001 | |
| Monthly acute headache medication days | |||
Change from baseline | -3.0 | -2.9 | -1.6 |
| Difference from placebo | -1.4 | -1.3 | |
| p-value | <0.001 | <0.001 | |
Figure 1 displays the mean change from baseline in the average monthly number of migraine days in Study 1.
Figure 1: Change from Baseline in Monthly Migraine Days in Study 1 a

Figure 2 shows the distribution of change from baseline in mean monthly migraine days in bins of 2 days by treatment group in Study 1. A treatment benefit over placebo for both doses of AJOVY is seen across a range of changes from baseline in monthly migraine days.
Figure 2: Distribution of Change from Baseline in Mean Monthly Migraine Days by Treatment Group in Study 1

Chronic Migraine
Study 2 (NCT 02621931) included adults with a history of chronic migraine (patients with ≥15 headache days per month). All patients were randomized (1:1:1) to receive subcutaneous injections of either AJOVY 675 mg starting dose followed by 225 mg monthly, 675 mg every 3 months (quarterly), or placebo monthly, over a 3-month treatment period. Patients were allowed to use acute headache treatments during the study. A subset of patients (21%) was allowed to use one additional concomitant, preventive medication.
The study excluded patients with a history of significant cardiovascular disease, vascular ischemia, or thrombotic events, such as cerebrovascular accident, transient ischemic attacks, deep vein thrombosis, or pulmonary embolism.
The primary efficacy endpoint was the mean change from baseline in the monthly average number of headache days of at least moderate severity during the 3-month treatment period. The secondary endpoints were the mean change from baseline in the monthly average number of migraine days during the 3-month treatment period, the proportion of patients reaching at least 50% reduction in the monthly average number of headache days of at least moderate severity during the 3-month treatment period, the mean change from baseline in the monthly average number of days of use of any acute headache medication during the 3-month treatment period, and the mean change from baseline in the number of headache days of at least moderate severity during the first month of treatment.
In Study 2, a total of 1130 patients (991 females, 139 males), ranging in age from 18 to 70 years, were randomized. A total of 1034 patients completed the 3-month double-blind phase.
Both monthly and quarterly dosing regimens of AJOVY treatment demonstrated statistically significant improvement for key efficacy outcomes compared to placebo, as summarized in Table 4.
Study 2 Efficacy Endpoint | AJOVY 225 mg a Monthly (N=375) | AJOVY 675 mg Quarterly (N=375) | Placebo (N=371) |
| Baseline headache days of any severity b | 20.3 | 20.4 | 20.3 |
| Baseline headache days of at least moderate severity c | 12.8 | 13.2 | 13.3 |
Change from baseline in the monthly average number of headache days of at least moderate severity | -4.6 | -4.3 | -2.5 |
| Difference from placebo | -2.1 | -1.8 | |
| p-value | <0.001 | <0.001 | |
Change from baseline in the monthly average number of migraine days in patients | -5.0 | -4.9 | -3.2 |
Change from baseline in monthly average number of headache days of at least moderate severity at 4 weeks after 1 st dose | -4.6 | -4.6 | -2.3 |
Percentage of patients with ≥ 50% reduction in monthly average number of headache days of at least moderate severity | 40.8% | 37.6% | 18.1% |
Change from baseline in monthly average number of days of acute headache medication | -4.2 | -3.7 | -1.9 |
a In Study 2, patients received a 675 mg starting dose. b Used for chronic migraine diagnosis. c Used for primary endpoint analysis.
Figure 3 displays the mean change from baseline in the average monthly number of headache days of at least moderate severity in Study 2.
Figure 3: Change from Baseline in Monthly Headache Days of At Least Moderate Severity in Study 2 a

Figure 4 shows the distribution of change from baseline in monthly headache days of at least moderate severity at month 3 in bins of 3 days by treatment group. A treatment benefit over placebo for both dosing regimens of AJOVY is seen across a range of changes from baseline in headache days.
Figure 4: Distribution of Mean Change from Baseline in Monthly Headache Days of At Least Moderate Severity by Treatment Group in Study 2

•In Study 2, patients received a 675 mg starting dose.
Pediatric Patients 6 to 17 Years of Age
The efficacy of AJOVY for the preventive treatment of episodic migraine in pediatric patients 6 to 17 years of age was evaluated in a multicenter, randomized, 3-month, double-blind, placebo-controlled study (Study 3).
Episodic Migraine
Study 3 (NCT 04458857) included pediatric patients 6 to 17 years of age with a history of episodic migraine (patients with <15 headache days per month). All patients were randomized (1:1) to receive monthly subcutaneous injections of either AJOVY or placebo, over a 3-month period. Patients who weighed 45 kg or more received AJOVY 225 mg and patients who weighed under 45 kg received AJOVY 120 mg [see Dosage and Administration (2.1)] . Patients were allowed to use acute headache treatments during the study. A subset of patients (21%) was allowed to use up to two additional concomitant preventive medications. The study excluded patients with clinically significant cardiovascular disease.
The primary efficacy endpoint was the mean change from baseline in the monthly average number of migraine days during the 3-month treatment period. Secondary endpoints included the proportion of patients reaching at least a 50% reduction in monthly average number of migraine days during the 3-month treatment period; the mean change from baseline in the monthly average number of days of use of any acute headache medication during the 3-month treatment period; and the mean change from baseline in monthly average number of headache days of at least moderate severity during the 3-month treatment period.
In Study 3, a total of 235 patients (130 females, 105 males) were randomized. A total of 225 patients completed the 3-month, double-blind treatment period.
AJOVY demonstrated statistically significant improvements for efficacy endpoints compared to placebo over the 3-month period, as summarized in Table 5.
Study 3 Efficacy Endpoint | AJOVY (N=123) | Placebo (N=111 a ) |
| Monthly migraine days (MMD) | ||
| Baseline migraine days | 7.8 | 7.5 |
| Change from baseline | -2.5 | -1.4 |
| Difference from placebo | -1.0 | |
| p-value | 0.021 | |
| ≥50% MMD responders | ||
| % responders | 47.2% | 27.0% |
| Difference from placebo | 20.2% | |
| p-value | 0.002 | |
| Monthly acute headache medication days | ||
| Change from baseline | -2.1 | -1.0 |
| Difference from placebo | -1.1 | |
| p-value | 0.002 | |
| Monthly headache days of at least moderate severity | ||
| Change from baseline | -2.6 | -1.5 |
| Difference from placebo | -1.1 | |
| p-value | 0.017 | |
a One patient in the placebo group was excluded from the analysis due to not having at least 10 days of post-baseline efficacy data.
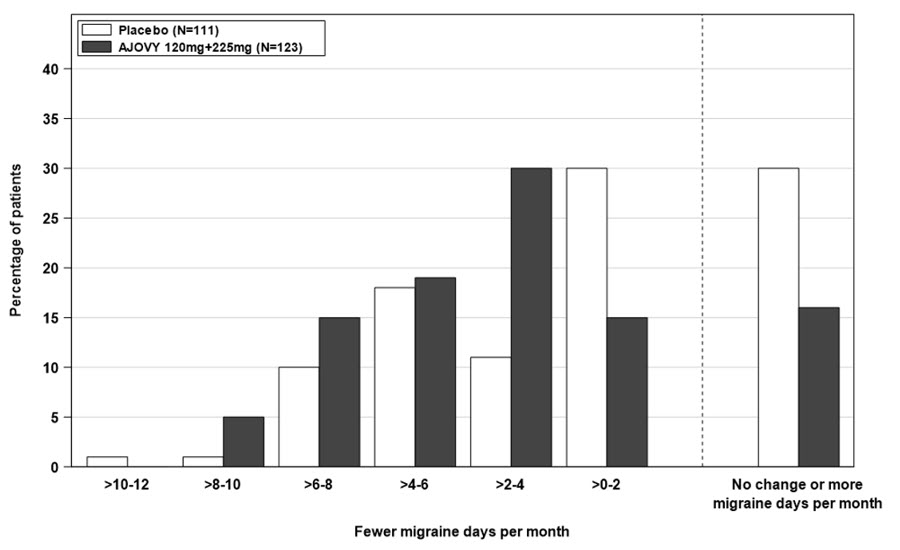
Figure 5 displays the mean change from baseline in the average monthly number of migraine days in Study 3.
Figure 5: Distribution of Change from Baseline in Mean Monthly Migraine Days by Placebo and Combined AJOVY Group (Full Analysis Set) in Study 3.
HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
How Supplied
AJOVY (fremanezumab-vfrm) injection is a sterile, preservative-free, clear to opalescent, colorless to slightly yellow solution for subcutaneous administration.
AJOVY is not made with natural rubber latex.
AJOVY is supplied as follows:
Prefilled Autoinjector
- Pack of 1 autoinjector: 225 mg/1.5 mL single-dose prefilled autoinjector NDC 51759-202-10
- Pack of 3 autoinjectors: 3 x 225 mg/1.5mL single-dose prefilled autoinjectors NDC 51759-202-22
Prefilled Syringe
- Pack of 1 syringe: 225 mg/1.5 mL single-dose prefilled syringe NDC 51759-204-10
Storage and Handling
- Store refrigerated at 2°C to 8°C (36°F to 46°F) in the original outer carton to protect from light.
- If necessary, AJOVY may be kept in the original carton at room temperature up to 30°C (86°F) for a maximum of 7 days. After removal from the refrigerator, AJOVY must be used within 7 days or discarded. Once stored at room temperature, do not place back in the refrigerator.
- Do not freeze.
- Do not expose to extreme heat or direct sunlight.
- Do not shake.
Instructions for Use
AJOVY ® (a-JO-vee) (fremanezumab-vfrm) injection prefilled autoinjector, for subcutaneous use
For subcutaneous injection only.
Read and follow the Instructions for Use for your AJOVY prefilled autoinjector before you start using it and each time you get a refill.
Important:
- AJOVY prefilled autoinjector is for single-time (one-time) use only. Put AJOVY in a FDA-cleared sharps disposal or puncture-resistant container right away after use. Do not throw away (dispose of) your used sharps disposal container in your household trash.
- Before injecting, let AJOVY sit at room temperature for 30 minutes.
- Keep AJOVY prefilled autoinjector out of the reach of small children.
- After you remove the protective cap from AJOVY, to prevent infection, do not touch the needle.
- Do not inject AJOVY in your veins (intravenously).
- Do not re-use your AJOVY prefilled autoinjector as this could cause injury or infection.
- Do not share your AJOVY prefilled autoinjector with another person. You may give another person an infection or get an infection from them.
You or your caregiver may give AJOVY. You should not get your first dose of AJOVY until you or your caregiver receive training from a healthcare provider on the right way to use AJOVY.
Storage Conditions:
- Store AJOVY in the refrigerator between 36°F to 46°F (2°C to 8°C).
- Keep AJOVY in the carton it comes in to protect from light.
- If needed, AJOVY may be stored at room temperature up to 86°F (30°C) in the carton it comes in for up to 7 days. Do not use AJOVY if it has been out of the refrigerator for 7 days or longer. Throw away (dispose of) AJOVY in a sharps disposal or puncture-resistant container if it has been out of the refrigerator for 7 days or longer. Once stored at room temperature, do not place back in the refrigerator.
- Do not freeze. If AJOVY freezes, throw it away in a sharps disposal container.
- Keep AJOVY out of extreme heat and direct sunlight.
Do not shake AJOVY.
AJOVY prefilled autoinjector (Before use). See Figure A.
Figure A
AJOVY prefilled autoinjector (After use). See Figure B.
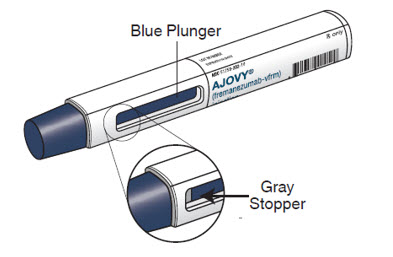
Figure B
- The blue plunger moves down the viewing window during the injection. The blue plunger fills the window when the injection is complete. Note : When the blue plunger has filled the viewing window you will still be able to see the gray stopper, as shown in Figure B.
- When injecting AJOVY, hold the prefilled autoinjector so that your hand does not cover the viewing window.
 Read this before you inject.
Read this before you inject.
Step 1. Check the dose your healthcare provider has prescribed.
AJOVY comes as a single-dose (one time) prefilled autoinjector. Your healthcare provider will prescribe the dose that is best for you.
- If your healthcare provider has prescribed 225 mg of AJOVY each month for you, give 1 injection each month, using a 225 mg prefilled AJOVY autoinjector.
- If your healthcare provider has prescribed 675 mg of AJOVY every 3 months for you, give 3 separate injections, one after another, using a different 225 mg prefilled AJOVY autoinjector for each injection. Give these injections 1 time every 3 months.
Before you inject, always check the label of your single-dose prefilled autoinjector to make sure you have the correct medicine and the correct dose of AJOVY. If you are not sure of your dose, ask your healthcare provider.
How do I inject AJOVY?
Step 2. Remove the prefilled autoinjector from the carton.
- You may need to use more than 1 prefilled autoinjector depending on your prescribed dose.
- Remove the autoinjector from the carton (see Figure C).
- Do not shake the prefilled autoinjector at any time, as this could affect the way the medicine works.
Important: If there are any unused autoinjectors left in the carton, put the carton and unused autoinjectors back in the refrigerator.
Figure C
Step 3. Gather the supplies you will need to inject AJOVY.
- Gather the following supplies (see Figure D) and the number of AJOVY 225 mg prefilled autoinjectors you will need to give your prescribed dose:
- If your dose is 225 mg, you will need 1 AJOVY 225 mg prefilled autoinjector.
- If your dose is 675 mg, you will need 3 AJOVY 225 mg prefilled autoinjectors.
- Alcohol swabs (not supplied).
- Gauze pads or cotton balls (not supplied).
- Sharps disposal or puncture-resistant container (not supplied).

Figure D
Step 4. Let AJOVY reach room temperature.
- Place the supplies you have gathered on a clean, flat surface.
- Wait for 30 minutes to allow the medicine to reach room temperature.
- Do not leave the prefilled autoinjector in direct sunlight.
- Do not warm up the AJOVY prefilled autoinjector using a heat source such as hot water or a microwave.

Step 5. Wash your hands.
- Wash your hands with soap and water and dry well with a clean towel. Be careful not to touch your face or hair after washing your hands.
Step 6. Look closely at your AJOVY prefilled autoinjector.
Note : You may see air bubbles in the prefilled autoinjector. This is normal. Do not remove the air bubbles from the prefilled autoinjector before giving your injection.
Injecting AJOVY with these air bubbles will not harm you.
|
|
|
|
|
|
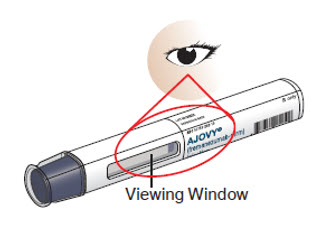
Figure E
Step 7: Choose your injection area.
- Choose an injection area from the following areas (see Figure F):
- your stomach area (abdomen), avoid about 2 inches around the belly button.
- the front of your thighs , an area that is at least 2 inches above the knee and 2 inches below the groin.
- the back of your upper arms , in the fleshy area of the upper back portion.
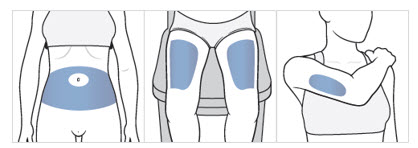
Figure F
Note : There are some injection areas on your body that are hard to reach (like the back of your arm). You may need help from someone who has been instructed on how to give your injection if you cannot reach certain injection areas.
Step 8. Clean your injection area.
- Clean the chosen injection area using a new alcohol swab. Let your skin dry.
- Do not inject AJOVY into an area that is tender, red, bruised, callused, tattooed, hard, or that has scars or stretch marks.
- Do not inject AJOVY in the same injection site that you inject other medicine.
- If you want to use the same injection area for the 3 separate injections needed for the 675 mg dose, make sure the second and third injections are not at the same spot you used for the other injections.
Step 9. Remove protective cap and do not replace.
- Pick up the prefilled autoinjector in 1 hand.
- Hold the prefilled autoinjector as shown in Figure G and pull the protective cap straight off with your other hand. Do not twist.
- Throw away the protective cap right away.
- Do not put the protective cap back on the prefilled autoinjector, to avoid injury and infection.
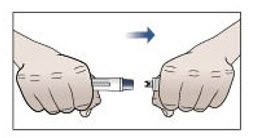
Figure G
Step 10. Give your injection.
- 10.1 Place the prefilled autoinjector at a 90 degree angle against your skin at the injection site you have cleaned (see Figure H).
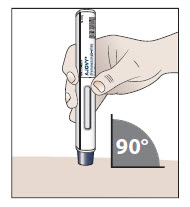
Figure H
10.2 Press down on the prefilled autoinjector and keep holding it down against the skin for about 30 seconds. Do not remove pressure until the 3 steps below are complete. | ||
| 1.000000000000000e+00 You hear the first “click” (this means the injection has started and the blue plunger starts to move). | 2.000000000000000e+00 You hear a second “click” (about 15 seconds after the first click. The plunger will be moving to the bottom of the viewing window as the medicine is being injected.) | 3.000000000000000e+00 You wait another 10 seconds. (to make sure all the medicine is injected). |
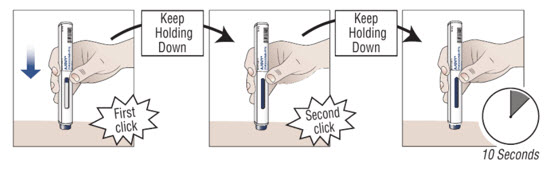 | ||
10.3 Check that the blue plunger has filled the viewing window and remove the autoinjector from the skin by lifting the prefilled autoinjector straight up (see Figure I) .
Note : When the blue plunger has filled the viewing window you will be able to see the gray stopper .
As the prefilled autoinjector is lifted from the skin, the needle shield returns to the original (before use) position and locks into place, covering the needle.
Do not try to put the protective cap back on the used prefilled autoinjector as it is no longer needed.
Do not try to re-use the prefilled autoinjector.
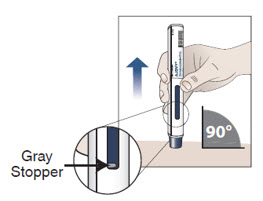
Figure I
Step 11. Apply pressure to the injection site.
- Use a clean, dry cotton ball, or gauze pad to gently press on the injection site for a few seconds.
- Do not rub the injection site.
- Do not re-use the prefilled autoinjector.
Step 12. Dispose of your prefilled autoinjector right away.

- Put your used prefilled autoinjectors in a FDA-cleared sharps disposal container right away after use.
- Do not throw away (dispose of) prefilled autoinjectors in your household trash. Do not recycle your used sharps disposal container.
- If you do not have a FDA-cleared sharps disposal container, you may use a household container that is:
- made of a heavy-duty plastic,
- can be closed with a tight-fitting, puncture-resistant lid, without sharps being able to come out,
- upright and stable during use,
- leak-resistant, and
- properly labeled to warn of hazardous waste inside the container.
- When your sharps disposal container is almost full, you will need to follow your community guidelines for the right way to dispose of your sharps disposal container. There may be state or local laws about how you should throw away used autoinjectors. For more information about safe sharps disposal, and for specific information about sharps disposal in the state that you live in, go to the FDA’s website at: http://www.fda.gov/safesharpsdisposal
- Do not dispose of your used sharps disposal container in your household trash unless your community guidelines permit this. Do not recycle your used sharps disposal container.
Injection Complete
This Instructions for Use has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
Manufactured by: Teva Pharmaceuticals USA, Inc. North Wales, PA 19454 US License No. 2016
© 2025 Teva Pharmaceuticals USA, Inc.
AJOIFU-AI-005 Revised: 8/2025
Mechanism of Action
Fremanezumab-vfrm is a humanized monoclonal antibody that binds to calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) ligand and blocks its binding to the receptor.