Get your patient on Braftovi (Encorafenib)
Braftovi prior authorization resources
Most recent state uniform prior authorization forms
Brand Resources
Braftovi patient education
Patient toolkit
Dosage & administration
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Melanoma
- Confirm the presence of BRAF V600E or V600K mutation in tumor specimens prior to the initiation of BRAFTOVI. (2.1 )
- The recommended dose is 450 mg orally once daily in combination with binimetinib. (2.2 )
CRC
- Confirm the presence of BRAF V600E mutation in plasma or tumor specimens prior to the initiation of BRAFTOVI. (2.1 )
- The recommended dose is 300 mg orally once daily in combination with
NSCLC
- Confirm the presence of BRAF V600E mutation in tumor or plasma specimens prior to initiating BRAFTOVI. (2.1 )
- The recommended dose is 450 mg orally once daily in combination with binimetinib. (2.2 )
Take BRAFTOVI with or without food. (2.4 )
Patient Selection
BRAF V600E or V600K Mutation-Positive Unresectable or Metastatic Melanoma
Confirm the presence of a BRAF V600E or V600K mutation in tumor specimens prior to initiating BRAFTOVI [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) , Clinical Studies (14.1) ] . Information on FDA-authorized tests for the detection of BRAF V600E and V600K mutations in melanoma is available at: http://www.fda.gov/CompanionDiagnostics .
BRAF V600E Mutation-Positive Metastatic Colorectal Cancer (CRC)
Confirm the presence of a BRAF V600E mutation in plasma or tumor tissue prior to initiating BRAFTOVI [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) , Clinical Studies (14.2 , 14.3) ]. If no mutation is detected in a plasma specimen, test tumor tissue. Information on FDA- authorized tests for the detection of BRAF V600E mutations in CRC is available at: http://www.fda.gov/CompanionDiagnostics .
BRAF V600E Mutation-Positive Metastatic Non‑Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC)
Confirm the presence of a BRAF V600E mutation in tumor or plasma specimens prior to initiating BRAFTOVI [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) , Clinical Studies (14.3) ] . If no mutation is detected in a plasma specimen, test tumor tissue. Information on FDA- authorized tests for the detection of BRAF V600E mutations in NSCLC is available at: http://www.fda.gov/CompanionDiagnostics .
Recommended Dosage for BRAF V600E or V600K Mutation-Positive Unresectable or Metastatic Melanoma and for BRAF V600E Mutation-Positive Metastatic Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC)
The recommended dosage of BRAFTOVI is 450 mg (six 75 mg capsules) orally once daily in combination with binimetinib until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity. Refer to the binimetinib prescribing information for recommended binimetinib dosing information.
Recommended Dosage for BRAF V600E Mutation-Positive Metastatic Colorectal Cancer (CRC)
The recommended dosage of BRAFTOVI is 300 mg (four 75 mg capsules) orally once daily until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity in combination with:
- biweekly cetuximab and mFOLFOX6 (fluorouracil, leucovorin and oxaliplatin) or biweekly cetuximab and FOLFIRI (fluorouracil, leucovorin and irinotecan) [see Clinical Studies (14.2) ]
- weekly cetuximab [see Clinical Studies (14.2) ].
Administration
BRAFTOVI may be taken with or without food [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ] . Do not take a missed dose of BRAFTOVI within 12 hours of the next dose of BRAFTOVI.
Do not take an additional dose if vomiting occurs after BRAFTOVI administration but continue with the next scheduled dose.
Dosage Modifications for Adverse Reactions
BRAF V600E or V600K Mutation-Positive Unresectable or Metastatic Melanoma or BRAF V600E Mutation-Positive Metastatic NSCLC
If binimetinib is withheld, reduce BRAFTOVI to a maximum dose of 300 mg (four 75 mg capsules) once daily until binimetinib is resumed [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9) ] .
Dose reductions for adverse reactions associated with BRAFTOVI are presented in Table 1.
Table 1: Recommended Dose Reductions for BRAFTOVI for Adverse Reactions – Melanoma or NSCLC
Action | Recommended Dose |
First dose reduction | 300 mg (four 75 mg capsules) orally once daily |
Second dose reduction | 225 mg (three 75 mg capsules) orally once daily |
Subsequent modification | Permanently discontinue if unable to tolerate BRAFTOVI 225 mg (three 75 mg capsules) once daily |
BRAF V600E Mutation-Positive Metastatic Colorectal Cancer (CRC)
When BRAFTOVI is administered in combination with cetuximab and mFOLFOX6 or FOLFIRI
- Continue BRAFTOVI with mFOLFOX6 or FOLFIRI if cetuximab is permanently discontinued.
- Permanently discontinue BRAFTOVI if cetuximab and mFOLFOX6 or FOLFIRI are permanently discontinued.
When BRAFTOVI is administered in combination with cetuximab
- Permanently discontinue BRAFTOVI when cetuximab is permanently discontinued.
Dose reductions for adverse reactions associated with BRAFTOVI are presented in Table 2.
Action | Recommended Dose |
First dose reduction | 225 mg (three 75 mg capsules) orally once daily |
Second dose reduction | 150 mg (two 75 mg capsules) orally once daily |
Subsequent modification | Permanently discontinue if unable to tolerate BRAFTOVI 150 mg (two 75 mg capsules) once daily |
BRAF V600E or V600K Mutation-Positive Unresectable or Metastatic Melanoma, BRAF V600E Mutation-Positive Metastatic Colorectal Cancer (CRC), or BRAF V600E Mutation-Positive NSCLC
Dosage modifications for adverse reactions associated with BRAFTOVI are presented in Table 3.
| Severity of Adverse Reaction National Cancer Institute Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (NCI CTCAE) version 4.03. | Dose Modification for BRAFTOVI |
|---|---|
New Primary Malignancies [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) ] | |
Noncutaneous RAS Mutation-positive Malignancies | Permanently discontinue BRAFTOVI. |
Cardiomyopathy [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3) ] | |
| Reduce BRAFTOVI by one dose level [see Dosage and Administration (2.3) ] .
|
Hepatotoxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4) ] | |
| Maintain BRAFTOVI dose.
|
| See Other Adverse Reactions . |
Uveitis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6) ] | |
| If Grade 1 or 2 does not respond to specific ocular therapy, or for Grade 3 uveitis, withhold BRAFTOVI for up to 6 weeks.
|
| Permanently discontinue BRAFTOVI. |
QTc Prolongation [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7) ] | |
| Withhold BRAFTOVI until QTcF less than or equal to 500 ms. Resume at reduced dose.
|
| Permanently discontinue BRAFTOVI. |
Dermatologic [Other than Hand-foot Skin Reaction (HFSR)] [see Adverse Reactions (6.1) ] | |
| If no improvement within 2 weeks, withhold BRAFTOVI until Grade 0–1. Resume at same dose. |
| Withhold BRAFTOVI until Grade 0–1. Resume at same dose if first occurrence or reduce dose if recurrent. |
| Permanently discontinue BRAFTOVI. |
Other Adverse Reactions (including Hemorrhage) [see Warnings and Precautions (5) ] and HFSR [see Adverse Reactions (6.1) ] Dose modification of BRAFTOVI when administered with binimetinib or with cetuximab is not recommended for new primary cutaneous malignancies; ocular events other than uveitis, iritis, and iridocyclitis; interstitial lung disease/pneumonitis; creatine phosphokinase (CPK) elevation; rhabdomyolysis; and venous thromboembolism. | |
| Withhold BRAFTOVI for up to 4 weeks.
|
| Permanently discontinue BRAFTOVI or
|
| Consider permanently discontinuing BRAFTOVI. |
| Permanently discontinue BRAFTOVI. |
Refer to the binimetinib or cetuximab prescribing information for dose modifications for adverse reactions associated with each product, as appropriate.
Dose Modifications for Coadministration with Strong or Moderate CYP3A4 Inhibitors
Avoid coadministration of BRAFTOVI with strong or moderate CYP3A4 inhibitors. If coadministration is unavoidable, reduce the BRAFTOVI dose according to the recommendations in Table 4. After the inhibitor has been discontinued for 3 to 5 elimination half-lives, resume the BRAFTOVI dose that was taken prior to initiating the CYP3A4 inhibitor [see Drug Interactions (7.1) , Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ] .
Current Daily Dose Current daily dose refers to recommended dose of BRAFTOVI based on indication or reductions for adverse reactions based on dosing recommendations in Table 1 (Melanoma) and Table 2 (CRC). | Dose for Coadministration with Moderate CYP3A4 Inhibitor | Dose for Coadministration with Strong CYP3A4 Inhibitor |
450 mg | 225 mg (three 75 mg capsules) | 150 mg (two 75 mg capsules) |
300 mg | 150 mg (two 75 mg capsules) | 75 mg |
225 mg | 75 mg | 75 mg |
150 mg | 75 mg | 75 mg Encorafenib exposure at the 75 mg QD BRAFTOVI dosage when coadministered with a strong CYP3A4 inhibitor is expected to be higher than at the 150 mg QD dosage in the absence of a CYP3A4 inhibitor and similar to exposure at the 225 mg QD dosage in the absence of a CYP3A4 inhibitor. Monitor patients closely for adverse reactions and use clinical judgment when using BRAFTOVI with strong CYP3A4 inhibitors at the 150 mg dose level. |

Braftovi prescribing information
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
BRAFTOVI is a kinase inhibitor indicated:
Melanoma
- in combination with binimetinib, for the treatment of patients with unresectable or metastatic melanoma with a BRAF V600E or V600K mutation, as detected by an FDA-authorized test. (1.1 , 2.1 )
Colorectal Cancer (CRC)
- in combination with cetuximab and fluorouracil-based chemotherapy, for the treatment of adult patients with metastatic colorectal cancer (mCRC) with a BRAF V600E mutation, as detected by an FDA‑authorized test. (1.2 , 2.1 )
- in combination with cetuximab, for the treatment of adult patients with mCRC with a BRAF V600E mutation, as detected by an FDA-authorized test, after prior therapy. (1.2 , 2.1 )
Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC)
- in combination with binimetinib, for the treatment of adult patients with metastatic non–small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) with a BRAF V600E mutation, as detected by an FDA-authorized test. (1.3 , 2.1 )
Limitations of Use
BRAFTOVI is not indicated for treatment of patients with wild-type BRAF melanoma, wild-type BRAF CRC, or wild-type BRAF NSCLC. (1.4 , 5.2 )
BRAF V600E or V600K Mutation–Positive Unresectable or Metastatic Melanoma
BRAFTOVI is indicated, in combination with binimetinib, for the treatment of patients with unresectable or metastatic melanoma with a BRAF V600E or V600K mutation, as detected by an FDA-authorized test [see Dosage and Administration (2.1) ] .
BRAF V600E Mutation-Positive Metastatic Colorectal Cancer (mCRC)
- BRAFTOVI is indicated, in combination with cetuximab and fluorouracil-based chemotherapy , for the treatment of adult patients with metastatic colorectal cancer (mCRC) with a BRAF V600E mutation, as detected by an FDA- authorized test [see Dosage and Administration (2.1) ].
- BRAFTOVI is indicated, in combination with cetuximab, for the treatment of adult patients with mCRC with a BRAF V600E mutation, as detected by an FDA- authorized test, after prior therapy [see Dosage and Administration (2.1) ].
BRAF V600E Mutation-Positive Metastatic Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC)
BRAFTOVI is indicated, in combination with binimetinib, for the treatment of adult patients with metastatic non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) with a BRAF V600E mutation, as detected by an FDA-authorized test [see Dosage and Administration (2.1) ] .
Limitations of Use
BRAFTOVI is not indicated for treatment of patients with wild-type BRAF melanoma, wild-type BRAF CRC, or wild-type BRAF NSCLC [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)] .
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Melanoma
- Confirm the presence of BRAF V600E or V600K mutation in tumor specimens prior to the initiation of BRAFTOVI. (2.1 )
- The recommended dose is 450 mg orally once daily in combination with binimetinib. (2.2 )
CRC
- Confirm the presence of BRAF V600E mutation in plasma or tumor specimens prior to the initiation of BRAFTOVI. (2.1 )
- The recommended dose is 300 mg orally once daily in combination with
NSCLC
- Confirm the presence of BRAF V600E mutation in tumor or plasma specimens prior to initiating BRAFTOVI. (2.1 )
- The recommended dose is 450 mg orally once daily in combination with binimetinib. (2.2 )
Take BRAFTOVI with or without food. (2.4 )
Patient Selection
BRAF V600E or V600K Mutation-Positive Unresectable or Metastatic Melanoma
Confirm the presence of a BRAF V600E or V600K mutation in tumor specimens prior to initiating BRAFTOVI [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) , Clinical Studies (14.1) ] . Information on FDA-authorized tests for the detection of BRAF V600E and V600K mutations in melanoma is available at: http://www.fda.gov/CompanionDiagnostics .
BRAF V600E Mutation-Positive Metastatic Colorectal Cancer (CRC)
Confirm the presence of a BRAF V600E mutation in plasma or tumor tissue prior to initiating BRAFTOVI [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) , Clinical Studies (14.2 , 14.3) ]. If no mutation is detected in a plasma specimen, test tumor tissue. Information on FDA- authorized tests for the detection of BRAF V600E mutations in CRC is available at: http://www.fda.gov/CompanionDiagnostics .
BRAF V600E Mutation-Positive Metastatic Non‑Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC)
Confirm the presence of a BRAF V600E mutation in tumor or plasma specimens prior to initiating BRAFTOVI [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) , Clinical Studies (14.3) ] . If no mutation is detected in a plasma specimen, test tumor tissue. Information on FDA- authorized tests for the detection of BRAF V600E mutations in NSCLC is available at: http://www.fda.gov/CompanionDiagnostics .
Recommended Dosage for BRAF V600E or V600K Mutation-Positive Unresectable or Metastatic Melanoma and for BRAF V600E Mutation-Positive Metastatic Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC)
The recommended dosage of BRAFTOVI is 450 mg (six 75 mg capsules) orally once daily in combination with binimetinib until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity. Refer to the binimetinib prescribing information for recommended binimetinib dosing information.
Recommended Dosage for BRAF V600E Mutation-Positive Metastatic Colorectal Cancer (CRC)
The recommended dosage of BRAFTOVI is 300 mg (four 75 mg capsules) orally once daily until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity in combination with:
- biweekly cetuximab and mFOLFOX6 (fluorouracil, leucovorin and oxaliplatin) or biweekly cetuximab and FOLFIRI (fluorouracil, leucovorin and irinotecan) [see Clinical Studies (14.2) ]
- weekly cetuximab [see Clinical Studies (14.2) ].
Administration
BRAFTOVI may be taken with or without food [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ] . Do not take a missed dose of BRAFTOVI within 12 hours of the next dose of BRAFTOVI.
Do not take an additional dose if vomiting occurs after BRAFTOVI administration but continue with the next scheduled dose.
Dosage Modifications for Adverse Reactions
BRAF V600E or V600K Mutation-Positive Unresectable or Metastatic Melanoma or BRAF V600E Mutation-Positive Metastatic NSCLC
If binimetinib is withheld, reduce BRAFTOVI to a maximum dose of 300 mg (four 75 mg capsules) once daily until binimetinib is resumed [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9) ] .
Dose reductions for adverse reactions associated with BRAFTOVI are presented in Table 1.
Table 1: Recommended Dose Reductions for BRAFTOVI for Adverse Reactions – Melanoma or NSCLC
Action | Recommended Dose |
First dose reduction | 300 mg (four 75 mg capsules) orally once daily |
Second dose reduction | 225 mg (three 75 mg capsules) orally once daily |
Subsequent modification | Permanently discontinue if unable to tolerate BRAFTOVI 225 mg (three 75 mg capsules) once daily |
BRAF V600E Mutation-Positive Metastatic Colorectal Cancer (CRC)
When BRAFTOVI is administered in combination with cetuximab and mFOLFOX6 or FOLFIRI
- Continue BRAFTOVI with mFOLFOX6 or FOLFIRI if cetuximab is permanently discontinued.
- Permanently discontinue BRAFTOVI if cetuximab and mFOLFOX6 or FOLFIRI are permanently discontinued.
When BRAFTOVI is administered in combination with cetuximab
- Permanently discontinue BRAFTOVI when cetuximab is permanently discontinued.
Dose reductions for adverse reactions associated with BRAFTOVI are presented in Table 2.
Action | Recommended Dose |
First dose reduction | 225 mg (three 75 mg capsules) orally once daily |
Second dose reduction | 150 mg (two 75 mg capsules) orally once daily |
Subsequent modification | Permanently discontinue if unable to tolerate BRAFTOVI 150 mg (two 75 mg capsules) once daily |
BRAF V600E or V600K Mutation-Positive Unresectable or Metastatic Melanoma, BRAF V600E Mutation-Positive Metastatic Colorectal Cancer (CRC), or BRAF V600E Mutation-Positive NSCLC
Dosage modifications for adverse reactions associated with BRAFTOVI are presented in Table 3.
| Severity of Adverse Reaction National Cancer Institute Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (NCI CTCAE) version 4.03. | Dose Modification for BRAFTOVI |
|---|---|
New Primary Malignancies [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) ] | |
Noncutaneous RAS Mutation-positive Malignancies | Permanently discontinue BRAFTOVI. |
Cardiomyopathy [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3) ] | |
| Reduce BRAFTOVI by one dose level [see Dosage and Administration (2.3) ] .
|
Hepatotoxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4) ] | |
| Maintain BRAFTOVI dose.
|
| See Other Adverse Reactions . |
Uveitis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6) ] | |
| If Grade 1 or 2 does not respond to specific ocular therapy, or for Grade 3 uveitis, withhold BRAFTOVI for up to 6 weeks.
|
| Permanently discontinue BRAFTOVI. |
QTc Prolongation [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7) ] | |
| Withhold BRAFTOVI until QTcF less than or equal to 500 ms. Resume at reduced dose.
|
| Permanently discontinue BRAFTOVI. |
Dermatologic [Other than Hand-foot Skin Reaction (HFSR)] [see Adverse Reactions (6.1) ] | |
| If no improvement within 2 weeks, withhold BRAFTOVI until Grade 0–1. Resume at same dose. |
| Withhold BRAFTOVI until Grade 0–1. Resume at same dose if first occurrence or reduce dose if recurrent. |
| Permanently discontinue BRAFTOVI. |
Other Adverse Reactions (including Hemorrhage) [see Warnings and Precautions (5) ] and HFSR [see Adverse Reactions (6.1) ] Dose modification of BRAFTOVI when administered with binimetinib or with cetuximab is not recommended for new primary cutaneous malignancies; ocular events other than uveitis, iritis, and iridocyclitis; interstitial lung disease/pneumonitis; creatine phosphokinase (CPK) elevation; rhabdomyolysis; and venous thromboembolism. | |
| Withhold BRAFTOVI for up to 4 weeks.
|
| Permanently discontinue BRAFTOVI or Withhold BRAFTOVI for up to 4 weeks.
|
| Consider permanently discontinuing BRAFTOVI. |
| Permanently discontinue BRAFTOVI. |
Refer to the binimetinib or cetuximab prescribing information for dose modifications for adverse reactions associated with each product, as appropriate.
Dose Modifications for Coadministration with Strong or Moderate CYP3A4 Inhibitors
Avoid coadministration of BRAFTOVI with strong or moderate CYP3A4 inhibitors. If coadministration is unavoidable, reduce the BRAFTOVI dose according to the recommendations in Table 4. After the inhibitor has been discontinued for 3 to 5 elimination half-lives, resume the BRAFTOVI dose that was taken prior to initiating the CYP3A4 inhibitor [see Drug Interactions (7.1) , Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ] .
Current Daily Dose Current daily dose refers to recommended dose of BRAFTOVI based on indication or reductions for adverse reactions based on dosing recommendations in Table 1 (Melanoma) and Table 2 (CRC). | Dose for Coadministration with Moderate CYP3A4 Inhibitor | Dose for Coadministration with Strong CYP3A4 Inhibitor |
450 mg | 225 mg (three 75 mg capsules) | 150 mg (two 75 mg capsules) |
300 mg | 150 mg (two 75 mg capsules) | 75 mg |
225 mg | 75 mg | 75 mg |
150 mg | 75 mg | 75 mg Encorafenib exposure at the 75 mg QD BRAFTOVI dosage when coadministered with a strong CYP3A4 inhibitor is expected to be higher than at the 150 mg QD dosage in the absence of a CYP3A4 inhibitor and similar to exposure at the 225 mg QD dosage in the absence of a CYP3A4 inhibitor. Monitor patients closely for adverse reactions and use clinical judgment when using BRAFTOVI with strong CYP3A4 inhibitors at the 150 mg dose level. |
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Capsules: 75 mg, hard gelatin, stylized "A" on beige cap and "LGX 75mg" on white body.
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
Pregnancy
Risk Summary
Based on its mechanism of action, BRAFTOVI can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.1) ] . There are no available clinical data on the use of BRAFTOVI during pregnancy. In animal reproduction studies, encorafenib produced embryo-fetal developmental changes in rats and rabbits and was an abortifacient in rabbits at doses greater than or equal to those resulting in exposures approximately 26 (in the rat) and 178 (in the rabbit) times the human exposure at the clinical dose of 450 mg, with no clear findings at lower doses (see Data ) . Advise pregnant women and females of reproductive potential of the potential risk to a fetus.
In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2% to 4% and 15% to 20%, respectively.
Data
Animal Data
In reproductive toxicity studies, administration of encorafenib to rats during the period of organogenesis resulted in maternal toxicity, decreased fetal weights, and increased incidence of total skeletal variations at a dose of 20 mg/kg/day (approximately 26 times the human exposure based on area under the concentration-time curve [AUC] at the recommended clinical dose of 450 mg once daily). In pregnant rabbits, administration of encorafenib during the period of organogenesis resulted in maternal toxicity, decreased fetal body weights, increased incidence of total skeletal variations and increased post-implantation loss, including total loss of pregnancy at a dose of 75 mg/kg/day (approximately 178 times the human exposure based on AUC at the recommended clinical dose of 450 mg once daily). While formal placental transfer studies have not been performed, encorafenib exposure in the fetal plasma of both rats and rabbits was up to 1.7% and 0.8%, respectively, of maternal exposure.
Lactation
Risk Summary
There are no data on the presence of encorafenib or its metabolites in human milk or the effects of encorafenib on the breastfed child, or the effects on milk production. Because of the potential for serious adverse reactions in a breastfed child from BRAFTOVI, advise women not to breastfeed during treatment with BRAFTOVI and for 2 weeks after the last dose.
Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
BRAFTOVI can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1) ] .
Pregnancy Testing
Verify the pregnancy status of females of reproductive potential prior to initiating BRAFTOVI [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1) ].
Contraception
Females
Advise females of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with BRAFTOVI and for 2 weeks after the last dose. Counsel patients to use a nonhormonal method of contraception since BRAFTOVI has the potential to render hormonal contraceptives ineffective [see Drug Interactions (7.2) ] .
Infertility
Males
Based on findings in male rats at doses approximately 13 times the human exposure at the 450 mg clinical dose, use of BRAFTOVI may impact fertility in males [see Nonclinical Toxicology (13.1) ] .
Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of BRAFTOVI have not been established in pediatric patients.
Geriatric Use
Of the 690 patients with BRAF mutation-positive melanoma who received BRAFTOVI in combination with binimetinib across multiple clinical trials, 20% were aged 65 to 74 years and 8% were aged 75 years and older [see Clinical Studies (14.1) ] .
Of the 232 patients with BRAF V600E mutation-positive metastatic CRC who received BRAFTOVI in combination with cetuximab and mFOLFOX6, 84 (36%) were 65 years of age and over and 16 (7%) were 75 years of age and over [see Clinical Studies (14.2) ] .
Of the 71 patients with BRAF V600E mutation-positive metastatic CRC who received BRAFTOVI in combination with cetuximab and FOLFIRI, 35 (49%) were 65 years of age and over and 9 (13%) were 75 years of age and over [see Clinical Studies (14.2) ] .
Of the 216 patients with BRAF V600E mutation-positive metastatic CRC who received BRAFTOVI in combination with cetuximab, 62 (29%) were 65 years of age to up to 75 years of age, while 20 (9%) were 75 years of age and over [see Clinical Studies (14.2) ] .
Of the 98 patients with BRAF V600E mutation-positive metastatic NSCLC who received BRAFTOVI with binimetinib, 62 (63%) were 65 years of age and over and 20 (20%) were 75 years and over [see Clinical Studies (14.3) ] .
No overall differences in the safety or effectiveness of BRAFTOVI plus binimetinib, BRAFTOVI plus cetuximab, or BRAFTOVI plus cetuximab and mFOLFOX6 or FOLFIRI were observed in older patients as compared to younger patients.
Hepatic Impairment
No BRAFTOVI dosage adjustment is recommended in patients with mild hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh Class A) [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ] . A recommended dosage has not been established in patients with moderate (Child-Pugh Class B) or severe (Child-Pugh Class C) hepatic impairment.
Renal Impairment
No BRAFTOVI dosage adjustment is recommended in patients with mild to moderate renal impairment (CLcr 30 to <90 mL/min) [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ] . A recommended dosage has not been established in patients with severe renal impairment (CLcr <30 mL/min).
CONTRAINDICATIONS
None.
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- New Primary Malignancies, cutaneous and noncutaneous : Can occur. Monitor for malignancies and perform dermatologic evaluations prior to, while on therapy, and following discontinuation of treatment. (5.1 )
- Tumor Promotion in BRAF Wild-Type Tumors : Increased cell proliferation can occur with BRAF inhibitors. (5.2 )
- Cardiomyopathy : Assess left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) before initiating treatment with BRAFTOVI and binimetinib, and after one month of treatment, then every 2 to 3 months thereafter. The safety of BRAFTOVI in combination with binimetinib has not been established in patients with LVEF below 50%. (5.3 )
- Hepatotoxicity : Monitor liver function tests before and during treatment with BRAFTOVI and binimetinib and as clinically indicated. (5.4 )
- Hemorrhage : Major hemorrhagic events can occur in patients receiving BRAFTOVI and binimetinib. (5.5 )
- Uveitis : Perform ophthalmologic evaluation at regular intervals and for any visual disturbances. (5.6 )
- QT Prolongation : Monitor electrolytes before and during treatment. Correct electrolyte abnormalities and control for cardiac risk factors for QT prolongation. Withhold BRAFTOVI for QTc of 500 ms or greater. (5.7 )
- Embryo-Fetal Toxicity : Can cause fetal harm. Advise females with reproductive potential of potential risk to the fetus and to use effective nonhormonal method of contraception. (5.8 , 8.1 , 8.3 )
- Risks Associated with BRAFTOVI as a Single Agent : If binimetinib is temporarily interrupted or permanently discontinued, reduce the dose of BRAFTOVI as recommended. (5.9 )
- Risks Associated with Combination Treatment : BRAFTOVI is indicated for use as part of a regimen in combination with binimetinib or cetuximab. (5.10 )
New Primary Malignancies
New primary malignancies, cutaneous and noncutaneous, have been observed in patients treated with BRAF inhibitors and can occur with BRAFTOVI.
Cutaneous Malignancies
In COLUMBUS, cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma (cuSCC), including keratoacanthoma (KA), occurred in 2.6%, and basal cell carcinoma occurred in 1.6% of patients who received BRAFTOVI in combination with binimetinib. Median time to first occurrence of cuSCC/KA was 5.8 months (range 1 to 9 months) [see Adverse Reactions (6.1) ] .
For patients who received BRAFTOVI as a single agent, cuSCC/KA was reported in 8%, basal cell carcinoma in 1%, and a new primary melanoma in 5% of patients.
In BEACON CRC, cuSCC/KA occurred in 1.4% of patients with CRC, and a new primary melanoma occurred in 1.4% of patients who received BRAFTOVI in combination with cetuximab.
In PHAROS, cuSCC and skin papilloma, each occurred in 2% of patients who received BRAFTOVI in combination with binimetinib.
In BREAKWATER, the following cutaneous malignancies occurred in patients receiving BRAFTOVI in combination with cetuximab and mFOLFOX6: melanocytic nevus in 5.6%, skin papilloma in 3% , basal cell carcinoma in 1.3%, squamous cell carcinoma of skin in 0.9%, keratoacanthoma in 0.4% and malignant melanoma in situ in 0.4%. In patients who received BRAFTOVI in combination with cetuximab and FOLFIRI, skin papilloma occurred in 2.8% and keratoacanthoma in 1.4% of patients.
Perform dermatologic evaluations prior to initiating treatment, every 2 months during treatment, and for up to 6 months following discontinuation of treatment. Manage suspicious skin lesions with excision and dermatopathologic evaluation. Dose modification is not recommended for new primary cutaneous malignancies.
Noncutaneous Malignancies
Based on its mechanism of action, BRAFTOVI may promote malignancies associated with activation of RAS through mutation or other mechanisms [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) ] . Monitor patients receiving BRAFTOVI for signs and symptoms of noncutaneous malignancies. Discontinue BRAFTOVI for RAS mutation-positive noncutaneous malignancies [see Dosage and Administration (2.5) ] .
Tumor Promotion in BRAF Wild-Type Tumors
In vitro experiments have demonstrated paradoxical activation of MAP-kinase signaling and increased cell proliferation in BRAF wild-type cells, which are exposed to BRAF inhibitors. Confirm evidence of BRAF V600E or V600K mutation prior to initiating BRAFTOVI [see Indications and Usage (1) , Dosage and Administration (2.1) ] .
Cardiomyopathy
Cardiomyopathy, manifesting as left ventricular dysfunction associated with symptomatic or asymptomatic decreases in ejection fraction, has been reported in patients treated with BRAFTOVI in combination with binimetinib. In COLUMBUS, evidence of cardiomyopathy (decreased in LVEF below the institutional LLN with an absolute decreased in LVEF ≥10% below baseline as detected by echocardiography or MUGA) occurred in 7% of patients receiving BRAFTOVI plus binimetinib. Grade 3 left ventricular dysfunction occurred in 1.6% of patients. The median time to first occurrence of left ventricular dysfunction (any grade) in patients receiving BRAFTOVI in combination with binimetinib was 3.6 months (range 0 to 21 months). Cardiomyopathy resolved in 87% of patients receiving BRAFTOVI plus binimetinib.
In PHAROS, evidence of cardiomyopathy (decrease in LVEF below the institutional LLN with an absolute decrease in LVEF ≥10% below baseline as detected by echocardiography or MUGA) occurred in 11% of patients receiving BRAFTOVI in combination with binimetinib. Grade 3 left ventricular dysfunction occurred in 1% of patients. Cardiomyopathy resolved in 82% of patients receiving BRAFTOVI plus binimetinib.
Assess ejection fraction by echocardiogram or MUGA scan prior to initiating treatment, one month after initiating treatment, and every 2 to 3 months during treatment. The safety of BRAFTOVI in combination with binimetinib has not been established in patients with baseline ejection fraction that is either below 50% or below the institutional lower limit of normal (LLN). Patients with cardiovascular risk factors should be monitored closely when treated with BRAFTOVI.
Withhold, reduce dose, or permanently discontinue based on severity of adverse reaction [see Dosage and Administration (2.3) , Adverse Reactions (6.1) ] .
Hepatotoxicity
Hepatotoxicity can occur when BRAFTOVI is administered in combination with binimetinib. In COLUMBUS, the incidence of Grade 3 or 4 increases in liver function laboratory tests in patients receiving BRAFTOVI in combination with binimetinib was 6% for alanine aminotransferase (ALT), 2.6% for aspartate aminotransferase (AST), and 0.5% for alkaline phosphatase. In PHAROS, the incidence of Grade 3 or 4 increases in liver function laboratory tests in patients receiving BRAFTOVI in combination with binimetinib was 10% for AST, 9% for ALT, and 3.2% for alkaline phosphatase.
In BREAKWATER, the incidence of Grade 3 or 4 increases in liver function laboratory tests in patients receiving BRAFTOVI in combination with cetuximab and mFOLFOX6 was 2.6% for alkaline phosphatase, and 1.3% each for ALT and AST. In patients receiving BRAFTOVI in combination with cetuximab and FOLFIRI, the incidence of Grade 3 or 4 increases in liver function laboratory tests was 1.5% each for ALT and AST.
Monitor liver laboratory tests before initiation of BRAFTOVI, monthly during treatment, and as clinically indicated. Withhold, reduce dose, or permanently discontinue based on severity of adverse reaction [see Dosage and Administration (2.3) , Adverse Reactions (6.1) ] .
Hemorrhage
In COLUMBUS, hemorrhage occurred in 19% of patients receiving BRAFTOVI in combination with binimetinib; Grade 3 or greater hemorrhage occurred in 3.2% of patients. The most frequent hemorrhagic events were gastrointestinal, including rectal hemorrhage (4.2%), hematochezia (3.1%), and hemorrhoidal hemorrhage (1%). Fatal intracranial hemorrhage in the setting of new or progressive brain metastases occurred in 1.6% of patients.
In BEACON CRC, hemorrhage occurred in 19% of patients receiving BRAFTOVI in combination with cetuximab; Grade 3 or higher hemorrhage occurred in 1.9% of patients, including fatal gastrointestinal hemorrhage in 0.5% of patients. The most frequent hemorrhagic events were epistaxis (6.9%), hematochezia (2.3%), and rectal hemorrhage (2.3%).
In PHAROS, hemorrhage occurred in 12% of patients receiving BRAFTOVI in combination with binimetinib including fatal hemorrhage intracranial (1%); Grade 3 or 4 hemorrhage occurred in 4.1% of patients. The most frequent hemorrhagic events were anal hemorrhage and hemothorax (2% each).
In BREAKWATER, hemorrhage occurred in 34 % of patients receiving BRAFTOVI in combination with cetuximab and mFOLFOX6; Grade 3 or 4 hemorrhage occurred in 3% of patients. In patients receiving BRAFTOVI in combination with cetuximab and FOLFIRI, hemorrhage occurred in 21% of patients.
Withhold, reduce dose, or permanently discontinue based on severity of adverse reaction [see Dosage and Administration (2.5) , Adverse Reactions (6.1) ] .
Uveitis
Uveitis, including iritis and iridocyclitis, has been reported in patients treated with BRAFTOVI in combination with binimetinib. In COLUMBUS, the incidence of uveitis among patients treated with BRAFTOVI in combination with binimetinib was 4%. In PHAROS, the incidence of uveitis among patients treated with BRAFTOVI in combination with binimetinib was 1%. In BREAKWATER, the incidence of uveitis among patients who received BRAFTOVI in combination with cetuximab and mFOLFOX6 was 0.4%.
Assess for visual symptoms at each visit. Perform an ophthalmologic evaluation at regular intervals and for new or worsening visual disturbances, and to follow new or persistent ophthalmologic findings. Withhold, reduce dose, or permanently discontinue based on severity of adverse reaction [see Dosage and Administration (2.5) , Adverse Reactions (6.1) ] .
QT Prolongation
BRAFTOVI is associated with dose-dependent QTc interval prolongation in some patients [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.2) ] . In COLUMBUS, an increase in QTcF to >500 ms was measured in 0.5% (1/192) of patients who received BRAFTOVI in combination with binimetinib. In PHAROS, an increase in QTcF to >500 ms was measured in 2.1% (2/95) of patients who received BRAFTOVI in combination with binimetinib.
In BREAKWATER, an increase of QTcF >500 ms was measured in 4% (9/226) of patients receiving BRAFTOVI in combination with cetuximab and mFOLFOX6. In patients receiving BRAFTOVI in combination with cetuximab and FOLFIRI, an increase of QTcF >500 ms was measured in 1.5% (1/65) of patients.
Monitor patients who already have or who are at significant risk of developing QTc prolongation, including patients with known long QT syndromes, clinically significant bradyarrhythmias, severe or uncontrolled heart failure and those taking other medicinal products associated with QT prolongation. Correct hypokalemia and hypomagnesemia prior to and during BRAFTOVI administration. Withhold, reduce dose, or permanently discontinue for QTc >500 ms [see Dosage and Administration (2.5) , Adverse Reactions (6.1) ] .
Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
Based on its mechanism of action, BRAFTOVI can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. Encorafenib produced embryo-fetal developmental changes in rats and rabbits and was an abortifacient in rabbits at doses greater than or equal to those resulting in exposures approximately 26 (in the rat) and 178 (in the rabbit) times the human exposure at the recommended dose of 450 mg, with no clear findings at lower doses.
Advise pregnant women and females of reproductive potential of the potential risk to a fetus. Advise females of reproductive potential to use an effective, nonhormonal method of contraception since BRAFTOVI can render hormonal contraceptives ineffective, during treatment and for 2 weeks after the last dose of BRAFTOVI [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1 , 8.3) ] .
Risks Associated with BRAFTOVI as a Single Agent
BRAFTOVI when used as a single agent is associated with an increased risk of certain adverse reactions compared to when BRAFTOVI is used in combination with binimetinib. In COLUMBUS, Grades 3 or 4 dermatologic reactions occurred in 21% of patients treated with BRAFTOVI single agent compared to 2% of patients treated with BRAFTOVI in combination with binimetinib [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) , Adverse Reactions (6.1) ] .
If binimetinib is temporarily interrupted or permanently discontinued, reduce the dose of BRAFTOVI as recommended [see Dosage and Administration (2.5) ] .
Risks Associated with Combination Treatment
BRAFTOVI is indicated for use as part of a regimen in combination with binimetinib, in combination with cetuximab, in combination with cetuximab and mFOLFOX6 or FOLFIRI . Refer to the prescribing information for binimetinib, cetuximab and individual product components of mFOLFOX6 and FOLFIRI for additional risk information.
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following adverse reactions are described elsewhere in the labeling:
- New Primary Malignancies [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) ]
- Tumor Promotion in BRAF Wild-Type Tumors [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) ]
- Cardiomyopathy [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3) ]
- Hepatotoxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4) ]
- Hemorrhage [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5) ]
- Uveitis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6) ]
- QT Prolongation [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7) ]
- Embryo-Fetal Toxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8) ]
- Risks Associated with BRAFTOVI as a Single Agent [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9) ]
- Risks Associated with Combination Treatment [see Warnings and Precautions (5.10) ]
Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
BRAF V600E or V600K Mutation-Positive Unresectable or Metastatic Melanoma
The safety of BRAFTOVI in combination with binimetinib is described in 192 patients with BRAF V600 mutation-positive unresectable or metastatic melanoma who received BRAFTOVI (450 mg once daily) in combination with binimetinib (45 mg twice daily) in a randomized open-label, active-controlled trial (COLUMBUS).
The COLUMBUS trial [see Clinical Studies (14.1) ] excluded patients with a history of Gilbert's syndrome, abnormal left ventricular ejection fraction, prolonged QTc (>480 ms), uncontrolled hypertension, and history or current evidence of retinal vein occlusion. The median duration of exposure was 11.8 months for patients treated with BRAFTOVI in combination with binimetinib and 6.2 months for patients treated with vemurafenib.
The most common (≥25%) adverse reactions in patients receiving BRAFTOVI in combination with binimetinib were fatigue, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, and arthralgia.
Adverse reactions leading to dose interruptions of BRAFTOVI occurred in 30% of patients receiving BRAFTOVI in combination with binimetinib; the most common were nausea (7%), vomiting (7%), and pyrexia (4%). Adverse reactions leading to dose reductions of BRAFTOVI occurred in 14% of patients receiving BRAFTOVI in combination with binimetinib; the most common were arthralgia (2%), fatigue (2%), and nausea (2%). Five percent (5%) of patients receiving BRAFTOVI in combination with binimetinib experienced an adverse reaction that resulted in permanent discontinuation of BRAFTOVI; the most common were hemorrhage in 2% and headache in 1% of patients.
Table 5 and Table 6 present adverse drug reactions and laboratory abnormalities, respectively, identified in COLUMBUS. The COLUMBUS trial was not designed to demonstrate a statistically significant difference in adverse reaction rates for BRAFTOVI in combination with binimetinib, as compared to vemurafenib, for any specific adverse reaction listed in Table 5.
Adverse Reaction | BRAFTOVI with binimetinib N=192 | Vemurafenib N=186 | ||
All Grades (%) | Grades 3 and 4 Grade 4 adverse reactions limited to fatigue (n=1), pruritus (n=1), and rash (n=1) in the BRAFTOVI with binimetinib arm. (%) | All Grades (%) | Grades 3 and 4 (%) | |
General Disorders and Administration Site Conditions | ||||
Fatigue Represents a composite of multiple, related preferred terms. | 43 | 3 | 46 | 6 |
Pyrexia | 18 | 4 | 30 | 0 |
Gastrointestinal Disorders | ||||
Nausea | 41 | 2 | 34 | 2 |
Vomiting | 30 | 2 | 16 | 1 |
Abdominal pain | 28 | 4 | 16 | 1 |
Constipation | 22 | 0 | 6 | 1 |
Musculoskeletal and Connective Tissue Disorders | ||||
Arthralgia | 26 | 1 | 46 | 6 |
Myopathy | 23 | 0 | 22 | 1 |
Pain in extremity | 11 | 1 | 13 | 1 |
Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue Disorders | ||||
Hyperkeratosis | 23 | 1 | 49 | 1 |
Rash | 22 | 1 | 53 | 13 |
Dry skin | 16 | 0 | 26 | 0 |
Alopecia | 14 | 0 | 38 | 0 |
Pruritus | 13 | 1 | 21 | 1 |
Nervous System Disorders | ||||
Headache | 22 | 2 | 20 | 1 |
Dizziness | 15 | 3 | 4 | 0 |
Peripheral neuropathy | 12 | 1 | 13 | 2 |
Vascular Disorders | ||||
Hemorrhage | 19 | 3 | 9 | 2 |
BRAFTOVI when used as a single agent increases the risk of certain adverse reactions compared to BRAFTOVI in combination with binimetinib. In patients receiving BRAFTOVI 300 mg orally once daily as a single agent, the following adverse reactions were observed at a higher rate (≥5%) compared to patients receiving BRAFTOVI in combination with binimetinib: palmar-plantar erythrodysesthesia syndrome (51% vs. 7%), hyperkeratosis (57% vs. 23%), dry skin (38% vs. 16%), erythema (16% vs. 7%), rash (41% vs. 22%), alopecia (56% vs. 14%), pruritus (31% vs. 13%), arthralgia (44% vs. 26%), myopathy (33% vs. 23%), back pain (15% vs. 9%), dysgeusia (13% vs. 6%), and acneiform dermatitis (8% vs. 3%).
Other clinically important adverse reactions occurring in <10% of patients who received BRAFTOVI in combination with binimetinib were:
Nervous system disorders: Facial paresis
Gastrointestinal disorders: Pancreatitis
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders: Panniculitis, Photosensitivity
Immune system disorders: Drug hypersensitivity
Laboratory Abnormality | BRAFTOVI with binimetinib Grades per National Cancer Institute CTCAE v4.03. N=192 | Vemurafenib N=186 | ||
All Grades (%) | Grades 3 and 4 (%) | All Grades (%) | Grades 3 and 4 (%) | |
Hematology | ||||
Anemia | 36 | 3.6 | 34 | 2.2 |
Leukopenia | 13 | 0 | 10 | 0.5 |
Lymphopenia | 13 | 2.1 | 30 | 7 |
Neutropenia | 13 | 3.1 | 4.8 | 0.5 |
Chemistry | ||||
Increased Creatinine | 93 | 3.6 | 92 | 1.1 |
Increased Gamma Glutamyl Transferase | 45 | 11 | 34 | 4.8 |
Increased ALT | 29 | 6 | 27 | 2.2 |
Increased AST | 27 | 2.6 | 24 | 1.6 |
Hyperglycemia | 28 | 5 | 20 | 2.7 |
Increased Alkaline Phosphatase | 21 | 0.5 | 35 | 2.2 |
Hyponatremia | 18 | 3.6 | 15 | 0.5 |
Hypermagnesemia | 10 | 1.0 | 26 | 0.5 |
BRAF V600E Mutation-Positive Metastatic Colorectal Cancer (mCRC) in Combination with Cetuximab and fluorouracil-based chemotherapy
The safety of BRAFTOVI 300 mg once daily in combination with cetuximab (500 mg/m 2 every 2 weeks) and mFOLFOX6 was evaluated in 232 patients with BRAF V600E mutation-positive metastatic CRC in a randomized, open-label, active-controlled trial (BREAKWATER) [see Clinical Studies (14.2) ] . In a separate cohort of BREAKWATER (Cohort 3), 139 patients with BRAF V600E mutation-positive mCRC were evaluated; of which 71 patients received BRAFTOVI in combination with cetuximab (500 mg/m 2 every 2 weeks) and FOLFIRI. Patients with pancreatitis, leptomeningeal disease, chronic inflammatory bowel disease requiring medical intervention, as well as clinically significant cardiovascular diseases [e.g., myocardial infarction, acute coronary syndromes, NYHA Class ≥II congestive heart failure, prolonged QTcF interval (≥480 ms), history of prolonged QT syndrome] and active infectious conditions were excluded.
BRAFTOVI in combination with cetuximab and mFOLFOX6
Among patients who received BRAFTOVI, 73% were exposed for 6 months or longer and 48% were exposed for one year or longer.
Serious adverse reactions occurred in 46% of patients who received BRAFTOVI in combination with cetuximab and mFOLFOX6. Serious adverse reactions in >3% of patients included intestinal obstruction (4.7%), pyrexia (3.9%), sepsis (3.4%), and abdominal pain (3.4%).
Fatal intestinal obstruction occurred in 0.9%, and fatal large intestinal perforation and gastrointestinal perforation occurred in 0.4% (each) of patients who received BRAFTOVI in combination with cetuximab and mFOLFOX6.
Permanent discontinuation of BRAFTOVI due to an adverse reaction occurred in 14% of patients. Adverse reactions which resulted in permanent discontinuation of BRAFTOVI in ≥1% of patients included increased lipase and sepsis.
Dosage interruptions of BRAFTOVI due to an adverse reaction occurred in 68% of patients. Adverse reactions which required dosage interruption in ≥5% included neutropenia, anemia, pyrexia, COVID-19, and diarrhea.
Dose reductions of BRAFTOVI due to an adverse reaction occurred in 25% of patients. Adverse reactions leading to dose reductions of BRAFTOVI in ≥2% of patients included fatigue, anemia, arthralgia, increased lipase, nausea, neurotoxicity, and vomiting.
The most common (≥25%) adverse reactions of BRAFTOVI when used in combination with cetuximab and mFOLFOX6 were peripheral neuropathy, nausea, fatigue, diarrhea, decreased appetite, rash, vomiting, hemorrhage, abdominal pain, arthralgia, pyrexia, and constipation.
The most common Grade 3 or 4 laboratory abnormalities (≥10%) of BRAFTOVI when used in combination with cetuximab and mFOLFOX6 were increased lipase, decreased neutrophil count, decreased hemoglobin, decreased white blood cell count, and increased glucose.
Table 7 and Table 8 present adverse drug reactions and laboratory abnormalities, respectively, identified in patients receiving BRAFTOVI in combination with cetuximab and mFOLFOX6 in BREAKWATER.
Adverse Reaction | BRAFTOVI with cetuximab and mFOLFOX6 N=232 | mFOLFOX6 with or without bevacizumab or FOLFOXIRI with or without bevacizumab or CAPOX with or without bevacizumab N=229 | mFOLFOX6 with or without bevacizumab N=115 Represents a subset of the control arm (mFOLFOX6 with or without bevacizumab or FOLFOXIRI with or without bevacizumab or CAPOX with or without bevacizumab). | |||
All Grades (%) | Grade 3 or 4 (%) | All Grades (%) | Grade 3 or 4 (%) | All Grades (%) | Grade 3 or 4 (%) | |
Nervous System Disorders | ||||||
Peripheral neuropathy Represents multiple related terms. | 64 | 19 | 53 | 9 | 57 | 10 |
Headache | 15 | 0.4 | 9 | 0 | 12 | 0 |
Dysgeusia | 15 | 0 | 14 | 0 | 19 | 0 |
Neurotoxicity | 11 | 6 | 8 | 0 | 12 | 0 |
Gastrointestinal Disorders | ||||||
Nausea | 54 | 3 | 50 | 3.9 | 44 | 2.6 |
Diarrhea | 42 | 1.3 | 50 | 4.8 | 44 | 2.6 |
Vomiting | 36 | 3.9 | 22 | 2.2 | 17 | 1.7 |
Abdominal pain | 32 | 5 | 31 | 1.7 | 30 | 1.7 |
Constipation | 27 | 0.4 | 23 | 0.4 | 25 | 0.9 |
Stomatitis | 17 | 2.2 | 16 | 1.3 | 19 | 1.7 |
General Disorders and Administration Site Conditions | ||||||
Fatigue | 53 | 7 | 41 | 4.8 | 45 | 7 |
Pyrexia | 29 | 2.2 | 16 | 0.4 | 17 | 0.9 |
Metabolism and Nutrition Disorders | ||||||
Decreased appetite | 38 | 2.2 | 27 | 1.3 | 30 | 2.6 |
Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue Disorders | ||||||
Rash | 36 | 1.3 | 6 | 0 | 5 | 0 |
Alopecia | 23 | 0 | 11 | 0 | 12 | 0 |
Dry skin | 22 | 0.4 | 6 | 0 | 5 | 0 |
Dermatitis acneiform | 20 | 0.9 | 1.3 | 0 | 0.9 | 0 |
Skin hyperpigmentation | 19 | 0 | 3.1 | 0 | 1.7 | 0 |
Pruritus | 14 | 0 | 3.9 | 0.4 | 5 | 0.9 |
Vascular Disorders | ||||||
Hemorrhage | 34 | 2.6 | 21 | 1.3 | 15 | 1.7 |
Edema | 11 | 0 | 4.4 | 0 | 6 | 0 |
Musculoskeletal and Connective Tissue Disorders | ||||||
Arthralgia | 32 | 2.6 | 6 | 0.4 | 7 | 0.9 |
Myopathy | 19 | 0 | 4.8 | 0.4 | 6 | 0.9 |
Musculoskeletal pain | 14 | 0.9 | 10 | 1.3 | 13 | 1.7 |
Infections and Infestations | ||||||
COVID-19 | 16 | 0.9 | 17 | 0.4 | 16 | 0.9 |
Respiratory tract infection | 11 | 0.9 | 11 | 0.4 | 9 | 0.9 |
Psychiatric Disorders | ||||||
Insomnia | 13 | 0 | 9 | 0 | 5 | 0 |
Other clinically important adverse reactions occurring in <10% of patients who received BRAFTOVI in combination with cetuximab and mFOLFOX6 were:
Immune system disorders: Drug hypersensitivity
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders: Hyperkeratosis
Gastrointestinal disorders: Pancreatitis
Laboratory Abnormality The denominator used to calculate the rate varied from 220 to 227 based on the number of patients with a baseline and at least one post-treatment value. | BRAFTOVI with cetuximab and mFOLFOX6 | mFOLFOX6 with or without bevacizumab or FOLFOXIRI with or without bevacizumab or CAPOX with or without bevacizumab | mFOLFOX6 with or without bevacizumab Represents a subset of the control arm (mFOLFOX6 with or without bevacizumab or FOLFOXIRI with or without bevacizumab or CAPOX with or without bevacizumab). | |||
All Grades (%) | Grade 3 or 4 (%) | All Grades (%) | Grade 3 or 4 (%) | All Grades (%) | Grade 3 or 4 (%) | |
Hematology | ||||||
Hemoglobin decreased | 68 | 19 | 50 | 6 | 45 | 7 |
Activated partial thromboplastin time prolonged | 67 | 5 | 43 | 1 | 50 | 2 |
Neutrophil count decreased | 66 | 37 | 63 | 35 | 62 | 33 |
White blood cell decreased | 66 | 12 | 59 | 8 | 56 | 6 |
Platelet count decreased | 65 | 1 | 57 | 3 | 61 | 4 |
INR increased | 47 | 1 | 23 | 1 | 24 | 2 |
Chemistry | ||||||
Lipase increased | 85 | 53 | 57 | 28 | 53 | 23 |
Creatinine increased | 70 | 1 | 72 | 1 | 75 | 0 |
Glucose increased | 56 | 11 | 40 | 2 | 39 | 1 |
Alanine aminotransferase increased | 43 | 1 | 44 | 3 | 46 | 4 |
Albumin decreased | 42 | 1 | 27 | 1 | 25 | 1 |
Aspartate aminotransferase increased | 40 | 1 | 41 | 2 | 37 | 3 |
Alkaline phosphatase increased | 40 | 3 | 35 | 1 | 32 | 3 |
Potassium decreased | 38 | 5 | 23 | 5 | 17 | 3 |
Calcium decreased | 33 | 4 | 22 | 2 | 19 | 2 |
Magnesium decreased | 27 | 1 | 12 | 1 | 9 | 0 |
Sodium decreased | 23 | 3 | 17 | 4 | 16 | 5 |
BRAFTOVI in combination with cetuximab and FOLFIRI
Among patients who received BRAFTOVI, 81% were exposed for 6 months or longer and 17% were exposed for one year or longer.
Serious adverse reactions occurred in 39% of patients who received BRAFTOVI in combination with cetuximab and FOLFIRI. Serious adverse reactions in >3% of patients included febrile neutropenia (5.6%) and infusion related reaction (4.2%).
Fatal gastrointestinal perforation occurred in 1.4% of patients who received BRAFTOVI in combination with cetuximab and FOLFIRI.
Permanent discontinuation of BRAFTOVI due to an adverse reaction occurred in 9% of patients. Adverse reactions which resulted in permanent discontinuation of BRAFTOVI in ≥1% of patients included completed suicide, diarrhea, dyspnea, gastrointestinal perforation, infusion related reaction and pyrexia.
Dosage interruptions of BRAFTOVI due to an adverse reaction occurred in 55% of patients. Adverse reactions which required dosage interruption in ≥5% included neutropenia, diarrhea, and febrile neutropenia.
Dose reductions of BRAFTOVI due to an adverse reaction occurred in 20% of patients. Adverse reactions leading to dose reductions of BRAFTOVI in ≥2% of patients included nausea, vomiting, decreased appetite, fatigue, and diarrhea.
The most common (≥25%) adverse reactions of BRAFTOVI when used in combination with cetuximab and FOLFIRI were nausea, diarrhea, fatigue, vomiting, alopecia, constipation, abdominal pain, decreased appetite, and rash.
The most common Grade 3 or 4 laboratory abnormalities (≥10%) of BRAFTOVI when used in combination with cetuximab and FOLFIRI were decreased neutrophil count, increased lipase, decreased white blood cell count, and decreased hemoglobin.
Table 9 and Table 10 present adverse drug reactions and laboratory abnormalities, respectively, identified in patients receiving BRAFTOVI in combination with cetuximab and FOLFIRI in Cohort 3 of BREAKWATER.
Adverse Reaction | BRAFTOVI with cetuximab and FOLFIRI N=71 | FOLFIRI with or without bevacizumab N=68 | ||
All Grades (%) | Grade 3 or 4 (%) | All Grades (%) | Grade 3 or 4 (%) | |
Gastrointestinal Disorders | ||||
Nausea | 61 | 2.8 | 57 | 1.5 |
Diarrhea Represents multiple related terms. | 55 | 10 | 49 | 9 |
Vomiting | 47 | 2.8 | 31 | 0 |
Constipation | 31 | 1.4 | 29 | 1.5 |
Abdominal pain | 30 | 0 | 22 | 1.5 |
General Disorders and Administration Site Conditions | ||||
Fatigue | 47 | 4.2 | 50 | 6 |
Pyrexia | 17 | 0 | 4.4 | 1.5 |
Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue Disorders | ||||
Alopecia | 35 | 1.4 | 22 | 0 |
Rash | 27 | 0 | 1.5 | 0 |
Dry skin | 24 | 0 | 6 | 0 |
Skin hyperpigmentation | 24 | 0 | 2.9 | 0 |
Palmar-plantar erythrodysaesthesia syndrome | 17 | 0 | 7 | 0 |
Dermatitis acneiform | 11 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
Pruritus | 11 | 0 | 4.4 | 0 |
Metabolism and Nutrition Disorders | ||||
Decreased appetite | 30 | 4.2 | 32 | 2.9 |
Musculoskeletal and Connective Tissue Disorders | ||||
Arthralgia | 24 | 0 | 4.4 | 0 |
Myopathy | 13 | 0 | 9 | 0 |
Vascular Disorders | ||||
Hemorrhage | 21 | 0 | 22 | 0 |
Nervous System Disorders | ||||
Dysgeusia | 14 | 0 | 4.4 | 0 |
Headache | 13 | 0 | 13 | 0 |
Psychiatric Disorders | ||||
Insomnia | 13 | 0 | 13 | 0 |
Neoplasms Benign, Malignant and Unspecified (Including Cysts and Polyps) | ||||
Melanocytic nevus | 11 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
Cardiac Disorders | ||||
Arrhythmia | 11 | 0 | 1.5 | 0 |
Other clinically important adverse reactions occurring in <10% of patients who received BRAFTOVI in combination with cetuximab and FOLFIRI were:
Immune system disorders: Drug hypersensitivity
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders: Hyperkeratosis
Gastrointestinal disorders: Pancreatitis
Nervous system disorders: Peripheral neuropathy
Laboratory Abnormality The denominator used to calculate the rate varied from 65 to 68 based on the number of patients with a baseline and at least one post‑treatment value. | BRAFTOVI with cetuximab and FOLFIRI | FOLFIRI with or without bevacizumab | ||
All Grades (%) | Grade 3 or 4 (%) | All Grades (%) | Grade 3 or 4 (%) | |
Hematology | ||||
White blood cell decreased | 72 | 20 | 67 | 6 |
Neutrophil count decreased | 69 | 30 | 62 | 32 |
Hemoglobin decreased | 61 | 10 | 58 | 3 |
INR increased | 43 | 0 | 21 | 0 |
Activated partial thromboplastin time prolonged | 33 | 2 | 43 | 0 |
Platelet count decreased | 21 | 0 | 26 | 0 |
Chemistry | ||||
Creatinine increased | 59 | 2 | 82 | 3 |
Lipase increased | 46 | 22 | 32 | 12 |
Glucose increased | 43 | 8 | 35 | 3 |
Alanine aminotransferase increased | 34 | 2 | 33 | 3 |
Albumin decreased | 34 | 2 | 26 | 0 |
Potassium decreased | 34 | 6 | 18 | 6 |
Calcium decreased | 27 | 2 | 24 | 5 |
Alkaline phosphatase increased | 22 | 0 | 36 | 5 |
BRAF V600E Mutation-Positive Metastatic Colorectal Cancer (CRC) in Combination with Cetuximab
The safety of BRAFTOVI 300 mg once daily in combination with cetuximab (400 mg/m 2 initial dose, followed by 250 mg/m 2 weekly) was evaluated in 216 patients with BRAF V600E mutation–positive metastatic CRC in a randomized, open-label, active-controlled trial (BEACON CRC). The BEACON CRC trial [see Clinical Studies (14.3) ] excluded patients with a history of Gilbert’s syndrome, abnormal left ventricular ejection fraction, prolonged QTc (>480 ms), uncontrolled hypertension, and history or current evidence of retinal vein occlusion. The median duration of exposure was 4.4 months for patients treated with BRAFTOVI in combination with cetuximab and 1.6 months for patients treated with either irinotecan or infusional 5-fluorouracil (5-FU)/folinic acid (FA)/irinotecan (FOLFIRI) in combination with cetuximab.
The most common (≥25%) adverse reactions in patients receiving BRAFTOVI in combination with cetuximab were fatigue, nausea, diarrhea, dermatitis acneiform, abdominal pain, decreased appetite, arthralgia, and rash.
Adverse reactions leading to dose interruptions of BRAFTOVI occurred in 33% of patients receiving BRAFTOVI in combination with cetuximab; the most common were vomiting (4%), fatigue (4%), nausea (4%), pyrexia (3%), and diarrhea (3%). Adverse reactions leading to dose reductions of BRAFTOVI occurred in 9% of patients receiving BRAFTOVI in combination with cetuximab; the most common were fatigue (2%), arthralgia (2%), and peripheral neuropathy (2%). Ten percent (10%) of patients receiving BRAFTOVI in combination with cetuximab experienced an adverse reaction that resulted in permanent discontinuation of BRAFTOVI. None of the adverse reactions leading to permanent discontinuation of BRAFTOVI occurred in more than one patient (>0.5%).
Table 11 and Table 12 present adverse drug reactions and laboratory abnormalities, respectively, identified in BEACON CRC.
Adverse Reaction | BRAFTOVI with cetuximab N=216 | Irinotecan with cetuximab or FOLFIRI with cetuximab N=193 | ||
All Grades (%) | ≥Grade 3 Grade 4-5 adverse reactions in the BRAFTOVI with cetuximab arm were limited to Grade 5 hemorrhage (n=1). (%) | All Grades (%) | ≥Grade 3 (%) | |
General Disorders and Administration Site Conditions | ||||
Fatigue Represents a composite of multiple, related preferred terms. | 51 | 7 | 50 | 8 |
Pyrexia | 17 | 1 | 15 | 1 |
Gastrointestinal Disorders | ||||
Nausea | 34 | 1 | 41 | 1 |
Diarrhea | 33 | 2 | 48 | 10 |
Abdominal pain | 30 | 4 | 32 | 5 |
Vomiting | 21 | 1 | 29 | 3 |
Constipation | 15 | 0 | 18 | 1 |
Metabolism and Nutrition Disorders | ||||
Decreased appetite | 27 | 1 | 27 | 3 |
Musculoskeletal and Connective Tissue Disorders | ||||
Arthralgia | 27 | 1 | 3 | 0 |
Myopathy | 15 | 1 | 4 | 0 |
Pain in extremity | 10 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue Disorders | ||||
Dermatitis acneiform | 32 | 1 | 43 | 3 |
Rash | 26 | 0 | 26 | 2 |
Pruritus | 14 | 0 | 6 | 0 |
Melanocytic nevus | 14 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
Dry skin | 13 | 0 | 12 | 1 |
Nervous System Disorders | ||||
Headache | 20 | 0 | 3 | 0 |
Peripheral neuropathy | 12 | 1 | 6 | 0 |
Vascular Disorders | ||||
Hemorrhage | 19 | 2 | 9 | 0 |
Psychiatric Disorders | ||||
Insomnia | 13 | 0 | 6 | 0 |
Other clinically important adverse reactions occurring in <10% of patients who received BRAFTOVI in combination with cetuximab were:
Gastrointestinal disorders: Pancreatitis
Laboratory Abnormality Based on the number of patients with available baseline and at least one on-treatment laboratory test. | BRAFTOVI with cetuximab | Irinotecan with cetuximab or FOLFIRI with cetuximab | ||
All Grades (%) | Grades 3 and 4 (%) | All Grades (%) | Grades 3 and 4 (%) | |
Hematology | ||||
Anemia | 34 | 4 | 48 | 5 |
Lymphopenia | 24 | 7 | 35 | 5 |
Increased activated partial thromboplastin time | 13 | 1 | 7 | 1 |
Chemistry | ||||
Hypomagnesemia | 19 | 0 | 22 | 1 |
Increased alkaline phosphatase | 18 | 4 | 30 | 7 |
Increased ALT | 17 | 0 | 29 | 3 |
Increased AST | 15 | 1 | 22 | 2 |
Hypokalemia | 12 | 3 | 32 | 5 |
Hyponatremia | 11 | 2 | 13 | 2 |
BRAF V600E Mutation-Positive Metastatic Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC)
The safety of BRAFTOVI in combination with binimetinib was evaluated in 98 patients with BRAF V600E mutation-positive metastatic NSCLC who received BRAFTOVI (450 mg once daily) in combination with binimetinib (45 mg twice daily) in an open-label, single-arm trial (PHAROS).
The PHAROS trial [see Clinical Studies (14.3) ] excluded patients with abnormal left ventricular ejection fraction, prolonged QTc (>480 ms), uncontrolled hypertension, and history or current evidence of retinal vein occlusion. The median duration of treatment for BRAFTOVI and binimetinib was 9.2 and 8.4 months, respectively.
The most common (≥25%) adverse reactions in patients receiving BRAFTOVI were fatigue, nausea, diarrhea, musculoskeletal pain, vomiting, abdominal pain, visual impairment, constipation, dyspnea, rash, and cough.
Adverse reactions leading to dose interruptions of BRAFTOVI occurred in 59% of patients receiving BRAFTOVI; the most common (≥5%) were diarrhea (17%); nausea (13%); musculoskeletal pain, fatigue (8% each); AST increased (7%); ALT increased, anemia, hemorrhage, vomiting (6% each); and acute kidney injury (5%). Adverse reactions leading to dose reductions of BRAFTOVI occurred in 30% of patients receiving BRAFTOVI; the most common (≥5%) were diarrhea, nausea (8% each); AST increased and fatigue (5% each). A total of 16% of patients receiving BRAFTOVI experienced an adverse reaction that resulted in permanent discontinuation of BRAFTOVI; the most common (≥2%) were diarrhea, musculoskeletal pain (3.1% each); fatigue, rash, nausea, visual impairment, and vomiting (2% each). None of the other adverse reactions leading to permanent discontinuation of BRAFTOVI occurred in more than 1 patient.
Serious adverse reactions occurred in 38% of patients who received BRAFTOVI in combination with binimetinib. Serious adverse reactions occurring in ≥2% of patients were hemorrhage (6%); diarrhea (4.1%); anemia, dyspnea, pneumonia (3.1% each); arrhythmia, device related infection, edema, myocardial infarction, and pleural effusion (2% each). Fatal adverse reactions occurred in 2% of patients who received BRAFTOVI (450 mg once daily) in combination with binimetinib, including intracranial hemorrhage and myocardial infarction (1% each).
Table 13 and Table 14 present adverse drug reactions and laboratory abnormalities, respectively, identified in PHAROS.
Adverse Reaction | BRAFTOVI with binimetinib N=98 | |
All Grades (%) | Grades 3 and 4 One Grade 5 adverse reaction of hemorrhage occurred. (%) | |
General Disorders and Administration Site Conditions | ||
Fatigue Fatigue includes fatigue, asthenia. | 61 | 8 |
Edema Edema includes edema peripheral, generalized edema, swelling, localized edema, face edema. | 23 | 1 |
Pyrexia | 22 | 0 |
Gastrointestinal Disorders | ||
Nausea | 58 | 3.1 |
Diarrhea Diarrhea includes diarrhea, colitis. | 52 | 7 |
Vomiting | 37 | 1 |
Abdominal pain Abdominal pain includes abdominal pain, abdominal pain upper, abdominal discomfort, epigastric discomfort. | 32 | 1 |
Constipation | 27 | 0 |
Eye Disorders | ||
Visual impairment Visual impairment includes vision blurred, visual impairment, vitreous floaters, photophobia, visual acuity reduced, photopsia. | 29 | 2 |
Musculoskeletal and Connective Tissue Disorders | ||
Musculoskeletal pain Musculoskeletal pain includes back pain, arthralgia, pain in extremity, myalgia, musculoskeletal chest pain, noncardiac chest pain, neck pain. | 48 | 4.1 |
Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue Disorders | ||
Rash Rash includes rash, rash macular, rash maculo-papular, rash papular, rash pustular, dermatitis acneiform, palmar-plantar erythrodysesthesia syndrome, eczema, skin exfoliation. | 27 | 3.1 |
Pruritis Pruritis includes pruritus, pruritus genital. | 16 | 0 |
Dry skin | 13 | 0 |
Alopecia | 12 | 0 |
Respiratory, Thoracic and Mediastinal Disorders | ||
Dyspnea Dyspnea includes dyspnea, dyspnea exertional. | 27 | 8 |
Cough Cough includes cough, productive cough. | 26 | 0 |
Nervous System Disorders | ||
Dizziness Dizziness includes dizziness, balance disorder. | 17 | 1 |
Headache | 11 | 0 |
Metabolism and Nutrition Disorders | ||
Decreased appetite | 14 | 1 |
Vascular Disorders | ||
Hemorrhage Hemorrhage includes anal hemorrhage, hemothorax, gastrointestinal hemorrhage, hematochezia, hematuria, hemoptysis, hemorrhage intracranial, hyphema, small intestinal hemorrhage, upper gastrointestinal hemorrhage, vaginal hemorrhage. | 12 | 4.1 |
Hypertension | 10 | 5 |
Cardiac Disorders | ||
Left ventricular dysfunction/cardiomyopathy Left ventricular dysfunction/cardiomyopathy includes ejection fraction decreased, cardiac failure, cardiac failure congestive. | 11 | 1 |
Investigations | ||
Weight increased | 11 | 1 |
Psychiatric Disorders | ||
Insomnia | 10 | 0 |
Other clinically important adverse reactions occurring in <10% of patients who received BRAFTOVI in combination with binimetinib were:
Nervous system disorders: Peripheral neuropathy, Dysgeusia, Facial paresis
Gastrointestinal disorders: Pancreatitis
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders: Hyperkeratosis, Erythema, Photosensitivity
Immune system disorders: Drug hypersensitivity
Laboratory Abnormality Based on the number of patients with available baseline and at least one on-treatment laboratory test. | BRAFTOVI with binimetinib | |
All Grades (%) | Grades 3 and 4 (%) | |
Hematology | ||
Anemia | 47 | 11 |
Lymphopenia | 24 | 6 |
Thrombocytopenia | 20 | 1.1 |
Leukopenia | 12 | 0 |
Neutropenia | 12 | 1.1 |
Chemistry | ||
Increased creatinine | 91 | 3.2 |
Hyperglycemia | 48 | 6 |
Increased creatine kinase | 41 | 3.3 |
Lipase increased | 40 | 14 |
Increased ALT | 34 | 9 |
Hypoalbuminemia | 32 | 0 |
Increased AST | 31 | 10 |
Increased alkaline phosphatase | 31 | 3.2 |
Hyperkalemia | 31 | 2.1 |
Hyponatremia | 26 | 11 |
Serum amylase increased | 22 | 1.1 |
Hypocalcemia | 12 | 2.1 |
DRUG INTERACTIONS
- Strong or moderate CYP3A4 inhibitors: Avoid coadministration. If unavoidable, reduce BRAFTOVI dosage. (2.6 , 7.1 )
- Strong CYP3A4 inducers: Avoid coadministration. (7.1 )
- Sensitive CYP3A4 substrates: Avoid coadministration with CYP3A4 substrates (including hormonal contraceptives) for which a decrease in plasma concentration may lead to reduced efficacy of the substrate. (7.2 )
- Transporters: Dose reductions of drugs that are substrates of OATP1B1, OATP1B3, or BCRP may be required when used concomitantly with BRAFTOVI. (7.2 , 12.3 )
Effect of Other Drugs on BRAFTOVI
Strong or Moderate CYP3A4 Inhibitors
Coadministration of BRAFTOVI with a strong or moderate CYP3A4 inhibitor increases encorafenib plasma concentrations [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ] and may increase encorafenib adverse reactions. Avoid coadministration of BRAFTOVI with strong or moderate CYP3A4 inhibitors, including grapefruit juice. If coadministration is unavoidable, reduce the BRAFTOVI dose [see Dosage and Administration (2.6) ] .
Strong CYP3A4 Inducers
Coadministration of BRAFTOVI with a strong CYP3A4 inducer may decrease encorafenib plasma concentrations [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ] and may decrease encorafenib efficacy. Avoid coadministration of BRAFTOVI with strong CYP3A4 inducers.
Effect of BRAFTOVI on Other Drugs
Sensitive CYP3A4 Substrates
BRAFTOVI is a strong CYP3A4 inducer at steady-state. Concomitant use of BRAFTOVI may decrease the plasma concentrations of CYP3A4 substrates (including hormonal contraceptives), [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ] , which may reduce the efficacy of these substrates. Avoid the coadministration of BRAFTOVI with CYP3A4 substrates for which a decrease in plasma concentration may lead to reduced efficacy of the substrate. If the coadministration cannot be avoided, see the CYP3A4 substrate product labeling for recommendations.
OATP1B1, OATP1B3, or BCRP Substrates
Coadministration of BRAFTOVI with OATP1B1, OATP1B3, or BCRP substrates can result in increased concentrations of the substrates, and may increase toxicity of these agents. When used in combination, monitor patients closely for signs and symptoms of increased exposure and consider adjusting the dose of these substrates [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ].
Drugs That Prolong the QT Interval
BRAFTOVI is associated with dose-dependent QTc interval prolongation [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7) , Clinical Pharmacology (12.2) ] . Avoid coadministration of BRAFTOVI with drugs known to prolong the QT/QTc interval.
DESCRIPTION
Encorafenib is a kinase inhibitor. The chemical name is methyl N -{(2 S )-1-[(4-{3-[5-chloro-2-fluoro-3-(methanesulfonamido)phenyl]-1-(propan-2-yl)-1 H -pyrazol-4-yl}pyrimidin-2-yl)amino]propan-2-yl}carbamate. The molecular formula is C 22 H 27 ClFN 7 O 4 S and the molecular weight is 540 daltons. The chemical structure of encorafenib is shown below:

Encorafenib is a white to almost white powder. In aqueous media, encorafenib is slightly soluble at pH 1, very slightly soluble at pH 2, and insoluble at pH 3 and higher.
BRAFTOVI (encorafenib) capsules for oral use contain 75 mg of encorafenib with the following inactive ingredients: copovidone, poloxamer 188, microcrystalline cellulose, succinic acid, crospovidone, colloidal silicon dioxide, magnesium stearate (vegetable origin). The capsule shell contains gelatin, titanium dioxide, iron oxide red, iron oxide yellow, ferrosoferric oxide, monogramming ink (pharmaceutical glaze, ferrosoferric oxide, propylene glycol).
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Mechanism of Action
Encorafenib is a kinase inhibitor that targets BRAF V600E, as well as wild-type BRAF and CRAF in in vitro cell-free assays with IC 50 values of 0.35, 0.47, and 0.3 nM, respectively. Mutations in the BRAF gene, such as BRAF V600E, can result in constitutively activated BRAF kinases that may stimulate tumor cell growth. Encorafenib was also able to bind to other kinases in vitro including JNK1, JNK2, JNK3, LIMK1, LIMK2, MEK4, and STK36 and reduce ligand binding to these kinases at clinically achievable concentrations (≤0.9 µM).
Encorafenib inhibited in vitro growth of tumor cell lines expressing BRAF V600 E, D, and K mutations. In mice implanted with tumor cells expressing BRAF V600E , encorafenib induced tumor regressions associated with RAF/MEK/ERK pathway suppression.
Encorafenib and binimetinib target two different kinases in the RAS/RAF/MEK/ERK pathway. Compared with either drug alone, coadministration of encorafenib and binimetinib resulted in greater anti-proliferative activity in vitro in BRAF mutation-positive cell lines and greater anti-tumor activity with respect to tumor growth inhibition in BRAF V600E mutant human melanoma xenograft studies in mice. Additionally, the combination of encorafenib and binimetinib delayed the emergence of resistance in BRAF V600E mutant human melanoma xenografts in mice compared to either drug alone. In a BRAF V600E mutant NSCLC patient-derived xenograft model in mice, coadministration of encorafenib and binimetinib resulted in greater anti-tumor activity compared to binimetinib alone, with respect to tumor growth inhibition. Increased tumor growth delay after dosing cessation was also observed with the coadministration compared to either drug alone.
In the setting of BRAF-mutant CRC, induction of EGFR-mediated MAPK pathway activation has been identified as a mechanism of resistance to BRAF inhibitors. Combinations of a BRAF inhibitor and agents targeting EGFR have been shown to overcome this resistance mechanism in nonclinical models. Coadministration of encorafenib and cetuximab had an anti-tumor effect greater than either drug alone, in a mouse model of colorectal cancer with mutated BRAF V600E.
Pharmacodynamics
Cardiac Electrophysiology
A dedicated study to evaluate the QT prolongation potential of BRAFTOVI has not been conducted. BRAFTOVI is associated with dose-dependent QTc interval prolongation. Based on a central tendency analysis of QTc in a study of adult patients with melanoma who received the recommended dose of BRAFTOVI in combination with binimetinib, the largest mean (90% CI) QTcF change from baseline (ΔQTcF) was 18 (14 to 22) ms [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7) ] .
Pharmacokinetics
The pharmacokinetics of encorafenib were studied in healthy subjects and patients with solid tumors, including advanced and unresectable or metastatic cutaneous melanoma harboring a BRAF V600E or V600K mutation, BRAF V600E mutation-positive metastatic CRC. After a single dose, systemic exposure of encorafenib was dose proportional over the dose range of 50 mg to 700 mg (0.1 to 1.6 times the maximum recommended dose of 450 mg). After once-daily dosing, systemic exposure of encorafenib was less than dose proportional over the dose range of 50 mg to 800 mg (0.1 to 1.8 times the maximum recommended dose of 450 mg). Steady-state was reached within 15 days, with exposure being 50% lower compared to Day 1; intersubject variability (CV%) of AUC ranged from 12% to 69%.
Absorption
The median T max of encorafenib is 2 hours. At least 86% of the dose is absorbed.
Effect of Food
Following administration of a single dose of BRAFTOVI 100 mg (0.2 times the maximum recommended dose of 450 mg) with a high-fat, high-calorie meal (consisting of approximately 150 calories from protein, 350 calories from carbohydrates, and 500 calories from fat) the mean maximum encorafenib concentration (C max ) decreased by 36% and there was no effect on AUC.
Distribution
The geometric mean (CV%) of apparent volume of distribution is 164 L (70%). The protein binding of encorafenib is 86% in vitro. The blood-to-plasma concentration ratio is 0.58.
Elimination
The mean (CV%) terminal half-life (t 1/2 ) of encorafenib is 3.5 hours (17%), and the apparent clearance is 14 L/h (54%) at day 1, increasing to 32 L/h (59%) at steady-state at the maximum recommended dose of 450 mg.
Metabolism
Encorafenib is primarily metabolized by CYP3A4 (83%) and to a lesser extent by CYP2C19 (16%) and CYP2D6 (1%).
Excretion
Following a single radiolabeled dose of 100 mg encorafenib, 47% (5% unchanged) of the administered dose was recovered in feces and 47% (2% unchanged) in urine.
Specific Populations
No clinically significant differences in the pharmacokinetics of encorafenib were observed based on age (19 to 94 years), sex, body weight (34 to 168 kg), mild hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh Class A), and mild or moderate renal impairment (CLcr 30 to <90 mL/min). The effect of race or ethnicity, moderate or severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh Class B or C), and severe renal impairment (CLcr <30 mL/min) on encorafenib pharmacokinetics have not been studied.
Drug Interaction Studies
Clinical Studies
CYP3A4 Inhibitors: Coadministration of posaconazole (strong CYP3A4 inhibitor) or diltiazem (moderate CYP3A4 inhibitor) increased AUC of encorafenib by 183% and 83%, respectively, and increased C max by 68% and 45%, respectively, after a single dose of 50 mg BRAFTOVI (0.1 times the maximum recommended dose of 450 mg).
Strong CYP3A4 Inducers: The effect of a strong CYP3A4 inducer on encorafenib exposure has not been studied [see Drug Interactions (7.1) ] .
Moderate CYP3A4 Inducers: Repeat dose administration of BRAFTOVI 450 mg once daily and binimetinib 45 mg twice daily with modafinil, a moderate CYP3A4 inducer, decreased encorafenib steady-state AUC by 24% and C max by 20%, compared to BRAFTOVI alone.
Effect of encorafenib on CYP3A4 Substrates: Repeat dose administration of BRAFTOVI 450 mg once daily and binimetinib 45 mg twice daily with a single dose of midazolam 2 mg, a sensitive CYP3A4 substrate, decreased midazolam AUC by 82% and C max by 74% relative to midazolam 2 mg alone.
Effect of encorafenib on Other CYP Substrates: There was no clinically significant effect of repeat dose administration of BRAFTOVI 450 mg once daily and binimetinib 45 mg twice daily on the exposure of substrates of CYP1A2, CYP2B6, CYP2C9, CYP2C19, and CYP2D6.
Proton Pump Inhibitors: No clinically significant differences in encorafenib pharmacokinetics were observed when coadministered with rabeprazole.
Binimetinib: No clinically significant differences in the pharmacokinetics of binimetinib (UGT1A1 substrate) were observed when coadministered with BRAFTOVI (UGT1A1 inhibitor).
Oxaliplatin: No clinically significant differences in the pharmacokinetics of oxaliplatin were observed when BRAFTOVI 300 mg once daily was coadministered with mFOLFOX6.
Irinotecan: No clinically significant differences in the pharmacokinetics of irinotecan or SN-38 were observed when repeat dose BRAFTOVI 300 mg once daily was coadministered with FOLFIRI.
Transporters: Repeat dose administration of BRAFTOVI 450 mg once daily and binimetinib 45 mg twice daily with a single dose of rosuvastatin (a sensitive substrate for OATP1B1, OATP1B3, and BCRP) increased rosuvastatin C max by 168% and AUC by 57%.
In Vitro Studies
CYP/UGT Enzymes: Encorafenib is a reversible inhibitor of UGT1A1.
Transporters: Encorafenib is a substrate of P-glycoprotein (P-gp) but not of breast cancer resistance protein (BCRP), multidrug resistance-associated protein 2 (MRP2), organic anion transporting polypeptide (OATP1B1, OATP1B3) or organic cation transporter (OCT1) at clinically relevant plasma concentrations.
Encorafenib is an inhibitor of P-gp, BCRP, OCT2, organic anion transporter (OAT1, OAT3), OATP1B1, and OATP1B3, but not of OCT1 or MRP2 at clinically relevant plasma concentrations.
NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenicity studies with encorafenib have not been conducted. Encorafenib was not genotoxic in studies evaluating reverse mutations in bacteria, chromosomal aberrations in mammalian cells, or micronuclei in bone marrow of rats.
No dedicated fertility studies were performed with encorafenib in animals. In a general toxicology study in rats, decreased testes and epididymis weights, tubular degeneration in testes, and oligospermia in epididymides were observed at doses approximately 13 times the human exposure at the 450 mg clinical dose based on AUC. No effects on reproductive organs were observed in either sex in any of the nonhuman primate toxicity studies.
Animal Toxicology and/or Pharmacology
Adverse histopathology findings of hyperplasia and hyperkeratosis occurred in the stomach of rats at encorafenib doses of 20 mg/kg/day (approximately 14 times the human exposure at the 450 mg clinical dose based on AUC) or greater, in both 4 and 13-week studies.
CLINICAL STUDIES
BRAF V600E or V600K Mutation-Positive Unresectable or Metastatic Melanoma
BRAFTOVI in combination with binimetinib was evaluated in a randomized, active-controlled, open-label, multicenter trial (COLUMBUS; NCT01909453). Eligible patients were required to have BRAF V600E or V600K mutation-positive unresectable or metastatic melanoma, as detected using the bioMerieux THxID™ BRAF assay. Patients were permitted to have received immunotherapy in the adjuvant setting and one prior line of immunotherapy for unresectable locally advanced or metastatic disease. Prior use of BRAF inhibitors or MEK inhibitors was prohibited. Randomization was stratified by American Joint Committee on Cancer (AJCC) Stage (IIIB, IIIC, IVM1a or IVM1b, versus IVM1c), Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group (ECOG) performance status (0 versus 1), and prior immunotherapy for unresectable or metastatic disease (yes versus no).
Patients were randomized (1:1:1) to receive BRAFTOVI 450 mg once daily in combination with binimetinib 45 mg twice daily (BRAFTOVI in combination with binimetinib), BRAFTOVI 300 mg once daily, or vemurafenib 960 mg twice daily. Treatment continued until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity. Only the results of the approved dosing (BRAFTOVI 450 mg in combination with binimetinib 45 mg) are described below.
The major efficacy outcome measure was progression-free survival (PFS), as assessed by a blinded independent central review, to compare BRAFTOVI in combination with binimetinib with vemurafenib. Additional efficacy outcome measures included overall survival (OS), as well as objective response rate (ORR) and duration of response (DoR) which were assessed by central review.
A total of 577 patients were randomized, 192 to the BRAFTOVI in combination with binimetinib arm, 194 to the BRAFTOVI arm, and 191 to the vemurafenib arm. Of the 383 patients randomized to either the BRAFTOVI in combination with binimetinib or the vemurafenib arms, the median age was 56 years (20 to 89 years), 59% were male, 91% were White, and 72% had baseline ECOG performance status of 0. Ninety-five percent (95%) had metastatic disease, 65% were Stage IVM1c, and 4% received prior CTLA-4, PD-1, or PD-L1 directed antibodies. Twenty-eight percent (28%) had elevated baseline serum lactate dehydrogenase (LDH), 45% had ≥3 organs with tumor involvement at baseline, and 3% had brain metastases. Based on centralized testing, 100% of patients' tumors tested positive for BRAF mutations; BRAF V600E (88%), BRAF V600K (11%), or both (<1%).
BRAFTOVI in combination with binimetinib demonstrated a statistically significant improvement in PFS compared to vemurafenib. Efficacy results are summarized in Table 15 and Figure 1.
| CI = Confidence interval; CR = Complete response; DoR = Duration of response; HR = Hazard ratio; NE = Not estimable; ORR = Overall response rate; OS = Overall survival; PFS = Progression-free survival; PR = Partial response. | ||
BRAFTOVI with binimetinib N=192 | Vemurafenib N=191 | |
Progression-Free Survival | ||
Number of events (%) | 98 (51) | 106 (55) |
Progressive disease | 88 (46) | 104 (54) |
Death | 10 (5) | 2 (1) |
Median PFS, months (95% CI) | 14.9 (11.0, 18.5) | 7.3 (5.6, 8.2) |
HR (95% CI) Estimated with Cox proportional hazard model adjusted by the following stratification factors: American Joint Committee on Cancer (AJCC) Stage (IIIB, IIIC, IVM1a or IVM1b, versus IVM1c) and Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group (ECOG) performance status (0 versus 1). | 0.54 (0.41, 0.71) | |
P -value Log-rank test adjusted by the same stratification factors. | <0.0001 | |
Overall Survival Based on a cutoff date of 82.4 months after the date of the PFS analysis. | ||
Number of events (%) | 139 (72) | 147 (77) |
Median OS, months (95% CI) | 33.6 (24.4, 39.2) | 16.9 (14.0, 24.5) |
HR (95% CI) | 0.67 (0.53, 0.84) | |
Overall Response Rate | ||
ORR (95% CI) | 63% (56%, 70%) | 40% (33%, 48%) |
CR | 8% | 6% |
PR | 55% | 35% |
Duration of Response | ||
Median DoR, months (95% CI) | 16.6 (12.2, 20.4) | 12.3 (6.9, 16.9) |
Figure 1: Kaplan-Meier Curves for Progression-Free Survival in COLUMBUS

BRAF V600E Mutation-Positive Metastatic Colorectal Cancer (mCRC)
BREAKWATER - BRAFTOVI with Cetuximab and mFOLFOX6
BRAFTOVI in combination with cetuximab and mFOLFOX6 was evaluated in a randomized, active-controlled, open-label, multicenter trial (BREAKWATER CRC; NCT04607421). Eligible patients were required to have BRAF V600E mutation-positive metastatic colorectal cancer (CRC), as detected using the Qiagen therascreen BRAF V600E RGQ polymerase chain reaction (PCR) Kit. Other key eligibility criteria included no prior systemic treatment in the metastatic setting, absence of prior treatment with any selective BRAF inhibitor or EGFR inhibitor, tumor that is not microsatellite instability-high (MSI-H) or mismatch repair deficient (dMMR) unless the patient is ineligible to receive immune checkpoint inhibitors, tumor that is not RAS-mutated or for which RAS mutation status is unknown, and Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group (ECOG) performance status 0-1. Randomization was stratified by ECOG performance status (0 versus 1) and region (US/Canada versus Europe versus Rest of World).
Patients were initially randomized 1:1:1 to one of the following treatment arms, and then 1:1 after discontinuation of enrollment of the BRAFTOVI+cetuximab arm (158 patients):
- BRAFTOVI 300 mg orally once daily in combination with cetuximab 500 mg/m 2 IV infusion every 2 weeks (BRAFTOVI+cetuximab arm)
- BRAFTOVI 300 mg orally once daily in combination with cetuximab 500 mg/m 2 IV infusion every 2 weeks and mFOLFOX6 every 2 weeks (BRAFTOVI+cetuximab+mFOLFOX6 arm)
- mFOLFOX6 (every 2 weeks), or FOLFOXIRI (every 2 weeks), or CAPOX (every 3 weeks), each with or without bevacizumab (administered per prescribing instructions)
mFOLFOX6 consisted of oxaliplatin 85 mg/m 2 , leucovorin 400 mg/m 2 , 5-FU 400 mg/m 2 IV bolus, then 5-FU 2400 mg/m 2 continuous IV infusion over 46-48 hours; CAPOX consisted of oxaliplatin 130 mg/m 2 IV infusion and capecitabine 1000 mg/m 2 oral tablet twice daily on Days 1-14; FOLFOXIRI consisted of irinotecan 165 mg/m 2 , oxaliplatin 85 mg/m 2 , leucovorin 400 mg/m 2 , 5-FU 2400 or 3200 mg/m 2 (per local standard of care) continuous IV infusion over 46-48 hours.
Treatment continued until disease progression, unacceptable toxicity, withdrawal of consent, lost to follow-up, or death. Only the results of the approved regimen (BRAFTOVI in combination with cetuximab and mFOLFOX6) are described below.
The major efficacy outcome measures were confirmed objective response rate (ORR) and progression‑free survival as assessed by BICR. Additional efficacy outcome measures included overall survival (OS) and duration of response (DoR) as assessed by BICR. PFS and OS were evaluated in all randomized patients. ORR and DoR were evaluated in the first 110 participants randomized in each arm.
A total of 236 patients were randomized to the BRAFTOVI+cetuximab+mFOLFOX6 arm and 243 to the control arm. Of these patients, the median age was 61 years, 49% were female, 59% were White, 37% were Asian, 0.4% were Multiracial, 0.2% were Black or African American, and 2.5% were not reported. Twelve percent (12%) were Hispanic or Latino, 81% were not Hispanic or Latino, and 7% were not reported. Fifty-four percent (54%) had baseline ECOG performance status of 0.
BRAFTOVI in combination with cetuximab and mFOLFOX6 demonstrated statistically significant improvements in ORR, PFS, and OS compared to the active comparator. Efficacy results are summarized in Table 16.
| CI = Confidence interval; CR = Complete response; DoR = Duration of response; N = Number of patients; NE = Not estimable; ORR = Objective response rate; PR = Partial response; HR = Hazard ratio; OS = Overall survival; PFS = Progression-free survival. | ||
Efficacy Parameter | BRAFTOVI with cetuximab and mFOLFOX6 N=236 | mFOLFOX6 ± bevacizumab or FOLFOXIRI ± bevacizumab or CAPOX ± bevacizumab N=243 |
Progression-Free Survival | ||
Number of events (%) | 122 (52) | 132 (54) |
Progressive disease | 105 (45) | 109 (45) |
Death | 17 (7) | 23 (9) |
Median PFS, months (95% CI) | 12.8 (11.2, 15.9) | 7.1 (6.8, 8.5) |
HR (95% CI) Hazard ratio based on stratified Cox proportional hazards model. Stratified by ECOG performance status and geographic region at randomization. | 0.53 (0.41, 0.68) | |
P -value Stratified log-rank test. Tested at 1-sided alpha level of 0.023. | <0.0001 | |
Objective Response Rate ORR Subset included the first 110 participants in each arm. | ||
ORR (95% CI) | 61% (52%, 70%) | 40% (31%, 49%) |
CR | 2.7% | 1.8% |
PR | 58% | 38% |
P -value Cochran-Mantel-Haenszel test; tested at 1-sided alpha level of 0.001. | 0.0008 | |
Duration of Response | ||
Median DoR, months (95% CI) | 13.9 (8.5, NE) | 11.1 (6.7, 12.7) |
Overall Survival Interim OS analysis conducted at 81.5% of total events required for final analysis. | ||
Number of events (%) | 94 (40%) | 148 (61%) |
Median OS, months (95% CI) | 30.3 (21.7, NE) | 15.1 (13.7, 17.7) |
HR (95% CI) | 0.49 (0.38, 0.63) | |
P -value Stratified log-rank test. Tested at 1-sided alpha level of 0.012. | <0.0001 | |
- Figure 2: Kaplan-Meier Curves for Progression-Free Survival in BREAKWATER (BRAFTOVI plus cetuximab and mFOLFOX6)

- Figure 3: Kaplan-Meier Curves for Overall Survival in BREAKWATER (BRAFTOVI plus cetuximab and mFOLFOX6)
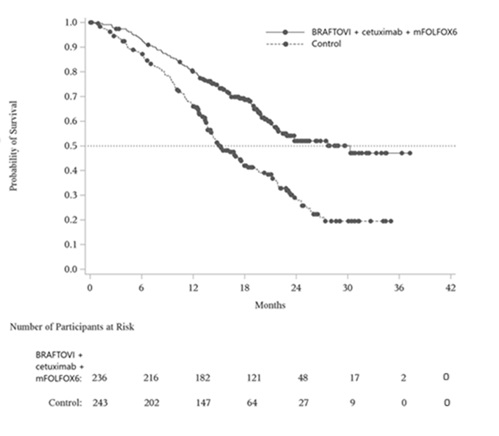
BREAKWATER - BRAFTOVI with Cetuximab and FOLFIRI
BRAFTOVI in combination with cetuximab and FOLFIRI (fluorouracil, leucovorin and irinotecan) was evaluated in a separate cohort (Cohort 3) of BREAKWATER CRC (NCT04607421).
Patients were randomized 1:1 to one of the following treatment arms:
- BRAFTOVI 300 mg orally once daily in combination with cetuximab 500 mg/m 2 IV infusion every 2 weeks and FOLFIRI every 2 weeks (BRAFTOVI+cetuximab+FOLFIRI arm)
- FOLFIRI (every 2 weeks) with or without bevacizumab (administered per prescribing instructions)
FOLFIRI consisted of irinotecan 180 mg/m 2 (90 minute IV infusion); leucovorin 400 mg/m 2 (120 minute IV infusion); and 5-FU (400 mg/m 2 IV bolus, then 5-FU 2400 mg/m 2 continuous IV infusion over 46 - 48 hours).
Treatment continued until disease progression, unacceptable toxicity, withdrawal of consent, lost to follow-up, or death.
The major efficacy outcome measure was confirmed objective response rate (ORR) as assessed by BICR. An additional efficacy outcome measure included duration of response (DoR) as assessed by BICR.
A total of 73 patients were randomized to the BRAFTOVI+cetuximab+FOLFIRI arm and 74 to the control arm. Of these patients, the median age was 62 years, 54% were female, 61% were White, 33% were Asian, 1.4% were Native Hawaiian or Other Pacific Islander, 0.7% were Multiracial, and 3.4% were not reported; 10% were Hispanic or Latino, 83% were not Hispanic or Latino, and 7% were not reported. There were no Black or African American patients enrolled in Cohort 3 of BREAKWATER. Sixty percent (60%) had baseline ECOG performance status of 0.
BRAFTOVI in combination with cetuximab and FOLFIRI demonstrated a statistically significant improvement in ORR compared to the active comparator. Efficacy results are summarized in Table 17.
| CI = Confidence interval; CR = Complete response; DoR = Duration of response; N = Number of patients; ORR = Objective response rate; PR = Partial response. | ||
Efficacy Parameter | BRAFTOVI with cetuximab and FOLFIRI N=73 | FOLFIRI with or without bevacizumab N=74 |
Objective Response Rate | ||
ORR (95% CI) | 64% (53%, 74%) | 39% (29%, 51%) |
CR | 4.1% | 1.4% |
PR | 60% | 38% |
P -value Stratified by ECOG performance status at randomization. Cochran-Mantel-Haenszel test; tested at 1-sided alpha level of 0.025. | 0.0011 | |
Duration of Response | ||
% with DoR ≥6 months | 57% | 35% |
BEACON CRC-BRAFTOVI with Cetuximab following prior therapy
BRAFTOVI in combination with cetuximab was evaluated in a randomized, active-controlled, open-label, multicenter trial (BEACON CRC; NCT02928224). Eligible patients were required to have BRAF V600E mutation-positive metastatic colorectal cancer (CRC), as detected using the Qiagen therascreen BRAF V600E RGQ polymerase chain reaction (PCR) Kit, with disease progression after 1 or 2 prior regimens. Other key eligibility criteria included absence of prior treatment with a RAF, MEK, or EGFR inhibitor, eligibility to receive cetuximab per local labeling with respect to tumor RAS status, and ECOG performance status (PS) 0-1. Randomization was stratified by Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group (ECOG) performance status (0 versus 1), prior use of irinotecan (yes versus no), and cetuximab product used (US‑licensed versus EU-authorized).
Patients were randomized 1:1:1 to one of the following treatment arms:
- BRAFTOVI 300 mg orally once daily in combination with cetuximab (BRAFTOVI/cetuximab arm)
- BRAFTOVI 300 mg orally once daily in combination with binimetinib and cetuximab
- Irinotecan with cetuximab or FOLFIRI with cetuximab (control arm)
The dosage of cetuximab in all patients was 400 mg/m 2 intravenously for the first dose followed by 250 mg/m 2 weekly.
Patients in the control arm received cetuximab with either irinotecan 180 mg/m 2 intravenously on Days 1 and 15 of each 28‑day cycle or FOLFIRI intravenously (irinotecan 180 mg/m 2 on Days 1 and 15; folinic acid 400 mg/m 2 on Days 1 and 15; then 5-FU 400 mg/m 2 bolus on Days 1 and 15 followed by 5-FU 2400 mg/m 2 /day by continuous infusion over 2 days).
Treatment continued until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity. Only the results of the approved regimen (BRAFTOVI in combination with cetuximab) are described below.
The major efficacy outcome measure was overall survival (OS). Additional efficacy outcome measures included progression-free survival (PFS), overall response rate (ORR), and duration of response (DoR) as assessed by blinded independent central review (BICR). OS and PFS were assessed in all randomized patients. ORR and DoR were assessed in the subset of the first 220 patients included in the randomized portion of the BRAFTOVI/cetuximab and control arm of the study.
A total of 220 patients were randomized to the BRAFTOVI/cetuximab arm and 221 to the control arm. Of these 441 patients, the median age was 61 years; 53% were female; 80% were White, 15% were Asian, and 5% were other or not reported. Four percent (4%) were Hispanic or Latino, 90% were not Hispanic or Latino, and 6% were not reported or unknown. Fifty percent (50%) had baseline ECOG performance status of 0; 66% received 1 prior therapy and 34% received 2; 93% received prior oxaliplatin and 52% received prior irinotecan.
BRAFTOVI in combination with cetuximab demonstrated a statistically significant improvement in OS, ORR, and PFS compared to the active comparator. Efficacy results are summarized in Table 18 and Figure 4
| CI = Confidence interval; CR = Complete response; DoR = Duration of response; HR = Hazard ratio; NR = Not reached; ORR = Overall response rate; OS = Overall survival; PFS = Progression-free survival; PR = Partial response. | ||
BRAFTOVI with cetuximab N=220 | Irinotecan with cetuximab or FOLFIRI with cetuximab N=221 | |
Overall Survival | ||
Number of Events (%) | 93 (42) | 114 (52) |
Median OS, months (95% CI) | 8.4 (7.5, 11.0) | 5.4 (4.8, 6.6) |
HR (95% CI) Stratified by ECOG PS, source of cetuximab (US-licensed versus EU-authorized) and prior irinotecan use at randomization. Stratified Cox proportional hazard model. | 0.60 (0.45, 0.79) | |
P -value Stratified log-rank test, tested at alpha level of 0.0084. | 0.0003 | |
Overall Response Rate (per BICR) | ||
ORR (95% CI) BRAFTOVI/cetuximab arm (n=113) and control arm (n=107). | 20% (13%, 29%) | 2% (0%, 7%) |
CR | 5% | 0% |
PR | 15% | 2% |
P -value Cochran-Mantel-Haenszel test; tested at alpha level of 0.05. | <0.0001 | |
Median DoR, months (95% CI) | 6.1 (4.1, 8.3) | NR (2.6, NR) |
Progression‑Free Survival (per BICR) | ||
Number of events (%) | 133 (60) | 128 (58) |
Progressive disease | 110 (50) | 101 (46) |
Death | 23 (10) | 27 (12) |
Median PFS, months (95% CI) | 4.2 (3.7, 5.4) | 1.5 (1.4, 1.7) |
HR (95% CI) | 0.40 (0.31, 0.52) | |
P -value Stratified log-rank test, tested at alpha level of 0.0234. | <0.0001 | |
Figure 4: Kaplan-Meier Curves for Overall Survival in BEACON CRC
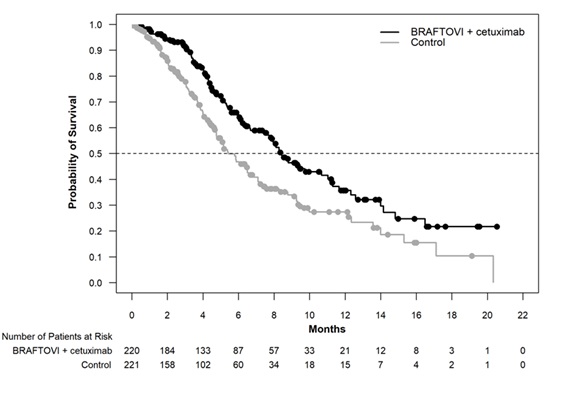
BRAF V600E Mutation-Positive Metastatic Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
BRAFTOVI in combination with binimetinib was evaluated in an open-label, multicenter, single-arm study in patients with BRAF V600E mutation-positive metastatic non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) (PHAROS; NCT03915951). Eligible patients had a diagnosis of histologically-confirmed metastatic NSCLC with BRAF V600E mutation that was treatment-naïve or had been previously treated with 1 prior line of systemic therapy in the metastatic setting (platinum-based chemotherapy and/or anti-PD-1/PD-L1 therapies), age 18 years or older, Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group (ECOG) performance status (PS) of 0 or 1, and measurable disease as defined by Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors (RECIST) v1.1. Prior use of BRAF inhibitors or MEK inhibitors was not allowed.
Patients received BRAFTOVI 450 mg once daily and binimetinib 45 mg orally twice daily until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity. The major efficacy outcome measures were objective response rate (ORR) per RECIST v1.1 and duration of response (DoR) as assessed by independent review committee (IRC).
In the efficacy population, BRAF V600E mutation status was determined by prospective local testing using tumor tissue (78%) or blood (22%) specimens. Of the 98 patients with BRAF V600E mutation, 6 patients were enrolled into the trial based on testing of their tumor tissue specimens with the FoundationOne CDx tissue test. Of the remaining 92 patients enrolled based on local testing, 68 patients had their tumor tissue specimens retrospectively confirmed as having BRAF V600E positive status by the FoundationOne CDx tissue test. The remaining patients had either BRAF V600E negative status (n=5) or had unevaluable results (n=19) by the FoundationOne CDx tissue test. In addition, plasma samples from 81 out of 98 patients were retrospectively tested using the FoundationOne Liquid CDx assay. Of the 81 patients, 48 were confirmed positive for BRAF V600E, while 33 patients were BRAF V600E mutation negative by FoundationOne Liquid CDx assay. The remaining 17 samples had unevaluable results with FoundationOne Liquid CDx assay.
The efficacy population included 59 treatment-naïve patients and 39 previously-treated patients. Among these 98 patients, the median age was 70 years (range: 47 to 86); 53% female; 88% White, 7% Asian, 3% Black or African American, and 1% American Indian or Alaska Native; 99% were not Hispanic or Latino; 13% were current smokers and 57% were former smokers; 73% had ECOG PS of 1; and 97% had adenocarcinoma. All patients had metastatic disease, and 8% had brain metastases at baseline.
Efficacy results for patients with BRAF V600E mutation-positive metastatic NSCLC are summarized in Table 19.
| CI = Confidence interval; CR = Complete response; DoR = Duration of response; N = Number of patients; NE = Not estimable; ORR = Objective response rate; PR = Partial response. | ||
BRAFTOVI with binimetinib | ||
Efficacy Parameter | Treatment‑naïve (N=59) | Previously‑treated (N=39) |
Objective Response Rate Assessed by Independent Central Review (ICR). | ||
ORR (95% CI) | 75% (62, 85) | 46% (30, 63) |
CR | 15% | 10% |
PR | 59% | 36% |
Duration of Response Based on observed duration of response. | N=44 | N=18 |
Range in months | 1.4, 51.6+ | 3.8, 45.8+ |
% with DoR ≥12 months | 64% | 44% |
% with DoR ≥24 months | 43% | 22% |
HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
BRAFTOVI (encorafenib) is supplied as 75 mg hard gelatin capsules.
75 mg: stylized "A" on beige cap and "LGX 75mg" on white body, available in cartons (NDC 70255-025-01) containing two bottles of 90 capsules each (NDC 70255-025-02) and cartons (NDC 70255-025-03) containing two bottles of 60 capsules each (NDC 70255-025-04).
Store at 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F); excursions permitted between 15°C and 30°C (59°F and 86°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature]. Do not use if safety seal under cap is broken or missing. Dispense in original bottle. Do not remove desiccant. Protect from moisture. Keep container tightly closed.
Mechanism of Action
Encorafenib is a kinase inhibitor that targets BRAF V600E, as well as wild-type BRAF and CRAF in in vitro cell-free assays with IC 50 values of 0.35, 0.47, and 0.3 nM, respectively. Mutations in the BRAF gene, such as BRAF V600E, can result in constitutively activated BRAF kinases that may stimulate tumor cell growth. Encorafenib was also able to bind to other kinases in vitro including JNK1, JNK2, JNK3, LIMK1, LIMK2, MEK4, and STK36 and reduce ligand binding to these kinases at clinically achievable concentrations (≤0.9 µM).
Encorafenib inhibited in vitro growth of tumor cell lines expressing BRAF V600 E, D, and K mutations. In mice implanted with tumor cells expressing BRAF V600E , encorafenib induced tumor regressions associated with RAF/MEK/ERK pathway suppression.
Encorafenib and binimetinib target two different kinases in the RAS/RAF/MEK/ERK pathway. Compared with either drug alone, coadministration of encorafenib and binimetinib resulted in greater anti-proliferative activity in vitro in BRAF mutation-positive cell lines and greater anti-tumor activity with respect to tumor growth inhibition in BRAF V600E mutant human melanoma xenograft studies in mice. Additionally, the combination of encorafenib and binimetinib delayed the emergence of resistance in BRAF V600E mutant human melanoma xenografts in mice compared to either drug alone. In a BRAF V600E mutant NSCLC patient-derived xenograft model in mice, coadministration of encorafenib and binimetinib resulted in greater anti-tumor activity compared to binimetinib alone, with respect to tumor growth inhibition. Increased tumor growth delay after dosing cessation was also observed with the coadministration compared to either drug alone.
In the setting of BRAF-mutant CRC, induction of EGFR-mediated MAPK pathway activation has been identified as a mechanism of resistance to BRAF inhibitors. Combinations of a BRAF inhibitor and agents targeting EGFR have been shown to overcome this resistance mechanism in nonclinical models. Coadministration of encorafenib and cetuximab had an anti-tumor effect greater than either drug alone, in a mouse model of colorectal cancer with mutated BRAF V600E.