Get your patient on Cequa (Cyclosporine)
Cequa prior authorization resources
Most recent state uniform prior authorization forms
Brand Resources
Cequa patient education
Patient toolkit
Dosage & administration
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Instill one drop of CEQUA twice daily (approximately 12 hours apart) into each eye. CEQUA can be used concomitantly with artificial tears, allowing a 15 minute interval between products. Discard the vial immediately after using in both eyes. (2 )

By using PrescriberAI, you agree to the AI Terms of Use.
Cequa prescribing information
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
CEQUA ophthalmic solution is a calcineurin inhibitor immunosuppressant indicated to increase tear production in patients with keratoconjunctivitis sicca (dry eye). (1 )
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Instill one drop of CEQUA twice daily (approximately 12 hours apart) into each eye. CEQUA can be used concomitantly with artificial tears, allowing a 15 minute interval between products. Discard the vial immediately after using in both eyes. (2 )
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Ophthalmic solution containing cyclosporine 0.9 mg/mL (3 )
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
Pregnancy
Risk Summary
There are no adequate and well-controlled studies of CEQUA administration in pregnant women to inform a drug-associated risk. Oral administration of cyclosporine to pregnant rats or rabbits did not produce teratogenicity at clinically relevant doses [see Data].
Data
Animal Data
Oral administration of cyclosporine oral solution (USP) to pregnant rats or rabbits was teratogenic at maternally toxic doses of 30 mg/kg/day in rats and 100 mg/kg/day in rabbits, as indicated by increased pre- and postnatal mortality, reduced fetal weight and skeletal retardations. These doses (normalized to body weight) were approximately 3200 and 21000 times higher than the maximum recommended human ophthalmic dose (MRHOD) of 1.5 mcg/kg/day, respectively. No adverse embryofetal effects were observed in rats or rabbits receiving cyclosporine during organogenesis at oral doses up to 17 mg/kg/day or 30 mg/kg/day, respectively (approximately 1800 and 6400 times higher than the MRHOD, respectively).
An oral dose of 45 mg/kg/day cyclosporine (approximately 4800 times higher than MRHOD) administered to rats from Day 15 of pregnancy until Day 21 postpartum produced maternal toxicity and an increase in postnatal mortality in offspring. No adverse effects in dams or offspring were observed at oral doses up to 15 mg/kg/day (approximately 1600 times greater than the MRHOD).
Lactation
Risk Summary
Cyclosporine blood concentrations are low following topical ocular administration of CEQUA [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3 )] . There is no information regarding the presence of cyclosporine in human milk following topical administration or on the effects of CEQUA on the breastfed infants and milk production. Administration of oral cyclosporine to rats during lactation did not produce adverse effects in offspring at clinically relevant doses [see Pregnancy (8.1 )] . The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother’s clinical need for CEQUA and any potential adverse effects on the breast-fed child from cyclosporine.
Pediatric Use
The safety and efficacy of CEQUA ophthalmic solution have not been established in pediatric patients below the age of 18.
Geriatric Use
No overall differences in safety or effectiveness have been observed between elderly and younger adult patients.
CONTRAINDICATIONS
None. (4 )
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
To avoid the potential for eye injury and contamination, advise patients not to touch the vial tip to the eye or other surfaces (5.1 ).
Potential for Eye Injury and Contamination
To avoid the potential for eye injury and contamination, advise patients not to touch the vial tip to the eye or other surfaces.
Use with Contact Lenses
CEQUA should not be administered while wearing contact lenses. If contact lenses are worn, they should be removed prior to administration of the solution. Lenses may be reinserted 15 minutes following administration of CEQUA ophthalmic solution.
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The most common adverse reactions following the use of CEQUA (cyclosporine ophthalmic solution) 0.09% was instillation site pain (22%) and conjunctival hyperemia (6%) (6.1 ).
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Sun Pharmaceutical Industries, Inc. at 1-800-406-7984 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
In clinical trials, 769 subjects received at least 1 dose of cyclosporine ophthalmic solution. The majority of the treated subjects were female (83%). The most common adverse reactions reported in greater than 5% of subjects were pain on instillation of drops (22%) and conjunctival hyperemia (6%). Other adverse reactions reported in 1% to 5% of the patients were blepharitis, eye irritation, headache, and urinary tract infection.
DESCRIPTION
CEQUA (cyclosporine ophthalmic solution) 0.09% contains a topical calcineurin inhibitor immunosuppressant. Cyclosporine’s chemical name is Cyclo[[(E)-(2S,3R,4R)-3-hydroxy-4-methyl-2-(methylamino)-6-octenoyl]-L-2-aminobutyryl-N-methylglycyl-N-methyl-L-leucyl-L-valyl-N-methyl-L-leucyl-L-alanyl-D-alanyl-N-methyl-L-leucyl-N-methyl-L-leucyl-N-methyl-L-valyl] and it has the following structure:
Structural Formula
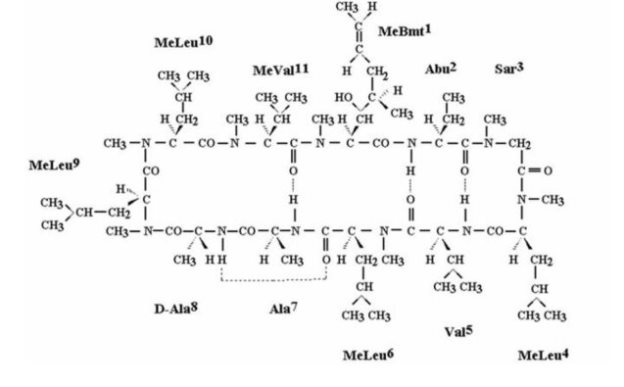
Formula: C 62 H 111 N 11 O 12 Mol. Wt.: 1202.6
Cyclosporine is a white powder that is insoluble in water. CEQUA is supplied as a sterile, clear, colorless ophthalmic solution for topical ophthalmic use. It has an osmolality of 160 to 190 mOsmol/kg and a pH of 6.5-7.2. Each mL of CEQUA contains:
- Active: cyclosporine 0.09%
- Inactives: Polyoxyl 40 Hydrogenated Castor Oil, Octoxynol-40, polyvinylpyrrolidone, sodium phosphate monobasic dihydrate, sodium phosphate dibasic anhydrous, sodium chloride, water for injection, and sodium hydroxide or hydrochloric acid to adjust pH.
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Mechanism of Action
Cyclosporine is a calcineurin inhibitor immunosuppressant agent when administered systemically. In patients whose tear production is presumed to be suppressed due to ocular inflammation associated with keratoconjunctivitis sicca, topical administration of cyclosporine is thought to act as a partial immunomodulator. The exact mechanism of action is not known.
Pharmacokinetics
Blood concentrations of cyclosporine after twice daily topical ocular administration of CEQUA into each eye of healthy subjects for up to 7 days, and once on Day 8, were either not detectable or were marginally above the lower limit of assay quantitation of 0.100 ng/mL (range 0.101 to 0.195 ng/mL) for up to 2 hours after a single dose, and up to 4 hours after multiple doses.
NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenesis
Systemic carcinogenicity studies were carried out in male and female mice and rats. In the 78-week oral (diet) mouse study, at doses of 1, 4, and 16 mg/kg/day, evidence of a statistically significant trend was found for lymphocytic lymphomas in females, and the incidence of hepatocellular carcinomas in mid-dose males significantly exceeded the control value.
In the 24-month oral (diet) rat study, conducted at 0.5, 2, and 8 mg/kg/day, pancreatic islet cell adenomas significantly exceeded the control rate in the low dose level. The hepatocellular carcinomas and pancreatic islet cell adenomas were not dose related. The low doses in mice and rats are approximately 55 times higher than the maximum recommended human ophthalmic dose (1.5 mcg/kg/day), normalized to body surface area.
Mutagenesis
In genetic toxicity tests, cyclosporine has not been found to be mutagenic/genotoxic in the Ames Test, the V79-HGPRT Test, the micronucleus test in mice and Chinese hamsters, the chromosome-aberration tests in Chinese hamster bone-marrow, the mouse dominant lethal assay, and the DNA-repair test in sperm from treated mice. Cyclosporine was positive in an in vitro sister chromatid exchange (SCE) assay using human lymphocytes.
Impairment of Fertility
Oral administration of cyclosporine to rats for 12 weeks (male) and 2 weeks (female) prior to mating produced no adverse effects on fertility at doses up to 15 mg/kg/day (1620 times higher than the maximum recommended human ophthalmic dose).
CLINICAL STUDIES
Two multicenter, randomized, adequate and well-controlled clinical studies treated 1,048 patients with keratoconjunctivitis sicca (NCT # 02254265 and NCT # 02688556). In both studies, compared to vehicle at Day 84, there was a statistically significant (p<0.01) higher percentage of eyes with increases of ≥ 10 mm from baseline in Schirmer wetting. This effect was seen in approximately 17% of CEQUA-treated patients versus approximately 9% of vehicle-treated patients.
Tear Production | ||||
OTX-101-2014-001 | OTX-101-2016-001 | |||
CEQUA N=152 | Vehicle N=152 | CEQUA N=371 | Vehicle N=373 | |
≥ 10-mm increase in tear production (% of eyes) at Day 84 | 16.8% | 8.6% | 16.6% | 9.2% |
Difference (95% CI) | 8.2% (1.9%, 14.6%) | 7.3% (3.3%, 11.3%) | ||
p-value versus vehicle | <0.01 | <0.01 | ||
HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
CEQUA ophthalmic solution is packaged in sterile, preservative-free, single-use vials. Each vial
contains 0.25 mL fill in a 0.9 mL LDPE vial; 10 vials (2 cards of 5 vials) are packaged in a
polyfoil aluminum pouch; 6 pouches are packaged in a box. The entire contents of each box of
60 vials must be dispensed intact.
60 Single-Use Vials 0.25 mL each - NDC 47335-506-96
Storage: Store at 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F). Store single-use vials in the original foil pouch.
Mechanism of Action
Cyclosporine is a calcineurin inhibitor immunosuppressant agent when administered systemically. In patients whose tear production is presumed to be suppressed due to ocular inflammation associated with keratoconjunctivitis sicca, topical administration of cyclosporine is thought to act as a partial immunomodulator. The exact mechanism of action is not known.