Get your patient on Clindagel (Clindamycin)
Clindagel prior authorization resources
Most recent state uniform prior authorization forms
Dosage & administration
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Apply a thin film of CLINDAGEL once daily to the skin where acne lesions appear. Use enough to cover the entire affected area lightly.
Keep container tightly closed.

By using PrescriberAI, you agree to the AI Terms of Use.
Clindagel prescribing information
CLINICAL STUDIES
In one 12-week multicenter, randomized, evaluator-blind, vehicle-controlled, parallel comparison clinical trial in which patients used CLINDAGEL (clindamycin phosphate topical gel, 1%) once daily or the vehicle gel once daily, in the treatment of acne vulgaris of mild to moderate severity, CLINDAGEL applied once daily was more effective than the vehicle applied once daily. The mean percent reductions in lesion counts at the end of treatment in this study are shown in the following table:
| Lesions | CLINDAGEL QD N=162 | Vehicle Gel QD N=82 |
|---|---|---|
Inflammatory | 51% | 40% P<0.05 |
Noninflammatory | 25% | 12% |
Total | 38% | 27% |
There was a trend in the investigator’s global assessment of the results, which favored CLINDAGEL QD over the vehicle QD.
In a contact sensitization study, four of the 200 subjects appeared to develop suggestive evidence of allergic contact sensitization to CLINDAGEL. There was no signal for contact sensitization in the clinical trials under normal use conditions.
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Apply a thin film of CLINDAGEL once daily to the skin where acne lesions appear. Use enough to cover the entire affected area lightly.
Keep container tightly closed.
CONTRAINDICATIONS
CLINDAGEL is contraindicated in individuals with a history of hypersensitivity to preparations containing clindamycin or lincomycin, a history of regional enteritis or ulcerative colitis, or a history of antibiotic-associated colitis.
ADVERSE REACTIONS
In the one well-controlled clinical study comparing CLINDAGEL and its vehicle, the incidence of skin and appendages adverse events occurring in ≥1% of the patients in either group is presented in the following table:
| Number (%) of Patients | ||
|---|---|---|
| Body System/Adverse Event | CLINDAGEL QD N=168 | Vehicle Gel QD N=84 |
Skin and Appendages Disorders | ||
| 0 (0.0) | 1 (1.2) |
| 0 (0.0) | 1 (1.2) |
| 0 (0.0) | 1 (1.2) |
| 0 (0.0) | 1 (1.2) |
| 0 (0.0) | 1 (1.2) |
| 1 (0.6) | 1 (1.2) |
| 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) |
| 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) |
| 1 (0.6) | 0 (0.0) |
Orally and parenterally administered clindamycin has been associated with severe colitis, which may end fatally.
Cases of diarrhea, bloody diarrhea, and colitis (including pseudomembranous colitis) have been reported as adverse reactions in patients treated with oral and parenteral formulations of clindamycin and rarely with topical clindamycin (see WARNINGS ). Abdominal pain and gastrointestinal disturbances, as well as gram-negative folliculitis, have also been reported in association with the use of topical formulations of clindamycin.
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Bausch Health US, LLC at 1-800-321-4576 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
DESCRIPTION
CLINDAGEL (clindamycin phosphate) topical gel, 1%, a topical antibiotic, contains clindamycin phosphate, USP, at a concentration equivalent to 10 mg clindamycin per gram in a gel vehicle consisting of carbomer 941, methylparaben, polyethylene glycol 400, propylene glycol, purified water, and sodium hydroxide. Chemically, clindamycin phosphate is a water-soluble ester of the semi-synthetic antibiotic produced by a 7 (S)-chlorosubstitution of the 7 (R)-hydroxyl group of the parent antibiotic, lincomycin, and has the structural formula represented below:
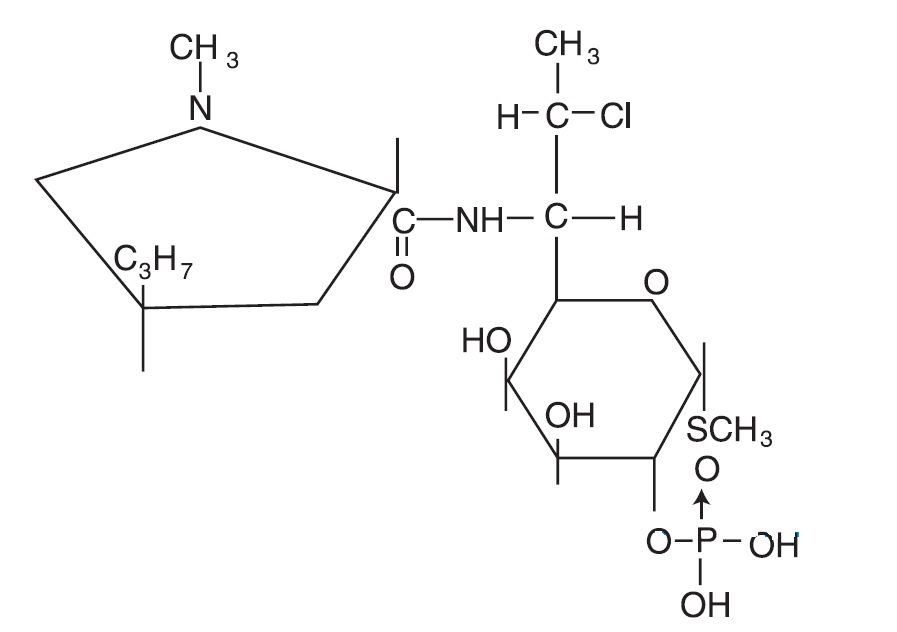
The chemical name for clindamycin phosphate is methyl 7-chloro-6,7,8-trideoxy-6-(1-methyl- trans -4-propyl-L-2-pyrrolidinecarboxamido)-1-thio-L- threo -α-D- galacto -octopyranoside 2-(dihydrogen phosphate).
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Pharmacokinetics: In an open-label, parallel group study of 24 patients with acne vulgaris, once-daily topical administration of approximately 3 to 12 grams/day of CLINDAGEL for 5 days resulted in peak plasma clindamycin concentrations that were less than 5.5 ng/mL.
Following multiple applications of C LINDAGEL less than 0.04% of the total dose was excreted in the urine.
Microbiology: Although clindamycin phosphate is inactive in vitro , rapid in vitro hydrolysis converts this compound to clindamycin, which has antibacterial activity. Clindamycin inhibits bacteria protein synthesis at the ribosomal level by binding to the 50S ribosomal subunit and affecting the process of peptide chain initiation. In vitro studies indicated that clindamycin inhibited all tested Propionibacterium acnes cultures at a minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) of 0.4 mcg/mL. Cross-resistance has been demonstrated between clindamycin and erythromycin.
HOW SUPPLIED
CLINDAGEL containing clindamycin phosphate equivalent to 10 mg clindamycin per gram is available in the following size:
75 mL bottle - NDC 16781-462-75
Store at controlled room temperature 20°to 25°C (68° to 77°F); excursions permitted between 15° to 30°C (59° to 86°F). Do not store in direct sunlight.
Retain in carton until contents are used.
Distributed by: Bausch Health US, LLC Bridgewater, NJ 08807 USA
Manufactured by: Bausch Health Companies Inc. Laval, Quebec H7L 4A8, Canada
CLINDAGEL is a trademark of Bausch Health Companies Inc. or its affiliates.
© 2020 Bausch Health Companies Inc. or its affiliates
9706100
Rev. 01/20