Get your patient on Cotellic [cotellic + Zelboraf] (Cobimetinib)
Cotellic [Cotellic + Zelboraf] patient education
Patient toolkit
Dosage & administration
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- Confirm the presence of BRAF V600E or V600K mutation in tumor specimens prior to initiation of COTELLIC with vemurafenib for patients with melanoma. (2.1 )
- The recommended dose is 60 mg orally once daily for the first 21 days of each 28-day cycle until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity. Take COTELLIC with or without food. (2.2 )
Patient Selection for Treatment of Melanoma
Confirm the presence of BRAF V600E or V600K mutation in tumor specimens prior to initiation of treatment with COTELLIC with vemurafenib. Information on FDA-approved tests for the detection of BRAF V600 mutations in melanoma is available at: http://www.fda.gov/CompanionDiagnostics .
Recommended Dosage
The recommended dosage regimen of COTELLIC is 60 mg (three 20 mg tablets) orally taken once daily for the first 21 days of each 28-day cycle until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity [see Clinical Studies (14) ] .
Take COTELLIC with or without food [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ] .
If a dose of COTELLIC is missed or if vomiting occurs when the dose is taken, resume dosing with the next scheduled dose.
Dose Modifications
Concurrent CYP3A Inhibitors
Do not take strong or moderate CYP3A inhibitors while taking COTELLIC.
If concurrent short term (14 days or less) use of moderate CYP3A inhibitors is unavoidable for patients who are taking COTELLIC 60 mg, reduce COTELLIC dose to 20 mg. After discontinuation of a moderate CYP3A inhibitor, resume previous dose of COTELLIC 60 mg [see Drug Interactions (7.1) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ] .
Use an alternative to a strong or moderate CYP3A inhibitor in patients who are taking a reduced dose of COTELLIC (40 or 20 mg daily) [see Drug Interactions (7.1) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ] .
Adverse Reactions
Review the Full Prescribing Information for vemurafenib for recommended dose modifications.
| First Dose Reduction | 40 mg orally once daily |
| Second Dose Reduction | 20 mg orally once daily |
| Subsequent Modification | Permanently discontinue COTELLIC if unable to tolerate 20 mg orally once daily |
| Severity of Adverse Reaction National Cancer Institute Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events version 4.0 (NCI CTCAE v4.0) | Dose Modification for COTELLIC |
|---|---|
| New Primary Malignancies (cutaneous and non-cutaneous) | No dose modification is required. |
| Hemorrhage | |
| Grade 3 | Withhold COTELLIC for up to 4 weeks.
|
| Grade 4 | Permanently discontinue. |
| Cardiomyopathy | |
| Asymptomatic, absolute decrease in LVEF from baseline of greater than 10% and less than institutional lower limit of normal (LLN) | Withhold COTELLIC for 2 weeks; repeat LVEF. Resume at next lower dose if all of the following are present:
Permanently discontinue if any of the following are present:
|
| Symptomatic LVEF decrease from baseline | Withhold COTELLIC for up to 4 weeks, repeat LVEF. Resume at next lower dose if all of the following are present:
Permanently discontinue if any of the following are present:
|
| Dermatologic Reactions | |
| Grade 2 (intolerable), Grade 3 or 4 | Withhold or reduce dose. |
| Serous Retinopathy or Retinal Vein Occlusion | |
| Serous retinopathy | Withhold COTELLIC for up to 4 weeks.
|
| Retinal vein occlusion | Permanently discontinue COTELLIC. |
| Liver Laboratory Abnormalities and Hepatotoxicity | |
| First occurrence Grade 4 | Withhold COTELLIC for up to 4 weeks.
|
| Recurrent Grade 4 | Permanently discontinue COTELLIC. |
| Rhabdomyolysis and Creatine Phosphokinase (CPK) elevations | |
| Withhold COTELLIC for up to 4 weeks.
|
| Photosensitivity | |
| Grade 2 (intolerable), Grade 3 or Grade 4 | Withhold COTELLIC for up to 4 weeks.
|
| Other | |
| Withhold COTELLIC for up to 4 weeks.
|
| First occurrence of any Grade 4 adverse reaction |
|
| Recurrent Grade 4 adverse reaction | Permanently discontinue COTELLIC. |

By using PrescriberAI, you agree to the AI Terms of Use.
Cotellic [Cotellic + Zelboraf] prescribing information
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
COTELLIC ® is a kinase inhibitor indicated:
Unresectable or Metastatic Melanoma
COTELLIC ® is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with unresectable or metastatic melanoma with a BRAF V600E or V600K mutation, in combination with vemurafenib.
Histiocytic Neoplasms
COTELLIC®, as a single agent, is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with histiocytic neoplasms.
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- Confirm the presence of BRAF V600E or V600K mutation in tumor specimens prior to initiation of COTELLIC with vemurafenib for patients with melanoma. (2.1 )
- The recommended dose is 60 mg orally once daily for the first 21 days of each 28-day cycle until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity. Take COTELLIC with or without food. (2.2 )
Patient Selection for Treatment of Melanoma
Confirm the presence of BRAF V600E or V600K mutation in tumor specimens prior to initiation of treatment with COTELLIC with vemurafenib. Information on FDA-approved tests for the detection of BRAF V600 mutations in melanoma is available at: http://www.fda.gov/CompanionDiagnostics .
Recommended Dosage
The recommended dosage regimen of COTELLIC is 60 mg (three 20 mg tablets) orally taken once daily for the first 21 days of each 28-day cycle until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity [see Clinical Studies (14) ] .
Take COTELLIC with or without food [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ] .
If a dose of COTELLIC is missed or if vomiting occurs when the dose is taken, resume dosing with the next scheduled dose.
Dose Modifications
Concurrent CYP3A Inhibitors
Do not take strong or moderate CYP3A inhibitors while taking COTELLIC.
If concurrent short term (14 days or less) use of moderate CYP3A inhibitors is unavoidable for patients who are taking COTELLIC 60 mg, reduce COTELLIC dose to 20 mg. After discontinuation of a moderate CYP3A inhibitor, resume previous dose of COTELLIC 60 mg [see Drug Interactions (7.1) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ] .
Use an alternative to a strong or moderate CYP3A inhibitor in patients who are taking a reduced dose of COTELLIC (40 or 20 mg daily) [see Drug Interactions (7.1) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ] .
Adverse Reactions
Review the Full Prescribing Information for vemurafenib for recommended dose modifications.
| First Dose Reduction | 40 mg orally once daily |
| Second Dose Reduction | 20 mg orally once daily |
| Subsequent Modification | Permanently discontinue COTELLIC if unable to tolerate 20 mg orally once daily |
| Severity of Adverse Reaction National Cancer Institute Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events version 4.0 (NCI CTCAE v4.0) | Dose Modification for COTELLIC |
|---|---|
| New Primary Malignancies (cutaneous and non-cutaneous) | No dose modification is required. |
| Hemorrhage | |
| Grade 3 | Withhold COTELLIC for up to 4 weeks.
|
| Grade 4 | Permanently discontinue. |
| Cardiomyopathy | |
| Asymptomatic, absolute decrease in LVEF from baseline of greater than 10% and less than institutional lower limit of normal (LLN) | Withhold COTELLIC for 2 weeks; repeat LVEF. Resume at next lower dose if all of the following are present:
Permanently discontinue if any of the following are present:
|
| Symptomatic LVEF decrease from baseline | Withhold COTELLIC for up to 4 weeks, repeat LVEF. Resume at next lower dose if all of the following are present:
Permanently discontinue if any of the following are present:
|
| Dermatologic Reactions | |
| Grade 2 (intolerable), Grade 3 or 4 | Withhold or reduce dose. |
| Serous Retinopathy or Retinal Vein Occlusion | |
| Serous retinopathy | Withhold COTELLIC for up to 4 weeks.
|
| Retinal vein occlusion | Permanently discontinue COTELLIC. |
| Liver Laboratory Abnormalities and Hepatotoxicity | |
| First occurrence Grade 4 | Withhold COTELLIC for up to 4 weeks.
|
| Recurrent Grade 4 | Permanently discontinue COTELLIC. |
| Rhabdomyolysis and Creatine Phosphokinase (CPK) elevations | |
| Withhold COTELLIC for up to 4 weeks.
|
| Photosensitivity | |
| Grade 2 (intolerable), Grade 3 or Grade 4 | Withhold COTELLIC for up to 4 weeks.
|
| Other | |
| Withhold COTELLIC for up to 4 weeks.
|
| First occurrence of any Grade 4 adverse reaction |
|
| Recurrent Grade 4 adverse reaction | Permanently discontinue COTELLIC. |
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Tablets: 20 mg, white, round, film-coated, debossed on one side with "COB".
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
Lactation: Do not breastfeed while taking COTELLIC. (8.2 )
Pregnancy
Risk Summary
Based on findings from animal reproduction studies and its mechanism of action, COTELLIC can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.1) ]. There are no available data on the use of COTELLIC during pregnancy. In animal reproduction studies, oral administration of cobimetinib in pregnant rats during organogenesis was teratogenic and embryotoxic at exposures (AUC) that were 0.9 to 1.4-times those observed in humans at the recommended human dose of 60 mg [see Data ] . Advise pregnant women of the potential risk to a fetus.
In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2–4% and 15–20%, respectively.
Data
Animal Data
Administration of cobimetinib to pregnant rats during the period of organogenesis resulted in increased post-implantation loss, including total litter loss, at exposures (AUC) of 0.9–1.4 times those in humans at the recommended dose of 60 mg. Post-implantation loss was primarily due to early resorptions. Fetal malformations of the great vessels and skull (eye sockets) occurred at the same exposures.
Lactation
Risk Summary
There is no information regarding the presence of cobimetinib in human milk, effects on the breastfed infant, or effects on milk production. Because of the potential for serious adverse reactions in a breastfed infant, advise a nursing woman not to breastfeed during treatment with COTELLIC and for 2 weeks after the final dose.
Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
Contraception
Females
COTELLIC can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1) ] . Advise females of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with COTELLIC and for 2 weeks after the final dose of COTELLIC.
Infertility
Females and Males
Based on findings in animals, COTELLIC may reduce fertility in females and males of reproductive potential [see Nonclinical Toxicology (13.1) ] .
Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of COTELLIC have not been established in pediatric patients.
The safety and effectiveness of COTELLIC were assessed, but not established, in a multi-center, open-label, dose-escalation study in 55 pediatric patients aged 2 to 17 years with solid tumors [NCT02639546]. No new safety events were observed in pediatric patients in this trial.
Exposure in pediatric patients who received COTELLIC at the maximum tolerated dosage were lower than those previously observed in adults who received the approved recommended dosage.
Juvenile Animal Data
In a 4-week juvenile rat toxicology study, daily oral doses of 3 mg/kg (approximately 0.13–0.5 times the adult human AUC at the recommended dose of 60 mg) between postnatal Days 10–17 (approximately equivalent to ages 1–2 years in humans) were associated with mortality, the cause of which was not defined.
Geriatric Use
Clinical studies of COTELLIC did not include sufficient numbers of patients aged 65 years and older to determine whether they respond differently from younger patients.
Hepatic Impairment
Adjustment in the starting dose of COTELLIC is not required in patients with mild (Child-Pugh score A), moderate (Child-Pugh B) or severe (Child-Pugh C) hepatic impairment [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ] .
Renal Impairment
No dedicated pharmacokinetic trial in patients with renal impairment has been conducted. Dose adjustment is not recommended for mild to moderate renal impairment (CLcr 30 to 89 mL/min) based on the results of the population pharmacokinetic analysis. A recommended dose has not been established for patients with severe renal impairment [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ].
CONTRAINDICATIONS
None.
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
Review the Full Prescribing Information for vemurafenib for information on the serious risks of vemurafenib.
New Primary Malignancies
New primary malignancies, cutaneous and non-cutaneous, can occur with COTELLIC.
Cutaneous Malignancies :
In Trial 1, the following cutaneous malignancies or premalignant conditions occurred in the COTELLIC with vemurafenib arm and the vemurafenib arm, respectively: cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma (cuSCC) or keratoacanthoma (KA) (6% and 20%), basal cell carcinoma (4.5% and 2.4%), and second primary melanoma (0.8% and 2.4%). Among patients receiving COTELLIC with vemurafenib, the median time to detection of first cuSCC/KA was 4 months (range: 2 to 11 months), and the median time to detection of basal cell carcinoma was 4 months (range: 27 days to 13 months). The time to onset in the two patients with second primary melanoma was 9 months and 12 months.
Perform dermatologic evaluations prior to initiation of therapy and every 2 months while on therapy. Manage suspicious skin lesions with excision and dermatopathologic evaluation. No dose modifications are recommended for COTELLIC [see Dosage and Administration (2.3) ] . Conduct dermatologic monitoring for 6 months following discontinuation of COTELLIC when administered with vemurafenib.
Non-Cutaneous Malignancies :
Based on its mechanism of action, vemurafenib may promote growth and development of malignancies [refer to the Full Prescribing Information for vemurafenib] . In Trial 1, 0.8% of patients in the COTELLIC with vemurafenib arm and 1.2% of patients in the vemurafenib arm developed non-cutaneous malignancies.
Monitor patients receiving COTELLIC, when administered with vemurafenib, for signs or symptoms of non-cutaneous malignancies.
Hemorrhage
Hemorrhage, including major hemorrhages defined as symptomatic bleeding in a critical area or organ, can occur with COTELLIC.
In Trial 1, the incidence of Grade 3–4 hemorrhages was 1.2% in patients receiving COTELLIC with vemurafenib and 0.8% in patients receiving vemurafenib. Hemorrhage (all grades) was 13% in patients receiving COTELLIC with vemurafenib and 7% in patients receiving vemurafenib. Cerebral hemorrhage occurred in 0.8% of patients receiving COTELLIC with vemurafenib and in none of the patients receiving vemurafenib. Gastrointestinal tract hemorrhage (3.6% vs 1.2%), reproductive system hemorrhage (2.0% vs 0.4%), and hematuria (2.4% vs 0.8%) also occurred at a higher incidence in patients receiving COTELLIC with vemurafenib compared with patients receiving vemurafenib.
In Trial 2, in patients with histiocytic neoplasms, 19% of patients experienced hemorrhage events (all were of grade 1 severity).
Withhold COTELLIC for Grade 3 hemorrhagic events. If improved to Grade 0 or 1 within 4 weeks, resume COTELLIC at a lower dose level. Discontinue COTELLIC for Grade 4 hemorrhagic events and any Grade 3 hemorrhagic events that do not improve [see Dosage and Administration (2.3) ] .
Cardiomyopathy
Cardiomyopathy, defined as symptomatic and asymptomatic decline in left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF), can occur with COTELLIC. The safety of COTELLIC has not been established in patients with a baseline LVEF that is either below institutional lower limit of normal (LLN) or below 50%.
In Trial 1, patients were assessed for decreases in LVEF by echocardiograms or MUGA at baseline, Week 5, Week 17, Week 29, Week 43, and then every 4 to 6 months thereafter while receiving treatment. Grade 2 or 3 decrease in LVEF occurred in 26% of patients receiving COTELLIC with vemurafenib and 19% of patients receiving vemurafenib. The median time to first onset of LVEF decrease was 4 months (range 23 days to 13 months). Of the patients with decreased LVEF, 22% had dose interruption and/or reduction and 14% required permanent discontinuation. Decreased LVEF resolved to above the LLN or within 10% of baseline in 62% of patients receiving COTELLIC with a median time to resolution of 3 months (range: 4 days to 12 months).
In Trial 2, in patients with histiocytic neoplasms, 8% of patients experienced grade 2 ejection fraction decreased and 12% experienced grade 3-4 events. The median time to first onset of LVEF decrease was 29 days (range 22 days to 114 days). Of the patients with decreased LVEF, all had dose interruption and/or reduction and none required permanent discontinuation. Decreased LVEF resolved to above the LLN or within 10% of baseline in 60% of patients receiving COTELLIC with a median time to resolution of 31 days (range: 13 days to 126 days).
Evaluate LVEF prior to initiation, 1 month after initiation, and every 3 months thereafter until discontinuation of COTELLIC. Manage events of left ventricular dysfunction through treatment interruption, reduction, or discontinuation [see Dosage and Administration (2.3) ] . In patients restarting COTELLIC after a dose reduction or interruption, evaluate LVEF at approximately 2 weeks, 4 weeks, 10 weeks, and 16 weeks, and then as clinically indicated.
Severe Dermatologic Reactions
Severe rash and other skin reactions can occur with COTELLIC.
In Trial 1, Grade 3 to 4 rash, occurred in 16% of patients receiving COTELLIC with vemurafenib and in 17% of patients receiving vemurafenib, including Grade 4 rash in 1.6% of patients receiving COTELLIC with vemurafenib and 0.8% of the patients receiving vemurafenib. The incidence of rash resulting in hospitalization was 3.2% in patients receiving COTELLIC with vemurafenib and 2.0% in patients receiving vemurafenib. In patients receiving COTELLIC, the median time to onset of Grade 3 or 4 rash events was 11 days (range: 3 days to 2.8 months). Among patients with Grade 3 or 4 rash events, 95% experienced complete resolution with the median time to resolution of 21 days (range 4 days to 17 months).
In Trial 2, in patients with histiocytic neoplasms, 81% of patients experienced rash events (all were of grade 1-2 severity).
Interrupt, reduce the dose, or discontinue COTELLIC [see Dosage and Administration (2.3) ].
Serous Retinopathy and Retinal Vein Occlusion
Ocular toxicities can occur with COTELLIC, including serous retinopathy (fluid accumulation under layers of the retina).
In Trial 1, ophthalmologic examinations including retinal evaluation were performed pretreatment and at regular intervals during treatment. Symptomatic and asymptomatic serous retinopathy was identified in 26% of patients receiving COTELLIC with vemurafenib. The majority of these events were reported as chorioretinopathy (13%) or retinal detachment (12%). The time to first onset of serous retinopathy events ranged between 2 days to 9 months. The reported duration of serous retinopathy ranged between 1 day to 15 months. One patient in each arm developed retinal vein occlusion.
In Trial 2, in patients with histiocytic neoplasms, 4% experienced grade 2 retinopathy and 4% experienced grade 3 retinal vascular disorder.
Perform an ophthalmological evaluation at regular intervals and any time a patient reports new or worsening visual disturbances. If serous retinopathy is diagnosed, interrupt COTELLIC until visual symptoms improve. Manage serous retinopathy with treatment interruption, dose reduction, or with treatment discontinuation [see Dosage and Administration (2.3) ] .
Hepatotoxicity
Hepatotoxicity can occur with COTELLIC .
The incidences of Grade 3 or 4 liver laboratory abnormalities in Trial 1 among patients receiving COTELLIC with vemurafenib compared to patients receiving vemurafenib were: 11% vs. 5% for alanine aminotransferase, 8% vs. 2.1% for aspartate aminotransferase, 1.6% vs. 1.2% for total bilirubin, and 7% vs. 3.3% for alkaline phosphatase [see Adverse Drug Reactions (6.1) ] . Concurrent elevation in ALT >3 times the upper limit of normal (ULN) and bilirubin >2 × ULN in the absence of significant alkaline phosphatase >2 × ULN occurred in one patient (0.4%) receiving COTELLIC with vemurafenib and no patients receiving single-agent vemurafenib.
In Trial 2, in patients with histiocytic neoplasms, 9% of the patients receiving COTELLIC experienced grade 3 or 4 aspartate aminotransferase increased and 5% of the patients experienced grade 3 or 4 alanine aminotransferase increased.
Monitor liver laboratory tests before initiation of COTELLIC and monthly during treatment, or more frequently as clinically indicated. Manage Grade 3 and 4 liver laboratory abnormalities with dose interruption, reduction, or discontinuation of COTELLIC [see Dosage and Administration (2.3) ] .
Rhabdomyolysis
Rhabdomyolysis can occur with COTELLIC.
In Trial 1, Grade 3 or 4 CPK elevations, including asymptomatic elevations over baseline, occurred in 14% of patients receiving COTELLIC with vemurafenib and 0.5% of patients receiving vemurafenib. The median time to first occurrence of Grade 3 or 4 CPK elevations was 16 days (range: 12 days to 11 months) in patients receiving COTELLIC with vemurafenib; the median time to complete resolution was 15 days (range: 9 days to 11 months). Elevation of serum CPK increase of more than 10 times the baseline value with a concurrent increase in serum creatinine of 1.5 times or greater compared to baseline occurred in 3.6% of patients receiving COTELLIC with vemurafenib and in 0.4% of patients receiving vemurafenib.
Obtain baseline serum CPK and creatinine levels prior to initiating COTELLIC, periodically during treatment, and as clinically indicated. If CPK is elevated, evaluate for signs and symptoms of rhabdomyolysis or other causes. Depending on the severity of symptoms or CPK elevation, dose interruption or discontinuation of COTELLIC may be required [see Dosage and Administration (2.3) ] .
In Trial 2, in patients with histiocytic neoplasms, 27% of patients experienced grade 2 CPK elevation and 27% of patients experienced grade 3-4 CPK elevation.
Severe Photosensitivity
Photosensitivity, including severe cases, can occur with COTELLIC.
In Trial 1, photosensitivity was reported in 47% of patients receiving COTELLIC with vemurafenib: 43% of patients with Grades 1 or 2 photosensitivity and the remaining 4% with Grade 3 photosensitivity. Median time to first onset of photosensitivity of any grade was 2 months (range: 1 day to 14 months) in patients receiving COTELLIC with vemurafenib, and the median duration of photosensitivity was 3 months (range: 2 days to 14 months). Among the 47% of patients with photosensitivity reactions on COTELLIC with vemurafenib, 63% experienced resolution of photosensitivity reactions.
Advise patients to avoid sun exposure, wear protective clothing and use a broad-spectrum UVA/UVB sunscreen and lip balm (SPF ≥30) when outdoors. Manage intolerable Grade 2 or greater photosensitivity with dose modifications [see Dosage and Administration (2.3) ].
Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
Based on its mechanism of action and findings from animal reproduction studies, COTELLIC can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. In animal reproduction studies, oral administration of cobimetinib in pregnant rats during the period of organogenesis was teratogenic and embryotoxic at doses resulting in exposures [area under the curves (AUCs)] that were 0.9 to 1.4-times those observed in humans at the recommended human dose of 60 mg. Advise pregnant women of the potential risk to a fetus. Advise females of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with COTELLIC, and for 2 weeks following the final dose of COTELLIC [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1 , 8.3) , Clinical Pharmacology (12.1) ] .
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following adverse reactions are discussed in greater detail in other sections of the label:
- New Primary Cutaneous Malignancies [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) ]
- Hemorrhage [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) ]
- Cardiomyopathy [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3) ]
- Serious Dermatologic Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4) ]
- Serous Retinopathy and Retinal Vein Occlusion [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5) ]
- Hepatotoxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6) ]
- Rhabdomyolysis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7) ]
- Severe Photosensitivity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8) ]
Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
Unresectable or Metastatic Melanoma
The safety of COTELLIC was evaluated in Trial 1, a randomized (1:1), double-blind, active-controlled trial in previously untreated patients with BRAF V600 mutation-positive, unresectable or metastatic melanoma [see Clinical Studies (14) ] . All patients received vemurafenib 960 mg twice daily on Days 1–28 and received either COTELLIC 60 mg once daily (n=247) or placebo (n=246) on Days 1–21 of each 28-day treatment cycle until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity. In the COTELLIC plus vemurafenib arm, 66% percent of patients were exposed for greater than 6 months and 24% of patients were exposed for greater than 1 year. Patients with abnormal liver function tests, history of acute coronary syndrome within 6 months, evidence of Class II or greater congestive heart failure (New York Heart Association), active central nervous system lesions, or evidence of retinal pathology were excluded from Trial 1. The demographics and baseline tumor characteristics of patients enrolled in Trial 1 are summarized in Clinical Studies [see Clinical Studies (14) ].
In Trial 1, 15% of patients receiving COTELLIC experienced an adverse reaction that resulted in permanent discontinuation of COTELLIC. The most common adverse reactions resulting in permanent discontinuation were liver laboratory abnormalities defined as increased aspartate aminotransferase (AST) (2.4%), increased gamma glutamyltransferase (GGT) (1.6%) and increased alanine aminotransferase (ALT) (1.6%); rash (1.6%); pyrexia (1.2%); and retinal detachment (2%). Among the 247 patients receiving COTELLIC, adverse reactions led to dose interruption or reductions in 55%. The most common reasons for dose interruptions or reductions of COTELLIC were rash (11%) , diarrhea (9%), chorioretinopathy (7%), pyrexia (6%), vomiting (6%), nausea (5%), and increased creatine phosphokinase (CPK) (4.9%). The most common (≥20%) adverse reactions with COTELLIC were diarrhea, photosensitivity reaction, nausea, pyrexia, and vomiting.
| Adverse reactions | COTELLIC + Vemurafenib (n=247) | Placebo + Vemurafenib (n=246) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| All Grades NCI CTCAE, v4.0. (%) | Grades 3–4 (%) | All Grades (%) | Grades 3–4 (%) | |
| GASTROINTESTINAL DISORDERS | ||||
| Diarrhea | 60 | 6 | 31 | 1 |
| Nausea | 41 | 1 | 25 | 1 |
| Vomiting | 24 | 1 | 13 | 1 |
| Stomatitis Includes stomatitis, aphthous stomatitis, mouth ulceration, and mucosal inflammation | 14 | 1 | 8 | 0 |
| SKIN AND SUBCUTANEOUS TISSUE DISORDERS | ||||
| Photosensitivity reaction Includes solar dermatitis, sunburn, photosensitivity reaction | 46 | 4 | 35 | 0 |
| Acneiform dermatitis | 16 | 2 | 11 | 1 |
| GENERAL DISORDERS AND ADMINISTRATION SITE CONDITIONS | ||||
| Pyrexia | 28 | 2 | 23 | 0 |
| Chills | 10 | 0 | 5 | 0 |
| VASCULAR DISORDERS | ||||
| Hypertension | 15 | 4 | 8 | 2 |
| Hemorrhage Includes hemorrhage, rectal hemorrhage, melena, hemorrhoidal hemorrhage, gastrointestinal hemorrhage, hematemesis, hematochezia, gingival bleeding, metrorrhagia, uterine hemorrhage, hemorrhagic ovarian cyst, menometrorrhagia, menorrhagia, vaginal hemorrhage, hemoptysis, pulmonary, cerebral, subarachnoid hemorrhage, subgaleal hematoma, hematuria, epistaxis, contusion, traumatic hematoma, ecchymosis, purpura, nail bed bleeding, ocular, eye, conjunctival, and retinal hemorrhage | 13 | 1 | 7 | <1 |
| EYE DISORDERS | ||||
| Vision impaired Includes vision blurred, visual acuity reduced, visual impairment | 15 | <1 | 4 | 0 |
| Chorioretinopathy | 13 | <1 | <1 | 0 |
| Retinal detachment Includes retinal detachment, detachment of retinal pigment epithelium, detachment of macular retinal pigment epithelium | 12 | 2 | <1 | 0 |
The following clinically relevant adverse reactions (all grades) of COTELLIC were reported with <10% incidence in Trial 1:
Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders: Pneumonitis
| Laboratory | COTELLIC + Vemurafenib | Placebo + Vemurafenib | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| All Grades NCI CTCAE v4.0. | Grades 3–4 | All Grades | Grades 3–4 | |
| % | % | % | % | |
| AST - aspartate aminotransferase, ALT - alanine aminotransferase, GGT - gamma-glutamyltransferase | ||||
| Chemistry | ||||
| Increased creatinine | 100 | 3.3 | 100 | 0.4 |
| Increased AST | 73 | 8 | 44 | 2.1 |
| Increased ALT | 68 | 11 | 55 | 5 |
| Increased alkaline phosphatase | 71 | 7 | 56 | 3.3 |
| Increased creatine phosphokinase Increase creatine phosphokinase, n=213 for COTELLIC and 217 for vemurafenib. | 79 | 14 | 16 | 0.5 |
| Hypophosphatemia | 68 | 12 | 38 | 6 |
| Increased GGT | 65 | 21 | 61 | 17 |
| Hyponatremia | 38 | 6 | 33 | 2.1 |
| Hypoalbuminemia | 42 | 0.8 | 20 | 0.4 |
| Hypokalemia | 25 | 4.5 | 17 | 3.3 |
| Hyperkalemia | 26 | 2.9 | 15 | 0.4 |
| Hypocalcemia | 24 | 0.4 | 10 | 1.7 |
| Hematology | ||||
| Anemia | 69 | 2.5 | 57 | 3.3 |
| Lymphopenia Lymphopenia, n=185 for COTELLIC, and 181 for vemurafenib. | 73 | 10 | 55 | 8 |
| Thrombocytopenia | 18 | 0 | 10 | 0 |
Histiocytic Neoplasms
The safety of COTELLIC was evaluated in Trial 2, a single-center single-arm trial in patients with histiocytic neoplasms [see Clinical Studies (14) ] . In Trial 2, 26 patients with histiocytic neoplasms received COTELLIC 60 mg once daily for 21 days on, then 7 days off, in a 28-day treatment cycle. The median treatment duration was 10.7 months. Table 5 presents adverse reactions in at least 15% of patients reported with histiocytic neoplasms treated with COTELLIC. Table 6 presents laboratory abnormalities of grades ≥3 reported in patients with histiocytic neoplasms treated COTELLIC.
In Trial 2, 4 patients (15%) receiving COTELLIC experienced an adverse reaction that resulted in permanent discontinuation of COTELLIC. One patient discontinued due to worsening of underlying dyspnea and hypoxia; one patient discontinued due to retinal vascular disorder; one patient discontinued due to hyponatremia; and the other patient discontinued due to pneumonia.
| Body Systems Adverse reactions | All Grades NCI CTCAE v4.0. (%) (n=26) | Grades ≥3(%) (n=26) |
|---|---|---|
| GASTROINTESTINAL DISORDERS | ||
| Diarrhea | 62 | 8 |
| Nausea | 46 | 0 |
| Dyspepsia Gastritis, and gastroesophageal reflux disease. | 27 | 0 |
| Vomiting | 27 | 0 |
| Dry Mouth | 15 | 0 |
| Oral pain Oral dysesthesia and oropharyngeal pain. | 15 | 0 |
| GENERAL DISORDERS AND ADMINISTRATION SITE CONDITIONS | ||
| Fatigue Malaise | 42 | 0 |
| Edema Facial edema, edema genital, edema peripheral, periorbital edema, and lymphoedema. | 42 | 4 |
| Pain | 15 | 0 |
| INFECTIONS AND INFESTATIONS | ||
| Infections Influenza like illness, mucosal infection, paronychia, pharyngitis, pneumonia, bronchitis, sepsis, sinusitis, skin infection, tooth infection, upper respiratory tract infection., and urinary tract infection. | 62 | 23 |
| Urinary tract infection | 23 | 8 |
| Pulmonary infections Pneumonia and bronchitis. | 19 | 12 |
| INJURY, POISONING AND PROCEDURAL COMPLICATIONS | ||
| Fall | 15 | 4 |
| INVESTIGATIONS | ||
| Decreased Ejection Fraction | 19 | 12 |
| RENAL AND URINARY | ||
| Acute kidney injury | 15 | 12 |
| RESPIRATORY, THORACIC AND MEDIASTINAL DISORDERS | ||
| Dyspnea | 27 | 15 |
| Cough | 15 | 0 |
| SKIN AND SUBCUTANEOUS TISSUE DISORDERS | ||
| Acneiform dermatitis | 65 | 0 |
| Dry skin | 31 | 0 |
| Maculo-papular rash | 31 | 0 |
| Pruritus | 31 | 4 |
| VASCULAR DISORDERS | ||
| Hemorrhage Epistaxis, contusion, purpura, hematoma, and rectal hemorrhage. | 19 | 0 |
| Hypertension | 15 | 4 |
The following clinically relevant adverse reactions (all grades) of COTELLIC were reported with <15% incidence in Trial 2:
Eye disorders : Vision blurred (12%), retinal vascular disorder (4%) and retinopathy (4%).
Gastrointestinal disorders : Stomatitis (12%)
Nervous system disorders : Headache (12%)
Respiratory, thoracic, and mediastinal disorders : Hypoxia (12%), pulmonary edema (4%), and respiratory failure (8%).
| Grades 3–4 NCI CTCAE v4.0 % | |
|---|---|
| AST - aspartate aminotransferase, ALT - alanine aminotransferase | |
| Chemistry | |
| Increased blood creatine phosphokinase | 27 |
| Hyponatremia | 18 |
| Hypokalemia | 12 |
| Increased blood creatinine | 9 |
| Increased AST | 9 |
| Hypocalcemia | 9 |
| Increased ALT | 5 |
| Hematology | |
| Lymphopenia | 27 |
| Leukopenia | 9 |
| Anemia | 8 |
| Neutropenia | 5 |
DRUG INTERACTIONS
Avoid concomitant administration of COTELLIC with strong or moderate CYP3A inducers or inhibitors. (2.3 , 7.1 , 7.2 )
Effect of Strong or Moderate CYP3A Inhibitors on COTELLIC
Coadministration of COTELLIC with itraconazole (a strong CYP3A4 inhibitor) increased cobimetinib systemic exposure by 6.7-fold. Avoid concurrent use of COTELLIC and strong or moderate CYP3A inhibitors. If concurrent short term (14 days or less) use of moderate CYP3A inhibitors including certain antibiotics (e.g., erythromycin, ciprofloxacin) is unavoidable for patients who are taking COTELLIC 60 mg, reduce COTELLIC dose to 20 mg. After discontinuation of a moderate CYP3A inhibitor, resume COTELLIC at the previous dose [see Dosage and Administration (2.3) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ] . Use an alternative to a strong or moderate CYP3A inhibitor in patients who are taking a reduced dose of COTELLIC (40 or 20 mg daily) [see Dosage and Administration (2.3) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ] .
Effect of Strong or Moderate CYP3A Inducers on COTELLIC
Coadministration of COTELLIC with a strong CYP3A inducer may decrease cobimetinib systemic exposure by more than 80% and reduce its efficacy. Avoid concurrent use of COTELLIC and strong or moderate CYP3A inducers including but not limited to carbamazepine, efavirenz, phenytoin, rifampin, and St. John's Wort [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ] .
DESCRIPTION
Cobimetinib fumarate is a kinase inhibitor. The chemical name is ( S )-[3,4-difluoro-2-(2-fluoro-4-iodophenylamino)phenyl] [3-hydroxy-3-(piperidin-2-yl)azetidin-1-yl]methanone hemifumarate. It has a molecular formula C 46 H 46 F 6 I 2 N 6 O 8 (2 C 21 H 21 F 3 IN 3 O 2 ∙ C 4 H 4 O 4 ) with a molecular mass of 1178.71 as a fumarate salt. Cobimetinib fumarate has the following chemical structure:
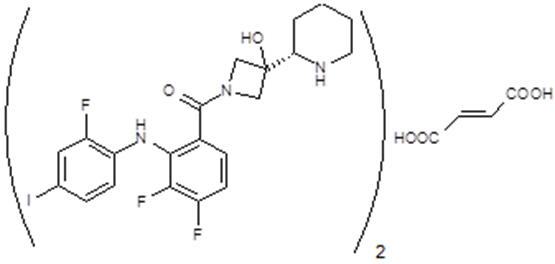
Cobimetinib is a fumarate salt appearing as white to off-white solid and exhibits a pH dependent solubility.
COTELLIC (cobimetinib) tablets are supplied as white, round, film-coated 20 mg tablets for oral administration, debossed on one side with "COB". Each 20 mg tablet contains 22 mg of cobimetinib fumarate, which corresponds to 20 mg of the cobimetinib free base.
The inactive ingredients of COTELLIC are: Tablet Core: microcrystalline cellulose, lactose monohydrate, croscarmellose sodium, magnesium stearate. Coating: polyvinyl alcohol, titanium dioxide, polyethylene glycol 3350, talc.
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Mechanism of Action
Cobimetinib is a reversible inhibitor of mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK)/extracellular signal regulated kinase 1 (MEK1) and MEK2. MEK proteins are upstream regulators of the extracellular signal-related kinase (ERK) pathway, which promotes cellular proliferation. BRAF V600E and K mutations result in constitutive activation of the BRAF pathway which includes MEK1 and MEK2. In mice implanted with tumor cell lines expressing BRAF V600E, cobimetinib inhibited tumor cell growth.
Cobimetinib and vemurafenib target two different kinases in the RAS/RAF/MEK/ERK pathway. Compared to either drug alone, coadministration of cobimetinib and vemurafenib resulted in increased apoptosis in vitro and reduced tumor growth in mouse implantation models of tumor cell lines harboring BRAF V600E mutations. Cobimetinib also prevented vemurafenib-mediated growth enhancement of a wild-type BRAF tumor cell line in an in vivo mouse implantation model.
Pharmacodynamics
Cardiac Electrophysiology
Clinically relevant QT prolongation has been reported with vemurafenib, further QTc prolongation was not observed when cobimetinib 60 mg daily was co-administered with vemurafenib. Monitor ECG and electrolytes before initiating treatment and routinely during treatment with cobimetinib, when administered with vemurafenib. Review the Full Prescribing Information for vemurafenib for details.
Pharmacokinetics
The pharmacokinetics of cobimetinib was studied in healthy subjects and cancer patients. Cobimetinib exhibits linear pharmacokinetics in the dose range of 3.5 to 100 mg (i.e., 0.06 to 1.7 times the recommended dosage). Following oral administration of COTELLIC 60 mg once daily, steady-state was reached by 9 days with a mean accumulation ratio of 2.4-fold (44% CV).
Absorption
Following oral dosing of 60 mg once daily in cancer patients, the median time to achieve peak plasma levels (T max ) was 2.4 (range:1–24) hours, geometric mean steady-state AUC 0-24h was 4340 ng∙h/mL (61% CV) and C max was 273 ng/mL (60% CV). The absolute bioavailability of COTELLIC was 46% (90% CI: 40%, 53%) in healthy subjects. A high-fat meal (comprised of approximately 150 calories from protein, 250 calories from carbohydrate, and 500–600 calories from fat) had no effect on cobimetinib AUC and C max after a single 20 mg COTELLIC was administered to healthy subjects.
Distribution
Cobimetinib is 95% bound to human plasma proteins in vitro, independent of drug concentration. No preferential binding to human red blood cells was observed (blood to plasma ratio of 0.93). The estimated apparent volume of distribution was 806 L in cancer patients based on a population PK analysis.
Elimination
Following oral administration of COTELLIC 60 mg once daily in cancer patients, the mean elimination half-life (t 1/2 ) was 44 (range: 23–70) hours and the mean apparent clearance (CL/F) was 13.8 L/h (61% CV).
Metabolism
CYP3A oxidation and UGT2B7 glucuronidation were the major pathways of cobimetinib metabolism in vitro. Following oral administration of a single 20 mg radiolabeled cobimetinib dose, no oxidative metabolites >10% of total circulating radioactivity were observed.
Excretion
Following oral administration of a single 20 mg radiolabeled cobimetinib dose, 76% of the dose was recovered in the feces (with 6.6% as unchanged drug) and 17.8% of the dose was recovered in the urine (with 1.6% as unchanged drug).
Specific Populations
Age, Sex, and Race/Ethnicity: Based on the population pharmacokinetic analysis, age (19–88 years), sex, or race/ethnicity does not have a clinically important effect on the systemic exposure of cobimetinib.
Hepatic Impairment
Following a single 10 mg COTELLIC dose, the geometric mean total cobimetinib exposure (AUC inf ) values were similar in subjects with mild or moderate hepatic impairment and was decreased by 31% in subjects with severe hepatic impairment compared to subjects with normal hepatic function. [ see Use in Specific Populations (8.6) ].
Renal Impairment
Cobimetinib undergoes minimal renal elimination. Cobimetinib exposures were similar in 151 patients with mild renal impairment (CLcr 60 to 89 mL/min), 48 patients with moderate renal impairment (CLcr 30 to 59 mL/min) and 286 patients with normal renal function (CLcr ≥90 mL/min) [see Use in Specific Populations (8.7) ].
Drug Interaction Studies
Vemurafenib: Coadministration of COTELLIC 60 mg once daily and vemurafenib 960 mg twice daily resulted in no clinically relevant pharmacokinetic drug interactions.
Effect of Strong and Moderate CYP3A Inhibitors on Cobimetinib: In vitro studies show that cobimetinib is a substrate of CYP3A. Coadministration of itraconazole (a strong CYP3A inhibitor) 200 mg once daily for 14 days with a single 10 mg cobimetinib dose increased mean cobimetinib AUC (90% CI) by 6.7-fold (5.6, 8.0) and mean C max (90% CI) by 3.2-fold (2.7, 3.7) in 15 healthy subjects. Simulations showed that predicted steady-state concentrations of cobimetinib at a reduced dose of 20 mg administered concurrently with short-term (less than 14 days) treatment of a moderate CYP3A inhibitor were similar to observed steady-state concentrations of cobimetinib at the 60 mg dose alone [see Drug Interactions (7.1) ] .
Effect of Strong and Moderate CYP3A Inducers on Cobimetinib: Based on simulations, cobimetinib exposures would decrease by 83% when coadministered with a strong CYP3A inducer and by 73% when coadministered with a moderate CYP3A inducer [see Drug Interactions (7.2) ] .
Effect of Cobimetinib on CYP Substrates: Coadministration of cobimetinib 60 mg once daily for 15 days with a single 30 mg dose of dextromethorphan (sensitive CYP2D6 substrate) or a single 2 mg dose of midazolam (sensitive CYP3A substrate) to 20 patients with solid tumors did not change dextromethorphan or midazolam systemic exposure. In vitro data indicated that cobimetinib may inhibit CYP3A and CYP2D6. Cobimetinib at clinically relevant concentrations is not an inhibitor of CYP1A2, 2B6, 2C8, 2C9 and 2C19 or inducer of CYP1A2, 2B6 and 3A4.
Effect of Transporters on Cobimetinib: Cobimetinib is a substrate of efflux transporter P-glycoprotein (P-gp), but is not a substrate of Breast Cancer Resistance Protein (BCRP), Organic Anion Transporting Polypeptide (OATP1B1 or OATP1B3) or Organic Cation Transporter (OCT1) in vitro. Drugs that inhibit P-gp may increase cobimetinib concentrations.
Effect of Cobimetinib on Transporters: In vitro data suggest that cobimetinib at clinically relevant concentrations does not inhibit P-gp, BCRP, OATP1B1, OATP1B3, OCT1, OAT1, OAT3, or OCT2.
Effect of Gastric Acid Reducing Drugs on Cobimetinib: Coadministration of a proton pump inhibitor, rabeprazole 20 mg once daily for 5 days, with a single dose of 20 mg COTELLIC under fed and fasted conditions did not result in a clinically important change in cobimetinib exposure.
NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenicity studies with cobimetinib have not been conducted. Cobimetinib was not genotoxic in studies evaluating reverse mutations in bacteria, chromosomal aberrations in mammalian cells, and micronuclei in bone marrow of rats.
No dedicated fertility studies have been performed with cobimetinib in animals; however, effects on reproductive tissues observed in general toxicology studies conducted in animals suggest that there is potential for cobimetinib to impair fertility. In female rats, degenerative changes included increased apoptosis/necrosis of corpora lutea and vaginal epithelial cells at cobimetinib doses approximately twice those in humans at the clinically recommended dose of 60 mg based on body surface area. In male dogs, testicular degeneration occurred at exposures as low as approximately 0.1 times the exposure in humans at the clinically recommended dose of 60 mg.
CLINICAL STUDIES
Unresectable or Metastatic Melanoma
The safety and efficacy of COTELLIC was established in a multicenter, randomized (1:1), double-blinded, placebo-controlled trial conducted in 495 patients with previously untreated, BRAF V600 mutation-positive, unresectable or metastatic, melanoma. The presence of BRAF V600 mutation was detected using the cobas ® 4800 BRAF V600 mutation test. All patients received vemurafenib 960 mg orally twice daily on days 1–28 and were randomized to receive COTELLIC 60 mg or matching placebo orally once daily on days 1–21 of an every 28-day cycle. Randomization was stratified by geographic region (North America vs. Europe vs. Australia/New Zealand/others) and disease stage (unresectable Stage IIIc, M1a, or M1b vs. Stage M1c). Treatment continued until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity. Patients randomized to receive placebo were not offered COTELLIC at the time of disease progression.
The major efficacy outcome was investigator-assessed progression-free survival (PFS) per RECIST v1.1. Additional efficacy outcomes were investigator-assessed confirmed objective response rate, overall survival, PFS as assessed by blinded independent central review, and duration of response.
The median age of the study population was 55 years (range 23 to 88 years), 58% of patients were male, 93% were White and 5% had no race reported, 60% had stage M1c disease, 72% had a baseline ECOG performance status of 0, 45% had an elevated baseline serum lactate dehydrogenase (LDH), 10% had received prior adjuvant therapy, and <1% had previously treated brain metastases. Patients with available tumor samples were retrospectively tested using next generation sequencing to further classify mutations as V600E or V600K; test results were obtained on 81% of randomized patients. Of these, 86% were identified as having a V600E mutation and 14% as having a V600K mutation.
Efficacy results are summarized in Table 7 and Figure 1 .
| COTELLIC + Vemurafenib (n=247) | Placebo + Vemurafenib (n=248) | |
|---|---|---|
| CI - Confidence Intervals; NE - not estimable | ||
| Progression-Free Survival (Investigator-Assessed) | ||
| Number of Events (%) | 143 (58%) | 180 (73%) |
| Progression | 131 | 169 |
| Death | 12 | 11 |
| Median PFS, months (95% CI) | 12.3 (9.5, 13.4) | 7.2 (5.6, 7.5) |
| Hazard Ratio (95% CI) | 0.56 (0.45, 0.70) | |
| p-value (stratified log-rank test) | <0.001 | |
| Overall Survival Based on the final overall survival analysis, conducted after 16 months from the PFS primary analysis | ||
| Number of Deaths (%) | 114 (46.2%) | 141 (56.9%) |
| Median OS, months (95% CI) | 22.3 (20.3, NE) | 17.4 (15.0, 19.8) |
| Hazard Ratio (95% CI) | 0.69 (0.54,0.88) | |
| p -value (stratified log-rank test) | 0.0032 | |
| Objective Response Rate | ||
| Objective Response Rate | 70% | 50% |
| (95% CI) | (64%, 75%) | (44%, 56%) |
| Complete Response | 16% | 10% |
| Partial Response | 54% | 40% |
| p-value | <0.001 | |
| Median Duration of Response, months (95% CI) | 13.0 (11.1, 16.6) | 9.2 (7.5, 12.8) |
Figure 1 Kaplan-Meier Curves of Overall Survival
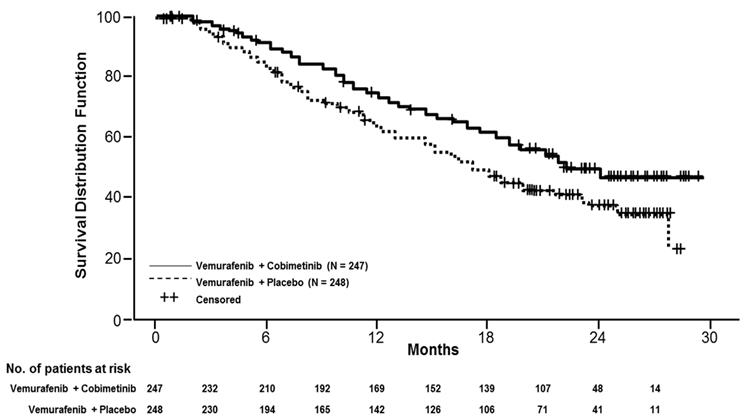
The effect on PFS was also supported by analysis of PFS based on the assessment by blinded independent review. A trend favoring the COTELLIC with vemurafenib arm was observed in exploratory subgroup analyses of PFS, OS, and ORR in both BRAF V600 mutation subtypes (V600E or V600K) in the 81% of patients in this trial where BRAF V600 mutation type was determined.
Histiocytic Neoplasms
A single-center, single-arm trial (Trial 2) was conducted to evaluate the efficacy, safety, and tolerability of COTELLIC as a single agent in adult patients with histologically confirmed histiocytic neoplasms of any mutational status. Patients with documented BRAF V600E mutations were enrolled if they were unable to access a BRAF inhibitor or discontinued a BRAF inhibitor due to toxicity. Enrolled patients had multi-system disease, recurrent or refractory disease, or single-system disease that is unlikely to benefit from conventional therapies, based on best available evidence.
The trial included 26 patients with histiocytic neoplasms including Langerhans Cell Histiocytosis (n=4), Rosai-Dorfman Disease (n=4), Erdheim-Chester Disease (n=13), Xanthogranuloma (n=2) and Mixed Histiocytosis (n=3). Patients with BRAF V600 mutant positive (n=6) and BRAF V600 Wild type (n=20) received COTELLIC. Twenty-one patients (81%) had received prior systemic therapies. The median age was 50.5 years (range, 18 to 79 years). Sixty-five percent of patients were men (n=17) and 35% were women (n=9). The majority of patients were White (85%), 8% were Black or African American and 4% were Asian; 96% were neither Hispanic nor Latino.
Patients were treated with COTELLIC 60 mg once daily for 21 days on, then 7 days off, in a 28-day treatment cycle (n=26). Eighteen patients required a dose reduction to 40 mg, and five patients required an additional dose reduction to 20 mg. The median duration of treatment following a dose reduction to 40 mg and 20 mg was 6.6 months and 3.9 months respectively.
The major efficacy outcome was best overall response rate (BORR), maintained on two occasions at least four weeks apart, as assessed by the investigator using the PET Response Criteria (PRC). Other clinical outcomes included PRC-based duration of response (DOR), and BORR maintained on two occasions at least four weeks apart, as assessed by investigator using RECIST v1.1.
The median duration of follow-up was 11.4 months (range, 0.2 to 36.8 months). The median time to PRC-based response was 2.0 (range, 0.2 to 17.3 months). The median PRC-based DOR was 31 months (range, 2 to 31 months). See Table 8 below for efficacy results.
| Response | PET Response, Complete Response by PRC was defined as a normalization of all lesions' (target and non-target) standardized uptake values (SUV) to background SUVliver (or SUVbrain for brain lesions only) , Partial Response by PRC was defined as a ≥50% decrease from baseline in sum of SUV of all target lesions relative to SUVliver (or SUVbrain for brain lesions only) Enrolled Patients (n=26) 24 PET-evaluable patients out of 26 enrolled patients. 1 patient had missing baseline scan. 1 patient had short follow-up duration (not enrolled at least 16 weeks prior to the clinical cutoff date (CCOD) | RECIST Response, Enrolled Patients (n=26) 19 RECIST-evaluable patients out of 26 enrolled patients. 6 patients had missing baseline scans; these patients had lesions that were not measurable by RECIST 1.1 definition. 1 patient had short follow-up duration (not enrolled at least 16 weeks prior to CCOD) |
|---|---|---|
| Overall response rate, n (%) | 20 (76.9%) | 12 (46.2%) |
| (95% Clopper-Pearson CI) | (56.4, 91) | (26.6, 66.6) |
| Best Response, n (%) | ||
| Complete Response | 16 (61.5%) | 3 (11.5%) |
| Partial Response | 4 (15.4%) | 9 (34.6%) |
HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
COTELLIC (cobimetinib) is supplied as 20 mg film-coated tablets debossed on one side with "COB". COTELLIC tablets are available in bottles of 63 tablets.
NDC 50242-717-01
Storage and Stability: Store at room temperature below 30°C (86°F).
Mechanism of Action
Cobimetinib is a reversible inhibitor of mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK)/extracellular signal regulated kinase 1 (MEK1) and MEK2. MEK proteins are upstream regulators of the extracellular signal-related kinase (ERK) pathway, which promotes cellular proliferation. BRAF V600E and K mutations result in constitutive activation of the BRAF pathway which includes MEK1 and MEK2. In mice implanted with tumor cell lines expressing BRAF V600E, cobimetinib inhibited tumor cell growth.
Cobimetinib and vemurafenib target two different kinases in the RAS/RAF/MEK/ERK pathway. Compared to either drug alone, coadministration of cobimetinib and vemurafenib resulted in increased apoptosis in vitro and reduced tumor growth in mouse implantation models of tumor cell lines harboring BRAF V600E mutations. Cobimetinib also prevented vemurafenib-mediated growth enhancement of a wild-type BRAF tumor cell line in an in vivo mouse implantation model.