Eliquis prior authorization resources
Most recent state uniform prior authorization forms
Brand Resources
Patient education
Patient education materials
Treatment initiation and patient onboarding
Dosing resources
Clinical information
Insurance resources
Prior authorization & coverage support
Financial assistance & copay programs
Other resources
Dosage & administration
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- Reduction of risk of stroke and systemic embolism in nonvalvular atrial fibrillation:
- The recommended dose is 5 mg orally twice daily. (2.1)
- In patients with at least 2 of the following characteristics: age greater than or equal to 80 years, body weight less than or equal to 60 kg, or serum creatinine greater than or equal to 1.5 mg/dL, the recommended dose is 2.5 mg orally twice daily. (2.1)
- Prophylaxis of DVT following hip or knee replacement surgery:
- The recommended dose is 2.5 mg orally twice daily. (2.1)
- Treatment of DVT and PE:
- The recommended dose is 10 mg taken orally twice daily for 7 days, followed by 5 mg taken orally twice daily. (2.1)
- Reduction in the risk of recurrent DVT and PE following initial therapy:
- The recommended dose is 2.5 mg taken orally twice daily. (2.1)
- Treatment of VTE and reduction in the risk of recurrent VTE in pediatric patients from birth and older after at least 5 days of initial anticoagulant treatment:
- See dosing recommendations in the Full Prescribing Information (2.2)
Recommended Dose in Adult Patients
Reduction of Risk of Stroke and Systemic Embolism in Patients with Nonvalvular Atrial Fibrillation
The recommended dose of ELIQUIS for most patients is 5 mg taken orally twice daily.
The recommended dose of ELIQUIS is 2.5 mg twice daily in patients with at least two of the following characteristics:
- age greater than or equal to 80 years
- body weight less than or equal to 60 kg
- serum creatinine greater than or equal to 1.5 mg/dL
Prophylaxis of Deep Vein Thrombosis Following Hip or Knee Replacement Surgery
The recommended dose of ELIQUIS is 2.5 mg taken orally twice daily. The initial dose should be taken 12 to 24 hours after surgery.
- In patients undergoing hip replacement surgery, the recommended duration of treatment is 35 days.
- In patients undergoing knee replacement surgery, the recommended duration of treatment is 12 days.
Treatment of DVT and PE
The recommended dose of ELIQUIS is 10 mg taken orally twice daily for the first 7 days of therapy. After 7 days, the recommended dose is 5 mg taken orally twice daily.
Reduction in the Risk of Recurrence of DVT and PE
The recommended dose of ELIQUIS is 2.5 mg taken orally twice daily after at least 6 months of treatment for DVT or PE [see Clinical Studies (14.3) ] .
2.2 Recommended Dose in Pediatric Patients
Treatment of Venous Thromboembolism (VTE) and Reduction in the Risk of Recurrent VTE in Pediatric Patients
The recommended dose of ELIQUIS is based on the patient’s weight, see Table 1. Adjust the dose according to weight-tier as treatment progresses. Initiate ELIQUIS treatment for pediatric patients from birth to less than 18 years of age following at least 5 days of initial anticoagulation therapy. Individualize duration of overall therapy after careful assessment of the treatment benefit and the risk for bleeding.
Table 1: Dose Recommendation in Pediatric Patients from Birth to less than 18 Years of Age for the Treatment of VTE and Reduction in the Risk of Recurrent VTE
Days 1-7 | Days 8 and beyond | ||
Presentation | Body weight (kg) | Dosing schedule | Dosing schedule |
Powder in Capsule 0.15 mg For pediatric use | 2.6 to less than 4 | 0.3 mg twice daily | 0.15 mg twice daily |
Tablet 0.5 mg For pediatric use | 4 to less than 6 | 1 mg twice daily | 0.5 mg twice daily |
6 to less than 9 | 2 mg twice daily | 1 mg twice daily | |
9 to less than 12 | 3 mg twice daily | 1.5 mg twice daily | |
12 to less than 18 | 4 mg twice daily | 2 mg twice daily | |
18 to less than 25 | 6 mg twice daily | 3 mg twice daily | |
25 to less than 35 | 8 mg twice daily | 4 mg twice daily | |
Tablets 2.5 mg and 5 mg | greater than or equal to 35 | 10 mg twice daily | 5 mg twice daily |
ELIQUIS is not recommended for use in pediatric patients less than 2.6 kg because ELIQUIS was not studied in these patients.
Missed Dose
If a dose of ELIQUIS is not taken at the scheduled time, the dose should be taken as soon as possible on the same day and twice-daily administration should be resumed. The dose should not be doubled to make up for a missed dose.
Temporary Interruption for Surgery and Other Interventions
ELIQUIS should be discontinued at least 48 hours prior to elective surgery or invasive procedures with a moderate or high risk of unacceptable or clinically significant bleeding [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) ] . ELIQUIS should be discontinued at least 24 hours prior to elective surgery or invasive procedures with a low risk of bleeding or where the bleeding would be non-critical in location and easily controlled. Bridging anticoagulation during the 24 to 48 hours after stopping ELIQUIS and prior to the intervention is not generally required. ELIQUIS should be restarted after the surgical or other procedures as soon as adequate hemostasis has been established.
Converting from or to ELIQUIS
Switching from warfarin to ELIQUIS: Warfarin should be discontinued and ELIQUIS started when the international normalized ratio (INR) is below 2.0.
Switching from ELIQUIS to warfarin: ELIQUIS affects INR, so that initial INR measurements during the transition to warfarin may not be useful for determining the appropriate dose of warfarin. One approach is to discontinue ELIQUIS and begin both a parenteral anticoagulant and warfarin at the time the next dose of ELIQUIS would have been taken, discontinuing the parenteral anticoagulant when INR reaches an acceptable range.
Switching from ELIQUIS to anticoagulants other than warfarin (oral or parenteral): Discontinue ELIQUIS and begin taking the new anticoagulant other than warfarin at the usual time of the next dose of ELIQUIS.
Switching from anticoagulants other than warfarin (oral or parenteral) to ELIQUIS: Discontinue the anticoagulant other than warfarin and begin taking ELIQUIS at the usual time of the next dose of the anticoagulant other than warfarin.
Combined P-gp and Strong CYP3A4 Inhibitors
For adult patients receiving ELIQUIS doses of 5 mg or 10 mg twice daily, reduce the dose by 50% when ELIQUIS is coadministered with drugs that are combined P-glycoprotein (P-gp) and strong cytochrome P450 3A4 (CYP3A4) inhibitors (e.g., ketoconazole, itraconazole, ritonavir) [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ] .
In patients already taking 2.5 mg twice daily, avoid coadministration of ELIQUIS with combined P-gp and strong CYP3A4 inhibitors [see Drug Interactions (7.1) ] .
Administration Options
Adult and pediatric patients weighing greater than or equal to 35 kg.
For patients who are unable to swallow whole tablets, 5 mg and 2.5 mg ELIQUIS tablets may be crushed and suspended in water, 5% dextrose in water (D5W), or apple juice, or mixed with applesauce and promptly administered orally [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ] . Alternatively, ELIQUIS tablets may be crushed and suspended in 60 mL of water or D5W and promptly delivered through a 12 French nasogastric tube [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ] .
Following administration of the dose, the nasogastric tube should be flushed with an additional 20 mL of water or D5W.
Crushed ELIQUIS tablets are stable in water, D5W, apple juice, and applesauce for up to 4 hours.
Pediatric patients weighing less than 35 kg.
Capsules
The 0.15 mg ELIQUIS SPRINKLE capsule must be opened, and the entire contents sprinkled in water or infant formula, mixed, and administered as described in the Instructions for Use (IFU). The liquid mixtures should be administered within 2 hours. Do not swallow capsule.
Tablets for oral suspension
The 0.5 mg ELIQUIS tablet in a packet for oral suspension should be mixed with water, infant formula, apple juice, or apple sauce as described in the IFU. The liquid mixtures with water, infant formula or apple juice should be administered within 2 hours and the mixture in apple sauce should be administered immediately. Each packet is for single use only. For pediatric patients who have difficulty swallowing, the liquid mixture can be delivered through a 5 French, 6.5 French or 12 French nasogastric tube or gastrostomy tube. See IFU.
Coverage
See specific coverage requirements, including prior authorization and step therapies.

By using PrescriberAI, you agree to the AI Terms of Use.
Eliquis prescribing information
WARNING: (A) PREMATURE DISCONTINUATION OF ELIQUIS INCREASES THE RISK OF THROMBOTIC EVENTS (B) SPINAL/EPIDURAL HEMATOMA
(A) PREMATURE DISCONTINUATION OF ELIQUIS INCREASES THE RISK OF THROMBOTIC EVENTS
Premature discontinuation of any oral anticoagulant, including ELIQUIS, increases the risk of thrombotic events. If anticoagulation with ELIQUIS is discontinued for a reason other than pathological bleeding or completion of a course of therapy, consider coverage with another anticoagulant [see Dosage and Administration (2.5) , Warnings and Precautions (5.1) , and Clinical Studies (14.1) ] .
(B) SPINAL/EPIDURAL HEMATOMA
Epidural or spinal hematomas may occur in patients treated with ELIQUIS who are receiving neuraxial anesthesia or undergoing spinal puncture. These hematomas may result in long-term or permanent paralysis. Consider these risks when scheduling patients for spinal procedures. Factors that can increase the risk of developing epidural or spinal hematomas in these patients include:
- use of indwelling epidural catheters
- concomitant use of other drugs that affect hemostasis, such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), platelet inhibitors, other anticoagulants
- a history of traumatic or repeated epidural or spinal punctures
- a history of spinal deformity or spinal surgery
- optimal timing between the administration of ELIQUIS and neuraxial procedures is not known
[see Warnings and Precautions (5.3) ]
Monitor patients frequently for signs and symptoms of neurological impairment. If neurological compromise is noted, urgent treatment is necessary [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3) ] .
Consider the benefits and risks before neuraxial intervention in patients anticoagulated or to be anticoagulated [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3) ] .
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
ELIQUIS is a factor Xa inhibitor indicated:
- to reduce the risk of stroke and systemic embolism in adult patients with nonvalvular atrial fibrillation. (1.1)
- for the prophylaxis of deep vein thrombosis (DVT), which may lead to pulmonary embolism (PE), in adult patients who have undergone hip or knee replacement surgery. (1.2)
- for the treatment of DVT and PE, and for the reduction in the risk of recurrent DVT and PE in adult patients following initial therapy. (1.3 , 1.4 , 1.5)
- Treatment of venous thromboembolism (VTE) and reduction in the risk of recurrent VTE in pediatric patients from birth and older after at least 5 days of initial anticoagulant treatment. (1.6)
Reduction of Risk of Stroke and Systemic Embolism in Nonvalvular Atrial Fibrillation
ELIQUIS is indicated to reduce the risk of stroke and systemic embolism in adult patients with nonvalvular atrial fibrillation.
Prophylaxis of Deep Vein Thrombosis Following Hip or Knee Replacement Surgery
ELIQUIS is indicated for the prophylaxis of deep vein thrombosis (DVT), which may lead to pulmonary embolism (PE), in adult patients who have undergone hip or knee replacement surgery.
Treatment of Deep Vein Thrombosis
ELIQUIS is indicated for the treatment of adults with deep vein thrombosis (DVT).
Treatment of Pulmonary Embolism
ELIQUIS is indicated for the treatment of adults with pulmonary embolism (PE).
Reduction in the Risk of Recurrence of Deep Vein Thrombosis and Pulmonary Embolism
ELIQUIS is indicated to reduce the risk of recurrent deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and pulmonary embolism (PE) in adult patients following initial therapy.
1.6 Treatment of Venous Thromboembolism and Reduction in the Risk of Recurrent Venous Thromboembolism in Pediatric Patients
ELIQUIS is indicated for the treatment of venous thromboembolism (VTE) and reduction in the risk of recurrent VTE in pediatric patients from birth and older after at least 5 days of initial anticoagulant treatment.
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- Reduction of risk of stroke and systemic embolism in nonvalvular atrial fibrillation:
- The recommended dose is 5 mg orally twice daily. (2.1)
- In patients with at least 2 of the following characteristics: age greater than or equal to 80 years, body weight less than or equal to 60 kg, or serum creatinine greater than or equal to 1.5 mg/dL, the recommended dose is 2.5 mg orally twice daily. (2.1)
- Prophylaxis of DVT following hip or knee replacement surgery:
- The recommended dose is 2.5 mg orally twice daily. (2.1)
- Treatment of DVT and PE:
- The recommended dose is 10 mg taken orally twice daily for 7 days, followed by 5 mg taken orally twice daily. (2.1)
- Reduction in the risk of recurrent DVT and PE following initial therapy:
- The recommended dose is 2.5 mg taken orally twice daily. (2.1)
- Treatment of VTE and reduction in the risk of recurrent VTE in pediatric patients from birth and older after at least 5 days of initial anticoagulant treatment:
- See dosing recommendations in the Full Prescribing Information (2.2)
Recommended Dose in Adult Patients
Reduction of Risk of Stroke and Systemic Embolism in Patients with Nonvalvular Atrial Fibrillation
The recommended dose of ELIQUIS for most patients is 5 mg taken orally twice daily.
The recommended dose of ELIQUIS is 2.5 mg twice daily in patients with at least two of the following characteristics:
- age greater than or equal to 80 years
- body weight less than or equal to 60 kg
- serum creatinine greater than or equal to 1.5 mg/dL
Prophylaxis of Deep Vein Thrombosis Following Hip or Knee Replacement Surgery
The recommended dose of ELIQUIS is 2.5 mg taken orally twice daily. The initial dose should be taken 12 to 24 hours after surgery.
- In patients undergoing hip replacement surgery, the recommended duration of treatment is 35 days.
- In patients undergoing knee replacement surgery, the recommended duration of treatment is 12 days.
Treatment of DVT and PE
The recommended dose of ELIQUIS is 10 mg taken orally twice daily for the first 7 days of therapy. After 7 days, the recommended dose is 5 mg taken orally twice daily.
Reduction in the Risk of Recurrence of DVT and PE
The recommended dose of ELIQUIS is 2.5 mg taken orally twice daily after at least 6 months of treatment for DVT or PE [see Clinical Studies (14.3) ] .
2.2 Recommended Dose in Pediatric Patients
Treatment of Venous Thromboembolism (VTE) and Reduction in the Risk of Recurrent VTE in Pediatric Patients
The recommended dose of ELIQUIS is based on the patient’s weight, see Table 1. Adjust the dose according to weight-tier as treatment progresses. Initiate ELIQUIS treatment for pediatric patients from birth to less than 18 years of age following at least 5 days of initial anticoagulation therapy. Individualize duration of overall therapy after careful assessment of the treatment benefit and the risk for bleeding.
Table 1: Dose Recommendation in Pediatric Patients from Birth to less than 18 Years of Age for the Treatment of VTE and Reduction in the Risk of Recurrent VTE
Days 1-7 | Days 8 and beyond | ||
Presentation | Body weight (kg) | Dosing schedule | Dosing schedule |
Powder in Capsule 0.15 mg For pediatric use | 2.6 to less than 4 | 0.3 mg twice daily | 0.15 mg twice daily |
Tablet 0.5 mg For pediatric use | 4 to less than 6 | 1 mg twice daily | 0.5 mg twice daily |
6 to less than 9 | 2 mg twice daily | 1 mg twice daily | |
9 to less than 12 | 3 mg twice daily | 1.5 mg twice daily | |
12 to less than 18 | 4 mg twice daily | 2 mg twice daily | |
18 to less than 25 | 6 mg twice daily | 3 mg twice daily | |
25 to less than 35 | 8 mg twice daily | 4 mg twice daily | |
Tablets 2.5 mg and 5 mg | greater than or equal to 35 | 10 mg twice daily | 5 mg twice daily |
ELIQUIS is not recommended for use in pediatric patients less than 2.6 kg because ELIQUIS was not studied in these patients.
Missed Dose
If a dose of ELIQUIS is not taken at the scheduled time, the dose should be taken as soon as possible on the same day and twice-daily administration should be resumed. The dose should not be doubled to make up for a missed dose.
Temporary Interruption for Surgery and Other Interventions
ELIQUIS should be discontinued at least 48 hours prior to elective surgery or invasive procedures with a moderate or high risk of unacceptable or clinically significant bleeding [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) ] . ELIQUIS should be discontinued at least 24 hours prior to elective surgery or invasive procedures with a low risk of bleeding or where the bleeding would be non-critical in location and easily controlled. Bridging anticoagulation during the 24 to 48 hours after stopping ELIQUIS and prior to the intervention is not generally required. ELIQUIS should be restarted after the surgical or other procedures as soon as adequate hemostasis has been established.
Converting from or to ELIQUIS
Switching from warfarin to ELIQUIS: Warfarin should be discontinued and ELIQUIS started when the international normalized ratio (INR) is below 2.0.
Switching from ELIQUIS to warfarin: ELIQUIS affects INR, so that initial INR measurements during the transition to warfarin may not be useful for determining the appropriate dose of warfarin. One approach is to discontinue ELIQUIS and begin both a parenteral anticoagulant and warfarin at the time the next dose of ELIQUIS would have been taken, discontinuing the parenteral anticoagulant when INR reaches an acceptable range.
Switching from ELIQUIS to anticoagulants other than warfarin (oral or parenteral): Discontinue ELIQUIS and begin taking the new anticoagulant other than warfarin at the usual time of the next dose of ELIQUIS.
Switching from anticoagulants other than warfarin (oral or parenteral) to ELIQUIS: Discontinue the anticoagulant other than warfarin and begin taking ELIQUIS at the usual time of the next dose of the anticoagulant other than warfarin.
Combined P-gp and Strong CYP3A4 Inhibitors
For adult patients receiving ELIQUIS doses of 5 mg or 10 mg twice daily, reduce the dose by 50% when ELIQUIS is coadministered with drugs that are combined P-glycoprotein (P-gp) and strong cytochrome P450 3A4 (CYP3A4) inhibitors (e.g., ketoconazole, itraconazole, ritonavir) [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ] .
In patients already taking 2.5 mg twice daily, avoid coadministration of ELIQUIS with combined P-gp and strong CYP3A4 inhibitors [see Drug Interactions (7.1) ] .
Administration Options
Adult and pediatric patients weighing greater than or equal to 35 kg.
For patients who are unable to swallow whole tablets, 5 mg and 2.5 mg ELIQUIS tablets may be crushed and suspended in water, 5% dextrose in water (D5W), or apple juice, or mixed with applesauce and promptly administered orally [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ] . Alternatively, ELIQUIS tablets may be crushed and suspended in 60 mL of water or D5W and promptly delivered through a 12 French nasogastric tube [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ] .
Following administration of the dose, the nasogastric tube should be flushed with an additional 20 mL of water or D5W.
Crushed ELIQUIS tablets are stable in water, D5W, apple juice, and applesauce for up to 4 hours.
Pediatric patients weighing less than 35 kg.
Capsules
The 0.15 mg ELIQUIS SPRINKLE capsule must be opened, and the entire contents sprinkled in water or infant formula, mixed, and administered as described in the Instructions for Use (IFU). The liquid mixtures should be administered within 2 hours. Do not swallow capsule.
Tablets for oral suspension
The 0.5 mg ELIQUIS tablet in a packet for oral suspension should be mixed with water, infant formula, apple juice, or apple sauce as described in the IFU. The liquid mixtures with water, infant formula or apple juice should be administered within 2 hours and the mixture in apple sauce should be administered immediately. Each packet is for single use only. For pediatric patients who have difficulty swallowing, the liquid mixture can be delivered through a 5 French, 6.5 French or 12 French nasogastric tube or gastrostomy tube. See IFU.
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
- 0.5 mg, pink, round, film-coated tablets for oral suspension packaged in packets. 1-count (0.5 mg), 3-count (1.5 mg), and 4-count (2 mg).
- 2.5 mg, yellow, round, biconvex, film-coated tablets with “893” debossed on one side and “2½” on the other side.
- 5 mg, pink, oval-shaped, biconvex, film-coated tablets with “894” debossed on one side and “5” on the other side.
- 0.15 mg, white to pale yellow powder for oral suspension, in a yellow opaque capsule marked “898”.
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
Pregnancy
Risk Summary
The limited available data on ELIQUIS use in pregnant women are insufficient to inform drug-associated risks of major birth defects, miscarriage, or adverse developmental outcomes. Treatment may increase the risk of bleeding during pregnancy and delivery. In animal reproduction studies, no adverse developmental effects were seen when apixaban was administered to rats (orally), rabbits (intravenously) and mice (orally) during organogenesis at unbound apixaban exposure levels up to 4, 1 and 19 times, respectively, the human exposure based on area under plasma-concentration time curve (AUC) at the Maximum Recommended Human Dose (MRHD) of 5 mg twice daily.
The estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated populations is unknown. All pregnancies have a background risk of birth defect, loss, or other adverse outcomes. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2% to 4% and 15% to 20%, respectively.
Clinical Considerations
Disease-associated maternal and/or embryo/fetal risk
Pregnancy confers an increased risk of thromboembolism that is higher for women with underlying thromboembolic disease and certain high-risk pregnancy conditions. Published data describe that women with a previous history of venous thrombosis are at high risk for recurrence during pregnancy.
Fetal/Neonatal adverse reactions
Use of anticoagulants, including ELIQUIS, may increase the risk of bleeding in the fetus and neonate.
Labor or delivery
All patients receiving anticoagulants, including pregnant women, are at risk for bleeding. ELIQUIS use during labor or delivery in women who are receiving neuraxial anesthesia may result in epidural or spinal hematomas. Consider use of a shorter acting anticoagulant as delivery approaches [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3) ] .
Data
Animal Data
No developmental toxicities were observed when apixaban was administered during organogenesis to rats (orally), rabbits (intravenously) and mice (orally) at unbound apixaban exposure levels 4, 1, and 19 times, respectively, the human exposures at the MRHD. There was no evidence of fetal bleeding, although conceptus exposure was confirmed in rats and rabbits. Oral administration of apixaban to rat dams from gestation day 6 through lactation day 21 at maternal unbound apixaban exposures ranging from 1.4 to 5 times the human exposures at the MRHD was not associated with reduced maternal mortality or reduced conceptus/neonatal viability, although increased incidences of peri-vaginal bleeding were observed in dams at all doses. There was no evidence of neonatal bleeding.
Lactation
Risk Summary
There are no data on the presence of apixaban or its metabolites in human milk, the effects on the breastfed child, or the effects on milk production. Apixaban and/or its metabolites were present in the milk of rats (see Data). Because human exposure through milk is unknown, breastfeeding is not recommended during treatment with ELIQUIS.
Data
Animal Data
Maximal plasma concentrations were observed after 30 minutes following a single oral administration of a 5 mg dose to lactating rats. Maximal milk concentrations were observed 6 hours after dosing. The milk to plasma AUC (0-24) ratio is 30:1 indicating that apixaban can accumulate in milk. The concentrations of apixaban in animal milk does not necessarily predict the concentration of drug in human milk.
Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
Females of reproductive potential requiring anticoagulation should discuss pregnancy planning with their physician.
The risk of clinically significant uterine bleeding, potentially requiring gynecological surgical interventions, identified with oral anticoagulants including ELIQUIS should be assessed in females of reproductive potential and those with abnormal uterine bleeding.
Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of ELIQUIS for the treatment of VTE and the reduction in the risk of recurrent VTE have been established in pediatric patients aged birth and older. Use of ELIQUIS for this indication is supported by evidence from adequate and well-controlled studies in adults with additional pharmacokinetic, safety, and efficacy data in pediatric patients. These studies included a randomized, active controlled, open label, multi-center study of ELIQUIS [see Adverse Reactions (6.1) and Clinical Studies (14.4) ] .
Geriatric Use
Of the total subjects in the ARISTOTLE and AVERROES clinical studies, >69% were 65 years of age and older, and >31% were 75 years of age and older. In the ADVANCE-1, ADVANCE-2, and ADVANCE-3 clinical studies, 50% of subjects were 65 years of age and older, while 16% were 75 years of age and older. In the AMPLIFY and AMPLIFY-EXT clinical studies, >32% of subjects were 65 years of age and older and >13% were 75 years of age and older. No clinically significant differences in safety or effectiveness were observed when comparing subjects in different age groups.
Renal Impairment
Reduction of Risk of Stroke and Systemic Embolism in Patients with Nonvalvular Atrial Fibrillation
The recommended dose is 2.5 mg twice daily in patients with at least two of the following characteristics [see Dosage and Administration (2.1) ] :
- age greater than or equal to 80 years
- body weight less than or equal to 60 kg
- serum creatinine greater than or equal to 1.5 mg/dL
Patients with End-Stage Renal Disease on Dialysis
Clinical efficacy and safety studies with ELIQUIS did not enroll patients with end-stage renal disease (ESRD) on dialysis. In patients with ESRD maintained on intermittent hemodialysis, administration of ELIQUIS at the usually recommended dose [see Dosage and Administration (2.1) ] will result in concentrations of apixaban and pharmacodynamic activity similar to those observed in the ARISTOTLE study [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ] . It is not known whether these concentrations will lead to similar stroke reduction and bleeding risk in patients with ESRD on dialysis as was seen in ARISTOTLE.
Prophylaxis of Deep Vein Thrombosis Following Hip or Knee Replacement Surgery, and Treatment of DVT and PE and Reduction in the Risk of Recurrence of DVT and PE
No dose adjustment is recommended for patients with renal impairment, including those with ESRD on dialysis [see Dosage and Administration (2.1) ] . Clinical efficacy and safety studies with ELIQUIS did not enroll patients with ESRD on dialysis or patients with a CrCl <15 mL/min; therefore, dosing recommendations are based on pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic (anti-FXa activity) data in subjects with ESRD maintained on dialysis [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ] .
Treatment of Venous Thromboembolism (VTE) and Reduction in the Risk of Recurrent VTE in Pediatric Patients
In pediatric patients equal to or greater than 2 years of age, ELIQUIS is not recommended in patients with an estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) <30 mL/min/1.73 m 2 body surface area (BSA).
In patients less than 2 years of age, ELIQUIS is not recommended in patients with inadequate renal function defined by sex and postnatal age as used in the pediatric VTE trial for ELIQUIS (see Table 12 below).
To estimate GFR, the pediatric VTE trial for ELIQUIS used the updated Schwartz formula, eGFR (ml/min/1.73m 2 ) = 0.413 • height (cm)/serum creatinine (mg/dL) for serum creatinine measured by an enzymatic creatinine method calibrated to be traceable to isotope dilution mass spectrometry (IDMS).
| Postnatal age (gender) | Threshold eGFR used to define inadequate renal function (mL/min/1.73 m 2 ) |
|---|---|
| Inadequate renal function was defined as <30% of 1 standard deviation (SD) below normal GFR for age and size as | |
| determined by the updated Schwartz formula for ages up to 2 years. Beyond 2 years of age, the qualifying GFR for | |
| the pediatric VTE study was ≥30 mL/min/1.73m 2 . | |
1 week (males and females) | <8 |
2–8 weeks (males and females) | <12 |
>8 weeks to <2 years (males and females) | <22 |
Hepatic Impairment
No dose adjustment is required in patients with mild hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh class A).
Because patients with moderate hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh class B) may have intrinsic coagulation abnormalities and there is limited clinical experience with ELIQUIS in these patients, dosing recommendations cannot be provided [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.2) ] .
ELIQUIS is not recommended in patients with severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh class C) [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.2) ] .
ELIQUIS has not been studied in pediatric patients with hepatic impairment.
CONTRAINDICATIONS
ELIQUIS is contraindicated in patients with the following conditions:
- Active pathological bleeding [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) and Adverse Reactions (6.1) ]
- Severe hypersensitivity reaction to ELIQUIS (e.g., anaphylactic reactions) [see Adverse Reactions (6.1) ]
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- ELIQUIS can cause serious, potentially fatal, bleeding. Promptly evaluate signs and symptoms of blood loss. An agent to reverse the anti-factor Xa activity of apixaban is available. (5.2)
- Prosthetic heart valves: ELIQUIS use not recommended. (5.4)
- Increased Risk of Thrombosis in Patients with Triple Positive Antiphospholipid Syndrome: ELIQUIS use not recommended. (5.6)
Increased Risk of Thrombotic Events after Premature Discontinuation
Premature discontinuation of any oral anticoagulant, including ELIQUIS, in the absence of adequate alternative anticoagulation increases the risk of thrombotic events. An increased rate of stroke was observed during the transition from ELIQUIS to warfarin in clinical trials in atrial fibrillation patients. If ELIQUIS is discontinued for a reason other than pathological bleeding or completion of a course of therapy, consider coverage with another anticoagulant [see Dosage and Administration (2.5) and Clinical Studies (14.1) ] .
Bleeding
ELIQUIS increases the risk of bleeding and can cause serious, potentially fatal, bleeding [see Dosage and Administration (2.1) and Adverse Reactions (6.1) ] .
Concomitant use of drugs affecting hemostasis increases the risk of bleeding. These include aspirin and other antiplatelet agents, other anticoagulants, heparin, thrombolytic agents, selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors, serotonin norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors, and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) [see Drug Interactions (7.3) ] .
Advise patients of signs and symptoms of blood loss and to report them immediately or go to an emergency room. Discontinue ELIQUIS in patients with active pathological hemorrhage.
Reversal of Anticoagulant Effect
A specific reversal agent (andexanet alfa) antagonizing the pharmacodynamic effect of apixaban is available for adults. However, its safety and efficacy have not been established in pediatric patients (refer to the USPI of andexanet alfa). The pharmacodynamic effect of ELIQUIS can be expected to persist for at least 24 hours after the last dose, i.e., for about two drug half-lives. Prothrombin complex concentrate (PCC), activated prothrombin complex concentrate or recombinant factor VIIa may be considered, but have not been evaluated in clinical studies [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.2) ] . When PCCs are used, monitoring for the anticoagulation effect of apixaban using a clotting test (PT, INR, or aPTT) or anti-factor Xa (FXa) activity is not useful and is not recommended. Activated oral charcoal reduces absorption of apixaban, thereby lowering apixaban plasma concentration [see Overdosage (10)] .
Hemodialysis does not appear to have a substantial impact on apixaban exposure [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ] . Protamine sulfate and vitamin K are not expected to affect the anticoagulant activity of apixaban. There is no experience with antifibrinolytic agents (tranexamic acid, aminocaproic acid) in individuals receiving apixaban. There is no experience with systemic hemostatics (desmopressin) in individuals receiving ELIQUIS, and they are not expected to be effective as a reversal agent.
Spinal/Epidural Anesthesia or Puncture
When neuraxial anesthesia (spinal/epidural anesthesia) or spinal/epidural puncture is employed, patients treated with antithrombotic agents for prevention of thromboembolic complications are at risk of developing an epidural or spinal hematoma which can result in long-term or permanent paralysis.
The risk of these events may be increased by the postoperative use of indwelling epidural catheters or the concomitant use of medicinal products affecting hemostasis. Indwelling epidural or intrathecal catheters should not be removed earlier than 24 hours after the last administration of ELIQUIS. The next dose of ELIQUIS should not be administered earlier than 5 hours after the removal of the catheter. The risk may also be increased by traumatic or repeated epidural or spinal puncture. If traumatic puncture occurs, delay the administration of ELIQUIS for 48 hours.
Monitor patients frequently for signs and symptoms of neurological impairment (e.g., numbness or weakness of the legs, or bowel or bladder dysfunction). If neurological compromise is noted, urgent diagnosis and treatment is necessary. Prior to neuraxial intervention the physician should consider the potential benefit versus the risk in anticoagulated patients or in patients to be anticoagulated for thromboprophylaxis.
No data are available on the timing of the placement or removal of neuraxial catheters in pediatric patients while on ELIQUIS. In such cases, discontinue ELIQUIS and consider a short acting parenteral anticoagulant.
Patients with Prosthetic Heart Valves
The safety and efficacy of ELIQUIS have not been studied in patients with prosthetic heart valves. Therefore, use of ELIQUIS is not recommended in these patients.
Acute PE in Hemodynamically Unstable Patients or Patients who Require Thrombolysis or Pulmonary Embolectomy
Initiation of ELIQUIS is not recommended as an alternative to unfractionated heparin for the initial treatment of patients with PE who present with hemodynamic instability or who may receive thrombolysis or pulmonary embolectomy.
Increased Risk of Thrombosis in Patients with Triple Positive Antiphospholipid Syndrome
Direct-acting oral anticoagulants (DOACs), including ELIQUIS, are not recommended for use in patients with triple-positive antiphospholipid syndrome (APS). For patients with APS (especially those who are triple positive [positive for lupus anticoagulant, anticardiolipin, and anti-beta 2-glycoprotein I antibodies]), treatment with DOACs has been associated with increased rates of recurrent thrombotic events compared with vitamin K antagonist therapy.
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following clinically significant adverse reactions are discussed in greater detail in other sections of the prescribing information.
- Increased Risk of Thrombotic Events After Premature Discontinuation [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) ]
- Bleeding [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) ]
- Spinal/Epidural Anesthesia or Puncture [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3) ]
Clinical Trials Experience
Adult Patients
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
Reduction of Risk of Stroke and Systemic Embolism in Patients with Nonvalvular Atrial Fibrillation
The safety of ELIQUIS was evaluated in the ARISTOTLE and AVERROES studies [see Clinical Studies (14) ] , including 11,284 patients exposed to ELIQUIS 5 mg twice daily and 602 patients exposed to ELIQUIS 2.5 mg twice daily. The duration of ELIQUIS exposure was ≥12 months for 9375 patients and ≥24 months for 3369 patients in the two studies. In ARISTOTLE, the mean duration of exposure was 89 weeks (>15,000 patient-years). In AVERROES, the mean duration of exposure was approximately 59 weeks (>3000 patient-years).
The most common reason for treatment discontinuation in both studies was for bleeding-related adverse reactions; in ARISTOTLE this occurred in 1.7% and 2.5% of patients treated with ELIQUIS and warfarin, respectively, and in AVERROES, in 1.5% and 1.3% on ELIQUIS and aspirin, respectively.
Bleeding in Patients with Nonvalvular Atrial Fibrillation in ARISTOTLE and AVERROES
Tables 2 and 3 show the number of patients experiencing major bleeding during the treatment period and the bleeding rate (percentage of subjects with at least one bleeding event per 100 patient-years) in ARISTOTLE and AVERROES.
| ELIQUIS N=9088 n (per 100 pt-year) | Warfarin N=9052 n (per 100 pt-year) | Hazard Ratio (95% CI) | P-value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| • Bleeding events within each subcategory were counted once per subject, but subjects may have contributed events to multiple endpoints. Bleeding events were counted during treatment or within 2 days of stopping study treatment (on-treatment period). | ||||
| † Defined as clinically overt bleeding accompanied by one or more of the following: a decrease in hemoglobin of ≥2 g/dL, a transfusion of 2 or more units of packed red blood cells, bleeding at a critical site: intracranial, intraspinal, intraocular, pericardial, intra-articular, intramuscular with compartment syndrome, retroperitoneal or with fatal outcome. | ||||
| ‡ Intracranial bleed includes intracerebral, intraventricular, subdural, and subarachnoid bleeding. Any type of hemorrhagic stroke was adjudicated and counted as an intracranial major bleed. | ||||
| § On-treatment analysis based on the safety population, compared to ITT analysis presented in Section 14. | ||||
| ¶ GI bleed includes upper GI, lower GI, and rectal bleeding. | ||||
| •• Fatal bleeding is an adjudicated death with the primary cause of death as intracranial bleeding or non-intracranial bleeding during the on-treatment period. | ||||
Major † | 327 (2.13) | 462 (3.09) | 0.69 (0.60, 0.80) | <0.0001 |
Intracranial (ICH) ‡ | 52 (0.33) | 125 (0.82) | 0.41 (0.30, 0.57) | |
Hemorrhagic stroke § | 38 (0.24) | 74 (0.49) | 0.51 (0.34, 0.75) | |
Other ICH | 15 (0.10) | 51 (0.34) | 0.29 (0.16, 0.51) | |
Gastrointestinal (GI) ¶ | 128 (0.83) | 141 (0.93) | 0.89 (0.70, 1.14) | |
Fatal•• | 10 (0.06) | 37 (0.24) | 0.27 (0.13, 0.53) | |
Intracranial | 4 (0.03) | 30 (0.20) | 0.13 (0.05, 0.37) | |
Non-intracranial | 6 (0.04) | 7 (0.05) | 0.84 (0.28, 2.15) | |
In ARISTOTLE, the results for major bleeding were generally consistent across most major subgroups including age, weight, CHADS 2 score (a scale from 0 to 6 used to estimate risk of stroke, with higher scores predicting greater risk), prior warfarin use, geographic region, and aspirin use at randomization (Figure 1). Subjects treated with ELIQUIS with diabetes bled more (3% per year) than did subjects without diabetes (1.9% per year).
Figure 1: Major Bleeding Hazard Ratios by Baseline Characteristics – ARISTOTLE Study
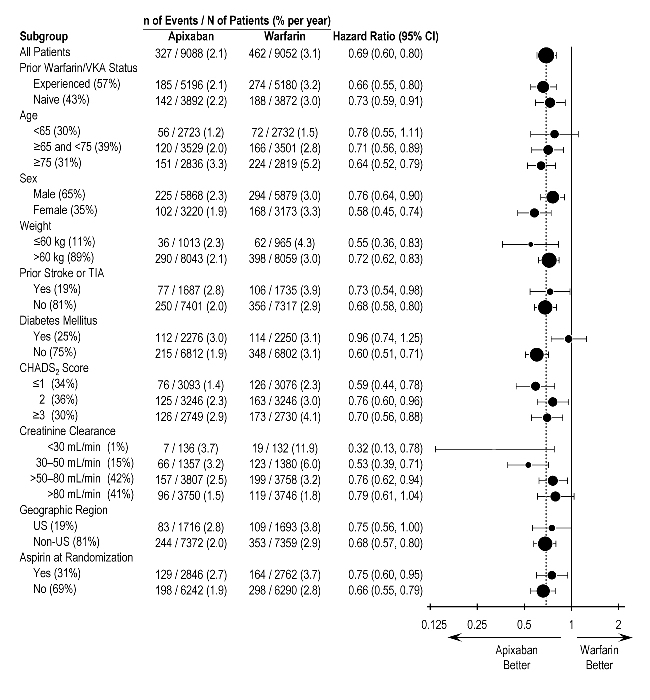
Note: The figure above presents effects in various subgroups, all of which are baseline characteristics and all of which were prespecified, if not the groupings. The 95% confidence limits that are shown do not take into account how many comparisons were made, nor do they reflect the effect of a particular factor after adjustment for all other factors. Apparent homogeneity or heterogeneity among groups should not be over-interpreted.
| ELIQUIS N=2798 n (%/year) | Aspirin N=2780 n (%/year) | Hazard Ratio (95% CI) | P-value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Major | 45 (1.41) | 29 (0.92) | 1.54 (0.96, 2.45) | 0.07 |
Fatal | 5 (0.16) | 5 (0.16) | 0.99 (0.23, 4.29) | |
Intracranial | 11 (0.34) | 11 (0.35) | 0.99 (0.39, 2.51) |
Events associated with each endpoint were counted once per subject, but subjects may have contributed events to multiple endpoints.
Other Adverse Reactions
Hypersensitivity reactions (including drug hypersensitivity, such as skin rash, and anaphylactic reactions, such as allergic edema) and syncope were reported in <1% of patients receiving ELIQUIS.
Prophylaxis of Deep Vein Thrombosis Following Hip or Knee Replacement Surgery
The safety of ELIQUIS has been evaluated in 1 Phase II and 3 Phase III studies including 5924 patients exposed to ELIQUIS 2.5 mg twice daily undergoing major orthopedic surgery of the lower limbs (elective hip replacement or elective knee replacement) treated for up to 38 days.
In total, 11% of the patients treated with ELIQUIS 2.5 mg twice daily experienced adverse reactions.
Bleeding results during the treatment period in the Phase III studies are shown in Table 4. Bleeding was assessed in each study beginning with the first dose of double-blind study drug.
| Bleeding Endpoint• | ADVANCE-3 Hip Replacement Surgery | ADVANCE-2 Knee Replacement Surgery | ADVANCE-1 Knee Replacement Surgery | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| • All bleeding criteria included surgical site bleeding. | ||||||
| † Includes 13 subjects with major bleeding events that occurred before the first dose of ELIQUIS (administered 12 to 24 hours post surgery). | ||||||
| ‡ Includes 5 subjects with major bleeding events that occurred before the first dose of ELIQUIS (administered 12 to 24 hours post surgery). | ||||||
| § Intracranial, intraspinal, intraocular, pericardial, an operated joint requiring re-operation or intervention, intramuscular with compartment syndrome, or retroperitoneal. Bleeding into an operated joint requiring re-operation or intervention was present in all patients with this category of bleeding. Events and event rates include one enoxaparin-treated patient in ADVANCE-1 who also had intracranial hemorrhage. | ||||||
| ¶ CRNM = clinically relevant nonmajor. | ||||||
ELIQUIS 2.5 mg po bid 35±3 days | Enoxaparin 40 mg sc qd 35±3 days | ELIQUIS 2.5 mg po bid 12±2 days | Enoxaparin 40 mg sc qd 12±2 days | ELIQUIS 2.5 mg po bid 12±2 days | Enoxaparin 30 mg sc q12h 12±2 days | |
First dose 12 to 24 hours post surgery | First dose 9 to 15 hours prior to surgery | First dose 12 to 24 hours post surgery | First dose 9 to 15 hours prior to surgery | First dose 12 to 24 hours post surgery | First dose 12 to 24 hours post surgery | |
All treated | N=2673 | N=2659 | N=1501 | N=1508 | N=1596 | N=1588 |
Major (including surgical site) | 22 (0.82%) † | 18 (0.68%) | 9 (0.60%) ‡ | 14 (0.93%) | 11 (0.69%) | 22 (1.39%) |
Fatal | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 (0.06%) |
Hgb decrease ≥2 g/dL | 13 (0.49%) | 10 (0.38%) | 8 (0.53%) | 9 (0.60%) | 10 (0.63%) | 16 (1.01%) |
Transfusion of ≥2 units RBC | 16 (0.60%) | 14 (0.53%) | 5 (0.33%) | 9 (0.60%) | 9 (0.56%) | 18 (1.13%) |
Bleed at critical site § | 1 (0.04%) | 1 (0.04%) | 1 (0.07%) | 2 (0.13%) | 1 (0.06%) | 4 (0.25%) |
Major + CRNM ¶ | 129 (4.83%) | 134 (5.04%) | 53 (3.53%) | 72 (4.77%) | 46 (2.88%) | 68 (4.28%) |
All | 313 (11.71%) | 334 (12.56%) | 104 (6.93%) | 126 (8.36%) | 85 (5.33%) | 108 (6.80%) |
Adverse reactions occurring in ≥1% of patients undergoing hip or knee replacement surgery in the 1 Phase II study and the 3 Phase III studies are listed in Table 5.
| ELIQUIS, n (%) 2.5 mg po bid N=5924 | Enoxaparin, n (%) 40 mg sc qd or 30 mg sc q12h N=5904 | |
|---|---|---|
Nausea | 153 (2.6) | 159 (2.7) |
Anemia (including postoperative and hemorrhagic anemia, and respective laboratory parameters) | 153 (2.6) | 178 (3.0) |
Contusion | 83 (1.4) | 115 (1.9) |
Hemorrhage (including hematoma, and vaginal and urethral hemorrhage) | 67 (1.1) | 81 (1.4) |
Postprocedural hemorrhage (including postprocedural hematoma, wound hemorrhage, vessel puncture-site hematoma, and catheter-site hemorrhage) | 54 (0.9) | 60 (1.0) |
Transaminases increased (including alanine aminotransferase increased and alanine aminotransferase abnormal) | 50 (0.8) | 71 (1.2) |
Aspartate aminotransferase increased | 47 (0.8) | 69 (1.2) |
Gamma-glutamyltransferase increased | 38 (0.6) | 65 (1.1) |
Less common adverse reactions in ELIQUIS-treated patients undergoing hip or knee replacement surgery occurring at a frequency of ≥0.1% to <1%:
Blood and lymphatic system disorders: thrombocytopenia (including platelet count decreases)
Vascular disorders: hypotension (including procedural hypotension)
Respiratory, thoracic, and mediastinal disorders: epistaxis
Gastrointestinal disorders: gastrointestinal hemorrhage (including hematemesis and melena), hematochezia
Hepatobiliary disorders: liver function test abnormal, blood alkaline phosphatase increased, blood bilirubin increased
Renal and urinary disorders: hematuria (including respective laboratory parameters)
Injury, poisoning, and procedural complications: wound secretion, incision-site hemorrhage (including incision-site hematoma), operative hemorrhage
Less common adverse reactions in ELIQUIS-treated patients undergoing hip or knee replacement surgery occurring at a frequency of <0.1%:
Gingival bleeding, hemoptysis, hypersensitivity, muscle hemorrhage, ocular hemorrhage (including conjunctival hemorrhage), rectal hemorrhage
Treatment of DVT and PE and Reduction in the Risk of Recurrence of DVT or PE
The safety of ELIQUIS has been evaluated in the AMPLIFY and AMPLIFY-EXT studies, including 2676 patients exposed to ELIQUIS 10 mg twice daily, 3359 patients exposed to ELIQUIS 5 mg twice daily, and 840 patients exposed to ELIQUIS 2.5 mg twice daily.
Common adverse reactions (≥1%) were gingival bleeding, epistaxis, contusion, hematuria, rectal hemorrhage, hematoma, menorrhagia, and hemoptysis.
AMPLIFY Study
The mean duration of exposure to ELIQUIS was 154 days and to enoxaparin/warfarin was 152 days in the AMPLIFY study. Adverse reactions related to bleeding occurred in 417 (15.6%) ELIQUIS-treated patients compared to 661 (24.6%) enoxaparin/warfarin-treated patients. The discontinuation rate due to bleeding events was 0.7% in the ELIQUIS-treated patients compared to 1.7% in enoxaparin/warfarin-treated patients in the AMPLIFY study.
In the AMPLIFY study, ELIQUIS was statistically superior to enoxaparin/warfarin in the primary safety endpoint of major bleeding (relative risk 0.31, 95% CI [0.17, 0.55], P-value <0.0001).
Bleeding results from the AMPLIFY study are summarized in Table 6.
| • CRNM = clinically relevant nonmajor bleeding. | |||
| Events associated with each endpoint were counted once per subject, but subjects may have contributed events to multiple endpoints. | |||
ELIQUIS N=2676 n (%) | Enoxaparin/Warfarin N=2689 n (%) | Relative Risk (95% CI) | |
Major | 15 (0.6) | 49 (1.8) | 0.31 (0.17, 0.55) p<0.0001 |
CRNM• | 103 (3.9) | 215 (8.0) | |
Major + CRNM | 115 (4.3) | 261 (9.7) | |
Minor | 313 (11.7) | 505 (18.8) | |
All | 402 (15.0) | 676 (25.1) | |
Adverse reactions occurring in ≥1% of patients in the AMPLIFY study are listed in Table 7.
ELIQUIS N=2676 n (%) | Enoxaparin/Warfarin N=2689 n (%) | |
Epistaxis | 77 (2.9) | 146 (5.4) |
Contusion | 49 (1.8) | 97 (3.6) |
Hematuria | 46 (1.7) | 102 (3.8) |
Menorrhagia | 38 (1.4) | 30 (1.1) |
Hematoma | 35 (1.3) | 76 (2.8) |
Hemoptysis | 32 (1.2) | 31 (1.2) |
Rectal hemorrhage | 26 (1.0) | 39 (1.5) |
Gingival bleeding | 26 (1.0) | 50 (1.9) |
AMPLIFY-EXT Study
The mean duration of exposure to ELIQUIS was approximately 330 days and to placebo was 312 days in the AMPLIFY-EXT study. Adverse reactions related to bleeding occurred in 219 (13.3%) ELIQUIS-treated patients compared to 72 (8.7%) placebo-treated patients. The discontinuation rate due to bleeding events was approximately 1% in the ELIQUIS-treated patients compared to 0.4% in those patients in the placebo group in the AMPLIFY-EXT study.
Bleeding results from the AMPLIFY-EXT study are summarized in Table 8.
| • CRNM = clinically relevant nonmajor bleeding. | |||
| Events associated with each endpoint were counted once per subject, but subjects may have contributed events to multiple endpoints. | |||
ELIQUIS 2.5 mg bid N=840 n (%) | ELIQUIS 5 mg bid N=811 n (%) | Placebo N=826 n (%) | |
Major | 2 (0.2) | 1 (0.1) | 4 (0.5) |
CRNM• | 25 (3.0) | 34 (4.2) | 19 (2.3) |
Major + CRNM | 27 (3.2) | 35 (4.3) | 22 (2.7) |
Minor | 75 (8.9) | 98 (12.1) | 58 (7.0) |
All | 94 (11.2) | 121 (14.9) | 74 (9.0) |
Adverse reactions occurring in ≥1% of patients in the AMPLIFY-EXT study are listed in Table 9.
ELIQUIS 2.5 mg bid N=840 n (%) | ELIQUIS 5 mg bid N=811 n (%) | Placebo N=826 n (%) | |
Epistaxis | 13 (1.5) | 29 (3.6) | 9 (1.1) |
Hematuria | 12 (1.4) | 17 (2.1) | 9 (1.1) |
Hematoma | 13 (1.5) | 16 (2.0) | 10 (1.2) |
Contusion | 18 (2.1) | 18 (2.2) | 18 (2.2) |
Gingival bleeding | 12 (1.4) | 9 (1.1) | 3 (0.4) |
Other Adverse Reactions
Less common adverse reactions in ELIQUIS-treated patients in the AMPLIFY or AMPLIFY-EXT studies occurring at a frequency of ≥0.1% to <1%:
Blood and lymphatic system disorders: hemorrhagic anemia
Gastrointestinal disorders: hematochezia, hemorrhoidal hemorrhage, gastrointestinal hemorrhage, hematemesis, melena, anal hemorrhage
Injury, poisoning, and procedural complications: wound hemorrhage, postprocedural hemorrhage, traumatic hematoma, periorbital hematoma
Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders: muscle hemorrhage
Reproductive system and breast disorders: vaginal hemorrhage, metrorrhagia, menometrorrhagia, genital hemorrhage
Vascular disorders: hemorrhage
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders: ecchymosis, skin hemorrhage, petechiae
Eye disorders: conjunctival hemorrhage, retinal hemorrhage, eye hemorrhage
Investigations: blood urine present, occult blood positive, occult blood, red blood cells urine positive
General disorders and administration-site conditions: injection-site hematoma, vessel puncture-site hematoma
Pediatric Patients
Treatment of Venous Thromboembolism (VTE) and Reduction in the Risk of Recurrent VTE in Pediatric Patients
The safety assessment of ELIQUIS is based on data from CV185325, a phase 3 study in 225 patients from birth and older. Patients were randomized 2:1 to receive body weight-adjusted doses of an age-appropriate formulation of ELIQUIS or standard of care. The standard of care treatments included unfractionated heparin (UFH), low molecular weight heparin (LMWH), or vitamin K antagonist (VKA).
Overall, the safety profile of ELIQUIS in pediatric patients from birth and older was generally similar to that in adults and consistent across different pediatric age groups. In pediatric patients, excessive menstrual bleeding occurred in 17 (11%) patients in the ELIQUIS group and 3 (4%) patients in the standard of care group. Epistaxis occurred in 24 (16%) patients in the ELIQUIS group and 14 (19%) patients in the standard of care group.
Bleeding results from Study CV185325 in pediatric patients with VTE are summarized in Table 10.
| • CRNM = clinically relevant nonmajor bleeding. | ||
| (1) 95% Confidence Interval calculated using the Clopper-Pearson exact method | ||
| Events associated with each endpoint were counted once per subject, but subjects may have contributed events to multiple endpoints. | ||
| •• UFH/LMWH for patients less than 2 years of age and UFH/LMWH/VKA for those equal to or greater than 2 years of age. | ||
ELIQUIS N=152 | Standard of care •• N=73 | |
Major Bleeding | ||
Number (%) Subjects with Event 95% Confidence Interval (1) | 0 | 0 |
CRNM• | ||
Number (%) Subjects with Event | 2 (1.3) | 1 (1.4) |
95% Confidence Interval (1) | (0.2, 4.7) | (0.0, 7.4) |
Minor Bleeding | ||
Number (%) Subjects with Event | 54 (35.5) | 21 (28.8) |
95% Confidence Interval (1) | (27.9, 43.7) | (18.8, 40.6) |
All | ||
Number (%) Subjects with Event | 55 (36.2) | 21 (28.8) |
95% Confidence Interval (1) | (28.6, 44.4) | (18.8, 40.6) |
Non-bleeding adverse reactions occurring in ≥10% of patients in study CV185325 are listed in Table 11.
Number of Subjects Evaluable for Adverse Reaction | ELIQUIS N=152 n (%) | Standard of Care N=73 n (%) |
Headache | 25 (16.4) | 11 (15.1) |
Vomiting | 21 (13.8) | 5 (6.8) |
DRUG INTERACTIONS
Combined P-gp and Strong CYP3A4 Inhibitors
For patients receiving ELIQUIS 5 mg or 10 mg twice daily, the dose of ELIQUIS should be decreased by 50% when coadministered with drugs that are combined P-gp and strong CYP3A4 inhibitors (e.g., ketoconazole, itraconazole, ritonavir) [see Dosage and Administration (2.6) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ] .
For patients receiving ELIQUIS at a dose of 2.5 mg twice daily, avoid coadministration with combined P-gp and strong CYP3A4 inhibitors [see Dosage and Administration (2.6) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ] .
Concomitant administration of combined P-gp and strong CYP3A4 inhibitors has not been studied in pediatric patients.
Apixaban is a substrate of both CYP3A4 and P-gp. Concomitant use with drugs that are combined P-gp and strong CYP3A4 inhibitors increases exposure to apixaban [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ] which increases the risk for bleeding.
Clarithromycin
Although clarithromycin is a combined P-gp and strong CYP3A4 inhibitor, pharmacokinetic data suggest that no dose adjustment is necessary with concomitant administration with ELIQUIS [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ] .
Combined P-gp and Strong CYP3A4 Inducers
Avoid concomitant use of ELIQUIS with combined P-gp and strong CYP3A4 inducers (e.g., rifampin, carbamazepine, phenytoin, St. John’s wort) because such drugs will decrease exposure to apixaban [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ] .
Apixaban is a substrate of both CYP3A4 and P-gp. Concomitant use with drugs that are combined P-gp and strong CYP3A4 inducers decreases exposure to apixaban [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ] which increases the risk for stroke and other thromboembolic events.
Anticoagulants and Antiplatelet Agents
Coadministration of antiplatelet agents, fibrinolytics, heparin, aspirin, and chronic NSAID use increases the risk of bleeding.
APPRAISE-2, a placebo-controlled clinical trial of ELIQUIS in high-risk, post-acute coronary syndrome patients treated with aspirin or the combination of aspirin and clopidogrel, was terminated early due to a higher rate of bleeding with ELIQUIS compared to placebo. The rate of ISTH major bleeding was 2.8% per year with ELIQUIS versus 0.6% per year with placebo in patients receiving single antiplatelet therapy and was 5.9% per year with ELIQUIS versus 2.5% per year with placebo in those receiving dual antiplatelet therapy.
In ARISTOTLE, concomitant use of aspirin increased the bleeding risk on ELIQUIS from 1.8% per year to 3.4% per year and concomitant use of aspirin and warfarin increased the bleeding risk from 2.7% per year to 4.6% per year. In this clinical trial, there was limited (2.3%) use of dual antiplatelet therapy with ELIQUIS.
DESCRIPTION
ELIQUIS (apixaban), a factor Xa (FXa) inhibitor, is chemically described as 1-(4-methoxyphenyl)-7-oxo-6-[4-(2-oxopiperidin-1-yl)phenyl]-4,5,6,7-tetrahydro-1 H -pyrazolo[3,4- c ]pyridine-3-carboxamide. Its molecular formula is C 25 H 25 N 5 O 4 , which corresponds to a molecular weight of 459.5. Apixaban has the following structural formula:

Apixaban is a white to pale-yellow powder. At physiological pH (1.2-6.8), apixaban does not ionize; its aqueous solubility across the physiological pH range is ~0.04 mg/mL.
ELIQUIS tablets 2.5 mg and 5 mg are available for oral administration and contain the following inactive ingredients: anhydrous lactose, microcrystalline cellulose, croscarmellose sodium, sodium lauryl sulfate, and magnesium stearate. The film coating contains lactose monohydrate, hypromellose, titanium dioxide, triacetin, and yellow iron oxide (2.5 mg tablets) or red iron oxide (5 mg tablets).
ELIQUIS 0.5 mg film coated tablets for oral suspension are supplied in packets containing 1 (0.5 mg), 3 (1.5 mg) or 4 (2 mg) apixaban tablets. The inactive ingredients are anhydrous lactose, microcrystalline cellulose, croscarmellose sodium, sodium lauryl sulfate, and magnesium stearate. The film coating contains lactose monohydrate, hypromellose, titanium dioxide, triacetin, and red iron oxide.
ELIQUIS SPRINKLE 0.15 mg for oral suspension is supplied as a white to off-white powder in capsules, which contain 0.15 mg apixaban and the following inactive ingredients: hypromellose and sugar spheres.
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Mechanism of Action
Apixaban is a selective inhibitor of FXa. It does not require antithrombin III for antithrombotic activity. Apixaban inhibits free and clot-bound FXa, and prothrombinase activity. Apixaban has no direct effect on platelet aggregation, but indirectly inhibits platelet aggregation induced by thrombin. By inhibiting FXa, apixaban decreases thrombin generation and thrombus development.
Pharmacodynamics
As a result of FXa inhibition, apixaban prolongs clotting tests such as prothrombin time (PT), INR, and activated partial thromboplastin time (aPTT). Changes observed in these clotting tests at the expected therapeutic dose, however, are small, subject to a high degree of variability, and not useful in monitoring the anticoagulation effect of apixaban.
The Rotachrom ® Heparin chromogenic assay was used to measure the effect of apixaban on FXa activity in humans primarily during the apixaban adult development program. A concentration-dependent increase in anti-FXa activity was observed in the dose range tested and was similar in healthy subjects and patients with AF.
This test is not recommended for assessing the anticoagulant effect of apixaban.
Effect of PCCs on Pharmacodynamics of ELIQUIS
There is no clinical experience to reverse bleeding with the use of 4-factor PCC products in individuals who have received ELIQUIS.
Effects of 4-factor PCCs on the pharmacodynamics of apixaban were studied in healthy subjects. Following administration of apixaban dosed to steady state, endogenous thrombin potential (ETP) returned to pre-apixaban levels 4 hours after the initiation of a 30-minute PCC infusion, compared to 45 hours with placebo. Mean ETP levels continued to increase and exceeded pre-apixaban levels reaching a maximum (34%-51% increase over pre-apixaban levels) at 21 hours after initiating PCC and remained elevated (21%-27% increase) at the end of the study (69 hours after initiation of PCC). The clinical relevance of this increase in ETP is unknown.
Pharmacodynamic Drug Interaction Studies
Pharmacodynamic drug interaction studies with aspirin, clopidogrel, aspirin and clopidogrel, prasugrel, enoxaparin, and naproxen were conducted. No pharmacodynamic interactions were observed with aspirin, clopidogrel, or prasugrel [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) ] . A 50% to 60% increase in anti-FXa activity was observed when ELIQUIS was coadministered with enoxaparin or naproxen.
Specific Populations
Renal impairment: Anti-FXa activity adjusted for exposure to apixaban was similar across renal function categories.
Hepatic impairment: Changes in anti-FXa activity were similar in patients with mild-to-moderate hepatic impairment and healthy subjects. However, in patients with moderate hepatic impairment, there is no clear understanding of the impact of this degree of hepatic function impairment on the coagulation cascade and its relationship to efficacy and bleeding. Patients with severe hepatic impairment were not studied.
Pediatric patients: In pediatric patients treated with apixaban, the correlation between anti-FXa activity and plasma concentration is linear with a slope close to 1.
Cardiac Electrophysiology
Apixaban has no effect on the QTc interval in humans at doses up to 50 mg.
Pharmacokinetics
Apixaban demonstrates linear pharmacokinetics with dose-proportional increases in exposure for oral doses up to 10 mg.
Absorption
The absolute bioavailability of apixaban is approximately 50% for doses up to 10 mg of ELIQUIS. Food does not affect the bioavailability of apixaban. Maximum concentrations (C max ) of apixaban appear 3 to 4 hours after oral administration of ELIQUIS. At doses ≥25 mg, apixaban displays dissolution-limited absorption with decreased bioavailability. Following oral administration of 10 mg of apixaban as 2 crushed 5 mg tablets suspended in 30 mL of water, exposure was similar to that after oral administration of 2 intact 5 mg tablets. Following oral administration of 10 mg of apixaban as 2 crushed 5 mg tablets mixed with 30 g of applesauce, the C max and AUC were 20% and 16% lower, respectively, when compared to administration of 2 intact 5 mg tablets. Following administration of a crushed 5 mg ELIQUIS tablet that was suspended in 60 mL D5W and delivered through a nasogastric tube, exposure was similar to that seen in other clinical trials involving healthy volunteers receiving a single oral 5 mg tablet dose.
Distribution
Plasma protein binding in humans is approximately 87%. The volume of distribution (Vss) is approximately 21 liters.
Metabolism
Approximately 25% of an orally administered apixaban dose is recovered in urine and feces as metabolites. Apixaban is metabolized mainly via CYP3A4 with minor contributions from CYP1A2, 2C8, 2C9, 2C19, and 2J2. O-demethylation and hydroxylation at the 3-oxopiperidinyl moiety are the major sites of biotransformation.
Unchanged apixaban is the major drug-related component in human plasma; there are no active circulating metabolites.
Elimination
Apixaban is eliminated in both urine and feces. Renal excretion accounts for about 27% of total clearance. Biliary and direct intestinal excretion contributes to elimination of apixaban in the feces.
Apixaban has a total clearance of approximately 3.3 L/hour and an apparent half-life of approximately 12 hours following oral administration.
Apixaban is a substrate of transport proteins: P-gp and breast cancer resistance protein.
Drug Interaction Studies
In i n vitro apixaban studies at concentrations significantly greater than therapeutic exposures, no inhibitory effect on the activity of CYP1A2, CYP2A6, CYP2B6, CYP2C8, CYP2C9, CYP2D6, CYP3A4/5, or CYP2C19, nor induction effect on the activity of CYP1A2, CYP2B6, or CYP3A4/5 were observed. Therefore, apixaban is not expected to alter the metabolic clearance of coadministered drugs that are metabolized by these enzymes. Apixaban is not a significant inhibitor of P-gp.
The effects of coadministered drugs on the pharmacokinetics of apixaban are summarized in Figure 2 [see also Warnings and Precautions (5.2) and Drug Interactions (7) ] .
Figure 2: Effect of Coadministered Drugs on the Pharmacokinetics of Apixaban

In dedicated studies conducted in healthy subjects, famotidine, atenolol, prasugrel, and enoxaparin did not meaningfully alter the pharmacokinetics of apixaban.
In studies conducted in healthy subjects, apixaban did not meaningfully alter the pharmacokinetics of digoxin, naproxen, atenolol, prasugrel, or acetylsalicylic acid.
Specific Populations
The effects of level of renal impairment, age, body weight, and level of hepatic impairment on the pharmacokinetics of apixaban are summarized in Figure 3.
Figure 3: Effect of Specific Populations on the Pharmacokinetics of Apixaban

• ESRD subjects treated with intermittent hemodialysis; reported PK findings are following single dose of apixaban posthemodialysis. † Results reflect CrCl of 15 mL/min based on regression analysis. ‡ Dashed vertical lines illustrate pharmacokinetic changes that were used to inform dosing recommendations. § No dose adjustment is recommended for nonvalvular atrial fibrillation patients unless at least 2 of the following patient characteristics (age greater than or equal to 80 years, body weight less than or equal to 60 kg, or serum creatinine greater than or equal to 1.5 mg/dL) are present.
Gender: A study in healthy subjects comparing the pharmacokinetics in males and females showed no meaningful difference.
Race: The results across pharmacokinetic studies in normal subjects showed no differences in apixaban pharmacokinetics among White/Caucasian, Asian, and Black/African American subjects. No dose adjustment is required based on race/ethnicity.
Hemodialysis in ESRD subjects: Systemic exposure to apixaban administered as a single 5 mg dose in ESRD subjects dosed immediately after the completion of a 4-hour hemodialysis session (postdialysis) is 36% higher when compared to subjects with normal renal function (Figure 3). The systemic exposure to apixaban administered 2 hours prior to a 4-hour hemodialysis session with a dialysate flow rate of 500 mL/min and a blood flow rate in the range of 350 to 500 mL/min is 17% higher compared to those with normal renal function. The dialysis clearance of apixaban is approximately 18 mL/min. The systemic exposure of apixaban is 14% lower on dialysis when compared to not on dialysis.
Protein binding was similar (92%-94%) between healthy controls and ESRD subjects during the on-dialysis and off-dialysis periods.
Pediatric Patients: Apixaban reached maximum concentration (C max ) in pediatric patients approximately 2 hours after single-dose administration. In pediatric patients, apixaban has a total apparent clearance of about 3.0 L/h.
An exploratory analysis in pediatric patients did not reveal relevant differences in apixaban exposure based on gender or race.
NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenesis: Apixaban was not carcinogenic when administered to mice and rats for up to 2 years. The systemic exposures (AUCs) of unbound apixaban in male and female mice at the highest doses tested (1500 and 3000 mg/kg/day) were 9 and 20 times, respectively, the human exposure of unbound drug at the MRHD of 10 mg/day. Systemic exposures of unbound apixaban in male and female rats at the highest dose tested (600 mg/kg/day) were 2 and 4 times, respectively, the human exposure.
Mutagenesis: Apixaban was neither mutagenic in the bacterial reverse mutation (Ames) assay, nor clastogenic in Chinese hamster ovary cells in vitro , in a 1-month in vivo/in vitro cytogenetics study in rat peripheral blood lymphocytes, or in a rat micronucleus study in vivo .
Impairment of Fertility: Apixaban had no effect on fertility in male or female rats when given at doses up to 600 mg/kg/day, a dose resulting in unbound apixaban exposure levels that are 3 and 4 times, respectively, the human exposure.
Apixaban administered to female rats at doses up to 1000 mg/kg/day from implantation through the end of lactation produced no adverse findings in male offspring (F1 generation) at doses up to 1000 mg/kg/day, a dose resulting in exposure to unbound apixaban that is 5 times the human exposure. Adverse effects in the F1-generation female offspring were limited to decreased mating and fertility indices at ≥200 mg/kg/day (a dose resulting in exposure to unbound apixaban that is ≥5 times the human exposure).
CLINICAL STUDIES
Reduction of Risk of Stroke and Systemic Embolism in Nonvalvular Atrial Fibrillation
ARISTOTLE
Evidence for the efficacy and safety of ELIQUIS was derived from ARISTOTLE, a multinational, double-blind study in patients with nonvalvular AF comparing the effects of ELIQUIS and warfarin on the risk of stroke and non-central nervous system (CNS) systemic embolism. In ARISTOTLE, patients were randomized to ELIQUIS 5 mg orally twice daily (or 2.5 mg twice daily in subjects with at least 2 of the following characteristics: age greater than or equal to 80 years, body weight less than or equal to 60 kg, or serum creatinine greater than or equal to 1.5 mg/dL) or to warfarin (targeted to an INR range of 2.0-3.0). Patients had to have one or more of the following additional risk factors for stroke:
- prior stroke or transient ischemic attack (TIA)
- prior systemic embolism
- age greater than or equal to 75 years
- arterial hypertension requiring treatment
- diabetes mellitus
- heart failure ≥New York Heart Association Class 2
- left ventricular ejection fraction ≤40%
The primary objective of ARISTOTLE was to determine whether ELIQUIS 5 mg twice daily (or 2.5 mg twice daily) was effective (noninferior to warfarin) in reducing the risk of stroke (ischemic or hemorrhagic) and systemic embolism. Superiority of ELIQUIS to warfarin was also examined for the primary endpoint (rate of stroke and systemic embolism), major bleeding, and death from any cause.
A total of 18,201 patients were randomized and followed on study treatment for a median of 89 weeks. Forty-three percent of patients were vitamin K antagonist (VKA) “naive,” defined as having received ≤30 consecutive days of treatment with warfarin or another VKA before entering the study. The mean age was 69 years and the mean CHADS 2 score (a scale from 0 to 6 used to estimate risk of stroke, with higher scores predicting greater risk) was 2.1. The population was 65% male, 83% Caucasian, 14% Asian, and 1% Black. There was a history of stroke, TIA, or non-CNS systemic embolism in 19% of patients. Concomitant diseases of patients in this study included hypertension 88%, diabetes 25%, congestive heart failure (or left ventricular ejection fraction ≤40%) 35%, and prior myocardial infarction 14%. Patients treated with warfarin in ARISTOTLE had a mean percentage of time in therapeutic range (INR 2.0-3.0) of 62%.
ELIQUIS was superior to warfarin for the primary endpoint of reducing the risk of stroke and systemic embolism (Table 13 and Figure 4). Superiority to warfarin was primarily attributable to a reduction in hemorrhagic stroke and ischemic strokes with hemorrhagic conversion compared to warfarin. Purely ischemic strokes occurred with similar rates on both drugs.
ELIQUIS also showed significantly fewer major bleeds than warfarin [see Adverse Reactions (6.1) ] .
| ELIQUIS N=9120 n (%/year) | Warfarin N=9081 n (%/year) | Hazard Ratio (95% CI) | P-value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| The primary endpoint was based on the time to first event (one per subject). Component counts are for subjects with any event, not necessarily the first. | ||||
Stroke or systemic embolism | 212 (1.27) | 265 (1.60) | 0.79 (0.66, 0.95) | 0.01 |
Stroke | 199 (1.19) | 250 (1.51) | 0.79 (0.65, 0.95) | |
Ischemic without hemorrhage | 140 (0.83) | 136 (0.82) | 1.02 (0.81, 1.29) | |
Ischemic with hemorrhagic conversion | 12 (0.07) | 20 (0.12) | 0.60 (0.29, 1.23) | |
Hemorrhagic | 40 (0.24) | 78 (0.47) | 0.51 (0.35, 0.75) | |
Unknown | 14 (0.08) | 21 (0.13) | 0.65 (0.33, 1.29) | |
Systemic embolism | 15 (0.09) | 17 (0.10) | 0.87 (0.44, 1.75) | |
Figure 4: Kaplan-Meier Estimate of Time to First Stroke or Systemic Embolism in ARISTOTLE (Intent-to-Treat Population)
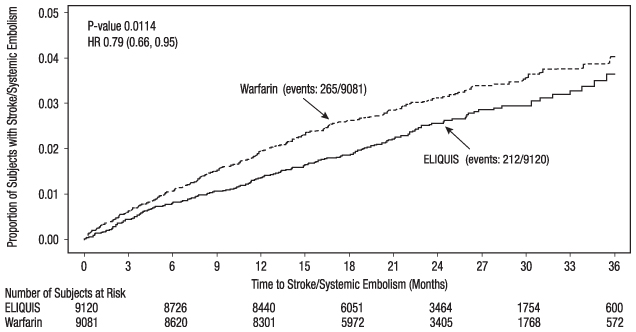
All-cause death was assessed using a sequential testing strategy that allowed testing for superiority if effects on earlier endpoints (stroke plus systemic embolus and major bleeding) were demonstrated. ELIQUIS treatment resulted in a significantly lower rate of all-cause death (p = 0.046) than did treatment with warfarin, primarily because of a reduction in cardiovascular death, particularly stroke deaths. Non-vascular death rates were similar in the treatment arms.
In ARISTOTLE, the results for the primary efficacy endpoint were generally consistent across most major subgroups including weight, CHADS 2 score (a scale from 0 to 6 used to predict risk of stroke in patients with AF, with higher scores predicting greater risk), prior warfarin use, level of renal impairment, geographic region, and aspirin use at randomization (Figure 5).
Figure 5: Stroke and Systemic Embolism Hazard Ratios by Baseline Characteristics – ARISTOTLE Study
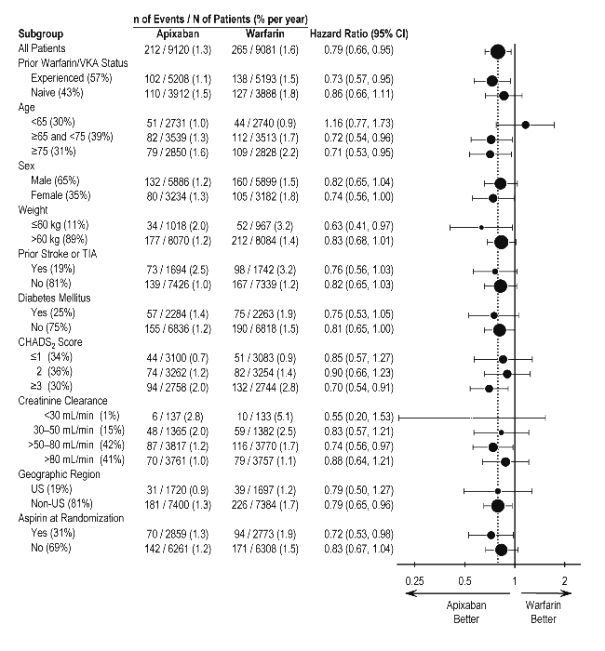
Note: The figure above presents effects in various subgroups, all of which are baseline characteristics and all of which were prespecified, if not the groupings. The 95% confidence limits that are shown do not take into account how many comparisons were made, nor do they reflect the effect of a particular factor after adjustment for all other factors. Apparent homogeneity or heterogeneity among groups should not be over-interpreted.
At the end of the ARISTOTLE study, warfarin patients who completed the study were generally maintained on a VKA with no interruption of anticoagulation. ELIQUIS patients who completed the study were generally switched to a VKA with a 2-day period of coadministration of ELIQUIS and VKA, so that some patients may not have been adequately anticoagulated after stopping ELIQUIS until attaining a stable and therapeutic INR. During the 30 days following the end of the study, there were 21 stroke or systemic embolism events in the 6791 patients (0.3%) in the ELIQUIS arm compared to 5 in the 6569 patients (0.1%) in the warfarin arm [see Dosage and Administration (2.4) ] .
AVERROES
In AVERROES, patients with nonvalvular atrial fibrillation thought not to be candidates for warfarin therapy were randomized to treatment with ELIQUIS 5 mg orally twice daily (or 2.5 mg twice daily in selected patients) or aspirin 81 to 324 mg once daily. The primary objective of the study was to determine if ELIQUIS was superior to aspirin for preventing the composite outcome of stroke or systemic embolism. AVERROES was stopped early on the basis of a prespecified interim analysis showing a significant reduction in stroke and systemic embolism for ELIQUIS compared to aspirin that was associated with a modest increase in major bleeding (Table 14) [see Adverse Reactions (6.1) ] .
| ELIQUIS N=2807 n (%/year) | Aspirin N=2791 n (%/year) | Hazard Ratio (95% CI) | P-value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Stroke or systemic embolism | 51 (1.62) | 113 (3.63) | 0.45 (0.32, 0.62) | <0.0001 |
Stroke | ||||
Ischemic or undetermined | 43 (1.37) | 97 (3.11) | 0.44 (0.31, 0.63) | |
Hemorrhagic | 6 (0.19) | 9 (0.28) | 0.67 (0.24, 1.88) | |
Systemic embolism | 2 (0.06) | 13 (0.41) | 0.15 (0.03, 0.68) | |
MI | 24 (0.76) | 28 (0.89) | 0.86 (0.50, 1.48) | |
All-cause death | 111 (3.51) | 140 (4.42) | 0.79 (0.62, 1.02) | 0.068 |
Vascular death | 84 (2.65) | 96 (3.03) | 0.87 (0.65, 1.17) |
Prophylaxis of Deep Vein Thrombosis Following Hip or Knee Replacement Surgery
The clinical evidence for the effectiveness of ELIQUIS is derived from the ADVANCE-1, ADVANCE-2, and ADVANCE-3 clinical trials in adult patients undergoing elective hip (ADVANCE-3) or knee (ADVANCE-2 and ADVANCE-1) replacement surgery. A total of 11,659 patients were randomized in 3 double-blind, multi-national studies. Included in this total were 1866 patients age 75 or older, 1161 patients with low body weight (≤60 kg), 2528 patients with Body Mass Index ≥33 kg/m 2 , and 625 patients with severe or moderate renal impairment.
In the ADVANCE-3 study, 5407 patients undergoing elective hip replacement surgery were randomized to receive either ELIQUIS 2.5 mg orally twice daily or enoxaparin 40 mg subcutaneously once daily. The first dose of ELIQUIS was given 12 to 24 hours post surgery, whereas enoxaparin was started 9 to 15 hours prior to surgery. Treatment duration was 32 to 38 days.
In patients undergoing elective knee replacement surgery, ELIQUIS 2.5 mg orally twice daily was compared to enoxaparin 40 mg subcutaneously once daily (ADVANCE-2, N=3057) or enoxaparin 30 mg subcutaneously every 12 hours (ADVANCE-1, N=3195). In the ADVANCE-2 study, the first dose of ELIQUIS was given 12 to 24 hours postsurgery, whereas enoxaparin was started 9 to 15 hours prior to surgery. In the ADVANCE-1 study, both ELIQUIS and enoxaparin were initiated 12 to 24 hours post surgery. Treatment duration in both ADVANCE-2 and ADVANCE-1 was 10 to 14 days.
In all 3 studies, the primary endpoint was a composite of adjudicated asymptomatic and symptomatic DVT, nonfatal PE, and all-cause death at the end of the double-blind intended treatment period. In ADVANCE-3 and ADVANCE-2, the primary endpoint was tested for noninferiority, then superiority, of ELIQUIS to enoxaparin. In ADVANCE-1, the primary endpoint was tested for noninferiority of ELIQUIS to enoxaparin.
The efficacy data are provided in Tables 15 and 16.
| • Events associated with each endpoint were counted once per subject but subjects may have contributed events to multiple endpoints. † Total VTE includes symptomatic and asymptomatic DVT and PE. ‡ Includes symptomatic and asymptomatic DVT. | |||
ADVANCE-3 | |||
Events During 35-Day Treatment Period | ELIQUIS 2.5 mg po bid | Enoxaparin 40 mg sc qd | Relative Risk (95% CI) P-value |
Number of Patients | N=1949 | N=1917 | |
Total VTE † /All-cause death | 27 (1.39%) (0.95, 2.02) | 74 (3.86%) (3.08, 4.83) | 0.36 (0.22, 0.54) p<0.0001 |
Number of Patients | N=2708 | N=2699 | |
All-cause death | 3 (0.11%) (0.02, 0.35) | 1 (0.04%) (0.00, 0.24) | |
PE | 3 (0.11%) (0.02, 0.35) | 5 (0.19%) (0.07, 0.45) | |
Symptomatic DVT | 1 (0.04%) (0.00, 0.24) | 5 (0.19%) (0.07, 0.45) | |
Number of Patients | N=2196 | N=2190 | |
Proximal DVT ‡ | 7 (0.32%) (0.14, 0.68) | 20 (0.91%) (0.59, 1.42) | |
Number of Patients | N=1951 | N=1908 | |
Distal DVT ‡ | 20 (1.03%) (0.66, 1.59) | 57 (2.99%) (2.31, 3.86) | |
| ADVANCE-1 | ADVANCE-2 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| • Events associated with each endpoint were counted once per subject but subjects may have contributed events to multiple endpoints. † Total VTE includes symptomatic and asymptomatic DVT and PE. ‡ Includes symptomatic and asymptomatic DVT. | ||||||
Events during 12-day treatment period | ELIQUIS 2.5 mg po bid | Enoxaparin 30 mg sc q12h | Relative Risk (95% CI) P-value | ELIQUIS 2.5 mg po bid | Enoxaparin 40 mg sc qd | Relative Risk (95% CI) P-value |
Number of Patients | N=1157 | N=1130 | N=976 | N=997 | ||
Total VTE † /All-cause death | 104 (8.99%) (7.47, 10.79) | 100 (8.85%) (7.33, 10.66) | 1.02 (0.78, 1.32) NS | 147 (15.06%) (12.95, 17.46) | 243 (24.37%) (21.81, 27.14) | 0.62 (0.51, 0.74) p<0.0001 |
Number of Patients | N=1599 | N=1596 | N=1528 | N=1529 | ||
All-cause death | 3 (0.19%) (0.04, 0.59) | 3 (0.19%) (0.04, 0.59) | 2 (0.13%) (0.01, 0.52) | 0 (0%) (0.00, 0.31) | ||
PE | 16 (1.0%) (0.61, 1.64) | 7 (0.44%) (0.20, 0.93) | 4 (0.26%) (0.08, 0.70) | 0 (0%) (0.00, 0.31) | ||
Symptomatic DVT | 3 (0.19%) (0.04, 0.59) | 7 (0.44%) (0.20, 0.93) | 3 (0.20%) (0.04, 0.61) | 7 (0.46%) (0.20, 0.97) | ||
Number of Patients | N=1254 | N=1207 | N=1192 | N=1199 | ||
Proximal DVT ‡ | 9 (0.72%) (0.36, 1.39) | 11 (0.91%) (0.49, 1.65) | 9 (0.76%) (0.38, 1.46) | 26 (2.17%) (1.47, 3.18) | ||
Number of Patients | N=1146 | N=1133 | N=978 | N=1000 | ||
Distal DVT ‡ | 83 (7.24%) (5.88, 8.91) | 91 (8.03%) (6.58, 9.78) | 142 (14.52%) (12.45, 16.88) | 239 (23.9%) (21.36, 26.65) | ||
The efficacy profile of ELIQUIS was generally consistent across subgroups of interest for this indication (e.g., age, gender, race, body weight, renal impairment).
Treatment of DVT and PE and Reduction in the Risk of Recurrence of DVT and PE
Efficacy and safety of ELIQUIS for the treatment of DVT and PE, and for the reduction in the risk of recurrent DVT and PE following 6 to 12 months of anticoagulant treatment was derived from the AMPLIFY and AMPLIFY-EXT studies. Both studies were randomized, parallel-group, double-blind trials in patients with symptomatic proximal DVT and/or symptomatic PE. All key safety and efficacy endpoints were adjudicated in a blinded manner by an independent committee.
AMPLIFY
The primary objective of AMPLIFY was to determine whether ELIQUIS was noninferior to enoxaparin/warfarin for the incidence of recurrent VTE (venous thromboembolism) or VTE-related death. Patients with an objectively confirmed symptomatic DVT and/or PE were randomized to treatment with ELIQUIS 10 mg twice daily orally for 7 days followed by ELIQUIS 5 mg twice daily orally for 6 months, or enoxaparin 1 mg/kg twice daily subcutaneously for at least 5 days (until INR ≥2) followed by warfarin (target INR range 2.0-3.0) orally for 6 months. Patients who required thrombectomy, insertion of a caval filter, or use of a fibrinolytic agent, and patients with creatinine clearance <25 mL/min, significant liver disease, an existing heart valve or atrial fibrillation, or active bleeding were excluded from the AMPLIFY study. Patients were allowed to enter the study with or without prior parenteral anticoagulation (up to 48 hours).
A total of 5244 patients were evaluable for efficacy and were followed for a mean of 154 days in the ELIQUIS group and 152 days in the enoxaparin/warfarin group. The mean age was 57 years. The AMPLIFY study population was 59% male, 83% Caucasian, 8% Asian, and 4% Black. For patients randomized to warfarin, the mean percentage of time in therapeutic range (INR 2.0-3.0) was 60.9%.
Approximately 90% of patients enrolled in AMPLIFY had an unprovoked DVT or PE at baseline. The remaining 10% of patients with a provoked DVT or PE were required to have an additional ongoing risk factor in order to be randomized, which included previous episode of DVT or PE, immobilization, history of cancer, active cancer, and known prothrombotic genotype.
ELIQUIS was shown to be noninferior to enoxaparin/warfarin in the AMPLIFY study for the primary endpoint of recurrent symptomatic VTE (nonfatal DVT or nonfatal PE) or VTE-related death over 6 months of therapy (Table 17).
| ELIQUIS N=2609 n | Enoxaparin/Warfarin N=2635 n | Relative Risk (95% CI) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| • Noninferior compared to enoxaparin/warfarin (P-value <0.0001). † Events associated with each endpoint were counted once per subject, but subjects may have contributed events to multiple endpoints. | |||
VTE or VTE-related death• | 59 (2.3%) | 71 (2.7%) | 0.84 (0.60, 1.18) |
DVT † | 22 (0.8%) | 35 (1.3%) | |
PE † | 27 (1.0%) | 25 (0.9%) | |
VTE-related death † | 12 (0.4%) | 16 (0.6%) | |
VTE or all-cause death | 84 (3.2%) | 104 (4.0%) | 0.82 (0.61, 1.08) |
VTE or CV-related death | 61 (2.3%) | 77 (2.9%) | 0.80 (0.57, 1.11) |
In the AMPLIFY study, patients were stratified according to their index event of PE (with or without DVT) or DVT (without PE). Efficacy in the initial treatment of VTE was consistent between the two subgroups.
AMPLIFY-EXT
Patients who had been treated for DVT and/or PE for 6 to 12 months with anticoagulant therapy without having a recurrent event were randomized to treatment with ELIQUIS 2.5 mg orally twice daily, ELIQUIS 5 mg orally twice daily, or placebo for 12 months. Approximately one-third of patients participated in the AMPLIFY study prior to enrollment in the AMPLIFY-EXT study.
A total of 2482 patients were randomized to study treatment and were followed for a mean of approximately 330 days in the ELIQUIS group and 312 days in the placebo group. The mean age in the AMPLIFY-EXT study was 57 years. The study population was 57% male, 85% Caucasian, 5% Asian, and 3% Black.
The AMPLIFY-EXT study enrolled patients with either an unprovoked DVT or PE at baseline (approximately 92%) or patients with a provoked baseline event and one additional risk factor for recurrence (approximately 8%). However, patients who had experienced multiple episodes of unprovoked DVT or PE were excluded from the AMPLIFY-EXT study. In the AMPLIFY-EXT study, both doses of ELIQUIS were superior to placebo in the primary endpoint of symptomatic, recurrent VTE (nonfatal DVT or nonfatal PE), or all-cause death (Table 18).
| Relative Risk (95% CI) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ELIQUIS 2.5 mg bid N=840 | ELIQUIS 5 mg bid N=813 | Placebo N=829 | ELIQUIS 2.5 mg bid vs Placebo | ELIQUIS 5 mg bid vs Placebo | |
n (%) | |||||
Recurrent VTE or all-cause death | 32 (3.8) | 34 (4.2) | 96 (11.6) | 0.33 (0.22, 0.48) p<0.0001 | 0.36 (0.25, 0.53) p<0.0001 |
DVT• | 19 (2.3) | 28 (3.4) | 72 (8.7) | ||
PE• | 23 (2.7) | 25 (3.1) | 37 (4.5) | ||
All-cause death | 22 (2.6) | 25 (3.1) | 33 (4.0) | ||
• Patients with more than one event are counted in multiple rows.
Treatment of VTE and Prevention of Recurrent VTE in Pediatric Patients from birth and older
Study CV185325
ELIQUIS for the treatment of venous thromboembolism (VTE) and reduction in the risk of recurrent VTE was evaluated in Study CV185325, a multicenter, randomized, active-controlled, open-label, multi-center study in 229 pediatric patients from birth to less than 18 years with confirmed VTE. This was a descriptive study and no formal inferences were performed. There were 137 patients aged 12 to < 18 years, 44 patients aged 2 to < 12 years, 32 patients aged 28 days to less than 2 years and 16 patients from birth to less than 27 days. Overall, the median age was 14.2 years with a range of 0.04 to 18.0 years. Neonates and infants were excluded from enrollment if they were < 34 weeks’ gestation (until age of > 6 months) or had a body weight of < 2.6 kg. For pre-term infants born between 34 and <37 weeks gestation, neonates who reached 37 weeks starting from actual date of birth (postnatal age), from 27 day neonatal period starting from actual date of birth (postnatal age), or from when the postmenstrual age (gestational age defined as time elapsed between first day of last normal menstrual period and the day of delivery plus postnatal age) and enrolled the neonate no more than 27 days thereafter. There were 101 (44.1%) males, and 128 (55.9%) females in the study. One hundred and seventy-five (76.4%) patients were White, 31 (13.5%) were Black, 9 (3.9%) were Asian, 4 (1.7%) were Other, 2 (0.9%) were Multiracial and 1 (0.4%) was American Indian or Alaska Native, and 7 (3.1%) were missing this information. Twenty-five (10.9%) were Hispanic or Latino and 204 (89.1%) were not Hispanic or Latino.
Index VTE was classified as deep venous thrombosis (DVT), pulmonary embolism (PE), device-related thrombosis (neonatal population only), and other VTE (i.e. cerebral vein and sinus thrombosis, renal vein thrombosis, intracardiac thrombus). Prior to randomization, patients could be treated with SOC anticoagulation for up to 14 days; overall mean (SD) duration of treatment with SOC anticoagulation prior to randomization was 4.9 (2.6) days, and for 92.9% of patients the duration was between 0 and 7 days. Patients were randomized according to a 2:1 ratio to receive either an age-appropriate formulation and body weight-adjusted doses of ELIQUIS or SOC. For patients 2 to less than 18 years, SOC was comprised of low molecular weight heparins (LMWH), unfractionated heparins (UFH) or vitamin K antagonists (VKA). For patients 28 days to less than 2 years of age, SOC was limited to heparins (UFH or LMWH). The main treatment phase lasted 6 to 12 weeks for patients aged birth to less than 2 years, and 12 weeks for patients aged greater than 2 years. Patients aged 28 days to less than 18 years who were randomized to receive apixaban had the option to continue apixaban treatment for 6 to 12 additional weeks in the extension phase.
A diagnostic imaging test was obtained at baseline, at week 6, and end of treatment for patients ≥2 years of age and at baseline and end of treatment for <2 years of age.
| • Recurrent VTE, defined as either contiguous progression or non-contiguous new thrombus and including, but not limited to DVT, PE and paradoxical embolism. | ||
| (1) 95% Confidence Interval calculated using the Clopper-Pearson exact method | ||
| •• UFH/LMWH for patients less than 2 years of age and UFH/LMWH/VKA for those equal to or greater than 2 years of age. | ||
| ••• no VTE related mortality was observed in either treatment arms during the study. | ||
ELIQUIS N=155 | Standard of care •• N=74 | |
Symptomatic and asymptomatic recurrent VTE• and VTE• related mortality••• | ||
Number (%) Subjects with Event | 4 (2.6) | 2 (2.7) |
95% Confidence Interval (1) | (0.7, 6.5) | (0.3, 9.4) |
HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
How Supplied
ELIQUIS (apixaban) tablets for oral use, ELIQUIS (apixaban) tablets for oral suspension, and ELIQUIS SPRINKLE (apixaban) for oral suspension are available as listed in the table below.
Strength | Dosage form/Description | Markings | Package Size | NDC Code |
0.15 mg | Powder In a yellow, opaque capsule | Printed with “898” | Bottles of 28 | 0003-0898-28 |
0.5 mg | Film-coated Tablet for oral suspension, Pink, round | N/A | Carton of 28 packets 28 count tablet carton (1 tablet per packet) 84 count tablet carton (3 tablets per packet) 112 count tablet carton (4 tablets per packet) | 0003-1028-28 0003-3084-28 0003-4112-28 |
2.5 mg | Film-coated Tablet Yellow, round, biconvex | Debossed with “893” on one side and “2½” on the other side | Bottles of 60 Hospital Unit-Dose Blister Package of 100 | 0003-0893-21 0003-0893-31 |
5 mg | Film-coated Tablet Pink, oval, biconvex | Debossed with “894” on one side and “5” on the other side | Bottles of 60 Bottles of 74 Hospital Unit-Dose Blister Package of 100 30-Day Starter Pack for Treatment of DVT and PE Containing 74 Tablets (1 blister pack of 42 tablets and 1 blister pack of 32 tablets) | 0003-0894-21 0003-0894-70 0003-0894-31 0003-3764-74 |
Storage and Handling
Store ELIQUIS and ELIQUIS SPRINKLE at 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F); excursions permitted between 15°C to 30°C (59°F to 86°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature].
INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE
ELIQUIS ® (ELL EH KWISS) (APIXABAN) TABLETS FOR ORAL SUSPENSION
Important information you need to know before giving a dose of ELIQUIS tablets for oral suspension (ELIQUIS tablets):
|
Preparing the prescribed dose of ELIQUIS tablets
There are 2 ways you can mix and give ELIQUIS tablets:
- With liquid method, using an oral dosing syringe, or
- With food method, using a small bowl and spoon.
You will need a medicine cup and oral dosing syringe (liquid mixing method) or a cup and small spoon (food mixing method) to give this medicine.
Liquid Mixing Method
❏ Step 1: Prepare Supplies
You can ask your pharmacist for the oral dosing syringe and medicine cup. | Packet(s)  | Small spoon (not included)  | ||||||
Medicine cup (not included)
| Oral dosing syringe (not included) Small scissors (not included)  | |||||||
Mixing liquid (use infant formula, water or apple juice) (not included)  | ||||||||
❏ Step 2: Check prescription label for prescribed dose
|  | |||||||
❏ Step 3: Tap and open packet
| 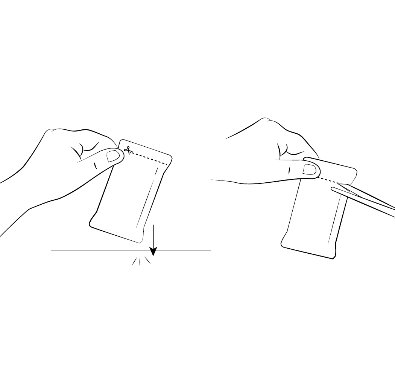 | |||||||
❏ Step 4: Empty the packet
| 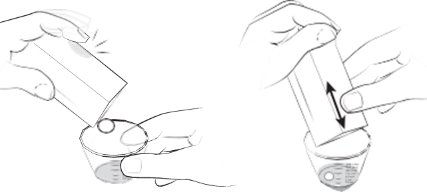 | |||||||
❏ Step 5: Add liquid to the medicine cup
Use water, infant formula, or apple juice only as the liquid. Do not use any other type of liquid. Important: To make sure your child gets the full dose, do not put the medicine in a baby bottle. | 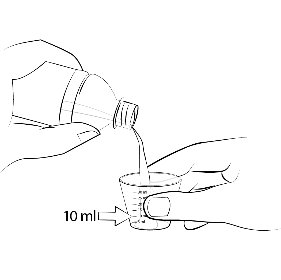 | |||||||
❏ Step 6: Mix medicine and liquid
| 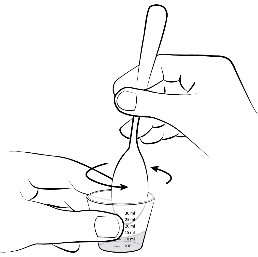 | 5 to 7 minutes  | ||||||
❏ Step 7: Give oral suspension This is a 2-part process to make sure all the medicine is given. Follow Part 1 and Part 2. Part 1 : Pull up all liquid mixture with the oral dosing syringe and give all medicine in syringe. | ||||||||
Push plunger all the way down. | Place the syringe tip into the cup and pull up all the liquid mixture. | With the child seated upright or slightly inclined (tilted back), place the oral syringe into the mouth with the tip along either cheek. Slowly push the plunger all the way down to give all medicine in the syringe. | ||||||
 | 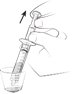 | 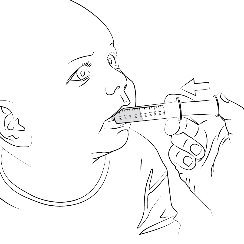 | ||||||
Part 2 : Repeat Steps 5 through 7 to give any remaining medicine in the cup: | ||||||||
Add about 5 mL (1 teaspoon) liquid to medicine cup. For children with fluid restrictions, your healthcare provider will tell you if you can use 2.5 mL (½ teaspoon) of liquid. | Gently stir liquid with small spoon. | Push plunger all the way down. | Place the syringe tip into cup and pull up all the liquid mixture. | With the child seated upright or slightly inclined (tilted back), place the oral syringe into the mouth with the tip along either cheek. Slowly push the plunger all the way down to give all medicine in the syringe. | ||||
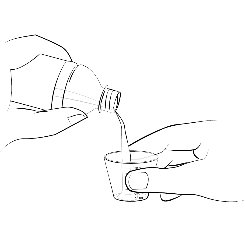 | 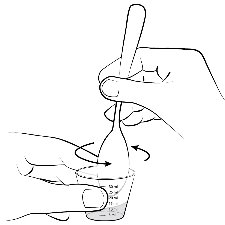 | 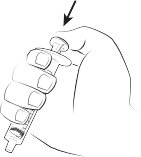 | 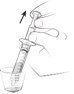 |  | ||||
❏ Step 8: Washing parts
| 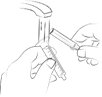 | |||||||
Food Mixing Method
❏ Step 1: Prepare Supplies
|  Packet(s) |  Small spoon (not included) |
 Small scissors (not included) | ||
 Apple sauce (not included) |  Small bowl (not included) | |
❏ Step 2: Check prescription label for prescribed dose
|  | |
❏ Step 3: Prepare for mixing
|  | |
❏ Step 4: Tap and open packet
|  | |
❏ Step 5: Empty the packet
| 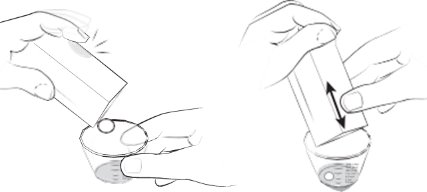 | |
❏ Step 6: Mix medicine and food
The tablet(s) do not need to disperse (evenly mix) in the food. |  | |
❏ Step 7: Give medicine
| 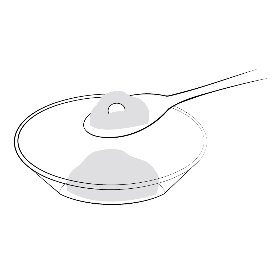 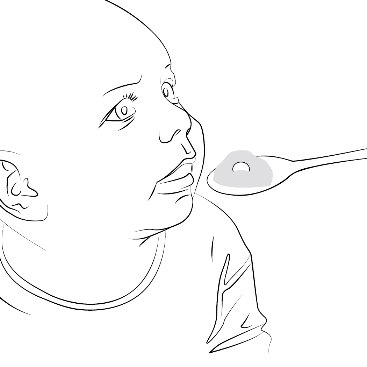 | |
❏ Step 8: Washing parts
|  | |
Giving ELIQUIS tablets prepared as a suspension through a nasogastric tube (NG tube) or gastrostomy tube (G tube): Follow steps 1 through 6 to prepare the dose to be given. Follow the manufacturer instructions for how to place the syringe tip into the tube and give the medicine to your child. After the medicine has been placed into the tube, using the syringe flush the tube with additional water or infant formula. The flush volume is shown in the table below. 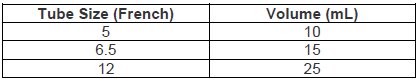 Talk to your healthcare provider if you have any questions. How should I store ELIQUIS tablets? Store ELIQUIS at room temperature between 68°F to 77°F (20°C to 25°C). Keep ELIQUIS and all medicines out of the reach of children. Marketed by: Bristol-Myers Squibb Company Princeton, NJ 08543 USA and Pfizer Inc New York, NY 10001 USA All other trademarks are property of their respective companies. For more information, call 1-855-354-7847 (1-855-ELIQUIS) or go to www.ELIQUIS.com. | ||
This Instructions for Use has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. | Issued: 04/2025 |
Mechanism of Action
Apixaban is a selective inhibitor of FXa. It does not require antithrombin III for antithrombotic activity. Apixaban inhibits free and clot-bound FXa, and prothrombinase activity. Apixaban has no direct effect on platelet aggregation, but indirectly inhibits platelet aggregation induced by thrombin. By inhibiting FXa, apixaban decreases thrombin generation and thrombus development.
