Get your patient on Genotropin (Somatropin)
Genotropin prior authorization resources
Most recent state uniform prior authorization forms
Genotropin patient education
Patient toolkit
Dosage & administration
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
The weekly dose should be divided into 6 or 7 subcutaneous injections. GENOTROPIN must not be injected intravenously.
Therapy with GENOTROPIN should be supervised by a physician who is experienced in the diagnosis and management of pediatric patients with growth failure associated with growth hormone deficiency (GHD), Prader-Willi syndrome (PWS), Turner syndrome (TS), those who were born small for gestational age (SGA) or Idiopathic Short Stature (ISS), and adult patients with either childhood onset or adult onset GHD.
Dosing of Pediatric Patients
General Pediatric Dosing Information
The GENOTROPIN dosage and administration schedule should be individualized based on the growth response of each patient.
Response to somatropin therapy in pediatric patients tends to decrease with time. However, in pediatric patients, the failure to increase growth rate, particularly during the first year of therapy, indicates the need for close assessment of compliance and evaluation for other causes of growth failure, such as hypothyroidism, undernutrition, advanced bone age and antibodies to recombinant human GH (rhGH).
Treatment with GENOTROPIN for short stature should be discontinued when the epiphyses are fused.
Pediatric Growth Hormone Deficiency (GHD)
Generally, a dose of 0.16 to 0.24 mg/kg body weight/week is recommended.
Prader-Willi Syndrome
Generally, a dose of 0.24 mg/kg body weight/week is recommended.
Turner Syndrom e
Generally, a dose of 0.33 mg/kg body weight/week is recommended.
Idiopathic Short Stature
Generally, a dose up to 0.47 mg/kg body weight/week is recommended.
Small for Gestational Age Recent literature has recommended initial treatment with larger doses of somatropin (e.g., 0.48 mg/kg/week), especially in very short children (i.e., height SDS <–3), and/or older/ pubertal children, and that a reduction in dosage (e.g., gradually towards 0.24 mg/kg/week) should be considered if substantial catch-up growth is observed during the first few years of therapy. On the other hand, in younger SGA children (e.g., approximately <4 years) (who respond the best in general) with less severe short stature (i.e., baseline height SDS values between -2 and -3), consideration should be given to initiating treatment at a lower dose (e.g., 0.24 mg/kg/week), and titrating the dose as needed over time. In all children, clinicians should carefully monitor the growth response, and adjust the somatropin dose as necessary.
Generally, a dose of up to 0.48 mg/kg body weight/week is recommended.
Dosing of Adult Patients
Adult Growth Hormone Deficiency (GHD)
Either of two approaches to GENOTROPIN dosing may be followed: a non-weight based regimen or a weight based regimen.
Non-weight based — based on published consensus guidelines, a starting dose of approximately 0.2 mg/day (range, 0.15–0.30 mg/day) may be used without consideration of body weight. This dose can be increased gradually every 1–2 months by increments of approximately 0.1–0.2 mg/day, according to individual patient requirements based on the clinical response and serum insulin-like growth factor I (IGF-I) concentrations. The dose should be decreased as necessary on the basis of adverse events and/or serum IGF-I concentrations above the age- and gender-specific normal range. Maintenance dosages vary considerably from person to person, and between male and female patients.
Weight based — based on the dosing regimen used in the original adult GHD registration trials, the recommended dosage at the start of treatment is not more than 0.04 mg/kg/week. The dose may be increased according to individual patient requirements to not more than 0.08 mg/kg/week at 4–8 week intervals. Clinical response, side effects, and determination of age- and gender-adjusted serum IGF-I concentrations should be used as guidance in dose titration.
A lower starting dose and smaller dose increments should be considered for older patients, who are more prone to the adverse effects of somatropin than younger individuals. In addition, obese individuals are more likely to manifest adverse effects when treated with a weight-based regimen. In order to reach the defined treatment goal, estrogen-replete women may need higher doses than men. Oral estrogen administration may increase the dose requirements in women.
Preparation and Administration
The GENOTROPIN 5 and 12 mg cartridges are color-coded to help ensure proper use with the GENOTROPIN PEN delivery device. The 5 mg cartridge has a green tip to match the green pen window on the Pen 5, while the 12 mg cartridge has a purple tip to match the purple pen window on the Pen 12.
Parenteral drug products should always be inspected visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration, whenever solution and container permit. GENOTROPIN MUST NOT BE INJECTED if the solution is cloudy or contains particulate matter. Use it only if it is clear and colorless.
GENOTROPIN may be given in the thigh, buttocks, or abdomen; the site of SC injections should be rotated daily to help prevent lipoatrophy.

Genotropin prescribing information
Warnings and Precautions, Slipped Capital Femoral Epiphysis in Pediatric Patients (5.10 ) | 07/2025 |
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
GENOTROPIN is a recombinant human growth hormone indicated for:
Pediatric Patients
GENOTROPIN is indicated for the treatment of pediatric patients who have growth failure due to an inadequate secretion of endogenous growth hormone.
GENOTROPIN is indicated for the treatment of pediatric patients who have growth failure due to Prader-Willi syndrome (PWS). The diagnosis of PWS should be confirmed by appropriate genetic testing [see Contraindications (4) ] .
GENOTROPIN is indicated for the treatment of growth failure in pediatric patients born small for gestational age (SGA) who fail to manifest catch-up growth by age 2 years.
GENOTROPIN is indicated for the treatment of growth failure associated with Turner syndrome.
GENOTROPIN is indicated for the treatment of idiopathic short stature (ISS), also called non-growth hormone-deficient short stature, defined by height standard deviation score (SDS) ≤-2.25, and associated with growth rates unlikely to permit attainment of adult height in the normal range, in pediatric patients whose epiphyses are not closed and for whom diagnostic evaluation excludes other causes associated with short stature that should be observed or treated by other means.
Adult Patients
GENOTROPIN is indicated for replacement of endogenous growth hormone in adults with growth hormone deficiency who meet either of the following two criteria:
Adult Onset (AO): Patients who have growth hormone deficiency, either alone or associated with multiple hormone deficiencies (hypopituitarism), as a result of pituitary disease, hypothalamic disease, surgery, radiation therapy, or trauma; or
Childhood Onset (CO) : Patients who were growth hormone deficient during childhood as a result of congenital, genetic, acquired, or idiopathic causes.
Patients who were treated with somatropin for growth hormone deficiency in childhood and whose epiphyses are closed should be reevaluated before continuation of somatropin therapy at the reduced dose level recommended for growth hormone deficient adults. According to current standards, confirmation of the diagnosis of adult growth hormone deficiency in both groups involves an appropriate growth hormone provocative test with two exceptions: (1) patients with multiple other pituitary hormone deficiencies due to organic disease; and (2) patients with congenital/genetic growth hormone deficiency.
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
The weekly dose should be divided into 6 or 7 subcutaneous injections. GENOTROPIN must not be injected intravenously.
Therapy with GENOTROPIN should be supervised by a physician who is experienced in the diagnosis and management of pediatric patients with growth failure associated with growth hormone deficiency (GHD), Prader-Willi syndrome (PWS), Turner syndrome (TS), those who were born small for gestational age (SGA) or Idiopathic Short Stature (ISS), and adult patients with either childhood onset or adult onset GHD.
Dosing of Pediatric Patients
General Pediatric Dosing Information
The GENOTROPIN dosage and administration schedule should be individualized based on the growth response of each patient.
Response to somatropin therapy in pediatric patients tends to decrease with time. However, in pediatric patients, the failure to increase growth rate, particularly during the first year of therapy, indicates the need for close assessment of compliance and evaluation for other causes of growth failure, such as hypothyroidism, undernutrition, advanced bone age and antibodies to recombinant human GH (rhGH).
Treatment with GENOTROPIN for short stature should be discontinued when the epiphyses are fused.
Pediatric Growth Hormone Deficiency (GHD)
Generally, a dose of 0.16 to 0.24 mg/kg body weight/week is recommended.
Prader-Willi Syndrome
Generally, a dose of 0.24 mg/kg body weight/week is recommended.
Turner Syndrom e
Generally, a dose of 0.33 mg/kg body weight/week is recommended.
Idiopathic Short Stature
Generally, a dose up to 0.47 mg/kg body weight/week is recommended.
Small for Gestational Age Recent literature has recommended initial treatment with larger doses of somatropin (e.g., 0.48 mg/kg/week), especially in very short children (i.e., height SDS <–3), and/or older/ pubertal children, and that a reduction in dosage (e.g., gradually towards 0.24 mg/kg/week) should be considered if substantial catch-up growth is observed during the first few years of therapy. On the other hand, in younger SGA children (e.g., approximately <4 years) (who respond the best in general) with less severe short stature (i.e., baseline height SDS values between -2 and -3), consideration should be given to initiating treatment at a lower dose (e.g., 0.24 mg/kg/week), and titrating the dose as needed over time. In all children, clinicians should carefully monitor the growth response, and adjust the somatropin dose as necessary.
Generally, a dose of up to 0.48 mg/kg body weight/week is recommended.
Dosing of Adult Patients
Adult Growth Hormone Deficiency (GHD)
Either of two approaches to GENOTROPIN dosing may be followed: a non-weight based regimen or a weight based regimen.
Non-weight based — based on published consensus guidelines, a starting dose of approximately 0.2 mg/day (range, 0.15–0.30 mg/day) may be used without consideration of body weight. This dose can be increased gradually every 1–2 months by increments of approximately 0.1–0.2 mg/day, according to individual patient requirements based on the clinical response and serum insulin-like growth factor I (IGF-I) concentrations. The dose should be decreased as necessary on the basis of adverse events and/or serum IGF-I concentrations above the age- and gender-specific normal range. Maintenance dosages vary considerably from person to person, and between male and female patients.
Weight based — based on the dosing regimen used in the original adult GHD registration trials, the recommended dosage at the start of treatment is not more than 0.04 mg/kg/week. The dose may be increased according to individual patient requirements to not more than 0.08 mg/kg/week at 4–8 week intervals. Clinical response, side effects, and determination of age- and gender-adjusted serum IGF-I concentrations should be used as guidance in dose titration.
A lower starting dose and smaller dose increments should be considered for older patients, who are more prone to the adverse effects of somatropin than younger individuals. In addition, obese individuals are more likely to manifest adverse effects when treated with a weight-based regimen. In order to reach the defined treatment goal, estrogen-replete women may need higher doses than men. Oral estrogen administration may increase the dose requirements in women.
Preparation and Administration
The GENOTROPIN 5 and 12 mg cartridges are color-coded to help ensure proper use with the GENOTROPIN PEN delivery device. The 5 mg cartridge has a green tip to match the green pen window on the Pen 5, while the 12 mg cartridge has a purple tip to match the purple pen window on the Pen 12.
Parenteral drug products should always be inspected visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration, whenever solution and container permit. GENOTROPIN MUST NOT BE INJECTED if the solution is cloudy or contains particulate matter. Use it only if it is clear and colorless.
GENOTROPIN may be given in the thigh, buttocks, or abdomen; the site of SC injections should be rotated daily to help prevent lipoatrophy.
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
GENOTROPIN is a white, lyophilized powder available as:
- For injection: 5 mg or 12 mg in a single-patient-use two-chamber cartridge
- For injection: 0.2 mg, 0.4 mg, 0.6 mg, 0.8 mg, 1 mg, 1.2 mg, 1.4 mg, 1.6 mg, 1.8 mg, or 2 mg in a single‑dose Growth Hormone Delivery Device containing a two-chamber cartridge (GENOTROPIN MINIQUICK)
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
Pregnancy
Risk Summary
Limited available data with somatropin use in pregnant women are insufficient to determine a drug-associated risk of adverse developmental outcomes. In animal studies (rats and rabbits), there was no evidence of embryo‑fetal or neonatal harm following somatropin administration during organogenesis at doses approximately 24 times and 19 times the recommended human therapeutic levels, respectively, based on body surface area (see Data ) .
The estimated background risk of birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population is unknown. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2-4% and 15-20%, respectively.
Data
Animal Data
Animal reproduction studies with somatropin during the period of organogenesis at doses of 0.3, 1, and 3.3 mg/kg/day administered subcutaneously (SC) in pregnant rats and 0.08, 0.3, and 1.3 mg/kg/day administered intramuscularly in pregnant rabbits were not teratogenic (highest doses approximately 24 times and 19 times the recommended human therapeutic levels, respectively, based on body surface area).
In perinatal and postnatal studies in rats, somatropin doses of 0.3, 1, and 3.3 mg/kg/day produced growth‑promoting effects in the dams but not in the fetuses. Young rats at the highest dose showed increased weight gain during suckling but the effect was not apparent by 10 weeks of age. No adverse effects were observed on gestation, morphogenesis, parturition, lactation, postnatal development, or reproductive capacity of the offspring due to somatropin.
Lactation
Risk Summary
There is no information regarding the presence of somatropin in human milk. Limited published data indicate that exogenous somatropin does not increase normal breastmilk concentrations of growth hormone. No adverse effects related to somatropin in the breastfeed infant have been reported. The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother’s clinical need for GENOTROPIN and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed infant from GENOTROPIN or from the underlying maternal condition.
Pediatric Use
Safety and effectiveness of GENOTROPIN in pediatric patients have been established in growth failure due to Prader-Willi syndrome (PWS), growth failure in children born small for gestational age (SGA) with no catch-up growth by age 2 years, growth failure associated with Turner syndrome, idiopathic short stature (ISS) and growth failure due to inadequate secretion of endogenous growth hormone.
Growth Failure Due to Prader-Willi Syndrome (PWS)
Safety and effectiveness of GENOTROPIN have been established in pediatric patients with growth failure due to Prader-Willi syndrome based on data from two randomized, open-label, controlled clinical trials with GENOTROPIN in 43 pediatric patients. There have been reports of sudden death after initiating therapy with somatropin in pediatric patients with Prader-Willi syndrome who had one or more of the following risk factors: severe obesity, history of upper airway obstruction or sleep apnea, or unidentified respiratory infection. Male patients with one or more of these factors may be at greater risk than females. Patients with Prader-Willi syndrome should be evaluated for signs of upper airway obstruction and sleep apnea before initiation of treatment with somatropin [see Contraindications (4) , Warnings and Precautions (5.2) , Clinical Studies (14.2) ] .
Short Stature in Pediatric Patients Born Small for Gestational Age (SGA) with No Catch-up Growth by Age 2
Safety and effectiveness of GENOTROPIN have been established in pediatric patients with short stature born SGA with no catch-up growth based on data from 4 randomized, open-label, controlled clinical trials with GENOTROPIN in 209 pediatric patients [see Clinical Studies (14.3) ] .
Short Stature associated with Turner Syndrome
Safety and effectiveness of GENOTROPIN have been established in pediatric patients with short stature associated with Turner syndrome based on data from two randomized, open-label, clinical trials with GENOTROPIN in 38 pediatric patients [see Clinical Studies (14.4) ].
Idiopathic Short Stature (ISS)
Safety and effectiveness of GENOTROPIN have been established in pediatric patients with ISS based on data from one randomized, open-label, clinical trial with GENOTROPIN in 102 pediatric patients [see Clinical Studies (14.5) ] .
Geriatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of GENOTROPIN in patients aged 65 and over have not been evaluated in clinical studies. Elderly patients may be more sensitive to the action of GENOTROPIN, and therefore may be more prone to develop adverse reactions. A lower starting dose and smaller dose increments should be considered for older patients [see Dosage and Administration (2.2) ].
CONTRAINDICATIONS
- Acute Critical Illness (4 )
- Children with Prader-Willi syndrome who are severely obese or have severe respiratory impairment – reports of sudden death (4 )
- Active Malignancy (4 )
- Hypersensitivity to somatropin or excipients (4 )
- Active Proliferative or Severe Non-Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy (4 )
- Children with closed epiphyses (4 )
GENOTROPIN is contraindicated in patients with:
• Acute Critical Illness
Treatment with pharmacologic amounts of somatropin is contraindicated in patients with acute critical illness due to complications following open heart surgery, abdominal surgery or multiple accidental trauma, or those with acute respiratory failure [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) ].
• Prader-Willi Syndrome in Children
Somatropin is contraindicated in patients with Prader-Willi syndrome who are severely obese, have a history of upper airway obstruction or sleep apnea, or have severe respiratory impairment. There have been reports of sudden death when somatropin was used in such patients [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) ].
• Active Malignancy
In general, somatropin is contraindicated in the presence of active malignancy. Any preexisting malignancy should be inactive and its treatment complete prior to instituting therapy with somatropin. Somatropin should be discontinued if there is evidence of recurrent activity. Since growth hormone deficiency may be an early sign of the presence of a pituitary tumor (or, rarely, other brain tumors), the presence of such tumors should be ruled out prior to initiation of treatment. Somatropin should not be used in patients with any evidence of progression or recurrence of an underlying intracranial tumor.
• Hypersensitivity
GENOTROPIN is contraindicated in patients with a known hypersensitivity to somatropin or any of its excipients. The 5 mg and 12 mg presentations of GENOTROPIN lyophilized powder contain m-cresol as a preservative. Systemic hypersensitivity reactions have been reported with postmarketing use of somatropins [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6) ] .
• Diabetic Retinopathy
Somatropin is contraindicated in patients with active proliferative or severe non-proliferative diabetic retinopathy.
• Closed Epiphyses
Somatropin should not be used for growth promotion in pediatric patients with closed epiphyses.
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- Acute Critical Illness: Potential benefit of treatment continuation should be weighed against the potential risk (5.1 )
- Prader-Willi Syndrome in Children: Evaluate for signs of upper airway obstruction and sleep apnea before initiation of treatment Discontinue treatment if these signs occur (5.2 )
- Neoplasm: Monitor patients with preexisting tumors for progression or recurrence. Increased risk of a second neoplasm in childhood cancer survivors treated with somatropin in particular meningiomas in patients treated with radiation to the head for their first neoplasm (5.3 )
- Impaired Glucose Tolerance and Diabetes Mellitus: May be unmasked Periodically monitor glucose levels in all patients. Doses of concurrent antihyperglycemic drugs in diabetics may require adjustment (5.4 )
- Intracranial Hypertension: Exclude preexisting papilledema. May develop and is usually reversible after discontinuation or dose reduction (5.5 )
- Hypersensitivity: Serious hypersensitivity reactions may occur. In the event of an allergic reaction, seek prompt medical attention (5.6 )
- Fluid Retention (i.e., edema, arthralgia, carpal tunnel syndrome – especially in adults): May occur frequently. Reduce dose as necessary (5.7 )
- Hypoadrenalism: Monitor patients for reduced serum cortisol levels and/or need for glucocorticoid dose increases in those with known hypoadrenalism (5.8 )
- Hypothyroidism: May first become evident or worsen. Monitor thyroid function periodically (5.9 )
- Slipped Capital Femoral Epiphysis: May develop. Evaluate children with the onset of a limp or hip/knee pain (5.10 )
- Progression of Preexisting Scoliosis: Monitor any child with scoliosis for progression of the curve (5.11 )
- Pancreatitis: Consider pancreatitis in patients with persistent severe abdominal pain (5.15 )
Acute Critical Illness
Increased mortality in patients with acute critical illness due to complications following open heart surgery, abdominal surgery or multiple accidental trauma, or those with acute respiratory failure has been reported after treatment with pharmacologic amounts of somatropin [see Contraindications (4) ]. Two placebo-controlled clinical trials in non-growth hormone deficient adult patients (n=522) with these conditions in intensive care units revealed a significant increase in mortality (42% vs. 19%) among somatropin-treated patients (doses 5.3–8 mg/day) compared to those receiving placebo. The safety of continuing somatropin treatment in patients receiving replacement doses for approved indications who concurrently develop these illnesses has not been established. Therefore, the potential benefit of treatment continuation with somatropin in patients having acute critical illnesses should be weighed against the potential risk.
Prader-Willi Syndrome in Children
There have been reports of fatalities after initiating therapy with somatropin in pediatric patients with Prader-Willi syndrome who had one or more of the following risk factors: severe obesity, history of upper airway obstruction or sleep apnea, or unidentified respiratory infection. Male patients with one or more of these factors may be at greater risk than females. Patients with Prader-Willi syndrome should be evaluated for signs of upper airway obstruction and sleep apnea before initiation of treatment with somatropin. If during treatment with somatropin, patients show signs of upper airway obstruction (including onset of or increased snoring) and/or new onset sleep apnea, treatment should be interrupted. All patients with Prader-Willi syndrome treated with somatropin should also have effective weight control and be monitored for signs of respiratory infection, which should be diagnosed as early as possible and treated aggressively [see Contraindications (4) ].
Neoplasms
In childhood cancer survivors who were treated with radiation to the brain/head for their first neoplasm and who developed subsequent GHD and were treated with somatropin, an increased risk of a second neoplasm has been reported. Intracranial tumors, in particular meningiomas, were the most common of these second neoplasms. In adults, it is unknown whether there is any relationship between somatropin replacement therapy and CNS tumor recurrence [see Contraindications (4) ] .
Monitor all patients with a history of GHD secondary to an intracranial neoplasm routinely while on somatropin therapy for progression or recurrence of the tumor.
Because children with certain rare genetic causes of short stature have an increased risk of developing malignancies, practitioners should thoroughly consider the risks and benefits of starting somatropin in these patients. If treatment with somatropin is initiated, these patients should be carefully monitored for development of neoplasms.
Monitor patients on somatropin therapy carefully for increased growth, or potential malignant changes, of preexisting nevi.
Impaired Glucose Tolerance and Diabetes Mellitus
Treatment with somatropin may decrease insulin sensitivity, particularly at higher doses in susceptible patients. As a result, previously undiagnosed impaired glucose tolerance and overt diabetes mellitus may be unmasked during somatropin treatment. New-onset Type 2 diabetes mellitus has been reported. Therefore, glucose levels should be monitored periodically in all patients treated with somatropin, especially in those with risk factors for diabetes mellitus, such as obesity, Turner syndrome, or a family history of diabetes mellitus. Patients with preexisting type 1 or type 2 diabetes mellitus or impaired glucose tolerance should be monitored closely during somatropin therapy. The doses of antihyperglycemic drugs (i.e., insulin or oral/injectable agents) may require adjustment when somatropin therapy is instituted in these patients.
Intracranial Hypertension
Intracranial hypertension (IH) with papilledema, visual changes, headache, nausea and/or vomiting has been reported in a small number of patients treated with somatropins. Symptoms usually occurred within the first eight (8) weeks after the initiation of somatropin therapy. In all reported cases, IH-associated signs and symptoms rapidly resolved after cessation of therapy or a reduction of the somatropin dose. Fundoscopic examination should be performed routinely before initiating treatment with somatropin to exclude preexisting papilledema, and periodically during the course of somatropin therapy. If papilledema is observed by fundoscopy during somatropin treatment, treatment should be stopped. If somatropin-induced IH is diagnosed, treatment with somatropin can be restarted at a lower dose after IH-associated signs and symptoms have resolved. Patients with Turner syndrome and Prader-Willi syndrome may be at increased risk for the development of IH.
Severe Hypersensitivity
Serious systemic hypersensitivity reactions including anaphylactic reactions and angioedema have been reported with postmarketing use of somatropins. Patients and caregivers should be informed that such reactions are possible and that prompt medical attention should be sought if an allergic reaction occurs [see Contraindications (4) ].
Fluid Retention
Fluid retention during somatropin replacement therapy in adults may occur. Clinical manifestations of fluid retention (e.g., edema, arthralgia, myalgia, nerve compression syndromes including carpal tunnel syndrome/paresthesia) are usually transient and dose dependent.
Hypoadrenalism
Patients receiving somatropin therapy who have or are at risk for pituitary hormone deficiency(s) may be at risk for reduced serum cortisol levels and/or unmasking of central (secondary) hypoadrenalism. In addition, patients treated with glucocorticoid replacement for previously diagnosed hypoadrenalism may require an increase in their maintenance or stress doses following initiation of somatropin treatment [see Drug Interactions (7.1) ].
Hypothyroidism
Undiagnosed/untreated hypothyroidism may prevent an optimal response to somatropin, in particular, the growth response in children. Patients with Turner syndrome have an inherently increased risk of developing autoimmune thyroid disease and primary hypothyroidism. In patients with growth hormone deficiency, central (secondary) hypothyroidism may first become evident or worsen during somatropin treatment. Therefore, patients treated with somatropin should have periodic thyroid function tests and thyroid hormone replacement therapy should be initiated or appropriately adjusted when indicated.
Slipped Capital Femoral Epiphyses in Pediatric Patients
Slipped capital femoral epiphyses may occur more frequently in patients with endocrine disorders (including GHD and Turner syndrome) or in patients undergoing rapid growth. Slipped capital femoral epiphysis may lead to osteonecrosis. Cases of slipped capital femoral epiphysis with or without osteonecrosis have been reported in pediatric patients with short stature receiving somatropin, including GENOTROPIN. Any pediatric patient with the onset of a limp or complaints of hip or knee pain during GENOTROPIN therapy should be evaluated for slipped capital femoral epiphysis and osteonecrosis and managed accordingly.
Progression of Preexisting Scoliosis in Pediatric Patients
Progression of scoliosis can occur in patients who experience rapid growth. Because somatropin increases growth rate, patients with a history of scoliosis who are treated with somatropin should be monitored for progression of scoliosis. However, somatropin has not been shown to increase the occurrence of scoliosis. Skeletal abnormalities including scoliosis are commonly seen in untreated Turner syndrome patients. Scoliosis is also commonly seen in untreated patients with Prader-Willi syndrome. Physicians should be alert to these abnormalities, which may manifest during somatropin therapy.
Otitis Media and Cardiovascular Disorders in Turner Syndrome
Patients with Turner syndrome should be evaluated carefully for otitis media and other ear disorders since these patients have an increased risk of ear and hearing disorders. Somatropin treatment may increase the occurrence of otitis media in patients with Turner syndrome. In addition, patients with Turner syndrome should be monitored closely for cardiovascular disorders (e.g., stroke, aortic aneurysm/dissection, hypertension) as these patients are also at risk for these conditions.
Lipoatrophy
When somatropin is administered subcutaneously at the same site over a long period of time, tissue atrophy may result. This can be avoided by rotating the injection site [see Dosage and Administration (2.3) ] .
Laboratory Tests
Serum levels of inorganic phosphorus, alkaline phosphatase, parathyroid hormone (PTH) and IGF-I may increase during somatropin therapy.
Pancreatitis
Cases of pancreatitis have been reported rarely in children and adults receiving somatropin treatment, with some evidence supporting a greater risk in children compared with adults. Published literature indicates that girls who have Turner syndrome may be at greater risk than other somatropin-treated children. Pancreatitis should be considered in any somatropin–treated patient, especially a child, who develops persistent severe abdominal pain.
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following important adverse reactions are also described elsewhere in the labeling:
- Increased mortality in patients with acute critical illness [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) ]
- Fatalities in children with Prader-Willi syndrome [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) ]
- Neoplasms [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3) ]
- Glucose intolerance and diabetes mellitus [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4) ]
- Intracranial hypertension [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5) ]
- Severe hypersensitivity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6) ]
- Fluid retention [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7) ]
- Hypoadrenalism [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8) ]
- Hypothyroidism [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9) ]
- Slipped capital femoral epiphysis in pediatric patients [see Warnings and Precautions (5.10) ]
- Progression of preexisting scoliosis in pediatric patients [see Warnings and Precautions (5.11) ]
- Otitis media and cardiovascular disorders in patients with Turner syndrome [see Warnings and Precautions (5.12) ]
- Lipoatrophy [see Warnings and Precautions (5.13) ]
- Pancreatitis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.15) ]
Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed during the clinical trials performed with one somatropin formulation cannot always be directly compared to the rates observed during the clinical trials performed with a second somatropin formulation, and may not reflect the adverse reaction rates observed in practice.
Clinical Trials in children with GHD
In clinical studies with GENOTROPIN in pediatric GHD patients, the following events were reported infrequently: injection site reactions, including pain or burning associated with the injection, fibrosis, nodules, rash, inflammation, pigmentation, or bleeding; lipoatrophy; headache; hematuria; hypothyroidism; and mild hyperglycemia.
Clinical Trials in PWS
In two clinical studies with GENOTROPIN in pediatric patients with Prader-Willi syndrome, the following drug-related events were reported: edema, aggressiveness, arthralgia, benign intracranial hypertension, hair loss, headache, and myalgia.
Clinical Trials in children with SGA
In clinical studies of 273 pediatric patients born small for gestational age treated with GENOTROPIN, the following clinically significant events were reported: mild transient hyperglycemia, one patient with benign intracranial hypertension, two patients with central precocious puberty, two patients with jaw prominence, and several patients with aggravation of preexisting scoliosis, injection site reactions, and self-limited progression of pigmented nevi. Anti-hGH antibodies were not detected in any of the patients treated with GENOTROPIN.
Clinical Trials in children with Turner Syndrome
In two clinical studies with GENOTROPIN in pediatric patients with Turner syndrome, the most frequently reported adverse events were respiratory illnesses (influenza, tonsillitis, otitis, sinusitis), joint pain, and urinary tract infection. The only treatment-related adverse event that occurred in more than 1 patient was joint pain.
Clinical Trials in children with Idiopathic Short Stature
In two open-label clinical studies with GENOTROPIN in pediatric patients with ISS, the most commonly encountered adverse events include upper respiratory tract infections, influenza, tonsillitis, nasopharyngitis, gastroenteritis, headaches, increased appetite, pyrexia, fracture, altered mood, and arthralgia. In one of the two studies, during GENOTROPIN treatment, the mean IGF-1 standard deviation (SD) scores were maintained in the normal range. IGF-1 SD scores above +2 SD were observed as follows: 1 subject (3%), 10 subjects (30%) and 16 subjects (38%) in the untreated control, 0. 23 and the 0.47 mg/kg/week groups, respectively, had at least one measurement; while 0 subjects (0%), 2 subjects (7%) and 6 subjects (14%) had two or more consecutive IGF-1 measurements above +2 SD.
Clinical Trials in adults with GHD
In clinical trials with GENOTROPIN in 1,145 GHD adults, the majority of the adverse events consisted of mild to moderate symptoms of fluid retention, including peripheral swelling, arthralgia, pain and stiffness of the extremities, peripheral edema, myalgia, paresthesia, and hypoesthesia. These events were reported early during therapy and tended to be transient and/or responsive to dosage reduction.
Table 1 displays the adverse events reported by 5% or more of adult GHD patients in clinical trials after various durations of treatment with GENOTROPIN. Also presented are the corresponding incidence rates of these adverse events in placebo patients during the 6-month double-blind portion of the clinical trials.
| Double Blind Phase | Open Label Phase GENOTROPIN | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Adverse Event | Placebo 0–6 mo. n = 572 % Patients | GENOTROPIN 0–6 mo. n = 573 % Patients | 6–12 mo. n = 504 % Patients | 12–18 mo. n = 63 % Patients | 18–24 mo. n = 60 % Patients |
| n = number of patients receiving treatment during the indicated period. %= percentage of patients who reported the event during the indicated period. | |||||
Swelling, peripheral | 5.1 | 17.5 Increased significantly when compared to placebo, P ≤.025: Fisher´s Exact Test (one-sided) | 5.6 | 0 | 1.7 |
Arthralgia | 4.2 | 17.3 | 6.9 | 6.3 | 3.3 |
Upper respiratory infection | 14.5 | 15.5 | 13.1 | 15.9 | 13.3 |
Pain, extremities | 5.9 | 14.7 | 6.7 | 1.6 | 3.3 |
Edema, peripheral | 2.6 | 10.8 | 3.0 | 0 | 0 |
Paresthesia | 1.9 | 9.6 | 2.2 | 3.2 | 0 |
Headache | 7.7 | 9.9 | 6.2 | 0 | 0 |
Stiffness of extremities | 1.6 | 7.9 | 2.4 | 1.6 | 0 |
Fatigue | 3.8 | 5.8 | 4.6 | 6.3 | 1.7 |
Myalgia | 1.6 | 4.9 | 2.0 | 4.8 | 6.7 |
Back pain | 4.4 | 2.8 | 3.4 | 4.8 | 5.0 |
Post-Trial Extension Studies in Adults
In expanded post-trial extension studies, diabetes mellitus developed in 12 of 3,031 patients (0.4%) during treatment with GENOTROPIN. All 12 patients had predisposing factors, e.g., elevated glycated hemoglobin levels and/or marked obesity, prior to receiving GENOTROPIN. Of the 3,031 patients receiving GENOTROPIN, 61 (2%) developed symptoms of carpal tunnel syndrome, which lessened after dosage reduction or treatment interruption (52) or surgery (9). Other adverse events that have been reported include generalized edema and hypoesthesia.
Periplasmic Escherichia coli Peptides
Preparations of GENOTROPIN contain a small amount of periplasmic Escherichia coli peptides (PECP). Anti-PECP antibodies are found in a small number of patients treated with GENOTROPIN, but these appear to be of no clinical significance.
Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during post-approval use of somatropin or GENOTROPIN. Because these adverse events are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Serious systemic hypersensitivity reactions including anaphylactic reactions and angioedema have been reported with postmarketing use of somatropins [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6) ].
Leukemia has been reported in a small number of GHD children treated with somatropin, somatrem (methionylated rhGH) and GH of pituitary origin. It is uncertain whether these cases of leukemia are related to GH therapy, the pathology of GHD itself, or other associated treatments such as radiation therapy. On the basis of current evidence, experts have not been able to conclude that GH therapy per se was responsible for these cases of leukemia. The risk for children with GHD, if any, remains to be established [see Contraindications (4) and Warnings and Precautions (5.3) ].
The following serious adverse reactions have been observed with use of somatropin (including events observed in patients who received brands of somatropin other than GENOTROPIN): acute critical illness [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) ] , sudden death [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) ] , intracranial tumors [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3) ] , central hypothyroidism [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9) ] , cardiovascular disorders, and pancreatitis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.15) ] .
Slipped capital femoral epiphysis and osteonecrosis/avascular necrosis (including Legg-Calvé-Perthes disease) have been reported in children treated with growth hormone [see Warnings and Precautions (5.10) ]. Cases have been reported with GENOTROPIN .
The following additional adverse reactions have been observed during the appropriate use of somatropin: headaches (children and adults), gynecomastia (children), and significant diabetic retinopathy.
New-onset type 2 diabetes mellitus has been reported.
DRUG INTERACTIONS
Inhibition of 11ß-Hydroxysteroid Dehydrogenase Type 1: May require the initiation of glucocorticoid replacement therapy. Patients treated with glucocorticoid replacement for previously diagnosed hypoadrenalism may require an increase in their maintenance doses (7.1 , 7.2 ).
- Glucocorticoid Replacement: Should be carefully adjusted (7.2 )
- Cytochrome P450-Metabolized Drugs: Monitor carefully if used with somatropin (7.3 )
- Oral Estrogen: Larger doses of somatropin may be required in women (7.4 )
- Insulin and/or Oral/Injectable Hypoglycemic Agents: May require adjustment (7.5 )
11 β-Hydroxysteroid Dehydrogenase Type 1
The microsomal enzyme 11β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1 (11βHSD-1) is required for conversion of cortisone to its active metabolite, cortisol, in hepatic and adipose tissue. GH and somatropin inhibit 11βHSD-1. Consequently, individuals with untreated GH deficiency have relative increases in 11βHSD-1 and serum cortisol. Introduction of somatropin treatment may result in inhibition of 11βHSD-1 and reduced serum cortisol concentrations. As a consequence, previously undiagnosed central (secondary) hypoadrenalism may be unmasked and glucocorticoid replacement may be required in patients treated with somatropin. In addition, patients treated with glucocorticoid replacement for previously diagnosed hypoadrenalism may require an increase in their maintenance or stress doses following initiation of somatropin treatment; this may be especially true for patients treated with cortisone acetate and prednisone since conversion of these drugs to their biologically active metabolites is dependent on the activity of 11βHSD-1 [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8 )] .
Pharmacologic Glucocorticoid Therapy and Supraphysiologic Glucocorticoid Treatment
Pharmacologic glucocorticoid therapy and supraphysiologic glucocorticoid treatment may attenuate the growth‑promoting effects of somatropin in children. Therefore, glucocorticoid replacement dosing should be carefully adjusted in children receiving concomitant somatropin and glucocorticoid treatments to avoid both hypoadrenalism and an inhibitory effect on growth.
Cytochrome P450-Metabolized Drugs
Limited published data indicate that somatropin treatment increases cytochrome P450 (CYP450)-mediated antipyrine clearance in man. These data suggest that somatropin administration may alter the clearance of compounds known to be metabolized by CYP450 liver enzymes (e.g., corticosteroids, sex steroids, anticonvulsants, cyclosporine). Careful monitoring is advisable when somatropin is administered in combination with other drugs known to be metabolized by CYP450 liver enzymes. However, formal drug interaction studies have not been conducted.
Oral Estrogen
In patients on oral estrogen replacement, a larger dose of somatropin may be required to achieve the defined treatment goal [see Dosage and Administration (2.2) ].
Insulin and/or Oral/Injectable Hypoglycemic Agents
In patients with diabetes mellitus requiring drug therapy, the dose of insulin and/or oral/injectable agent may require adjustment when somatropin therapy is initiated [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4) ].
DESCRIPTION
Somatropin is a human growth hormone produced by recombinant DNA technology in Escherichia coli. The protein is comprised of 191 amino acid residues and has a molecular weight of 22,124 daltons. The amino acid sequence is identical to that of human growth hormone of pituitary origin.
GENOTROPIN (somatropin) for injection is a sterile, white, lyophilized powder in a single-patient-use or single-dose, two-chamber cartridge intended for subcutaneous injection after reconstitution. The front chamber contains somatropin and the rear chamber contains diluent.
GENOTROPIN 5 mg is a single-patient-use, two-chamber cartridge. GENOTROPIN 5 mg is designed for use with a reusable device (GENOTROPIN PEN 5) for product reconstitution and drug delivery. After reconstitution, each mL contains 5 mg of somatropin, dibasic sodium phosphate (0.27 mg), glycine (2 mg), mannitol (41 mg), metacresol (3 mg) (as a preservative), monobasic sodium phosphate (0.28 mg) and water for injection. The reconstituted concentration is 5 mg/mL with a deliverable volume of 1 mL.
GENOTROPIN 12 mg is a single‑patient‑use, two-chamber cartridge. GENOTROPIN 12 mg is designed for use with a reusable device (GENOTROPIN PEN 12) for product reconstitution and drug delivery. After reconstitution, each mL contains 12 mg of somatropin, dibasic sodium phosphate (0.4 mg), glycine (2 mg), mannitol (40 mg), metacresol (3 mg) (as a preservative), monobasic sodium phosphate (0.41 mg) and water for injection. The reconstituted concentration is 12 mg/mL with a deliverable volume of 1 mL.
GENOTROPIN MINIQUICK is a single-dose Growth Hormone Delivery Device containing a two-chamber cartridge supplied in the following strengths: 0.2 mg, 0.4 mg, 0.6 mg, 0.8 mg, 1 mg, 1.2 mg, 1.4 mg, 1.6 mg, 1.8 mg, or 2 mg. After reconstitution, each 0.25 mL contains 0.2 mg, 0.4 mg, 0.6 mg, 0.8 mg, 1 mg, 1.2 mg, 1.4 mg, 1.6 mg, 1.8 mg, or 2 mg of somatropin, dibasic sodium phosphate (0.03 mg), glycine (0.21 mg), mannitol (12.5 mg), monobasic sodium phosphate (0.05 mg) and water for injection. Each cartridge provides a deliverable volume of 0.25 mL.
The reconstituted recombinant somatropin solution has an osmolality of approximately 300 mOsm/kg, and a pH of approximately 6.7.
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Mechanism of Action
In vitro, preclinical, and clinical tests have demonstrated that GENOTROPIN lyophilized powder is therapeutically equivalent to human growth hormone of pituitary origin and achieves similar pharmacokinetic profiles in normal adults. In pediatric patients who have growth hormone deficiency (GHD), have Prader-Willi syndrome (PWS), were born small for gestational age (SGA), have Turner syndrome (TS), or have Idiopathic short stature (ISS), treatment with GENOTROPIN stimulates linear growth. In patients with GHD or PWS, treatment with GENOTROPIN also normalizes concentrations of IGF-I (Insulin-like Growth Factor-I/Somatomedin C). In adults with GHD, treatment with GENOTROPIN results in reduced fat mass, increased lean body mass, metabolic alterations that include beneficial changes in lipid metabolism, and normalization of IGF-I concentrations.
In addition, the following actions have been demonstrated for GENOTROPIN and/or somatropin.
Pharmacodynamics
Tissue Growth
- Skeletal Growth: GENOTROPIN stimulates skeletal growth in pediatric patients with GHD, PWS, SGA, TS, or ISS. The measurable increase in body length after administration of GENOTROPIN results from an effect on the epiphyseal plates of long bones. Concentrations of IGF-I, which may play a role in skeletal growth, are generally low in the serum of pediatric patients with GHD, PWS, or SGA, but tend to increase during treatment with GENOTROPIN. Elevations in mean serum alkaline phosphatase concentration are also seen.
- Cell Growth: It has been shown that there are fewer skeletal muscle cells in short-statured pediatric patients who lack endogenous growth hormone as compared with the normal pediatric population. Treatment with somatropin results in an increase in both the number and size of muscle cells.
Protein Metabolism
Linear growth is facilitated in part by increased cellular protein synthesis. Nitrogen retention, as demonstrated by decreased urinary nitrogen excretion and serum urea nitrogen, follows the initiation of therapy with GENOTROPIN.
Carbohydrate Metabolism
Pediatric patients with hypopituitarism sometimes experience fasting hypoglycemia that is improved by treatment with GENOTROPIN. Large doses of growth hormone may impair glucose tolerance.
Lipid Metabolism
In GHD patients, administration of somatropin has resulted in lipid mobilization, reduction in body fat stores, and increased plasma fatty acids.
Mineral Metabolism
Somatropin induces retention of sodium, potassium, and phosphorus. Serum concentrations of inorganic phosphate are increased in patients with GHD after therapy with GENOTROPIN. Serum calcium is not significantly altered by GENOTROPIN. Growth hormone could increase calciuria.
Body Composition
Adult GHD patients treated with GENOTROPIN at the recommended adult dose [see Dosage and Administration (2) ] demonstrate a decrease in fat mass and an increase in lean body mass. When these alterations are coupled with the increase in total body water, the overall effect of GENOTROPIN is to modify body composition, an effect that is maintained with continued treatment.
Pharmacokinetics
Absorption
Following a 0.03 mg/kg subcutaneous (SC) injection in the thigh of 1.3 mg/mL GENOTROPIN to adult GHD patients, approximately 80% of the dose was systemically available as compared with that available following intravenous dosing. Results were comparable in both male and female patients. Similar bioavailability has been observed in healthy adult male subjects.
In healthy adult males, following an SC injection in the thigh of 0.03 mg/kg, the extent of absorption (AUC) of a concentration of 5.3 mg/mL GENOTROPIN was 35% greater than that for 1.3 mg/mL GENOTROPIN. The mean (± standard deviation) peak (C max ) serum levels were 23.0 (± 9.4) ng/mL and 17.4 (± 9.2) ng/mL, respectively.
In a similar study involving pediatric GHD patients, 5.3 mg/mL GENOTROPIN yielded a mean AUC that was 17% greater than that for 1.3 mg/mL GENOTROPIN. The mean C max levels were 21.0 ng/mL and 16.3 ng/mL, respectively.
Adult GHD patients received two single SC doses of 0.03 mg/kg of GENOTROPIN at a concentration of 1.3 mg/mL, with a one- to four-week washout period between injections. Mean C max levels were 12.4 ng/mL (first injection) and 12.2 ng/mL (second injection), achieved at approximately six hours after dosing.
There are no data on the bioequivalence between the 12 mg/mL formulation and either the 1.3 mg/mL or the 5.3 mg/mL formulations.
Distribution
The mean volume of distribution of GENOTROPIN following administration to GHD adults was estimated to be 1.3 (± 0.8) L/kg.
Metabolism
The metabolic fate of GENOTROPIN involves classical protein catabolism in both the liver and kidneys. In renal cells, at least a portion of the breakdown products are returned to the systemic circulation. The mean terminal half-life of intravenous GENOTROPIN in normal adults is 0.4 hours, whereas subcutaneously administered GENOTROPIN has a half-life of 3.0 hours in GHD adults. The observed difference is due to slow absorption from the subcutaneous injection site.
Excretion
The mean clearance of subcutaneously administered GENOTROPIN in 16 GHD adult patients was 0.3 (± 0.11) L/hrs/kg.
Special Populations
Pediatric: The pharmacokinetics of GENOTROPIN are similar in GHD pediatric and adult patients.
Gender: No gender studies have been performed in pediatric patients; however, in GHD adults, the absolute bioavailability of GENOTROPIN was similar in males and females.
Race: No studies have been conducted with GENOTROPIN to assess pharmacokinetic differences among races.
Renal or hepatic insufficiency: No studies have been conducted with GENOTROPIN in these patient populations.
| Bioavailability (%) (N=15) | T max (hours) (N=16) | CL/F (L/hr × kg) (N=16) | Vss/F (L/kg) (N=16) | T 1/2 (hours) (N=16) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T max = time of maximum plasma concentration CL/F = plasma clearance Vss/F = volume of distribution | |||||
| T 1/2 = terminal half-life SD = standard deviation CI = confidence interval | |||||
Mean | 80.5 | 5.9 | 0.3 | 1.3 | 3.0 |
(± SD) | The absolute bioavailability was estimated under the assumption that the log-transformed data follow a normal distribution. The mean and standard deviation of the log-transformed data were mean = 0.22 (± 0.241). | (± 1.65) | (± 0.11) | (± 0.80) | (± 1.44) |
95% CI | 70.5 – 92.1 | 5.0 – 6.7 | 0.2 – 0.4 | 0.9 – 1.8 | 2.2 – 3.7 |
Immunogenicity
The observed incidence of anti-drug antibodies is highly dependent on the sensitivity and specificity of the assay. Differences in assay methods preclude meaningful comparisons of the incidence of anti-drug antibodies in the studies described below with the incidence of anti-drug antibodies in other studies, including those of GENOTROPIN or other somatropins.
In the case of growth hormone, antibodies with binding capacities lower than 2 mg/mL have not been associated with growth attenuation. In a very small number of patients treated with somatropin, when binding capacity was greater than 2 mg/mL, interference with the growth response was observed.
In 419 pediatric patients evaluated in clinical studies with GENOTROPIN lyophilized powder, 244 had been treated previously with GENOTROPIN or other growth hormone preparations and 175 had received no previous growth hormone therapy. Antibodies to growth hormone (anti-hGH antibodies) were present in six previously treated patients at baseline. Three of the six became negative for anti-hGH antibodies during 6 to 12 months of treatment with GENOTROPIN. Of the remaining 413 patients, eight (1.9%) developed detectable anti-hGH antibodies during treatment with GENOTROPIN; none had an antibody binding capacity >2 mg/L. There was no evidence that the growth response to GENOTROPIN was affected in these antibody-positive patients.
NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenicity studies have not been conducted with GENOTROPIN. No potential mutagenicity of GENOTROPIN was revealed in a battery of tests including induction of gene mutations in bacteria (the Ames test), gene mutations in mammalian cells grown in vitro (mouse L5178Y cells), and chromosomal damage in intact animals (bone marrow cells in rats).
In a fertility study in male and female rats receiving SC doses during gametogenesis (2 weeks prior to mating for females and 9 weeks prior to mating for males) and continuing up to 7 days of pregnancy, 3.3 mg/kg/day (approximately 24 times human dose by body surface area) produced anestrus or extended estrus cycles in females and fewer and less motile sperm in males. Lower copulation and pregnancy rates were also observed at 3.3 mg/kg/day. At 1 mg/kg/day (approximately 7 times human dose by body surface area), rats showed slightly extended estrus cycles, whereas at 0.3 mg/kg/day no effects were noted (approximately 2 times human dose by body surface).
CLINICAL STUDIES
Adult Growth Hormone Deficiency (GHD)
GENOTROPIN lyophilized powder was compared with placebo in six randomized clinical trials involving a total of 172 adult GHD patients. These trials included a 6-month double-blind treatment period, during which 85 patients received GENOTROPIN and 87 patients received placebo, followed by an open-label treatment period in which participating patients received GENOTROPIN for up to a total of 24 months. GENOTROPIN was administered as a daily SC injection at a dose of 0.04 mg/kg/week for the first month of treatment and 0.08 mg/kg/week for subsequent months.
Beneficial changes in body composition were observed at the end of the 6-month treatment period for the patients receiving GENOTROPIN as compared with the placebo patients. Lean body mass, total body water, and lean/fat ratio increased while total body fat mass and waist circumference decreased. These effects on body composition were maintained when treatment was continued beyond 6 months. Bone mineral density declined after 6 months of treatment but returned to baseline values after 12 months of treatment.
Prader-Willi Syndrome (PWS)
The safety and efficacy of GENOTROPIN in the treatment of pediatric patients with Prader-Willi syndrome (PWS) were evaluated in two randomized, open-label, controlled clinical trials. Patients received either GENOTROPIN or no treatment for the first year of the studies, while all patients received GENOTROPIN during the second year. GENOTROPIN was administered as a daily SC injection, and the dose was calculated for each patient every 3 months. In Study 1, the treatment group received GENOTROPIN at a dose of 0.24 mg/kg/week during the entire study. During the second year, the control group received GENOTROPIN at a dose of 0.48 mg/kg/week. In Study 2, the treatment group received GENOTROPIN at a dose of 0.36 mg/kg/week during the entire study. During the second year, the control group received GENOTROPIN at a dose of 0.36 mg/kg/week.
Patients who received GENOTROPIN showed significant increases in linear growth during the first year of study, compared with patients who received no treatment (see Table 3 ). Linear growth continued to increase in the second year, when both groups received treatment with GENOTROPIN.
| Study 1 | Study 2 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GENOTROPIN | Untreated Control n=12 | GENOTROPIN | Untreated Control n=9 | |
| (0.24 mg/kg/week) n=15 | (0.36 mg/kg/week) n=7 | |||
Linear growth (cm) Baseline height | 112.7 ± 14.9 | 109.5 ± 12.0 | 120.3 ± 17.5 | 120.5 ± 11.2 |
Growth from months 0 to 12 | 11.6 p ≤ 0.001 ± 2.3 | 5.0 ± 1.2 | 10.7± 2.3 | 4.3 ± 1.5 |
Height Standard Deviation Score (SDS) for age Baseline SDS | -1.6 ± 1.3 | -1.8 ± 1.5 | -2.6 ± 1.7 | -2.1 ± 1.4 |
SDS at 12 months | -0.5 p ≤ 0.002 (when comparing SDS change at 12 months) ± 1.3 | -1.9 ± 1.4 | -1.4± 1.5 | -2.2 ± 1.4 |
Changes in body composition were also observed in the patients receiving GENOTROPIN (see Table 4 ). These changes included a decrease in the amount of fat mass, and increases in the amount of lean body mass and the ratio of lean-to-fat tissue, while changes in body weight were similar to those seen in patients who received no treatment. Treatment with GENOTROPIN did not accelerate bone age, compared with patients who received no treatment.
| GENOTROPIN | Untreated Control n=10 | |
|---|---|---|
| n=14 | ||
Fat mass (kg) | ||
Baseline | 12.3 ± 6.8 | 9.4 ± 4.9 |
Change from months 0 to 12 | -0.9 p < 0.005 ± 2.2 | 2.3 ± 2.4 |
Lean body mass (kg) | ||
Baseline | 15.6 ± 5.7 | 14.3 ± 4.0 |
Change from months 0 to 12 | 4.7± 1.9 | 0.7 ± 2.4 |
Lean body mass/Fat mass | ||
Baseline | 1.4 ± 0.4 | 1.8 ± 0.8 |
Change from months 0 to 12 | 1.0± 1.4 | -0.1 ± 0.6 |
Body weight (kg) n=15 for the group receiving GENOTROPIN; n=12 for the Control group | ||
Baseline | 27.2 ± 12.0 | 23.2 ± 7.0 |
Change from months 0 to 12 | 3.7 n.s. ± 2.0 | 3.5 ± 1.9 |
Small for Gestational Age
Pediatric Patients Born Small for Gestational Age (SGA) Who Fail to Manifest Catch-up Growth by Age 2
The safety and efficacy of GENOTROPIN in the treatment of pediatric patients born small for gestational age (SGA) were evaluated in 4 randomized, open-label, controlled clinical trials. Patients (age range of 2 to 8 years) were observed for 12 months before being randomized to receive either GENOTROPIN (two doses per study, most often 0.24 and 0.48 mg/kg/week) as a daily SC injection or no treatment for the first 24 months of the studies. After 24 months in the studies, all patients received GENOTROPIN.
Patients who received any dose of GENOTROPIN showed significant increases in growth during the first 24 months of study, compared with patients who received no treatment (see Table 5 ). Children receiving 0.48 mg/kg/week demonstrated a significant improvement in height standard deviation score (SDS) compared with children treated with 0.24 mg/kg/week. Both of these doses resulted in a slower but constant increase in growth between months 24 to 72 (data not shown).
| GENOTROPIN | GENOTROPIN | Untreated Control n=40 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| (0.24 mg/kg/week) n=76 | (0.48 mg/kg/week) n=93 | ||
Height Standard Deviation Score (SDS) | |||
Baseline SDS | -3.2 ± 0.8 | -3.4 ± 1.0 | -3.1 ± 0.9 |
SDS at 24 months | -2.0 ± 0.8 | -1.7 ± 1.0 | -2.9 ± 0.9 |
Change in SDS from baseline to month 24 | 1.2 p = 0.0001 vs Untreated Control group ± 0.5 | 1.7 p = 0.0001 vs group treated with GENOTROPIN 0.24 mg/kg/week ± 0.6 | 0.1 ± 0.3 |
Turner Syndrome
Two randomized, open-label, clinical trials were conducted that evaluated the efficacy and safety of GENOTROPIN in Turner syndrome patients with short stature. Turner syndrome patients were treated with GENOTROPIN alone or GENOTROPIN plus adjunctive hormonal therapy (ethinylestradiol or oxandrolone). A total of 38 patients were treated with GENOTROPIN alone in the two studies. In Study 055, 22 patients were treated for 12 months, and in Study 092, 16 patients were treated for 12 months. Patients received GENOTROPIN at a dose between 0.13 to 0.33 mg/kg/week.
SDS for height velocity and height are expressed using either the Tanner (Study 055) or Sempé (Study 092) standards for age-matched normal children as well as the Ranke standard (both studies) for age-matched, untreated Turner syndrome patients. As seen in Table 6, height velocity SDS and height SDS values were smaller at baseline and after treatment with GENOTROPIN when the normative standards were utilized as opposed to the Turner syndrome standard.
Both studies demonstrated statistically significant increases from baseline in all of the linear growth variables (i.e., mean height velocity, height velocity SDS, and height SDS) after treatment with GENOTROPIN (see Table 6 ). The linear growth response was greater in Study 055 wherein patients were treated with a larger dose of GENOTROPIN.
| GENOTROPIN 0.33 mg/kg/week Study 055^ n=22 | GENOTROPIN 0.13–0.23 mg/kg/week Study 092# n=16 | |
|---|---|---|
| SDS = Standard Deviation Score Ranke standard based on age-matched, untreated Turner syndrome patients Tanner^/Sempé# standards based on age-matched normal children p<0.05, for all changes from baseline | ||
Height Velocity (cm/yr) | ||
Baseline | 4.1 ± 1.5 | 3.9 ± 1.0 |
Month 12 | 7.8 ± 1.6 | 6.1 ± 0.9 |
Change from baseline (95% CI) | 3.7 (3.0, 4.3) | 2.2 (1.5, 2.9) |
Height Velocity SDS (Tanner^/Sempé# Standards) | (n=20) | |
Baseline | -2.3 ± 1.4 | -1.6 ± 0.6 |
Month 12 | 2.2 ± 2.3 | 0.7 ± 1.3 |
Change from baseline (95% CI) | 4.6 (3.5, 5.6) | 2.2 (1.4, 3.0) |
Height Velocity SDS (Ranke Standard) | ||
Baseline | -0.1 ± 1.2 | -0.4 ± 0.6 |
Month 12 | 4.2 ± 1.2 | 2.3 ± 1.2 |
Change from baseline (95% CI) | 4.3 (3.5, 5.0) | 2.7 (1.8, 3.5) |
Height SDS (Tanner^/Sempé# Standards) | ||
Baseline | -3.1 ± 1.0 | -3.2 ± 1.0 |
Month 12 | -2.7 ± 1.1 | -2.9 ± 1.0 |
Change from baseline (95% CI) | 0.4 (0.3, 0.6) | 0.3 (0.1, 0.4) |
Height SDS (Ranke Standard) | ||
Baseline | -0.2 ± 0.8 | -0.3 ± 0.8 |
Month 12 | 0.6 ± 0.9 | 0.1 ± 0.8 |
Change from baseline (95% CI) | 0.8 (0.7, 0.9) | 0.5 (0.4, 0.5) |
Idiopathic Short Stature
The long-term efficacy and safety of GENOTROPIN in patients with idiopathic short stature (ISS) were evaluated in one randomized, open-label, clinical trial that enrolled 177 children. Patients were enrolled on the basis of short stature, stimulated GH secretion >10 ng/mL, and prepubertal status (criteria for idiopathic short stature were retrospectively applied and included 126 patients). All patients were observed for height progression for 12 months and were subsequently randomized to GENOTROPIN or observation only and followed to final height. Two GENOTROPIN doses were evaluated in this trial: 0.23 mg/kg/week (0.033 mg/kg/day) and 0.47 mg/kg/week (0.067 mg/kg/day). Baseline patient characteristics for the ISS patients who remained prepubertal at randomization (n= 105) were: mean (± SD): chronological age 11.4 (1.3) years, height SDS -2.4 (0.4), height velocity SDS -1.1 (0.8), and height velocity 4.4 (0.9) cm/yr, IGF-1 SDS -0.8 (1.4). Patients were treated for a median duration of 5.7 years. Results for final height SDS are displayed by treatment arm in Table 7. GENOTROPIN therapy improved final height in ISS children relative to untreated controls. The observed mean gain in final height was 9.8 cm for females and 5.0 cm for males for both doses combined compared to untreated control subjects. A height gain of 1 SDS was observed in 10% of untreated subjects, 50% of subjects receiving 0.23 mg/kg/week and 69% of subjects receiving 0.47 mg/kg/week.
| Untreated (n=30) | GEN 0.033 (n=30) | GEN 0.067 (n=42) | GEN 0.033 vs. Untreated (95% CI) | GEN 0.067 vs. Untreated (95% CI) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ••Least square means based on ANCOVA (final height SDS and final height SDS minus baseline predicted height SDS were adjusted for baseline height SDS) | |||||
Baseline height SDS | |||||
Final height SDS minus baseline | 0.41 (0.58) | 0.95 (0.75) | 1.36 (0.64) | +0.53 (0.20, 0.87) p=0.0022 | +0.94 (0.63, 1.26) p<0.0001 |
Baseline predicted ht | |||||
Final height SDS minus baseline predicted final height SDS | 0.23 (0.66) | 0.73 (0.63) | 1.05 (0.83) | +0.60 (0.09, 1.11) p=0.0217 | +0.90 (0.42, 1.39) p=0.0004 |
HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
How Supplied
GENOTROPIN (somatropin) for injection is a white, lyophilized powder in a single-patient-use or single-dose, two-chamber cartridge intended for subcutaneous injection after reconstitution. The front chamber contains somatropin and the rear chamber contains the diluent.
GENOTROPIN lyophilized powder is available in the following packages:
5 mg single‑patient‑use two-chamber cartridge (with preservative)
- After reconstitution the final concentration is 5 mg/mL
- For use with the GENOTROPIN PEN 5 Growth Hormone Delivery Device.
- Package of 1 NDC 0013-2626-81
12 mg single‑patient‑use two-chamber cartridge (with preservative)
- After reconstitution the final concentration is 12 mg/mL
- For use with the GENOTROPIN PEN 12 Growth Hormone Delivery Device.
- Package of 1 NDC 0013-2646-81
GENOTROPIN MINIQUICK, a single-dose Growth Hormone Delivery Device containing a two-chamber cartridge of GENOTROPIN (without preservative)
- After reconstitution, each GENOTROPIN MINIQUICK delivers 0.25 mL, regardless of strength.
GENOTROPIN MINIQUICK is available in the following strengths, each in a package of 7:
Strength | NDC Number |
0.2 mg | NDC 0013-2649-02 |
0.4 mg | NDC 0013-2650-02 |
0.6 mg | NDC 0013-2651-02 |
0.8 mg | NDC 0013-2652-02 |
1 mg | NDC 0013-2653-02 |
1.2 mg | NDC 0013-2654-02 |
1.4 mg | NDC 0013-2655-02 |
1.6 mg | NDC 0013-2656-02 |
1.8 mg | NDC 0013-2657-02 |
2 mg | NDC 0013-2658-02 |
Storage and Handling
The 5 mg and 12 mg GENOTROPIN single-patient-use cartridges:
- Store GENOTROPIN lyophilized powder under refrigeration at 36°F to 46°F (2°C to 8°C) until the expiration date. Store in the package to protect from light. Do not freeze.
- After reconstitution, store the pen (with the cartridge) in the pen box with the pen cap on to protect from light. Store under refrigeration at 36°F to 46°F (2°C to 8°C) between each use, for up to 28 days. Do not shake. Discard the cartridge and any unused medication after 28 days. Use a GENOTROPIN PEN 5, a medical device, to reconstitute the 5 mg two-chamber cartridge, and use a GENOTROPIN PEN 12 to reconstitute the 12 mg two-chamber cartridge.
The 0.2 mg, 0.4 mg, 0.6 mg, 0.8 mg, 1.0 mg, 1.2 mg, 1.4 mg, 1.6 mg, 1.8 mg and 2 mg single-dose Growth Hormone Delivery Devices containing a two-chamber cartridge (GENOTROPIN MINIQUICK):
- Store GENOTROPIN MINIQUICK under refrigeration at 36°F to 46°F (2°C to 8°C) until the expiration date. If needed, may be stored for up to 3 months at room temperature at or below 77°F (25°C) prior to reconstitution. Do not freeze.
- After reconstitution, store GENOTROPIN MINIQUICK in the package with the pen cap on to protect from light. If needed, may be stored under refrigeration at 36°F to 46°F (2°C to 8°C) for up to 24 hours before use. Do not shake. The GENOTROPIN MINIQUICK should be used only once and then discarded.
Instructions for Use

INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE GENOTROPIN 5 (JEEN-o-tro-pin 5) GENOTROPIN PEN 5 is a medical device used to mix and inject doses of reconstituted GENOTROPIN (somatropin) for injection. Use this device only for administration of GENOTROPIN.
Important Note |
Please read these instructions completely before using the GENOTROPIN PEN 5. These instructions need to be followed step by step. Please do not use the GENOTROPIN PEN 5 unless your healthcare provider has trained you. If there is anything you do not understand or cannot do, call the Pfizer Bridge Program toll-free number at 1-800-645-1280. If you have any questions about your dose or your treatment with GENOTROPIN, call your healthcare provider. |
Your pen should not be used near electrical or electronic equipment, including mobile phones. If your pen has been damaged, it should not be used and should be disposed of as instructed by your healthcare provider. |
GENOTROPIN PEN 5 is a reusable multi-dose device holding a 2-chamber cartridge of GENOTROPIN, used to mix and inject GENOTROPIN during a 2 year use period.
For your injection you will need:
- 1 GENOTROPIN PEN 5 device
- 1 GENOTROPIN 5 mg single-patient-use 2-chamber cartridge
- 1 new 29 gauge (29 G), 30 gauge (30 G), or 31 gauge (31 G) Becton Dickinson pen needle
- Alcohol swab (not included)
- 1 sharps disposal container. See " Throwing away (disposing of) used needles, cartridges and your GENOTROPIN PEN 5 " in Step 14.
Parts of the GENOTROPIN PEN 5 ( See Figure A )
Figure A |
Storage instructions for your GENOTROPIN PEN 5
- Between uses, store your pen (with the cartridge) in the refrigerator 36°F to 46°F (2°C to 8°C) in its protective case. Always remove the needle before storing.
- Do not freeze . Protect from light.
- Throw away the cartridge within 28 days after mixing, even if the cartridge is not empty.
- When travelling, keep your pen in its protective case and carry it in an insulated bag to protect it from heat or freezing. Put your pen back in the refrigerator as soon as possible.
Using your GENOTROPIN PEN 5
Step 1.
Wash your hands well with soap and water before using the GENOTROPIN PEN 5.
Step 2. Attach the Needle
| Figure B |
| Figure C |
| Figure D |
Step 3. Insert the 2-Chamber Cartridge of GENOTROPIN Use only the 5 mg cartridge. | |
| Figure E |
| Figure F |
Step 4. Prepare your Pen
| Figure G |
| Figure H |
| Figure I |
Step 5. Mix your GENOTROPIN
| Figure J |
Step 6. Examine the Solution
| Figure K |
| Figure L |
Step 7. Release Trapped Air
| |
| |
| Figure M |
| |
| Figure N |
| Figure O |
Step 8. Attach the Needle Guard (Optional) The needle guard is intended to hide the needle before, during and after injection and to reduce needle injury. You can choose to use the needle guard, if desired. | |
| Figure P |
My daily dose is | |
Step 9. Dial Your Prescribed Dose
| Figure Q |
Step 10. Inject your GENOTROPIN
| Figure R |
| Figure S |
Step 11. Throw away the Needle and Store your GENOTROPIN PEN 5
| Figure T |
Step 12. Your Next Injection If you already have a cartridge in your pen, prepare the pen and give the injection as follows: | |
| Figure U |
| Figure V |
| Figure W |
Step 13. To Replace the Cartridge
| Figure X |
| Figure Y |
Figure Z |
Step 14. Throwing away (disposing of) used needles, cartridges and your GENOTROPIN PEN 5 Put the used needles and cartridges in a FDA-cleared sharps disposal container right away after use. Do not throw away (dispose of) the needles and cartridges in the household trash.
If you do not have a FDA-cleared sharps disposal container, you may use a household container that is:
- Made of a heavy-duty plastic,
- Can be closed with a tight fitting, puncture-resistant lid, without sharps being able to come out,
- Upright and stable during use,
- Leak-resistant, and
- Properly labeled to warn of hazardous waste inside the container.
When your sharps disposal container is almost full, you will need to follow your community guidelines for the right way to dispose of your sharps disposal container. There may be state or local laws about how you should throw away used needles and cartridges. For more information about safe sharps disposal, and for specific information about sharps disposal in the state that you live in, go to the FDA's website at: http://www.fda.gov/safesharpsdisposal .
- Do not reuse needles.
- Do not throw away (dispose of) your used sharps disposal container in your household trash unless your community guidelines permit this.
- Do not recycle your used sharps disposal container.
Important : Always keep the sharps disposal container out of the reach of children.
Dispose of the entire GENOTROPIN PEN 5 as electronic waste per state and local regulations.
Customizing your Pen
Your pen is supplied with 2 colored clip-on panels, so that you can customize the look of your pen. To remove the clip-on panel from the pen, insert the lip of the front cap into the groove under the front end of the panel, and pry the panel off. The new panel simply clicks into place ( See Figure AA ). | Figure AA |
Caring for your Pen To clean your pen, wipe the outside surface with a damp cloth. Do not put the pen in water or this may damage your pen. Do not use alcohol or any other cleaning agents to clean the pen, as they may damage the plastic body. To clean the needle guard, wipe it with a damp cloth or alcohol pad.
| Questions and Answers | |
|---|---|
| Question | Answer |
How long is the use period of my pen? | The pen has a use period of 2 years starting from the first use by the patient. |
How can I tell how much GENOTROPIN is left in my pen? | The indicative scale along the side of the cartridge window is a guide. The number that aligns with the front edge of the rubber stopper shows you how many milligrams are left in the cartridge. If your cartridge is nearly empty you can also dial the injection button until it cannot go any further. The dose display will then show the maximum dose that can be delivered. When the cartridge is empty, the injection button will not turn any further. |
If the display does not work, can my pen still be used? | Contact your healthcare provider as soon as possible to get a new pen. |
What happens if I dial the injection button beyond the maximum dose ('2.0' mg)? | Some liquid may appear from the needle tip, and the numbers may disappear from the dose display. This is normal and will not affect your injection. To correct this, turn the injection button in the opposite direction of the arrow until numbers reappear on the dose display. Then dial back to your correct dose. |
Why is it difficult to turn or push the injection button? | The injection button may become difficult to turn or to push. This may occur if the pen gets dirty due to contact with food, liquids or GENOTROPIN, or if the needle becomes clogged. Contact your healthcare provider if the issue does not resolve. |
Display Information:
Steady | 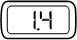 | The selected dose size. The number indicates the dose size (in mg) that your pen will deliver if the injection button is fully pressed in. |
Steady | 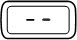 | A dose is not set. The injection button has been turned too far in the opposite direction to the arrow on the injection button while setting the dose. |
Flashing | 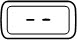 | The injection button is rotated too fast or too slow. Point your pen away from your face, press the injection button, press the red release button and continue preparing your dose. |
Flashing |  | The injection button is rotated too fast or too slow. Point your pen away from your face, press the injection button, press the red release button and continue preparing your dose. |
Flashing | 1 month before the end of the 2 year use period. | |
(5 seconds) |  | This is normal. The dose can be set and read from the display. Contact your healthcare provider as soon as possible to get a new Pen. |
Steady |  | Pen has reached the end of its use period of 2 years. |
The display will continue to show | ||
Flashing | Battery charge is low and will be empty in 1 month. Afterwards the dose can be set and your pen can be used correctly. Contact your healthcare provider as soon as possible to get a new Pen. | |
(5 seconds) |  | |
Steady |  | Battery power low. The dose cannot be displayed. Contact your healthcare provider right away to get a new Pen. |
Steady |  | Blank screen To save the battery energy, the dose display is activated for 2 minutes and then automatically disappears. Although the display is no longer visible, the dose remains available for delivery |
If you have any questions about your dose or your treatment with GENOTROPIN, call your healthcare provider right away.
Use this device only for the person for whom it was prescribed.
This Instructions for Use has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
Caution: Federal law restricts this device to sale by or on the order of a physician.
Manufactured by:
Pharmacia & Upjohn Company LLC
A subsidiary of Pfizer Inc.
New York, NY 10001
U.S. License No. 1216

LAB-0225-10.0
Revised August 2024
Mechanism of Action
In vitro, preclinical, and clinical tests have demonstrated that GENOTROPIN lyophilized powder is therapeutically equivalent to human growth hormone of pituitary origin and achieves similar pharmacokinetic profiles in normal adults. In pediatric patients who have growth hormone deficiency (GHD), have Prader-Willi syndrome (PWS), were born small for gestational age (SGA), have Turner syndrome (TS), or have Idiopathic short stature (ISS), treatment with GENOTROPIN stimulates linear growth. In patients with GHD or PWS, treatment with GENOTROPIN also normalizes concentrations of IGF-I (Insulin-like Growth Factor-I/Somatomedin C). In adults with GHD, treatment with GENOTROPIN results in reduced fat mass, increased lean body mass, metabolic alterations that include beneficial changes in lipid metabolism, and normalization of IGF-I concentrations.
In addition, the following actions have been demonstrated for GENOTROPIN and/or somatropin.
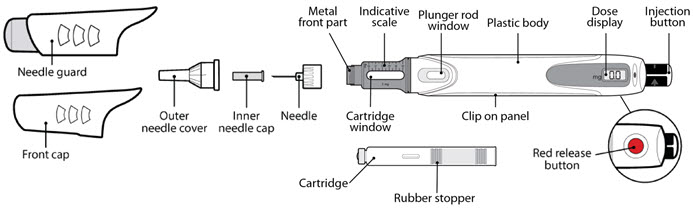
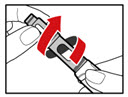
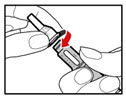
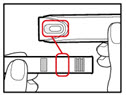
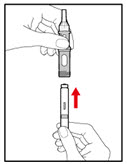
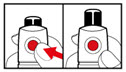
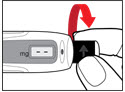
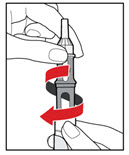
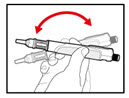
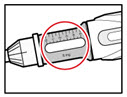
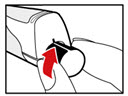
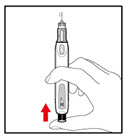
 mg (write in your daily dose)
mg (write in your daily dose) 
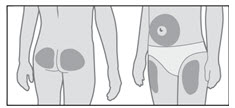
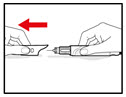
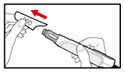
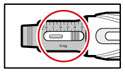
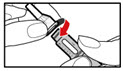
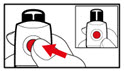
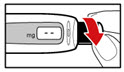
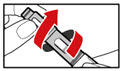
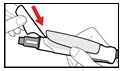
 until the battery is completely empty. This does not indicate a problem with the pen. Your pen can still be used correctly, but the dose size will not be displayed. Contact your healthcare provider right away to get a new Pen.
until the battery is completely empty. This does not indicate a problem with the pen. Your pen can still be used correctly, but the dose size will not be displayed. Contact your healthcare provider right away to get a new Pen.