Get your patient on Jemperli (Dostarlimab)
Jemperli prior authorization resources
Most recent state uniform prior authorization forms
Brand Resources
Jemperli patient education
Patient toolkit
Dosage & administration
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- JEMPERLI, in combination with carboplatin and paclitaxel, for primary advanced or recurrent EC: 500 mg every 3 weeks for 6 cycles followed by 1,000 mg monotherapy every 6 weeks for all cycles thereafter. (2.2 )
- JEMPERLI, as a single agent, for dMMR recurrent or advanced EC: 500 mg every 3 weeks for 4 cycles followed by 1,000 mg every 6 weeks for all cycles thereafter. (2.2 )
- JEMPERLI, as a single agent, for dMMR recurrent or advanced solid tumors: 500 mg every 3 weeks for 4 cycles followed by 1,000 mg every 6 weeks for all cycles thereafter. (2.2 )
- Administer as an intravenous infusion over 30 minutes. (2.2 )
- For complete dosing instructions, see full prescribing information.
Patient Selection
Single Agent
Select patients for treatment with JEMPERLI as a single agent based on the presence of dMMR in tumor specimens in:
- recurrent or advanced EC [see Clinical Studies (14.1 )] .
- recurrent or advanced solid tumors [see Clinical Studies (14.2 )] .
Information on FDA-approved tests for the detection of dMMR status is available at https://www.fda.gov/companiondiagnostics .
Because the effect of prior chemotherapy on test results for dMMR in patients with high-grade gliomas is unclear, it is recommended to test for this marker in the primary tumor specimen obtained prior to initiation of temozolomide chemotherapy in patients with high-grade gliomas.
Recommended Dosage
The recommended dosage for JEMPERLI is presented in Table 1 .
| dMMR = Mismatch Repair Deficient; EC = endometrial cancer. | ||
| a 30-minute intravenous infusion. | ||
| b Refer to the Prescribing Information for the agents administered in combination with JEMPERLI, as appropriate. | ||
Indication | Recommended Dosage | Duration/Timing of Treatment |
Combination Therapy | ||
Adults with primary advanced or recurrent EC | 500 mg a JEMPERLI every 3 weeks for 6 cycles in combination with carboplatin and paclitaxel b followed by 1,000 mg JEMPERLI as monotherapy every 6 weeks for all cycles thereafter. Administer JEMPERLI prior to carboplatin and paclitaxel when given on the same day. | Until disease progression, unacceptable toxicity, or up to 3 years. |
Monotherapy | ||
Adults with dMMR recurrent or advanced EC and dMMR recurrent or advanced solid tumors | 500 mg a JEMPERLI every 3 weeks for 4 cycles followed by 1,000 mg a JEMPERLI every 6 weeks for all cycles thereafter. | Until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity. |
Dosage Modifications for Adverse Reactions
No dose reductions of JEMPERLI are recommended. In general, withhold JEMPERLI for severe (Grade 3) immune‑mediated adverse reactions. Permanently discontinue JEMPERLI for life‑threatening (Grade 4) immune‑mediated adverse reactions, recurrent severe (Grade 3) immune-mediated reactions that require systemic immunosuppressive treatment, or an inability to reduce corticosteroid dose to 10 mg or less of prednisone equivalent per day within 12 weeks of initiating steroids.
Dosage modifications for JEMPERLI for adverse reactions that require management different from these general guidelines are summarized in Table 2 .
| ALT = alanine aminotransferase; AST = aspartate aminotransferase; DRESS = drug rash with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms; SJS = Stevens-Johnson syndrome; TEN = toxic epidermal necrolysis; ULN = upper limit of normal. a Based on National Cancer Institute Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events, Version 5.0. b Resume in patients with complete or partial resolution (Grade 0 to 1) after corticosteroid taper. Permanently discontinue if no complete or partial resolution within 12 weeks of initiating steroids or inability to reduce prednisone to less than 10 mg/day (or equivalent) within 12 weeks of initiating steroids. c If AST and ALT are less than or equal to ULN at baseline in patients with liver involvement, withhold or permanently discontinue JEMPERLI based on recommendations for hepatitis with no liver involvement. | ||
Adverse Reaction | Severity a | Dosage Modification |
Immune-Mediated Adverse Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1 )] | ||
Pneumonitis | Grade 2 | Withhold b |
Grade 3 or 4 or recurrent Grade 2 | Permanently discontinue | |
Colitis | Grade 2 or 3 | Withhold b |
Grade 4 | Permanently discontinue | |
Hepatitis with no tumor involvement of the liver | AST or ALT increases to more than 3 and up to 8 times ULN or Total bilirubin increases to more than 1.5 and up to 3 times ULN | Withhold b |
AST or ALT increases to more than 8 times ULN or Total bilirubin increases to more than 3 times ULN | Permanently discontinue | |
Hepatitis with tumor involvement of the liver c | Baseline AST or ALT is more than 1 and up to 3 times ULN and increases to more than 5 and up to 10 times ULN or Baseline AST or ALT is more than 3 and up to 5 times ULN and increases to more than 8 and up to 10 times ULN | Withhold b |
AST or ALT increases to more than 10 times ULN or Total bilirubin increases to more than 3 times ULN | Permanently discontinue | |
Endocrinopathies | Grade 2, 3, or 4 | Withhold until clinically stable or permanently discontinue, depending on severity b |
Nephritis with renal dysfunction | Grade 2 or 3 increased blood creatinine | Withhold b |
Grade 4 increased blood creatinine | Permanently discontinue | |
Exfoliative dermatologic conditions | Suspected SJS, TEN, or DRESS | Withhold b |
Confirmed SJS, TEN, or DRESS | Permanently discontinue | |
Myocarditis | Grade 2, 3, or 4 | Permanently discontinue |
Neurological toxicities | Grade 2 | Withhold b |
Grade 3 or 4 | Permanently discontinue | |
Other Adverse Reactions | ||
Infusion-related reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2 )] | Grade 1 or 2 | Interrupt or slow the rate of infusion |
Grade 3 or 4 | Permanently discontinue | |
Preparation and Administration
Preparation for Intravenous Infusion
- Visually inspect the solution for particulate matter and discoloration. The solution is clear to slightly opalescent, colorless to yellow. Discard the vial if visible particles are observed.
- Do not shake.
- JEMPERLI is compatible with an infusion bag made of polyolefin, ethylene vinyl acetate, or polyvinyl chloride with di(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate (DEHP).
- For the 500-mg dose, withdraw 10 mL of JEMPERLI from a vial using a disposable sterile syringe made of polypropylene and dilute into an intravenous infusion bag containing 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP or 5% Dextrose Injection, USP to a final concentration between 2 to 10 mg/mL (maximum 250 mL).
- For the 1,000-mg dose, withdraw 10 mL from each of 2 vials (withdraw 20 mL total) and dilute into an intravenous bag containing 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP or 5% Dextrose Injection, USP to a final concentration between 4 to 10 mg/mL (maximum 250 mL).
- Mix diluted solution by gentle inversion. Do not shake.
- Discard any unused portion left in the vial.
Storage of Infusion Solution
Store in the original carton until time of preparation in order to protect from light. The prepared dose may be stored either:
- At room temperature for no more than 6 hours from the time of preparation until the end of infusion.
- Under refrigeration at 2°C to 8°C (36ºF to 46ºF) for no more than 24 hours from time of preparation until end of infusion. If refrigerated, allow the diluted solution to come to room temperature prior to administration.
Discard after 6 hours at room temperature or after 24 hours under refrigeration.
Do not freeze.
Administration
Administer infusion solution intravenously over 30 minutes through an intravenous line using tubing made of polyvinyl chloride or platinum cured silicon; fittings made of polyvinyl chloride or polycarbonate; and a sterile, non-pyrogenic, low‑protein binding, 0.2-micron, in-line or add-on filter.
JEMPERLI must not be administered as an intravenous push or bolus injection. Do not co‑administer other drugs through the same infusion line.

By using PrescriberAI, you agree to the AI Terms of Use.
Jemperli prescribing information
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
JEMPERLI is a programmed death receptor-1 (PD-1)–blocking antibody indicated:
Endometrial Cancer
- in combination with carboplatin and paclitaxel, followed by JEMPERLI as a single agent, for the treatment of adult patients with primary advanced or recurrent endometrial cancer (EC). (1.1 )
- as a single agent for the treatment of adult patients with mismatch repair deficient (dMMR) recurrent or advanced EC, as determined by an FDA-approved test, that has progressed on or following prior treatment with a platinum-containing regimen in any setting and are not candidates for curative surgery or radiation. (1.1 , 2.1 )
Mismatch Repair Deficient Recurrent or Advanced Solid Tumors
- as a single agent for the treatment of adult patients with dMMR recurrent or advanced solid tumors, as determined by an FDA-approved test, that have progressed on or following prior treatment and who have no satisfactory alternative treatment options. 1 (1.2 , 2.1 )
1 This indication is approved under accelerated approval based on tumor response rate and durability of response. Continued approval for this indication may be contingent upon verification and description of clinical benefit in a confirmatory trial(s). (1.2 )
Endometrial Cancer
JEMPERLI, in combination with carboplatin and paclitaxel, followed by JEMPERLI as a single agent, is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with primary advanced or recurrent endometrial cancer (EC).
JEMPERLI, as a single agent, is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with mismatch repair deficient (dMMR) recurrent or advanced EC, as determined by an FDA-approved test, that has progressed on or following prior treatment with a platinum-containing regimen in any setting and are not candidates for curative surgery or radiation [see Dosage and Administration (2.1 )].
Mismatch Repair Deficient Recurrent or Advanced Solid Tumors
JEMPERLI, as a single agent, is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with dMMR recurrent or advanced solid tumors, as determined by an FDA-approved test, that have progressed on or following prior treatment and who have no satisfactory alternative treatment options [see Dosage and Administration (2.1 )]. This indication is approved under accelerated approval based on tumor response rate and durability of response [see Clinical Studies (14.2 )]. Continued approval for this indication may be contingent upon verification and description of clinical benefit in a confirmatory trial(s).
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- JEMPERLI, in combination with carboplatin and paclitaxel, for primary advanced or recurrent EC: 500 mg every 3 weeks for 6 cycles followed by 1,000 mg monotherapy every 6 weeks for all cycles thereafter. (2.2 )
- JEMPERLI, as a single agent, for dMMR recurrent or advanced EC: 500 mg every 3 weeks for 4 cycles followed by 1,000 mg every 6 weeks for all cycles thereafter. (2.2 )
- JEMPERLI, as a single agent, for dMMR recurrent or advanced solid tumors: 500 mg every 3 weeks for 4 cycles followed by 1,000 mg every 6 weeks for all cycles thereafter. (2.2 )
- Administer as an intravenous infusion over 30 minutes. (2.2 )
- For complete dosing instructions, see full prescribing information.
Patient Selection
Single Agent
Select patients for treatment with JEMPERLI as a single agent based on the presence of dMMR in tumor specimens in:
- recurrent or advanced EC [see Clinical Studies (14.1 )] .
- recurrent or advanced solid tumors [see Clinical Studies (14.2 )] .
Information on FDA-approved tests for the detection of dMMR status is available at https://www.fda.gov/companiondiagnostics .
Because the effect of prior chemotherapy on test results for dMMR in patients with high-grade gliomas is unclear, it is recommended to test for this marker in the primary tumor specimen obtained prior to initiation of temozolomide chemotherapy in patients with high-grade gliomas.
Recommended Dosage
The recommended dosage for JEMPERLI is presented in Table 1 .
| dMMR = Mismatch Repair Deficient; EC = endometrial cancer. | ||
| a 30-minute intravenous infusion. | ||
| b Refer to the Prescribing Information for the agents administered in combination with JEMPERLI, as appropriate. | ||
Indication | Recommended Dosage | Duration/Timing of Treatment |
Combination Therapy | ||
Adults with primary advanced or recurrent EC | 500 mg a JEMPERLI every 3 weeks for 6 cycles in combination with carboplatin and paclitaxel b followed by 1,000 mg JEMPERLI as monotherapy every 6 weeks for all cycles thereafter. Administer JEMPERLI prior to carboplatin and paclitaxel when given on the same day. | Until disease progression, unacceptable toxicity, or up to 3 years. |
Monotherapy | ||
Adults with dMMR recurrent or advanced EC and dMMR recurrent or advanced solid tumors | 500 mg a JEMPERLI every 3 weeks for 4 cycles followed by 1,000 mg a JEMPERLI every 6 weeks for all cycles thereafter. | Until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity. |
Dosage Modifications for Adverse Reactions
No dose reductions of JEMPERLI are recommended. In general, withhold JEMPERLI for severe (Grade 3) immune‑mediated adverse reactions. Permanently discontinue JEMPERLI for life‑threatening (Grade 4) immune‑mediated adverse reactions, recurrent severe (Grade 3) immune-mediated reactions that require systemic immunosuppressive treatment, or an inability to reduce corticosteroid dose to 10 mg or less of prednisone equivalent per day within 12 weeks of initiating steroids.
Dosage modifications for JEMPERLI for adverse reactions that require management different from these general guidelines are summarized in Table 2 .
| ALT = alanine aminotransferase; AST = aspartate aminotransferase; DRESS = drug rash with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms; SJS = Stevens-Johnson syndrome; TEN = toxic epidermal necrolysis; ULN = upper limit of normal. a Based on National Cancer Institute Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events, Version 5.0. b Resume in patients with complete or partial resolution (Grade 0 to 1) after corticosteroid taper. Permanently discontinue if no complete or partial resolution within 12 weeks of initiating steroids or inability to reduce prednisone to less than 10 mg/day (or equivalent) within 12 weeks of initiating steroids. c If AST and ALT are less than or equal to ULN at baseline in patients with liver involvement, withhold or permanently discontinue JEMPERLI based on recommendations for hepatitis with no liver involvement. | ||
Adverse Reaction | Severity a | Dosage Modification |
Immune-Mediated Adverse Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1 )] | ||
Pneumonitis | Grade 2 | Withhold b |
Grade 3 or 4 or recurrent Grade 2 | Permanently discontinue | |
Colitis | Grade 2 or 3 | Withhold b |
Grade 4 | Permanently discontinue | |
Hepatitis with no tumor involvement of the liver | AST or ALT increases to more than 3 and up to 8 times ULN or Total bilirubin increases to more than 1.5 and up to 3 times ULN | Withhold b |
AST or ALT increases to more than 8 times ULN or Total bilirubin increases to more than 3 times ULN | Permanently discontinue | |
Hepatitis with tumor involvement of the liver c | Baseline AST or ALT is more than 1 and up to 3 times ULN and increases to more than 5 and up to 10 times ULN or Baseline AST or ALT is more than 3 and up to 5 times ULN and increases to more than 8 and up to 10 times ULN | Withhold b |
AST or ALT increases to more than 10 times ULN or Total bilirubin increases to more than 3 times ULN | Permanently discontinue | |
Endocrinopathies | Grade 2, 3, or 4 | Withhold until clinically stable or permanently discontinue, depending on severity b |
Nephritis with renal dysfunction | Grade 2 or 3 increased blood creatinine | Withhold b |
Grade 4 increased blood creatinine | Permanently discontinue | |
Exfoliative dermatologic conditions | Suspected SJS, TEN, or DRESS | Withhold b |
Confirmed SJS, TEN, or DRESS | Permanently discontinue | |
Myocarditis | Grade 2, 3, or 4 | Permanently discontinue |
Neurological toxicities | Grade 2 | Withhold b |
Grade 3 or 4 | Permanently discontinue | |
Other Adverse Reactions | ||
Infusion-related reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2 )] | Grade 1 or 2 | Interrupt or slow the rate of infusion |
Grade 3 or 4 | Permanently discontinue | |
Preparation and Administration
Preparation for Intravenous Infusion
- Visually inspect the solution for particulate matter and discoloration. The solution is clear to slightly opalescent, colorless to yellow. Discard the vial if visible particles are observed.
- Do not shake.
- JEMPERLI is compatible with an infusion bag made of polyolefin, ethylene vinyl acetate, or polyvinyl chloride with di(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate (DEHP).
- For the 500-mg dose, withdraw 10 mL of JEMPERLI from a vial using a disposable sterile syringe made of polypropylene and dilute into an intravenous infusion bag containing 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP or 5% Dextrose Injection, USP to a final concentration between 2 to 10 mg/mL (maximum 250 mL).
- For the 1,000-mg dose, withdraw 10 mL from each of 2 vials (withdraw 20 mL total) and dilute into an intravenous bag containing 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP or 5% Dextrose Injection, USP to a final concentration between 4 to 10 mg/mL (maximum 250 mL).
- Mix diluted solution by gentle inversion. Do not shake.
- Discard any unused portion left in the vial.
Storage of Infusion Solution
Store in the original carton until time of preparation in order to protect from light. The prepared dose may be stored either:
- At room temperature for no more than 6 hours from the time of preparation until the end of infusion.
- Under refrigeration at 2°C to 8°C (36ºF to 46ºF) for no more than 24 hours from time of preparation until end of infusion. If refrigerated, allow the diluted solution to come to room temperature prior to administration.
Discard after 6 hours at room temperature or after 24 hours under refrigeration.
Do not freeze.
Administration
Administer infusion solution intravenously over 30 minutes through an intravenous line using tubing made of polyvinyl chloride or platinum cured silicon; fittings made of polyvinyl chloride or polycarbonate; and a sterile, non-pyrogenic, low‑protein binding, 0.2-micron, in-line or add-on filter.
JEMPERLI must not be administered as an intravenous push or bolus injection. Do not co‑administer other drugs through the same infusion line.
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Injection: 500 mg/10 mL (50 mg/mL) clear to slightly opalescent, colorless to yellow solution in a single-dose vial for intravenous infusion after dilution.
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
Lactation: Advise not to breastfeed. (8.2 )
Pregnancy
Risk Summary
Based on its mechanism of action, JEMPERLI can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.1 )] . There are no available data on the use of JEMPERLI in pregnant women. Animal studies have demonstrated that inhibition of the PD-1/PD-L1 pathway can lead to increased risk of immune-mediated rejection of the developing fetus resulting in fetal death (see ) . Human IgG4 immunoglobulins (IgG4) are known to cross the placental barrier; therefore, dostarlimab-gxly has the potential to be transmitted from the mother to the developing fetus. Advise women of the potential risk to a fetus.
In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2% to 4% and 15% to 20%, respectively.
Data
Animal Data: Animal reproduction studies have not been conducted with JEMPERLI to evaluate its effect on reproduction and fetal development. A central function of the PD-1/PD-L1 pathway is to preserve pregnancy by maintaining maternal immune tolerance to the fetus. In murine models of pregnancy, blockade of PD-L1 signaling has been shown to disrupt tolerance to the fetus and to result in an increase in fetal loss; therefore, potential risks of administering JEMPERLI during pregnancy include increased rates of abortion or stillbirth. As reported in the literature, there were no malformations related to the blockade of PD-1/PD-L1 signaling in the offspring of these animals; however, immune-mediated disorders occurred in PD-1 and PD-L1 knockout mice. Based on its mechanism of action, fetal exposure to dostarlimab-gxly may increase the risk of developing immune-mediated disorders or altering the normal immune response.
Lactation
Risk Summary
There is no information regarding the presence of dostarlimab-gxly in human milk or its effects on the breastfed child or on milk production. Maternal IgG is known to be present in human milk. The effects of local gastrointestinal exposure and limited systemic exposure in the breastfed child to JEMPERLI are unknown. Because of the potential for serious adverse reactions in a breastfed child, advise women not to breastfeed during treatment and for 4 months after the last dose of JEMPERLI.
Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
JEMPERLI can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1 )] .
Pregnancy Testing
Verify pregnancy status in females of reproductive potential prior to initiating JEMPERLI [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1 )] .
Contraception
Females: Advise females of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with JEMPERLI and for 4 months after the last dose.
Pediatric Use
The safety and efficacy of JEMPERLI have not been established in pediatric patients.
Geriatric Use
In Combination with Carboplatin and Paclitaxel
Of the 241 patients treated with JEMPERLI in RUBY, 52.3% were younger than 65 years, 36.5% were aged 65 through 74 years, and 11.2% were 75 years or older. No overall differences in safety or effectiveness were observed between these patients and younger patients.
As a Single Agent
Of the 605 patients treated with JEMPERLI in GARNET, 51.6% were younger than 65 years, 36.9% were aged 65 through 74 years, and 11.5% were 75 years or older. No overall differences in safety or effectiveness were observed between these patients and younger patients.
CONTRAINDICATIONS
None.
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- Immune-mediated adverse reactions, which may be severe or fatal, can occur in any organ system or tissue, including the following: immune‑mediated pneumonitis, immune-mediated colitis, immune‑mediated hepatitis, immune-mediated endocrinopathies, immune-mediated nephritis with renal dysfunction, immune‑mediated dermatologic adverse reactions, and solid organ transplant rejection. Monitor for signs and symptoms of immune‑mediated adverse reactions. Evaluate clinical chemistries, including liver enzymes, creatinine, and thyroid function, at baseline and periodically during treatment. Withhold or permanently discontinue JEMPERLI and administer corticosteroids based on the severity of reaction. (2.3 , 5.1 )
- Infusion-related reactions: Interrupt, slow the rate of infusion, or permanently discontinue JEMPERLI based on severity of reaction. (2.3 , 5.2 )
- Complications of allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT): Fatal and other serious complications can occur in patients who receive allogeneic HSCT before or after being treated with a PD‑1/PD-L1–blocking antibody. (5.3 )
- Embryo-fetal toxicity: Can cause fetal harm. Advise females of reproductive potential of the potential risk to a fetus and to use effective contraception. (5.4 , 8.1 , 8.3 )
Severe and Fatal Immune-Mediated Adverse Reactions
JEMPERLI is a monoclonal antibody that belongs to a class of drugs that bind to either the programmed death receptor-1 (PD-1) or PD-ligand 1 (PD-L1), blocking the PD-1/PD-L1 pathway, thereby removing inhibition of the immune response, potentially breaking peripheral tolerance, and inducing immune-mediated adverse reactions. Important immune-mediated adverse reactions listed in WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS may not include all possible severe and fatal immune‑mediated reactions.
Immune-mediated adverse reactions, which can be severe or fatal, can occur in any organ system or tissue. Immune‑mediated adverse reactions can occur at any time after starting a PD-1/PD-L1–blocking antibody. While immune-mediated adverse reactions usually manifest during treatment with PD-1/PD-L1–blocking antibodies, they can also manifest after discontinuation of PD-1/PD-L1–blocking antibodies.
Early identification and management of immune-mediated adverse reactions are essential to ensure safe use of PD‑1/PD‑L1–blocking antibodies. Monitor closely for symptoms and signs that may be clinical manifestations of underlying immune-mediated adverse reactions. Evaluate liver enzymes, creatinine, and thyroid function tests at baseline and periodically during treatment. In cases of suspected immune-mediated adverse reactions, initiate appropriate workup to exclude alternative etiologies, including infection. Institute medical management promptly, including specialty consultation as appropriate.
Withhold or permanently discontinue JEMPERLI depending on severity [see Dosage and Administration (2.3 )] . In general, if JEMPERLI requires interruption or discontinuation, administer systemic corticosteroids (1 to 2 mg/kg/day prednisone or equivalent) until improvement to Grade 1 or less. Upon improvement to Grade 1 or less, initiate corticosteroid taper and continue to taper over at least 1 month. Consider administration of other systemic immunosuppressants in patients whose immune-mediated adverse reaction is not controlled with corticosteroids.
Toxicity management guidelines for adverse reactions that do not necessarily require systemic steroids (e.g., endocrinopathies, dermatologic reactions) are discussed below.
Immune-Mediated Pneumonitis
JEMPERLI can cause immune-mediated pneumonitis, which can be fatal. In patients treated with other PD-1/PD-L1–blocking antibodies, the incidence of pneumonitis is higher in patients who have received prior thoracic radiation.
Immune-mediated pneumonitis occurred in 2.3% (14/605) of patients receiving JEMPERLI, including Grade 2 (1.3%), Grade 3 (0.8%) and Grade 4 (0.2%) pneumonitis. Pneumonitis led to discontinuation of JEMPERLI in 1.3% of patients.
Systemic corticosteroids were required in 79% (11/14) of patients with pneumonitis. Pneumonitis resolved in 11 of the 14 patients. JEMPERLI was withheld for 9 patients. Five patients reinitiated JEMPERLI after symptom improvement; of these, 2 patients had recurrence of pneumonitis.
Immune-Mediated Colitis
JEMPERLI can cause immune-mediated colitis. Cytomegalovirus infection/reactivation have occurred in patients with corticosteroid-refractory immune-mediated colitis treated with PD-1/PD-L1–blocking antibodies. In cases of corticosteroid-refractory colitis, consider repeating infectious workup to exclude alternative etiologies.
Immune-mediated colitis occurred in 1.3% (8/605) of patients receiving JEMPERLI, including Grade 2 (0.7%) and Grade 3 (0.7%) adverse reactions. Colitis led to discontinuation of JEMPERLI in 1 (0.2%) patient.
Systemic corticosteroids were required in 75% (6/8) of patients with colitis. Colitis resolved in 5 of the 8 patients. Of the 4 patients in whom JEMPERLI was withheld for colitis, all reinitiated treatment with JEMPERLI; of these, 1 patient had recurrence of colitis.
Immune-Mediated Hepatitis
JEMPERLI can cause immune-mediated hepatitis, which can be fatal.
Immune-mediated hepatitis occurred in 0.5% (3/605) of patients receiving JEMPERLI, all were Grade 3. Hepatitis led to discontinuation of JEMPERLI in 1 (0.2%) patient. Systemic corticosteroids were required in 2 patients with hepatitis and the events resolved in 2 of the 3 patients.
Immune-Mediated Endocrinopathies
Adrenal Insufficiency: JEMPERLI can cause primary or secondary adrenal insufficiency. For Grade 2 or higher adrenal insufficiency, initiate symptomatic treatment per institutional guidelines, including hormone replacement as clinically indicated. Withhold or permanently discontinue JEMPERLI depending on severity [see Dosage and Administration (2.3 )] .
Adrenal insufficiency occurred in 1.2% (7/605) patients receiving JEMPERLI, including Grade 2 (0.5%) and Grade 3 (0.7%). Adrenal insufficiency resulted in discontinuation in 1 (0.2%) patient and resolved in 4 of the 7 patients. Of the 4 patients in whom JEMPERLI was withheld for adrenal insufficiency, all reinitiated treatment with JEMPERLI. Systemic corticosteroids were required in 5 of the 7 patients with adrenal insufficiency.
Hypophysitis: JEMPERLI can cause immune-mediated hypophysitis. Hypophysitis can present with acute symptoms associated with mass effect such as headache, photophobia, or visual field cuts. Hypophysitis can cause hypopituitarism. Initiate hormone replacement as clinically indicated. Withhold or permanently discontinue JEMPERLI depending on severity [see Dosage and Administration (2.3 )] .
JEMPERLI in Combination with Carboplatin and Paclitaxel: Hypophysitis (Grade 3) occurred in 0.4% (1/241) of patients receiving JEMPERLI in combination with carboplatin and paclitaxel. Systemic corticosteroids were required, and the event resolved. JEMPERLI was withheld and the patient reinitiated treatment.
JEMPERLI as a Single Agent: Hypophysitis (Grade 2) occurred in 0.2% (1/605) of patients receiving JEMPERLI as a single agent. Systemic corticosteroids were required, and the event did not resolve. JEMPERLI was withheld and the patient reinitiated treatment.
Thyroid Disorders: JEMPERLI can cause immune-mediated thyroid disorders. Thyroiditis can present with or without endocrinopathy. Hypothyroidism can follow hyperthyroidism. Initiate thyroid hormone replacement or medical management of hyperthyroidism as clinically indicated. Withhold or permanently discontinue JEMPERLI depending on severity [see Dosage and Administration (2.3 )] .
Thyroiditis: Thyroiditis occurred in 0.5% (3/605) of patients receiving JEMPERLI; all were Grade 2. Systemic corticosteroids were required in 1 of 3 patients and anti-thyroid therapy was required for 2 of 3 patients with thyroiditis. JEMPERLI was withheld for 1 patient and the patient reinitiated treatment. None of the events of thyroiditis resolved; there were no discontinuations of JEMPERLI due to thyroiditis.
Hypothyroidism: JEMPERLI in Combination with Carboplatin and Paclitaxel: Hypothyroidism occurred in 12% (30/241) of patients receiving JEMPERLI in combination with carboplatin and paclitaxel, all of which were Grade 2. Hypothyroidism led to discontinuation of JEMPERLI in 1 patient and resolved in 23% (7/30) of patients. JEMPERLI was withheld for 5 patients and all reinitiated treatment with JEMPERLI. Thyroid hormone replacement was required for 27 of the 30 patients with hypothyroidism.
JEMPERLI as a Single Agent: Hypothyroidism occurred in 8% (46/605) of patients receiving JEMPERLI as a single agent, all of which were Grade 2. Hypothyroidism did not lead to discontinuation of JEMPERLI and resolved in 37% (17/46) of patients. JEMPERLI was withheld for 2 patients and both reinitiated treatment. Thyroid hormone replacement therapy was required for 45 of the 46 patients with hypothyroidism.
Hyperthyroidism: JEMPERLI in Combination with Carboplatin and Paclitaxel: Hyperthyroidism occurred in 3.3% (8/241) of patients receiving JEMPERLI in combination with carboplatin and paclitaxel, including Grade 2 (2.9%) and Grade 3 (0.4%). Hyperthyroidism did not lead to discontinuation of JEMPERLI and resolved in 75% (6/8) of patients . JEMPERLI was withheld for 1 patient and the patient reinitiated treatment. Anti-thyroid therapy was required for 2 of the 8 patients while systemic corticosteroids were required for 1 of the 8 patients with hyperthyroidism.
JEMPERLI as a Single Agent: Hyperthyroidism occurred in 2.3% (14/605) of patients receiving JEMPERLI as a single agent, including Grade 2 (2.1%) and Grade 3 (0.2%). Hyperthyroidism did not lead to discontinuation of JEMPERLI and resolved in 71% (10/14) of the 14 patients. JEMPERLI was withheld for 2 patients and both reinitiated treatment. Anti-thyroid therapy was required for 10 of the 14 patients with hyperthyroidism.
Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus, Which Can Present with Diabetic Ketoacidosis: JEMPERLI can cause type 1 diabetes mellitus, which can present with diabetic ketoacidosis. Monitor patients for hyperglycemia or other signs and symptoms of diabetes. Initiate treatment with insulin as clinically indicated. Withhold or permanently discontinue JEMPERLI depending on severity [see Dosage and Administration (2.3 )] .
JEMPERLI in Combination with Carboplatin and Paclitaxel: Type 1 diabetes mellitus (Grade 3) occurred in 0.4% (1/241) of patients receiving JEMPERLI in combination with carboplatin and paclitaxel. Type 1 diabetes mellitus led to withholding JEMPERLI; the patient reinitiated treatment and required long-term insulin therapy.
JEMPERLI as a Single Agent: Type 1 diabetes mellitus occurred in 0.2% (1/605) of patients receiving JEMPERLI as a single agent, which was Grade 3. Type 1 diabetes mellitus did not result in treatment discontinuation and did not resolve.
Immune-Mediated Nephritis with Renal Dysfunction
JEMPERLI can cause immune-mediated nephritis, which can be fatal. Nephritis, including tubulointerstitial nephritis, occurred in 0.5% (3/605) of patients receiving JEMPERLI; all were Grade 2. Nephritis led to discontinuation of JEMPERLI in 1 (0.2%) patient and resolved in all patients. JEMPERLI was withheld for 1 patient and the patient reinitiated treatment. Systemic corticosteroids were required in 2 of the 3 patients experiencing nephritis.
Immune-Mediated Dermatologic Adverse Reactions
JEMPERLI can cause immune-mediated rash or dermatitis. Bullous and exfoliative dermatitis, including Stevens-Johnson syndrome (SJS), toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN), and drug rash with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS), have occurred with PD‑1/PD‑L1–blocking antibodies. Topical emollients and/or topical corticosteroids may be adequate to treat mild to moderate non-bullous/exfoliative rashes. Withhold or permanently discontinue JEMPERLI depending on severity [see Dosage and Administration (2.3 )] .
Other Immune-Mediated Adverse Reactions
The following clinically significant immune-mediated adverse reactions occurred in <1% of the 605 patients treated with JEMPERLI or were reported with the use of other PD-1/PD-L1–blocking antibodies. Severe or fatal cases have been reported for some of these adverse reactions.
Nervous System: Meningitis, encephalitis, myelitis and demyelination, myasthenic syndrome/myasthenia gravis, Guillain‑Barré syndrome, nerve paresis, autoimmune neuropathy.
Cardiac/Vascular: Myocarditis, pericarditis, vasculitis.
Ocular: Uveitis, iritis, other ocular inflammatory toxicities. Some cases can be associated with retinal detachment. Various grades of visual impairment to include blindness can occur. If uveitis occurs in combination with other immune‑mediated adverse reactions, consider a Vogt‑Koyanagi-Harada-like syndrome, as this may require treatment with systemic steroids to reduce the risk of permanent vision loss.
Gastrointestinal: Pancreatitis, including increases in serum amylase and lipase levels, gastritis, duodenitis.
Musculoskeletal and Connective Tissue: Myositis/polymyositis, rhabdomyolysis and associated sequelae including renal failure, arthritis, polymyalgia rheumatica.
Endocrine: Hypoparathyroidism.
Other (Hematologic/Immune): Autoimmune hemolytic anemia, aplastic anemia, hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis, systemic inflammatory response syndrome, histiocytic necrotizing lymphadenitis (Kikuchi lymphadenitis), sarcoidosis, immune thrombocytopenia, solid organ transplant rejection, other transplant (including corneal graft) rejection.
Infusion-Related Reactions
Severe or life-threatening infusion-related reactions have been reported with PD-1/PD-L1–blocking antibodies. Severe infusion-related reactions (Grade 3) occurred in 0.2% (1/605) of patients receiving JEMPERLI. All patients recovered from the infusion-related reactions.
Monitor patients for signs and symptoms of infusion-related reactions. Interrupt or slow the rate of infusion or permanently discontinue JEMPERLI based on severity of reaction [see Dosage and Administration (2.3 )] .
Complications of Allogeneic HSCT
Fatal and other serious complications can occur in patients who receive allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) before or after being treated with a PD-1/PD-L1–blocking antibody. Transplant-related complications include hyperacute graft-versus-host disease (GVHD), acute GVHD, chronic GVHD, hepatic veno-occlusive disease after reduced intensity conditioning, and steroid-requiring febrile syndrome (without an identified infectious cause). These complications may occur despite intervening therapy between PD-1/PD-L1 blockade and allogeneic HSCT.
Follow patients closely for evidence of transplant-related complications and intervene promptly. Consider the benefit versus risks of treatment with a PD-1/PD-L1–blocking antibody prior to or after an allogeneic HSCT.
Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
Based on its mechanism of action, JEMPERLI can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. Animal studies have demonstrated that inhibition of the PD-1/PD-L1 pathway can lead to increased risk of immune-mediated rejection of the developing fetus, resulting in fetal death. Advise pregnant women of the potential risk to a fetus. Advise females of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with JEMPERLI and for 4 months after the last dose [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1 , 8.3 )] .
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following clinically significant adverse reactions are described elsewhere in the labeling:
Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared with rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
The safety population described in the Warnings and Precautions for use of JEMPERLI in combination with carboplatin and paclitaxel was evaluated in 241 patients with primary advanced or recurrent EC in the randomized, double-blind, active-controlled RUBY trial.
Additionally, the pooled safety population described in Warnings and Precautions reflects exposure to JEMPERLI as a single agent in 605 patients with advanced or recurrent solid tumors in the non-randomized, open-label, multicohort GARNET trial that enrolled 314 patients with EC and 291 patients with other solid tumors. JEMPERLI was administered intravenously at doses of 500 mg every 3 weeks for 4 cycles followed by 1,000 mg every 6 weeks until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity. Among the 605 patients, 32% were exposed for >1 year and 19% were exposed for >2 years.
Primary Advanced or Recurrent Endometrial Cancer: JEMPERLI in Combination with Carboplatin and Paclitaxel
The safety of JEMPERLI in patients with primary advanced or recurrent EC was evaluated in RUBY [see Clinical Studies (14.1)] . Patients received JEMPERLI 500 mg (n = 241) or placebo (n = 246) in combination with carboplatin and paclitaxel every 3 weeks for 6 cycles followed by JEMPERLI 1,000 mg or placebo every 6 weeks until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity. Among the 241 patients, 38.6% were exposed for >1 year and 24.1% were exposed for >2 years.
Serious adverse reactions occurred in 39% of patients receiving JEMPERLI in combination with carboplatin and paclitaxel; the most common serious adverse reactions were sepsis, including urosepsis (3.7%), and pulmonary embolism (3.3%). Fatal adverse reactions occurred in 1.2% of patients receiving JEMPERLI including septic shock (0.8%) and myelosuppression (0.4%).
In patients receiving JEMPERLI in combination with carboplatin and paclitaxel, JEMPERLI was permanently discontinued due to adverse reactions in 46 patients (19%). Adverse reactions that required permanent discontinuation in ≥2 patients included 3 cases (1.2%) of rash maculo-papular, and 2 cases (0.8%) each of increased alanine aminotransferase (ALT), increased aspartate aminotransferase (AST), diarrhea, pancreatitis, fatigue, pneumonitis, and arthralgia.
Dosage interruptions due to an adverse reaction occurred in 37% of patients who received JEMPERLI in combination with carboplatin and paclitaxel. Adverse reactions that required dosage interruption in ≥5% of patients who received JEMPERLI in combination with carboplatin and paclitaxel were anemia, thrombocytopenia, and peripheral neuropathy.
The most common adverse reactions, including laboratory abnormalities (≥20%), were decreased hemoglobin, increased creatinine, peripheral neuropathy, decreased white blood cell count, fatigue, nausea, alopecia, decreased platelets, increased glucose, decreased lymphocytes, decreased magnesium, decreased neutrophils, increased AST, arthralgia, rash, constipation, diarrhea, increased ALT, decreased potassium, decreased albumin, decreased sodium, increased alkaline phosphatase, abdominal pain, dyspnea, decreased appetite, increased amylase, decreased phosphate, urinary tract infection, and vomiting.
Table 3 summarizes the adverse reactions that occurred in ≥20% of patients with primary advanced or recurrent EC receiving JEMPERLI in combination with carboplatin and paclitaxel in RUBY.
| Graded per National Cancer Institute Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events Version 4.03. | ||||
| a Includes neuropathy peripheral and peripheral sensory neuropathy. | ||||
| b Includes fatigue and asthenia. | ||||
| c Includes abdominal pain, abdominal pain upper, abdominal pain lower, gastrointestinal pain, abdominal discomfort, epigastric discomfort, and abdominal tenderness. | ||||
| d Includes rash, rash maculo-papular, palmar-plantar erythrodysesthesia syndrome, rash pustular, skin exfoliation, and vulvovaginal rash. | ||||
| e Includes dyspnea and dyspnea exertional. | ||||
| f Includes urinary tract infection, urinary tract infection bacterial, cystitis, and pyelonephritis. | ||||
Adverse Reaction | JEMPERLI with Carboplatin and Paclitaxel N = 241 | Placebo withCarboplatin and Paclitaxel N = 246 | ||
All Grades % | Grade 3 or 4 % | All Grades % | Grade 3 or 4 % | |
Nervous System Disorders | ||||
Peripheral neuropathy a | 64 | 4.1 | 61 | 2.0 |
General | ||||
Fatigue b | 56 | 3.3 | 63 | 5 |
Gastrointestinal Disorders | ||||
Nausea | 54 | 2.9 | 46 | 1.6 |
Constipation | 35 | 0.4 | 36 | 0 |
Diarrhea | 32 | 1.7 | 29 | 0.8 |
Abdominal pain c | 24 | 2.5 | 29 | 2 |
Vomiting | 20 | 1.7 | 20 | 1.6 |
Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue | ||||
Alopecia | 54 | 0 | 50 | 1.2 |
Rash d | 37 | 7 | 18 | 1.2 |
Musculoskeletal and Connective Tissue | ||||
Arthralgia | 37 | 1.2 | 35 | 0.4 |
Respiratory, Thoracic and Mediastinal Disorders | ||||
Dyspnea e | 23 | 1.7 | 26 | 0.8 |
Metabolism and Nutrition Disorders | ||||
Decreased appetite | 22 | 2.1 | 18 | 0.4 |
Infections and Infestations | ||||
Urinary tract infection f | 21 | 3.3 | 18 | 1.6 |
Clinically relevant adverse reactions in <20% of patients with primary advanced or recurrent EC who received JEMPERLI in combination with carboplatin and paclitaxel included:
Endocrine Disorders: Hypothyroidism, hyperthyroidism, thyroiditis, adrenal insufficiency.
Eye Disorders: Keratitis, uveitis.
Gastrointestinal Disorders: Colitis, pancreatitis.
Metabolism and Nutrition Disorders: Type 1 diabetes mellitus.
Musculoskeletal and Connective Tissue Disorders: Immune-mediated arthritis.
Respiratory, Thoracic, and Mediastinal Disorders: Pneumonitis.
Cardiac Disorders: Myocarditis.
Nervous System Disorders: Encephalopathy.
Vascular Disorders: Hypertension, hemorrhage.
Table 4 summarizes the laboratory abnormalities in patients with primary advanced or recurrent EC receiving JEMPERLI in combination with carboplatin and paclitaxel in RUBY.
| ALT = alanine aminotransferase; AST = aspartate aminotransferase. | ||||
| a Consists of new onset of laboratory abnormality or worsening of baseline laboratory abnormality. | ||||
Laboratory Test | JEMPERLI with Carboplatin and Paclitaxel N = 241 | Placebo with Carboplatin and Paclitaxel N = 246 | ||
All Grades a % | Grade 3 or 4 a % | All Grades a % | Grade 3 or 4 a % | |
Hematology | ||||
Decreased hemoglobin | 79 | 14 | 83 | 16 |
Decreased white blood cell count | 62 | 13 | 58 | 11 |
Decreased platelet count | 48 | 4.1 | 48 | 7 |
Decreased lymphocytes | 44 | 14 | 39 | 13 |
Decreased neutrophils | 42 | 14 | 52 | 18 |
Chemistry | ||||
Increased creatinine | 75 | 1.7 | 82 | 0.4 |
Increased glucose | 47 | 10 | 44 | 10 |
Increased AST | 38 | 3.3 | 23 | 1.6 |
Increased ALT | 30 | 2.5 | 19 | 0.8 |
Decreased albumin | 29 | 0.8 | 21 | 0 |
Increased alkaline phosphatase | 28 | 1.7 | 22 | 0.4 |
Increased amylase | 21 | 5 | 11 | 1.6 |
Electrolytes | ||||
Decreased magnesium | 44 | 2.1 | 47 | 2 |
Decreased potassium | 30 | 6 | 29 | 4.1 |
Decreased sodium | 29 | 6 | 22 | 3.7 |
Decreased phosphate | 21 | 1.2 | 18 | 3.7 |
Mismatch Repair Deficient Recurrent or Advanced Endometrial Cancer: JEMPERLI as a Single Agent
The safety of JEMPERLI was evaluated in GARNET in 150 patients with advanced or recurrent dMMR EC who received at least 1 dose of JEMPERLI [see Clinical Studies (14.1 )] . Patients received JEMPERLI 500 mg every 3 weeks for 4 cycles followed by 1,000 mg every 6 weeks as an intravenous infusion until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity. Patients with autoimmune disease that required systemic therapy within 2 years of treatment or a medical condition that required immunosuppression were ineligible. Among patients receiving JEMPERLI, 41% were exposed for >1 year and 23% were exposed for >2 years.
A fatal adverse reaction occurred in one patient (0.7%) who received JEMPERLI, due to concurrent immune-mediated encephalitis and urinary tract infection.
Serious adverse reactions occurred in 38% of patients receiving JEMPERLI. Serious adverse reactions in >2% of patients included urinary tract infection (4%), sepsis (3.3%), acute kidney injury (2.7%), and abdominal pain (2.7%).
JEMPERLI was permanently discontinued due to adverse reactions in 15 (10%) patients, including increased transaminases, sepsis, bronchitis, pneumonitis, rash, pruritus, pancreatitis, encephalitis, and nephritis. Dosage interruptions due to an adverse reaction occurred in 28% of patients who received JEMPERLI. Adverse reactions that required dosage interruption in >1% of patients who received JEMPERLI were anemia, diarrhea, asthenia, colitis, sepsis, and pneumonitis.
The most common adverse reactions (≥20%) were fatigue/asthenia, anemia, nausea, diarrhea, constipation, vomiting, and rash.
Table 5 summarizes the adverse reactions that occurred in ≥10% of patients with dMMR EC on JEMPERLI in GARNET.
| dMMR = Mismatch Repair Deficient. | ||
| Toxicity was graded per National Cancer Institute Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events Version 4.03. a Includes fatigue and asthenia. b Includes anemia, decreased hemoglobin, iron deficiency, and iron deficiency anemia. | ||
| c Includes rash, rash maculo-papular, rash pruritic, erythema, and pemphigoid. | ||
| d Includes increased alanine aminotransferase, increased aspartate aminotransferase, increased transaminases, and hypertransaminasemia. | ||
Adverse Reaction | JEMPERLI N = 150 | |
All Grades % | Grade 3 or 4 % | |
General and administration site | ||
Fatigue a Pyrexia | 49 13 | 3.3 0 |
Blood and lymphatic system Anemia b | 35 | 18 |
Gastrointestinal | ||
Nausea | 32 | 0.7 |
Diarrhea | 29 | 2.7 |
Constipation | 23 | 0.7 |
Vomiting | 23 | 0.7 |
Skin and subcutaneous tissue Rash c Pruritus | 21 19 | 0 1.3 |
Infections Urinary tract infection | 19 | 4 |
Metabolism and nutrition | ||
Decreased appetite | 15 | 0 |
Respiratory, thoracic, and mediastinal | ||
Cough | 15 | 0 |
Musculoskeletal and connective tissue | ||
Myalgia | 10 | 0 |
Investigations Increased transaminases d | 13 | 4 |
Endocrine Disorders Hypothyroidism | 11 | 0 |
Clinically relevant adverse reactions in <10% of patients who received JEMPERLI included:
Endocrine Disorders: Hyperthyroidism, adrenal insufficiency, hypophysitis.
Eye Disorders: Iridocyclitis, uveitis.
Gastrointestinal Disorders: Colitis, pancreatitis, enterocolitis, gastritis.
General Disorders and Administration Site Conditions: Chills.
Musculoskeletal and Connective Tissue Disorders: Immune-mediated myositis, immune-mediated arthritis.
Nervous System Disorders: Encephalitis.
Renal and Urinary Disorders: Nephritis.
Respiratory, Thoracic, and Mediastinal Disorders: Pneumonitis, interstitial lung disease.
Table 6 summarizes laboratory abnormalities worsening from baseline to Grade 3 or 4 in ≥1% of patients with dMMR EC on JEMPERLI in GARNET.
| dMMR = Mismatch Repair Deficient. | ||
| a Consists of new onset of laboratory abnormality or worsening of baseline laboratory abnormality. | ||
Laboratory Test | JEMPERLI N = 150 | |
All Grades a % | Grade 3 or 4 a % | |
Hematology | ||
Decreased lymphocytes | 46 | 15 |
Decreased leukocytes Decreased neutrophils | 21 17 | 2 2.7 |
Chemistry | ||
Decreased albumin | 36 | 2.7 |
Increased creatinine | 33 | 3.4 |
Increased alkaline phosphatase | 31 | 2.7 |
Increased aspartate aminotransferase | 31 | 2 |
Increased alanine aminotransferase | 25 | 4.7 |
Electrolytes | ||
Decreased sodium Decreased magnesium Decreased potassium | 29 28 22 | 5 2 2 |
Increased calcium | 8 | 2 |
Mismatch Repair Deficient Recurrent or Advanced Solid Tumors
The safety of JEMPERLI was investigated in 267 patients with recurrent or advanced dMMR solid tumors enrolled in GARNET [see Clinical Studies (14.2 )] . Patients received JEMPERLI 500 mg every 3 weeks for 4 cycles followed by 1,000 mg every 6 weeks as an intravenous infusion until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity. Patients with autoimmune disease that required systemic therapy within 2 years of treatment or a medical condition that required immunosuppression were ineligible. The median duration of exposure to JEMPERLI was 25 weeks (range: 1 to 139 weeks).
Serious adverse reactions occurred in 34% of patients receiving JEMPERLI. Serious adverse reactions in >2% of patients included abdominal pain (3.7%), sepsis (2.6%), and acute kidney injury (2.2%). Fatal adverse reaction occurred in 1 patient who received JEMPERLI due to respiratory failure.
JEMPERLI was permanently discontinued due to adverse reactions in 9% patients; the most common adverse reaction (≥1%) leading to discontinuation was increased alanine aminotransferase (1.1%).
Dosage interruptions due to an adverse reaction occurred in 23% of patients who received JEMPERLI. Adverse reactions that required dosage interruption in ≥1% of patients who received JEMPERLI were anemia, pneumonitis, diarrhea, adrenal insufficiency, increased alanine aminotransferase, and increased aspartate aminotransferase.
The most common adverse reactions (≥20%) were fatigue/asthenia, anemia, diarrhea, and nausea.
Table 7 summarizes the adverse reactions that occurred in ≥10% of patients with dMMR recurrent or advanced solid tumors in GARNET.
| dMMR = Mismatch Repair Deficient. | ||
| Toxicity was graded per National Cancer Institute Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events Version 4.03. a Includes fatigue and asthenia. b Includes anemia, decreased hemoglobin, iron deficiency, and iron deficiency anemia. c Includes rash, rash maculopapular, rash macular, rash erythematous, rash papular, erythema, toxic skin eruption, and pemphigoid. | ||
| d Includes increased alanine aminotransferase, increased aspartate aminotransferase, increased transaminases, and hypertransaminasemia. | ||
Adverse Reaction | JEMPERLI N = 267 | |
All Grades % | Grade 3 or 4 % | |
General and administration site | ||
Fatigue a | 42 | 3.4 |
Pyrexia | 12 | 0 |
Blood and lymphatic system | ||
Anemia b | 30 | 11 |
Gastrointestinal | ||
Diarrhea | 25 | 1.5 |
Nausea | 22 | 0.4 |
Vomiting | 17 | 1.5 |
Constipation | 16 | 0.4 |
Skin and subcutaneous tissue | ||
Pruritus | 15 | 0.4 |
Rash c | 14 | 0.4 |
Respiratory, thoracic, and mediastinal | ||
Cough | 13 | 0 |
Metabolism and nutrition | ||
Decreased appetite | 12 | 0.4 |
Investigations | ||
Increased transaminases d | 12 | 3 |
Clinically relevant adverse reactions in <10% of patients who received JEMPERLI included:
Endocrine Disorders: Hypothyroidism, hyperthyroidism, adrenal insufficiency, hypophysitis, autoimmune thyroiditis.
Eye Disorders: Uveitis.
Gastrointestinal Disorders: Colitis, enterocolitis, enterocolitis hemorrhage, pancreatitis, acute pancreatitis.
General Disorders and Administration Site Conditions: Chills.
Injury, Poisoning, and Procedural Complications: Infusion related reaction.
Hepatobiliary Disorders: Hepatocellular injury.
Musculoskeletal and Connective Tissue Disorders: Myalgia.
Renal and Urinary Disorders: Nephritis, tubulointerstitial nephritis.
Respiratory, Thoracic, and Mediastinal Disorders: Pneumonitis, interstitial lung disease.
Table 8 summarizes laboratory abnormalities worsening from baseline to Grade 3 or 4 in ≥1% of patients with dMMR recurrent or advanced solid tumors in GARNET.
| dMMR = Mismatch Repair Deficient. | ||
| a Consists of new onset of laboratory abnormality or worsening of baseline laboratory abnormality. | ||
Laboratory Test | JEMPERLI N = 267 | |
All Grades a % | Grade 3 or 4 a % | |
Hematology | ||
Decreased lymphocytes | 33 | 7 |
Decreased leukocytes | 18 | 1.1 |
Decreased neutrophils | 12 | 1.5 |
Chemistry | ||
Decreased albumin | 26 | 2.2 |
Increased alkaline phosphatase | 26 | 3.4 |
Increased aspartate aminotransferase | 26 | 1.5 |
Increased alanine aminotransferase | 22 | 1.9 |
Increased creatinine | 21 | 1.1 |
Increased total bilirubin | 7 | 1.5 |
Electrolytes | ||
Decreased sodium | 21 | 4.9 |
Decreased magnesium | 16 | 1.1 |
Decreased potassium | 14 | 1.1 |
Increased potassium | 14 | 1.1 |
Increased calcium | 6 | 1.1 |
Increased magnesium | 4.1 | 1.5 |
Decreased calcium | 2.6 | 1.5 |
DESCRIPTION
Dostarlimab-gxly is a programmed death receptor-1 (PD-1)–blocking IgG 4 humanized monoclonal antibody. Dostarlimab‑gxly is produced in Chinese hamster ovary cells and has a calculated molecular weight of about 144 kDa.
JEMPERLI (dostarlimab-gxly) injection is a sterile, clear to slightly opalescent, colorless to yellow solution essentially free from visible particles. It is supplied as single-dose vials.
Each vial contains 500 mg of JEMPERLI in 10 mL of solution with a pH of 6. Each mL of solution contains 50 mg of dostarlimab-gxly, citric acid monohydrate (0.48 mg), L-arginine hydrochloride (21.07 mg), polysorbate 80 (0.2 mg), sodium chloride (1.81 mg), trisodium citrate dihydrate (6.68 mg), and Water for Injection, USP.
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Mechanism of Action
Binding of the PD-1 ligands, PD-L1 and PD-L2, to the PD-1 receptor found on T cells inhibits T-cell proliferation and cytokine production. Upregulation of PD-1 ligands occurs in some tumors, and signaling through this pathway can contribute to inhibition of active T-cell immune surveillance of tumors. Dostarlimab-gxly is a humanized monoclonal antibody of the IgG4 isotype that binds to the PD-1 receptor and blocks its interaction with PD-L1 and PD-L2, releasing PD-1 pathway-mediated inhibition of the immune response, including the anti-tumor immune response. In syngeneic mouse tumor models, blocking PD-1 activity resulted in decreased tumor growth.
Pharmacodynamics
The exposure-response relationship and time course of pharmacodynamic response for safety and effectiveness of dostarlimab-gxly have not been fully characterized.
Dostarlimab-gxly provides sustained target engagement as measured by direct PD-1 binding and stimulation of IL-2 production throughout the dosing interval at the recommended dosage.
Pharmacokinetics
The pharmacokinetics of dostarlimab-gxly as a single agent and in combination with carboplatin and paclitaxel were evaluated in patients with various solid tumors, including patients with EC. Mean C max , AUC 0-inf , and AUC 0-tau increased proportionally over the dose range of 1 to 10 mg/kg. The Cycle 1 mean (coefficient of variation [%CV]) C max and AUC 0-tau of dostarlimab-gxly as a single agent were 171 mcg/mL (20%) and 35,730 mcg•h/mL (20%), respectively at the dosage of 500 mg once every 3 weeks and 309 mcg/mL (31%) and 95,820 mcg•h/mL (29%), respectively at the dosage of 1,000 mg every 6 weeks.
Distribution
The mean (%CV) volume of distribution of dostarlimab-gxly at steady state is approximately 5.8 L (15%).
Elimination
The mean terminal elimination half-life of dostarlimab-gxly at steady state is 23.5 days and its mean (%CV) clearance at steady state is 0.007 L/h (30%).
Metabolism: Dostarlimab-gxly is expected to be metabolized into small peptides and amino acids by catabolic pathways.
Specific Populations
No clinically significant differences in the pharmacokinetics of dostarlimab-gxly were observed based on age (24 to 86 years), sex, race/ethnicity (75% White, 2% Asian, and 5% African American), tumor type, and renal impairment based on the estimated creatinine clearance (eGFR ≥15 mL/min/1.73 m 2 ), and mild to moderate hepatic impairment [total bilirubin (TB) >ULN to 3 times ULN or AST>ULN to any AST].
Drug Interaction Studies
Dostarlimab exposure when administered in combination with carboplatin and paclitaxel was comparable to single agent exposure and there was no evidence to suggest a clinically relevant change of dostarlimab-gxly clearance over time in patients with recurrent or advanced EC.
Immunogenicity
The observed incidence of anti-drug antibodies is highly dependent on the sensitivity and specificity of the assay. Differences in assay methods preclude meaningful comparisons of the incidence of anti-drug antibodies in the studies described below with the incidence of anti-drug antibodies in other studies, including those of JEMPERLI or of other dostarlimab-gxly products.
The immunogenicity of dostarlimab-gxly was evaluated in RUBY at a dosage of 500 mg every 3 weeks for 6 cycles followed by 1,000 mg every 6 weeks thereafter; there was no formation of anti-drug antibodies and neutralizing antibodies in 225 patients receiving JEMPERLI at the recommended dosage.
The immunogenicity of dostarlimab-gxly was evaluated in GARNET at a dose of 500 mg every 3 weeks for 4 cycles followed by 1,000 mg every 6 weeks thereafter. Anti‑drug antibodies against dostarlimab-gxly were detected in 2.1% (8/384) of patients who received JEMPERLI at the recommended dosage. Neutralizing antibodies were detected in 1% (4/384) of patients.
Because of the small number of patients who developed anti-drug antibodies, the effect of immunogenicity on the pharmacokinetics, efficacy, and safety of dostarlimab-gxly is inconclusive.
NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
No studies have been performed to assess the potential of dostarlimab-gxly for carcinogenicity or genotoxicity.
Fertility studies have not been conducted with dostarlimab-gxly. In 1- and 3-month repeat‑dose toxicology studies in monkeys, there were no notable effects in the male and female reproductive organs; however, many animals in these studies were not sexually mature.
Animal Toxicology and/or Pharmacology
In animal models, inhibition of PD-L1/PD-1 signaling increased the severity of some infections and enhanced inflammatory responses. Mycobacterium tuberculosis -infected PD-1 knockout mice exhibit markedly decreased survival compared with wild-type controls, which correlated with increased bacterial proliferation and inflammatory responses in these animals. PD-1 blockade using a primate anti-PD-1 antibody was also shown to exacerbate M. tuberculosis infection in rhesus macaques. PD-L1 and PD-1 knockout mice and mice receiving PD-L1–blocking antibody have also shown decreased survival following infection with lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus.
CLINICAL STUDIES
Endometrial Cancer
In Combination with Carboplatin and Paclitaxel for the Treatment of Primary Advanced or Recurrent Endometrial Cancer
The efficacy of JEMPERLI in combination with carboplatin and paclitaxel, followed by JEMPERLI as a single agent, was evaluated in RUBY (NCT03981796), a randomized, multicenter, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial conducted in 494 patients with primary advanced or recurrent EC.
The trial enrolled patients with primary Stage III or Stage IV disease (per FIGO Staging Classification), including Stage IIIA to IIIC1 patients with evaluable or measurable disease, Stage IIIC1 patients with carcinosarcoma, clear cell, serous, or mixed histology regardless of presence of evaluable or measurable disease, Stage IIIC2 or Stage IV disease regardless of presence of evaluable or measurable disease. The trial also enrolled patients with first recurrent disease with a low potential for cure by radiation therapy or surgery alone or in combination, including patients who were naïve to systemic anticancer therapy or who had received prior neo-adjuvant/adjuvant systemic anticancer therapy and had a recurrence or disease progression ≥6 months after completing treatment.
Patients were randomized (1:1) to one of the following treatments arms:
- JEMPERLI 500 mg, carboplatin AUC 5 mg/mL/min, paclitaxel 175 mg/m 2 intravenously on Day 1 of each 21-day cycle for 6 cycles followed by JEMPERLI 1,000 mg intravenously every 6 weeks. JEMPERLI was administered prior to chemotherapy on Day 1.
- Placebo, carboplatin AUC 5 mg/mL/min, paclitaxel 175 mg/m 2 intravenously on Day 1 of each 21-day cycle for 6 cycles followed by placebo intravenously every 6 weeks.
Randomization was stratified by mismatch repair (MMR)/microsatellite instability (MSI) status, prior external pelvic radiotherapy, and disease status (recurrent, primary Stage III, or primary Stage IV). Treatment with JEMPERLI continued until disease progression, unacceptable toxicity, or a maximum of 3 years. Administration of JEMPERLI was permitted beyond disease progression (defined by Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors [RECIST] v1.1) if the patient was clinically stable and considered to be deriving clinical benefit by the investigator.
Assessment of tumor status was performed every 6 weeks through Week 25, every 9 weeks through Week 52 and every 12 weeks thereafter. The major efficacy outcomes were Progression-Free Survival (PFS) using RECIST v1.1 as assessed by investigator in the dMMR/MSI-H and overall populations, and Overall Survival (OS) in the overall population. Additional efficacy outcome measures included Objective Response Rate (ORR) per RECIST v1.1 as assessed by investigator and Duration of Response (DOR).
Among the 494 patients evaluated, the baseline characteristics were: median age 65 years (51% aged 65 years or older); 77% White, 12% Black, 3% Asian, 3% Hispanic or Latino; Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group (ECOG) Performance Status 0 (63%) or 1 (37%); and primary stage III (18%); primary stage IV (34%) and recurrent EC (48%). Overall, 24% were dMMR/MSI-H tumors and 76% were mismatch repair proficient (MMRp)/microsatellite stable (MSS) tumors.
Efficacy results are presented in Table 9 and Figures , and . Treatment with JEMPERLI in combination with carboplatin and paclitaxel demonstrated statistically significant improvements in OS in the overall population and PFS in both the dMMR/MSI-H and overall population versus placebo in combination with carboplatin and paclitaxel. Pre-specified exploratory analyses of PFS and OS were performed in patients with MMRp/MSS EC.
| dMMR = Mismatch Repair Deficient; MSI-H = Microsatellite Instability-High; NR = Not Reached; + = ongoing at last assessment. | ||||
| a Based on stratified Cox regression model. | ||||
| b One-sided P-value based on stratified log-rank test. | ||||
| c Confirmed responses. | ||||
Endpoint | Overall Population | dMMR/MSI-H Population | ||
JEMPERLI with Carboplatin and Paclitaxel N = 245 | Placebo with Carboplatin and Paclitaxel N = 249 | JEMPERLI with Carboplatin and Paclitaxel N = 60 | Placebo withCarboplatin and Paclitaxel N = 62 | |
Overall Survival (OS) | ||||
Number (%) of patients with event | 109 (44) | 144 (58) | 15 (25) | 35 (56) |
Median in months (95% CI) | 44.6 (32.6, NR) | 28.2 (22.1, 35.6) | NR (NR, NR) | 30.8 (18.7, NR) |
Hazard ratio (95% CI) a | 0.69 (0.54, 0.89) | 0.34 (0.18, 0.62) | ||
P -value b | 0.002 | Not tested | ||
Progression-Free Survival (PFS) | ||||
Number (%) of patients with event | 135 (55) | 177 (71) | 23 (38) | 47 (76) |
Median in months (95% CI) | 11.8 (9.6, 17.1) | 7.9 (7.6, 9.5) | 30.3 (11.8, NR) | 7.7 (5.6, 9.7) |
Hazard ratio (95% CI) a | 0.64 (0.51, 0.80) | 0.29 (0.17, 0.50) | ||
P- value b | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | ||
Objective Response Rate (ORR) c | ||||
Number of participants with measurable disease at baseline (n) | 172 | 185 | 42 | 45 |
ORR (95% CI) | 68% (60, 75) | 57% (50, 65) | 74% (58, 86) | 62% (47, 76) |
Complete response rate | 20% | 12% | 26% | 11% |
Partial response rate | 48% | 45% | 48% | 51% |
Duration of Response (DOR) c | ||||
Median in months (range) | 10.8 (1.3+, 28.9+) | 6.4 (1.4+, 27.2+) | NR (3.4, 28.3+) | 5.4 (2.7, 27.2+) |
In patients with MMRp/MSS EC (n = 372), the OS hazard ratio (HR) was 0.82 (95% CI: 0.62, 1.08) with a median OS of 32.5 (95% CI: 28.6, NR) months for JEMPERLI in combination with carboplatin and paclitaxel versus 28.2 (95% CI: 21.9, 36.1) months for placebo in combination with carboplatin and paclitaxel. The PFS HR was 0.78 (95% CI: 0.60, 1.00) with a median PFS of 9.8 (95% CI: 9.0, 12.6) months for JEMPERLI in combination with carboplatin and paclitaxel (n = 185) versus 7.9 (95% CI: 7.6, 9.8) months for placebo in combination with carboplatin and paclitaxel (n = 187).
Figure 1. Kaplan-Meier Curve for Overall Survival in Patients (Overall Population) with Endometrial Cancer in RUBY

Figure 2. Kaplan-Meier Curve for Progression-Free Survival in Patients (Overall Population) with Endometrial Cancer in RUBY
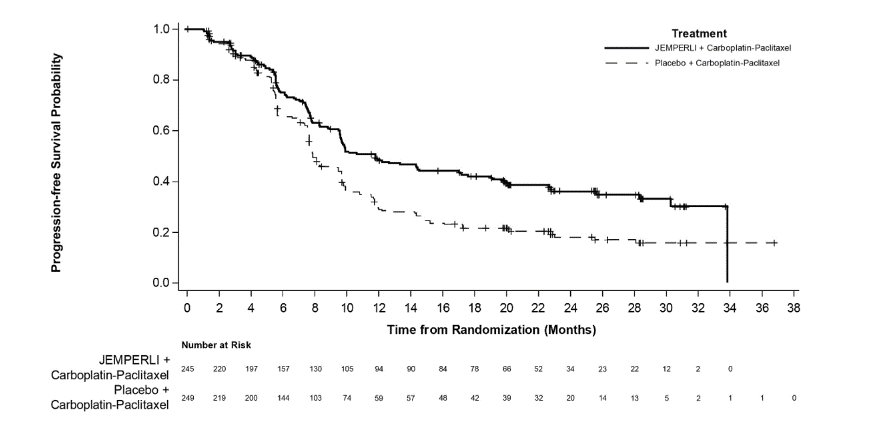
Figure 3. Kaplan-Meier Curve for Progression-Free Survival in Patients with dMMR/MSI-H Endometrial Cancer in RUBY
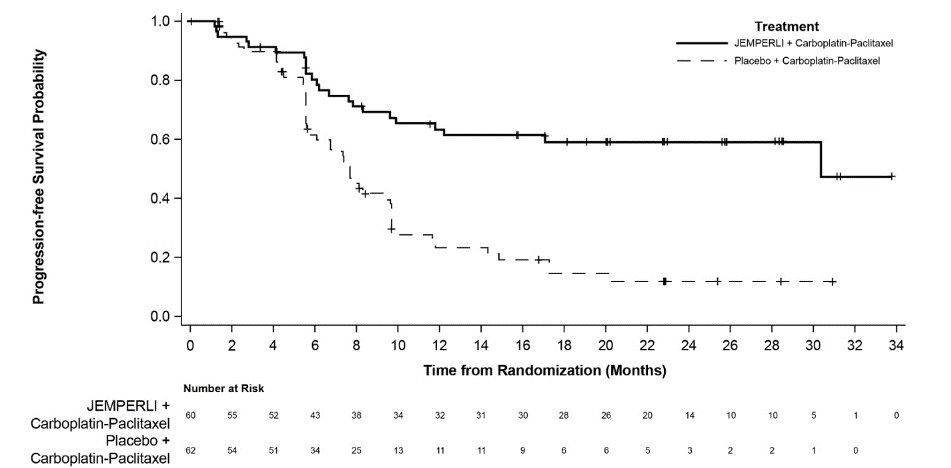
dMMR = Mismatch Repair Deficient; MSI-H = Microsatellite Instability High.
As a Single Agent for the Treatment of dMMR Recurrent or Advanced Endometrial Cancer
The efficacy of JEMPERLI as a single agent was evaluated in the GARNET trial (NCT02715284), a multicenter, multicohort, open-label trial conducted in patients with advanced solid tumors. The efficacy population consisted of a cohort of 141 patients with dMMR recurrent or advanced EC who had progressed on or after treatment with a platinum‑containing regimen. Patients with prior treatment with PD‑1/PD‑L1–blocking antibodies or other immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy and patients with autoimmune disease that required systemic therapy with immunosuppressant agents within 2 years were excluded from the trial.
Patients received JEMPERLI 500 mg intravenously every 3 weeks for 4 doses followed by 1,000 mg intravenously every 6 weeks. Treatment continued until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity. The major efficacy outcome measures were ORR and DOR as assessed by blinded independent central review (BICR) according to the RECIST v 1.1.
The baseline characteristics were: median age 65 years (53% aged 65 years or older); 77% White, 4% Asian, 3% Black, 4% Hispanic or Latino; and Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group Performance Status 0 (38%) or 1 (62%).
The most common histology seen was endometrioid carcinoma type 1 (65%), Grade 3 endometrioid (15%), followed by serous (5%), mixed (5%) and undifferentiated (2.8%).
All patients with dMMR EC had received prior anticancer treatment, with 89% of patients receiving prior anticancer surgery and 71% receiving prior anticancer radiotherapy. Sixty-three percent of patients had one prior line of anticancer treatment and 37% had two or more prior lines. Forty-eight patients (34%) received treatment only in the neoadjuvant or adjuvant setting before participating in the study.
The dMMR tumor status was retrospectively confirmed using the VENTANA MMR RxDx Panel assay.
Efficacy results are presented in Table 10 .
| dMMR = Mismatch Repair Deficient; + = ongoing at last assessment. a Based on confirmed response by blinded independent central review. | |
| b Median follow up for duration of response was 27.9 months measured from time of first response. | |
Endpoint | JEMPERLI N = 141 |
Overall response rate a | |
ORR (95% CI) | 45.4% (37.0, 54.0) |
Complete response rate | 15.6% |
Partial response rate | 29.8% |
Duration of response b | |
Median in months | Not reached |
(range) | (1.2+, 52.8+) |
Patients with duration ≥12 months | 85.9% |
Patients with duration >24 months | 54.7% |
Mismatch Repair Deficient Recurrent or Advanced Solid Tumors
The efficacy of JEMPERLI as a single agent was evaluated in GARNET (NCT02715284), a non‑randomized, multicenter, open-label, multicohort trial. The efficacy population consisted of a cohort of 209 patients with dMMR recurrent or advanced solid tumors who progressed following systemic therapy and had no satisfactory alternative treatment options. Patients with dMMR EC must have progressed on or after treatment with a platinum-containing regimen. Patients with dMMR colorectal cancer must have progressed after or been intolerant to a fluoropyrimidine, oxaliplatin, and irinotecan.
Patients with prior treatment with PD‑1/PD‑L1–blocking antibodies or other immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy and patients with autoimmune disease that required systemic therapy with immunosuppressant agents within 2 years were excluded from the trial.
Patients received JEMPERLI 500 mg intravenously every 3 weeks for 4 doses followed by 1,000 mg intravenously every 6 weeks. Treatment continued until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity.
The major efficacy outcome measures were ORR and DOR as determined by a BICR according to RECIST v 1.1.
The baseline characteristics were female (77%); median age 63 years (47% aged 65 years or older); 63% White, 3% Asian, 2% Black; and Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group Performance Status 0 (39%) or 1 (61%).
At time of trial entry, 97.2% of patients (103/106) with non-endometrial dMMR solid tumors had Stage IV disease, and 68.0% (70/103) of patients with dMMR endometrial tumors had FIGO Stage IV disease.
Approximately 43% of patients had received 1 prior line of systemic anticancer treatment, 36% had received 2 prior lines, and 21% had received 3 or more prior lines.
The dMMR tumor status was retrospectively confirmed using the VENTANA MMR RxDx Panel assay.
Efficacy results are presented in Tables 11 and 12 .
| dMMR = Mismatch Repair Deficient; + = ongoing at last assessment. a Based on confirmed response by blinded independent central review. | |
| b Median follow-up for duration of response was 17.5 months measured from time of first response. | |
Endpoint | JEMPERLI N = 209 |
Overall response rate a | |
ORR (95% CI) | 41.6% (34.9, 48.6) |
Complete response rate | 9.1% |
Partial response rate | 32.5% |
Duration of response b | |
Median in months | 34.7 |
(range) | 2.6, 35.8+ |
Patients with duration ≥6 months | 95.4% |
| CR = complete response; CRC = colorectal cancer; dMMR = Mismatch Repair Deficient; DOR = Duration of Response; EC = endometrial cancer; ORR = Overall Response Rate; PD = progressive disease; PR = partial response; SD = stable disease; + = ongoing at last assessment. | ||||
| a Exact, 2-sided 95% CI for binomial proportion. | ||||
Tumor Type | Patients N | ORR (per RECIST v 1.1) | DOR | |
n (%) | 95% CI a | Range (months) | ||
EC | 103 | 46 (44.7) | (34.9, 54.8) | 2.6, 35.8+ |
non-EC | 106 | 41 (38.7) | (29.4, 48.6) | 5.6, 30.1+ |
CRC | 69 | 25 (36.2) | (25.0, 48.7) | 5.6, 30.1+ |
Small intestinal cancer | 12 | 4 (33.3) | (9.9, 65.1) | 11.1+, 28.0+ |
Gastric cancers | 8 | 3 (37.5) | (8.5, 75.5) | 8.4+, 17.5 |
Pancreatic carcinoma | 4 | 0 (0.0) | (0.0, 60.2) | NA |
Biliary neoplasm | 2 | CR, CR | NA | 8.4+, 13.5+ |
Liver cancer | 2 | PR, PD | NA | 13.8+ |
Ovarian cancer | 2 | PR, SD | NA | 25.1+ |
Adrenal cortical | 1 | PR | NA | 19.5+ |
Breast cancer | 1 | CR | NA | 16.8+ |
Esophageal cancer | 1 | PD | NA | NA |
Genital neoplasm malignant female | 1 | PR | NA | 22.2+ |
Pleural | 1 | PR | NA | 15.2+ |
Renal cell carcinoma | 1 | SD | NA | NA |
Unknown origin | 1 | PR | NA | 20.4+ |
HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
JEMPERLI (dostarlimab-gxly) injection is a clear to slightly opalescent, colorless to yellow solution supplied in a carton containing one 500 mg/10 mL (50 mg/mL), single-dose vial (NDC 0173-0898-03).
Store vial refrigerated at 2°C to 8°C (36°F to 46°F) in original carton to protect from light. Do not freeze or shake.
Mechanism of Action
Binding of the PD-1 ligands, PD-L1 and PD-L2, to the PD-1 receptor found on T cells inhibits T-cell proliferation and cytokine production. Upregulation of PD-1 ligands occurs in some tumors, and signaling through this pathway can contribute to inhibition of active T-cell immune surveillance of tumors. Dostarlimab-gxly is a humanized monoclonal antibody of the IgG4 isotype that binds to the PD-1 receptor and blocks its interaction with PD-L1 and PD-L2, releasing PD-1 pathway-mediated inhibition of the immune response, including the anti-tumor immune response. In syngeneic mouse tumor models, blocking PD-1 activity resulted in decreased tumor growth.