Kombiglyze XR prior authorization resources
Most recent Kombiglyze XR prior authorization forms
Most recent state uniform prior authorization forms
Kombiglyze XR patient education
Patient toolkit
Dosage & administration
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- Administer once daily with the evening meal. (2.1)
- Individualize the starting dosage based on the patient’s current regimen then adjust the dosage based on effectiveness and tolerability. (2.1)
- Do not exceed a daily dosage of 5 mg saxagliptin/2,000 mg metformin HCl extended-release. (2.1)
- Swallow whole. Never crush, cut, or chew. (2.1)
- Limit the saxagliptin dosage to 2.5 mg daily for patients also taking strong cytochrome P450 3A4/5 inhibitors (e.g., ketoconazole). (2.3 , 7.1)
- Assess renal function prior to initiation of KOMBIGLYZE XR and periodically thereafter. (2.2)
- Do not use in patients with eGFR below 30 mL/min/1.73 m 2 .
- Initiation is not recommended in patients with eGFR between 30 - 45 mL/min/1.73 m 2 .
- Assess risk/benefit of continuing if eGFR falls below 45 mL/min/1.73 m 2 .
- Limit the saxagliptin component to 2.5 mg daily if eGFR is less than 45 mL/min/1.73 m 2 .
- Discontinue if eGFR falls below 30 mL/min/1.73 m 2 .
- KOMBIGLYZE XR may need to be discontinued at time of, or prior to, iodinated contrast imaging procedures. (2.4)
Recommended Dosage and Administration
Individualize the starting dosage of KOMBIGLYZE XR based on the patient’s current regimen and the available strengths of KOMBIGLYZE XR [ see Dosage Forms and Strengths (3) ].
Administer KOMBIGLYZE XR once daily with the evening meal, with gradual dose titration to reduce the gastrointestinal side effects associated with metformin HCl [ see Adverse Reactions (6.1) ].
The recommended starting dosage of KOMBIGLYZE XR in patients who need 5 mg of saxagliptin and who are not currently treated with metformin HCl is one KOMBIGLYZE XR tablet containing 5 mg saxagliptin and 500 mg metformin HCl extended-release once daily with gradual dose escalation to reduce the gastrointestinal side effects due to metformin HCl.
In patients treated with metformin HCl, the recommended starting dosage of KOMBIGLYZE XR should provide metformin HCl at the dose already being taken, or the nearest therapeutically appropriate dose. Following a switch from metformin HCl immediate-release to KOMBIGLYZE XR, closely monitor glycemic control and adjust the dosage accordingly.
Patients who need 2.5 mg saxagliptin in combination with metformin HCl extended-release may be treated with KOMBIGLYZE XR 2.5 mg/1,000 mg. Patients who need 2.5 mg saxagliptin who are either metformin HCl naive or who require a dose of metformin HCl higher than 1,000 mg should use the individual components.
Gradually titrate the dosage of KOMBIGLYZE XR, as needed, after assessing therapeutic response and tolerability, up to a maximum recommended dosage of KOMBIGLYZE XR (5 mg for saxagliptin and 2,000 mg for metformin HCl extended-release orally once daily).
Inform patients that KOMBIGLYZE XR tablets must be swallowed whole and never crushed, cut, or chewed. Occasionally, the inactive ingredients of KOMBIGLYZE XR will be eliminated in the feces as a soft, hydrated mass that may resemble the original tablet.
If a dose is missed, advise patients not to take an extra dose. Resume treatment with the next dose.
Recommendations for Dosage and Administration in Renal Impairment
Assess renal function prior to initiation of KOMBIGLYZE XR and then as clinically indicated [ see Use in Specific Populations (8.6) ].
The recommended dosage of KOMBIGLYZE XR in patients with an estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) greater than or equal to 45 mL/minute/1.73 m2 is the same as the recommended dosage in patients with normal renal function [ see Dosage and Administration (2.1) ].
In patients taking KOMBIGLYZE XR whose eGFR later falls below 45 mL/minute/1.73 m2, assess the benefit risk of continuing therapy and limit dose of the saxagliptin component to 2.5 mg once daily.
Initiation of KOMBIGLYZE XR in patients with an eGFR between 30 – 45 mL/minute/1.73 m2 is not recommended.
KOMBIGLYZE XR is contraindicated in patients with an eGFR below 30 mL/minute/1.73 m2.
Discontinue KOMBIGLYZE XR if the patient’s eGFR later falls below 30 mL/minute/1.73 m2 [ see Contraindications (4) and Warnings and Precautions (5.1) ].
Dosage Modifications with Concomitant Use of Strong CYP3A4/5 Inhibitors
The maximum recommended dosage of KOMBIGLYZE XR is 2.5 mg of saxagliptin and 1,000 mg of metformin HCl given orally once daily when used concomitantly with strong cytochrome P450 3A4/5 (CYP3A4/5) inhibitors (e.g., ketoconazole, atazanavir, clarithromycin, indinavir, itraconazole, nefazodone, nelfinavir, ritonavir, saquinavir, and telithromycin) [ see Dosage and Administration (2.1) , Drug Interactions (7.1) , and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ].
Discontinuation for Iodinated Contrast Imaging Procedures
Discontinue KOMBIGLYZE XR at the time of, or prior to, an iodinated contrast imaging procedure in patients with an eGFR less than 60 mL/min/1.73 m2; a history of liver disease, alcoholism or heart failure; or in any patient who will be administered intra-arterial iodinated contrast. Re-evaluate eGFR 48 hours after the imaging procedure; restart KOMBIGLYZE XR if renal function is stable [ see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) ].

By using PrescriberAI, you agree to the AI Terms of Use.
Kombiglyze XR prescribing information
WARNING: LACTIC ACIDOSIS
• Post-marketing cases of metformin-associated lactic acidosis have resulted in death, hypothermia, hypotension, and resistant bradyarrhythmias. The onset of metformin-associated lactic acidosis is often subtle, accompanied only by nonspecific symptoms such as malaise, myalgias, respiratory distress, somnolence, and abdominal pain. Metformin-associated lactic acidosis was characterized by elevated blood lactate levels (> 5 mmol/Liter), anion gap acidosis (without evidence of ketonuria or ketonemia), an increased lactate/pyruvate ratio; and metformin plasma levels generally >5 mcg/mL [ see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) ].
• Risk factors for metformin-associated lactic acidosis include renal impairment, concomitant use of certain drugs (e.g., carbonic anhydrase inhibitors such as topiramate), age 65 years old or greater, having a radiological study with contrast, surgery and other procedures, hypoxic states (e.g., acute congestive heart failure), excessive alcohol intake, and hepatic impairment.
• Steps to reduce the risk of and manage metformin-associated lactic acidosis in these high risk groups are provided in the full prescribing information [ see Dosage and Administration (2.2) , Contraindications (4) , Warnings and Precautions (5.1) , Drug Interactions (7) , and Use in Specific Populations (8.6 , 8.7 ) ].
• If metformin-associated lactic acidosis is suspected, immediately discontinue KOMBIGLYZE XR and institute general supportive measures in a hospital setting. Prompt hemodialysis is recommended [ see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) ].
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
KOMBIGLYZE XR is indicated as an adjunct to diet and exercise to improve glycemic control in adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus [ see Clinical Studies (14) ].
Limitations of Use
KOMBIGLYZE XR is not recommended for the treatment of type 1 diabetes mellitus or diabetic ketoacidosis.
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- Administer once daily with the evening meal. (2.1)
- Individualize the starting dosage based on the patient’s current regimen then adjust the dosage based on effectiveness and tolerability. (2.1)
- Do not exceed a daily dosage of 5 mg saxagliptin/2,000 mg metformin HCl extended-release. (2.1)
- Swallow whole. Never crush, cut, or chew. (2.1)
- Limit the saxagliptin dosage to 2.5 mg daily for patients also taking strong cytochrome P450 3A4/5 inhibitors (e.g., ketoconazole). (2.3 , 7.1)
- Assess renal function prior to initiation of KOMBIGLYZE XR and periodically thereafter. (2.2)
- Do not use in patients with eGFR below 30 mL/min/1.73 m 2 .
- Initiation is not recommended in patients with eGFR between 30 - 45 mL/min/1.73 m 2 .
- Assess risk/benefit of continuing if eGFR falls below 45 mL/min/1.73 m 2 .
- Limit the saxagliptin component to 2.5 mg daily if eGFR is less than 45 mL/min/1.73 m 2 .
- Discontinue if eGFR falls below 30 mL/min/1.73 m 2 .
- KOMBIGLYZE XR may need to be discontinued at time of, or prior to, iodinated contrast imaging procedures. (2.4)
Recommended Dosage and Administration
Individualize the starting dosage of KOMBIGLYZE XR based on the patient’s current regimen and the available strengths of KOMBIGLYZE XR [ see Dosage Forms and Strengths (3) ].
Administer KOMBIGLYZE XR once daily with the evening meal, with gradual dose titration to reduce the gastrointestinal side effects associated with metformin HCl [ see Adverse Reactions (6.1) ].
The recommended starting dosage of KOMBIGLYZE XR in patients who need 5 mg of saxagliptin and who are not currently treated with metformin HCl is one KOMBIGLYZE XR tablet containing 5 mg saxagliptin and 500 mg metformin HCl extended-release once daily with gradual dose escalation to reduce the gastrointestinal side effects due to metformin HCl.
In patients treated with metformin HCl, the recommended starting dosage of KOMBIGLYZE XR should provide metformin HCl at the dose already being taken, or the nearest therapeutically appropriate dose. Following a switch from metformin HCl immediate-release to KOMBIGLYZE XR, closely monitor glycemic control and adjust the dosage accordingly.
Patients who need 2.5 mg saxagliptin in combination with metformin HCl extended-release may be treated with KOMBIGLYZE XR 2.5 mg/1,000 mg. Patients who need 2.5 mg saxagliptin who are either metformin HCl naive or who require a dose of metformin HCl higher than 1,000 mg should use the individual components.
Gradually titrate the dosage of KOMBIGLYZE XR, as needed, after assessing therapeutic response and tolerability, up to a maximum recommended dosage of KOMBIGLYZE XR (5 mg for saxagliptin and 2,000 mg for metformin HCl extended-release orally once daily).
Inform patients that KOMBIGLYZE XR tablets must be swallowed whole and never crushed, cut, or chewed. Occasionally, the inactive ingredients of KOMBIGLYZE XR will be eliminated in the feces as a soft, hydrated mass that may resemble the original tablet.
If a dose is missed, advise patients not to take an extra dose. Resume treatment with the next dose.
Recommendations for Dosage and Administration in Renal Impairment
Assess renal function prior to initiation of KOMBIGLYZE XR and then as clinically indicated [ see Use in Specific Populations (8.6) ].
The recommended dosage of KOMBIGLYZE XR in patients with an estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) greater than or equal to 45 mL/minute/1.73 m2 is the same as the recommended dosage in patients with normal renal function [ see Dosage and Administration (2.1) ].
In patients taking KOMBIGLYZE XR whose eGFR later falls below 45 mL/minute/1.73 m2, assess the benefit risk of continuing therapy and limit dose of the saxagliptin component to 2.5 mg once daily.
Initiation of KOMBIGLYZE XR in patients with an eGFR between 30 – 45 mL/minute/1.73 m2 is not recommended.
KOMBIGLYZE XR is contraindicated in patients with an eGFR below 30 mL/minute/1.73 m2.
Discontinue KOMBIGLYZE XR if the patient’s eGFR later falls below 30 mL/minute/1.73 m2 [ see Contraindications (4) and Warnings and Precautions (5.1) ].
Dosage Modifications with Concomitant Use of Strong CYP3A4/5 Inhibitors
The maximum recommended dosage of KOMBIGLYZE XR is 2.5 mg of saxagliptin and 1,000 mg of metformin HCl given orally once daily when used concomitantly with strong cytochrome P450 3A4/5 (CYP3A4/5) inhibitors (e.g., ketoconazole, atazanavir, clarithromycin, indinavir, itraconazole, nefazodone, nelfinavir, ritonavir, saquinavir, and telithromycin) [ see Dosage and Administration (2.1) , Drug Interactions (7.1) , and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ].
Discontinuation for Iodinated Contrast Imaging Procedures
Discontinue KOMBIGLYZE XR at the time of, or prior to, an iodinated contrast imaging procedure in patients with an eGFR less than 60 mL/min/1.73 m2; a history of liver disease, alcoholism or heart failure; or in any patient who will be administered intra-arterial iodinated contrast. Re-evaluate eGFR 48 hours after the imaging procedure; restart KOMBIGLYZE XR if renal function is stable [ see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) ].
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Extended-Release Tablets:
- 5 mg of saxagliptin and 500 mg of metformin HCl: light brown to brown, biconvex, capsule-shaped, film-coated tablets with “5/500” printed on one side and “4221” printed on the reverse side, in blue ink.
- 5 mg of saxagliptin and 1,000 mg of metformin HCl: pink, biconvex, capsule-shaped, film-coated tablets with “5/1000” printed on one side and “4223” printed on the reverse side, in blue ink.
- 2.5 mg of saxagliptin and 1,000 mg of metformin HCl: pale yellow to light yellow, biconvex, capsule-shaped, film-coated tablets with “2.5/1000” printed on one side and “4222” printed on the reverse side, in blue ink.
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
Pregnancy
Risk Summary
Limited available data with KOMBIGLYZE XR or saxagliptin in pregnant women are not sufficient to determine a drug-associated risk for major birth defects and miscarriage. Published trials with metformin use during pregnancy have not reported a clear association with metformin and major birth defect or miscarriage risk [ see Data ].
No adverse developmental effects independent of maternal toxicity were observed when saxagliptin and metformin were administered separately or in combination to pregnant rats and rabbits during the period of organogenesis [ see Data ].
The estimated background risk of major birth defects is 6 to 10% in women with pre-gestational diabetes with an HbA1c greater than 7 and has been reported to be as high as 20 to 25% in women with an HbA1c greater than 10. The estimated background risk of miscarriage for the indicated population is unknown. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2 to 4% and 15 to 20%, respectively.
Clinical Considerations
Disease-associated maternal and/or embryo/fetal risk
Poorly controlled diabetes in pregnancy increases the maternal risk for diabetic ketoacidosis, preeclampsia, spontaneous abortions, preterm delivery, still birth and delivery complications. Poorly controlled diabetes increases the fetal risk for major birth defects, stillbirth, and macrosomia related morbidity.
Data
Animal Data
Saxagliptin
In embryo-fetal development studies, saxagliptin was administered to pregnant rats and rabbits during the period of organogenesis, corresponding to the first trimester of human pregnancy. No adverse developmental effects were observed in either species at exposures 1503- and 152-times the 5 mg clinical dose in rats and rabbits, respectively, based on AUC. Saxagliptin crosses the placenta into the fetus following dosing in pregnant rats.
In a prenatal and postnatal development study, no adverse developmental effects were observed in maternal rats administered saxagliptin from gestation day 6 through lactation day 21 at exposures up to 470-times the 5 mg clinical dose, based on AUC.
Metformin HCI
Metformin hydrochloride did not cause adverse developmental effect when administered to pregnant Sprague Dawley rats and rabbits up to 600 mg/kg/day during the period of organogenesis. This represents an exposure of about 2- and 6-times a 2,000 mg clinical dose based on body surface area (mg/m 2 ) for rats and rabbits, respectively.
Saxagliptin and Metformin
Saxagliptin and metformin coadministered to pregnant rats and rabbits during the period of organogenesis did not result in adverse developmental effects considered clinically relevant in either species. Doses tested in rats provided exposure up to 100- and 10-times clinical exposure, and doses tested in rabbits provided exposure up to 249- and 1-times clinical exposure relative to the clinical dose of 5 mg saxagliptin and 2,000 mg metformin. Minor skeletal abnormalities associated with maternal toxicity were observed in rats. In rabbits, coadministration was poorly tolerated in a subset of mothers (12 of 30), resulting in death, moribundity, or abortion. However, among surviving mothers with evaluable litters, maternal toxicity was limited to marginal reductions in body weight over the course of gestation days 21 to 29, associated with fetal body weight decrements of 7%, and a low incidence of delayed ossification of the fetal hyoid bone.
Lactation
Risk Summary
There is no information regarding the presence of KOMBIGLYZE XR or saxagliptin in human milk, the effects on the breastfed infant, or the effects on milk production. Limited published studies report that metformin is present in human milk [ see Data ]. However, there is insufficient information on the effects of metformin on the breastfed infant and no available information on the effects of metformin on milk production. Saxagliptin is present in the milk of lactating rats [ see Data ].
The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother’s clinical need for KOMBIGLYZE XR and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed child from KOMBIGLYZE XR or from the underlying maternal condition.
Data
Human Data
Published clinical lactation studies report that metformin is present in human milk which resulted in infant doses approximately 0.11% to 1% of the maternal weight-adjusted dosage and a milk/plasma ratio ranging between 0.13 and 1. However, the studies were not designed to definitely establish the risk of use of metformin during lactation because of small sample size and limited adverse event data collected in infants.
Animal Data
No studies in lactating animals have been conducted with the combined components of KOMBIGLYZE XR. In studies performed with the individual components, both saxagliptin and metformin are secreted in the milk of lactating rats. Saxagliptin is secreted in the milk of lactating rats at approximately a 1:1 ratio with plasma drug concentrations.
Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of KOMBIGLYZE XR as an adjunct to diet and exercise to improve glycemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus have not been established in pediatric patients.
Effectiveness of saxagliptin was not demonstrated in a 26-week, placebo-controlled, double-blind randomized clinical trial with a 26-week safety extension (NCT03199053) in 164 pediatric patients aged 10 to 17 years with inadequately controlled type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Geriatric Use
KOMBIGLYZE XR
Elderly patients are more likely to have decreased renal function. Assess renal function more frequently in the elderly [ see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ].
Saxagliptin
In the seven, double-blind, controlled clinical safety and efficacy trials of saxagliptin, a total of 4751 (42.0%) of the 11301 patients randomized to saxagliptin were 65 years and over, and 1210 (10.7%) were 75 years and over. No overall differences in safety or effectiveness were observed between patients 65 years of age and older and younger adult patients.
Metformin HCI
Controlled clinical trials of metformin did not include sufficient numbers of elderly patients to determine whether they respond differently than younger patients. In general, dose selection for an elderly patient should be cautious, usually starting at the low end of the dosing range, reflecting the greater frequency of decreased hepatic, renal, or cardiac function, and of concomitant disease or other drug therapy and the higher risk of lactic acidosis. Assess renal function more frequently in elderly patients [ see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) ].
Renal Impairment
Saxagliptin
In a 12-week randomized placebo-controlled trial, saxagliptin 2.5 mg was administered to 85 patients with moderate (n=48) or severe (n=18) renal impairment or end-stage renal disease (ESRD) (n=19) [ see Clinical Studies (14) ]. The incidence of adverse events, including serious adverse events and discontinuations due to adverse events, was similar between saxagliptin and placebo. The overall incidence of reported hypoglycemia was 20% among patients treated with saxagliptin 2.5 mg and 22% among patients treated with placebo. Four saxagliptin-treated patients (4.7%) and three placebo-treated patients (3.5%) reported at least one episode of confirmed symptomatic hypoglycemia (accompanying fingerstick glucose ≤50 mg/dL).
Metformin HCI
Metformin is substantially excreted by the kidney, and the risk of metformin accumulation and lactic acidosis increases with the degree of renal impairment. KOMBIGLYZE XR is contraindicated in severe renal impairment, patients with an estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) below 30 mL/min/1.73 m 2 [ see Dosage and Administration (2.2) , Contraindications (4) , Warnings and Precautions (5.1) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ].
Hepatic Impairment
Use of metformin in patients with hepatic impairment has been associated with some cases of lactic acidosis. KOMBIGLYZE XR is not recommended in patients with hepatic impairment [ see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) ].
CONTRAINDICATIONS
KOMBIGLYZE XR is contraindicated in patients with:
- Severe renal impairment (eGFR below 30 mL/min/1.73 m2).
- Acute or chronic metabolic acidosis, including diabetic ketoacidosis. Diabetic ketoacidosis should be treated with insulin.
- A history of a serious hypersensitivity reaction to saxagliptin, metformin HCl, or any of the ingredients in KOMBLIGLYZE XR. Reactions such as anaphylaxis, angioedema, or exfoliative skin conditions have been reported [ see Warnings and Precautions (5.6) and Adverse Reactions (6.2) ].
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- Pancreatitis: There have been postmarketing reports of acute pancreatitis. If pancreatitis is suspected, promptly discontinue KOMBIGLYZE XR. (5.2)
- Heart Failure: Consider the risks and benefits of KOMBIGLYZE XR in patients who have known risk factors for heart failure. Monitor patients for signs and symptoms. (5.3 )
- Vitamin B 12 Deficiency: Metformin may lower vitamin B 12 levels. Measure hematological parameters annually. (5.4 )
- Hypoglycemia with Concomitant Use of Insulin or Insulin Secretagogues: Consider a lower dosage of insulin or insulin secretagogue when used in combination with KOMBIGLYZE XR. (5.5 )
- Hypersensitivity-Related Events: There have been post-marketing reports of serious hypersensitivity reactions, such as anaphylaxis, angioedema, and exfoliative skin conditions in patients treated with saxagliptin. If hypersensitivity reactions occur, discontinue KOMBIGLYZE XR, treat promptly, and monitor until signs and symptoms resolve. (5.6 )
- Arthralgia: Severe and disabling arthralgia has been reported in patients taking DPP4 inhibitors. Consider as a possible cause for severe joint pain and discontinue drug if appropriate. (5.7 )
- Bullous Pemphigoid : There have been postmarketing reports of bullous pemphigoid requiring hospitalization in patients taking DPP-4 inhibitors. Tell patients to report development of blisters or erosions. If bullous pemphigoid is suspected, discontinue KOMBIGLYZE XR (5.8 ).
Lactic Acidosis
There have been postmarketing cases of metformin-associated lactic acidosis, including fatal cases. These cases had a subtle onset and were accompanied by nonspecific symptoms such as malaise, myalgias, abdominal pain, respiratory distress, or increased somnolence; however, hypothermia, hypotension and resistant bradyarrhythmias have occurred with severe acidosis.
Metformin-associated lactic acidosis was characterized by elevated blood lactate concentrations (>5 mmol/Liter), anion gap acidosis (without evidence of ketonuria or ketonemia), and an increased lactate: pyruvate ratio; metformin plasma levels generally >5 mcg/mL. Metformin decreases liver uptake of lactate increasing lactate blood levels which may increase the risk of lactic acidosis, especially in patients at risk.
If metformin-associated lactic acidosis is suspected, general supportive measures should be instituted promptly in a hospital setting, along with immediate discontinuation of KOMBIGLYZE XR.
In KOMBIGLYZE XR-treated patients with a diagnosis or strong suspicion of lactic acidosis, prompt hemodialysis is recommended to correct the acidosis and remove accumulated metformin (metformin HCl is dialyzable, with a clearance of up to 170 mL/minute under good hemodynamic conditions). Hemodialysis has often resulted in reversal of symptoms and recovery.
Educate patients and their families about the symptoms of lactic acidosis and if these symptoms occur instruct them to discontinue KOMBIGLYZE XR and report these symptoms to their health care provider.
For each of the known and possible risk factors for metformin-associated lactic acidosis, recommendations to reduce the risk of and manage metformin-associated lactic acidosis are provided below:
Renal Impairment: The post-marketing metformin-associated lactic acidosis cases primarily occurred in patients with significant renal impairment. The risk of metformin accumulation and metformin-associated lactic acidosis increases with the severity of renal impairment because metformin is substantially excreted by the kidney. Clinical recommendations based upon the patient’s renal function include [ see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ]:
- Before initiating KOMBIGLYZE XR, obtain an estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR).
- KOMBIGLYZE XR is contraindicated in patients with an eGFR less than 30 mL/minute/1.73 m 2 [ see Contraindications (4) ].
- Initiation of KOMBIGLYZE XR is not recommended in patients with eGFR between 30 and 45 mL/minute/1.73 m 2 .
- Obtain an eGFR at least annually in all patients taking KOMBIGLYZE XR. In patients at increased risk for the development of renal impairment (e.g., the elderly), renal function should be assessed more frequently.
- In patients taking KOMBIGLYZE XR whose eGFR later falls below 45 mL/minute/1.73 m 2 , assess the benefit and risk of continuing therapy.
Drug Interactions : The concomitant use of KOMBIGLYZE XR with specific drugs may increase the risk of metformin-associated lactic acidosis: those that impair renal function, result in significant hemodynamic change, interfere with acid-base balance or increase metformin accumulation [ see Drug Interactions (7) ]. Therefore, consider more frequent monitoring of patients.
Age 65 or Greater: The risk of metformin-associated lactic acidosis increases with the patient’s age because elderly patients have a greater likelihood of having hepatic, renal, or cardiac impairment than younger patients. Assess renal function more frequently in elderly patients [ see Use in Specific Populations (8.5) ].
Radiological Studies with Contrast : Administration of intravascular iodinated contrast agents in metformin-treated patients has led to an acute decrease in renal function and the occurrence of lactic acidosis. Stop KOMBIGLYZE XR at the time of, or prior to, an iodinated contrast imaging procedure in patients with an eGFR between 30 and 60 mL/min/1.73 m 2 ; in patients with a history of hepatic impairment, alcoholism, or heart failure; or in patients who will be administered intra-arterial iodinated contrast. Re-evaluate eGFR 48 hours after the imaging procedure, and restart KOMBIGLYZE XR if renal function is stable.
Surgery and Other Procedures : Withholding of food and fluids during surgical or other procedures may increase the risk for volume depletion, hypotension and renal impairment. KOMBIGLYZE XR should be temporarily discontinued while patients have restricted food and fluid intake.
Hypoxic States : Several of the post-marketing cases of metformin-associated lactic acidosis occurred in the setting of acute congestive heart failure (particularly when accompanied by hypoperfusion and hypoxemia). Cardiovascular collapse (shock), acute myocardial infarction, sepsis, and other conditions associated with hypoxemia have been associated with lactic acidosis and may also cause prerenal azotemia. When such events occur, discontinue KOMBIGLYZE XR.
Excessive Alcohol Intake : Alcohol potentiates the effect of metformin on lactate metabolism and this may increase the risk of metformin-associated lactic acidosis. Warn patients against excessive alcohol intake while receiving KOMBIGLYZE XR.
Hepatic Impairment : Patients with hepatic impairment have developed with cases of metformin-associated lactic acidosis. This may be due to impaired lactate clearance resulting in higher lactate blood levels. Therefore, avoid use of KOMBIGLYZE XR in patients with clinical or laboratory evidence of hepatic disease.
Pancreatitis
There have been post-marketing reports of acute pancreatitis in patients taking saxagliptin. In a cardiovascular outcomes trial enrolling participants with established atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) or multiple risk factors for ASCVD (SAVOR trial), cases of definite acute pancreatitis were confirmed in 17 of 8240 (0.2%) patients receiving saxagliptin compared to 9 of 8173 (0.1%) receiving placebo. Pre-existing risk factors for pancreatitis were identified in 88% (15/17) of those patients receiving saxagliptin and in 100% (9/9) of those patients receiving placebo.
After initiation of KOMBIGLYZE XR, observe patients for signs and symptoms of pancreatitis. If pancreatitis is suspected, promptly discontinue KOMBIGLYZE XR and initiate appropriate management. It is unknown whether patients with a history of pancreatitis are at increased risk for the development of pancreatitis while using KOMBIGLYZE XR.
Heart Failure
In a cardiovascular outcomes trial enrolling participants with established ASCVD or multiple risk factors for ASCVD (SAVOR trial), more patients randomized to saxagliptin (289/8280, 3.5%) were hospitalized for heart failure compared to patients randomized to placebo (228/8212, 2.8%). In a time-to-first-event analysis the risk of hospitalization for heart failure was higher in the saxagliptin group (estimated Hazard Ratio: 1.27; 95% CI: 1.07, 1.51). Patients with a prior history of heart failure and patients with renal impairment had a higher risk for hospitalization for heart failure, irrespective of treatment assignment.
Consider the risks and benefits of KOMBIGLYZE XR prior to initiating treatment in patients at a higher risk for heart failure. Observe patients for signs and symptoms of heart failure during therapy. Advise patients of the characteristic symptoms of heart failure, and to immediately report such symptoms. If heart failure develops, evaluate and manage according to current standards of care and consider discontinuation of KOMBIGLYZE XR.
Vitamin B 12 Concentrations
In controlled clinical trials of metformin of 29-week duration, a decrease to subnormal levels of previously normal serum vitamin B12 levels, without clinical manifestations, was observed in approximately 7% of patients. Such decrease, possibly due to interference with B12 absorption from the B12-intrinsic factor complex, may be associated with anemia but appears to be rapidly reversible with discontinuation of metformin or vitamin B12 supplementation. Certain individuals (those with inadequate vitamin B12 or calcium intake or absorption) appear to be predisposed to developing subnormal vitamin B12 levels. Measure hematologic parameters on an annual basis and vitamin B12 at 2- to 3-year intervals in patients on KOMBIGLYZE XR and manage any abnormalities [ see Adverse Reactions (6.1) ].
Hypoglycemia with Concomitant Use of Insulin or Insulin Secretagogues
Saxagliptin
When saxagliptin was used in combination with insulin or an insulin secretagogue, the incidence of confirmed hypoglycemia was increased over that of placebo used in combination with insulin or an insulin secretagogue [ see Adverse Reactions (6.1) ]. Therefore, a lower dosage of insulin or an insulin secretagogue may be required to reduce the risk of hypoglycemia when used in combination with KOMBIGLYZE XR.
Metformin HCl
Hypoglycemia does not occur in patients receiving metformin alone under usual circumstances of use, but could occur when caloric intake is deficient, when strenuous exercise is not compensated by caloric supplementation, or during concomitant use with other glucose-lowering agents (such as sulfonylureas and insulin) or ethanol. Elderly, debilitated, or malnourished patients and those with adrenal or pituitary insufficiency or alcohol intoxication are particularly susceptible to hypoglycemic effects. Hypoglycemia may be difficult to recognize in the elderly and in people who are taking beta-adrenergic blocking drugs.
Inform patients using these concomitant medications of the risk of hypoglycemia and educate them on the signs and symptoms of hypoglycemia.
Hypersensitivity Reactions
There have been post-marketing reports of serious hypersensitivity reactions in patients treated with saxagliptin. These reactions include anaphylaxis, angioedema, and exfoliative skin conditions. Onset of these reactions occurred within the first 3 months after initiation of treatment with saxagliptin, with some reports occurring after the first dose. If a serious hypersensitivity reaction is suspected, discontinue KOMBIGLYZE XR, assess for other potential causes for the event, and institute alternative treatment for diabetes [ see Adverse Reactions (6.2) ].
Use caution in a patient with a history of angioedema to another dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP4) inhibitor because it is unknown whether such patients will be predisposed to angioedema with KOMBIGLYZE XR.
Severe and Disabling Arthralgia
There have been post-marketing reports of severe and disabling arthralgia in patients taking DPP4 inhibitors. The time to onset of symptoms following initiation of drug therapy varied from one day to years. Patients experienced relief of symptoms upon discontinuation of the medication. A subset of patients experienced a recurrence of symptoms when restarting the same drug or a different DPP4 inhibitor. Consider DPP4 inhibitors as a possible cause for severe joint pain and discontinue drug if appropriate.
Bullous Pemphigoid
Postmarketing cases of bullous pemphigoid requiring hospitalization have been reported with DPP 4 inhibitor use. In reported cases, patients typically recovered with topical or systemic immunosuppressive treatment and discontinuation of the DPP 4 inhibitor. Tell patients to report development of blisters or erosions while receiving KOMBIGLYZE XR. If bullous pemphigoid is suspected, KOMBIGLYZE XR should be discontinued and referral to a dermatologist should be considered for diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following serious adverse reactions are described below or elsewhere in the prescribing information:
- Lactic Acidosis [ see Boxed Warning and Warnings and Precautions (5.1) ]
- Pancreatitis [ see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) ]
- Heart Failure [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3) ]
- Vitamin B 12 Concentrations [ see Warnings and Precautions (5.4) ]
- Hypoglycemia with Concomitant Use of Insulin or Insulin Secretagogues [ see Warnings and Precautions (5.5) ]
- Hypersensitivity Reactions [ see Warnings and Precautions (5.6) ]
- Severe and disabling arthralgia [ see Warnings and Precautions (5.7) ]
- Bullous pemphigoid [ see Warnings and Precautions (5.8) ]
Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
Adverse Reactions in Placebo-Controlled Trials in Adults with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Metformin HCl
In placebo-controlled monotherapy trials of metformin HCl extended-release, diarrhea and nausea/vomiting were reported in >5% of metformin-treated patients and more commonly than in placebo-treated patients (9.6% versus 2.6% for diarrhea and 6.5% versus 1.5% for nausea/vomiting). Diarrhea led to discontinuation of trial medication in 0.6% of the patients treated with metformin HCl extended-release.
Saxagliptin
The data in Table 1 are derived from a pool of 5 placebo-controlled clinical trials [ see Clinical Studies (14) ]. These data shown in the table reflect exposure of 882 patients to saxagliptin and a mean duration of exposure to saxagliptin of 21 weeks. The mean age of these patients was 55 years, 1.4% were 75 years or older and 48.4% were male. The population was 67.5% White, 4.6% Black or African American, 17.4% Asian, 10.5% other races and 9.8% were of Hispanic or Latino ethnicity. At baseline the population had diabetes for an average of 5.2 years and a mean HbA1c of 8.2%. Baseline estimated renal function was normal or mildly impaired (eGFR ≥60mL/min/1.73m 2 ) in 91% of these patients.
Table 1 shows common adverse reactions, excluding hypoglycemia, associated with the use of saxagliptin. These adverse reactions occurred more commonly on saxagliptin than on placebo and occurred in at least 5% of patients treated with saxagliptin.
| % of Patients | ||
|---|---|---|
| Saxagliptin 5 mg N=882 | Placebo N=799 | |
Upper respiratory tract infection | 7.7 | 7.6 |
Urinary tract infection | 6.8 | 6.1 |
Headache | 6.5 | 5.9 |
In patients treated with saxagliptin 2.5 mg, headache (6.5%) was the only adverse reaction reported at a rate ≥5% and more commonly than in patients treated with placebo.
In the add-on to TZD trial, the incidence of peripheral edema was higher for saxagliptin 5 mg versus placebo (8.1% and 4.3%, respectively). The incidence of peripheral edema for saxagliptin 2.5 mg was 3.1%. None of the reported adverse reactions of peripheral edema resulted in trial drug discontinuation. Rates of peripheral edema for saxagliptin 2.5 mg and saxagliptin 5 mg versus placebo were 3.6% and 2% versus 3% given as monotherapy, 2.1% and 2.1% versus 2.2% given as add-on therapy to metformin HCl, and 2.4% and 1.2% versus 2.2% given as add-on therapy to glyburide.
The incidence rate of fractures was 1.0 and 0.6 per 100 patient-years, respectively, for saxagliptin (pooled analysis of 2.5 mg, 5 mg, and 10 mg) and placebo. The 10 mg saxagliptin dosage is not an approved dosage. The incidence rate of fracture events in patients who received saxagliptin did not increase over time. Causality has not been established and nonclinical studies have not demonstrated adverse effects of saxagliptin on bone.
An event of thrombocytopenia, consistent with a diagnosis of idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura, was observed in the clinical program. The relationship of this event to saxagliptin is not known.
Discontinuation of therapy due to adverse reactions occurred in 2.2%, 3.3%, and 1.8% of patients receiving saxagliptin 2.5 mg, saxagliptin 5 mg, and placebo, respectively. The most common adverse reactions (reported in at least 2 patients treated with saxagliptin 2.5 mg or at least 2 patients treated with saxagliptin 5 mg) associated with premature discontinuation of therapy included lymphopenia (0.1% and 0.5% versus 0%, respectively), rash (0.2% and 0.3% versus 0.3%), blood creatinine increased (0.3% and 0% versus 0%), and blood creatine phosphokinase increased (0.1% and 0.2% versus 0%).
Adverse Reactions with Concomitant Use with Insulin
In the add-on to insulin trial [ see Clinical Studies (14.1) ], the incidence of adverse events, including serious adverse events and discontinuations due to adverse events, was similar between saxagliptin and placebo, except for confirmed hypoglycemia [ see Adverse Reactions (6.1) ].
Adverse Reactions Associated with Saxagliptin Coadministered with Metformin HCl Immediate-Release in Treatment-Naive Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Table 2 shows the adverse reactions reported (regardless of investigator assessment of causality) in ≥5% of patients participating in an additional 24-week, active-controlled trial of coadministered saxagliptin and metformin HCl in treatment-naive patients.
| Number (%) of Patients | ||
|---|---|---|
| Saxagliptin 5 mg + Metformin HCl Metformin HCl immediate-release was initiated at a starting dose of 500 mg daily and titrated up to a maximum of 2,000 mg daily. N=320 | Placebo + MetforminHCl N=328 | |
Headache | 24 (7.5) | 17 (5.2) |
Nasopharyngitis | 22 (6.9) | 13 (4.0) |
In patients treated with the combination of saxagliptin and metformin HCl immediate-release, either as saxagliptin add-on to metformin HCl immediate-release therapy or as coadministration in treatment-naive patients, diarrhea was the only gastrointestinal-related event that occurred with an incidence ≥5% in any treatment group in both trials. In the saxagliptin add-on to metformin HCl immediate-release trial, the incidence of diarrhea was 9.9%, 5.8%, and 11.2% in the saxagliptin 2.5 mg, 5 mg, and placebo groups, respectively. When saxagliptin and metformin HCl immediate-release were coadministered in treatment-naive patients, the incidence of diarrhea was 6.9% in the saxagliptin 5 mg + metformin HCl immediate-release group and 7.3% in the placebo + metformin HCl immediate-release group.
Hypoglycemia
In the saxagliptin clinical trials, adverse reactions of hypoglycemia were based on all reports of hypoglycemia. A concurrent glucose measurement was not required or was normal in some patients. Therefore, it is not possible to conclusively determine that all these reports reflect true hypoglycemia.
The incidence of reported hypoglycemia for saxagliptin 2.5 mg and saxagliptin 5 mg versus placebo given as monotherapy was 4% and 5.6% versus 4.1%, respectively. In the add-on to metformin HCl immediate-release trial, the incidence of reported hypoglycemia was 7.8% with saxagliptin 2.5 mg, 5.8% with saxagliptin 5 mg, and 5% with placebo. When saxagliptin and metformin HCl immediate-release were coadministered in treatment-naive patients, the incidence of reported hypoglycemia was 3.4% in patients given saxagliptin 5 mg + metformin HCl immediate-release and 4% in patients given placebo + metformin HCl immediate-release.
In the active-controlled trial comparing add-on therapy with saxagliptin 5 mg to glipizide in patients inadequately controlled on metformin HCl alone, the incidence of reported hypoglycemia was 3% (19 events in 13 patients) with saxagliptin 5 mg versus 36.3% (750 events in 156 patients) with glipizide. Confirmed symptomatic hypoglycemia (accompanying fingerstick blood glucose ≤50 mg/dL) was reported in none of the saxagliptin-treated patients and in 35 glipizide-treated patients (8.1%) (p<0.0001).
In the saxagliptin add-on to insulin trial, the overall incidence of reported hypoglycemia was 18.4% for saxagliptin 5 mg and 19.9% for placebo. However, the incidence of confirmed symptomatic hypoglycemia (accompanying fingerstick blood glucose ≤50 mg/dL) was higher with saxagliptin 5 mg (5.3%) versus placebo (3.3%). Among the patients using insulin in combination with metformin HCl, the incidence of confirmed symptomatic hypoglycemia was 4.8% with saxagliptin versus 1.9% with placebo.
In the saxagliptin add-on to metformin HCl plus sulfonylurea trial, the overall incidence of reported hypoglycemia was 10.1% for saxagliptin 5 mg and 6.3% for placebo. Confirmed hypoglycemia was reported in 1.6% of the saxagliptin-treated patients and in none of the placebo-treated patients [ see Warnings and Precautions (5.5) ].
Hypersensitivity Reactions
Saxagliptin
Hypersensitivity reactions, such as urticaria and facial edema in the 5-trial pooled analysis up to Week 24 were reported in 1.5%, 1.5%, and 0.4% of patients who received saxagliptin 2.5 mg, saxagliptin 5 mg, and placebo, respectively. None of these events in patients who received saxagliptin required hospitalization or were reported as life-threatening by the investigators. One saxagliptin-treated patient in this pooled analysis discontinued due to generalized urticaria and facial edema.
Renal Impairment
In the SAVOR trial, adverse reactions related to renal impairment, including laboratory changes (i.e., doubling of serum creatinine compared with baseline and serum creatinine >6 mg/dL), were reported in 5.8% (483/8280) of saxagliptin-treated patients and 5.1% (422/8212) of placebo-treated patients. The most frequently reported adverse reactions included renal impairment (2.1% vs. 1.9%), acute renal failure (1.4% vs. 1.2%), and renal failure (0.8% vs. 0.9%), in the saxagliptin versus placebo groups, respectively. From baseline to the end of treatment, there was a mean decrease in eGFR of 2.5 mL/min/1.73m 2 for saxagliptin-treated patients and a mean decrease of 2.4 mL/min/1.73m 2 for placebo-treated patients. More patients randomized to saxagliptin (421/5227, 8.1%) compared to patients randomized to placebo (344/5073, 6.8%) had downward shifts in eGFR from >50 mL/min/1.73 m 2 (i.e., normal or mild renal impairment) to ≤50 mL/min/1.73 m 2 (i.e., moderate or severe renal impairment). The proportions of patients with renal adverse reactions increased with worsening baseline renal function and increased age, regardless of treatment assignment.
Infections
Saxagliptin
In the unblinded, controlled, clinical trial database for saxagliptin to date, there have been 6 (0.12%) reports of tuberculosis among the 4959 saxagliptin-treated patients (1.1 per 1000 patient-years) compared to no reports of tuberculosis among the 2868 comparator-treated patients. Two of these six cases were confirmed with laboratory testing. The remaining cases had limited information or had presumptive diagnoses of tuberculosis. None of the six cases occurred in the United States or in Western Europe. One case occurred in Canada in a patient originally from Indonesia who had recently visited Indonesia. The duration of treatment with saxagliptin until report of tuberculosis ranged from 144 to 929 days. Post-treatment lymphocyte counts were consistently within the reference range for four cases. One patient had lymphopenia prior to initiation of saxagliptin that remained stable throughout saxagliptin treatment. The final patient had an isolated lymphocyte count below normal approximately four months prior to the report of tuberculosis. There have been no spontaneous reports of tuberculosis associated with saxagliptin use. Causality has not been established and there are too few cases to date to determine whether tuberculosis is related to saxagliptin use.
There has been one case of a potential opportunistic infection in the unblinded, controlled clinical trial database to date in a saxagliptin-treated patient who developed suspected foodborne fatal salmonella sepsis after approximately 600 days of saxagliptin therapy. There have been no spontaneous reports of opportunistic infections associated with saxagliptin use.
Vital Signs
Saxagliptin
No clinically meaningful changes in vital signs have been observed in patients treated with saxagliptin alone or in combination with metformin HCl.
Laboratory Tests
Absolute Lymphocyte Counts
Saxagliptin
There was a dose-related mean decrease in absolute lymphocyte count observed with saxagliptin. From a baseline mean absolute lymphocyte count of approximately 2200 cells/microL, mean decreases of approximately 100 and 120 cells/microL with saxagliptin 5 mg and 10 mg, respectively, relative to placebo were observed at 24 weeks in a pooled analysis of five placebo-controlled clinical trials. Similar effects were observed when saxagliptin 5 mg and metformin HCl were coadministered in treatment-naive patients compared to placebo and metformin HCl. There was no difference observed for saxagliptin 2.5 mg relative to placebo. The proportion of patients who were reported to have a lymphocyte count ≤750 cells/microL was 0.5%, 1.5%, 1.4%, and 0.4% in the saxagliptin 2.5 mg, 5 mg, 10 mg, and placebo groups, respectively. In most patients, recurrence was not observed with repeated exposure to saxagliptin although some patients had recurrent decreases upon rechallenge that led to discontinuation of saxagliptin. The decreases in lymphocyte count were not associated with clinically relevant adverse reactions. The 10 mg saxagliptin dosage is not an approved dosage.
In the SAVOR trial mean decreases of approximately 84 cells/microL with saxagliptin relative to placebo was observed. The proportion of patients who experienced a decrease in lymphocyte counts to a count of ≤750 cells/microL was 1.6% (136/8280) and 1.0% (78/8212) on saxagliptin and placebo, respectively.
The clinical significance of this decrease in lymphocyte count relative to placebo is not known. When clinically indicated, such as in settings of unusual or prolonged infection, lymphocyte count should be measured. The effect of saxagliptin on lymphocyte counts in patients with lymphocyte abnormalities (e.g., human immunodeficiency virus) is unknown.
Vitamin B 12 Concentrations
Metformin HCl
In metformin clinical trials of 29 week duration, a decrease to subnormal levels of previously normal serum vitamin B12 levels was observed in approximately 7% of patients.
Postmarketing Experience
Additional adverse reactions have been identified during post-approval use of KOMBIGLYZE XR, saxagliptin, or metformin HCl. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is generally not possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Saxagliptin
- Gastrointestinal Disorders: Pancreatitis
- Immune System Disorders: Hypersensitivity reactions including anaphylaxis, angioedema, and exfoliative skin conditions
- Musculoskeletal and Connective Tissue Disorders: Rhabdomyolysis, Severe and disabling arthralgia
- Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue Disorders: Bullous pemphigoid
Metformin HCl
- Hepatobiliary Disorders : Cholestatic, hepatocellular, and mixed hepatocellular liver injury
DRUG INTERACTIONS
- Strong CYP3A4/5 inhibitors (e.g., ketoconazole) : Coadministration with KOMBIGLYZE XR significantly increases saxagliptin concentrations. Limit KOMBIGLYZE XR dosage to 2.5 mg/1,000 mg once daily when coadministered with a strong CYP3A4/5 inhibitor. (2.3 , 7.1 )
- Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors : May increase risk of lactic acidosis. Consider more frequent monitoring. (7.2)
- Drugs that reduce metformin clearance : May increase risk of lactic acidosis. Consider benefits and risks of concomitant use. (7.3)
- See full prescribing information for additional drug interactions. (7 )
Strong Inhibitors of CYP3A4/5 Enzymes
Ketoconazole significantly increased saxagliptin exposure. Similar significant increases in plasma concentrations of saxagliptin are anticipated with other strong CYP3A4/5 inhibitors (e.g., atazanavir, clarithromycin, indinavir, itraconazole, nefazodone, nelfinavir, ritonavir, saquinavir, and telithromycin). The dose of KOMBIGLYZE XR should be limited to 2.5 mg of saxagliptin when coadministered with a strong CYP3A4/5 inhibitor [ see Dosage and Administration (2.3) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ].
Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors
Topiramate or other carbonic anhydrase inhibitors (e.g., zonisamide, acetazolamide or dichlorphenamide) frequently causes a decrease in serum bicarbonate and induce non-anion gap, hyperchloremic metabolic acidosis. Concomitant use of these drugs with KOMBIGLYZE XR may increase the risk for lactic acidosis.
Drugs that Reduce Metformin Clearance
Concomitant use of drugs that interfere with common renal tubular transport systems involved in the renal elimination of metformin (e.g., organic cationic transporter-2 [OCT2]/multidrug and toxin extrusion [MATE] inhibitors such as ranolazine, vandetanib, dolutegravir, and cimetidine) could increase systemic exposure to metformin and may increase the risk for lactic acidosis [ see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ] . Consider the benefits and risks of concomitant use.
Alcohol
Alcohol is known to potentiate the effect of metformin on lactate metabolism. Warn patients against excessive alcohol intake while receiving KOMBIGLYZE XR.
Insulin or Insulin Secretagogues
Insulin and insulin secretagogues are known to cause hypoglycemia. Concomitant use of KOMBIGLYZE XR with insulin or an insulin secretagogue may require lower dosages of insulin or the insulin secretagogue to reduce the risk of hypoglycemia [ see Warnings and Precautions (5.5) ].
Drugs Affecting Glycemic Control
Certain drugs tend to produce hyperglycemia and may lead to loss of glycemic control. These medications include the thiazides and other diuretics, corticosteroids, phenothiazines, thyroid products, estrogens, oral contraceptives, phenytoin, nicotinic acid, sympathomimetics, calcium channel blocking drugs, and isoniazid. When such drugs are administered to a patient receiving KOMBIGLYZE XR, observe the patient closely for loss of blood glucose control. When such drugs are withdrawn from a patient receiving KOMBIGLYZE XR, observe the patient closely for hypoglycemia.
DESCRIPTION
KOMBIGLYZE XR (saxagliptin and metformin HCl extended-release) tablets contain two oral antihyperglycemic medications used in the management of type 2 diabetes mellitus: saxagliptin and metformin HCl.
Saxagliptin
Saxagliptin is an orally active inhibitor of the dipeptidyl-peptidase-4 (DPP4) enzyme.
Saxagliptin monohydrate is described chemically as (1 S ,3 S ,5 S )-2-[(2 S )-2-Amino-2-(3-hydroxytricyclo[3.3.1. 13,7 ]dec-1-yl)acetyl]-2-azabicyclo[3.1.0]hexane-3-carbonitrile, monohydrate or (1 S ,3 S ,5 S )-2-[(2 S )-2-Amino-2-(3-hydroxyadamantan-1-yl)acetyl]-2-azabicyclo[3.1.0]hexane-3-carbonitrile hydrate. The empirical formula is C 18 H 25 N 3 O 2 •H 2 O and the molecular weight is 333.43. The structural formula is:
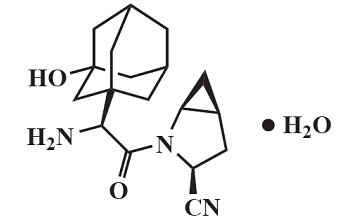
Saxagliptin monohydrate is a white to light yellow or light brown, non-hygroscopic, crystalline powder. It is sparingly soluble in water at 24°C ± 3°C, slightly soluble in ethyl acetate, and soluble in methanol, ethanol, isopropyl alcohol, acetonitrile, acetone, and polyethylene glycol 400 (PEG 400).
Metformin HCl
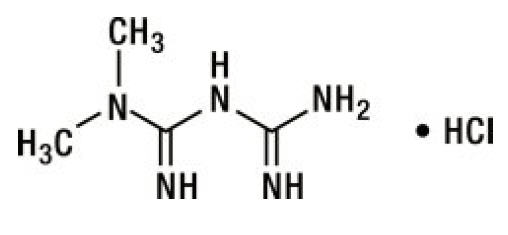
Metformin HCl ( N,N -dimethylimidodicarbonimidic diamide HCl) is a white to off-white crystalline compound with a molecular formula of C 4 H 11 N 5 • HCl and a molecular weight of 165.63. Metformin HCl is freely soluble in water, slightly soluble in alcohol, and is practically insoluble in acetone, ether, and chloroform. The pK a of metformin is 12.4. The pH of a 1% aqueous solution of metformin HCl is 6.68. The structural formula is:
KOMBIGLYZE XR
KOMBIGLYZE XR is available for oral administration as tablets containing either 5.58 mg saxagliptin HCl (anhydrous) equivalent to 5 mg saxagliptin and 500 mg metformin HCl (KOMBIGLYZE XR 5 mg/500 mg), or 5.58 mg saxagliptin HCl (anhydrous) equivalent to 5 mg saxagliptin and 1,000 mg metformin HCl (KOMBIGLYZE XR 5 mg/1,000 mg), or 2.79 mg saxagliptin HCl (anhydrous) equivalent to 2.5 mg saxagliptin and 1,000 mg metformin HCl (KOMBIGLYZE XR 2.5 mg/1,000 mg). Each film-coated tablet of KOMBIGLYZE XR contains the following inactive ingredients: carboxymethylcellulose sodium, hypromellose 2208, and magnesium stearate. The 5 mg/500 mg strength tablet of KOMBIGLYZE XR also contains microcrystalline cellulose and hypromellose 2910. In addition, the film coatings contain the following inactive ingredients: polyvinyl alcohol, polyethylene glycol 3350, titanium dioxide, talc, and iron oxides.
The biologically inert components of the tablet may occasionally remain intact during gastrointestinal transit and will be eliminated in the feces as a soft, hydrated mass.
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Mechanism of Action
KOMBIGLYZE XR
KOMBIGLYZE XR contains two antihyperglycemic medications: saxagliptin, a dipeptidyl-peptidase-4 (DPP4) inhibitor, and metformin HCl, a biguanide.
Saxagliptin
Increased concentrations of the incretin hormones such as glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) and glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP) are released into the bloodstream from the small intestine in response to meals. These hormones cause insulin release from the pancreatic beta cells in a glucose-dependent manner but are inactivated by the DPP4 enzyme within minutes. GLP-1 also lowers glucagon secretion from pancreatic alpha cells, reducing hepatic glucose production. In patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus, concentrations of GLP-1 are reduced but the insulin response to GLP-1 is preserved. Saxagliptin is a competitive DPP4 inhibitor that slows the inactivation of the incretin hormones, thereby increasing their bloodstream concentrations and reducing fasting and postprandial glucose concentrations in a glucose-dependent manner in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Metformin HCl
Metformin improves glucose tolerance in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus, lowering both basal and postprandial plasma glucose. Metformin decreases hepatic glucose production, decreases intestinal absorption of glucose, and improves insulin sensitivity by increasing peripheral glucose uptake and utilization. Unlike sulfonylureas, metformin does not produce hypoglycemia in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus or in healthy subjects except in unusual circumstances [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5) ] and does not cause hyperinsulinemia. With metformin therapy, insulin secretion remains unchanged while fasting insulin levels and day-long plasma insulin response may actually decrease.
Pharmacodynamics
Saxagliptin
In patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus, administration of saxagliptin inhibits DPP4 enzyme activity for a 24-hour period. After an oral glucose load or a meal, this DPP4 inhibition resulted in a 2- to 3-fold increase in circulating levels of active GLP-1 and GIP, decreased glucagon concentrations, and increased glucose-dependent insulin secretion from pancreatic beta cells. The rise in insulin and decrease in glucagon were associated with lower fasting glucose concentrations and reduced glucose excursion following an oral glucose load or a meal.
Cardiac Electrophysiology
Saxagliptin
In a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, 4-way crossover, active comparator trial using moxifloxacin in 40 healthy subjects, saxagliptin was not associated with clinically meaningful prolongation of the QTc interval or heart rate at daily doses up to 40 mg (8-times the MRHD).
Pharmacokinetics
KOMBIGLYZE XR
Bioequivalence and food effect of KOMBIGLYZE XR was characterized under low calorie diet. The low calorie diet consisted of 324 kcal with meal composition that contained 11.1% protein, 10.5% fat, and 78.4% carbohydrate. The results of bioequivalence studies in healthy subjects demonstrated that KOMBIGLYZE XR combination tablets are bioequivalent to coadministration of corresponding doses of saxagliptin (ONGLYZA) and metformin HCl extended-release as individual tablets under fed conditions.
Saxagliptin
The pharmacokinetics of saxagliptin and its active metabolite, 5-hydroxy saxagliptin were similar in healthy subjects and in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. The C max and AUC values of saxagliptin and its active metabolite increased proportionally in the 2.5 to 400 mg dose range. Following a 5 mg single oral dose of saxagliptin to healthy subjects, the mean plasma AUC values for saxagliptin and its active metabolite were 78 ng•h/mL and 214 ng•h/mL, respectively. The corresponding plasma C max values were 24 ng/mL and 47 ng/mL, respectively. The average variability (%CV) for AUC and C max for both saxagliptin and its active metabolite was less than 25%.
No appreciable accumulation of either saxagliptin or its active metabolite was observed with repeated once-daily dosing at any dose level. No dose- and time-dependence were observed in the clearance of saxagliptin and its active metabolite over 14 days of once-daily dosing with saxagliptin at doses ranging from 2.5 to 400 mg.
Metformin HCl
Metformin extended-release C max is achieved with a median value of 7 hours and a range of 4 to 8 hours. At steady state, the AUC and C max are less than dose proportional for metformin extended-release within the range of 500 to 2,000 mg. After repeated administration of metformin extended-release, metformin did not accumulate in plasma. Metformin is excreted unchanged in the urine and does not undergo hepatic metabolism. Peak plasma levels of metformin extended-release tablets are approximately 20% lower compared to the same dose of metformin immediate-release tablets, however, the extent of absorption (as measured by AUC) is similar between extended-release tablets and immediate-release tablets.
Absorption
Saxagliptin
The median time to maximum concentration (T max ) following the 5 mg once daily dose was 2 hours for saxagliptin and 4 hours for its active metabolite.
Metformin HCl
Following a single oral dose of metformin extended-release, C max is achieved with a median value of 7 hours and a range of 4 to 8 hours.
Effect of Food
Saxagliptin
Administration with a high-fat meal resulted in an increase in T max of saxagliptin by approximately 20 minutes as compared to fasted conditions. There was a 27% increase in the AUC of saxagliptin when given with a meal as compared to fasted conditions. Food has no significant effect on the pharmacokinetics of saxagliptin when administered as KOMBIGLYZE XR combination tablets.
Metformin HCl
Although the extent of metformin absorption (as measured by AUC) from the metformin extended-release tablet increased by approximately 50% when given with food, there was no effect of food on C max and T max of metformin. Both high and low fat meals had the same effect on the pharmacokinetics of metformin extended-release. Food has no significant effect on the pharmacokinetics of metformin when administered as KOMBIGLYZE XR combination tablets.
Distribution
Saxagliptin
The in vitro protein binding of saxagliptin and its active metabolite in human serum is negligible. Therefore, changes in blood protein levels in various disease states (e.g., renal or hepatic impairment) are not expected to alter the disposition of saxagliptin.
Metformin HCl
Distribution studies with extended-release metformin have not been conducted; however, the apparent volume of distribution (V/F) of metformin following single oral doses of immediate-release metformin 850 mg averaged 654 ± 358 L. Metformin is negligibly bound to plasma proteins, in contrast to sulfonylureas, which are more than 90% protein bound. Metformin partitions into erythrocytes, most likely as a function of time. Metformin is negligibly bound to plasma proteins and is, therefore, less likely to interact with highly protein-bound drugs such as salicylates, sulfonamides, chloramphenicol, and probenecid, as compared to the sulfonylureas, which are extensively bound to serum proteins.
Elimination
Metabolism
Saxagliptin
The metabolism of saxagliptin is primarily mediated by cytochrome P450 3A4/5 (CYP3A4/5). The major metabolite of saxagliptin is also a DPP4 inhibitor, which is one-half as potent as saxagliptin. Therefore, strong CYP3A4/5 inhibitors and inducers will alter the pharmacokinetics of saxagliptin and its active metabolite [ see Drug Interactions (7.1) ].
Metformin HCl
Intravenous single-dose studies in healthy subjects demonstrate that metformin is excreted unchanged in the urine and does not undergo hepatic metabolism (no metabolites have been identified in humans) or biliary excretion.
Metabolism studies with extended-release metformin tablets have not been conducted.
Excretion
Saxagliptin
Saxagliptin is eliminated by both renal and hepatic pathways. Following a single 50 mg dose of 14 C-saxagliptin, 24%, 36%, and 75% of the dose was excreted in the urine as saxagliptin, its active metabolite, and total radioactivity, respectively. The average renal clearance of saxagliptin (~230 mL/min) was greater than the average estimated glomerular filtration rate (~120 mL/min), suggesting some active renal excretion. A total of 22% of the administered radioactivity was recovered in feces representing the fraction of the saxagliptin dose excreted in bile and/or unabsorbed drug from the gastrointestinal tract. Following a single oral dose of saxagliptin 5 mg to healthy subjects, the mean plasma terminal half-life (t1/2) for saxagliptin and its active metabolite was 2.5 and 3.1 hours, respectively.
Metformin HCl
Renal clearance is approximately 3.5 times greater than creatinine clearance, which indicates that tubular secretion is the major route of metformin elimination. Following oral administration, approximately 90% of the absorbed drug is eliminated via the renal route within the first 24 hours, with a plasma elimination half-life of approximately 6.2 hours. In blood, the elimination half-life is approximately 17.6 hours, suggesting that the erythrocyte mass may be a compartment of distribution.
Specific Populations
Geriatric Patients
Saxagliptin
No dosage adjustment is recommended based on age alone. Elderly subjects (65-80 years) had 23% and 59% higher geometric mean C max and geometric mean AUC values, respectively, for saxagliptin than young subjects (18-40 years). Differences in active metabolite pharmacokinetics between elderly and young subjects generally reflected the differences observed in saxagliptin pharmacokinetics. The difference between the pharmacokinetics of saxagliptin and the active metabolite in young and elderly subjects is likely due to multiple factors including declining renal function and metabolic capacity with increasing age. Age was not identified as a significant covariate on the apparent clearance of saxagliptin and its active metabolite in the population pharmacokinetic analysis.
Metformin HCl
Limited data from controlled pharmacokinetic studies of metformin in healthy elderly subjects suggest that total plasma clearance of metformin is decreased, the half-life is prolonged, and C max is increased, compared to healthy young subjects. From these data, it appears that the change in metformin pharmacokinetics with aging is primarily accounted for by a change in renal function.
Male and Female Patients
Saxagliptin
No dosage adjustment is recommended based on gender. There were no differences observed in saxagliptin pharmacokinetics between males and females. Compared to males, females had approximately 25% higher exposure values for the active metabolite than males, but this difference is unlikely to be of clinical relevance. Gender was not identified as a significant covariate on the apparent clearance of saxagliptin and its active metabolite in the population pharmacokinetic analysis.
Metformin HCl
Metformin pharmacokinetic parameters did not differ significantly between healthy subjects and patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus when analyzed according to gender (males=19, females=16). Similarly, in controlled clinical studies in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus, the antihyperglycemic effect of metformin was comparable in males and females.
Racial or Ethnic Groups
Saxagliptin
No dosage adjustment is recommended based on race. The population pharmacokinetic analysis compared the pharmacokinetics of saxagliptin and its active metabolite in 309 White subjects with 105 subjects of other races (consisting of six racial groups). No significant difference in the pharmacokinetics of saxagliptin and its active metabolite were detected between these two populations.
Metformin HCl
No studies of metformin pharmacokinetic parameters according to race have been performed. In controlled clinical studies of metformin in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus, the antihyperglycemic effect was comparable in Whites (n=249), Black or African American (n=51), and Hispanic or Latino ethnicity (n=24).
Patients with Renal Impairment
Saxagliptin
A single-dose, open-label trial was conducted to evaluate the pharmacokinetics of saxagliptin (10 mg dose) in subjects with varying degrees of chronic renal impairment compared to subjects with normal renal function. The 10 mg dosage is not an approved dosage. The degree of renal impairment did not affect C max of saxagliptin or its metabolite. In subjects with moderate renal impairment with eGFR 30 to less than 45 mL/min/1.73 m 2 , severe renal impairment (eGFR 15 to less than 30 mL/min/1.73 m 2 ) and ESRD patient on hemodialysis, the AUC values of saxagliptin or its active metabolite were >2 fold higher than AUC values in subjects with normal renal function.
Metformin HCl
In patients with decreased renal function, the plasma and blood half-life of metformin is prolonged and the renal clearance is decreased [ see Contraindications (4) and Warnings and Precautions (5.1) ].
Patients with Hepatic Impairment
No pharmacokinetic studies of metformin have been conducted in patients with hepatic impairment.
Body Mass Index
Saxagliptin
No dosage adjustment is recommended based on body mass index (BMI) which was not identified as a significant covariate on the apparent clearance of saxagliptin or its active metabolite in the population pharmacokinetic analysis.
Drug Interaction Studies
Specific pharmacokinetic drug interaction studies with KOMBIGLYZE XR have not been performed, although such studies have been conducted with the individual saxagliptin and metformin components.
In Vitro Assessment of Drug Interactions
In in vitro studies, saxagliptin and its active metabolite did not inhibit CYP1A2, 2A6, 2B6, 2C9, 2C19, 2D6, 2E1, or 3A4, or induce CYP1A2, 2B6, 2C9, or 3A4. Therefore, saxagliptin is not expected to alter the metabolic clearance of coadministered drugs that are metabolized by these enzymes. Saxagliptin is a P-glycoprotein (P-gp) substrate, but is not a significant inhibitor or inducer of P-gp.
In Vivo Assessment of Drug Interactions
| Coadministered Drug | Dosage of Coadministered Drug Single dose unless otherwise noted. The 10 mg saxagliptin dose is not an approved dosage. | Dosage of Saxagliptin | Geometric Mean Ratio (ratio with/without coadministered drug) No Effect = 1.00 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AUC AUC = AUC(INF) for drugs given as single dose and AUC = AUC(TAU) for drugs given in multiple doses. | C max | ||||
No dosing adjustments required for the following: | |||||
Metformin | 1,000 mg | 100 mg | saxagliptin 5-hydroxy saxagliptin | 0.98 0.99 | 0.79 0.88 |
Glyburide | 5 mg | 10 mg | saxagliptin 5-hydroxy saxagliptin | 0.98 ND | 1.08 ND |
Pioglitazone Results exclude one patient. | 45 mg QD for 10 days | 10 mg QD for 5 days | saxagliptin 5-hydroxy saxagliptin | 1.11 ND | 1.11 ND |
Digoxin | 0.25 mg q6h first day followed by q12h second day followed by QD for 5 days | 10 mg QD for 7 days | saxagliptin 5-hydroxy saxagliptin | 1.05 1.06 | 0.99 1.02 |
Dapagliflozin | 10 mg single dose | 5 mg single dose | saxagliptin 5-hydroxy saxagliptin | ↓1% ↑9% | ↓7% ↑6% |
Simvastatin | 40 mg QD for 8 days | 10 mg QD for 4 days | saxagliptin 5-hydroxy saxagliptin | 1.12 1.02 | 1.21 1.08 |
Diltiazem | 360 mg LA QD for 9 days | 10 mg | saxagliptin 5-hydroxy saxagliptin | 2.09 0.66 | 1.63 0.57 |
Rifampin The plasma dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP4) activity inhibition over a 24-hour dose interval was not affected by rifampin. | 600 mg QD for 6 days | 5 mg | saxagliptin 5-hydroxy saxagliptin | 0.24 1.03 | 0.47 1.39 |
Omeprazole | 40 mg QD for 5 days | 10 mg | saxagliptin 5-hydroxy saxagliptin | 1.13 ND | 0.98 ND |
Aluminum hydroxide + magnesium hydroxide + simethicone | aluminum hydroxide: 2400 mg magnesium hydroxide: 2400 mg simethicone: 240 mg | 10 mg | saxagliptin 5-hydroxy saxagliptin | 0.97 ND | 0.74 ND |
Famotidine | 40 mg | 10 mg | saxagliptin 5-hydroxy saxagliptin | 1.03 ND | 1.14 ND |
Limit KOMBIGLYZE XR dose to 2.5 mg/1,000 mg once daily when coadministered with strong CYP3A4/5 inhibitors [ see Drug Interactions (7.1) and Dosage and Administration (2.2) ]: | |||||
Ketoconazole | 200 mg BID for 9 days | 100 mg | saxagliptin 5-hydroxy saxagliptin | 2.45 0.12 | 1.62 0.05 |
Ketoconazole | 200 mg BID for 7 days | 20 mg | saxagliptin 5-hydroxy saxagliptin | 3.67 ND | 2.44 ND |
ND=not determined; QD=once daily; q6h=every 6 hours; q12h=every 12 hours; BID=twice daily; LA=long acting.
| Coadministered Drug | Dosage of Coadministered Drug Single dose unless otherwise noted. The 10 mg saxagliptin dose is not an approved dosage. | Dosage of Saxagliptin | Geometric Mean Ratio (ratio with/without saxagliptin) No Effect = 1.00 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AUC AUC = AUC(INF) for drugs given as single dose and AUC = AUC(TAU) for drugs given in multiple doses. | C max | ||||
No dosing adjustments required for the following: | |||||
Metformin | 1000 mg | 100 mg | metformin | 1.20 | 1.09 |
Glyburide | 5 mg | 10 mg | glyburide | 1.06 | 1.16 |
Pioglitazone Results include all patients. | 45 mg QD for 10 days | 10 mg QD for 5 days | pioglitazone hydroxy-pioglitazone | 1.08 ND | 1.14 ND |
Digoxin | 0.25 mg q6h first day followed by q12h second day followed by QD for 5 days | 10 mg QD for 7 days | digoxin | 1.06 | 1.09 |
Simvastatin | 40 mg QD for 8 days | 10 mg QD for 4 days | simvastatin simvastatin acid | 1.04 1.16 | 0.88 1.00 |
Diltiazem | 360 mg LA QD for 9 days | 10 mg | diltiazem | 1.10 | 1.16 |
Ketoconazole | 200 mg BID for 9 days | 100 mg | ketoconazole | 0.87 | 0.84 |
Ethinyl estradiol and norgestimate | ethinyl estradiol 0.035 mg and norgestimate 0.250 mg for 21 days | 5 mg QD for 21 days | ethinyl estradiol norelgestromin norgestrel | 1.07 1.10 1.13 | 0.98 1.09 1.17 |
ND=not determined; QD=once daily; q6h=every 6 hours; q12h=every 12 hours; BID=twice daily; LA=long acting.
| Coadministered Drug | Dose of Coadministered Drug All metformin and coadministered drugs were given as single doses. | Dose of Metformin | Geometric Mean Ratio (ratio with/without coadministered drug) No Effect = 1.00 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AUC AUC = AUC(INF). | C max | ||||
No dosing adjustments required for the following: | |||||
Glyburide | 5 mg | 850 mg | metformin | 0.91 Ratio of arithmetic means. | 0.93 |
Furosemide | 40 mg | 850 mg | metformin | 1.09 | 1.22 |
Nifedipine | 10 mg | 850 mg | metformin | 1.16 | 1.21 |
Propranolol | 40 mg | 850 mg | metformin | 0.90 | 0.94 |
Ibuprofen | 400 mg | 850 mg | metformin | 1.05 | 1.07 |
Drugs that are eliminated by renal tubular secretion may increase the accumulation of metformin [ see Drug Interactions (7.3) ]. | |||||
Cimetidine | 400 mg | 850 mg | metformin | 1.40 | 1.61 |
| Coadministered Drug | Dose of Coadministered Drug All metformin and coadministered drugs were given as single doses. | Dose of Metformin | Geometric Mean Ratio (ratio with/without metformin) No Effect = 1.00 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AUC AUC = AUC(INF) unless otherwise noted. | C max | ||||
No dosing adjustments required for the following: | |||||
Glyburide | 5 mg | 850 mg | glyburide | 0.78 Ratio of arithmetic means, p-value of difference <0.05. | 0.63 |
Furosemide | 40 mg | 850 mg | furosemide | 0.87 | 0.69 |
Nifedipine | 10 mg | 850 mg | nifedipine | 1.10 AUC(0-24 hr) reported. | 1.08 |
Propranolol | 40 mg | 850 mg | propranolol | 1.01 | 1.02 |
Ibuprofen | 400 mg | 850 mg | ibuprofen | 0.97 Ratio of arithmetic means. | 1.01 |
Cimetidine | 400 mg | 850 mg | cimetidine | 0.95 | 1.01 |
NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
KOMBIGLYZE XR
No animal studies have been conducted with the combined products in KOMBIGLYZE XR to evaluate carcinogenesis, mutagenesis, or impairment of fertility. The following data are based on studies with saxagliptin and metformin administered individually.
Saxagliptin
Carcinogenesis
Carcinogenicity was evaluated in 2-year studies conducted in CD-1 mice and Sprague-Dawley rats. Saxagliptin did not increase the incidence of tumors in mice dosed orally at 50, 250, and 600 mg/kg up to 870-times (males) and 1165-times (females) the 5 mg/day clinical dose, based on AUC. Saxagliptin did not increase the incidence of tumors in rats dosed orally at 25, 75, 150, and 300 mg/kg up to 355-times (males) and 2217-times (females) the 5 mg/day clinical dose, based on AUC.
Mutagenesis
Saxagliptin was not mutagenic or clastogenic in a battery of genotoxicity tests (Ames bacterial mutagenesis, human and rat lymphocyte cytogenetics, rat bone marrow micronucleus and DNA repair assays). The active metabolite of saxagliptin was not mutagenic in an Ames bacterial assay.
Impairment of Fertility
Saxagliptin administered to rats had no effect on fertility or the ability to maintain a litter at exposures up to 603-times and 776-times the 5 mg clinical dose in males and females, based on AUC.
Metformin HCI
Carcinogenesis
Long-term carcinogenicity studies have been performed in rats (dosing duration of 104 weeks) and mice (dosing duration of 91 weeks) at doses up to and including 900 mg/kg/day and 1,500 mg/kg/day, respectively. These doses are both approximately 4 times the maximum recommended human daily dose of 2,000 mg based on body surface area comparisons. No evidence of carcinogenicity with metformin was found in either male or female mice. Similarly, there was no tumorigenic potential observed with metformin in male rats. There was, however, an increased incidence of benign stromal uterine polyps in female rats treated with 900 mg/kg/day.
Mutagenesis
There was no evidence of a mutagenic potential of metformin in the following in vitro tests: Ames test ( S. typhimurium ), gene mutation test (mouse lymphoma cells), or chromosomal aberrations test (human lymphocytes). Results in the in vivo mouse micronucleus test were also negative.
Impairment of Fertility
Fertility of male or female rats was unaffected by metformin when administered at doses as high as 600 mg/kg/day, which is approximately 3 times the maximum recommended human daily dose based on body surface area comparisons.
Animal Toxicology and/or Pharmacology
Saxagliptin
Saxagliptin produced adverse skin changes in the extremities of cynomolgus monkeys (scabs and/or ulceration of tail, digits, scrotum, and/or nose). Skin lesions were reversible within exposure approximately 20-times the 5 mg clinical dose, but in some cases were irreversible and necrotizing at higher exposures. Adverse skin changes were not observed at exposures similar to (1- to 3-times) the 5 mg clinical dose. Clinical correlates to skin lesions in monkeys have not been observed in human clinical trials of saxagliptin.
CLINICAL STUDIES
Glycemic Efficacy Trials
The effectiveness of KOMBIGLYZE XR has been established in clinical trials of coadministration of oral saxagliptin and metformin HCl immediate-release tablets in adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus inadequately controlled on metformin HCl alone and in treatment-naive patients inadequately controlled on diet and exercise alone. In these two trials, treatment with saxagliptin dosed in the morning plus metformin HCl immediate-release tablets at all doses produced statistically significant improvements in A1C, fasting plasma glucose (FPG), and 2-hour postprandial glucose (PPG) following a standard oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT), compared to control. Reductions in A1C were seen across subgroups including gender, age, race, and baseline BMI.
In these two trials, decrease in body weight in the treatment groups given saxagliptin in combination with metformin HCl immediate-release was similar to that in the groups given metformin HCl immediate-release alone. Saxagliptin plus metformin HCl immediate-release was not associated with significant changes from baseline in fasting serum lipids compared to metformin HCl alone.
The coadministration of saxagliptin and metformin HCl immediate-release tablets has also been evaluated in an active-controlled trial comparing add-on therapy with saxagliptin to glipizide in 858 patients inadequately controlled on metformin HCl alone, in a placebo-controlled trial where a subgroup of 314 patients inadequately controlled on insulin plus metformin HCl received add-on therapy with saxagliptin or placebo, a trial comparing saxagliptin to placebo in 257 patients inadequately controlled on metformin HCl plus a sulfonylurea, and a trial comparing saxagliptin to placebo in 315 patients inadequately controlled on dapagliflozin and metformin HCl.
In a 24-week, double-blind, randomized trial, patients treated with metformin HCl immediate-release 500 mg twice daily for at least 8 weeks were randomized to continued treatment with metformin HCl immediate-release 500 mg twice daily or to metformin HCl extended-release either 1,000 mg once daily or 1,500 mg once daily. The mean change in A1C from baseline to Week 24 was 0.1% (95% confidence interval 0%, 0.3%) for the metformin HCl immediate-release treatment arm, 0.3% (95% confidence interval 0.1%, 0.4%) for the 1,000 mg metformin HCl extended-release treatment arm, and 0.1% (95% confidence interval 0%, 0.3%) for the 1,500 mg metformin HCl extended-release treatment arm. Results of this trial suggest that patients receiving metformin HCl immediate-release treatment may be safely switched to metformin HCl extended-release once daily at the same total daily dose, up to 2,000 mg once daily. Following a switch from metformin HCl immediate-release to metformin HCl extended-release, glycemic control should be closely monitored and dosage adjustments made accordingly.
Saxagliptin Morning and Evening Dosing
A 24-week monotherapy trial was conducted to assess a range of dosing regimens for saxagliptin. Treatment-naive patients with inadequately controlled diabetes (A1C ≥7% to ≤10%) underwent a 2-week, single-blind diet, exercise, and placebo lead-in period. A total of 365 patients were randomized to 2.5 mg every morning, 5 mg every morning, 2.5 mg with possible titration to 5 mg every morning, or 5 mg every evening of saxagliptin, or placebo. Patients who failed to meet specific glycemic goals during the trial were treated with metformin HCI rescue therapy added on to placebo or saxagliptin; the number of patients randomized per treatment group ranged from 71 to 74.
Treatment with either saxagliptin 5 mg every morning or 5 mg every evening provided significant improvements in A1C versus placebo (mean placebo-corrected reductions of −0.4% and −0.3%, respectively).
Coadministration of Saxagliptin with Metformin HCI Immediate-Release in Treatment-Naive Patients
A total of 1306 treatment-naive patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus participated in this 24-week, randomized, double-blind, active-controlled trial to evaluate the efficacy and safety of saxagliptin coadministered with metformin HCl immediate-release in patients with inadequate glycemic control (A1C ≥8% to ≤12%) on diet and exercise alone. Patients were required to be treatment-naive to be enrolled in this trial.
Patients who met eligibility criteria were enrolled in a single-blind, 1-week, dietary and exercise placebo lead-in period. Patients were randomized to one of four treatment arms: saxagliptin 5 mg + metformin HCl immediate-release 500 mg, saxagliptin 10 mg + metformin HCl immediate-release 500 mg, saxagliptin 10 mg + placebo, or metformin HCl immediate-release 500 mg + placebo (the maximum recommended approved saxagliptin dose is 5 mg daily; the 10 mg daily dose of saxagliptin does not provide greater efficacy than the 5 mg daily dose and the 10 mg saxagliptin dosage is not an approved dosage). Saxagliptin was dosed once daily. In the 3 treatment groups using metformin HCl immediate-release, the metformin HCl dose was up-titrated weekly in 500 mg per day increments, as tolerated, to a maximum of 2,000 mg per day based on FPG. Patients who failed to meet specific glycemic goals during this trial were treated with pioglitazone rescue as add-on therapy.
Coadministration of saxagliptin 5 mg plus metformin HCl immediate-release provided significant improvements in A1C, FPG, and PPG compared with placebo plus metformin HCl immediate-release (Table 7).
| Efficacy Parameter | Saxagliptin 5 mg + Metformin HCI N=320 | Placebo + Metformin HCI N=328 |
|---|---|---|
Hemoglobin A1C (%) | N=306 | N=313 |
Baseline (mean) | 9.4 | 9.4 |
Change from baseline (adjusted mean Least squares mean adjusted for baseline value. ) | −2.5 | −2.0 |
Difference from placebo + metformin HCI (adjusted mean) | −0.5 p-value <0.0001 compared to placebo + metformin HCI. | |
95% Confidence Interval | (−0.7, −0.4) | |
Percent of patients achieving A1C <7% | 60% p-value <0.05 compared to placebo + metformin HCI. (185/307) | 41% (129/314) |
Fasting Plasma Glucose (mg/dL) | N=315 | N=320 |
Baseline (mean) | 199 | 199 |
Change from baseline (adjusted mean) | −60 | −47 |
Difference from placebo + metformin HCI (adjusted mean) | −13 | |
95% Confidence Interval | (−19, −6) | |
2-hour Postprandial Glucose (mg/dL) | N=146 | N=141 |
Baseline (mean) | 340 | 355 |
Change from baseline (adjusted mean) | −138 | −97 |
Difference from placebo + metformin HCI (adjusted mean) | −41 | |
95% Confidence Interval | (−57, −25) |
Addition of Saxagliptin to Metformin HCI Immediate-Release
A total of 743 patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus participated in this 24-week, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial to evaluate the efficacy and safety of saxagliptin in combination with metformin HCl immediate-release in patients with inadequate glycemic control (A1C ≥7% and ≤10%) on metformin HCl alone. To qualify for enrollment, patients were required to be on a stable dose of metformin HCl (1,500-2,550 mg daily) for at least 8 weeks.
Patients who met eligibility criteria were enrolled in a single-blind, 2-week, dietary and exercise placebo lead-in period during which patients received metformin HCl immediate-release at their pre-trial dose, up to 2500 mg daily, for the duration of the trial. Following the lead-in period, eligible patients were randomized to 2.5 mg, 5 mg, or 10 mg of saxagliptin or placebo in addition to their current dose of open-label metformin HCl immediate-release (the maximum recommended approved saxagliptin dose is 5 mg daily; the 10 mg daily dose of saxagliptin does not provide greater efficacy than the 5 mg daily dose and the 10 mg dosage is not an approved dosage). Patients who failed to meet specific glycemic goals during the trial were treated with pioglitazone rescue therapy, added on to existing trial medications. Dose titrations of saxagliptin and metformin HCl immediate-release were not permitted.
Saxagliptin 2.5 mg and 5 mg add-on to metformin HCl immediate-release provided significant improvements in A1C, FPG, and PPG compared with placebo add-on to metformin HCl immediate-release (Table 8). Mean changes from baseline for A1C over time and at endpoint are shown in Figure 1. The proportion of patients who discontinued for lack of glycemic control or who were rescued for meeting prespecified glycemic criteria was 15% in the saxagliptin 2.5 mg add-on to metformin HCl immediate-release group, 13% in the saxagliptin 5 mg add-on to metformin HCl immediate-release group, and 27% in the placebo add-on to metformin HCl immediate-release group.
| Efficacy Parameter | Saxagliptin 2.5 mg + Metformin HCI N=192 | Saxagliptin 5 mg + Metformin HCI N=191 | Placebo + Metformin HCI N=179 |
|---|---|---|---|
Hemoglobin A1C (%) | N=186 | N=186 | N=175 |
Baseline (mean) | 8.1 | 8.1 | 8.1 |
Change from baseline (adjusted mean Least squares mean adjusted for baseline value. ) | −0.6 | −0.7 | +0.1 |
Difference from placebo (adjusted mean) | −0.7 p-value <0.0001 compared to placebo + metformin HCI. | −0.8 | |
95% Confidence Interval | (−0.9, −0.5) | (−1.0, −0.6) | |
Percent of patients achieving A1C <7% | 37% p-value <0.05 compared to placebo + metformin HCI. (69/186) | 44%(81/186) | 17% (29/175) |
Fasting Plasma Glucose (mg/dL) | N=188 | N=187 | N=176 |
Baseline (mean) | 174 | 179 | 175 |
Change from baseline (adjusted mean) | −14 | −22 | +1 |
Difference from placebo (adjusted mean) | −16 | −23 | |
95% Confidence Interval | (−23, −9) | (−30, −16) | |
2-hour Postprandial Glucose (mg/dL) | N=155 | N=155 | N=135 |
Baseline (mean) | 294 | 296 | 295 |
Change from baseline (adjusted mean) | −62 | −58 | −18 |
Difference from placebo (adjusted mean) | −44 | −40 | |
95% Confidence Interval | (−60, −27) | (−56, −24) |
Figure 1: Mean Change from Baseline in A1C in a Placebo-Controlled Trial of Saxagliptin as Add-On Combination Therapy with Metformin HCI Immediate-Release•
| • Includes patients with a baseline and week 24 value. |
| Week 24 (LOCF) includes intent-to-treat population using last observation on trial prior to pioglitazone rescue therapy for patients needing rescue. Mean change from baseline is adjusted for baseline value. |
 |
Saxagliptin Add-On Combination Therapy with Metformin HCI Immediate-Release versus Glipizide Add-On Combination Therapy with Metformin HCI Immediate-Release
In this 52-week, active-controlled trial, a total of 858 patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and inadequate glycemic control (A1C >6.5% and ≤10%) on metformin HCl immediate-release alone were randomized to double-blind add-on therapy with saxagliptin or glipizide. Patients were required to be on a stable dose of metformin HCl immediate-release (at least 1,500 mg daily) for at least 8 weeks prior to enrollment.
Patients who met eligibility criteria were enrolled in a single-blind, 2-week, dietary and exercise placebo lead-in period during which patients received metformin HCl immediate-release (1,500-3,000 mg based on their pre-trial dose). Following the lead-in period, eligible patients were randomized to 5 mg of saxagliptin or 5 mg of glipizide in addition to their current dose of open-label metformin HCl immediate-release. Patients in the glipizide plus metformin HCl immediate-release group underwent blinded titration of the glipizide dose during the first 18 weeks of the trial up to a maximum glipizide dose of 20 mg per day. Titration was based on a goal FPG ≤110 mg/dL or the highest tolerable glipizide dose. Fifty percent (50%) of the glipizide-treated patients were titrated to the 20-mg daily dose; 21% of the glipizide-treated patients had a final daily glipizide dose of 5 mg or less. The mean final daily dose of glipizide was 15 mg.
After 52 weeks of treatment, saxagliptin and glipizide resulted in similar mean reductions from baseline in A1C when added to metformin HCl immediate-release therapy (Table 9). This conclusion may be limited to patients with baseline A1C comparable to those in the trial (91% of patients had baseline A1C <9%). From a baseline mean body weight of 89 kg, there was a statistically significant mean reduction of 1.1 kg in patients treated with saxagliptin compared to a mean weight gain of 1.1 kg in patients treated with glipizide (p<0.0001).
From a baseline mean body weight of 89 kg, there was a statistically significant mean reduction of 1.1 kg in patients treated with saxagliptin compared to a mean weight gain of 1.1 kg in patients treated with glipizide (p<0.0001).
| Efficacy Parameter | Saxagliptin 5 mg + Metformin HCI N=428 | Titrated Glipizide + Metformin HCI N=430 |
|---|---|---|
Hemoglobin A1C (%) | N=423 | N=423 |
Baseline (mean) | 7.7 | 7.6 |
Change from baseline (adjusted mean Least squares mean adjusted for baseline value. ) | −0.6 | −0.7 |
Difference from glipizide + metformin HCI (adjusted mean) | 0.1 | |
95% Confidence Interval | (−0.02, 0.2) Saxagliptin + metformin HCI is considered non-inferior to glipizide + metformin because the upper limit of this confidence interval is less than the prespecified non-inferiority margin of 0.35%. | |
Fasting Plasma Glucose (mg/dL) | N=420 | N=420 |
Baseline (mean) | 162 | 161 |
Change from baseline (adjusted mean) | −9 | −16 |
Difference from glipizide + metformin HCI (adjusted mean) | 6 | |
95% Confidence Interval | (2, 11) Significance not tested. |
Saxagliptin Add-On Combination Therapy with Insulin (with or without Metformin Immediate-Release)
A total of 455 patients with type 2 diabetes participated in this 24-week, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial to evaluate the efficacy and safety of saxagliptin in combination with insulin in patients with inadequate glycemic control (A1C ≥7.5% and ≤11%) on insulin alone (N=141) or on insulin in combination with a stable dose of metformin immediate-release (N=314). Patients were required to be on a stable dose of insulin (≥30 units to ≤150 units daily) with ≤20% variation in total daily dose for ≥8 weeks prior to screening. Patients entered the trial on intermediate- or long-acting (basal) insulin or premixed insulin. Patients using short-acting insulins were excluded unless the short-acting insulin was administered as part of a premixed insulin.
Patients who met eligibility criteria were enrolled in a single-blind, four-week, dietary and exercise placebo lead-in period during which patients received insulin (and metformin immediate-release if applicable) at their pretrial dose(s). Following the lead-in period, eligible patients were randomized to add-on therapy with either saxagliptin 5 mg or placebo. Doses of the antidiabetic therapies were to remain stable but patients were rescued and allowed to adjust the insulin regimen if specific glycemic goals were not met or if the investigator learned that the patient had self-increased the insulin dose by >20%. Data after rescue were excluded from the primary efficacy analyses.
Add-on therapy with saxagliptin 5 mg provided significant improvements from baseline to Week 24 in A1C and PPG compared with add-on placebo (Table 10). Similar mean reductions in A1C versus placebo were observed for patients using saxagliptin 5 mg add-on to insulin alone and saxagliptin 5 mg add-on to insulin in combination with metformin immediate-release (−0.4% and −0.4%, respectively). The percentage of patients who discontinued for lack of glycemic control or who were rescued was 23% in the saxagliptin group and 32% in the placebo group.
The mean daily insulin dose at baseline was 53 units in patients treated with saxagliptin 5 mg and 55 units in patients treated with placebo. The mean change from baseline in daily dose of insulin was 2 units for the saxagliptin 5 mg group and 5 units for the placebo group.
| Efficacy Parameter | Saxagliptin 5 mg + Insulin (+/− Metformin HCI) N=304 | Placebo + Insulin (+/− Metformin HCI) N=151 |
|---|---|---|
Hemoglobin A1C (%) | N=300 | N=149 |
Baseline (mean) | 8.7 | 8.7 |
Change from baseline (adjusted mean Least squares mean adjusted for baseline value and metformin HCI use at baseline. ) | −0.7 | −0.3 |
Difference from placebo (adjusted mean) | −0.4 p-value <0.0001 compared to placebo + insulin. | |
95% Confidence Interval | (−0.6, −0.2) | |
2-hour Postprandial Glucose (mg/dL) | N=262 | N=129 |
Baseline (mean) | 251 | 255 |
Change from baseline (adjusted mean) | −27 | −4 |
Difference from placebo (adjusted mean) | −23 p-value <0.05 compared to placebo + insulin. | |
95% Confidence Interval | (−37, −9) |
The change in fasting plasma glucose from baseline to Week 24 was also tested, but was not statistically significant. The percent of patients achieving an A1C <7% was 17% (52/300) with saxagliptin in combination with insulin compared to 7% (10/149) with placebo. Significance was not tested.
Saxagliptin Add-On Combination Therapy with Metformin HCI plus Sulfonylurea
A total of 257 patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus participated in this 24-week, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial to evaluate the efficacy and safety of saxagliptin in combination with metformin HCl plus a sulfonylurea in patients with inadequate glycemic control (A1C ≥7% and ≤10%). Patients were to be on a stable combined dose of metformin HCl extended-release or immediate-release (at maximum tolerated dose, with minimum dose for enrollment being 1,500 mg) and a sulfonylurea (at maximum tolerated dose, with minimum dose for enrollment being ≥50% of the maximum recommended dose) for 8 weeks prior to enrollment.
Patients who met eligibility criteria were entered in a 2-week enrollment period to allow assessment of inclusion/exclusion criteria. Following the 2-week enrollment period, eligible patients were randomized to either double-blind saxagliptin (5 mg once daily) or double-blind matching placebo for 24 weeks. During the 24-week double-blind treatment period, patients were to receive metformin HCl and a sulfonylurea at the same constant dose ascertained during enrollment. Sulfonylurea dose could be down titrated once in the case of a major hypoglycemic event or recurring minor hypoglycemic events. In the absence of hypoglycemia, titration (up or down) of trial medication during the treatment period was prohibited.
Saxagliptin in combination with metformin HCl plus a sulfonylurea provided significant improvements in A1C and PPG compared with placebo in combination with metformin HCl plus a sulfonylurea (Table 11). The percentage of patients who discontinued for lack of glycemic control was 6% in the saxagliptin group and 5% in the placebo group.
| Efficacy Parameter | Saxagliptin 5 mg + Metformin plus Sulfonylurea N=129 | Placebo + Metformin plus Sulfonylurea N=128 |
|---|---|---|
Hemoglobin A1C (%) | N=127 | N=127 |
Baseline (mean) | 8.4 | 8.2 |
Change from baseline (adjusted mean Least squares mean adjusted for baseline value. ) | −0.7 | −0.1 |
Difference from placebo (adjusted mean) | −0.7 p-value <0.0001 compared to placebo + metformin HCI plus sulfonylurea. | |
95% Confidence Interval | (−0.9, −0.5) | |
2-hour Postprandial Glucose (mg/dL) | N=115 | N=113 |
Baseline (mean) | 268 | 262 |
Change from baseline (adjusted mean) | −12 | 5 |
Difference from placebo (adjusted mean) | −17 p-value <0.05 compared to placebo + metformin HCI plus sulfonylurea. | |
95% Confidence Interval | (−32, −2) |
The change in fasting plasma glucose from baseline to Week 24 was also tested, but was not statistically significant. The percent of patients achieving an A1C <7% was 31% (39/127) with saxagliptin in combination with metformin HCI plus a sulfonylurea compared to 9% (12/127) with placebo. Significance was not tested.
Saxagliptin Add-on Combination Therapy with Metformin plus an SGLT2 Inhibitor
A total of 315 patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus participated in this 24 week randomized, double blind, placebo controlled trial to evaluate the efficacy and safety of saxagliptin added to dapagliflozin (an SGLT2 inhibitor) and metformin HCl in patients with a baseline of HbA1c ≥7% to ≤10.5%. The mean age of these patients was 54.6 years, 1.6% were 75 years or older and 52.7% were female. The population was 87.9% White, 6.3% Black or African American, 4.1% Asian, and 1.6% other races. At baseline the population had diabetes for an average of 7.7 years and a mean HbA1c of 7.9%. The mean eGFR at baseline was 93.4 mL/min/1.73 m 2 . Patients were required to be on a stable dose of metformin HCl (≥1,500 mg per day) for at least 8 weeks prior to enrollment. Eligible patients who completed the screening period entered the lead in treatment period, which included 16 weeks of open-label metformin HCl and 10 mg dapagliflozin treatment. Following the lead-in period, eligible patients were randomized to saxagliptin 5 mg (N=153) or placebo (N =162).
The group treated with add-on saxagliptin had statistically significant greater reductions in HbA1c from baseline versus the group treated with placebo (see Table 12).
Saxagliptin 5 mg (N=153) Number of randomized and treated patients. | Placebo (N=162) | |
In combination with Dapagliflozin and Metformin HCI | ||
Hemoglobin A1C (%) Analysis of Covariance including all post-baseline data regardless of rescue or treatment discontinuation. Model estimates calculated using multiple imputation to model washout of the treatment effect using placebo data for all patients having missing Week 24 data. | ||
Baseline (mean) | 8.0 | 7.9 |
Change from baseline (adjusted mean Least squares mean adjusted for baseline value. )
| −0.5 (−0.6, −0.4) | −0.2 (−0.3, −0.1) |
Difference from placebo (adjusted mean)
| −0.4 p-value <0.0001. (−0.5, −0.2) | |
The known proportion of patients achieving HbA1c <7% at Week 24 was 35.3% in the saxagliptin-treated group compared to 23.1% in the placebo-treated group.
Cardiovascular Safety Trial
The cardiovascular risk of saxagliptin was evaluated in SAVOR, a multicenter, multinational, randomized, double-blind trial comparing saxagliptin (N=8280) to placebo (N=8212), both administered in combination with standard of care, in adult patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus at high risk for atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. Of the randomized trial patients, 97.5% completed the trial, and the median duration of follow-up was approximately 2 years. The trial was event-driven, and patients were followed until a sufficient number of events were accrued.
Patients were at least 40 years of age, had A1C ≥6.5%, and multiple risk factors (21% of randomized patients) for cardiovascular disease (age ≥55 years for men and ≥60 years for women plus at least one additional risk factor of dyslipidemia, hypertension, or current cigarette smoking) or established (79% of the randomized patients) cardiovascular disease defined as a history of ischemic heart disease, peripheral vascular disease, or ischemic stroke. The majority of patients were male (67%) and White (75%) with a mean age of 65 years. Approximately 16% of the population had moderate (estimated glomerular filtration rate [eGFR] ≥30 to ≤50 mL/min) to severe (eGFR <30 mL/min) renal impairment, and 13% had a prior history of heart failure. Patients had a median duration of type 2 diabetes mellitus of approximately 10 years, and a mean baseline A1C level of 8.0%. Approximately 5% of patients were treated with diet and exercise only at baseline. Overall, the use of diabetes medications was balanced across treatment groups (metformin 69%, insulin 41%, sulfonylureas 40%, and TZDs 6%). The use of cardiovascular disease medications was also balanced (angiotensin-converting enzyme [ACE] inhibitors or angiotensin receptor blockers [ARBs] 79%, statins 78%, aspirin 75%, beta-blockers 62%, and non-aspirin antiplatelet medications 24%).
The primary analysis in SAVOR was time to first occurrence of a Major Adverse Cardiac Event (MACE). A major adverse cardiac event in SAVOR was defined as a cardiovascular death, or a nonfatal myocardial infarction (MI) or a nonfatal ischemic stroke. The trial was designed as a non-inferiority trial with a pre-specified risk margin of 1.3 for the hazard ratio of MACE, and was also powered for a superiority comparison if non-inferiority was demonstrated.
The results of SAVOR, including the contribution of each component to the primary composite endpoint are shown in Table 13. The incidence rate of MACE was similar in both treatment arms: 3.8 MACE per 100 patient-years on placebo vs. 3.8 MACE per 100 patient-years on saxagliptin. The estimated hazard ratio of MACE associated with saxagliptin relative to placebo was 1.00 with a 95.1% confidence interval of (0.89, 1.12). The upper bound of this confidence interval, 1.12, excluded a risk margin larger than 1.3.
|
|
| ||
Number of Patients (%) | Rate per 100 PY | Number of Patients (%) | Rate per 100 PY | (95.1% CI) |
Composite of first event of CV death, non-fatal MI or non-fatal ischemic stroke (MACE) | N=8280 | Total PY = 16308.8 | N=8212 | Total PY = 16156.0 |
613 (7.4) | 3.8 | 609 (7.4) | 3.8 | 1.00 (0.89, 1.12) |
CV death | 245 (3.0) | 1.5 | 234 (2.8) | 1.4 |
Non-fatal MI | 233 (2.8) | 1.4 | 260 (3.2) | 1.6 |
Non-fatal ischemic stroke | 135 (1.6) | 0.8 | 115 (1.4) | 0.7 |
The Kaplan-Meier-based cumulative event probability is presented in Figure 2 for time to first occurrence of the primary MACE composite endpoint by treatment arm. The curves for both saxagliptin and placebo arms are close together throughout the duration of the trial. The estimated cumulative event probability is approximately linear for both arms, indicating that the incidence of MACE for both arms was constant over the trial duration.
Vital status was obtained for 99% of patients in the trial. There were 798 deaths in the SAVOR trial. Numerically more patients (5.1%) died in the saxagliptin group than in the placebo group (4.6%). The risk of deaths from all cause (Table 14) was not statistically different between the treatment groups (HR: 1.11; 95.1% CI: 0.96, 1.27).
Saxagliptin | Placebo | Hazard Ratio | |||
Number of Patients (%) | Rate per 100 PY | Number of Patients (%) | Rate per 100 PY | (95.1% CI) | |
N=8280 | PY=16645.3 | N=8212 |
| ||
All-cause mortality | 420 (5.1) | 2.5 | 378 (4.6) | 2.3 | 1.11 (0.96, 1.27) |
CV death | 269 (3.2) | 1.6 | 260 (3.2) | 1.6 | |
Non-CV death | 151 (1.8) | 0.9 | 118 (1.4) | 0.7 | |
HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
How Supplied
KOMBIGLYZE ® XR (saxagliptin and metformin HCl extended-release) tablets have markings on both sides and are available in the strengths and packages listed in Table 15.
| Tablet Strength (saxagliptin and metformin HCl extended-release) | Film-Coated Tablet Color/Shape | Tablet Markings | Package Size | NDC Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
5 mg/500 mg | light brown to brown, biconvex, capsule-shaped | “5/500” on one side and “4221” on the reverse, in blue ink | Bottles of 30 | 0310-6135-30 |
5 mg/1,000 mg | pink, biconvex, capsule-shaped | “5/1000” on one side and “4223” on the reverse, in blue ink | Bottles of 30 | 0310-6145-30 |
2.5 mg/1,000 mg | pale yellow to light yellow, biconvex, capsule-shaped | “2.5/1000” on one side and “4222” on the reverse, in blue ink | Bottles of 60 | 0310-6125-60 |
Storage and Handling
Store at 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F); excursions permitted between 15°C and 30°C (59°F and 86°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature].
Mechanism of Action
KOMBIGLYZE XR
KOMBIGLYZE XR contains two antihyperglycemic medications: saxagliptin, a dipeptidyl-peptidase-4 (DPP4) inhibitor, and metformin HCl, a biguanide.
Saxagliptin
Increased concentrations of the incretin hormones such as glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) and glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP) are released into the bloodstream from the small intestine in response to meals. These hormones cause insulin release from the pancreatic beta cells in a glucose-dependent manner but are inactivated by the DPP4 enzyme within minutes. GLP-1 also lowers glucagon secretion from pancreatic alpha cells, reducing hepatic glucose production. In patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus, concentrations of GLP-1 are reduced but the insulin response to GLP-1 is preserved. Saxagliptin is a competitive DPP4 inhibitor that slows the inactivation of the incretin hormones, thereby increasing their bloodstream concentrations and reducing fasting and postprandial glucose concentrations in a glucose-dependent manner in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Metformin HCl
Metformin improves glucose tolerance in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus, lowering both basal and postprandial plasma glucose. Metformin decreases hepatic glucose production, decreases intestinal absorption of glucose, and improves insulin sensitivity by increasing peripheral glucose uptake and utilization. Unlike sulfonylureas, metformin does not produce hypoglycemia in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus or in healthy subjects except in unusual circumstances [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5) ] and does not cause hyperinsulinemia. With metformin therapy, insulin secretion remains unchanged while fasting insulin levels and day-long plasma insulin response may actually decrease.