Latisse prior authorization resources
Most recent state uniform prior authorization forms
Latisse patient education
Patient toolkit
Dosage & administration
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Ensure the face is clean, makeup and contact lenses are removed. Once nightly, place one drop of LATISSE ® (bimatoprost ophthalmic solution) 0.03% on the disposable sterile applicator supplied with the package and apply evenly along the skin of the upper eyelid margin at the base of the eyelashes. The upper lid margin in the area of lash growth should feel lightly moist without runoff. Blot any excess solution runoff outside the upper eyelid margin with a tissue or other absorbent cloth. Dispose of the applicator after one use. Repeat for the opposite eyelid margin using a new sterile applicator.
Do not reuse applicators and do not use any other brush/applicator to apply LATISSE ® .
Do not apply to the lower eyelash line [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3 , 5.4 ) and Patient Counseling Information (17) ] .
Additional applications of LATISSE ® will not increase the growth of eyelashes.
Upon discontinuation of treatment, eyelash growth is expected to return to its pre-treatment level.

By using PrescriberAI, you agree to the AI Terms of Use.
Latisse prescribing information
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
LATISSE ® (bimatoprost ophthalmic solution) 0.03% is indicated to treat hypotrichosis of the eyelashes by increasing their growth including length, thickness and darkness.
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Ensure the face is clean, makeup and contact lenses are removed. Once nightly, place one drop of LATISSE ® (bimatoprost ophthalmic solution) 0.03% on the disposable sterile applicator supplied with the package and apply evenly along the skin of the upper eyelid margin at the base of the eyelashes. The upper lid margin in the area of lash growth should feel lightly moist without runoff. Blot any excess solution runoff outside the upper eyelid margin with a tissue or other absorbent cloth. Dispose of the applicator after one use. Repeat for the opposite eyelid margin using a new sterile applicator.
Do not reuse applicators and do not use any other brush/applicator to apply LATISSE ® .
Do not apply to the lower eyelash line [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3 , 5.4 ) and Patient Counseling Information (17) ] .
Additional applications of LATISSE ® will not increase the growth of eyelashes.
Upon discontinuation of treatment, eyelash growth is expected to return to its pre-treatment level.
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Ophthalmic solution containing bimatoprost 0.3 mg/mL.
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
There are no adequate and well-controlled studies of LATISSE ® (bimatoprost ophthalmic solution) 0.03% administration in pregnant women. There is no increase in the risk of major birth defects or miscarriages based on bimatoprost postmarketing experience.
In embryofetal development studies, administration of bimatoprost to pregnant mice and rats during organogenesis resulted in abortion and early delivery at oral doses at least 33 times (mice) or 94 times (rats) the human exposure following topical ophthalmic administration of bimatoprost 0.03% to the cornea or conjunctival sac bilaterally once daily, based on the area under the curve (AUC). These adverse effects were not observed at 2.6 times (mice) and 47 times (rats) the human exposure following topical ophthalmic administration of bimatoprost 0.03% to the cornea or conjunctival sac bilaterally once daily, based on AUC.
In pre/postnatal development studies, administration of bimatoprost to pregnant rats from organogenesis to the end of lactation resulted in reduced gestation length and fetal body weight, and increased fetal and pup mortality at oral doses at least 41 times the human systemic exposure following topical ophthalmic administration of bimatoprost 0.03% to the cornea or conjunctival sac bilaterally once daily, based on AUC. No adverse effects were observed in rat offspring at exposures estimated at 14 times the human exposure following topical ophthalmic administration of bimatoprost 0.03% to the cornea or conjunctival sac bilaterally once daily, based on AUC.
Because animal reproductive studies are not always predictive of human response LATISSE ® 0.03% should be administered during pregnancy only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the fetus.
Data
Animal Data
In an embryofetal development rat study, abortion was observed in pregnant rats administered bimatoprost orally during organogenesis at 0.6 mg/kg/day (94 times the human systemic exposure following topical ophthalmic administration of bimatoprost 0.03% to the cornea or conjunctival sac bilaterally once daily, based on AUC). The No Observed Adverse Effect Level (NOAEL) for abortion was 0.3 mg/kg/day (estimated at 47 times the human systemic exposure following topical ophthalmic administration of bimatoprost 0.03% to the cornea or conjunctival sac bilaterally once daily based on AUC). No abnormalities were observed in rat fetuses at doses up to 0.6 mg/kg/day.
In an embryofetal development mouse study, abortion and early delivery were observed in pregnant mice administered bimatoprost orally during organogenesis at doses greater than or equal to 0.3 mg/kg/day (33 times the human systemic exposure following topical ophthalmic administration of bimatoprost 0.03% to the cornea or conjunctival sac bilaterally once daily, based on AUC). The NOAEL for abortion and early delivery was 0.1 mg/kg/day (2.6 times the human systemic exposure following topical ophthalmic administration of bimatoprost 0.03% to the cornea or conjunctival sac bilaterally once daily, based on AUC). No abnormalities were observed in mouse fetuses at doses up to 0.6 mg/kg/day (72 times the human systemic exposure following topical ophthalmic administration of bimatoprost 0.03% to the cornea or conjunctival sac bilaterally once daily, based on AUC).
In a pre/postnatal development study, treatment of pregnant rats with bimatoprost orally from gestation day 7 to lactation day 20 resulted in reduced gestation length, increased late resorptions, fetal deaths, and postnatal pup mortality, and reduced pup body weight at doses greater than or equal to 0.3 mg/kg/day. These effects were observed at exposures at least 41 times the human systemic exposure following topical ophthalmic administration of bimatoprost 0.03% to the cornea or conjunctival sac bilaterally once daily, based on AUC. The NOAEL for postnatal development and mating performance of the offspring was 0.1 mg/kg/day (estimated at 14 times the human systemic exposure following topical ophthalmic administration of bimatoprost 0.03% to the cornea or conjunctival sac bilaterally once daily, based on AUC).
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
It is not known whether topical ocular treatment with LATISSE ® 0.03% could result in sufficient systemic absorption to produce detectable quantities in human milk. In animal studies, bimatoprost has been shown to be present in breast milk of lactating rats at an intravenous dose (i.e., 1 mg/kg) 324 times the recommended human ophthalmic dose (on a mg/m 2 basis), however no animal data is available at clinically relevant doses.
The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother’s clinical need for LATISSE ® 0.03% and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed child from LATISSE ® 0.03%.
8.4 Pediatric Use
Use of LATISSE ® was evaluated in a sixteen-week double-masked, randomized, vehicle-controlled study conducted in pediatric patients who were post-chemotherapy or had alopecia areata, and adolescents who had hypotrichosis with no associated medical condition. No new safety issues were observed. The results of the Global Eyelash Assessment (GEA) are provided in Table 1.
| Age Range (years) | LATISSE ® | Vehicle | Difference (95% CI) | |
| Adolescents with hypotrichosis (N=40) | 15 - 17 | 19/26 (73%) | 1/14 (7%) | 66% (44%, 88%) |
| Post Chemotherapy Pediatric Patients (N=16) | 5 - 17 | 11/13 (85%) | 3/3 (100%) | -15% (-35%, 4%) |
| Alopecia Areata Pediatric Patients (N=15) | 5 - 17 | 4/9 (44%) | 2/6 (33%) | 11% (-39%, 61%) |
8.5 Geriatric Use
No overall clinical differences in safety or effectiveness have been observed between elderly and other adult patients.
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
LATISSE ® is contraindicated in patients with hypersensitivity to bimatoprost or to any of the ingredients [ see Adverse Reactions (6.2) ].
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- Concurrent administration of LATISSE ® and intraocular pressure (IOP)-lowering prostaglandin analogs in ocular hypertensive patients may decrease the IOP-lowering effect. Patients using these products concomitantly should be closely monitored for changes to their IOP. (5.1 )
- Pigmentation of the eyelids and iris may occur. Iris pigmentation is likely to be permanent. (5.2 , 5.3 )
5.1 Effects on Intraocular Pressure
Bimatoprost ophthalmic solution ( LUMIGAN ® ) lowers intraocular pressure (IOP) when instilled directly to the eye in patients with elevated IOP. In clinical trials, in patients with or without elevated IOP, LATISSE ® lowered IOP, however, the magnitude of the reduction was not cause for clinical concern.
In ocular hypertension studies with LUMIGAN ® , it has been shown that exposure of the eye to more than one dose of bimatoprost daily may decrease the intraocular pressure lowering effect. In patients using LUMIGAN ® or other prostaglandin analogs for the treatment of elevated intraocular pressure, the concomitant use of LATISSE ® may interfere with the desired reduction in IOP. Patients using prostaglandin analogs including LUMIGAN ® for IOP reduction should only use LATISSE ® after consulting with their physician and should be monitored for changes to their intraocular pressure.
5.2 Iris Pigmentation
Increased iris pigmentation has occurred when bimatoprost solution was administered. Patients should be advised about the potential for increased brown iris pigmentation which is likely to be permanent [see Adverse Reactions (6.2) ] .
The pigmentation change is due to increased melanin content in the melanocytes rather than to an increase in the number of melanocytes. The long term effects of increased pigmentation are not known. Iris color changes seen with administration of bimatoprost ophthalmic solution may not be noticeable for several months to years. Typically, the brown pigmentation around the pupil spreads concentrically towards the periphery of the iris and the entire iris or parts of the iris become more brownish. Neither nevi nor freckles of the iris appear to be affected by treatment. Treatment with LATISSE ® solution can be continued in patients who develop noticeably increased iris pigmentation.
5.3 Lid Pigmentation
Bimatoprost has been reported to cause pigment changes (darkening) to periorbital pigmented tissues and eyelashes. The pigmentation is expected to increase as long as bimatoprost is administered, but has been reported to be reversible upon discontinuation of bimatoprost in most patients.
5.4 Hair Growth Outside the Treatment Area
There is the potential for hair growth to occur in areas where LATISSE ® solution comes in repeated contact with the skin surface. It is important to apply LATISSE ® only to the skin of the upper eyelid margin at the base of the eyelashes using the accompanying sterile applicators, and to carefully blot any excess LATISSE ® from the eyelid margin to avoid it running onto the cheek or other skin areas.
5.5 Intraocular Inflammation
LATISSE ® solution should be used with caution in patients with active intraocular inflammation (e.g., uveitis) because the inflammation may be exacerbated.
5.6 Macular Edema
Macular edema, including cystoid macular edema, has been reported during treatment with bimatoprost ophthalmic solution ( LUMIGAN ® ) for elevated IOP. LATISSE ® should be used with caution in aphakic patients, in pseudophakic patients with a torn posterior lens capsule, or in patients with known risk factors for macular edema.
5.7 Contamination of LATISSE ® or Applicators
The LATISSE ® bottle must be kept intact during use. It is important to use LATISSE ® solution as instructed, by placing one drop on the single-use-per-eye applicator. The bottle tip should not be allowed to contact any other surface since it could become contaminated. The accompanying sterile applicators should only be used on one eye and then discarded since reuse of applicators increases the potential for contamination and infections. There have been reports of bacterial keratitis associated with the use of multiple-dose containers of topical ophthalmic products [see Patient Counseling Information (17) ] .
5.8 Use with Contact Lenses
LATISSE ® contains benzalkonium chloride, which may be absorbed by and cause discoloration of soft contact lenses. Contact lenses should be removed prior to application of solution and may be reinserted 15 minutes following its administration.
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following adverse reactions are described elsewhere in the labeling:
- Effects on Intraocular Pressure [ see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) ]
- Iris Pigmentation [ see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) ]
- Lid Pigmentation [ see Warnings and Precautions (5.3) ]
- Hair Growth Outside the Treatment Area [ see Warnings and Precautions (5.4) ]
- Intraocular Inflammation [ see Warnings and Precautions (5.5) ]
- Macular Edema [ see Warnings and Precautions (5.6) ]
- Hypersensitivity [ see Contraindications (4) ]
6.1 Clinical Trial Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
The following information is based on clinical trial results from a multicenter, double-masked, randomized, vehicle-controlled, parallel study including 278 adult patients for four months of treatment.
The most frequently reported adverse reactions were eye pruritus, conjunctival hyperemia, skin hyperpigmentation, ocular irritation, dry eye symptoms, and periorbital erythema. These reactions occurred in less than 4% of patients. Additional adverse reactions seen in clinical trials experience include foreign body sensation, hair growth abnormal, and iris hyperpigmentation.
Additional adverse reactions reported with bimatoprost ophthalmic solution ( LUMIGAN ® ) for the reduction of intraocular pressure include, ocular dryness, visual disturbance, ocular burning, eye pain, blepharitis, cataract, superficial punctate keratitis, eye discharge, tearing, photophobia, allergic conjunctivitis, asthenopia, conjunctival edema, iritis, infections (primarily colds and upper respiratory tract infections), headaches, and asthenia.
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during postapproval use of LATISSE ® . Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure. The reactions include dry skin of the eyelid and/or periocular area, eye swelling, eyelid edema, hordeolum, hypersensitivity (local allergic reactions), lacrimation increased, madarosis and trichorrhexis (temporary loss of a few lashes to loss of sections of eyelashes, and temporary eyelash breakage, respectively), periorbital and lid changes associated with periorbital fat atrophy and skin tightness resulting in deepening of eyelid sulcus and eyelid ptosis, rash (including macular and erythematous), skin discoloration (periorbital), skin exfoliation of the eyelid and/or periorbital area, trichiasis, and vision blurred.
11 DESCRIPTION
LATISSE ® (bimatoprost ophthalmic solution) 0.03% is a synthetic prostaglandin analog. Its chemical name is ( Z )-7-[(1 R ,2 R ,3 R ,5 S )-3,5-Dihydroxy-2-[(1 E ,3 S )-3-hydroxy-5-phenyl-1-pentenyl]cyclopentyl]- N -ethyl-5-heptenamide, and its molecular weight is 415.58. Its molecular formula is C 25 H 37 NO 4 . Its chemical structure is:
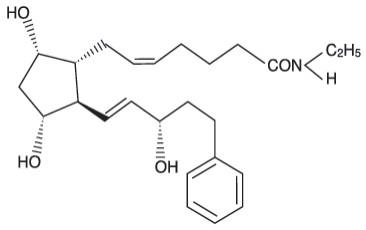
Bimatoprost is a powder, which is very soluble in ethyl alcohol and methyl alcohol and slightly soluble in water. LATISSE ® is a clear, isotonic, colorless, sterile ophthalmic solution with an osmolality of approximately 290 mOsmol/kg.
Contains: Active: bimatoprost 0.3 mg/mL; Preservative: benzalkonium chloride 0.05 mg/mL; Inactives: sodium chloride; sodium phosphate, dibasic; citric acid; and purified water. Sodium hydroxide and/or hydrochloric acid may be added to adjust pH. The pH during its shelf life ranges from 6.8 - 7.8.
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Bimatoprost is a structural prostaglandin analog. Although the precise mechanism of action is unknown, the growth of eyelashes is believed to occur by increasing the percent of hairs in, and the duration of the anagen or growth phase.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Absorption
After one drop of bimatoprost ophthalmic solution 0.03% was administered once daily into both eyes (cornea and/or conjunctival sac) of 15 healthy subjects for two weeks, blood concentrations peaked within 10 minutes after dosing and were below the lower limit of detection (0.025 ng/mL) in most subjects within 1.5 hours after dosing. Mean C max and AUC 0-24hr values were similar on days 7 and 14 at approximately 0.08 ng/mL and 0.09 ng●hr/mL, respectively, indicating that steady state was reached during the first week of ocular dosing. There was no significant systemic drug accumulation over time.
Distribution
Bimatoprost is moderately distributed into body tissues with a steady-state volume of distribution of 0.67 L/kg. In human blood, bimatoprost resides mainly in the plasma. Approximately 12% of bimatoprost remains unbound in human plasma.
Elimination
Metabolism
Bimatoprost is the major circulating species in the blood once it reaches the systemic circulation. Bimatoprost then undergoes oxidation, N-deethylation, and glucuronidation to form a diverse variety of metabolites.
Excretion
Following an intravenous dose of radiolabeled bimatoprost (3.12 mcg/kg) to six healthy subjects, the maximum blood concentration of unchanged drug was 12.2 ng/mL and decreased rapidly with an elimination half-life of approximately 45 minutes. The total blood clearance of bimatoprost was 1.5 L/hr/kg. Up to 67% of the administered dose was excreted in the urine while 25% of the dose was recovered in the feces.
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenesis
Bimatoprost was not carcinogenic in either mice or rats when administered by oral gavage for 104 weeks at doses up to 2 mg/kg/day and 1 mg/kg/day, respectively (192 and 291 times the human systemic exposure following topical ophthalmic administration of bimatoprost 0.03% to the cornea or conjunctival sac bilaterally once daily based on blood AUC levels).
Mutagenesis
Bimatoprost was not mutagenic or clastogenic in the Ames test, in the mouse lymphoma test, or in the in vivo mouse micronucleus tests.
Impairment of Fertility
Bimatoprost did not impair fertility in male or female rats up to doses of 0.6 mg/kg/day (103 times the human systemic exposure following topical ophthalmic administration of bimatoprost 0.03% to the cornea or conjunctival sac bilaterally once daily based on blood AUC levels).
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
LATISSE ® solution was evaluated for its effect on overall eyelash prominence in a multicenter, double-masked, randomized, vehicle-controlled, parallel study including 278 adult patients for four months of treatment. The primary efficacy endpoint in this study was an increase in overall eyelash prominence as measured by at least a 1-grade increase on the 4-point Global Eyelash Assessment (GEA) scale, from baseline to the end of the treatment period (week 16). LATISSE ® was more effective than vehicle as measured by the GEA score, with statistically significant differences seen at 8-week, 12-week, and 16-week ( primary endpoint ) treatment durations.
| Week | LATISSE ® N=137 N (%) | Vehicle N=141 N (%) |
| 1 | 7 (5%) | 3 (2%) |
| 4 | 20 (15%) | 11 (8%) |
| 8 | 69 (50%) | 21 (15%) |
| 12 | 95 (69%) | 28 (20%) |
| 16 | 107 (78%) | 26 (18%) |
| 20 | 103 (79%) | 27 (21%) |
In this study, patients were also evaluated for the effect of LATISSE ® solution on the length, thickness and darkness of their eyelashes. Improvements from baseline in eyelash growth as measured by digital image analysis assessing eyelash length, fullness/thickness, and darkness were statistically significantly more pronounced in the bimatoprost group at weeks 8, 12, and 16.
| Efficacy endpoint at Week 16 (Mean Change from Baseline) | LATISSE ® | Vehicle |
| Eyelash growth (length) (mm; % increase) | N=137 1.4; 25% | N=141 0.1; 2% |
| Fullness/thickness (mm 2 ; % increase) | N=136 0.7; 106% | N=140 0.1; 12% |
| Eyelash darkness (intensity•; % increase in darkness) | N=135 -20.2; -18% | N=138 -3.6; -3% |
• a negative value is representative of eyelash darkening
After the 16-week treatment period, a 4-week post-treatment period followed during which the effects of bimatoprost started to return toward baseline. The effect on eyelash growth is expected to abate following longer term discontinuation.
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
LATISSE ® (bimatoprost ophthalmic solution) 0.03% is supplied sterile in opaque white low-density polyethylene dispenser bottles and tips with turquoise polystyrene caps accompanied by sterile, disposable applicators:
3 mL in a 5 mL bottle with 70 applicators NDC 0023-3616-70 5 mL in a 5 mL bottle with 140 applicators NDC 0023-3616-05
Storage: Store at 2º to 25ºC (36º to 77ºF).
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Bimatoprost is a structural prostaglandin analog. Although the precise mechanism of action is unknown, the growth of eyelashes is believed to occur by increasing the percent of hairs in, and the duration of the anagen or growth phase.