Linzess prior authorization resources
Most recent state uniform prior authorization forms
Brand Resources
Linzess patient education
Patient toolkit
Dosage & administration
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
The recommended dosage in adults is:
- IBS-C : 290 mcg orally once daily. (2.1 )
- CIC : 145 mcg orally once daily or 72 mcg orally once daily based on individual presentation or tolerability. (2.1 )
The recommended dosage in pediatric patients:
- 7 years of age and older with IBS-C : 145 mcg orally once daily. (2.1 )
- 6 years of age and older with FC : 72 mcg orally once daily. (2.1 )
Administration Instructions (2.2 ):
- Take on empty stomach at least 30 minutes prior to a meal at approximately the same time each day.
- Do not crush or chew LINZESS capsule or capsule contents.
- For patients who have difficulty swallowing capsules whole or those with a nasogastric or gastrostomy tube, see full prescribing information for instructions for opening the capsule and administering with applesauce or water.
2.1 Recommended Dosage
Irritable Bowel Syndrome with Constipation (IBS-C) :
The recommended dosage of LINZESS is:
• Adults : 290 mcg orally once daily
• Pediatric patients 7 years of age and older : 145 mcg orally once daily
Chronic Idiopathic Constipation (CIC) in Adults
The recommended dosage of LINZESS in adults is 145 mcg orally once daily. A dosage of 72 mcg once daily may be used based on individual presentation or tolerability.
Functional Constipation (FC) in Pediatric Patients 6 Years of Age and Older
The recommended dosage of LINZESS in pediatric patients 6 years of age and older is 72 mcg orally once daily.
2.2 Preparation and Administration Instructions
• Take LINZESS on an empty stomach, at least 30 minutes prior to a meal, at approximately the same time each day.
• If a dose is missed, skip the missed dose and take the next dose at the regular time. Do not take 2 doses at the same time.
• Do not crush or chew LINZESS capsule or capsule contents.
• Swallow LINZESS capsule whole.
• For patients who are unable to swallow the capsule whole, LINZESS capsules can be opened and administered orally in either applesauce or with water or administered with water via a nasogastric or gastrostomy tube. Sprinkling of LINZESS beads on other soft foods or in other liquids has not been tested.
Oral Administration in Applesauce:
- Place one teaspoonful of room-temperature applesauce into a clean container.
- Open the capsule.
- Sprinkle the entire contents (beads) on applesauce.
- Consume the entire contents immediately. Do not chew the beads. Do not store the bead-applesauce mixture for later use.
Oral Administration in Water:
- Pour approximately 30 mL of room-temperature bottled water into a clean cup.
- Open the capsule.
- Sprinkle the entire contents (beads) into the water.
- Gently swirl beads and water for at least 20 seconds.
- Swallow the entire mixture of beads and water immediately.
- Add another 30 mL of water to any beads remaining in cup, swirl for 20 seconds, and swallow immediately.
- Do not store the bead-water mixture for later use.
Note: The drug is coated on the surface of the beads and will dissolve off the beads into the water. The beads will remain visible and will not dissolve. Therefore, it is not necessary to consume all the beads to deliver the complete dose.
Administration with Water via a Nasogastric or Gastrostomy Tube:
- Open the capsule and empty the beads into a clean container with 30 mL of room-temperature bottled water.
- Mix by gently swirling beads for at least 20 seconds.
- Draw-up the beads and water mixture into an appropriately sized catheter-tipped syringe and apply rapid and steady pressure (10 mL/10 seconds) to dispense the syringe contents into the tube.
- Add another 30 mL of water to any beads remaining in the container and repeat the process.
- After administering the bead-water mixture, flush nasogastric/ gastrostomy tube with a minimum of 10 mL of water.
Note: It is not necessary to flush all the beads through to deliver the complete dose.

By using PrescriberAI, you agree to the AI Terms of Use.
Linzess prescribing information
WARNING: RISK OF SERIOUS DEHYDRATION IN PEDIATRIC PATIENTS LESS THAN 2 YEARS OF AGE
LINZESS is contraindicated in patients less than 2 years of age; in nonclinical studies in neonatal mice, administration of a single, clinically relevant adult oral dose of linaclotide caused deaths due to dehydration [see Contraindications (4 ), Warnings and Precautions (5.1 ), Use in Specific Populations (8.4 )].
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
LINZESS is indicated for the treatment of:
• irritable bowel syndrome with constipation (IBS-C) in adults and pediatric patients 7 years of age and older
• chronic idiopathic constipation (CIC) in adults
• functional constipation (FC) in pediatric patients 6 years of age and older
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
The recommended dosage in adults is:
- IBS-C : 290 mcg orally once daily. (2.1 )
- CIC : 145 mcg orally once daily or 72 mcg orally once daily based on individual presentation or tolerability. (2.1 )
The recommended dosage in pediatric patients:
- 7 years of age and older with IBS-C : 145 mcg orally once daily. (2.1 )
- 6 years of age and older with FC : 72 mcg orally once daily. (2.1 )
Administration Instructions (2.2 ):
- Take on empty stomach at least 30 minutes prior to a meal at approximately the same time each day.
- Do not crush or chew LINZESS capsule or capsule contents.
- For patients who have difficulty swallowing capsules whole or those with a nasogastric or gastrostomy tube, see full prescribing information for instructions for opening the capsule and administering with applesauce or water.
2.1 Recommended Dosage
Irritable Bowel Syndrome with Constipation (IBS-C) :
The recommended dosage of LINZESS is:
• Adults : 290 mcg orally once daily
• Pediatric patients 7 years of age and older : 145 mcg orally once daily
Chronic Idiopathic Constipation (CIC) in Adults
The recommended dosage of LINZESS in adults is 145 mcg orally once daily. A dosage of 72 mcg once daily may be used based on individual presentation or tolerability.
Functional Constipation (FC) in Pediatric Patients 6 Years of Age and Older
The recommended dosage of LINZESS in pediatric patients 6 years of age and older is 72 mcg orally once daily.
2.2 Preparation and Administration Instructions
• Take LINZESS on an empty stomach, at least 30 minutes prior to a meal, at approximately the same time each day.
• If a dose is missed, skip the missed dose and take the next dose at the regular time. Do not take 2 doses at the same time.
• Do not crush or chew LINZESS capsule or capsule contents.
• Swallow LINZESS capsule whole.
• For patients who are unable to swallow the capsule whole, LINZESS capsules can be opened and administered orally in either applesauce or with water or administered with water via a nasogastric or gastrostomy tube. Sprinkling of LINZESS beads on other soft foods or in other liquids has not been tested.
Oral Administration in Applesauce:
- Place one teaspoonful of room-temperature applesauce into a clean container.
- Open the capsule.
- Sprinkle the entire contents (beads) on applesauce.
- Consume the entire contents immediately. Do not chew the beads. Do not store the bead-applesauce mixture for later use.
Oral Administration in Water:
- Pour approximately 30 mL of room-temperature bottled water into a clean cup.
- Open the capsule.
- Sprinkle the entire contents (beads) into the water.
- Gently swirl beads and water for at least 20 seconds.
- Swallow the entire mixture of beads and water immediately.
- Add another 30 mL of water to any beads remaining in cup, swirl for 20 seconds, and swallow immediately.
- Do not store the bead-water mixture for later use.
Note: The drug is coated on the surface of the beads and will dissolve off the beads into the water. The beads will remain visible and will not dissolve. Therefore, it is not necessary to consume all the beads to deliver the complete dose.
Administration with Water via a Nasogastric or Gastrostomy Tube:
- Open the capsule and empty the beads into a clean container with 30 mL of room-temperature bottled water.
- Mix by gently swirling beads for at least 20 seconds.
- Draw-up the beads and water mixture into an appropriately sized catheter-tipped syringe and apply rapid and steady pressure (10 mL/10 seconds) to dispense the syringe contents into the tube.
- Add another 30 mL of water to any beads remaining in the container and repeat the process.
- After administering the bead-water mixture, flush nasogastric/ gastrostomy tube with a minimum of 10 mL of water.
Note: It is not necessary to flush all the beads through to deliver the complete dose.
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
LINZESS capsules are white to off-white opaque:
- 72 mcg; gray imprint “FL 72”
- 145 mcg; gray imprint “FL 145”
- 290 mcg; gray imprint “FL 290”
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.000000000000000e+00 1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
Linaclotide and its active metabolite are negligibly absorbed systemically following oral administration [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3 )] , and maternal use is not expected to result in fetal exposure to the drug. The available data on LINZESS use in pregnant women are not sufficient to inform any drug-associated risk for major birth defects and miscarriage. In animal developmental studies, no effects on embryo-fetal development were observed with oral administration of linaclotide in rats and rabbits during organogenesis at doses much higher than the maximum recommended human dosage. Severe maternal toxicity associated with effects on fetal morphology were observed in mice ( see Data ) .
The estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population is unknown. All pregnancies have a background risk of birth defect, loss, or other adverse outcomes. In the United States general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2% to 4% and 15% to 20%, respectively.
Data
Animal Data
The potential for linaclotide to cause harm to embryo-fetal development was studied in rats, rabbits and mice. In pregnant mice, oral dose levels of at least 40,000 mcg/kg/day given during organogenesis produced severe maternal toxicity including death, reduction of gravid uterine and fetal weights, and effects on fetal morphology. Oral doses of 5,000 mcg/kg/day did not produce maternal toxicity or any adverse effects on embryo-fetal development in mice. Oral administration of up to 100,000 mcg/kg/day in rats and 40,000 mcg/kg/day in rabbits during organogenesis produced no maternal toxicity and no effects on embryo-fetal development. Additionally, oral administration of up to 100,000 mcg/kg/day in rats during organogenesis through lactation produced no developmental abnormalities or effects on growth, learning and memory, or fertility in the offspring through maturation.
The maximum recommended human dose is approximately 5 mcg/kg/day, based on a 60-kg body weight. Limited systemic exposure to linaclotide was achieved in animals during organogenesis (AUC = 40, 640, and 25 ng•hr/mL in rats, rabbits, and mice, respectively, at the highest dose levels). Linaclotide and its active metabolite are not measurable in human plasma following administration of the recommended clinical dosages. Therefore, animal and human doses should not be compared directly for evaluating relative exposure.
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
Linaclotide and its active metabolite were not detected in the milk of lactating women (see Data). In adults, concentrations of linaclotide and its active metabolite were below the limit of quantitation in plasma following multiple doses of LINZESS [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3 ) ] . Maternal use of LINZESS is not expected to result in exposure to linaclotide or its active metabolite in breastfed infants. There is no information on the effects of linaclotide or its active metabolite on milk production. The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother’s clinical need for LINZESS and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed infant from LINZESS or from the underlying maternal condition.
Data
Following oral administration of 72 mcg, 145 mcg, or 290 mcg of LINZESS once daily for 3 days to breastfeeding mothers taking linaclotide therapeutically, the concentrations of linaclotide and its metabolite were below the limits of quantitation (<0.25 ng/mL and <1 ng/mL, respectively) in all breast milk samples collected over 24 hours.
8.4 Pediatric Use
LINZESS is contraindicated in patients less than 2 years of age due to the risk of serious dehydration. In nonclinical studies, deaths occurred within 24 hours in neonatal mice (human age equivalent of approximately 0 to 28 days) following oral administration of linaclotide which increased fluid secretion as a consequence of age-dependent elevated GC-C agonism resulting in rapid and severe dehydration (see Juvenile Animal Toxicity Data ) .
In a clinical GC-C ontogeny study in children 6 months to less than 18 years of age (N=99) to measure GC-C mRNA expression levels in duodenal and colonic samples to evaluate the risk of diarrhea and severe dehydration due to GC-C agonism, there was insufficient data on GC-C intestinal expression to assess the risk of developing diarrhea and its potentially serious consequences in children less than 2 years of age [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1 )] .
Functional Constipation (FC)
The safety and effectiveness of LINZESS for the treatment of FC have been established in pediatric patients 6 years of age and older. Use of LINZESS for this indication is supported by evidence from adequate and well-controlled studies in adults and pediatric patients 6 to 17 years of age. The safety of LINZESS in adult and pediatric patients in these clinical studies was similar [see Adverse Reactions (6.1 ) and Clinical Studies (14.4 )] .
The safety and effectiveness of LINZESS for the treatment of FC have not been established in pediatric patients less than 6 years of age.
Irritable Bowel Syndrome with Constipation (IBS-C)
The safety and effectiveness of LINZESS for the treatment of IBS-C have been established in pediatric patients 7 years of age and older. Use of LINZESS for this indication is supported by evidence from adequate and well-controlled studies in adults and pediatric patients 7 to 17 years of age. The safety of LINZESS in adult and pediatric patients in these clinical studies was similar [see Adverse Reactions (6.1 ) and Clinical Studies (14.2 )] .
The safety and effectiveness of LINZESS for the treatment of IBS-C have not been established in pediatric patients less than 7 years of age.
Juvenile Animal Toxicity Data
In toxicology studies in neonatal mice, oral administration of linaclotide at 10 mcg/kg/day caused deaths on post-natal day 7 (human age equivalent of approximately 0 to 28 days). These deaths were due to rapid and severe dehydration produced by significant fluid shifts into the intestinal lumen resulting from GC-C agonism in neonatal mice [see Contraindications (4 ) and Warnings and Precautions (5.1 )] .
Tolerability to linaclotide increases with age in juvenile mice. In 2-week-old mice, linaclotide was well tolerated at a dose of 50 mcg/kg/day, but deaths occurred after a single oral dose of 100 mcg/kg. In 3-week-old mice, linaclotide was well tolerated at 100 mcg/kg/day, but deaths occurred after a single oral dose of 600 mcg/kg.
8.5 Geriatric Use
Irritable Bowel Syndrome with Constipation (IBS-C) Of 2219 IBS-C patients in the placebo-controlled clinical studies of LINZESS (Trials 1, 2, and 6), 154 (7%) were 65 years of age and over, while 34 (2%) were 75 years and over. Clinical studies of LINZESS did not include sufficient numbers of patients aged 65 years and over to determine whether they respond differently from younger patients.
Chronic Idiopathic Constipation (CIC) Of 2498 CIC patients in the placebo-controlled clinical studies of LINZESS (Trials 3, 4, and 5), 273 (11%) were 65 years of age and over, while 56 (2%) were 75 years and over. Clinical studies of LINZESS did not include sufficient numbers of patients aged 65 and over to determine whether they respond differently from younger patients. In general, dose selection for an elderly patient should be cautious reflecting the greater frequency of decreased hepatic, renal or cardiac function and of concomitant disease or other drug therapy.
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
Diarrhea: Patients may experience severe diarrhea. If severe diarrhea occurs, suspend dosing and rehydrate the patient. (5.2 )
5.1 Risk of Serious Dehydration in Pediatric Patients Less Than 2 Years of Age
LINZESS is contraindicated in patients less than 2 years of age. In neonatal mice (human age equivalent of approximately 0 to 28 days), linaclotide increased fluid secretion as a consequence of age-dependent elevated GC-C agonism which was associated with increased mortality within the first 24 hours due to dehydration. There was no age-dependent trend in GC-C intestinal expression in a clinical study of children 2 to less than 18 years of age; however, there are insufficient data available on GC-C intestinal expression in children less than 2 years of age to assess the risk of developing diarrhea and its potentially serious consequences in these patients [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2 ) and Use in Specific Populations (8.4 ) ] .
5.000000000000000e+00 2 Diarrhea
In adults, diarrhea was the most common adverse reaction of LINZESS-treated patients in the pooled IBS-C and CIC double-blind placebo-controlled trials. The incidence of diarrhea was similar between the IBS-C and CIC populations. Severe diarrhea was reported in 2% of adult patients with IBS-C or CIC treated with LINZESS 145 mcg or 290 mcg once daily, and in <1% of adult patients with CIC treated with LINZESS 72 mcg once daily [see Adverse Reactions (6.1 )] .
In pediatric patients, diarrhea was also the most common adverse reaction of LINZESS-treated patients in IBS-C and FC clinical trials. In two double-blind trials, diarrhea was reported in 4% of pediatric patients 6 to 17 years of age with FC treated with LINZESS 72 mcg once daily, and 7% and 8% of pediatric patients 7 to 17 years of age with IBS-C treated with LINZESS 145 mcg and 290 mcg once daily, respectively. In clinical trials, severe diarrhea was reported in one pediatric patient with FC treated with LINZESS 72 mcg once daily [see Adverse Reactions (6.1 )] and in one pediatric patient with IBS-C treated with LINZESS at a dosage higher than the recommended 145 mcg once daily dosage for IBS-C.
In post-marketing experience, severe diarrhea associated with dizziness, syncope, hypotension and electrolyte abnormalities (hypokalemia and hyponatremia) requiring hospitalization or intravenous fluid administration have been reported in patients treated with LINZESS.
If severe diarrhea occurs, suspend dosing and rehydrate the patient.
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
- Most common adverse reactions (≥2%) reported in adult patients with IBS-C or CIC are: diarrhea, abdominal pain, flatulence and abdominal distension. (6.1 )
- Most common adverse reaction (≥2%) reported in pediatric patients with FC or IBS-C is diarrhea. (6.1 )
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact AbbVie, Inc. at 1-800-678-1605 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared with rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
Demographic characteristics were comparable between treatment groups in all studies [see Clinical Studies (14.1 , 14.2 , 14.3 , 14.4 )] .
Irritable Bowel Syndrome with Constipation (IBS-C) in Adults
Most Common Adverse Reactions
The data described below reflect exposure to LINZESS in the two placebo-controlled clinical trials involving 1605 adult patients with IBS-C (Trials 1 and 2) [see Clinical Studies (14.1 )] . Patients were randomized to receive placebo or 290 mcg LINZESS once daily on an empty stomach for up to 26 weeks. Table 1 provides the incidence of adverse reactions reported in at least 2% of IBS-C patients in the LINZESS treatment group and at an incidence that was greater than in the placebo group.
| Adverse Reactions | LINZESS 290 mcg [N=807] % | Placebo [N=798] % |
| Gastrointestinal Diarrhea Abdominal pain b Flatulence Abdominal distension | 20 7 4 2 | 3 5 2 1 |
| Infections and Infestations Viral Gastroenteritis | 3 | 1 |
| Nervous System Disorders Headache | 4 | 3 |
a: Reported in at least 2% of LINZESS-treated patients and at an incidence greater than placebo
b: “Abdominal pain” term includes abdominal pain, upper abdominal pain, and lower abdominal pain.
Adverse reactions in an additional placebo-controlled trial in 614 IBS-C patients randomized to placebo or LINZESS 290 mcg once daily on an empty stomach for 12 weeks (Trial 6) were similar to those in Table 1.
Diarrhea
Diarrhea was the most commonly reported adverse reaction of the LINZESS-treated patients in the pooled IBS-C pivotal placebo-controlled trials. In these trials, 20% of LINZESS-treated patients reported diarrhea compared to 3% of placebo-treated patients. Severe diarrhea was reported in 2% of the LINZESS-treated patients versus less than 1% of the placebo-treated patients, and 5% of LINZESS-treated patients discontinued due to diarrhea vs less than 1% of placebo-treated patients. The majority of reported cases of diarrhea started within the first 2 weeks of LINZESS treatment [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2 )] .
Adverse Reactions Leading to Discontinuation
In placebo-controlled trials in patients with IBS-C, 9% of patients treated with LINZESS and 3% of patients treated with placebo discontinued prematurely due to adverse reactions. In the LINZESS-treatment group, the most common reasons for discontinuation due to adverse reactions were diarrhea (5%) and abdominal pain (1%). In comparison, less than 1% of patients in the placebo group withdrew due to diarrhea or abdominal pain.
Adverse Reactions Leading to Dose Reductions
In the open-label, long-term trials, 2147 patients with IBS-C received 290 mcg of LINZESS daily for up to 18 months. In these trials, 29% of patients had their dose reduced or suspended secondary to adverse reactions, the majority of which were diarrhea or other GI adverse reactions.
Less Common Adverse Reactions
Defecation urgency, fecal incontinence, vomiting, and gastroesophageal reflux disease were reported in <2% of patients in the LINZESS-treatment group and at an incidence greater than in the placebo treatment group.
Chronic Idiopathic Constipation (CIC) in Adults
Most Common Adverse Reactions
The data described below reflect exposure to LINZESS in the two double-blind placebo-controlled clinical trials of 1275 adult patients with CIC (Trials 3 and 4) [see Clinical Studies (14.3 )] . Patients were randomized to receive placebo or 145 mcg LINZESS or 290 mcg LINZESS once daily on an empty stomach, for at least 12 weeks. Table 2 provides the incidence of adverse reactions reported in at least 2% of CIC patients in the 145 mcg LINZESS treatment group and at an incidence that was greater than in the placebo treatment group.
| Adverse Reactions | LINZESS 145 mcg [N=430] % | Placebo [N=423] % |
| Gastrointestinal Diarrhea Abdominal pain b Flatulence Abdominal distension | 16 7 6 3 | 5 6 5 2 |
| Infections and InfestationsUpper respiratory tract infection Sinusitis | 5 3 | 4 2 |
a: Reported in at least 2% of LINZESS-treated patients and at an incidence greater than placebo
b: “Abdominal pain” term includes abdominal pain, upper abdominal pain, and lower abdominal pain.
The safety of a 72 mcg dose was evaluated in an additional placebo-controlled trial in which 1223 patients were randomized to LINZESS 72 mcg, 145 mcg, or placebo once daily for 12 weeks (Trial 5).
In Trial 5, adverse reactions that occurred at a frequency of ≥ 2% in LINZESS-treated patients (N=411 in each LINZESS 72 mcg and 145 mcg group) and at a higher rate than placebo (N=401) were:
- Diarrhea (LINZESS 72 mcg 19%; LINZESS 145 mcg 22%; placebo 7%)
- Abdominal distension (LINZESS 72 mcg 2%; LINZESS 145 mcg 1%; placebo < 1%)
Diarrhea
In Trials 3 and 4 (pooled) and Trial 5, diarrhea was the most commonly reported adverse reaction in LINZESS-treated patients in the CIC placebo-controlled studies.
In all trials, the majority of reported cases of diarrhea started within the first 2 weeks of LINZESS treatment.
Severe diarrhea was reported in less than 1% of the 72 mcg LINZESS-treated patients (Trial 5), in 2% of the 145 mcg LINZESS-treated patients (Trials 3, 4, and 5), and less than 1% of the placebo-treated patients (Trials 3, 4, and 5) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2 )] .
Adverse Reactions Leading to Discontinuation
In placebo-controlled trials in patients with CIC, 3% of patients treated with 72 mcg (Trial 5) and between 5% and 8% (Trials 3, 4, and 5) of patients treated with 145 mcg of LINZESS discontinued prematurely due to adverse reactions compared to between less than 1% and 4% (Trials 3, 4, and 5) of patients treated with placebo.
In patients treated with 72 mcg LINZESS, the most common reason for discontinuation due to adverse reactions was diarrhea (2% in Trial 5) and, in patients treated with 145 mcg LINZESS, the most common reasons for discontinuation due to adverse reactions were diarrhea (between 3% and 5% in Trials 3, 4, and 5) and abdominal pain (1% in Trials 3 and 4). In comparison, less than 1% of patients in the placebo group withdrew due to diarrhea or abdominal pain (Trials 3, 4, and 5).
Adverse Reactions Leading to Dose Reductions
In the open-label, long-term trials, 1129 patients with CIC received 290 mcg of LINZESS daily for up to 18 months. In these trials, 27% of patients had their dose reduced or suspended secondary to adverse reactions, the majority of which were diarrhea or other GI adverse reactions.
Less Common Adverse Reactions
Defecation urgency, fecal incontinence, dyspepsia, and viral gastroenteritis were reported in less than 2% of patients in the LINZESS treatment group and at an incidence greater than in the placebo treatment group.
Functional Constipation (FC) in Pediatric Patients 6 Years of Age and Older
The safety of LINZESS 72 mcg once daily was evaluated in pediatric patients 6 to 17 years of age with FC in a 12-week double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial (Trial 7) [see Clinical Studies (14.4 )] . There were 164 patients per treatment group.
Diarrhea was the most common adverse reaction and was reported in 4% of LINZESS-treated patients compared to 2% of placebo-treated patients. One patient in the LINZESS-treated group reported severe diarrhea and discontinued treatment. No patient in the placebo-treated group discontinued treatment due to severe diarrhea. Most reported cases of diarrhea started within the first 2 weeks of LINZESS treatment [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2 )] .
Other adverse reactions reported at a higher incidence in the LINZESS group than the placebo group included nausea (2 patients) and abdominal discomfort and dehydration (1 patient each).
IBS- C in Pediatric Patients 7 Years of Age and Older
The safety of LINZESS 145 mcg once daily was evaluated in 55 pediatric patients 7 to 17 years of age with IBS-C in a 12-week double-blind, parallel-group clinical trial (Trial 8) [see Clinical Studies (14.2 )] .
The safety profile in pediatric patients treated with LINZESS was similar to the safety profile from trials in adults with IBS-C and CIC and in pediatric patients with FC. Diarrhea was the most common adverse reaction reported in 7% of 145 mcg LINZESS-treated pediatric patients. Most reported cases of diarrhea started within the first 2 weeks of LINZESS treatment [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2 )] .
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during post approval use of LINZESS. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Hypersensitivity reactions : Anaphylaxis, angioedema, rash (including hives or urticaria)
Gastrointestinal reactions: Hematochezia, nausea, rectal hemorrhage
11 DESCRIPTION
LINZESS (linaclotide) is a guanylate cyclase-C (GC-C) agonist. Linaclotide is a 14-amino acid peptide with the following chemical name: L-cysteinyl-L-cysteinyl-L-glutamyl-L-tyrosyl-L-cysteinyl-L-cysteinyl-L-asparaginyl-L-prolyl-L-alanyl-L-cysteinyl-L-threonyl-glycyl-L-cysteinyl-L-tyrosine, cyclic (1-6), (2-10), (5-13)-tris (disulfide).
The molecular formula of linaclotide is C 59 H 79 N 15 O 21 S 6 and its molecular weight is 1526.8. The amino acid sequence for linaclotide is shown below:
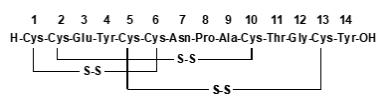
Linaclotide is an amorphous, white to off-white powder. It is slightly soluble in water and aqueous sodium chloride (0.9%). LINZESS contains linaclotide-coated beads in hard gelatin capsules. LINZESS is available as 72 mcg, 145 mcg and 290 mcg capsules for oral administration.
The inactive ingredients of LINZESS 72 mcg capsules include: calcium chloride dihydrate, L-histidine, microcrystalline cellulose, polyvinyl alcohol, and talc. The components of the capsule shell include gelatin and titanium dioxide.
The inactive ingredients of LINZESS 145 mcg and 290 mcg capsules include: calcium chloride dihydrate, hypromellose, L-leucine, and microcrystalline cellulose. The components of the capsule shell include gelatin and titanium dioxide.
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Linaclotide is structurally related to human guanylin and uroguanylin and functions as a guanylate cyclase-C (GC-C) agonist. Both linaclotide and its active metabolite bind to GC-C and act locally on the luminal surface of the intestinal epithelium. Activation of GC-C results in an increase in both intracellular and extracellular concentrations of cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP). Elevation in intracellular cGMP stimulates secretion of chloride and bicarbonate into the intestinal lumen, mainly through activation of the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) ion channel, resulting in increased intestinal fluid and accelerated transit. In animal models, linaclotide has been shown to both accelerate GI transit and reduce intestinal pain.
In an animal model of visceral pain, linaclotide reduced abdominal muscle contraction and decreased the activity of pain-sensing nerves by increasing extracellular cGMP.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
Food Effect
Taking LINZESS immediately after a high fat breakfast resulted in looser stools and a higher stool frequency compared with taking it in the fasted state [see Dosage and Administration (2.1 , 2.2 )] . In clinical trials, LINZESS was administered on an empty stomach, at least 30 minutes before a meal at approximately the same time each day.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Absorption
LINZESS is minimally absorbed with negligible systemic availability following oral administration. Concentrations of linaclotide and its active metabolite in plasma are below the limit of quantitation after oral doses of 72 mcg, 145 mcg, or 290 mcg were administered. Therefore, standard pharmacokinetic parameters such as area under the curve (AUC), maximum concentration (C max ), and half-life (t ½ ) cannot be calculated.
Food Effect
Neither linaclotide nor its active metabolite were detected in the plasma following administration of LINZESS 290 mcg once daily for 7 days both in the non-fed and fed state in healthy subjects.
Distribution
Given that linaclotide plasma concentrations following recommended oral doses are not measurable, linaclotide is not expected to be distributed to tissues to any clinically relevant extent.
Elimination
Metabolism
Linaclotide is metabolized within the gastrointestinal tract to its principal, active metabolite by loss of the terminal tyrosine moiety. Both linaclotide and the metabolite are proteolytically degraded within the intestinal lumen to smaller peptides and naturally occurring amino acids.
Excretion
Active peptide recovery in the stool samples of fed and fasted healthy subjects following administration of LINZESS 290 mcg once daily for seven days averaged about 5% (fasted) and about 3% (fed) and all of it as the active metabolite.
Specific Populations
Renal and Hepatic Impairment
Renal or hepatic impairment is not expected to affect the clearance of linaclotide or the active metabolite because linaclotide metabolism occurs within the gastrointestinal tract and plasma concentrations are not measurable in plasma following administration of the recommended dosage.
Drug Interaction Studies
No drug-drug interaction studies have been conducted with LINZESS. Systemic exposures of drug and active metabolite are negligible following oral administration.
Linaclotide does not interact with the cytochrome P450 enzyme system based on the results of in vitro studies. In addition, linaclotide does not interact with common efflux and uptake transporters (including the efflux transporter P-glycoprotein (P-gp)). Based on these in vitro data no drug-drug interactions through modulation of CYP enzymes or common transporters are anticipated.
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenesis
In 2-year carcinogenicity studies, linaclotide was not tumorigenic in rats at doses up to 3500 mcg/kg/day or in mice at doses up to 6000 mcg/kg/day. The maximum recommended human dose is approximately 5 mcg/kg/day based on a 60-kg body weight. Limited systemic exposure to linaclotide and its active metabolite was achieved at the tested dose levels in animals, whereas no detectable exposure occurred in humans. Therefore, animal and human doses should not be compared directly for evaluating relative exposure.
Mutagenesis
Linaclotide was not genotoxic in an in vitro bacterial reverse mutation (Ames) assay or in the in vitro chromosomal aberration assay in cultured human peripheral blood lymphocytes.
Impairment of Fertility
Linaclotide had no effect on fertility or reproductive function in male and female rats at oral doses of up to 100,000 mcg/kg/day.
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
14.1 Irritable Bowel Syndrome with Constipation (IBS-C) in Adults
The efficacy of LINZESS for the treatment of IBS-C was established in two double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomized, multicenter trials in adult patients (Trials 1 (NCT00948818) and 2 (NCT00938717)). A total of 800 patients in Trial 1 and 804 patients in Trial 2 [overall mean age of 44 years (range 18 to 87 years), 90% female, 77% white, 19% black, and 12% Hispanic] received treatment with LINZESS 290 mcg or placebo once daily and were evaluated for efficacy. All patients met Rome II criteria for IBS and were required, during the 2-week baseline period, to meet the following criteria:
- a mean abdominal pain score of at least 3 on a 0-to-10-point numeric rating scale
- less than 3 complete spontaneous bowel movements (CSBMs) per week [a CSBM is a spontaneous bowel movement (SBM) that is associated with a sense of complete evacuation; a SBM is a bowel movement occurring in the absence of laxative use], and
- less than or equal to 5 SBMs per week.
The trial designs were identical through the first 12 weeks, and thereafter differed only in that Trial 1 included a 4-week randomized withdrawal (RW) period, and Trial 2 continued for 14 additional weeks (total of 26 weeks) of double-blind treatment. During the trials, patients were allowed to continue stable doses of bulk laxatives or stool softeners but were not allowed to take laxatives, bismuth, prokinetic agents, or other drugs to treat IBS-C or chronic constipation.
Efficacy of LINZESS was assessed using overall responder analyses and change-from-baseline endpoints. Results for endpoints were based on information provided daily by patients in diaries.
The 4 primary efficacy responder endpoints were based on a patient being a weekly responder for either at least 9 out of the first 12 weeks of treatment or at least 6 out of the first 12 weeks of treatment. For the 9 out of 12 weeks combined primary responder endpoint, a patient had to have at least a 30% reduction from baseline in mean abdominal pain, at least 3 CSBMs and an increase of at least 1 CSBM from baseline, all in the same week, for at least 9 out of the first 12 weeks of treatment. Each of the 2 components of the 9 out of 12 weeks combined responder endpoint, abdominal pain and CSBMs, was also a primary endpoint.
For the 6 out of 12 weeks combined primary responder endpoint, a patient had to have at least a 30% reduction from baseline in mean abdominal pain and an increase of at least 1 CSBM from baseline, all in the same week, for at least 6 out of the first 12 weeks of treatment. To be considered a responder for this analysis, patients did not have to have at least 3 CSBMs per week.
The efficacy results for the 9 out of 12 weeks and the 6 out of 12 weeks responder endpoints are shown in Tables 3 and 4, respectively. In both trials, the proportion of patients who were responders to LINZESS 290 mcg was statistically significantly higher than with placebo.
| Trial 1 | Trial 2 | |||||
| LINZESS 290 mcg Once Daily (N=405) | Placebo (N=395) | Treatment Difference [95% CI] | LINZESS 290 mcg Once Daily (N=401) | Placebo (N=403) | Treatment Difference [95% CI] | |
| Combined Responder• (Abdominal Pain and CSBM Responder) | 12% | 5% | 7% [3.2%, 10.9%] | 13% | 3% | 10% [6.1%, 13.4%] |
| Abdominal Pain Responder• (≥ 30% Abdominal Pain Reduction) | 34% | 27% | 7% [0.9%, 13.6%] | 39% | 20% | 19% [13.2%, 25.4%] |
| CSBM Responder• (≥ 3 CSBMs and Increase ≥1 CSBM from Baseline) | 20% | 6% | 13% [8.6%, 17.7%] | 18% | 5% | 13% [8.7%, 17.3%] |
| • Primary Endpoints Note: Analyses based on first 12 weeks of treatment for both Trials 1 and 2 CI =Confidence Interval | ||||||
| Trial 1 | Trial 2 | |||||
| LINZESS 290 mcg Once Daily (N=405) | Placebo (N=395) | Treatment Difference [95% CI] | LINZESS 290 mcg Once Daily (N=401) | Placebo (N=403) | Treatment Difference [95% CI] | |
| Combined Responder• (Abdominal Pain and CSBM Responder) | 34% | 21% | 13% [6.5%, 18.7%] | 34% | 14% | 20% [14.0%, 25.5%] |
| Abdominal Pain Responder•• (≥ 30% Abdominal Pain Reduction) | 50% | 37% | 13% [5.8%, 19.5%] | 49% | 34% | 14% [7.6%, 21.1%] |
| CSBM Responder•• (Increase ≥ 1 CSBM from Baseline) | 49% | 30% | 19% [12.4%, 25.7%] | 48% | 23% | 25% [18.7%, 31.4%] |
| • Primary Endpoint, •• Secondary Endpoints Note: Analyses based on first 12 weeks of treatment for both Trials 1 and 2 CI =Confidence Interval | ||||||
In each trial, improvement from baseline in abdominal pain and CSBM frequency was seen over the first 12-weeks of the treatment periods. For change from baseline in the 11-point abdominal pain scale, LINZESS 290 mcg began to separate from placebo in the first week. Maximum effects were seen at weeks 6 - 9 and were maintained until the end of the study. The mean treatment difference from placebo at week 12 was a decrease in pain score of approximately 1.0 point in both trials (using an 11-point scale). Maximum effect on CSBM frequency occurred within the first week, and for change from baseline in CSBM frequency at week 12, the difference between placebo and LINZESS was approximately 1.5 CSBMs per week in both trials.
In each trial, in addition to improvements in abdominal pain and CSBM frequency over the first 12 weeks of the treatment period, improvements were observed in the following when LINZESS was compared to placebo: SBM frequency [SBMs/week], stool consistency [as measured by the Bristol Stool Form Scale (BSFS)], and amount of straining with bowel movements [amount of time pushing or physical effort to pass stool].
During the 4-week randomized withdrawal period in Trial 1, patients who received LINZESS during the 12-week treatment period were re-randomized to receive placebo or continue treatment on LINZESS 290 mcg. In LINZESS-treated patients re-randomized to placebo, CSBM frequency and abdominal-pain severity returned toward baseline within 1 week and did not result in worsening compared to baseline. Patients who continued on LINZESS maintained their response to therapy over the additional 4 weeks. Patients on placebo who were allocated to LINZESS had an increase in CSBM frequency and a decrease in abdominal pain levels that were similar to the levels observed in patients taking LINZESS during the treatment period.
Trial 6 (NCT03573908) was a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group trial that evaluated the safety and efficacy of LINZESS in patients with IBS-C over a 12-week treatment period followed by a 4-week randomized withdrawal period. A total of 614 patients [mean age of 47 years (range 18 to 85 years), 81% female, 63% white, 24% black, and 27% Hispanic] received treatment with LINZESS 290 mcg or placebo once daily and all patients met Rome III criteria for IBS-C.
The efficacy of LINZESS was assessed using a primary endpoint based on the mean abdominal score (composite of abdominal bloating, abdominal discomfort, and abdominal pain) across 12 weeks. The secondary endpoint was a responder analysis based on at least a 2.5-point improvement in the abdominal score from baseline for at least 6 out of 12 weeks as shown in Table 5.
| Trial 6 | |||
| LINZESS 290 mcg Once Daily (N= 306 ) | Placebo (N= 308 ) | Treatment Difference [95% CI] | |
| Baseline Abdominal Score | 6.4 | 6.5 | |
| Least Squares 12-week Mean C hange from B aseline in Abdominal Score • | -1.9 | -1.2 | -0.7 [-1.0, -0.4] |
| Abdominal Score 6 of 12- W eek Responder• • | 34% | 18.5% | 15.5% [8.6%, 22.3%] |
| • Primary Endpoint, •• Secondary Endpoint Each abdominal symptom was rated on a 0-to-10-point numeric rating scale where 0=no [symptom] and 10=worst possible [symptom]. CI = Confidence Interval | |||
14.2 Irritable Bowel Syndrome with Constipation (IBS-C) in Pediatric Patients 7 Years of Age and Older
The efficacy of LINZESS for the treatment of IBS-C in pediatric patients 7 to 17 years of age was established in a 12-week double-blind, parallel-group, randomized, multicenter, clinical trial (Trial 8; NCT04026113). A total of 108 patients were randomized to receive treatment with LINZESS 145 mcg once daily or a higher than recommended dosage of LINZESS. The higher LINZESS dosage group did not demonstrate additional treatment benefit compared to LINZESS 145 mcg once daily. A total of 53 patients who received LINZESS 145 mcg once daily were evaluated for efficacy. The evaluated patients had a mean age of 13 years (range 7 to 17 years); 57% were female; 34% identified as Hispanic or Latino; 72% identified as White, 25% as Black or African American, and 4% as Asian.
All patients met Rome III criteria for child/adolescent IBS-C requiring that, for at least once per week for at least 2 months before the screening visit, the participant experienced abdominal discomfort (an uncomfortable sensation not described as pain) or pain associated with 2 or more of the following at least 25% of the time:
- Improvement with defecation
- Onset associated with a change in frequency of stool
- Onset associated with a change in form (appearance) of stool
Patients were also required to have an average daytime abdominal pain score of ≥1 (on a 0-4 scale) and had an average of fewer than 3 SBMs per week during the 14 days before randomization.
The primary endpoint was the proportion of patients who achieved at least a 30% reduction in abdominal pain and an increase of at least 2 spontaneous bowel movements (SBMs)/week from baseline for at least 6 out of 12 weeks (combined responder). The result of the primary efficacy endpoint is shown in Table 6.
| Trial 8 | |
| LINZESS 145 mcg Once Daily n (%) [95% CI] N= 53 | |
| Combined Responder† (Abdominal Pain and SBM Responder) | 16 (30%) [18%, 44%] |
| Abdominal Pain Responder (≥ 30% Abdominal Pain Reduction) | 36 (68%) |
| SBM Responder (Increase ≥ 2 SBMs from Baseline) | 21 (40%) |
| † The primary endpoint of combined responder is defined as a patient who has at least a 30% reduction in abdominal pain and an increase of at least 2 SBMs/week from baseline for at least 6 out of 12 weeks. | |
Abdominal pain and SBM frequency improved during week 1 and improvement was maintained throughout the remainder of the 12-week treatment period.
14.3 Chronic Idiopathic Constipation (CIC) in Adults
The efficacy of LINZESS for the treatment of CIC was established in two double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomized, multicenter clinical trials in adult patients (Trials 3 and 4). A total of 642 patients in Trial 3 and 630 patients in Trial 4 [overall mean age of 48 years (range 18 to 85 years), 89% female, 76% white, 22% black, 10% Hispanic] received treatment with LINZESS 145 mcg, 290 mcg, or placebo once daily and were evaluated for efficacy. All patients met modified Rome II criteria for functional constipation. Modified Rome II criteria were less than 3 Spontaneous Bowel Movements (SBMs) per week and 1 of the following symptoms for at least 12 weeks, which need not be consecutive, in the preceding 12 months:
- Straining during greater than 25% of bowel movements
- Lumpy or hard stools during greater than 25% of bowel movements
- Sensation of incomplete evacuation during greater than 25% of bowel movements
Patients were also required to have less than 3 CSBMs per week and less than or equal to 6 SBMs per week during a 2-week baseline period. Patients were excluded if they met criteria for IBS-C or had fecal impaction that required emergency room treatment.
The trial designs were identical through the first 12 weeks. Trial 3 also included an additional 4-week randomized withdrawal (RW) period. During the trials, patients were allowed to continue stable doses of bulk laxatives or stool softeners but were not allowed to take laxatives, bismuth, prokinetic agents, or other drugs to treat chronic constipation.
The efficacy of LINZESS was assessed using a responder analysis and change-from-baseline endpoints. Results for endpoints were based on information provided daily by patients in diaries.
A CSBM responder in the CIC trials was defined as a patient who had at least 3 CSBMs and an increase of at least 1 CSBM from baseline in a given week for at least 9 weeks out of the 12-week treatment period. The CSBM responder rates are shown in Table 6. During the individual double-blind placebo-controlled trials, LINZESS 290 mcg did not consistently offer additional clinically meaningful treatment benefit over placebo than that observed with the LINZESS 145 mcg dose. Therefore, the 145 mcg dose is the recommended dose. Only the data for the approved 145 mcg dose of LINZESS are presented in Table 7.
In Trials 3 and 4, the proportion of patients who were CSBM responders was statistically significantly greater with the LINZESS 145 mcg dose than with placebo.
| Trial 3 | Trial 4 | |||||
| LINZESS 145 mcg Once Daily (N=217) | Placebo (N=209) | Treatment Difference [95% CI] | LINZESS 145 mcg Once Daily (N=213) | Placebo (N=215) | Treatment Difference [95% CI] | |
| CSBM Responder• (≥ 3 CSBMs and Increase ≥ 1 CSBM from Baseline) | 20% | 3% | 17% [11.0%, 22.8%] | 15% | 6% | 10% [4.2%, 15.7%] |
| •Primary Endpoint CI=Confidence Interval | ||||||
CSBM frequency reached maximum level during week 1 and was also demonstrated over the remainder of the 12-week treatment period in Trial 3 and Trial 4. For the mean change from baseline in CSBM frequency at week 12, the difference between placebo and LINZESS was approximately 1.5 CSBMs.
On average, patients who received LINZESS across the 2 trials had significantly greater improvements compared with patients receiving placebo in stool frequency (CSBMs/week and SBMs/week), and stool consistency (as measured by the BSFS).
In each trial, in addition to improvements in CSBM frequency over the first 12 weeks of the treatment period, improvements were observed in each of the following when LINZESS was compared to placebo: SBM frequency [SBMs/week], stool consistency [as measured by the BSFS], and amount of straining with bowel movements [amount of time pushing or physical effort to pass stool].
During the 4-week randomized withdrawal period in Trial 3, patients who received LINZESS during the 12-week treatment period were re-randomized to receive placebo or continue treatment on the same dose of LINZESS taken during the treatment period. In LINZESS-treated patients re-randomized to placebo, CSBM and SBM frequency returned toward baseline within 1 week and did not result in worsening compared to baseline. Patients who continued on LINZESS maintained their response to therapy over the additional 4 weeks. Patients on placebo who were allocated to LINZESS had an increase in CSBM and SBM frequency similar to the levels observed in patients taking LINZESS during the treatment period.
A 72 mcg dose of LINZESS was established in a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicenter clinical trial in adult patients (Trial 5). A total of 1223 patients [overall mean age of 46 years (range 18 to 90 years), 77% female, 71% white, 24% black, 43% Hispanic] received treatment with LINZESS 72 mcg or placebo once daily and were evaluated for efficacy. All patients met modified Rome III criteria for functional constipation. Trial 5 was identical to Trials 3 and 4 through the first 12 weeks. The efficacy of the 72 mcg dose was assessed using a responder analysis where a CSBM responder was defined as a patient who had at least 3 CSBMs and an increase of at least 1 CSBM from baseline in a given week for at least 9 weeks out of the 12-week treatment period, which was the same as the one defined in Trials 3 and 4. The response rates for the CSBM responder endpoint were 13% for LINZESS 72 mcg and 5% for placebo. The difference between LINZESS 72 mcg and placebo was 9% (95% CI: 4.8%, 12.5%).
A separate analysis was performed using an alternate CSBM responder definition. In this analysis a CSBM responder was defined as a patient who had at least 3 CSBMs and an increase of at least 1 CSBM from baseline in a given week for at least 9 weeks out of the 12-week treatment period and at least 3 of the last 4 weeks of the treatment period. The response rates for the alternate CSBM responder endpoint were 12% for LINZESS 72 mcg and 5% for placebo. The difference between LINZESS 72 mcg and placebo was 8% (95% CI: 3.9%, 11.5%).
1.400000000000000e+01 4 Functional Constipation (FC) in Pediatric Patients 6 Years of Age and Older
The efficacy of LINZESS for the treatment of FC in pediatric patients 6 to 17 years of age was established in a 12-week double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomized, multicenter, clinical trial (Trial 7; NCT04026113). A total of 328 patients received treatment with LINZESS 72 mcg or placebo once daily and were evaluated for efficacy. Patients in the trial had a mean age of 11 years (range 6 to 17 years); 55% were female; 45% identified as Hispanic or Latino; 70% identified as White, 26% as Black or African American, 2% as Asian, and 2% identified as another racial group. For trial enrollment, Rome III criteria for child/adolescent FC were modified to require that patients have less than 3 Spontaneous Bowel Movements (SBMs) per week (defined as a BM that occurred in the absence of laxative, enema, or suppository use on the calendar day of or before the BM) and 1 or more of the following criteria at least once per week for at least 2 months before the screening visit:
- History of stool withholding or excessive voluntary stool retention
- History of painful or hard bowel movements (BMs)
- History of large diameter stools that may obstruct the toilet
- Presence of a large fecal mass in the rectum
- At least 1 episode of fecal incontinence per week
Patients were also required to have an average of less than 3 SBMs per week during the 2-week baseline period. Patients were excluded if they met criteria for pediatric IBS-C or had fecal impaction. Patients were allowed to continue previously stable doses of bulk laxatives, fiber, stool softeners, or probiotics. During the trial, patients could use bisacodyl or senna as needed, but were not allowed to take other laxatives, bismuth, prokinetic agents, or other drugs to treat functional constipation.
The efficacy of LINZESS in the treatment of FC in pediatric patients 6 to 17 years of age was assessed using change-from-baseline endpoints. The primary efficacy endpoint was the 12-week change from baseline in SBM frequency rate. The results demonstrated that patients who received LINZESS had statistically significant improvements compared with placebo as shown in Table 8.
| Trial 7 | |||
| LINZESS 72 mcg Once Daily (N=164) | Placebo (N=164) | Treatment Difference [95% CI] | |
| Baseline SBM Frequency Rate | 1.2 | 1.3 | |
| Least Squares 12-week Mean Change from Baseline in SBM Frequency Rate• | 2.6 | 1.3 | 1.3 [0.7, 1.8] |
| • Primary Endpoint CI = Confidence Interval | |||
SBM frequency improved during week 1 and was maintained throughout the remainder of the 12-week treatment period.
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
How Supplied
| LINZESS Capsule Strength | Description | Packaging | NDC number |
| 72 mcg | White to off-white opaque hard gelatin capsules with gray imprint “FL 72” | Bottle of 30 | 0456-1203-30 |
| 145 mcg | White to off-white opaque hard gelatin capsules with gray imprint "FL 145" | Bottle of 30 | 0456-1201-30 |
| 290 mcg | White to off-white opaque hard gelatin capsules with gray imprint "FL 290" | Bottle of 30 | 0456-1202-30 |
Storage
Store at 25°C (77°F); excursions permitted between 15°C and 30°C (59°F and 86°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature].
Keep LINZESS in the original container. Do not subdivide or repackage. Protect from moisture. Do not remove desiccant from the container. Keep bottles tightly closed in a dry place.
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Linaclotide is structurally related to human guanylin and uroguanylin and functions as a guanylate cyclase-C (GC-C) agonist. Both linaclotide and its active metabolite bind to GC-C and act locally on the luminal surface of the intestinal epithelium. Activation of GC-C results in an increase in both intracellular and extracellular concentrations of cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP). Elevation in intracellular cGMP stimulates secretion of chloride and bicarbonate into the intestinal lumen, mainly through activation of the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) ion channel, resulting in increased intestinal fluid and accelerated transit. In animal models, linaclotide has been shown to both accelerate GI transit and reduce intestinal pain.
In an animal model of visceral pain, linaclotide reduced abdominal muscle contraction and decreased the activity of pain-sensing nerves by increasing extracellular cGMP.