Nubeqa prior authorization resources
Most recent state uniform prior authorization forms
Clinical information
Other resources
Dosage & administration
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Recommended Dosage : NUBEQA 600 mg (two 300 mg tablets) administered orally twice daily. Swallow tablets whole. Take NUBEQA with food. (2.1 )
For patients with mCSPC treated with NUBEQA in combination with docetaxel, administer the first cycle of docetaxel within 6 weeks after the start of NUBEQA treatment. (2.1 )
Patients should also receive a gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) agonist or antagonist concurrently or have had bilateral orchiectomy. (2.1 )
Recommended Dosage
The recommended dose of NUBEQA is 600 mg (two 300 mg tablets) taken orally, twice daily, with food [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ].
Continue treatment until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity occurs.
Patients receiving NUBEQA should also receive a gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) agonist or antagonist concurrently or have had a bilateral orchiectomy.
When used in combination with docetaxel for mCSPC, administer the first of 6 cycles of docetaxel within 6 weeks after the start of NUBEQA treatment. Refer to docetaxel prescribing information for additional dosing information, including dosage modifications. Treatment with NUBEQA may be continued until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity, even if a cycle of docetaxel is delayed, interrupted, or discontinued [see Dosage and Administration (2.2) ] .
Advise patients to swallow tablets whole with food, to take any missed dose as soon as they remember prior to the next scheduled dose, and not to take two doses together to make up for a missed dose.
Dosage Modification
If a patient experiences a greater than or equal to Grade 3 or an intolerable adverse reaction, withhold NUBEQA or reduce dosage to 300 mg twice daily until symptoms improve. NUBEQA may be resumed at a dose of 600 mg twice daily, when adverse reaction returns to baseline [see Adverse Reactions (6.1) ]. Dosage reduction below 300 mg twice daily is not recommended.
For patients who experience ischemic heart disease or seizure, additional dose modifications may be required [ see Warnings and Precautions (5.1 and 5.2) ].
Recommended Dosage in Patients with Severe Renal Impairment
For patients with severe renal impairment (eGFR 15–29 mL/min/1.73 m 2 ) not receiving hemodialysis, the recommended dose of NUBEQA is 300 mg twice daily [see Use in Specific Populations (8.6) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ] .
Recommended Dosage in Patients with Moderate Hepatic Impairment
For patients with moderate hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh Class B), the recommended dose of NUBEQA is 300 mg twice daily [see Use in Specific Populations (8.7) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ] .

By using PrescriberAI, you agree to the AI Terms of Use.
Nubeqa prescribing information
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
NUBEQA is an androgen receptor inhibitor indicated for the treatment of adult patients with:
NUBEQA is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with:
- non-metastatic castration resistant prostate cancer (nmCRPC)
- metastatic castration-sensitive prostate cancer (mCSPC)
- metastatic castration-sensitive prostate cancer (mCSPC) in combination with docetaxel.
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Recommended Dosage : NUBEQA 600 mg (two 300 mg tablets) administered orally twice daily. Swallow tablets whole. Take NUBEQA with food. (2.1 )
For patients with mCSPC treated with NUBEQA in combination with docetaxel, administer the first cycle of docetaxel within 6 weeks after the start of NUBEQA treatment. (2.1 )
Patients should also receive a gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) agonist or antagonist concurrently or have had bilateral orchiectomy. (2.1 )
Recommended Dosage
The recommended dose of NUBEQA is 600 mg (two 300 mg tablets) taken orally, twice daily, with food [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ].
Continue treatment until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity occurs.
Patients receiving NUBEQA should also receive a gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) agonist or antagonist concurrently or have had a bilateral orchiectomy.
When used in combination with docetaxel for mCSPC, administer the first of 6 cycles of docetaxel within 6 weeks after the start of NUBEQA treatment. Refer to docetaxel prescribing information for additional dosing information, including dosage modifications. Treatment with NUBEQA may be continued until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity, even if a cycle of docetaxel is delayed, interrupted, or discontinued [see Dosage and Administration (2.2) ] .
Advise patients to swallow tablets whole with food, to take any missed dose as soon as they remember prior to the next scheduled dose, and not to take two doses together to make up for a missed dose.
Dosage Modification
If a patient experiences a greater than or equal to Grade 3 or an intolerable adverse reaction, withhold NUBEQA or reduce dosage to 300 mg twice daily until symptoms improve. NUBEQA may be resumed at a dose of 600 mg twice daily, when adverse reaction returns to baseline [see Adverse Reactions (6.1) ]. Dosage reduction below 300 mg twice daily is not recommended.
For patients who experience ischemic heart disease or seizure, additional dose modifications may be required [ see Warnings and Precautions (5.1 and 5.2) ].
Recommended Dosage in Patients with Severe Renal Impairment
For patients with severe renal impairment (eGFR 15–29 mL/min/1.73 m 2 ) not receiving hemodialysis, the recommended dose of NUBEQA is 300 mg twice daily [see Use in Specific Populations (8.6) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ] .
Recommended Dosage in Patients with Moderate Hepatic Impairment
For patients with moderate hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh Class B), the recommended dose of NUBEQA is 300 mg twice daily [see Use in Specific Populations (8.7) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ] .
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Tablets (300 mg): white to off-white oval film-coated tablets marked with "300" on one side and "Bayer" on the other.
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
Pregnancy
Risk Summary
The safety and efficacy of NUBEQA have not been established in females. Based on its mechanism of action, NUBEQA can cause fetal harm and loss of pregnancy [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.1) ]. Animal embryo-fetal developmental toxicology studies were not conducted with darolutamide. There are no human data on the use of NUBEQA in pregnant females.
Lactation
Risk Summary
The safety and efficacy of NUBEQA have not been established in females. There are no data on the presence of darolutamide or its metabolites in human milk, the effect on the breastfed child, or the effect on milk production.
Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
Contraception
Males
Based on the mechanism of action, advise male patients with female partners of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment and for 1 week after the last dose of NUBEQA [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1) ].
Infertility
Males
Based on animal studies, NUBEQA may impair fertility in males of reproductive potential [see Nonclinical Toxicology (13.1) ] .
Pediatric Use
Safety and effectiveness of NUBEQA in pediatric patients have not been established.
Geriatric Use
Of the 954 patients who received NUBEQA in ARAMIS, 88% of patients were 65 years and over, and 49% were 75 years and over. Of the 445 patients who received NUBEQA in ARANOTE, 74% of patients were 65 years and over, and 30% were 75 years and over. Of the 652 patients who received NUBEQA in ARASENS, 63% of patients were 65 years and over, and 16% were 75 years and over. No overall differences in safety or efficacy were observed between these patients and younger patients in both studies.
Renal Impairment
Patients with severe renal impairment (eGFR 15–29 mL/min/1.73 m 2 ) who are not receiving hemodialysis have a higher exposure to NUBEQA and reduction of the dose is recommended [see Dosage and Administration (2.3) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ]. No dose reduction is needed for patients with mild or moderate renal impairment (eGFR 30-89 mL/min/1.73 m 2 ) . The effect of end stage renal disease (eGFR ≤15 mL/min/1.73 m 2 ) on darolutamide pharmacokinetics is unknown.
Hepatic Impairment
Patients with moderate hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh Class B) have a higher exposure to NUBEQA and reduction of the dose is recommended [see Dosage and Administration (2.4) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ]. No dose reduction is needed for patients with mild hepatic impairment. The effect of severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh C) on darolutamide pharmacokinetics is unknown.
CONTRAINDICATIONS
None.
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- Ischemic Heart Disease : Optimize management of cardiovascular risk factors. Monitor for signs and symptoms of coronary artery disease. Discontinue NUBEQA for Grade 3-4 events. (5.1 )
- Seizure : Consider discontinuation of NUBEQA in patients who develop a seizure during treatment. (5.2 )
- Embryo-Fetal Toxicity : NUBEQA can cause fetal harm and loss of pregnancy. Advise males with female partners of reproductive potential to use effective contraception. (5.3 , 8.1 , 8.3 )
Ischemic Heart Disease
Ischemic heart disease, including fatal cases, occurred in patients receiving NUBEQA.
In a pooled analysis of ARAMIS and ARANOTE, ischemic heart disease occurred in 3.4% of patients receiving NUBEQA and 2.2% receiving placebo, including Grade 3-4 events in 1.4% and 0.3%, respectively. Ischemic events led to death in 0.4% of patients receiving NUBEQA and 0.4% receiving placebo.
In ARASENS, ischemic heart disease occurred in 3.2% of patients receiving NUBEQA with docetaxel and 2% receiving placebo with docetaxel, including Grade 3-4 events in 1.3% and 1.1%, respectively. Ischemic events led to death in 0.3% of patients receiving NUBEQA with docetaxel and 0% receiving placebo with docetaxel.
Monitor for signs and symptoms of ischemic heart disease. Optimize management of cardiovascular risk factors, such as hypertension, diabetes, or dyslipidemia. Discontinue NUBEQA for Grade 3-4 ischemic heart disease.
Seizure
Seizure occurred in patients receiving NUBEQA.
In a pooled analysis of ARAMIS and ARANOTE, Grade 1-3 seizure occurred in 0.2% of patients receiving NUBEQA. Seizure occurred from 261 to 665 days after initiation of NUBEQA.
In ARASENS, seizure occurred in 0.8% of patients receiving NUBEQA with docetaxel, including two Grade 3 events. Seizure occurred from 38 to 1754 days after initiation of NUBEQA.
It is unknown whether anti-epileptic medications will prevent seizures with NUBEQA. Advise patients of the risk of developing a seizure while receiving NUBEQA and of engaging in any activity where sudden loss of consciousness could cause harm to themselves or others. Consider discontinuation of NUBEQA in patients who develop a seizure during treatment.
Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
The safety and efficacy of NUBEQA have not been established in females. Based on its mechanism of action, NUBEQA can cause fetal harm and loss of pregnancy when administered to a pregnant female [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.1) ] .
Advise males with female partners of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment and for 1 week after the last dose of NUBEQA [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1 , 8.3) ] .
ADVERSE REACTIONS
In nmCRPC and mCSPC : The most common adverse reactions (>10% with a ≥2% increase over placebo), including laboratory test abnormalities, are increased AST, decreased neutrophil count, increased bilirubin, fatigue, and increased ALT. (6.1 )
In mCSPC in combination with docetaxel : The most common adverse reactions (≥10% with a ≥2% increase over placebo) are constipation, rash, decreased appetite, hemorrhage, increased weight, and hypertension.
The most common laboratory test abnormalities (≥30%) are anemia, hyperglycemia, decreased lymphocyte count, decreased neutrophil count, increased AST, increased ALT, and hypocalcemia. (6.1 )
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Bayer HealthCare Pharmaceuticals Inc. at 1-888-842-2937 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or WWW.FDA.GOV/MEDWATCH.
Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
The pooled data in WARNINGS and PRECAUTIONS reflect two randomized clinical trials [ARAMIS, ARANOTE] in patients with nmCRPC (N = 954) and mCSPC (N = 445) treated with NUBEQA. In these trials, the median duration of treatment was 18.2 months (range 0.03 to 44.3) for patients who received NUBEQA [ see Clinical Studies (14) ]. In this pooled safety population, the most common adverse reactions (>10% with a ≥2% increase over placebo), including laboratory test abnormalities were increased AST, decreased neutrophil count, increased bilirubin, fatigue and increased ALT.
The safety of NUBEQA in combination with docetaxel in mCSPC is based on data from 1302 patients of whom 652 received at least one dose of NUBEQA in the ARASENS study [ see Clinical Studies (14) ].
Non-Metastatic Castration Resistant Prostate Cancer
ARAMIS
The safety of NUBEQA in nmCRPC patients was evaluated in ARAMIS, a randomized (2:1), double-blind, placebo-controlled, multi-center clinical study [see Clinical Studies (14) ] . Patients received either NUBEQA at a dose of 600 mg, or a placebo, twice a day. All patients in the ARAMIS study received a concomitant gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) analog or had a bilateral orchiectomy. Among patients who received NUBEQA, the median duration of exposure was 14.8 months (range: 0 to 44.3 months).
Serious adverse reactions occurred in 25% of patients receiving NUBEQA and in 20% of patients receiving placebo. Serious adverse reactions in ≥1% of patients who received NUBEQA included urinary retention, pneumonia and hematuria. Fatal adverse reactions occurred in 3.9% of patients receiving NUBEQA and 3.2% of patients receiving placebo. Fatal adverse reactions that occurred in ≥2 patients who received NUBEQA included death (0.4%), cardiac failure (0.3%), cardiac arrest (0.2%), general physical health deterioration (0.2%), and pulmonary embolism (0.2%).
Permanent discontinuation of NUBEQA due to adverse reactions occurred in 9% of patients receiving NUBEQA. The most common adverse reactions requiring permanent discontinuation in patients who received NUBEQA included cardiac failure (0.4%), and death (0.4%).
Dosage interruptions due to adverse reactions occurred in 13% of patients treated with NUBEQA. The most common adverse reactions requiring dosage interruption in patients who received NUBEQA included hypertension (0.6%), diarrhea (0.5%), and pneumonia (0.5%).
Dosage reductions due to adverse reactions occurred in 6% of patients treated with NUBEQA. The most common adverse reactions requiring dosage reduction in patients treated with NUBEQA included fatigue (0.7%), hypertension (0.3%), and nausea (0.3%).
The most common (>2% with a ≥2% increase compared to placebo) adverse reactions, including laboratory test abnormalities, were increased AST, decreased neutrophil count, fatigue, increased bilirubin, pain in extremity, and rash.
Table 1 summarizes the adverse reactions in ARAMIS.
| Adverse Reaction | NUBEQA (N=954) | Placebo (N=554) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| All Grades % | Grades 3 or 4 % | All Grades % | Grade 3 or 4 % | |
| Fatigue Includes fatigue and asthenia | 16 | 0.6 | 11 | 1.1 |
| Pain in extremity | 6 | 0 | 3 | 0.2 |
| Rash Includes rash, eczema, rash maculo-papular, dermatitis, erythema multiforme, rash macular, rash papular, rash pustular, skin exfoliation | 4 | 0.1 | 1.4 | 0 |
Clinically relevant adverse reactions occurring in 2% or more of patients treated with NUBEQA included ischemic heart disease (4%) and heart failure (2.1%).
Table 2 summarizes the laboratory test abnormalities in ARAMIS.
| Laboratory Abnormality | NUBEQA (N=954) The denominator used to calculate the rate varied based on the number of patients with a baseline value and at least one post-treatment value. | Placebo (N=554) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| All Grades % | Grade 3 or 4 % | All Grades % | Grade 3 or 4 % | |
AST increased | 23 | 0.5 | 14 | 0.2 |
Neutrophil count decreased | 20 | 4 | 9 | 0.6 |
Bilirubin increased | 16 | 0.1 | 7 | 0 |
Metastatic Castration-Sensitive Prostate Cancer
ARANOTE
The safety of NUBEQA in mCSPC patients was evaluated in ARANOTE, a randomized (2:1), double-blind, placebo-controlled, multi-center clinical study [see Clinical Studies (14) ]. Patients received either NUBEQA at a dose of 600 mg, or a placebo, twice a day. All patients in the ARANOTE study received a concomitant gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) agonist or antagonist or had a bilateral orchiectomy. Among patients who received NUBEQA, the median duration of exposure was 24 months (range: 0.03 to 39 months).
Serious adverse reactions occurred in 24% of patients receiving NUBEQA. Serious adverse reactions in ≥1% of patients who received NUBEQA included pneumonia (2%), urinary tract infection (1.8%), musculoskeletal pain (1.6%), hemorrhage (1.6%), arrhythmias (1.3%), and spinal cord compression (1.1%). Fatal adverse reactions occurred in 4.7% of patients receiving NUBEQA and those that occurred in ≥2 patients included sepsis (1.1%), craniocerebral injury (0.4%), and myocardial infarction (0.4%).
Permanent discontinuation of NUBEQA due to adverse reactions occurred in 6% of patients treated in the NUBEQA arm. The most common adverse reactions which resulted in permanent discontinuation of NUBEQA were increased ALT, increased AST, craniocerebral injury, myocardial infarction, and rash (all with 0.4%).
Dosage interruptions of NUBEQA due to adverse reactions occurred in 14% of patients treated in the NUBEQA arm. The most common adverse reactions requiring dosage interruption of NUBEQA were increased AST (1.6%), increased ALT (1.3%), and rash (1.3%).
Dosage reductions of NUBEQA due to adverse reactions occurred in 3.6% of patients treated in the NUBEQA arm. The most common adverse reactions requiring dosage reduction of NUBEQA were increased AST (0.7%), rash (0.7%), increased ALT (0.4%), and hypertension (0.4%).
Table 3 summarizes the adverse reactions in ARANOTE.
| Adverse Reaction | NUBEQA (N=445) | Placebo (N=221) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| All Grades (%) | Grade 3 or 4 (%) | All Grades (%) | Grade 3 or 4 (%) | |
| Urinary Tract Infection | 12 | 1.8 | 8 | 0.5 |
Clinically relevant adverse reactions in <10% of patients who received NUBEQA included arrhythmia (8.8%), pneumonia (3.6%), and myocardial infarction (0.7%).
Table 4 summarizes the laboratory test abnormalities in ARANOTE.
| Laboratory Abnormality | NUBEQA (N=445) The number of patients tested for a specific laboratory test parameter may be different. The incidence of each laboratory test abnormality was calculated accordingly. | Placebo (N=221) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| All Grades Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (CTCAE) version 5.0. Grade 4 laboratory test values were limited to neutrophil count decreased. % | Grade 3 or 4 % | All Grades % | Grade 3 or 4 % | |
| AST increased | 32 | 2.8 | 25 | 0.5 |
| ALT increased | 28 | 2.1 | 23 | 0.5 |
| Bilirubin increased | 17 | 0.5 | 7 | 0 |
| Neutrophil count decreased | 16 | 1.2 | 9 | 0.5 |
ARASENS
The safety of NUBEQA, in combination with docetaxel, in mCSPC patients was evaluated in ARASENS, a randomized (1:1), double-blind, placebo-controlled, multi-center clinical study [see Clinical Studies (14) ] . Patients were to receive either NUBEQA at a dose of 600 mg, or a placebo, twice a day in combination with docetaxel at a dose of 75 mg/m2 every 21 days for 6 cycles. All patients in the ARASENS study received a concomitant gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) agonist or antagonist or had a bilateral orchiectomy. Among patients who received NUBEQA, the median duration of exposure was 41 months (range: 0.1 to 56.5 months) vs. 16.7 months (range 0.3 to 55.8) with placebo. Eighty-eight percent and 86% of patients received the 6 planned cycles of docetaxel, in the NUBEQA with docetaxel arm and placebo with docetaxel arm, respectively.
Serious adverse reactions occurred in 45% of patients receiving NUBEQA with docetaxel. Serious adverse reactions in ≥ 2% of patients who received NUBEQA with docetaxel included febrile neutropenia (6%), neutrophil count decreased (2.8%), musculoskeletal pain (2.6%) and pneumonia (2.6%). Fatal adverse reactions occurred in 4% of patients receiving NUBEQA with docetaxel. Fatal adverse reactions in ≥2 patients who received NUBEQA included COVID-19/COVID-19 pneumonia (0.8%), myocardial infarction (0.3%), and sudden death (0.3%).
Permanent discontinuation of NUBEQA due to adverse reactions occurred in 14% of patients treated in the NUBEQA with docetaxel arm. The most common adverse reactions which resulted in permanent discontinuation of NUBEQA were rash (1.1%), musculoskeletal pain (0.9%), and increased aspartate aminotransferase (AST) (0.9%).
Dosage interruptions of NUBEQA due to adverse reactions occurred in 23% of patients treated in the NUBEQA with docetaxel arm. The most common (>2%) adverse reactions requiring dosage interruption of NUBEQA were increased alanine aminotransferase (ALT) (3.2%), increased AST (3.1%) and febrile neutropenia (2.1%).
Dosage reductions of NUBEQA due to adverse reactions occurred in 9% of patients treated in the NUBEQA with docetaxel arm. The most common (>2%) adverse reactions requiring dosage reduction of NUBEQA were increased ALT (2.8%) and increased AST (2.5%).
The most common ( > 10% with a ≥2% increase over placebo with docetaxel) adverse reactions are constipation, rash, decreased appetite, hemorrhage, increased weight, and hypertension. The most common laboratory test abnormalities (≥30%) are anemia, hyperglycemia, decreased lymphocyte count, decreased neutrophil count, increased AST, increased ALT, and hypocalcemia.
Table 5 summarizes the adverse reactions in ARASENS.
| Adverse Reaction | NUBEQA with docetaxel (N=652) | Placebo with docetaxel (N=650) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| All Grades % | Grades 3 or 4 % | All Grades % | Grades 3 or 4 % | |
| Constipation | 23 | 0.3 | 20 | 0.3 |
| Rash Rash includes rash, rash maculo-papular, palmar-plantar erythrodysesthesia syndrome, eczema, dermatitis, skin exfoliation, dermatitis acneiform, drug eruption, rash pruritic, rash erythematous, erythema multiforme, rash macular, dermatitis exfoliative generalized, penile rash, dyshidrotic eczema, rash papular, dermatitis bullous, rash follicular, rash pustular, rash vesicular, toxic skin eruption | 20 | 1.8 | 15 | 0.2 |
| Decreased Appetite | 19 | 0.2 | 13 | 0.6 |
| Hemorrhage Hemorrhage includes hematuria, epistaxis, anal hemorrhage, hemorrhoidal hemorrhage, rectal hemorrhage, upper gastrointestinal hemorrhage, hemoptysis, hemorrhage urinary tract, hemorrhagic stroke, subarachnoid hemorrhage, lower gastrointestinal hemorrhage, cystitis hemorrhagic, gastrointestinal hemorrhage, hemorrhage subcutaneous, intra-abdominal hemorrhage, nail bed bleeding, subdural hemorrhage | 18 | 1.4 | 13 | 1.4 |
| Weight Increased | 18 | 2.1 | 16 | 1.2 |
| Hypertension Hypertension includes hypertension, blood pressure increased, hypertensive emergency and hypertensive crisis. | 14 | 7 | 10 | 3.6 |
Clinically relevant adverse reactions in < 10% of patients who received NUBEQA with docetaxel included fractures (8%), ischemic heart disease (3.2%), seizures (0.6%), and drug-induced liver injury (0.3%).
Table 6 summarizes laboratory test abnormalities in the ARASENS study.
| Laboratory Abnormality | NUBEQA with docetaxel The denominator used to calculate the rate varied from 470 to 648 based on the number of patients with a baseline value and at least one post-treatment value. (N=652) | Placebo with docetaxel (N=650) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| All Grades % | Grade 3-4 % | All Grades % | Grade 3-4 % | |
| Anemia | 72 | 6 | 71 | 7 |
| Hyperglycemia | 57 | 7 | 53 | 10 |
| Lymphocyte count decreased | 52 | 12 | 49 | 13 |
| Neutrophil count decreased | 49 | 33 | 44 | 31 |
| AST increased ALT or AST increases to ≥5 × upper limit of normal (ULN) occurred in 5.3% of patients who received NUBEQA with docetaxel. ALT or AST increases to ≥20 × ULN occurred in 0.3% of patients who received NUBEQA with docetaxel. The median time to onset of any grade ALT or AST increases was 2.8 months (range: 0.03 to 46.9). | 40 | 3.6 | 35 | 2.3 |
| ALT increased | 37 | 3.7 | 31 | 2.9 |
| Hypocalcemia | 31 | 2.8 | 28 | 1.9 |
Clinically relevant laboratory test abnormalities in < 30% of patients who received NUBEQA with docetaxel included blood bilirubin increased (all grades 20%, Grade 3-4 0.5%) compared to placebo with docetaxel (all grades 10%, grades 3-4 0.3%).
DRUG INTERACTIONS
- Combined P-gp and Strong or Moderate CYP3A Inducers : Avoid concomitant use. (7.1 )
- Combined P-gp and Strong CYP3A Inhibitors : Monitor patients more frequently for NUBEQA adverse reactions. (7.1 )
- BCRP Substrates : Avoid concomitant use with drugs that are BCRP substrates where possible. If used together, monitor patients more frequently for adverse reactions and consider dose reduction of the BCRP substrate drug. (7.2 )
- OATP1B1 and OATP1B3 Substrates : Concomitant use of NUBEQA may increase the plasma concentrations of OATP1B1 or OATP1B3 substrates. If used together, monitor patients more frequently for adverse reactions and consider dose reduction of these drugs. (7.2 )
Effects of Other Drugs on NUBEQA
Combined P-gp and Strong or Moderate CYP3A4 Inducer
Concomitant use of NUBEQA with a combined P-gp and strong or moderate CYP3A4 inducer decreases darolutamide exposure which may decrease NUBEQA activity [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ] . Avoid concomitant use of NUBEQA with combined P-gp and strong or moderate CYP3A4 inducers.
Combined P-gp and Strong CYP3A4 Inhibitors
Concomitant use of NUBEQA with a combined P-gp and strong CYP3A4 inhibitor increases darolutamide exposure [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ] which may increase the risk of NUBEQA adverse reactions . Monitor patients more frequently for NUBEQA adverse reactions and modify NUBEQA dosage as needed [see Dosage and Administration (2.2) ] .
Effects of NUBEQA on Other Drugs
Breast Cancer Resistance Protein (BCRP) and Organic Anion Transporting Polypeptides (OATP) 1B1 and 1B3 Substrates
NUBEQA is an inhibitor of BCRP transporter. Concomitant use of NUBEQA increases the AUC and C max of BCRP substrates [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ], which may increase the risk of BCRP substrate-related toxicities.
Avoid concomitant use with drugs that are BCRP substrates where possible. If used together, monitor patients more frequently for adverse reactions, and consider dose reduction of the BCRP substrate drug.
NUBEQA is an inhibitor of OATP1B1 and OATP1B3 transporters. Concomitant use of NUBEQA may increase the plasma concentrations of OATP1B1 or OATP1B3 substrates. Monitor patients more frequently for adverse reactions of these drugs and consider dose reduction while patients are taking NUBEQA [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ] ,
Review the prescribing information of the BCRP, OATP1B1 and OATP1B3 substrates when used concomitantly with NUBEQA.
DESCRIPTION
NUBEQA is an androgen receptor inhibitor. The chemical name is N-{(2S)-1-[3-(3-chloro-4-cyanophenyl)-1H-pyrazol-1-yl]propan-2-yl}-5-(1-hydroxyethyl)-1H-pyrazole-3-carboxamide.
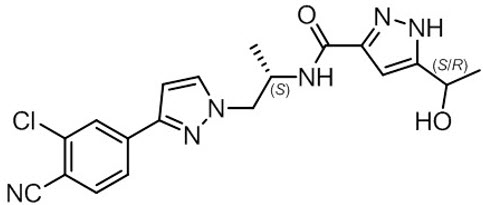
The molecular weight is 398.85 and the molecular formula is C 19 H 19 Cl N 6 O 2 . The structural formula is:
Darolutamide is an optically active with a specific rotation value [α] 20 D = 72.2 o •mL/(dm•g), white to greyish- or yellowish white crystalline powder, that is soluble in tetrahydrofuran, but practically insoluble in aqueous medium. Darolutamide has a pKa of 11.75.
NUBEQA (darolutamide) is supplied as film-coated tablets containing 300 mg of darolutamide for oral use. The inactive ingredients of the tablet are: calcium hydrogen phosphate, croscarmellose sodium, lactose monohydrate, magnesium stearate, povidone K 30, hypromellose 15 cP, macrogol 3350, and titanium dioxide.
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Mechanism of Action
Darolutamide is an androgen receptor (AR) inhibitor. Darolutamide competitively inhibits androgen binding, AR nuclear translocation, and AR-mediated transcription. A major metabolite, ketodarolutamide, exhibited similar in vitro activity to darolutamide. In addition, darolutamide functioned as a progesterone receptor (PR) antagonist in vitro (approximately 1% activity compared to AR). Darolutamide decreased prostate cancer cell proliferation in vitro and tumor volume in mouse xenograft models of prostate cancer.
Pharmacodynamics
PSA reduction was observed in CRPC patients receiving darolutamide doses of 100-900 mg twice a day, reaching a plateau of PSA reduction at the 600 mg twice daily dose.
Twice daily dosing of 600 mg darolutamide in nmCRPC patients resulted in undetectable PSA levels in 24% of patients at 12 months compared to 0.4% of patients in the placebo arm.
Twice daily dosing of 600 mg darolutamide in mCSPC patients resulted in undetectable PSA levels (<0.2 ng/mL) in 63% of patients compared to 19% of patients in the placebo arm.
Twice daily dosing of 600 mg darolutamide in combination with docetaxel in mCSPC patients resulted in undetectable PSA levels in 60% of patients at 12 months compared to 26% of patients in the placebo with docetaxel arm.
Cardiac Electrophysiology
The effect of darolutamide (600 mg twice daily) on the QTc interval was evaluated in a subgroup of 500 patients in the ARAMIS study. No large mean increase in QTc (i.e., > 20 ms) was detected.
Pharmacokinetics
Following administration of 600 mg twice daily, darolutamide mean (%CV) steady-state peak plasma concentration (C max ) is 4.79 mg/L (30.9%) and area under the plasma concentration-time curve from time 0 to 12 hours (AUC 12h ) is 52.82 h∙µg/mL (33.9%). Steady-state is reached 2–5 days after repeated dosing with food, with an approximate 2-fold accumulation.
The exposure (C max and AUC 12 ) of the darolutamide and the active metabolite ketodarolutamide increase in a nearly dose-proportional manner in the dose range of 100 to 700 mg (0.17 to 1.17 times the approved recommended dosage). No further increase in darolutamide exposure was observed at 900 mg twice daily (1.5 times the approved recommended dosage).
Absorption
Darolutamide C max is reached approximately 4 hours after administration of a single 600 mg oral dose.
The absolute bioavailability is approximately 30% following oral administration of a NUBEQA tablet containing 300 mg darolutamide under fasted conditions.
Food Effect
Bioavailability of darolutamide increased by 2.0- to 2.5‑fold when administered with food. A similar increase of exposure was observed for the active metabolite ketodarolutamide.
Distribution
The apparent volume of distribution of darolutamide after intravenous administration is 119 L.
Protein binding is 92% for darolutamide and 99.8% for the active metabolite, ketodarolutamide. Serum albumin is the main binding protein for darolutamide and ketodarolutamide.
Elimination
The effective half-life of darolutamide and ketodarolutamide is approximately 20 hours in patients. The clearance (%CV) of darolutamide following intravenous administration is 116 mL/min (39.7%).
Metabolism
Darolutamide is primarily metabolized by CYP3A4, as well as by UGT1A9 and UGT1A1. Ketodarolutamide total exposure in plasma is 1.7‑fold higher compared to darolutamide.
Excretion
After a single radiolabeled dose as an oral solution, a total of 63.4% of darolutamide‑related material is excreted in the urine (approximately 7% unchanged) and 32.4% (approximately 30% unchanged) in the feces. More than 95% of the dose was recovered within 7 days after administration.
Specific Populations
No clinically significant differences in the pharmacokinetics of darolutamide were observed based on age (41-95 years), race (White, Asian, Black or African American), mild to moderate renal impairment (eGFR 30–89 mL/min/1.73m 2 ), or mild hepatic impairment.
In non-cancer subjects with severe renal impairment (eGFR 15–29 mL/min/1.73 m 2 ) not receiving dialysis or with moderate hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh Class B), NUBEQA exposure increased by about 2.5- and 1.9-fold, respectively, compared to healthy subjects.
The effect of end-stage renal disease (eGFR <15 mL/min/1.73 m 2 ) or severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh C) on darolutamide pharmacokinetics has not been studied.
Drug Interaction Studies
Clinical Studies
Combined P-gp and Strong CYP3A4 Inducers
Concomitant use of rifampicin (a combined P-gp and strong CYP3A4 inducer) decreased mean darolutamide AUC 0-72 by 72% and C max by 52%. The decrease of darolutamide exposure by moderate CYP3A4 inducers is expected to be in the range of 36% – 58%.
Combined P-gp and Strong CYP3A4 Inhibitors
Itraconazole (a strong combined CYP3A4 and P-gp inhibitor) increased mean darolutamide AUC 0-72 by 1.7- and C max by 1.4-fold.
CYP3A4 substrates
Concomitant use of darolutamide decreased the mean AUC and C max of midazolam (CYP3A4 substrate) by 29% and 32%, respectively. No clinically relevant differences in the pharmacokinetics of midazolam were observed when used concomitantly with darolutamide.
BCRP, OATP1B1 and OATP1B3 Substrates
Concomitant use of darolutamide increased the mean AUC and C max of rosuvastatin (BCRP, OATP1B1 and OATP1B3 substrate) by approximately 5-fold.
Docetaxel
Administration of darolutamide in combination with docetaxel resulted in no clinically relevant changes in the pharmacokinetics of docetaxel in mCSPC patients. There were no clinically relevant changes in the pharmacokinetics of darolutamide, when used in combination with docetaxel .
P-gp Substrates
No clinically relevant differences in the pharmacokinetics of dabigatran (P-gp substrate) were observed when used concomitantly with darolutamide.
In vitro , darolutamide did not inhibit the major CYP enzymes (CYP1A2, 2A6, 2B6, 2C8, 2C9, 2C19, 2D6, 2E1, and 3A4) or transporters (MRP2, BSEP, OATs, OCTs, MATEs, OATP2B1, and NTCP) at clinically relevant concentrations.
NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Oral administration of darolutamide to male and female RasH2 transgenic mice for 26 weeks did not show carcinogenic potential at doses up to 1000 mg/kg/day.
Darolutamide was clastogenic in an in vitro chromosome aberration assay in human peripheral blood lymphocytes. Darolutamide did not induce mutations in the bacterial reverse mutation (Ames) assay and was not genotoxic in the in vivo combined bone marrow micronucleus assay and the Comet assay in the liver and duodenum of the rat.
Fertility studies in animals have not been conducted with darolutamide. In repeat-dose toxicity studies in male rats (up to 26 weeks) and dogs (up to 39 weeks), tubular dilatation of testes, hypospermia, and atrophy of seminal vesicles, testes, prostate gland and epididymides were observed at doses ≥ 100 mg/kg/day in rats (0.6 times the human exposure based on AUC) and ≥ 50 mg/kg/day in dogs (approximately 1 times the human exposure based on AUC).
CLINICAL STUDIES
Non-Metastatic Castration Resistant Prostate Cancer
ARAMIS (NCT02200614) was a multicenter, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial in 1509 patients with non-metastatic castration resistant prostate cancer with a prostate-specific antigen doubling time (PSADT) of ≤ 10 months. Randomization was stratified by PSADT and use of bone-targeted therapy at study entry. Patients with pelvic lymph nodes less than 2 cm in short axis below the aortic bifurcation were eligible to enter the study. Absence or presence of metastasis was assessed by blinded independent central review (BICR). PSA results were not blinded and were not used for treatment discontinuation.
Patients were randomized 2:1 to receive either 600 mg NUBEQA orally twice daily (n=955) or matching placebo (n=554). Treatment continued until radiographic disease progression as assessed by CT, MRI, 99m Tc bone scan by BICR, unacceptable toxicity or withdrawal. All patients received a gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) analog concurrently or had a bilateral orchiectomy.
The median age was 74 years (range 48–95) and 9% of patients were 85 years of age or older. The racial distribution included 79% White, 13% Asian, 3% Black or African American, while ethnicity included 3.1% Hispanic or Latino patients. A majority of patients (73%) had a Gleason score of 7 or higher at diagnosis. The median PSADT was 4.5 months. Forty-two percent of patients in both treatment arms had prior surgery or radiotherapy to the prostate. Eleven percent of patients had enlarged pelvic lymph nodes less than 2 cm at study entry. Six percent of patients were retrospectively identified by BICR as having metastases at baseline. Seventy-three percent of patients received prior treatment with an anti-androgen (bicalutamide or flutamide). All patients had an Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group Performance Status (ECOG PS) score of 0 or 1 at study entry. At baseline, 47% of patients reported no pain on the Brief Pain Inventory-Short Form (a 7-day diary average of the daily worst pain item). There were 12 patients (1.3%) enrolled on the NUBEQA arm with a history of seizure.
The major efficacy endpoint was metastasis free survival (MFS), defined as the time from randomization to the time of first evidence of BICR-confirmed distant metastasis or death from any cause within 33 weeks after the last evaluable scan, whichever occurred first. Distant metastasis was defined as new bone or soft tissue lesions or enlarged lymph nodes above the aortic bifurcation. Overall survival (OS), time to pain progression, and time to initiation of cytotoxic chemotherapy, were additional efficacy endpoints.
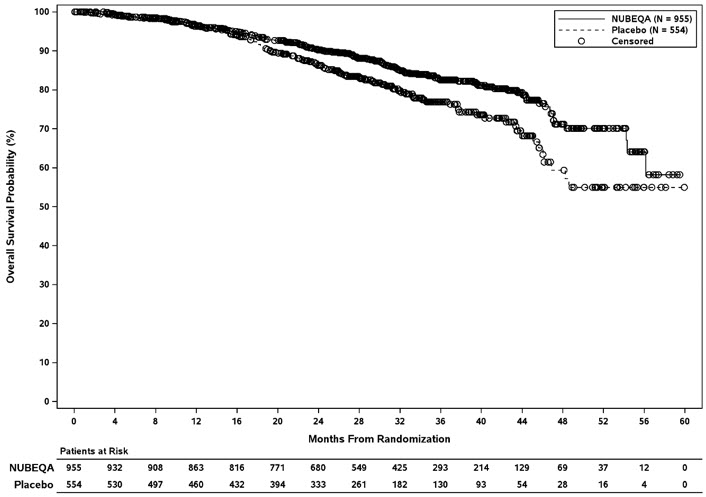
Treatment with NUBEQA resulted in a statistically significant improvement in MFS compared to placebo. At the protocol-specified final analysis of OS, treatment with NUBEQA resulted in a statistically significant improvement in OS compared to placebo. The final analysis of OS and time to initiation of cytotoxic chemotherapy was event-driven and conducted after 254 OS events had occurred. The efficacy results from ARAMIS are summarized in Table 7 and Figure 1.
| NUBEQA (N=955) | Placebo (N=554) | |
|---|---|---|
| NR: not reached | ||
| Metastasis-free survival Locoregional-only progression occurred in 6% of patients overall. | ||
| Distant Metastasis or Death (%) | 221 (23) | 216 (39) |
| Median, months (95% CI) Based on Kaplan-Meier estimates | 40.4 (34.3, NR) | 18.4 (15.5, 22.3) |
| Hazard Ratio (95% CI) Hazard ratio is based on a stratified Cox regression model. Hazard ratio < 1 favors NUBEQA. | 0.41 (0.34, 0.50) | |
| P-value The pre-specified final OS analysis was event-driven and occurred 14 months after the MFS analysis | <0.0001 | |
| Overall survival | ||
| Deaths (%) | 148 (15) | 106 (19) |
| Median, months (95% CI) | NR (56.1, NR) | NR (46.9, NR) |
| Hazard Ratio (95% CI) | 0.69 (0.53, 0.88) | |
| P-value P-value is based on a log-rank test stratified by PSADT (≤ 6 months vs. > 6 months) and use of osteoclast-targeted therapy (yes vs. no) | 0.003 | |
Figure 1: Kaplan-Meier Curve Metastasis Free Survival; Intent-To-Treat nmCRPC population (ARAMIS)
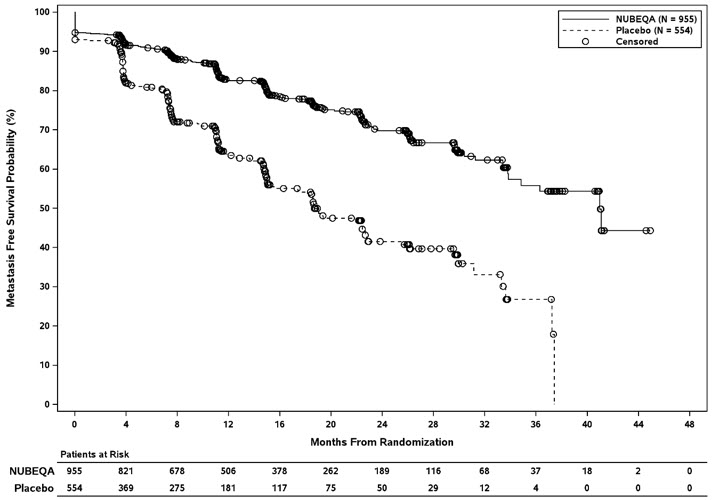
Figure 2: Kaplan-Meier curves of Overall Survival; Intent-To-Treat nmCRPC population (ARAMIS)
MFS results were consistent across patient subgroups for PSADT (≤ 6 months or > 6 months) or prior use of bone-targeting agents (yes or no).
Treatment with NUBEQA resulted in a statistically significant delay in time to pain progression (HR = 0.65, 95% CI= 0.53, 0.79; p < 0.0001). Time to pain progression was defined as at least a 2-point worsening from baseline of the pain score on Brief Pain Inventory Short Form or initiation of opioids and reported in 28% of all patients on study.
Treatment with NUBEQA resulted in a statistically significant delay in the initiation of cytotoxic chemotherapy (HR = 0.58, 95% CI = 0.44, 0.76; p < 0.0001).
Metastatic Castration Sensitive Prostate Cancer (mCSPC)
ARANOTE
ARANOTE (NCT02799602) was a multicenter, double-blind, placebo-controlled study in 669 patients with mCSPC. Patients were randomized 2:1 to receive 600 mg NUBEQA orally twice daily (n=446) or matching placebo (n=223). Patients with both high- and low-volume mCSPC were eligible for the study. High-volume disease was defined as presence of visceral metastases, or 4 or more bone lesions, with at least 1 metastasis beyond the vertebral column and pelvic bones. Randomization was stratified by presence of visceral metastasis and use of prior local therapy at study entry. All patients received a gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) agonist or antagonist concurrently or had a bilateral orchiectomy. Treatment with NUBEQA or placebo continued until progressive disease, change of antineoplastic therapy, unacceptable toxicity, death, or withdrawal.
The median age was 70 years (range 43-93) and 29% of patients were 75 years of age or older. The racial distribution was 56% White, 31% Asian, and 10% Black; while ethnicity included 24% Hispanic patients. Sixty-eight percent (68%) of patients had a Gleason score of 8 or higher at diagnosis. At study entry, ECOG PS of 0, 1, and 2 were 50%, 47%, and 3%, respectively. Seventy-three percent (73%) of patients had de novo disease and 22% had recurrent disease. Seventy-one percent (71%) of patients had high-volume disease, including 12% with visceral metastases, and 29% had low-volume disease. The median PSA level at baseline was 21 µg/L. One patient (0.2%) with a medical history of seizure was treated with NUBEQA in ARANOTE.
The major efficacy outcome measure was radiographic progression-free survival (rPFS), defined as the time from randomization to radiological disease progression or death by central blinded review. Radiographic disease progression was defined by identification of 2 or more new bone lesions on a bone scan with confirmation (Prostate Cancer Working Group 3 criteria) and/or progression in soft tissue disease. Additional efficacy outcome measure was overall survival (OS).
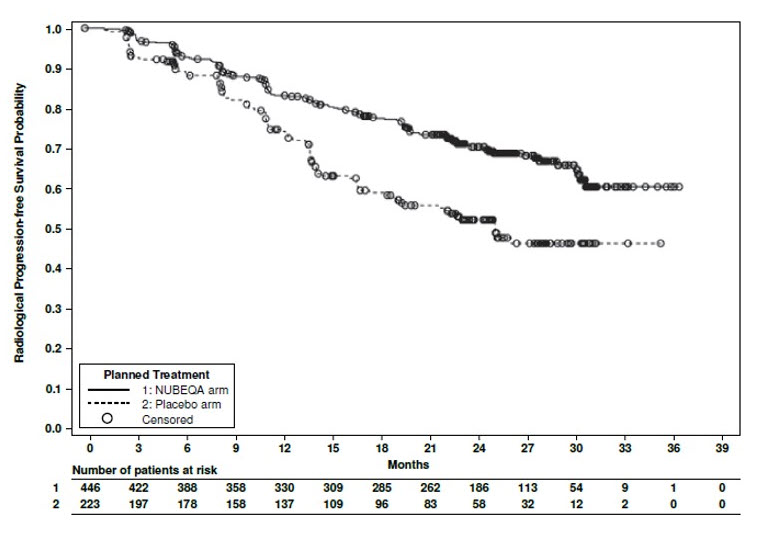
Treatment with NUBEQA resulted in a statistically significant improvement in rPFS compared to placebo. There was no statistically significant improvement in OS.
Efficacy results for ARANOTE are shown in Table 8 and Figure 3.
| Efficacy Endpoint | NUBEQA (N=446) | Placebo (N=223) |
|---|---|---|
| NR: not reached | ||
| NS: not statistically significant | ||
| Radiographic Progression-Free Survival | ||
| Patients with event, n (%) | 128 (29) | 94 (42) |
| Median, months (95% CI) | NR (NR, NR) | 25 (19, NR) |
| Hazard ratio (95% CI) Based on stratified Cox regression model | 0.54 (0.41, 0.71) | |
| p-value Based on stratified log-rank test | <0.0001 | |
| Overall Survival | ||
| Patients with event, n (%) | 115 (26) | 70 (31) |
| Median, months (95% CI) | NR (NR, NR) | NR (NR, NR) |
| Hazard Ratio (95% CI) | 0.78 (0.58, 1.05) | |
| p-value | NS | |
Figure 3: Kaplan-Meier Curves for Radiographic Progression-Free Survival; mCSPC population (ARANOTE)
ARASENS
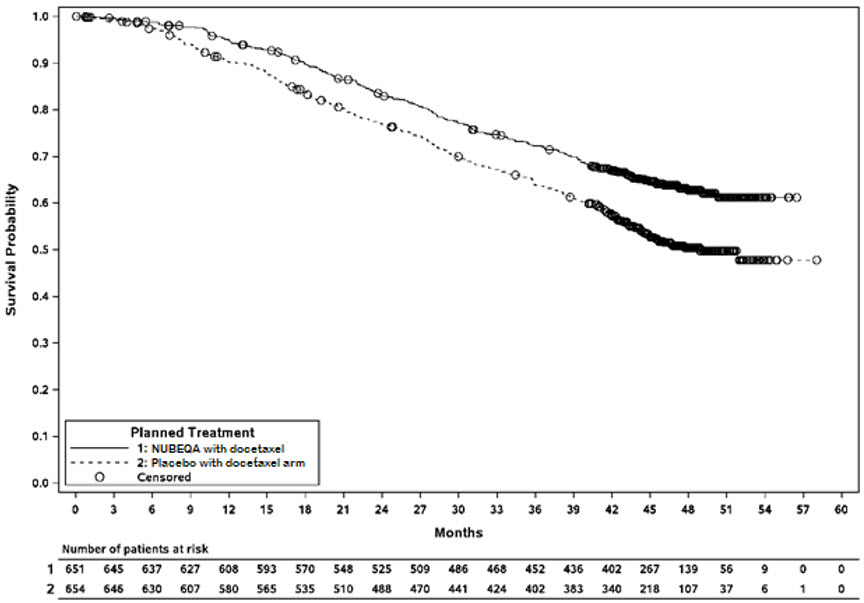
ARASENS (NCT02799602) was a multicenter, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial in 1306 patients with mCSPC. Patients were randomized 1:1 to receive 600 mg NUBEQA orally twice daily (n=651) or matching placebo (n=655), concomitantly with 75 mg/m 2 of docetaxel for 6 cycles. All patients received a gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) agonist or antagonist concurrently or had a bilateral orchiectomy. Treatment with NUBEQA or placebo continued until symptomatic progressive disease, change of antineoplastic therapy, or unacceptable toxicity. Patients with regional lymph node involvement only (M0) were excluded from the study. Patients were stratified by extent of disease (non–regional lymph nodes metastases only (M1a), bone metastases with or without lymph node metastases (M1b) or visceral metastases with or without lymph node metastases or with or without bone metastases (M1c)) and by alkaline phosphatase level (< or ≥ upper limit of normal) at study entry.
The median age was 67 years (range 41–89) and 17% of patients were 75 years of age or older. The racial distribution included 52% White, 36% Asian, 4% Black, while ethnicity included 7% Hispanic patients. Seventy-eight percent (78%) of patients had a Gleason score of ≥8 at diagnosis. Seventy one percent (71%) of patients had an ECOG performance status score of 0 and 29% patients had an ECOG performance status score of 1. There were 86% of patients with de novo and 13% with recurrent disease. At initial diagnosis of metastatic disease, 3% had M1a, 83% had M1b and 14% had M1c disease; alkaline phosphatase was < ULN in 45% of patients and ≥ ULN in 55% of patients; median PSA level at baseline was 30 µg/L and 24 µg/L for NUBEQA vs placebo group, respectively. Four patients (0.6%) with a medical history of seizure were treated with NUBEQA with docetaxel in ARASENS.
The major efficacy outcome measure was overall survival (OS). Time to pain progression was an additional efficacy outcome measure.
Treatment with NUBEQA with docetaxel resulted in a statistically significant improvement in OS compared to placebo with docetaxel. OS results were consistent across stratified subgroups (extent of disease and alkaline phosphatase level).
Efficacy results are shown in Table 9 and Figure 4.
| NUBEQA with docetaxel (N=651) | Placebo with docetaxel (N=654) One patient in the placebo arm was excluded from all analyses due to the violation of Good Clinical Practices | |
|---|---|---|
| NR: not reached | ||
| Overall survival | ||
| Deaths (%) | 229 (35) | 304 (46) |
| Median in months (95% CI) | NR (NR, NR) | 48.9 (44.4, NR) |
| Hazard Ratio (95% CI) Hazard ratio < 1 favors NUBEQA | 0.68 (0.57, 0.80) | |
| P-value P-value is one-sided, and based on a log-rank test stratified by extent of disease (non-regional lymph nodes metastases only or bone metastases with or without lymph node metastases or visceral metastases with or without lymph node metastases or with or without bone metastases) and Alkaline Phosphatase (ALP < ULN or ALP ≥ ULN) | <0.0001 | |
Figure 4: Kaplan-Meier curves of Overall Survival; mCSPC population (ARASENS)
Treatment with NUBEQA with docetaxel resulted in a statistically significant delay in time to pain progression (HR = 0.79, 95% CI= 0.66, 0.95; 1-sided p value = 0.006). Time to pain progression was defined as the time from randomization to the time of pain progression. Pain progression is defined as:
- An increase of 2 or more points in the "worst pain in 24 hours" score (WPS) from nadir observed at 2 consecutive evaluations at least 4 weeks apart, or initiation of short- or long-acting opioid use for pain for at least 7 consecutive days, for asymptomatic patients (WPS=0) at baseline
- An increase of 2 or more points in the "worst pain in 24 hours" score (WPS) from nadir observed at 2 consecutive evaluations at least 4 weeks apart, and a WPS of 4 or greater, or initiation of short- or long-acting opioid use for pain for at least 7 consecutive days, for symptomatic patients (WPS ≥ 1) at baseline
Patients with opioid use within 4 weeks before randomization were censored at randomization in this analysis (125 patients (19%) in the NUBEQA with docetaxel arm and 118 patients (18%) in the placebo with docetaxel arm).
HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
How Supplied
NUBEQA (darolutamide) 300 mg film-coated tablets are white to off-white, oval shaped tablets, marked with "300" on one side, and "BAYER" on the other side. NUBEQA 300 mg tablets are available in bottles of 120 tablets.
NDC 50419-395-01
Storage and Handling
Store at 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F); excursions permitted between 15°C and 30°C (59°F and 86°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature] .
Keep the bottle tightly closed after first opening.
Mechanism of Action
Darolutamide is an androgen receptor (AR) inhibitor. Darolutamide competitively inhibits androgen binding, AR nuclear translocation, and AR-mediated transcription. A major metabolite, ketodarolutamide, exhibited similar in vitro activity to darolutamide. In addition, darolutamide functioned as a progesterone receptor (PR) antagonist in vitro (approximately 1% activity compared to AR). Darolutamide decreased prostate cancer cell proliferation in vitro and tumor volume in mouse xenograft models of prostate cancer.