Get your patient on Orgovyx (Relugolix)
Orgovyx prior authorization resources
Most recent state uniform prior authorization forms
Brand Resources
Orgovyx patient education
Patient toolkit
Dosage & administration
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- Recommended Dosage: A loading dose of 360 mg on the first day of treatment followed by 120 mg taken orally once daily, at approximately the same time each day (2.1 ).
- ORGOVYX can be taken with or without food (2.1 , 12.3 ). Instruct patients to swallow tablets whole and not to crush or chew tablets (2.1 ).
Recommended Dosage
Initiate treatment of ORGOVYX with a loading dose of 360 mg on the first day and continue treatment with a 120 mg dose taken orally once daily at approximately the same time each day.
ORGOVYX can be taken with or without food [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3 )] . Instruct patients to swallow tablets whole and not to crush or chew tablets.
Advise patients to take a missed dose of ORGOVYX as soon as they remember. If the dose was missed by more than 12 hours, patients should not take the missed dose and resume with the next scheduled dose.
If treatment with ORGOVYX is interrupted for greater than 7 days, restart ORGOVYX with a loading dose of 360 mg on the first day, and continue with a dose of 120 mg once daily.
In patients treated with GnRH receptor agonists and antagonists for prostate cancer, treatment is usually continued upon development of nonmetastatic or metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer.
Dosage Modifications for P-gp Inhibitors
Avoid co-administration of ORGOVYX with oral P-gp inhibitors. If co-administration is unavoidable, take ORGOVYX first and separate dosing by at least 6 hours [ see Drug Interactions (7.1 ) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3 ) ] . Monitor patients for increased adverse reactions.
Treatment with ORGOVYX may be interrupted for up to two weeks if a short course of treatment with a P-gp inhibitor is required. Resume ORGOVYX after the P-gp inhibitor is discontinued. If treatment with ORGOVYX is interrupted for greater than 7 days, restart ORGOVYX with a loading dose of 360 mg on the first day and continue with a dose of 120 mg once daily.
Dosage Modifications for Combined P-gp and Strong CYP3A Inducers
Avoid co-administration of ORGOVYX with combined P-gp and strong CYP3A inducers. If co-administration is unavoidable, increase the ORGOVYX dose to 240 mg once daily. After discontinuation of the combined P-gp and strong CYP3A inducer, resume the recommended ORGOVYX dose of 120 mg once daily [see Drug Interactions (7.1 ) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3 )] .

Orgovyx prescribing information
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
ORGOVYX is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with advanced prostate cancer.
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- Recommended Dosage: A loading dose of 360 mg on the first day of treatment followed by 120 mg taken orally once daily, at approximately the same time each day (2.1 ).
- ORGOVYX can be taken with or without food (2.1 , 12.3 ). Instruct patients to swallow tablets whole and not to crush or chew tablets (2.1 ).
Recommended Dosage
Initiate treatment of ORGOVYX with a loading dose of 360 mg on the first day and continue treatment with a 120 mg dose taken orally once daily at approximately the same time each day.
ORGOVYX can be taken with or without food [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3 )] . Instruct patients to swallow tablets whole and not to crush or chew tablets.
Advise patients to take a missed dose of ORGOVYX as soon as they remember. If the dose was missed by more than 12 hours, patients should not take the missed dose and resume with the next scheduled dose.
If treatment with ORGOVYX is interrupted for greater than 7 days, restart ORGOVYX with a loading dose of 360 mg on the first day, and continue with a dose of 120 mg once daily.
In patients treated with GnRH receptor agonists and antagonists for prostate cancer, treatment is usually continued upon development of nonmetastatic or metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer.
Dosage Modifications for P-gp Inhibitors
Avoid co-administration of ORGOVYX with oral P-gp inhibitors. If co-administration is unavoidable, take ORGOVYX first and separate dosing by at least 6 hours [ see Drug Interactions (7.1 ) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3 ) ] . Monitor patients for increased adverse reactions.
Treatment with ORGOVYX may be interrupted for up to two weeks if a short course of treatment with a P-gp inhibitor is required. Resume ORGOVYX after the P-gp inhibitor is discontinued. If treatment with ORGOVYX is interrupted for greater than 7 days, restart ORGOVYX with a loading dose of 360 mg on the first day and continue with a dose of 120 mg once daily.
Dosage Modifications for Combined P-gp and Strong CYP3A Inducers
Avoid co-administration of ORGOVYX with combined P-gp and strong CYP3A inducers. If co-administration is unavoidable, increase the ORGOVYX dose to 240 mg once daily. After discontinuation of the combined P-gp and strong CYP3A inducer, resume the recommended ORGOVYX dose of 120 mg once daily [see Drug Interactions (7.1 ) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3 )] .
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Tablets: 120 mg, light red, almond-shaped, film-coated, and debossed with “R” on one side and “120” on the other side.
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
Pregnancy
Risk Summary
The safety and efficacy of ORGOVYX have not been established in females. Based on findings in animals and mechanism of action, ORGOVYX can cause fetal harm and loss of pregnancy when administered to a pregnant female [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.1 )] . There are no human data on the use of ORGOVYX in pregnant females to inform the drug-associated risk. In an animal reproduction study, oral administration of relugolix to pregnant rabbits during organogenesis caused embryo-fetal lethality at maternal exposures that were 0.3 times the human exposure at the recommended dose of 120 mg daily based on AUC ( see Data ). Advise patients of the potential risk to the fetus.
Data
Animal Data
In an embryo-fetal development study, oral administration of relugolix to pregnant rabbits during the period of organogenesis resulted in abortion, total litter loss, or decreased number of live fetuses at a dose of 9 mg/kg/day (approximately 0.3 times the human exposure at the recommended dose of 120 mg daily based on AUC).
Lactation
Risk Summary
The safety and efficacy of ORGOVYX have not been established in females.
Relugolix was detected in human breast milk ( see Data ). There are no data on the effects of relugolix or its metabolites on the breastfed child, or the effects on milk production.
Data
In a milk-only lactation study in 8 healthy adult lactating women, the mean total amount of relugolix recovered in human breast milk over the first 24 hours was 0.003 mg and over 120 hours (5 days) was 0.004 mg following a single, oral, maternal dose of 40 mg. The mean calculated daily infant dose was 0.0006 mg/kg/day using 0.003 mg (the amount recovered in human breast milk over the first 24 hours). The relative infant dose was 0.1% of the maternal weight-adjusted dose of 40 mg.
Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
Contraception
Males
Based on findings in animals and mechanism of action, advise male patients with female partners of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment and for 2 weeks after the last dose of ORGOVYX [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1 )].
Infertility
Pediatric Use
The safety and efficacy of ORGOVYX in pediatric patients have not been established.
Geriatric Use
Of the 622 patients who received ORGOVYX in the HERO study, 81% were 65 years of age or older, while 35% were 75 years of age or older. No overall differences in safety or effectiveness were observed between these subjects and younger subjects. There was no clinically relevant impact of age on the pharmacokinetics of ORGOVYX or testosterone response based on population pharmacokinetic and pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic analyses in men 45 to 91 years of age.
CONTRAINDICATIONS
ORGOVYX is contraindicated in patients with severe hypersensitivity to relugolix or to any of the product components.
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- QT/QTc Interval Prolongation: Androgen deprivation therapy may prolong the QT interval (5.1 ).
- Hypersensitivity: ORGOVYX can cause hypersensitivity reactions, including angioedema. Withhold ORGOVYX in patients who experience symptoms of hypersensitivity. Discontinue ORGOVYX for severe hypersensitivity reactions and manage as clinically indicated (5.2 ).
- Embryo-Fetal Toxicity: ORGOVYX can cause fetal harm. Advise males with female partners of reproductive potential to use effective contraception (5.3 , 8.1 , 8.3 ).
QT/QTc Interval Prolongation
Androgen deprivation therapy, such as ORGOVYX, may prolong the QT/QTc interval. Providers should consider whether the benefits of androgen deprivation therapy outweigh the potential risks in patients with congenital long QT syndrome, congestive heart failure, or frequent electrolyte abnormalities and in patients taking drugs known to prolong the QT interval. Electrolyte abnormalities should be corrected. Consider periodic monitoring of electrocardiograms and electrolytes [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.2 )].
Hypersensitivity Reactions
ORGOVYX is contraindicated in patients with severe hypersensitivity to relugolix or any of the product components [see Contraindications (4 )] . Hypersensitivity reactions, including pharyngeal edema and other serious cases of angioedema, have been reported postmarketing in patients treated with ORGOVYX.
In HERO, patients treated with relugolix reported angioedema (0.2%) [see Clinical Trials Experience (6.1 )] .
Advise patients who experience any symptoms of hypersensitivity to temporarily discontinue ORGOVYX and promptly seek medical care.
Discontinue ORGOVYX for severe hypersensitivity reactions and manage as clinically indicated.
Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
The safety and efficacy of ORGOVYX have not been established in females. Based on findings in animals and mechanism of action, ORGOVYX can cause fetal harm and loss of pregnancy when administered to a pregnant female. In an animal reproduction study, oral administration of relugolix to pregnant rabbits during the period of organogenesis caused embryo-fetal lethality at maternal exposures that were 0.3 times the human exposure at the recommended dose of 120 mg daily based on area under the curve (AUC). Advise males with female partners of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment and for 2 weeks after the last dose of ORGOVYX [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1 , 8.3 ) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.1 )] .
Laboratory Testing
Therapy with ORGOVYX results in suppression of the pituitary gonadal system. Results of diagnostic tests of the pituitary gonadotropic and gonadal functions conducted during and after ORGOVYX may be affected. The therapeutic effect of ORGOVYX should be monitored by measuring serum concentrations of prostate specific antigen (PSA) periodically. If PSA increases, serum concentrations of testosterone should be measured.
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following clinically significant adverse reactions are described elsewhere in the labeling:
- QT/QTc Interval Prolongation [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1 )] .
Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
The safety of ORGOVYX was evaluated in HERO, a randomized (2:1), open-label, clinical study in patients with advanced prostate cancer [see Clinical Studies (14 )] . Patients received orally administered ORGOVYX as a loading dose of 360 mg on the first day followed by 120 mg taken orally once daily (n = 622) or received leuprolide acetate administered by depot injection at doses of 22.5 mg (n = 264) or 11.25 mg (n = 44) per local guidelines every 12 weeks (n = 308). Leuprolide acetate 11.25 mg is a dosing regimen that is not recommended for this indication in the US. Among patients who received ORGOVYX, 91% were exposed for at least 48 weeks. Ninety-nine (16%) patients received concomitant radiotherapy and 17 (3%) patients received concomitant enzalutamide with ORGOVYX.
Serious adverse reactions occurred in 12% of patients receiving ORGOVYX. Serious adverse reactions in ≥ 0.5% of patients included myocardial infarction (0.8%), acute kidney injury (0.6%), arrhythmia (0.6%), hemorrhage (0.6%), and urinary tract infection (0.5%). Fatal adverse reactions occurred in 0.8% of patients receiving ORGOVYX including metastatic lung cancer (0.3%), myocardial infarction (0.3%), and acute kidney injury (0.2%). Fatal and non-fatal myocardial infarction and stroke were reported in 2.7% of patients receiving ORGOVYX.
Permanent discontinuation of ORGOVYX due to an adverse reaction occurred in 3.5% of patients. Adverse reactions which resulted in permanent discontinuation of ORGOVYX in ≥ 0.3 % of patients included atrioventricular block (0.3%), cardiac failure (0.3%), hemorrhage (0.3%), increased transaminases (0.3%), abdominal pain (0.3%), and pneumonia (0.3%).
Dosage interruptions of ORGOVYX due to an adverse reaction occurred in 2.7% of patients. Adverse reactions which required dosage interruption in ≥ 0.3% of patients included fracture (0.3%).
The most common adverse reactions (≥ 10%) and laboratory abnormalities (≥ 15%) were hot flush (54%), glucose increased (44%), triglycerides increased (35%), musculoskeletal pain (30%), hemoglobin decreased (28%), alanine aminotransferase increased (ALT) (27%), fatigue (26%), aspartate aminotransferase increased (AST) (18%), constipation (12%), and diarrhea (12%).
Table 1 summarizes the adverse reactions in HERO.
a Includes arthralgia, back pain, pain in extremity, musculoskeletal pain, myalgia, bone pain, neck pain, arthritis, musculoskeletal stiffness, non-cardiac chest pain, musculoskeletal chest pain, spinal pain, and musculoskeletal discomfort. | ||||
b Includes fatigue and asthenia. | ||||
c Includes diarrhea and colitis. | ||||
| Adverse Reaction | ORGOVYX N = 622 | Leuprolide Acetate N = 308 | ||
| All Grades (%) | Grade 3-4 (%) | All Grades (%) | Grade 3-4 (%) | |
| Vascular disorders | ||||
| Hot flush | 54 | 0.6 | 52 | 0 |
| Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders | ||||
| Musculoskeletal pain a | 30 | 1.1 | 29 | 1.6 |
| General | ||||
| Fatigue b | 26 | 0.3 | 24 | 0 |
| Gastrointestinal disorders | ||||
| Diarrhea c | 12 | 0.2 | 7 | 0 |
| Constipation | 12 | 0 | 10 | 0 |
Clinically relevant adverse reactions in < 10% of patients who received ORGOVYX included increased weight, insomnia, gynecomastia, hyperhidrosis, depression, decreased libido, and angioedema.
Table 2 summarizes the laboratory abnormalities in HERO.
| Laboratory Test | ORGOVYX a | Leuprolide Acetate a | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| All Grades (%) | Grade 3-4 (%) | All Grades (%) | Grade 3-4 (%) | |
a The denominator used to calculate the rate varied from 611 to 619 in the ORGOVYX arm and from 301 to 306 in the leuprolide arm based on the number of patients with a baseline value and at least one post-treatment value. | ||||
| Chemistry | ||||
| Glucose increased | 44 | 2.9 | 54 | 6 |
| Triglycerides increased | 35 | 2 | 36 | 0.7 |
| ALT increased | 27 | 0.3 | 28 | 0 |
| AST increased | 18 | 0 | 19 | 0.3 |
| Hematology | ||||
| Hemoglobin decreased | 28 | 0.5 | 29 | 0.7 |
Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during post-approval use of ORGOVYX. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Immune system disorders: hypersensitivity, including angioedema and urticaria.
DRUG INTERACTIONS
P-gp Inhibitors: Avoid co-administration. If unavoidable, take ORGOVYX first, separate dosing by at least 6 hours, and monitor patients more frequently for adverse reactions (2.2 , 7.1 ).
Combined P-gp and Strong CYP3A Inducers: Avoid co-administration. If unavoidable, increase the ORGOVYX dose to 240 mg once daily (2.3 , 7.1 ).
Effect of Other Drugs on ORGOVYX
P-gp Inhibitors
Relugolix is a P-gp substrate. Co-administration of ORGOVYX with an oral P-gp inhibitor increases relugolix exposure [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3 )], which may increase the risk of adverse reactions associated with ORGOVYX.
Avoid co-administration of ORGOVYX with oral P-gp inhibitors.
If co-administration with an oral P-gp inhibitor cannot be avoided, take ORGOVYX first and separate dosing by at least 6 hours. Monitor patients for increased adverse reactions [see Dosage and Administration (2.2 )] .
Treatment with ORGOVYX may be interrupted for up to two weeks if a short course of treatment with a P-gp inhibitor is required. Resume ORGOVYX after the P-gp inhibitor is discontinued. If treatment with ORGOVYX is interrupted for greater than 7 days, restart ORGOVYX with a loading dose of 360 mg on the first day and continue with a dose of 120 mg once daily.
Combined P-gp and Strong CYP3A Inducers
Relugolix is a P-gp and CYP3A substrate. Co-administration of ORGOVYX with a combined P-gp and strong CYP3A inducer decreases relugolix exposure, which may reduce the effects of ORGOVYX [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3 )].
Avoid co-administration of ORGOVYX with combined P-gp and strong CYP3A inducers.
If co-administration cannot be avoided, increase the ORGOVYX dose. After discontinuation of the combined P-gp and strong CYP3A inducer, resume ORGOVYX once daily at the same dose [see Dosage and Administration (2.3 )] .
DESCRIPTION
Relugolix is a nonpeptide small molecule, GnRH receptor antagonist. The chemical name is N-(4-{1-[(2,6-difluorophenyl)methyl]-5-[(dimethylamino)methyl]-3-(6-methoxypyridazin-3-yl)-2,4-dioxo-1,2,3,4-tetrahydrothieno[2,3-d]pyrimidin-6-yl}phenyl)-N'-methoxyurea.
The molecular weight is 623.63 daltons and the molecular formula is C 29 H 27 F 2 N 7 O 5 S. The structural formula is:
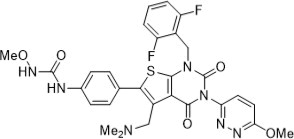
Relugolix is a white to off-white to slightly yellow solid with a solubility of 0.04 mg per mL in water at 25°C.
ORGOVYX is provided as film-coated tablets for oral administration. Each tablet contains 120 mg of relugolix. The inactive ingredients are mannitol, sodium starch glycolate, hydroxypropyl cellulose, magnesium stearate, hypromellose, titanium dioxide, ferric oxide red, and carnauba wax.
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Mechanism of Action
Relugolix is a nonpeptide GnRH receptor antagonist that competitively binds to pituitary GnRH receptors, thereby, reducing the release of luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), and consequently testosterone.
Pharmacodynamics
Pituitary and Gonadal Hormones
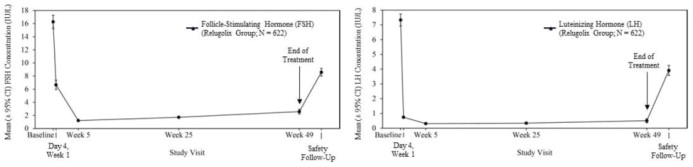
Relugolix reduced LH, FSH (Figure 1 ), and testosterone concentrations after oral administration of the recommended loading dose of 360 mg and a 120 mg dose once daily.
Out of 622 patients, 56% had testosterone concentrations at castrate levels (< 50 ng/dL) by the first sampling timepoint at Day 4, and 97% maintained castrate levels of testosterone through 48 weeks. In a substudy of 137 patients who did not receive subsequent androgen deprivation therapy for at least 90 days after discontinuation of relugolix, the cumulative incidence rate of achieving testosterone concentrations above the lower limit of the normal range (> 280 ng/dL) or baseline at 90 days was 55% [see Clinical Studies (14 )] .
Figure 1: Mean (± 95% CI) Follicle-Stimulating Hormone and Luteinizing Hormone Concentrations over Time in HERO
Cardiac Electrophysiology
At a single 60 mg or 360 mg relugolix dose (0.17 or 1 times the recommended loading dose, respectively), clinically significant QTc interval prolongation was not observed.
Pharmacokinetics
After administration of single doses ranging from 60 mg to 360 mg (0.17 to 1 times the recommended loading dose), total systemic exposure (AUC) and the maximum concentration (C max ) of relugolix increases in an approximately dose proportional manner. After administration of multiple doses of relugolix once daily, the AUC of relugolix increases in an approximately dose proportional manner while the C max increase is greater than dose proportional for doses from 20 mg to 180 mg (0.17 to 1.5 times the recommended daily dose).
After administration of a single 360 mg loading dose, the mean (± standard deviation [± SD]) AUC and C max of relugolix are 985 (± 742) ng.hr/mL and 215 (± 184) ng/mL, respectively. After administration of 120 mg once daily, the mean (± SD) AUC and C max of relugolix at steady-state are 407 (± 168) ng.hr/mL and 70 (± 65) ng/mL, respectively. The accumulation of relugolix upon once daily administration is approximately 2-fold.
Absorption
Relugolix is a substrate for intestinal P-gp. The mean (CV%) absolute bioavailability of relugolix is 12% (62%). The median (min, max) time to maximum concentration (T max ) of relugolix is 2.25 (0.5, 5.0) hours.
Effect of Food
No clinically significant differences in the pharmacokinetics of relugolix were observed following administration of a high-calorie, high-fat meal (approximately 800 to 1000 calories with 500, 220, and 124 from fat, carbohydrate, and protein, respectively).
Distribution
Plasma protein binding of relugolix is 68 to 71%, primarily to albumin and to a lesser extent to α 1 -acid glycoprotein. The mean blood-to-plasma ratio is 0.78.
Elimination
The mean effective half-life of relugolix is 25 hours and the mean (CV%) terminal elimination half-life is 61 (11%) hours. The mean (CV%) total clearance of relugolix is 29 (15%) L/h and the renal clearance is 8 L/h.
Metabolism
Relugolix is metabolized primarily by CYP3A and to a lesser extent by CYP2C8.
Excretion
After oral administration of a single 80 mg radiolabeled dose of relugolix, approximately 81% of the radioactivity was recovered in feces with 4.2% as unchanged and 4.1% in urine with 2.2% as unchanged.
Specific Populations
No clinically significant differences in the pharmacokinetics of relugolix were observed based on age (45 to 91 years), race/ethnicity (Asian [19%], White [71%], Black/African American [6%]), body weight (41 to 193 kg), mild to severe renal impairment (creatinine clearance [CLcr] 15 to 89 mL/min, as estimated by the Cockcroft-Gault equation), or mild to moderate hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh A or B). The effect of end-stage renal disease with or without hemodialysis or severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh C) on the pharmacokinetics of relugolix has not been evaluated.
Drug Interactions Studies
Clinical Studies
Combined P-gp and Moderate CYP3A Inhibitors: Co-administration with erythromycin (P-gp and moderate CYP3A inhibitor) increased the AUC and C max of relugolix by 3.5- and 2.9-fold respectively.
Combined P-gp and Strong CYP3A Inducers: Co-administration of relugolix with rifampin (P-gp and strong CYP3A inducer) decreased the AUC and C max of relugolix by 55% and 23%, respectively.
Other Drugs: No clinically significant differences in the pharmacokinetics of relugolix were observed when co-administered with voriconazole (strong CYP3A inhibitor), atorvastatin, enzalutamide, or acid-reducing agents. No clinically significant differences in the pharmacokinetics of midazolam (sensitive CYP3A substrate) or rosuvastatin (BCRP substrate), or dabigatran etexilate (P-gp substrate) were observed upon co-administration with relugolix.
In Vitro Studies
Cytochrome P450 (CYP) Enzymes: Relugolix is not an inhibitor of CYP1A2, CYP2B6, CYP2C8, CYP2C9, CYP2C19, CYP2D6, or CYP3A4. Relugolix is an inducer of CYP3A and CYP2B6, but not an inducer of CYP1A2.
Transporter Systems: Relugolix is a substrate of P-gp, but not a substrate of BCRP. Relugolix is an inhibitor of BCRP and P-gp, but not an inhibitor of OATP1B1, OATP1B3, OATP2B1, OAT1, OAT3, OCT2, MATE1, MATE2-K, or BSEP.
NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Two-year carcinogenicity studies were conducted in mice at oral relugolix doses up to 100 mg/kg/day and in rats at doses up to 600 mg/kg/day. Relugolix was not carcinogenic in mice or rats at exposures up to approximately 75 or 224 times, respectively, the human exposure at the recommended dose of 120 mg daily based on AUC.
Relugolix was not mutagenic in the in vitro bacterial reverse mutation (Ames) assay or clastogenic in the in vitro chromosomal aberration assay in Chinese hamster lung cells or the in vivo rat bone marrow micronucleus assay.
In human GnRH-receptor knock-in male mice, oral administration of relugolix decreased prostate and seminal vesicle weights at doses ≥ 3 mg/kg twice daily for 28 days. The effects of relugolix were reversible, except for testis weight, which did not fully recover within 28 days after drug withdrawal. In a 39-week repeat-dose toxicity study in monkeys, there were no significant effects on male reproductive organs at oral relugolix doses up to 50 mg/kg/day (approximately 53 times the human exposure at the recommended dose of 120 mg daily based on AUC).
Animal Toxicology and/or Pharmacology
Phospholipidosis (intracellular phospholipid accumulation) was observed in multiple organs and tissues (e.g., liver, pancreas, spleen, kidney, lymph nodes, lung, bone marrow, gastrointestinal tract or testes) after repeated oral administration of relugolix in rats and monkeys. In a rat 26-week toxicity study, phospholipidosis was observed at doses ≥ 100 mg/kg (approximately 18 times the human exposure at the recommended dose based on AUC). In a monkey 39-week toxicity study, this effect was observed at doses ≥ 1.5 mg/kg (approximately 0.6 times the human exposure at the recommended dose based on AUC) and demonstrated evidence of reversibility after cessation of treatment. The significance of this finding in humans is unknown.
CLINICAL STUDIES
HERO Study
The safety and efficacy of ORGOVYX was evaluated in HERO (NCT03085095), a randomized, open label study in men with advanced prostate cancer requiring at least 1 year of androgen deprivation therapy and defined as biochemical (PSA) or clinical relapse following local primary intervention, newly diagnosed castration-sensitive metastatic disease, or advanced localized disease.
A total of 934 patients were randomized to receive ORGOVYX or leuprolide in a 2:1 ratio for 48 weeks:
- ORGOVYX at a loading dose of 360 mg on the first day followed by daily doses of 120 mg orally.
- Leuprolide acetate 22.5 mg injection (or 11.25 mg in Japan and Taiwan) subcutaneously every 3 months. Leuprolide acetate 11.25 mg is a dosage regimen that is not recommended for this indication in the US.
Serum testosterone concentrations were measured at screening; on Days 1, 4, 8, 15, and 29 in the first month; then monthly until the end of the study.
The population (N = 930) across both treatment groups had a median age of 71 years (range 47 to 97 years). The ethnic/racial distribution was 68% White, 21% Asian, 4.9% Black, and 5% other. Disease stage was distributed as follows: 32% metastatic (M1), 31% locally advanced (T3/4 NX M0 or any T N1 M0), 28% localized (T1 or T2 N0 M0), and 10% not classifiable. The median testosterone concentration at baseline across the treatment groups was 408 ng/dL.
The major efficacy outcome measure was medical castration rate defined as achieving and maintaining serum testosterone suppression to castrate levels (< 50 ng/dL) by Day 29 through 48 weeks of treatment. Other endpoints included castration rates on Day 4 and 15 and castration rates with testosterone < 20 ng/dL at Day 15.
The efficacy results are shown in Table 3 and the time course of percent change from baseline in testosterone suppression by ORGOVYX and leuprolide during the 48 week treatment period are shown in Figure 2 .
a 11.25 mg is a dosage regimen that is not recommended for this indication in the US. The castration rate of the subgroup of patients receiving 22.5 mg leuprolide (n = 264) was 88.0% (95% CI: 83.4%, 91.4%). | ||
b Two patients in each arm did not receive the study treatment and were not included. | ||
c Kaplan-Meier estimates within group. | ||
| ORGOVYX 360/120 mg (N = 622) b | Leuprolide Acetate 22.5 or 11.25 mg a (N = 308) b | |
| Castration Rate (95% CI) c | 96.7% (94.9%, 97.9%) | 88.8% (84.6%, 91.8%) |
Figure 2: Mean (95% CI) Percent Change from Baseline in Testosterone Concentrations from Baseline to Week 49 by Treatment Group in HERO
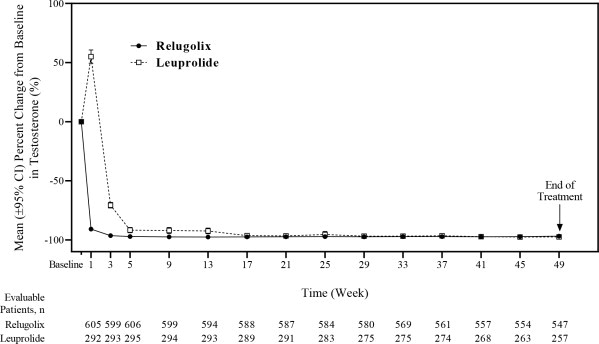
The percentages of patients who attained the medical castration levels of testosterone < 50 ng/dL and < 20 ng/dL within the first 29 days of treatment are summarized in Table 4 and the cumulative incidences of time to testosterone < 50 ng/dL or < 20 ng/dL are shown in Figure 3 .
| Testosterone < 50 ng/dL | Testosterone < 20 ng/dL | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ORGOVYX (N = 622) | Leuprolide Acetate (N = 308) | ORGOVYX (N = 622) | Leuprolide Acetate (N = 308) | |
a Kaplan-Meier estimates within group. | ||||
| Day 4 | 56% | 0% | 7% | 0% |
| Day 8 | 91% | 0% | 27% | 0% |
| Day 15 | 99% | 12% | 78% | 1% |
| Day 29 | 99% | 82% | 95% | 57% |
Figure 3: Cumulative Incidence of Time to Testosterone < 50 ng/dL and < 20 ng/dL in HERO


In the clinical trial, PSA levels were monitored and were lowered on average by 65% two weeks after administration of ORGOVYX, 83% after 4 weeks, 92% after 3 months and remained suppressed throughout the 48 weeks of treatment. These PSA results should be interpreted with caution because of the heterogeneity of the patient population studied. No evidence has shown that the rapidity of PSA decline is related to a clinical benefit.
A substudy was conducted in 137 patients who did not receive subsequent androgen deprivation therapy for at least 90 days after discontinuation of ORGOVYX. Based on Kaplan-Meier analyses, 55% of patients achieved testosterone levels above the lower limit of the normal range (> 280 ng/dL) or baseline at 90 days after discontinuation of ORGOVYX.
HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
How Supplied
The 120 mg tablets are film-coated, light red, almond shaped, and debossed with “R” on one side and “120” on the other side and are supplied in two configurations, bottles and blister packs. Each bottle (NDC 72974-120-01) contains 30 tablets and a desiccant and is closed with a child resistant induction seal cap. The blister cards contain nine tablets packaged in a carton (NDC 72974-120-02). Each ORGOVYX tablet contains 120 mg of relugolix.
Storage and Handling
- Store ORGOVYX at room temperature. Do not store above 30°C (86°F).
- Dispense to patients in original container only.
- For bottles, keep container tightly closed after first opening.
- Keep out of reach of children.
Mechanism of Action
Relugolix is a nonpeptide GnRH receptor antagonist that competitively binds to pituitary GnRH receptors, thereby, reducing the release of luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), and consequently testosterone.