Ozempic prior authorization resources
Most recent state uniform prior authorization forms
Brand Resources
Ozempic patient education
Patient toolkit
Dosage & administration
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- Administer once weekly at any time of day, with or without meals. (2.1 )
- Start at 0.25 mg once weekly. After 4 weeks, increase the dosage to 0.5 mg once weekly. (2.2 )
- If additional glycemic control is needed, increase the dosage to 1 mg once weekly after at least 4 weeks on the 0.5 mg dose. (2.2 )
- If additional glycemic control is needed, increase the dosage to 2 mg once weekly after at least 4 weeks on the 1 mg dosage. (2.2 )
- To reduce the risk of sustained eGFR decline, end-stage kidney disease and cardiovascular death, increase the dosage to 1 mg once weekly after at least 4 weeks on the 0.5 mg dosage. (1 , 2.2 )
- If a dose is missed, administer within 5 days of missed dose. (2.1 )
- Inject subcutaneously in the abdomen, thigh, or upper arm. (2.1 )
Important Administration Instructions
- Inspect OZEMPIC visually before use. It should appear clear and colorless. Do not use OZEMPIC if particulate matter and coloration is seen.
- Administer OZEMPIC once weekly, on the same day each week, at any time of the day, with or without meals.
- Inject OZEMPIC subcutaneously in the abdomen, thigh, or upper arm. Instruct patients to use a different injection site each week when injecting in the same body region.
- When using OZEMPIC with insulin, instruct patients to administer as separate injections and to never mix the products. It is acceptable to inject OZEMPIC and insulin in the same body region, but the injections should not be adjacent to each other.
- The day of weekly administration can be changed if necessary as long as the time between two doses is at least 2 days (>48 hours).
- If a dose is missed, administer OZEMPIC as soon as possible within 5 days after the missed dose. If more than 5 days have passed, skip the missed dose and administer the next dose on the regularly scheduled day. In each case, patients can then resume their regular once-weekly dosing schedule.
Recommended Dosage
Recommended Initiation Dosage
Initiate OZEMPIC with a dosage of 0.25 mg injected subcutaneously once weekly for 4 weeks. Follow the dosage escalation below to reduce the risk of gastrointestinal adverse reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7 ), Adverse Reactions (6.1 )].
After 4 weeks on the 0.25 mg dosage, increase the dosage to 0.5 mg once weekly.
Recommended Maintenance and Maximum Dosages for Glycemic Control
The recommended maintenance dosage is 0.5 mg, 1 mg, or 2 mg, injected subcutaneously once weekly, based on glycemic control.
If additional glycemic control is needed after at least 4 weeks on the:
- 0.5 mg dosage, the dosage may be increased to 1 mg once weekly.
- 1 mg dosage, the dosage may be increased to 2 mg once weekly.
The maximum recommended dosage is 2 mg once weekly.
Recommended Maintenance Dosage in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Chronic Kidney Disease
Increase the dosage to the maintenance dosage, 1 mg once weekly, after at least 4 weeks on the 0.5 mg dosage.

By using PrescriberAI, you agree to the AI Terms of Use.
Ozempic prescribing information
WARNING: RISK OF THYROID C-CELL TUMORS
- In rodents, semaglutide causes dose-dependent and treatment-duration-dependent thyroid C-cell tumors at clinically relevant exposures. It is unknown whether OZEMPIC causes thyroid C-cell tumors, including medullary thyroid carcinoma (MTC), in humans as human relevance of semaglutide-induced rodent thyroid C-cell tumors has not been determined [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1 ), Nonclinical Toxicology (13.1 )] .
- OZEMPIC is contraindicated in patients with a personal or family history of MTC or in patients with Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia syndrome type 2 (MEN 2) [see Contraindications (4 )] . Counsel patients regarding the potential risk for MTC with the use of OZEMPIC and inform them of symptoms of thyroid tumors (e.g., a mass in the neck, dysphagia, dyspnea, persistent hoarseness). Routine monitoring of serum calcitonin or using thyroid ultrasound is of uncertain value for early detection of MTC in patients treated with OZEMPIC [see Contraindications (4 ), Warnings and Precautions (5.1 )] .
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
OZEMPIC is indicated:
- as an adjunct to diet and exercise to improve glycemic control in adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus.
- to reduce the risk of major adverse cardiovascular events (cardiovascular death, non-fatal myocardial infarction or non-fatal stroke) in adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus and established cardiovascular disease.
- to reduce the risk of sustained eGFR decline, end-stage kidney disease, and cardiovascular death in adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus and chronic kidney disease .
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- Administer once weekly at any time of day, with or without meals. (2.1 )
- Start at 0.25 mg once weekly. After 4 weeks, increase the dosage to 0.5 mg once weekly. (2.2 )
- If additional glycemic control is needed, increase the dosage to 1 mg once weekly after at least 4 weeks on the 0.5 mg dose. (2.2 )
- If additional glycemic control is needed, increase the dosage to 2 mg once weekly after at least 4 weeks on the 1 mg dosage. (2.2 )
- To reduce the risk of sustained eGFR decline, end-stage kidney disease and cardiovascular death, increase the dosage to 1 mg once weekly after at least 4 weeks on the 0.5 mg dosage. (1 , 2.2 )
- If a dose is missed, administer within 5 days of missed dose. (2.1 )
- Inject subcutaneously in the abdomen, thigh, or upper arm. (2.1 )
Important Administration Instructions
- Inspect OZEMPIC visually before use. It should appear clear and colorless. Do not use OZEMPIC if particulate matter and coloration is seen.
- Administer OZEMPIC once weekly, on the same day each week, at any time of the day, with or without meals.
- Inject OZEMPIC subcutaneously in the abdomen, thigh, or upper arm. Instruct patients to use a different injection site each week when injecting in the same body region.
- When using OZEMPIC with insulin, instruct patients to administer as separate injections and to never mix the products. It is acceptable to inject OZEMPIC and insulin in the same body region, but the injections should not be adjacent to each other.
- The day of weekly administration can be changed if necessary as long as the time between two doses is at least 2 days (>48 hours).
- If a dose is missed, administer OZEMPIC as soon as possible within 5 days after the missed dose. If more than 5 days have passed, skip the missed dose and administer the next dose on the regularly scheduled day. In each case, patients can then resume their regular once-weekly dosing schedule.
Recommended Dosage
Recommended Initiation Dosage
Initiate OZEMPIC with a dosage of 0.25 mg injected subcutaneously once weekly for 4 weeks. Follow the dosage escalation below to reduce the risk of gastrointestinal adverse reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7 ), Adverse Reactions (6.1 )].
After 4 weeks on the 0.25 mg dosage, increase the dosage to 0.5 mg once weekly.
Recommended Maintenance and Maximum Dosages for Glycemic Control
The recommended maintenance dosage is 0.5 mg, 1 mg, or 2 mg, injected subcutaneously once weekly, based on glycemic control.
If additional glycemic control is needed after at least 4 weeks on the:
- 0.5 mg dosage, the dosage may be increased to 1 mg once weekly.
- 1 mg dosage, the dosage may be increased to 2 mg once weekly.
The maximum recommended dosage is 2 mg once weekly.
Recommended Maintenance Dosage in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Chronic Kidney Disease
Increase the dosage to the maintenance dosage, 1 mg once weekly, after at least 4 weeks on the 0.5 mg dosage.
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Injection: clear, colorless solution available in 3 prefilled, disposable, single-patient-use pens:
Dose per Injection | Total Strength per Total Volume | Strength per mL |
0.25 mg 0.5 mg | 2 mg / 3 mL | 0.68 mg/mL |
1 mg | 4 mg / 3 mL | 1.34 mg/mL |
2 mg | 8 mg / 3 mL | 2.68 mg/mL |
The 2 mg/1.5 mL (1.34 mg/mL) strength is not currently marketed by Novo Nordisk Inc.
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
Females and Males of Reproductive Potential : Discontinue OZEMPIC in women at least 2 months before a planned pregnancy due to the long washout period for semaglutide. (8.3 )
Pregnancy
Risk Summary
There are limited data with semaglutide use in pregnant women to inform a drug-associated risk for adverse developmental outcomes. There are clinical considerations regarding the risks of poorly controlled diabetes in pregnancy (see Clinical Considerations ). Based on animal reproduction studies, there may be potential risks to the fetus from exposure to semaglutide during pregnancy. OZEMPIC should be used during pregnancy only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the fetus.
In pregnant rats administered semaglutide during organogenesis, embryofetal mortality, structural abnormalities and alterations to growth occurred at maternal clinical exposure based on AUC. In rabbits and cynomolgus monkeys administered semaglutide during organogenesis, early pregnancy losses or structural abnormalities were observed at clinical exposure (rabbit) and ≥2-fold the MRHD (monkey). These findings coincided with a marked maternal body weight loss in both animal species (see Data ).
In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2 to 4% and 15 to 20%, respectively. The estimated background risk of major birth defects is 6 to 10% in women with pre-gestational diabetes with a peri-conceptional HbA 1c >7 and has been reported to be as high as 20 to 25% in women with a peri-conceptional HbA 1c >10. The estimated background risk of miscarriage for the indicated population is unknown.
Clinical Considerations
Disease-Associated Maternal and/or Embryo/fetal Risk
Hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia occur more frequently during pregnancy in patients with pre-gestational diabetes. Poorly controlled diabetes during pregnancy increases the maternal risk for diabetic ketoacidosis, pre- eclampsia, spontaneous abortions, preterm delivery, and delivery complications. Poorly controlled diabetes increases the fetal risk for major birth defects, stillbirth, and macrosomia related morbidity.
Data
Animal Data
In a combined fertility and embryofetal development study in rats, subcutaneous doses of 0.01, 0.03 and 0.09 mg/kg/day (0.06-, 0.2-, and 0.6-fold the MRHD) were administered to males for 4 weeks prior to and throughout mating and to females for 2 weeks prior to mating, and throughout organogenesis to Gestation Day 17. In parental animals, pharmacologically mediated reductions in body weight gain and food consumption were observed at all dose levels. In the offspring, reduced growth and fetuses with visceral (heart blood vessels) and skeletal (cranial bones, vertebra, ribs) abnormalities were observed at the human exposure.
In an embryofetal development study in pregnant rabbits, subcutaneous doses of 0.0010, 0.0025 or 0.0075 mg/kg/day (0.02-, 0.2-, and 1.2-fold the MRHD) were administered throughout organogenesis from Gestation Day 6 to 19. Pharmacologically mediated reductions in maternal body weight gain and food consumption were observed at all dose levels. Early pregnancy losses and increased incidences of minor visceral (kidney, liver) and skeletal (sternebra) fetal abnormalities were observed at ≥0.0025 mg/kg/day, at clinically relevant exposures.
In an embryofetal development study in pregnant cynomolgus monkeys, subcutaneous doses of 0.015, 0.075, and 0.15 mg/kg twice weekly (0.5-, 3-, and 8-fold the MRHD) were administered throughout organogenesis, from Gestation Day 16 to 50. Pharmacologically mediated, marked initial maternal body weight loss and reductions in body weight gain and food consumption coincided with the occurrence of sporadic abnormalities (vertebra, sternebra, ribs) at ≥0.075 mg/kg twice weekly (≥3X human exposure).
In a pre- and postnatal development study in pregnant cynomolgus monkeys, subcutaneous doses of 0.015, 0.075, and 0.15 mg/kg twice weekly (0.3-, 2-, and 4-fold the MRHD) were administered from Gestation Day 16 to 140. Pharmacologically mediated marked initial maternal body weight loss and reductions in body weight gain and food consumption coincided with an increase in early pregnancy losses and led to delivery of slightly smaller offspring at ≥0.075 mg/kg twice weekly (≥2X human exposure).
Lactation
Risk Summary
There are no data on the presence of semaglutide in human milk, the effects on the breastfed infant, or the effects on milk production. Semaglutide was present in the milk of lactating rats, however, due to species-specific differences in lactation physiology, the clinical relevance of these data are not clear (see Data ). The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother’s clinical need for OZEMPIC and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed infant from OZEMPIC or from the underlying maternal condition.
Data
In lactating rats, semaglutide was detected in milk at levels 3- to 12- fold lower than in maternal plasma.
Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
Discontinue OZEMPIC in women at least 2 months before a planned pregnancy due to the long washout period for semaglutide [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1 )] .
Pediatric Use
Safety and efficacy of OZEMPIC have not been established in pediatric patients.
Geriatric Use
In the pool of placebo- and active-controlled glycemic control trials, 744 (23.6%) OZEMPIC-treated patients were 65 years of age and over and 102 OZEMPIC-treated patients (3.2%) patients were 75 years of age and over. In SUSTAIN 6, the cardiovascular outcome trial, 788 (48%) OZEMPIC-treated patients were 65 years of age and over and 157 OZEMPIC-treated patients (9.6%) patients were 75 years of age and over.
No overall differences in safety or efficacy were detected between these patients and younger patients, but greater sensitivity of some older individuals cannot be ruled out.
Renal Impairment
No dose adjustment of OZEMPIC is recommended for patients with renal impairment. In subjects with renal impairment including kidney failure, no clinically relevant change in semaglutide pharmacokinetics (PK) was observed [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3 )] .
Hepatic Impairment
No dose adjustment of OZEMPIC is recommended for patients with hepatic impairment. In a study in subjects with different degrees of hepatic impairment, no clinically relevant change in semaglutide pharmacokinetics (PK) was observed [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3 )] .
CONTRAINDICATIONS
OZEMPIC is contraindicated in patients with:
- A personal or family history of MTC or in patients with MEN 2 [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1 )] .
- A serious hypersensitivity reaction to semaglutide or to any of the excipients in OZEMPIC. Serious hypersensitivity reactions including anaphylaxis and angioedema have been reported with OZEMPIC [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8 )] .
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- Acute Pancreatitis: Has been observed in patients treated with GLP-1 receptor agonists, including semaglutide. Discontinue if pancreatitis is suspected. (5.2 )
- Diabetic Retinopathy Complications: Has been reported in a clinical trial. Patients with a history of diabetic retinopathy should be monitored. (5.3 )
- Never share an OZEMPIC pen between patients , even if the needle is changed. (5.4 )
- Hypoglycemia: Concomitant use with an insulin secretagogue or insulin may increase the risk of hypoglycemia, including severe hypoglycemia. Reducing dose of insulin secretagogue or insulin may be necessary. (5.5 )
- Acute Kidney Injury Due to Volume Depletion: Monitor renal function in patients reporting adverse reactions that could lead to volume depletion. (5.6 )
- Severe Gastrointestinal Adverse Reactions : Use has been associated with gastrointestinal adverse reactions, sometimes severe. OZEMPIC is not recommended in patients with severe gastroparesis. (5.7 )
- Hypersensitivity Reactions: Serious hypersensitivity reactions (e.g., anaphylaxis and angioedema) have been reported. Discontinue OZEMPIC if suspected and promptly seek medical advice. (5.8 )
- Acute Gallbladder Disease: If cholelithiasis or cholecystitis are suspected, gallbladder studies are indicated. (5.9 )
- Pulmonary Aspiration During General Anesthesia or Deep Sedation: Has been reported in patients receiving GLP-1 receptor agonists undergoing elective surgeries or procedures. Instruct patients to inform healthcare providers of any planned surgeries or procedures. (5.10 )
Risk of Thyroid C-Cell Tumors
In mice and rats, semaglutide caused a dose-dependent and treatment-duration-dependent increase in the incidence of thyroid C-cell tumors (adenomas and carcinomas) after lifetime exposure at clinically relevant plasma exposures [see Nonclinical Toxicology (13.1 )] . It is unknown whether OZEMPIC causes thyroid C-cell tumors, including MTC, in humans as human relevance of semaglutide-induced rodent thyroid C-cell tumors has not been determined.
Cases of MTC in patients treated with liraglutide, another GLP-1 receptor agonist, have been reported in the postmarketing period; the data in these reports are insufficient to establish or exclude a causal relationship between MTC and GLP-1 receptor agonist use in humans.
OZEMPIC is contraindicated in patients with a personal or family history of MTC or in patients with MEN 2. Counsel patients regarding the potential risk for MTC with the use of OZEMPIC and inform them of symptoms of thyroid tumors (e.g., a mass in the neck, dysphagia, dyspnea, persistent hoarseness).
Routine monitoring of serum calcitonin or using thyroid ultrasound is of uncertain value for early detection of MTC in patients treated with OZEMPIC. Such monitoring may increase the risk of unnecessary procedures, due to the low-test specificity for serum calcitonin and a high background incidence of thyroid disease. Significantly elevated serum calcitonin value may indicate MTC and patients with MTC usually have calcitonin values >50 ng/L. If serum calcitonin is measured and found to be elevated, the patient should be further evaluated. Patients with thyroid nodules noted on physical examination or neck imaging should also be further evaluated.
Acute Pancreatitis
Acute pancreatitis, including fatal and non-fatal hemorrhagic or necrotizing pancreatitis, has been observed in patients treated with GLP-1 receptor agonists, including semaglutide [see Adverse Reactions (6.1 )].
After initiation of OZEMPIC, observe patients carefully for signs and symptoms of acute pancreatitis which may include persistent or severe abdominal pain (sometimes radiating to the back) and which may or may not be accompanied by nausea or vomiting. If pancreatitis is suspected, discontinue OZEMPIC and initiate appropriate management.
Diabetic Retinopathy Complications
In a 2-year trial involving patients with type 2 diabetes and high cardiovascular risk, more events of diabetic retinopathy complications occurred in patients treated with OZEMPIC (3.0%) compared to placebo (1.8%). The absolute risk increase for diabetic retinopathy complications was larger among patients with a history of diabetic retinopathy at baseline (OZEMPIC 8.2%, placebo 5.2%) than among patients without a known history of diabetic retinopathy (OZEMPIC 0.7%, placebo 0.4%).
Rapid improvement in glucose control has been associated with a temporary worsening of diabetic retinopathy. The effect of long-term glycemic control with semaglutide on diabetic retinopathy complications has not been studied. Patients with a history of diabetic retinopathy should be monitored for progression of diabetic retinopathy.
Never Share an OZEMPIC Pen Between Patients
OZEMPIC pens must never be shared between patients, even if the needle is changed. Pen-sharing poses a risk for transmission of blood-borne pathogens.
Hypoglycemia with Concomitant Use of Insulin Secretagogues or Insulin
Patients receiving OZEMPIC in combination with an insulin secretagogue (e.g., sulfonylurea) or insulin may have an increased risk of hypoglycemia, including severe hypoglycemia [see Adverse Reactions (6.1 ), Drug Interactions (7 )].
The risk of hypoglycemia may be lowered by a reduction in the dose of sulfonylurea (or other concomitantly administered insulin secretagogue) or insulin. Inform patients using these concomitant medications of the risk of hypoglycemia and educate them on the signs and symptoms of hypoglycemia.
Acute Kidney Injury Due to Volume Depletion
There have been postmarketing reports of acute kidney injury, in some cases requiring hemodialysis, in patients treated with semaglutide. The majority of the reported events occurred in patients who experienced gastrointestinal reactions leading to dehydration such as nausea, vomiting, or diarrhea [see Adverse Reactions (6.1 )]. Monitor renal function in patients reporting adverse reactions to OZEMPIC that could lead to volume depletion, especially during dosage initiation and escalation of OZEMPIC.
Severe Gastrointestinal Adverse Reactions
Use of OZEMPIC has been associated with gastrointestinal adverse reactions, sometimes severe [see Adverse Reactions (6 )]. In OZEMPIC clinical trials, severe gastrointestinal adverse reactions were reported more frequently among patients receiving OZEMPIC (0.5 mg 0.4%, 1 mg 0.8%) than placebo (0%). Severe gastrointestinal adverse reactions have also been reported postmarketing with GLP-1 receptor agonists.
OZEMPIC is not recommended in patients with severe gastroparesis.
Hypersensitivity Reactions
Serious hypersensitivity reactions (e.g., anaphylaxis, angioedema) have been reported in patients treated with OZEMPIC. If hypersensitivity reactions occur, discontinue use of OZEMPIC; treat promptly per standard of care, and monitor until signs and symptoms resolve. Do not use in patients with a previous hypersensitivity to OZEMPIC [see Contraindications (4 ), Adverse Reactions (6.2 )] .
Anaphylaxis and angioedema have been reported with other GLP-1 receptor agonists. Use caution in a patient with a history of angioedema or anaphylaxis with another GLP-1 receptor agonist because it is unknown whether such patients will be predisposed to anaphylaxis with OZEMPIC.
Acute Gallbladder Disease
Acute events of gallbladder disease such as cholelithiasis or cholecystitis have been reported in GLP-1 receptor agonist trials and postmarketing. In placebo-controlled trials, cholelithiasis was reported in 1.5% and 0.4% of patients-treated with OZEMPIC 0.5 mg and 1 mg, respectively. Cholelithiasis was not reported in placebo-treated patients. If cholelithiasis is suspected, gallbladder studies and appropriate clinical follow-up are indicated.
Pulmonary Aspiration During General Anesthesia or Deep Sedation
OZEMPIC delays gastric emptying [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.2 ) ]. There have been rare postmarketing reports of pulmonary aspiration in patients receiving GLP-1 receptor agonists undergoing elective surgeries or procedures requiring general anesthesia or deep sedation who had residual gastric contents despite reported adherence to preoperative fasting recommendations.
Available data are insufficient to inform recommendations to mitigate the risk of pulmonary aspiration during general anesthesia or deep sedation in patients taking OZEMPIC, including whether modifying preoperative fasting recommendations or temporarily discontinuing OZEMPIC could reduce the incidence of retained gastric contents. Instruct patients to inform healthcare providers prior to any planned surgeries or procedures if they are taking OZEMPIC.
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following serious adverse reactions are described below or elsewhere in the prescribing information:
- Risk of Thyroid C-cell Tumors [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1 )]
- Acute Pancreatitis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) ]
- Diabetic Retinopathy Complications [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3 )]
- Hypoglycemia with Concomitant Use of Insulin Secretagogues or Insulin [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5 )]
- Acute Kidney Injury Due to Volume Depletion [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6 )]
- Severe Gastrointestinal Adverse Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7 )]
- Hypersensitivity Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8 )]
- Acute Gallbladder Disease [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9 )]
- Pulmonary Aspiration During General Anesthesia or Deep Sedation [see Warnings and Precautions (5.10 )]
Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
Pool of Placebo-Controlled Trials
The data in Table 1 are derived from 2 placebo-controlled trials (1 monotherapy trial and 1 trial in combination with basal insulin) in patients with type 2 diabetes [see Clinical Studies (14 )] . These data reflect exposure of 521 patients to OZEMPIC and a mean duration of exposure to OZEMPIC of 32.9 weeks. Across the treatment arms, the mean age of patients was 56 years, 3.4% were 75 years or older and 55% were male. In these trials 71% were White, 7% were Black or African American, and 19% were Asian; 21% identified as Hispanic or Latino ethnicity. At baseline, patients had type 2 diabetes for an average of 8.8 years and had a mean HbA 1c of 8.2%. At baseline, 8.9% of the population reported retinopathy. Baseline estimated renal function was normal (eGFR ≥90 mL/min/1.73m 2 ) in 57.2%, mildly impaired (eGFR 60 to 90 mL/min/1.73m 2 ) in 35.9% and moderately impaired (eGFR 30 to 60 mL/min/1.73m 2 ) in 6.9% of patients.
Pool of Placebo- and Active-Controlled Trials
The occurrence of adverse reactions was also evaluated in a larger pool of patients with type 2 diabetes
participating in 7 placebo- and active-controlled glycemic control trials [see Clinical Studies (14 )] including two trials in Japanese patients evaluating the use of OZEMPIC as monotherapy and add-on therapy to oral medications or insulin. In this pool, a total of 3150 patients with type 2 diabetes were treated with OZEMPIC for a mean duration of 44.9 weeks. Across the treatment arms, the mean age of patients was 57 years, 3.2% were 75 years or older and 57% were male. In these trials, 60% were White, 6% were Black or African American, and 31% were Asian; 16% identified as Hispanic or Latino ethnicity. At baseline, patients had type 2 diabetes for an average of 8.2 years and had a mean HbA 1c of 8.2%. At baseline, 7.8% of the population reported retinopathy. Baseline estimated renal function was normal (eGFR ≥90 mL/min/1.73m 2 ) in 63.1%, mildly impaired (eGFR 60 to 90 mL/min/1.73m 2 ) in 34.3%, and moderately impaired (eGFR 30 to 60 mL/min/1.73m 2 ) in 2.5% of the patients.
Common Adverse Reactions
Table 1 shows common adverse reactions, excluding hypoglycemia, associated with the use of OZEMPIC in the pool of placebo-controlled trials. These adverse reactions occurred more commonly on OZEMPIC than on placebo and occurred in at least 5% of patients treated with OZEMPIC.
Table 1. Adverse Reactions in Placebo-Controlled Trials Reported in ≥5% of OZEMPIC-Treated Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Adverse Reaction | Placebo (N=262) % | OZEMPIC 0.5 mg (N=260) % | OZEMPIC 1 mg (N=261) % |
Nausea | 6.1 | 15.8 | 20.3 |
Vomiting | 2.3 | 5 | 9.2 |
Diarrhea | 1.9 | 8.5 | 8.8 |
Abdominal pain | 4.6 | 7.3 | 5.7 |
Constipation | 1.5 | 5 | 3.1 |
In the pool of placebo- and active-controlled trials and in the 2-year cardiovascular outcomes trial, the types and frequency of common adverse reactions, excluding hypoglycemia, were similar to those listed in Table 1 .
In a clinical trial with 959 patients treated with OZEMPIC 1 mg or OZEMPIC 2 mg as add-on to metformin with or without sulfonylurea treatment for 40 weeks, no new safety signals were identified.
In the FLOW trial [see Clinical Studies (14.3 ) ] in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and chronic kidney disease, safety data collection was limited to serious adverse events and selected predefined categories of adverse events regardless of seriousness. There were no new serious or severe adverse reactions identified in this trial.
Gastrointestinal Adverse Reactions
In the pool of placebo-controlled trials, gastrointestinal adverse reactions occurred more frequently among patients receiving OZEMPIC than placebo (placebo 15.3%, OZEMPIC 0.5 mg 32.7%, OZEMPIC 1 mg 36.4%). The majority of reports of nausea, vomiting, and/or diarrhea occurred during dose escalation. More patients receiving OZEMPIC 0.5 mg (3.1%) and OZEMPIC 1 mg (3.8%) discontinued treatment due to gastrointestinal adverse reactions than patients receiving placebo (0.4%).
In the trial with OZEMPIC 1 mg and 2 mg, gastrointestinal adverse reactions occurred more frequently among patients receiving OZEMPIC 2 mg (34%) vs OZEMPIC 1 mg (30.8%).
- In addition to the reactions in Table 1 , the following gastrointestinal adverse reactions with a frequency of <5% were associated with OZEMPIC (frequencies listed, respectively, as: placebo; 0.5 mg; 1 mg): dyspepsia (1.9%, 3.5%, 2.7%), eructation (0%, 2.7%, 1.1%), flatulence (0.8%, 0.4%, 1.5%), gastroesophageal reflux disease (0%, 1.9%, 1.5%), and gastritis (0.8%, 0.8%, 0.4%).
Other Adverse Reactions
Hypoglycemia
Table 2 summarizes the incidence of events related to hypoglycemia by various definitions in the placebo-controlled trials.
Table 2. Hypoglycemia Adverse Reactions in Placebo-Controlled Trials in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Placebo | OZEMPIC 0.5 mg | OZEMPIC 1 mg | |
Monotherapy | |||
| N=129 | N=127 | N=130 |
| 0% | 0% | 0% |
| 0% | 1.6% | 3.8% |
| 1.6% | 0% | 0% |
Add-on to Basal Insulin with or without Metformin | |||
| N=132 | N=132 | N=131 |
| 0% | 0% | 1.5% |
| 15.2% | 16.7% | 29.8% |
| 5.3% | 8.3% | 10.7% |
† “Severe” hypoglycemia adverse reactions are episodes requiring the assistance of another person. | |||
Hypoglycemia was more frequent when OZEMPIC was used in combination with a sulfonylurea [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5 ), Clinical Studies (14 )]. Severe hypoglycemia occurred in 0.8% and 1.2% of patients when OZEMPIC 0.5 mg and 1 mg, respectively, was coadministered with a sulfonylurea. Documented symptomatic hypoglycemia occurred in 17.3% and 24.4% of patients when OZEMPIC 0.5 mg and 1 mg, respectively, was coadministered with a sulfonylurea. Severe or blood glucose confirmed symptomatic hypoglycemia occurred in 6.5% and 10.4% of patients when OZEMPIC 0.5 mg and 1 mg, respectively, was coadministered with a sulfonylurea.
Injection Site Reactions
In placebo-controlled trials, injection site reactions (e.g., injection-site discomfort, erythema) were reported in 0.2% of OZEMPIC-treated patients.
Increases in Amylase and Lipase
In placebo-controlled trials, patients exposed to OZEMPIC had a mean increase from baseline in amylase of 13% and lipase of 22%. These changes were not observed in placebo-treated patients.
Acute Pancreatitis
In glycemic control trials, acute pancreatitis was confirmed by adjudication in 7 OZEMPIC-treated patients (0.3 cases per 100 patient years) versus 3 in comparator-treated patients (0.2 cases per 100 patient years).
Cholelithiasis
In placebo-controlled trials, cholelithiasis was reported in 1.5% and 0.4% of patients-treated with OZEMPIC 0.5 mg and 1 mg, respectively. Cholelithiasis was not reported in placebo-treated patients.
Increases in Heart Rate
In placebo-controlled trials, OZEMPIC 0.5 mg and 1 mg resulted in a mean increase in heart rate of 2 to 3 beats per minute. There was a mean decrease in heart rate of 0.3 beats per minute in placebo-treated patients.
Fatigue, Dysgeusia and Dizziness
Other adverse reactions with a frequency of >0.4% were associated with OZEMPIC include fatigue, dysgeusia and dizziness.
Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been reported during post-approval use of semaglutide, the active ingredient of OZEMPIC. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Gastrointestinal: ileus, intestinal obstruction, severe constipation including fecal impaction
Hypersensitivity: anaphylaxis, angioedema, rash, urticaria
Hepatobiliary: cholecystitis, cholecystectomy
Neurologic: dysesthesia, headache
Pulmonary : Pulmonary aspiration has occurred in patients receiving GLP-1 receptor agonists undergoing elective surgeries or procedures requiring general anesthesia or deep sedation.
Renal: acute kidney injury
Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue: alopecia
DRUG INTERACTIONS
Oral Medications : OZEMPIC delays gastric emptying. May impact absorption of concomitantly administered oral medications. Use with caution. (7.2 )
Concomitant Use with an Insulin Secretagogue (e.g., Sulfonylurea) or with Insulin
OZEMPIC stimulates insulin release in the presence of elevated blood glucose concentrations. Patients receiving OZEMPIC in combination with an insulin secretagogue (e.g., sulfonylurea) or insulin may have an increased risk of hypoglycemia, including severe hypoglycemia.
When initiating OZEMPIC, consider reducing the dose of concomitantly administered insulin secretagogue (such as sulfonylureas) or insulin to reduce the risk of hypoglycemia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5 ), Adverse Reactions (6 )] .
Oral Medications
OZEMPIC causes a delay of gastric emptying, and thereby has the potential to impact the absorption of concomitantly administered oral medications. In clinical pharmacology trials, semaglutide did not affect the absorption of orally administered medications to any clinically relevant degree [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3 )] . Nonetheless, caution should be exercised when oral medications are concomitantly administered with OZEMPIC.
DESCRIPTION
OZEMPIC (semaglutide) injection, for subcutaneous use, contains semaglutide, a human GLP-1 receptor agonist (or GLP-1 analog). The peptide backbone is produced by yeast fermentation. The main protraction mechanism of semaglutide is albumin binding, facilitated by modification of position 26 lysine with a hydrophilic spacer and a C18 fatty di-acid. Furthermore, semaglutide is modified in position 8 to provide stabilization against degradation by the enzyme dipeptidyl-peptidase 4 (DPP-4). A minor modification was made in position 34 to ensure the attachment of only one fatty di-acid. The molecular formula is C 187 H 291 N 45 O 59 and the molecular weight is 4113.58 g/mol.
Structural formula:

OZEMPIC is a sterile, aqueous, clear, colorless solution. Each 3 mL prefilled single-patient-use pen contains semaglutide 2 mg (0.68 mg/mL), 4 mg (1.34 mg/mL), or 8 mg (2.68 mg/mL). Each 1 mL of OZEMPIC solution also contains the following inactive ingredients: disodium phosphate dihydrate, 1.42 mg; propylene glycol, 14 mg; phenol, 5.5 mg; and water for injections. OZEMPIC has a pH of approximately 7.4. Hydrochloric acid or sodium hydroxide may be added to adjust pH. The 2 mg/1.5 mL (1.34 mg/mL) strength is not currently marketed by Novo Nordisk Inc.
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Mechanism of Action
Semaglutide is a GLP-1 analogue with 94% sequence homology to human GLP-1. Semaglutide acts as a GLP-1 receptor agonist that selectively binds to and activates the GLP-1 receptor, the target for native GLP-1.
GLP-1 is a physiological hormone that has multiple actions on glucose, mediated by the GLP-1 receptors.
The principal mechanism of protraction resulting in the long half-life of semaglutide is albumin binding, which results in decreased renal clearance and protection from metabolic degradation. Furthermore, semaglutide is stabilized against degradation by the DPP-4 enzyme.
Semaglutide reduces blood glucose through a mechanism where it stimulates insulin secretion and lowers glucagon secretion, both in a glucose-dependent manner. Thus, when blood glucose is high, insulin secretion is stimulated, and glucagon secretion is inhibited. The mechanism of blood glucose lowering also involves a minor delay in gastric emptying in the early postprandial phase.
The mechanism of kidney-related risk reduction has not been established.
Pharmacodynamics
Semaglutide lowers fasting and postprandial blood glucose and reduces body weight. All pharmacodynamic evaluations were performed after 12 weeks of treatment (including dose escalation) at steady state with semaglutide 1 mg.
Fasting and Postprandial Glucose
Semaglutide reduces fasting and postprandial glucose concentrations. In patients with type 2 diabetes, treatment with semaglutide 1 mg resulted in reductions in glucose in terms of absolute change from baseline and relative reduction compared to placebo of 29 mg/dL (22%) for fasting glucose, 74 mg/dL (36%) for 2-hour postprandial glucose, and 30 mg/dL (22%) for mean 24-hour glucose concentration (see Figure 1 ).
Figure 1. Mean 24-hour Plasma Glucose Profiles (standardized meals) in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes before (Baseline) and after 12 Weeks of Treatment with Semaglutide or Placebo

Insulin Secretion
Both first-and second-phase insulin secretion are increased in patients with type 2 diabetes treated with OZEMPIC compared with placebo.
Glucagon Secretion
Semaglutide lowers the fasting and postprandial glucagon concentrations. In patients with type 2 diabetes, treatment with semaglutide resulted in the following relative reductions in glucagon compared to placebo, fasting glucagon (8%), postprandial glucagon response (14 to 15%), and mean 24-hour glucagon concentration (12%).
Glucose dependent insulin and glucagon secretion
Semaglutide lowers high blood glucose concentrations by stimulating insulin secretion and lowering glucagon secretion in a glucose-dependent manner. With semaglutide, the insulin secretion rate in patients with type 2 diabetes was similar to that of healthy subjects (see Figure 2 ).
Figure 2. Mean Insulin Secretion Rate Versus Glucose Concentration in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes during Graded Glucose Infusion before (Baseline) and after 12 Weeks of Treatment with Semaglutide or Placebo and in Untreated Healthy Subjects

During induced hypoglycemia, semaglutide did not alter the counter regulatory responses of increased glucagon compared to placebo and did not impair the decrease of C-peptide in patients with type 2 diabetes.
Gastric emptying
Semaglutide causes a delay of early postprandial gastric emptying, thereby reducing the rate at which glucose appears in the circulation postprandially.
Cardiac electrophysiology (QTc)
The effect of semaglutide on cardiac repolarization was tested in a thorough QTc trial. Semaglutide does not prolong QTc intervals at doses up to 1.5 mg at steady-state.
Pharmacokinetics
Absorption
Absolute bioavailability of semaglutide is 89%. Maximum concentration of semaglutide is reached 1 to 3 days post dose.
Similar exposure is achieved with subcutaneous administration of semaglutide in the abdomen, thigh, or upper arm.
In patients with type 2 diabetes, semaglutide exposure increases in a dose-proportional manner for once-weekly doses of 0.5 mg, 1 mg and 2 mg. Steady-state exposure is achieved following 4 to 5 weeks of once-weekly administration. In patients with type 2 diabetes, the mean population-PK estimated steady-state concentrations following once-weekly subcutaneous administration of 0.5 mg and 1 mg semaglutide were approximately 65 ng/mL and 123 ng/mL, respectively. In the trial comparing semaglutide 1 mg and 2 mg, the mean steady state concentrations were 111.1 ng/mL and 222.1 ng/mL, respectively.
Distribution
The mean apparent volume of distribution of semaglutide following subcutaneous administration in patients with type 2 diabetes is approximately 12.5L. Semaglutide is extensively bound to plasma albumin (>99%).
Elimination
The apparent clearance of semaglutide in patients with type 2 diabetes is approximately 0.05 L/h. With an elimination half-life of approximately 1 week, semaglutide will be present in the circulation for about 5 weeks after the last dose.
Metabolism
The primary route of elimination for semaglutide is metabolism following proteolytic cleavage of the peptide backbone and sequential beta-oxidation of the fatty acid sidechain.
Excretion
The primary excretion routes of semaglutide-related material are via the urine and feces. Approximately 3% of the dose is excreted in the urine as intact semaglutide.
Specific Populations
Based on a population pharmacokinetic analysis, age, sex, race, and ethnicity, and renal impairment do not have a clinically meaningful effect on the pharmacokinetics of semaglutide. The exposure of semaglutide decreases with an increase in body weight. However, semaglutide doses of 0.5 mg and 1 mg provide adequate systemic exposure over the body weight range of 40 to 198 kg evaluated in the clinical trials. The effects of intrinsic factors on the pharmacokinetics of semaglutide are shown in Figure 3 .
Figure 3. Impact of Intrinsic Factors on Semaglutide Exposure

Patients with Renal impairment - Renal impairment does not impact the pharmacokinetics of semaglutide in a clinically relevant manner. This was shown in a study with a single dose of 0.5 mg semaglutide in patients with different degrees of renal impairment (mild, moderate, severe, or kidney failure) compared with subjects with normal renal function. This was also shown for subjects with both type 2 diabetes and renal impairment based on data from clinical studies ( Figure 3 ).
Patients with Hepatic impairment - Hepatic impairment does not have any impact on the exposure of semaglutide. The pharmacokinetics of semaglutide were evaluated in patients with different degrees of hepatic impairment (mild, moderate, severe) compared with subjects with normal hepatic function in a study with a single-dose of 0.5 mg semaglutide.
Pediatric Patients - Semaglutide has not been studied in pediatric patients.
Drug Interaction Studies
In vitro studies have shown very low potential for semaglutide to inhibit or induce CYP enzymes, and to inhibit drug transporters.
The delay of gastric emptying with semaglutide may influence the absorption of concomitantly administered oral medicinal products [ see Drug Interactions (7.2 ) ]. The potential effect of semaglutide on the absorption of co-administered oral medications was studied in trials at semaglutide 1 mg steady-state exposure.
No clinically relevant drug-drug interaction with semaglutide ( Figure 4 ) was observed based on the evaluated medications; therefore, no dose adjustment is required when co-administered with semaglutide. In a separate study, no apparent effect on the rate of gastric emptying was observed with semaglutide 2.4 mg.
Figure 4. Impact of Semaglutide on the Exposure of Coadministered Oral Medications

Relative exposure in terms of AUC and C max for each medication when given with semaglutide compared to without semaglutide. Metformin and oral contraceptive drug (ethinylestradiol/levonorgestrel) were assessed at steady state. Warfarin (S-warfarin/R-warfarin), digoxin and atorvastatin were assessed after a single dose.
Abbreviations: AUC: area under the curve. C max : maximum concentration. CI: confidence interval.
Immunogenicity
The observed incidence of anti-drug antibodies is highly dependent on the sensitivity and specificity of the assay. Differences in assay methods preclude meaningful comparisons of the incidence of anti-drug antibodies (ADAs) in the studies described below with the incidence of ADAs in other studies, including those of semaglutide or of other semaglutide products.
Across the placebo- and active-controlled glycemic control trials, 32 out of 3,150 (1%) OZEMPIC-treated patients developed ADAs to the active ingredient in OZEMPIC (i.e., semaglutide). Of the 32 semaglutide- treated patients that developed semaglutide ADAs, 19 patients (0.6% of the overall population) developed antibodies cross-reacting with native GLP-1. The in vitro neutralizing activity of the antibodies is uncertain at this time.
NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
In a 2-year carcinogenicity study in CD-1 mice, subcutaneous doses of 0.3, 1 and 3 mg/kg/day [2-, 11-, and 30-fold the maximum recommended human dose (MRHD) of 2 mg/week, based on AUC] were administered to the males, and 0.1, 0.3 and 1 mg/kg/day (1-, 2-, and 7-fold MRHD) were administered to the females. A statistically significant increase in thyroid C-cell adenomas and a numerical increase in C-cell carcinomas were observed in males and females at clinically relevant exposures.
- In a 2-year carcinogenicity study in Sprague Dawley rats, subcutaneous doses of 0.0025, 0.01, 0.025 and 0.1 mg/kg/day were administered (below quantification, 0.2-, 0.5-, and 3-fold the exposure at the MRHD). A statistically significant increase in thyroid C-cell adenomas was observed in males and females at all dose levels, and a statistically significant increase in thyroid C-cell carcinomas was observed in males at ≥0.01 mg/kg/day, at clinically relevant exposures.
Human relevance of thyroid C-cell tumors in rats is unknown and could not be determined by clinical studies or nonclinical studies [see Boxed Warning, Warnings and Precautions (5.1 )] .
Semaglutide was not mutagenic or clastogenic in a standard battery of genotoxicity tests (bacterial mutagenicity (Ames), human lymphocyte chromosome aberration, rat bone marrow micronucleus).
In a combined fertility and embryo-fetal development study in rats, subcutaneous doses of 0.01, 0.03 and 0.09 mg/kg/day (0.06-, 0.2-, and 0.6-fold the MRHD) were administered to male and female rats. Males were dosed for 4 weeks prior to mating, and females were dosed for 2 weeks prior to mating and throughout organogenesis until Gestation Day 17. No effects were observed on male fertility. In females, an increase in estrus cycle length was observed at all dose levels, together with a small reduction in numbers of corpora lutea at ≥0.03 mg/kg/day. These effects were likely an adaptive response secondary to the pharmacological effect of semaglutide on food consumption and body weight.
CLINICAL STUDIES
Glycemic Control Trials in Adults with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
OZEMPIC has been studied as monotherapy and in combination with metformin, metformin and sulfonylureas, metformin and/or thiazolidinedione, and basal insulin in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. The efficacy of OZEMPIC was compared with placebo, sitagliptin, exenatide extended-release (ER), and insulin glargine.
Most trials evaluated the use of OZEMPIC 0.5 mg, and 1 mg, with the exception of the trial comparing OZEMPIC and exenatide ER where only the 1 mg dose was studied. One trial evaluated the use of OZEMPIC 2 mg once weekly.
In patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus, OZEMPIC produced clinically relevant reduction from baseline in HbA 1c compared with placebo.
The efficacy of OZEMPIC was not impacted by age, gender, race, ethnicity, BMI at baseline, body weight (kg) at baseline, diabetes duration and level of renal function impairment.
Monotherapy Use of OZEMPIC in Adults with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
In a 30-week double-blind trial (NCT02054897), 388 patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus inadequately controlled with diet and exercise were randomized to OZEMPIC 0.5 mg or OZEMPIC 1 mg once weekly or placebo. Patients had a mean age of 54 years and 54% were men. The mean duration of type 2 diabetes was 4.2 years, and the mean BMI was 33 kg/m 2 . Overall, 64% were White, 8% were Black or African American, and 21% were Asian; 30% identified as Hispanic or Latino ethnicity.
Monotherapy with OZEMPIC 0.5 mg and 1 mg once weekly for 30 weeks resulted in a statistically significant reduction in HbA 1c compared with placebo (see Table 3 ).
Table 3. Results at Week 30 in a Trial of OZEMPIC as Monotherapy in Adult Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Inadequately Controlled with Diet and Exercise
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
| |||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
| |||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
- a The intent-to-treat population includes all randomized and exposed patients. At week 30 the primary HbA 1c endpoint was missing for 10%, 7% and 7% of patients and during the trial rescue medication was initiated by 20%, 5% and 4% of patients randomized to placebo, OZEMPIC 0.5 mg and OZEMPIC 1 mg, respectively. Missing data were imputed using multiple imputation based on retrieved dropouts.
- b Intent-to-treat analysis using ANCOVA adjusted for baseline value and country.
- c p <0.0001 (2-sided) for superiority, adjusted for multiplicity.
The mean baseline body weight was 89.1 kg, 89.8 kg, 96.9 kg in the placebo, OZEMPIC 0.5 mg, and OZEMPIC 1 mg arms, respectively. The mean changes from baseline to week 30 were -1.2 kg, -3.8 kg and -4.7 kg in the placebo, OZEMPIC 0.5 mg, and OZEMPIC 1 mg arms, respectively. The difference from placebo (95% CI) for OZEMPIC 0.5 mg was -2.6 kg (-3.8, -1.5), and for OZEMPIC 1 mg was -3.5 kg (-4.8, -2.2).
Combination Therapy Use of OZEMPIC in Adults with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Combination with metformin and/or thiazolidinediones
In a 56-week, double-blind trial (NCT01930188), 1231 patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus were randomized to OZEMPIC 0.5 mg once weekly, OZEMPIC 1 mg once weekly, or sitagliptin 100 mg once daily, all in combination with metformin (94%) and/or thiazolidinediones (6%). Patients had a mean age of 55 years and 51% were men. The mean duration of type 2 diabetes was 6.6 years, and the mean BMI was 32 kg/m 2 . Overall, 68% were White, 5% were Black or African American, and 25% were Asian; 17% identified as Hispanic or Latino ethnicity.
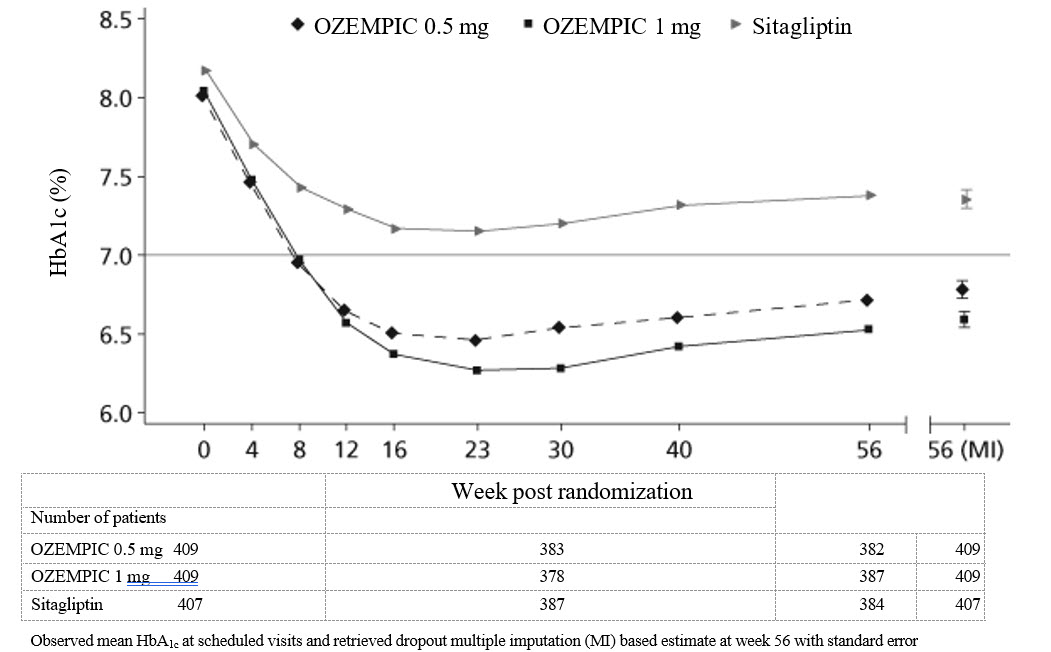
Treatment with OZEMPIC 0.5 mg and 1 mg once weekly for 56 weeks resulted in a statistically significant reduction in HbA1c compared to sitagliptin (see Table 4 and Figure 5 ).
Table 4. Results at Week 56 in a Trial of OZEMPIC Compared to Sitagliptin in Adult Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Combination with Metformin and/or Thiazolidinediones
OZEMPIC 0.5 mg | OZEMPIC 1 mg | Sitagliptin | |
Intent-to-Treat (ITT) Population (N) a | 409 | 409 | 407 |
HbA 1c (%) | |||
| 8 | 8 | 8.2 |
| -1.3 | -1.5 | -0.7 |
| -0.6 [-0.7, -0.4] c | -0.8 [-0.9, -0.6] c | |
Patients (%) achieving HbA 1c <7% | 66 | 73 | 40 |
FPG (mg/dL) | |||
| 168 | 167 | 173 |
| -35 | -43 | -23 |
- a The intent-to-treat population includes all randomized and exposed patients. At week 56 the primary HbA 1c endpoint was missing for 7%, 5% and 6% of patients and during the trial rescue medication was initiated by 5%, 2% and 19% of patients randomized to OZEMPIC 0.5 mg, OZEMPIC 1 mg and sitagliptin, respectively. Missing data were imputed using multiple imputation based on retrieved dropouts.
- b Intent-to-treat analysis using ANCOVA adjusted for baseline value and country.
- c p <0.0001 (2-sided) for superiority, adjusted for multiplicity.
The mean baseline body weight was 89.9 kg, 89.2 kg, 89.3 kg in the OZEMPIC 0.5 mg, OZEMPIC 1 mg, and sitagliptin arms, respectively. The mean changes from baseline to week 56 were -4.2 kg, -5.5 kg, and -1.7 kg for the OZEMPIC 0.5 mg, OZEMPIC 1 mg, and sitagliptin arms, respectively. The difference from sitagliptin (95% CI) for OZEMPIC 0.5 mg was -2.5 kg (-3.2, -1.8), and for OZEMPIC 1 mg was -3.8 kg (-4.5, -3.1).
Figure 5. Mean HbA 1c (%) Over Time - Baseline to Week 56
Combination with metformin or metformin with sulfonylurea
In a 56-week, open-label trial (NCT01885208), 813 patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus on metformin alone (49%), metformin with sulfonylurea (45%), or other (6%) were randomized to OZEMPIC 1 mg once weekly or exenatide 2 mg once weekly. Patients had a mean age of 57 years and 55% were men. The mean duration of type 2 diabetes was 9 years, and the mean BMI was 34 kg/m 2 . Overall, 84% were White, 7% were Black or African American, and 2% were Asian; 24% identified as Hispanic or Latino ethnicity.
Treatment with OZEMPIC 1 mg once weekly for 56 weeks resulted in a statistically significant reduction in HbA 1c compared to exenatide 2 mg once weekly (see Table 5 ).
Table 5. Results at Week 56 in a Trial of OZEMPIC Compared to Exenatide 2 mg Once Weekly in Adult Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Combination with Metformin or Metformin with Sulfonylurea
|
| |
|
|
|
| ||
| 8.4 | 8.3 |
| -1.4 | -0.9 |
| -0.5 [-0.7, -0.3] c | |
| 62 | 40 |
| ||
| 191 | 188 |
| -44 | -34 |
- a The intent-to-treat population includes all randomized and exposed patients. At week 56 the primary HbA 1c endpoint was missing for 9% and 11% of patients and during the trial rescue medication was initiated by 5% and 10% of patients randomized to OZEMPIC 1 mg and exenatide ER 2 mg, respectively. Missing data were imputed using multiple imputation based on retrieved dropouts.
- b Intent-to-treat analysis using ANCOVA adjusted for baseline value and country.
- c p <0.0001 (2-sided) for superiority, adjusted for multiplicity.
The mean baseline body weight was 96.2 kg and 95.4 kg in the OZEMPIC 1 mg and exenatide ER arms, respectively. The mean changes from baseline to week 56 were -4.8 kg and -2 kg in the OZEMPIC 1 mg and exenatide ER arms, respectively. The difference from exenatide ER (95% CI) for OZEMPIC 1 mg was -2.9 kg (-3.6, -2.1).
Combination with metformin or metformin with sulfonylurea
In a 30-week, open-label trial (NCT02128932), 1089 patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus were randomized to OZEMPIC 0.5 mg once weekly, OZEMPIC 1 mg once weekly, or insulin glargine once daily on a background of metformin (48%) or metformin and sulfonylurea (51%). Patients had a mean age of 57 years and 53% were men. The mean duration of type 2 diabetes was 8.6 years, and the mean BMI was 33 kg/m 2 . Overall, 77% were White, 9% were Black or African American, and 11% were Asian; 20% identified as Hispanic or Latino ethnicity.
Patients assigned to insulin glargine had a baseline mean HbA 1c of 8.1% and were started on a dose of 10 U once daily. Insulin glargine dose adjustments occurred throughout the trial period based on self-measured fasting plasma glucose before breakfast, targeting 71 to <100 mg/dL. In addition, investigators could titrate insulin glargine at their discretion between study visits. Only 26% of patients had been titrated to goal by the primary endpoint at week 30, at which time the mean daily insulin dose was 29 U per day.
Treatment with OZEMPIC 0.5 mg and 1 mg once weekly for 30 weeks resulted in a statistically significant reduction in HbA 1c compared with the insulin glargine titration implemented in this study protocol (see Table 6 ).
Table 6. Results at Week 30 in a Trial of OZEMPIC Compared to Insulin Glargine in Adult Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Combination with Metformin or Metformin with Sulfonylurea
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
| |||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
| |||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
- a The intent-to-treat population includes all randomized and exposed patients. At week 30 the primary HbA 1c endpoint was missing for 8%, 6% and 6% of patients and during the trial rescue medication was initiated by 4%, 3% and 1% of patients randomized to OZEMPIC 0.5 mg, OZEMPIC 1 mg and insulin glargine, respectively. Missing data were imputed using multiple imputation based on retrieved dropouts.
- b Intent-to-treat analysis using ANCOVA adjusted for baseline value, country and stratification factors.
- c p <0.0001 (2-sided) for superiority, adjusted for multiplicity.
- The mean baseline body weight was 93.7 kg, 94 kg, 92.6 kg in the OZEMPIC 0.5 mg, OZEMPIC 1 mg, and insulin glargine arms, respectively. The mean changes from baseline to week 30 were -3.2 kg, -4.7 kg and 0.9 kg in the OZEMPIC 0.5 mg, OZEMPIC 1 mg, and insulin glargine arms, respectively. The difference from insulin glargine (95% CI) for OZEMPIC 0.5 mg was -4.1 kg (-4.9, -3.3) and for OZEMPIC 1 mg was -5.6 kg (-6.4, -4.8).
- Combination with metformin or metformin with sulfonylurea
- In a 40-week, double-blind trial (NCT03989232), 961 patients with type 2 diabetes currently treated with metformin with or without sulfonylurea treatment were randomized to OZEMPIC 2 mg or OZEMPIC 1 mg once weekly. Patients had a mean age of 58 years and 58.6% were men. The mean duration of type 2 diabetes was 9.5 years and the mean BMI was 34.6 kg/m 2 . At randomization, 53.3% of patients were treated with sulfonylurea and metformin. Overall, 88.1% were White, 4.5% were Black or African American, and 7.2% were Asian; 11.6% identified as Hispanic or Latino ethnicity. Treatment with OZEMPIC 2 mg once weekly for 40 weeks resulted in a statistically significant reduction in HbA 1c compared with OZEMPIC 1 mg (see Table 7 ). Patients were stratified by region (Japan/outside Japan) at randomization.
Table 7. Results at Week 40 in a Trial of OZEMPIC 2 mg Compared to OZEMPIC 1 mg in Adult Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Combination With Metformin or Metformin with Sulfonylurea
|
| |
|
|
|
| ||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
| ||
|
|
|
|
|
|
- a The intent-to-treat population includes all randomized subjects. At week 40 the primary HbA1c endpoint was missing for 3% and 5% of patients randomized to OZEMPIC 1 mg and OZEMPIC 2 mg, respectively. Missing data were imputed using multiple imputation based on retrieved dropouts. For calculation of proportions, imputed values are dichotomized and the denominator is the number of all randomized subjects.
- b Intent-to-treat analysis using ANCOVA adjusted for baseline value and stratification factor.
- c p<0.01 (2-sided) for superiority, adjusted for multiplicity.
The mean baseline body weight was 98.6 kg and 100.1 kg in the OZEMPIC 1 mg and OZEMPIC 2 mg arms, respectively. The mean changes from baseline to week 40 were -5.6 kg and -6.4 kg in the OZEMPIC 1 mg and OZEMPIC 2 mg arms, respectively. The difference between treatment arms in body weight change from baseline at week 40 was not statistically significant.
Combination with basal insulin
In a 30-week, double-blind trial (NCT02305381), 397 patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus inadequately controlled with basal insulin, with or without metformin, were randomized to OZEMPIC 0.5 mg once weekly, OZEMPIC 1 mg once weekly, or placebo. Patients with HbA 1c ≤8.0% at screening reduced their insulin dose by 20% at start of the trial to reduce the risk of hypoglycemia. Patients had a mean age of 59 years and 56% were men. The mean duration of type 2 diabetes was 13 years, and the mean BMI was 32 kg/m 2 . Overall, 78% were White, 5% were Black or African American, and 17% were Asian; 12% identified as Hispanic or Latino ethnicity.
Treatment with OZEMPIC resulted in a statistically significant reduction in HbA 1c after 30 weeks of treatment compared to placebo (see Table 8 ).
Table 8. Results at Week 30 in a Trial of OZEMPIC in Adult Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Combination with Basal Insulin with or without Metformin
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
| |||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
| |||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
- a The intent-to-treat population includes all randomized and exposed patients. At week 30 the primary HbA 1c endpoint was missing for 7%, 5% and 5% of patients and during the trial rescue medication was initiated by 14%, 2% and 1% of patients randomized to placebo, OZEMPIC 0.5 mg and OZEMPIC 1 mg, respectively. Missing data were imputed using multiple imputation based on retrieved dropouts.
- b Intent-to-treat analysis using ANCOVA adjusted for baseline value, country and stratification factors.
- c p <0.0001 (2-sided) for superiority, adjusted for multiplicity.
The mean baseline body weight was 89.9 kg, 92.7 kg, and 92.5 kg in the placebo, OZEMPIC 0.5 mg, and OZEMPIC 1 mg arms, respectively. The mean changes from baseline to week 30 were -1.2 kg, -3.5 kg, and -6 kg in the placebo, OZEMPIC 0.5 mg, and OZEMPIC 1 mg arms, respectively. The difference from placebo (95% CI) for OZEMPIC 0.5 mg was -2.2 kg (-3.4, -1.1), and for OZEMPIC 1 mg was -4.7 kg (-5.8, -3.6).
Cardiovascular Outcomes Trial of OZEMPIC in Adults with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Cardiovascular Disease
SUSTAIN 6 (NCT01720446) was a multi-center, multi-national, placebo-controlled, double-blind cardiovascular outcomes trial. In this trial, 3,297 patients with inadequately controlled type 2 diabetes and atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease were randomized to OZEMPIC (0.5 mg or 1 mg) once weekly or placebo for a minimum observation time of 2 years. The trial compared the risk of Major Adverse Cardiovascular Event (MACE) between semaglutide and placebo when these were added to and used concomitantly with standard of care treatments for diabetes and cardiovascular disease. The primary endpoint, MACE, was the time to first occurrence of a three-part composite outcome which included cardiovascular death, non-fatal myocardial infarction and non-fatal stroke.
Patients eligible to enter the trial were; 50 years of age or older and had established, stable, cardiovascular, cerebrovascular, peripheral artery disease, chronic kidney disease or NYHA class II and III heart failure or were 60 years of age or older and had other specified risk factors for cardiovascular disease. In total, 1,940 patients (58.8%) had established cardiovascular disease without chronic kidney disease, 353 (10.7%) had chronic kidney disease only, and 442 (13.4%) had both cardiovascular disease and kidney disease; 562 patients (17%) had cardiovascular risk factors without established cardiovascular disease or chronic kidney disease. In the trial 453 patients (13.7%) had peripheral artery disease. The mean age at baseline was 65 years, and 61% were men. The mean duration of diabetes was 13.9 years, and mean BMI was 33 kg/m 2 . Overall, 83% were White, 7% were Black or African American, and 8% were Asian; 16% identified as Hispanic or Latino ethnicity. Concomitant diseases of patients in this trial included, but were not limited to, heart failure (24%), hypertension (93%), history of ischemic stroke (12%) and history of a myocardial infarction (33%). In total, 98.0% of the patients completed the trial and the vital status was known at the end of the trial for 99.6%.
For the primary analysis, a Cox proportional hazards model was used to test for non-inferiority of OZEMPIC to placebo for time to first MACE using a risk margin of 1.3. The statistical analysis plan pre specified that the 0.5 mg and 1 mg doses would be combined. Type-1 error was controlled across multiple tests using a hierarchical testing strategy.
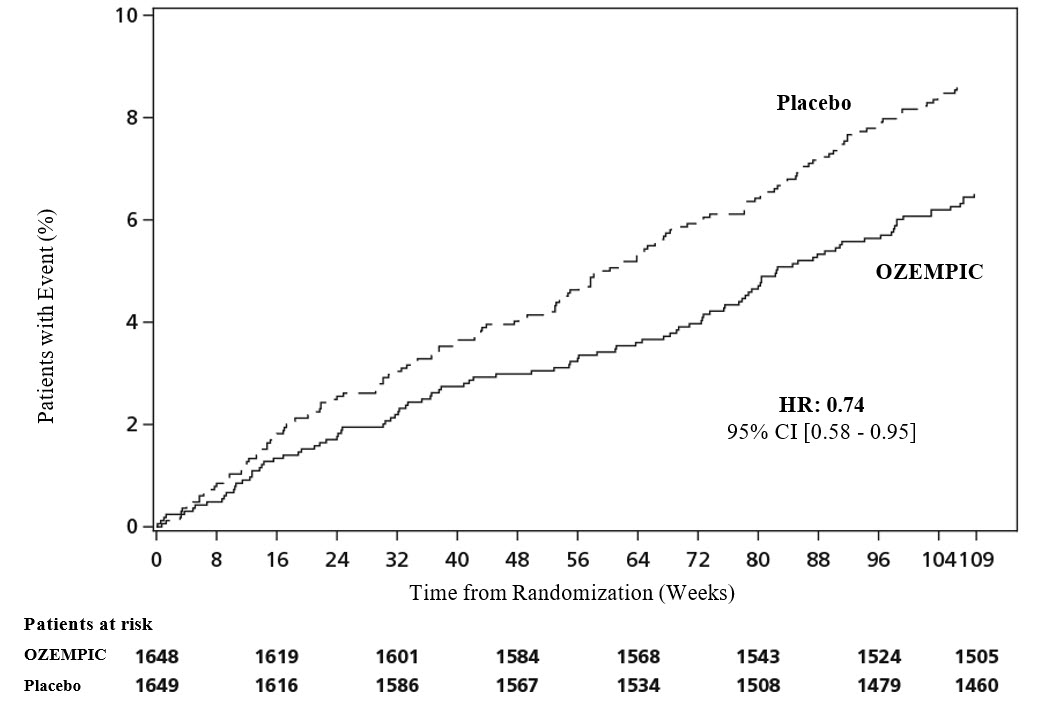
OZEMPIC significantly reduced the occurrence of MACE. The estimated hazard ratio for time to first MACE
was 0.74 (95% CI: 0.58, 0.95). Refer to Figure 6 and Table 9 .
Figure 6. Kaplan-Meier: Time to First Occurrence of a MACE in the SUSTAIN 6 Trial
The treatment effect for the primary composite endpoint and its components in the SUSTAIN 6 trial is shown in Table 9 .
Table 9. Treatment Effect for MACE and its Components, Median Study Observation Time of 2.1 Years
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
a Cox-proportional hazards models with treatment as factor and stratified by evidence of cardiovascular disease, insulin treatment and renal impairment.
Kidney Outcomes Trial of OZEMPIC in Adults with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Chronic Kidney Disease
FLOW (NCT03819153) was a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, event driven trial in adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus and chronic kidney disease (eGFR 25 to 75 mL/min/1.73 m 2 with urine albumin-to- creatinine ratio [UACR] >100 mg/g and <5000 mg/g). All patients needed to have an HbA 1c ≤10% at screening and be receiving standard of care background therapy, including a maximum tolerated labeled dose of a renin- angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS) blocking agent including an angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor or an angiotensin II receptor blocker (ARB), unless such treatment was contraindicated or not tolerated. The trial excluded patients with congenital or hereditary kidney diseases including polycystic kidney disease, autoimmune kidney diseases including glomerulonephritis or congenital urinary tract malformations.
A total of 3,533 patients were randomized to receive OZEMPIC 1 mg once weekly or placebo and were followed for a median of 41 months. The mean age of the study population was 67 years, and 70% of patients were male. Approximately 66% of the trial population was White, 24% Asian, and 5% Black or African American. At baseline, the mean eGFR was 47 mL/min/1.73m 2 , with 11% of patients having an eGFR <30 mL/min/1.73m 2 . Median baseline UACR was 568 mg/g with 69% of patients with a UACR >300 mg/g. At baseline, 95% of patients were treated with an ACE inhibitor or ARB, 16% were on sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors, 76% were on a statin, and 50% were on an antiplatelet agent.
OZEMPIC was superior to placebo in reducing the incidence of the primary composite endpoint of a sustained decline in eGFR of ≥50%, sustained eGFR <15 mL/min/1.73 m 2 , chronic renal replacement therapy, renal death, CV death (HR 0.76 [95% CI 0.66, 0.88], p=0.0003) as shown in Table 10 and Figure 7 . The treatment effect reflected a reduction in a sustained decline in eGFR of ≥50%, progression to kidney failure and CV death. There were few renal deaths during the trial.
OZEMPIC also reduced the annual rate of change in eGFR ( Figure 9 ), the incidence of a composite cardiovascular endpoint, consisting of non-fatal myocardial infarction (MI), non-fatal stroke, and cardiovascular death, and the incidence of all-cause death ( Table 10 and Figure 8 ).
The treatment effect on the primary composite endpoint was generally consistent across the pre-specified subgroups examined, including age, biological sex, eGFR and UACR. The treatment benefit on the primary composite endpoint was not evident in patients taking SGLT2 inhibitors at baseline, but there were few events in these patients.
Table 10: Analyses of the Primary and Secondary Endpoints and their Individual Components in FLOW Trial
|
|
| p-value 2 | |
| ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
| 0.0289 |
|
|
|
| 0.0104 |
1 Cox proportional hazards model with treatment as factor and stratified by baseline use of SGLT2-inhibitor at baseline (yes or no).
2 Two-sided p-value for the test of no difference. The significance level was 0.03224.
3 Sustained was defined as having 2 consecutive measurements ≥28 days apart fulfilling the criteria.
Figure 7. Cumulative Incidence: Time to First Occurrence of the Primary Composite Endpoint - Sustained Decline in eGFR ≥50%, Sustained eGFR<15 mL/min/1.73m 2 , Chronic Renal Replacement Therapy, Renal Death or CV Death

Cumulative incidence estimates are based on time from randomization to first composite renal event with non-CV and non-renal death modelled as competing risk. The x-axis is truncated at 52 months where approximately 5% of the population was in the trial.
Sustained was defined as having 2 consecutive measurements ≥28 days apart fulfilling the criteria.
Figure 8. Cumulative incidence: Time to First Occurrence of MACE in FLOW Trial 
- Cumulative incidence estimates are based on time from randomization to first EAC-confirmed MACE with non-CV death modelled as competing risk. The x-axis is truncated at 52 months where approximately 5% of the population was in the trial.
Figure 9. Observed Mean Plot: eGFR (mL/min/1.73m 2 ) by Week in FLOW Trial 
- Observed data from the in-trial period until week 104. Error bars are +/- 1.96 •standard error of the mean eGFR, which was calculated using the CKD-EPI 2009 formula.
- CKD-EPI: Chronic Kidney Disease Epidemiology Collaboration, eGFR: estimated glomerular filtration rate.
HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
How Supplied
Injection: clear, colorless solution of 0.68 mg/mL, 1.34 mg/mL or 2.68 mg/mL of semaglutide available in prefilled, disposable, single-patient-use pens in the following packaging configurations:
Dose per Injection | Use For | Total Strength per Total Volume | Doses per Pen | Carton Contents | NDC |
0.25 mg 0.5 mg | Initiation Maintenance | 2 mg/3 mL | 4 doses of 0.25 mg and 2 doses of 0.5 mg or 4 doses of 0.5 mg | 1 pen 6 NovoFine ® Plus needles | 0169-4181-13 |
1 mg | Maintenance | 4 mg/3 mL | 4 doses of 1 mg | 1 pen 4 NovoFine ® Plus needles | 0169-4130-13 |
2 mg | Maintenance | 8 mg/3 mL | 4 doses of 2 mg | 1 pen 4 NovoFine ® Plus needles | 0169-4772-12 |
The 2 mg/1.5 mL (1.34 mg/mL) strength (NDC 0169-4132-12) is not currently marketed by Novo Nordisk Inc.
Each OZEMPIC pen is for use by a single patient. An OZEMPIC pen must never be shared between patients, even if the needle is changed [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4 )] .
Recommended Storage
Prior to first use, OZEMPIC should be stored in a refrigerator between 36ºF to 46ºF (2ºC to 8ºC). Do not store in the freezer or directly adjacent to the refrigerator cooling element. Do not freeze OZEMPIC and do not use OZEMPIC if it has been frozen.
After first use of the OZEMPIC pen, the pen can be stored for 56 days at controlled room temperature 59°F to 86°F (15°C to 30°C) or in a refrigerator 36°F to 46°F (2°C to 8°C). Do not freeze. Keep the pen cap on when not in use. OZEMPIC should be protected from excessive heat and sunlight.
Always remove and safely discard the needle after each injection and store the OZEMPIC pen without an injection needle attached. Always use a new needle for each injection.
Recommended Storage Conditions for the OZEMPIC Pen
Prior to first use | After first use | |
Refrigerated 36°F to 46°F (2°C to 8°C) | Room Temperature 59°F to 86°F (15°C to 30°C) | Refrigerated 36°F to 46°F (2°C to 8°C) |
Until expiration date | 56 days | |
Instructions for Use - 0.25 mg or 0.5 mg doses, 2 mg/3 mL pen
INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE OZEMPIC ® [oh-ZEM-pick] (semaglutide) injection, for subcutaneous use 0.25 mg or 0.5 mg doses (pen delivers doses in 0.25 mg or 0.5 mg increments only) | ||
Supplies you will need to give your OZEMPIC injection:
|  | |
Step 1. Prepare your pen with a new needle | ||
|  | |
|  | |
|  | |
|  | |
|  | |
| 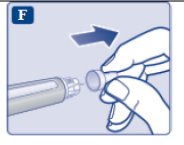 | |
Do not reuse or share your needles with other people. You may give other people a serious infection, or get a serious infection from them. Never use a bent or damaged needle. | ||
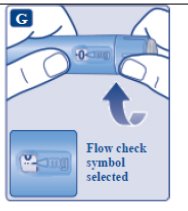
Step 2. First Time Use for Each New Pen: Check the OZEMPIC flow | ||
|  | |
| 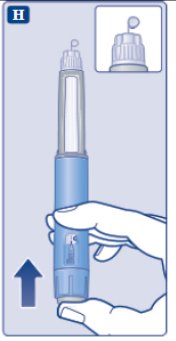 | |
If no drop appears, you will not inject any OZEMPIC, even though the dose counter may move. This may mean that there is a blocked or damaged needle. A small drop may remain at the needle tip, but it will not be injected. Only check the OZEMPIC flow before your first injection with each new pen. | ||
Step 3. Select your dose | ||
| 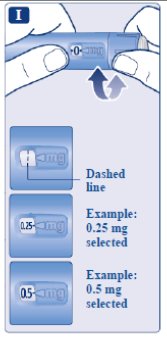 | |
You will hear a “click” every time you turn the dose selector. Do not set the dose by counting the number of clicks you hear. Only doses of 0.25 mg or 0.5 mg can be selected with the dose selector. The selected dose must line up exactly with the dose pointer to make sure that you get a correct dose. The dose selector changes the dose. Only the dose counter and dose pointer will show how many mg you select for each dose. You can select 0.25 mg or 0.5 mg for each dose. When your pen contains less than 0.5 or 0.25 mg, the dose counter stops before 0.5 mg or 0.25 mg is shown. The dose selector clicks differently when turned forward or backward. Do not count the pen clicks. | ||
How much OZEMPIC is left? | ||
| 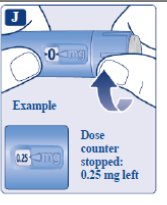 | |
Step 4. Inject your dose | ||
|  | |
|  | |
|  | |
|  | |
|  | |
How to identify a blocked or damaged needle?
How to handle a blocked needle? Change the needle as described in Step 5, and repeat all steps starting with Step 1: “Prepare your pen with a new needle”. Never touch the dose counter when you inject. This can stop the injection. You may see a drop of OZEMPIC at the needle tip after injecting. This is normal and does not affect your dose. | ||
Step 5. After your injection | ||
|  | |
|  | |
|  | |
|  | |
Always remove the needle from your pen. This will reduce the risk of contamination, infection, leakage of OZEMPIC, and blocked needles leading to the wrong dose. If the needle is blocked, you will not inject any OZEMPIC. Always dispose of the needle after each injection. | ||
Disposing of used OZEMPIC pens and needles:
| ||
| ||
| ||
Caring for your pen | ||
How should I store my OZEMPIC pen?
 For more information go to www.OZEMPIC.com Manufactured by: Novo Nordisk A/S DK-2880 Bagsvaerd Denmark For information about OZEMPIC contact: Novo Nordisk Inc. 800 Scudders Mill Road Plainsboro, NJ 08536 1-888-693-6742 Version: 2 OZEMPIC ® and NovoFine ® are registered trademarks of Novo Nordisk A/S. PATENT Information: https://www.novonordisk-us.com/products/product-patents.html © 2023 Novo Nordisk This Instructions for Use has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Revised: September 2023  | ||
Mechanism of Action
Semaglutide is a GLP-1 analogue with 94% sequence homology to human GLP-1. Semaglutide acts as a GLP-1 receptor agonist that selectively binds to and activates the GLP-1 receptor, the target for native GLP-1.
GLP-1 is a physiological hormone that has multiple actions on glucose, mediated by the GLP-1 receptors.
The principal mechanism of protraction resulting in the long half-life of semaglutide is albumin binding, which results in decreased renal clearance and protection from metabolic degradation. Furthermore, semaglutide is stabilized against degradation by the DPP-4 enzyme.
Semaglutide reduces blood glucose through a mechanism where it stimulates insulin secretion and lowers glucagon secretion, both in a glucose-dependent manner. Thus, when blood glucose is high, insulin secretion is stimulated, and glucagon secretion is inhibited. The mechanism of blood glucose lowering also involves a minor delay in gastric emptying in the early postprandial phase.
The mechanism of kidney-related risk reduction has not been established.
 If you are blind or have poor eyesight and cannot read the dose counter on the pen, do not use this pen without help . Get help from a person with good eyesight who is trained to use the OZEMPIC pen.
If you are blind or have poor eyesight and cannot read the dose counter on the pen, do not use this pen without help . Get help from a person with good eyesight who is trained to use the OZEMPIC pen.  Always use a new needle for each injection. This will reduce the risk of contamination, infection, leakage of OZEMPIC, and blocked needles leading to the wrong dose.
Always use a new needle for each injection. This will reduce the risk of contamination, infection, leakage of OZEMPIC, and blocked needles leading to the wrong dose.  ).
).  Always make sure that a drop appears at the needle tip before you use a new pen for the first time. This makes sure that OZEMPIC flows.
Always make sure that a drop appears at the needle tip before you use a new pen for the first time. This makes sure that OZEMPIC flows.  will guide
will guide  Always use the dose counter and the dose pointer to see how many mg you select.
Always use the dose counter and the dose pointer to see how many mg you select.  Always watch the dose counter to make sure you have injected your complete dose. Hold the dose button down until the dose counter shows 0.
Always watch the dose counter to make sure you have injected your complete dose. Hold the dose button down until the dose counter shows 0.  Never try to put the inner needle cap back on the needle. You may stick yourself with the needle.
Never try to put the inner needle cap back on the needle. You may stick yourself with the needle.  Important
Important