Rectiv
(Nitroglycerin)Dosage & Administration
Apply 1 inch of ointment (375 mg of ointment equivalent to 1.5 mg of nitroglycerin) intra-anally every 12 hours for up to 3 weeks. A finger covering, such as plastic-wrap, disposable surgical glove or a finger cot, should be placed on the finger to apply the ointment. To obtain a 1.5 mg dose of nitroglycerin, the covered finger is laid alongside the 1 inch dosing line on the carton.
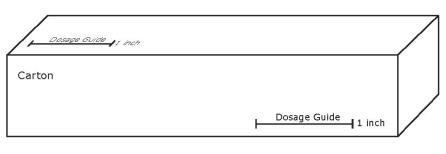
Refer to carton for accurate dosage guide.
The tube is gently squeezed until a line of ointment the length of the measuring line is expressed onto the covered finger. The ointment is gently inserted into the anal canal using the covered finger no further than to the first finger joint and the ointment is applied around the side of the anal canal. If this cannot be achieved due to pain, application of the ointment should be made directly to the outside of the anus. Treatment may be continued for up to three weeks.
RECTIV ointment is not for oral, ophthalmic, or intravaginal use. Hands should be washed after application of the ointment
Apply the ointment every 12 hours exactly as your doctor has told you to.
Cover your finger with plastic-wrap, a disposable surgical glove or a finger cot.
Lay the covered finger alongside the 1 inch dosing line marked on the side of the medicine box (see figure below) so that the tip of your finger is at one end of the dosing line. Starting at the tip of the finger, squeeze the ointment onto your finger for the same length marked on the box.

Refer to carton for accurate dosage guide.
Gently insert the finger with the ointment into the anal canal, up to the first finger joint. Carefully smear the ointment around the inner sides of the anal canal. If this cannot be achieved due to pain, application of the ointment should be made directly to the outside of the anus.
Throw away the finger covering in the garbage, out of the reach of children and pets. Wash your hands.
Active ingredient: nitroglycerin
Inactive ingredients: propylene glycol, lanolin, sorbitan sesquioleate, paraffin wax and white petrolatum.
PHARBIL Waltrop GmbH
Im Wirrigen 25
45731 Waltrop
Germany
AbbVie Inc.
North Chicago, IL 60064
© 2024 AbbVie. All rights reserved.
RECTIV and its design are trademarks of Allergan Sales, LLC, an AbbVie company.
By using PrescriberAI, you agree to the AI Terms of Use.
Rectiv Prescribing Information
RECTIV® (nitroglycerin) Ointment 0.4% is indicated for the treatment of moderate to severe pain associated with chronic anal fissure.
Apply 1 inch of ointment (375 mg of ointment equivalent to 1.5 mg of nitroglycerin) intra-anally every 12 hours for up to 3 weeks. A finger covering, such as plastic-wrap, disposable surgical glove or a finger cot, should be placed on the finger to apply the ointment. To obtain a 1.5 mg dose of nitroglycerin, the covered finger is laid alongside the 1 inch dosing line on the carton.

Refer to carton for accurate dosage guide.
The tube is gently squeezed until a line of ointment the length of the measuring line is expressed onto the covered finger. The ointment is gently inserted into the anal canal using the covered finger no further than to the first finger joint and the ointment is applied around the side of the anal canal. If this cannot be achieved due to pain, application of the ointment should be made directly to the outside of the anus. Treatment may be continued for up to three weeks.
RECTIV ointment is not for oral, ophthalmic, or intravaginal use. Hands should be washed after application of the ointment
Apply the ointment every 12 hours exactly as your doctor has told you to.
Cover your finger with plastic-wrap, a disposable surgical glove or a finger cot.
Lay the covered finger alongside the 1 inch dosing line marked on the side of the medicine box (see figure below) so that the tip of your finger is at one end of the dosing line. Starting at the tip of the finger, squeeze the ointment onto your finger for the same length marked on the box.

Refer to carton for accurate dosage guide.
Gently insert the finger with the ointment into the anal canal, up to the first finger joint. Carefully smear the ointment around the inner sides of the anal canal. If this cannot be achieved due to pain, application of the ointment should be made directly to the outside of the anus.
Throw away the finger covering in the garbage, out of the reach of children and pets. Wash your hands.
Active ingredient: nitroglycerin
Inactive ingredients: propylene glycol, lanolin, sorbitan sesquioleate, paraffin wax and white petrolatum.
PHARBIL Waltrop GmbH
Im Wirrigen 25
45731 Waltrop
Germany
AbbVie Inc.
North Chicago, IL 60064
© 2024 AbbVie. All rights reserved.
RECTIV and its design are trademarks of Allergan Sales, LLC, an AbbVie company.
Ointment, 0.4% w/w (4 mg /1 g) in 30 g tubes.
There are no data on the use of nitroglycerin ointment intra-anally during pregnancy to determine a drug-associated risk of major birth defects, miscarriage or other adverse maternal or fetal outcomes. In animal reproduction studies, no malformations were observed in offspring of pregnant rats and rabbits administered nitroglycerin by topical or dietary route during the period of organogenesis
The background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population is unknown. All pregnancies have a background risk of birth defect, loss, or other adverse outcomes. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2% to 4% and 15% to 20%, respectively.
Animal reproduction studies in rats and rabbits were conducted with topically applied nitroglycerin ointment at doses up to 80 mg/kg/day and 240 mg/kg/day, respectively. No toxic effects on dams or fetuses were seen at any dose tested.
An animal reproduction study was conducted in rats with nitroglycerin administered in the diet at levels up to 1% content (approximately 430 mg/kg/day) on days 6 to 15 of gestation. In offspring of the high-dose group, an increased but not statistically significant incidence of diaphragmatic hernias was noted together with decreased hyoid bone ossification. The latter finding probably reflects delayed development, thus indicating no clear evidence of a potential teratogenic effect of nitroglycerin.
- Use of PDE5 inhibitors (e.g. sildenafil, vardenafil and tadalafil) as these are shown to potentiate the hypotensive effects of organic nitrates. ().4.1PDE5 inhibitor use
Administration of RECTIV is contraindicated in patients who are using a selective inhibitor of cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP)-specific phosphodiesterase type 5 (PDE5), such as sildenafil, vardenafil, and tadalafil, as these are shown to potentiate the hypotensive effects of organic nitrates
[seeDRUG INTERACTIONS(7.1)]. - Severe anemia ()4.2Severe anemia
RECTIV is contraindicated in patients with severe anemia.
- Increased intracranial pressure ()4.3Increased intracranial pressure
RECTIV is contraindicated in patients with increased intracranial pressure.
- Known hypersensitivity to nitroglycerin, other nitrates and nitrites, or any components of the ointment. ()4.4Hypersensitivity
RECTIV is contraindicated in patients who have shown hypersensitivity to it or to other nitrates or nitrites. Skin reactions consistent with hypersensitivity have been observed with organic nitrates.
- Cardiovascular Disorders: Venous and arterial dilatation as a consequence of nitroglycerin treatment can result in hypotension. Exercise caution when treating patients with any of the following conditions: blood volume depletion, existing hypotension, cardiomyopathies, congestive heart failure, acute myocardial infarction, or poor cardiac function for other reasons ().5.000000000000000e+001Cardiovasculardisorders
Venous and arterial dilatation as a consequence of nitroglycerin treatment including RECTIV, can decrease venous blood returning to the heart and reduce arterial vascular resistance and systolic pressure. Exercise caution when treating patients with any of the following conditions: blood volume depletion, existing hypotension, cardiomyopathies, congestive heart failure, acute myocardial infarction, or poor cardiac function for other reasons. If patients with any of these conditions are treated with RECTIV, monitor cardiovascular status and clinical condition. The adverse reactions of RECTIV are likely to be more pronounced in the elderly.
- Headache: Nitroglycerin produces dose-related headaches which may be severe ()5.000000000000000e+002Headache
RECTIV produces dose-related headaches, which may be severe. Tolerance to headaches occurs.