Get your patient on Rezurock (Belumosudil)
Rezurock prior authorization resources
Most recent state uniform prior authorization forms
Brand Resources
Rezurock patient education
Patient toolkit
Dosage & administration
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Recommended Dosage : 200 mg taken orally once daily with food. (2.1 )
Recommended Dosage
The recommended dose of REZUROCK is 200 mg given orally once daily until progression of chronic GVHD that requires new systemic therapy.
Instruct the patient on the following:
- Swallow REZUROCK tablets whole. Do not cut, crush, or chew tablets.
- Take REZUROCK with a meal at approximately the same time each day [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ] .
- If a dose of REZUROCK is missed, instruct the patient to not take extra doses to make up the missed dose.
Treatment with REZUROCK has not been studied in patients with pre-existing severe renal impairment. For patients with pre-existing severe renal impairment, consider the risks and potential benefits before initiating treatment with REZUROCK [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ] .
Dosage Modifications for Adverse Reactions
Monitor total bilirubin, aspartate aminotransferase (AST), and alanine aminotransferase (ALT) at least monthly.
Modify the REZUROCK dosage for adverse reactions as per Table 1.
| Adverse Reaction | Severity Based on CTCAE v 4.03 | REZUROCK Dosage Modifications |
|---|---|---|
| Hepatotoxicity [see Adverse Reactions (6.1) ] | Grade 3 AST or ALT (5× to 20× ULN) or Grade 2 bilirubin (1.5× to 3× ULN) | Hold REZUROCK until recovery of bilirubin, AST and ALT to Grade 0–1, then resume REZUROCK at the recommended dose. |
| Grade 4 AST or ALT (more than 20× ULN) or Grade ≥3 bilirubin (more than 3× ULN) | Discontinue REZUROCK permanently. | |
| Other adverse reactions [see Adverse Reactions (6.1) ] | Grade 3 | Hold REZUROCK until recovery to Grade 0–1, then resume REZUROCK at the recommended dose level. |
| Grade 4 | Discontinue REZUROCK permanently. |
Dosage Modification Due to Drug Interactions
Strong CYP3A Inducers
Increase the dosage of REZUROCK to 200 mg twice daily when coadministered with strong CYP3A inducers [see Drug Interactions (7.1) ] .
Proton Pump Inhibitors
Increase the dosage of REZUROCK to 200 mg twice daily when coadministered with proton pump inhibitors [see Drug Interactions (7.1) ] .
Recommended Dosage in Patients with Hepatic Impairment
Avoid use in patients with moderate hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh B) or severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh C) without liver GVHD [see Use in Specific Populations (8.7) , Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ] .
No dosage adjustment is recommended when administering REZUROCK to patients with mild hepatic impairment [see Use in Specific Populations (8.7) , Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ] .

By using PrescriberAI, you agree to the AI Terms of Use.
Rezurock prescribing information
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
REZUROCK is indicated for the treatment of adult and pediatric patients 12 years and older with chronic graft-versus-host disease (chronic GVHD) after failure of at least two prior lines of systemic therapy.
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Recommended Dosage : 200 mg taken orally once daily with food. (2.1 )
Recommended Dosage
The recommended dose of REZUROCK is 200 mg given orally once daily until progression of chronic GVHD that requires new systemic therapy.
Instruct the patient on the following:
- Swallow REZUROCK tablets whole. Do not cut, crush, or chew tablets.
- Take REZUROCK with a meal at approximately the same time each day [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ] .
- If a dose of REZUROCK is missed, instruct the patient to not take extra doses to make up the missed dose.
Treatment with REZUROCK has not been studied in patients with pre-existing severe renal impairment. For patients with pre-existing severe renal impairment, consider the risks and potential benefits before initiating treatment with REZUROCK [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ] .
Dosage Modifications for Adverse Reactions
Monitor total bilirubin, aspartate aminotransferase (AST), and alanine aminotransferase (ALT) at least monthly.
Modify the REZUROCK dosage for adverse reactions as per Table 1.
| Adverse Reaction | Severity Based on CTCAE v 4.03 | REZUROCK Dosage Modifications |
|---|---|---|
| Hepatotoxicity [see Adverse Reactions (6.1) ] | Grade 3 AST or ALT (5× to 20× ULN) or Grade 2 bilirubin (1.5× to 3× ULN) | Hold REZUROCK until recovery of bilirubin, AST and ALT to Grade 0–1, then resume REZUROCK at the recommended dose. |
| Grade 4 AST or ALT (more than 20× ULN) or Grade ≥3 bilirubin (more than 3× ULN) | Discontinue REZUROCK permanently. | |
| Other adverse reactions [see Adverse Reactions (6.1) ] | Grade 3 | Hold REZUROCK until recovery to Grade 0–1, then resume REZUROCK at the recommended dose level. |
| Grade 4 | Discontinue REZUROCK permanently. |
Dosage Modification Due to Drug Interactions
Strong CYP3A Inducers
Increase the dosage of REZUROCK to 200 mg twice daily when coadministered with strong CYP3A inducers [see Drug Interactions (7.1) ] .
Proton Pump Inhibitors
Increase the dosage of REZUROCK to 200 mg twice daily when coadministered with proton pump inhibitors [see Drug Interactions (7.1) ] .
Recommended Dosage in Patients with Hepatic Impairment
Avoid use in patients with moderate hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh B) or severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh C) without liver GVHD [see Use in Specific Populations (8.7) , Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ] .
No dosage adjustment is recommended when administering REZUROCK to patients with mild hepatic impairment [see Use in Specific Populations (8.7) , Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ] .
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Each 200 mg belumosudil tablet is a pale yellow film-coated oblong tablet debossed with "KDM" on one side and "200" on the other side.
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
Pregnancy
Risk Summary
Based on findings from animal studies and the mechanism of action [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.1) ] , REZUROCK can cause fetal harm when administered to pregnant women. There are no available human data on REZUROCK use in pregnant women to evaluate for a drug-associated risk. In animal reproduction studies, administration of belumosudil to pregnant rats and rabbits during the period of organogenesis resulted in adverse developmental outcomes, including alterations to growth, embryo-fetal mortality, and embryo-fetal malformations at maternal exposures (AUC) approximately ≥1.4 (rat) and ≥0.08 (rabbit) times the human exposure (AUC) at the recommended dose (see Data ) . Advise pregnant women and females of reproductive potential of the potential risk to the fetus.
In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2 to 4% and 15 to 20%, respectively.
Data
Animal data
Embryo-fetal development studies were conducted in rats with administration of belumosudil to pregnant animals during the period of organogenesis at oral doses of 25, 50, 150, and 300 mg/kg/day in a pilot study and doses of 15, 50, and 150 mg/kg/day in a pivotal study. In the pilot study, maternal toxicity and embryo-fetal developmental effects were observed. Maternal toxicity (reduced body weight gain) occurred at 150 and 300 mg/kg/day doses. Increased post-implantation loss occurred at 50 and 300 mg/kg/day. Fetal-malformations were observed at ≥50 mg/kg/day and included absence of anus and tail, omphalocele, and dome shaped head. The exposure (AUC) at 50 mg/kg/day in rats is approximately 1.4 times the human exposure at the recommended dose of 200 mg.
In an embryo-fetal developmental study in rabbits, pregnant animals administered oral doses of belumosudil at 50, 125, and 225 mg/kg/day during the period of organogenesis resulted in maternal toxicity and embryo-fetal developmental effects. Maternal toxicity (body weight loss and mortality) was observed at doses ≥125 mg/kg/day. Embryo-fetal effects were observed at doses ≥50 mg/kg/day and included spontaneous abortion, increased post-implantation loss, decreased percentage of live fetuses, malformations, and decreased fetal body weight. Malformations included those in the tail (short), ribs (branched, fused or deformed), sternebrae (fused), and neural arches (fused, misaligned, and deformed). The exposure (AUC) at 50 mg/kg/day in rabbits is approximately 0.08 times the human exposure at the recommended dose of 200 mg.
Lactation
Risk Summary
There are no data available on the presence of belumosudil or its metabolites in human milk or the effects on the breastfed child, or milk production. Because of the potential for serious adverse reactions from belumosudil in the breastfed child, advise lactating women not to breastfeed during treatment with REZUROCK and for one week after the last dose.
Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
REZUROCK can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1) ] .
Pregnancy Testing
Verify the pregnancy status of females of reproductive potential prior to initiating treatment with REZUROCK.
Contraception
Females
Advise females of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with REZUROCK and for one week after the last dose of REZUROCK. If this drug is used during pregnancy or if the patient becomes pregnant while taking this drug, the patient should be informed of the potential hazard to a fetus.
Males
Advise males with female partners of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with REZUROCK and for one week after the last dose of REZUROCK.
Infertility
Females
Based on findings from rats, REZUROCK may impair female fertility [see Nonclinical Toxicology (13.1) ].
Males
Based on findings from rats and dogs, REZUROCK may impair male fertility [see Nonclinical Toxicology (13.1) ] .
Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of REZUROCK have been established in pediatric patients 12 years and older. Use of REZUROCK in this age group is supported by evidence from adequate and well-controlled studies of REZUROCK in adults with additional population pharmacokinetic data demonstrating that age and body weight had no clinically meaningful effect on the pharmacokinetics of drug substance, that the exposure of drug substance is expected to be similar between adults and pediatric patients age 12 years and older, and that the course of disease is sufficiently similar in adult and pediatric patients to allow extrapolation of data in adults to pediatric patients.
The safety and effectiveness of REZUROCK in pediatric patients less than 12 years old have not been established.
Geriatric Use
Of the 186 patients with chronic GVHD in clinical studies of REZUROCK, 26% were 65 years and older. No clinically meaningful differences in safety or effectiveness of REZUROCK were observed in comparison to younger patients.
Renal Impairment
Treatment with REZUROCK has not been studied in patients with pre-existing severe renal impairment. For patients with pre-existing severe renal impairment, consider the risks and potential benefits before initiating treatment with REZUROCK [see Dosage and Administration (2.1) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ] .
Hepatic Impairment
Avoid use in patients with moderate hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh B) or severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh C) without liver GVHD [see Dosage and Administration (2.4) , Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ] .
No dosage adjustment is recommended for patients with mild hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh A) [see Dosage and Administration (2.4) , Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ] .
CONTRAINDICATIONS
None.
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
Embryo-Fetal Toxicity : Can cause fetal harm. Advise females of reproductive potential of the potential risk to a fetus and to use effective contraception. (5.1 , 8.1 , 8.3 )
Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
Based on findings in animals and its mechanism of action, REZUROCK can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. In animal reproduction studies, administration of belumosudil to pregnant rats and rabbits during the period of organogenesis caused adverse developmental outcomes including embryo-fetal mortality and malformations at maternal exposures (AUC) less than those in patients at the recommended dose. Advise pregnant women of the potential risk to a fetus. Advise females of reproductive potential and males with female partners of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with REZUROCK and for one week after the last dose [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1 , 8.3) , Nonclinical Toxicology (13.1) ] .
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The most common (≥20%) adverse reactions, including laboratory abnormalities, are infections, asthenia, nausea, diarrhea, dyspnea, cough, edema, hemorrhage, abdominal pain, musculoskeletal pain, headache, phosphate decreased, gamma glutamyl transferase increased, lymphocytes decreased, and hypertension. (6.1 )
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Kadmon Pharmaceuticals, LLC at 1-800-633-1610 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
Clinical Trial Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely variable conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared with rates of clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
Chronic Graft versus Host Disease
In two clinical trials (Study KD025-213 and Study KD025-208), 83 adult patients with chronic GVHD were treated with REZUROCK 200 mg once daily [see Clinical Studies (14.1) ] . The median duration of treatment was 9.2 months (range 0.5 to 44.7 months).
Fatal adverse reaction was reported in one patient with severe nausea, vomiting, diarrhea and multi-organ failure.
Permanent discontinuation of REZUROCK due to adverse reactions occurred in 18% of patients. The adverse reactions which resulted in permanent discontinuation of REZUROCK in >3% of patients included nausea (4%). Adverse reactions leading to dose interruption occurred in 29% of patients. The adverse reactions leading to dose interruption in ≥2% were infections (11%), diarrhea (4%), and asthenia, dyspnea, hemorrhage, hypotension, liver function test abnormal, nausea, pyrexia, edema, and renal failure with (2% each).
The most common (≥20%) adverse reactions, including laboratory abnormalities, were infections, asthenia, nausea, diarrhea, dyspnea, cough, edema, hemorrhage, abdominal pain, musculoskeletal pain, headache, phosphate decreased, gamma glutamyl transferase increased, lymphocytes decreased, and hypertension.
Table 2 summarizes the nonlaboratory adverse reactions.
| Adverse Reaction | REZUROCK 200 mg once daily (N=83) | |
|---|---|---|
| All Grades (%) | Grades 3–4 (%) | |
| Infections and infestations | ||
| Infection (pathogen not specified) infection with an unspecified pathogen includes acute sinusitis, device related infection, ear infection, folliculitis, gastroenteritis, gastrointestinal infection, hordeolum, infectious colitis, lung infection, skin infection, tooth infection, urinary tract infection, wound infection, upper respiratory tract infection, pneumonia, conjunctivitis, sinusitis, respiratory tract infection, bronchitis, sepsis, septic shock. | 53 | 16 |
| Viral infection includes influenza, rhinovirus infection, gastroenteritis viral, viral upper respiratory tract infection, bronchitis viral, Epstein-Barr viremia, Epstein-Barr virus infection, parainfluenzae virus infection, Varicella zoster virus infection, viral infection. | 19 | 4 |
| Bacterial infection includes cellulitis, Helicobacter infection, Staphylococcal bacteremia, catheter site cellulitis, Clostridium difficile colitis, Escherichia urinary tract infection, gastroenteritis Escherichia coli, Pseudomonas infection, urinary tract infection bacterial. | 16 | 4 |
| General disorders and administration site conditions | ||
| Asthenia includes fatigue, asthenia, malaise. | 46 | 4 |
| Edema includes edema peripheral, generalized edema, face edema, localized edema, edema. | 27 | 1 |
| Pyrexia | 18 | 1 |
| Gastrointestinal | ||
| Nausea includes nausea, vomiting. | 42 | 4 |
| Diarrhea | 35 | 5 |
| Abdominal pain includes abdominal pain, abdominal pain upper, abdominal pain lower. | 22 | 1 |
| Dysphagia | 16 | 0 |
| Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal | ||
| Dyspnea includes dyspnea, dyspnea exertional, apnea, orthopnea, sleep apnea syndrome. | 33 | 5 |
| Cough includes cough, productive cough. | 30 | 0 |
| Nasal congestion | 12 | 0 |
| Vascular | ||
| Hemorrhage includes contusion, hematoma, epistaxis, increased tendency to bruise, conjunctival hemorrhage, hematochezia, mouth hemorrhage, catheter site hemorrhage, hematuria, hemothorax, purpura. | 23 | 5 |
| Hypertension | 21 | 7 |
| Musculoskeletal and connective tissue | ||
| Musculoskeletal pain includes pain in extremity, back pain, flank pain, limb discomfort, musculoskeletal chest pain, neck pain, musculoskeletal pain. | 22 | 4 |
| Muscle spasm | 17 | 0 |
| Arthralgia | 15 | 2 |
| Nervous system | ||
| Headache includes headache, migraine. | 21 | 0 |
| Metabolism and nutrition | ||
| Decreased appetite | 17 | 1 |
| Skin and subcutaneous | ||
| Rash includes rash, rash maculo-papular, rash erythematous, rash generalized, dermatitis exfoliative. | 12 | 0 |
| Pruritus includes pruritus, pruritus generalized. | 11 | 0 |
Table 3 summarizes the laboratory abnormalities in REZUROCK.
| REZUROCK 200 mg once daily | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Grade 0–1 Baseline | Grade 2–4 Max Post | Grade 3–4 Max Post | |
| Parameter | (N) | (%) | (%) |
| Chemistry | |||
| Phosphate decreased | 76 | 28 | 7 |
| Gamma Glutamyl Transferase increased | 47 | 21 | 11 |
| Calcium decreased | 82 | 12 | 1 |
| Alkaline Phosphatase increased | 80 | 9 | 0 |
| Potassium increased | 82 | 7 | 1 |
| Alanine Aminotransferase increased | 83 | 7 | 2 |
| Creatinine increased | 83 | 4 | 0 |
| Hematology | |||
| Lymphocytes decreased | 62 | 29 | 13 |
| Hemoglobin decreased | 79 | 11 | 1 |
| Platelets decreased | 82 | 10 | 5 |
| Neutrophil Count decreased | 83 | 8 | 4 |
DRUG INTERACTIONS
- Strong CYP3A Inducers : Increase REZUROCK dosage to 200 mg twice daily. (7.1 , 2.3 )
- Proton Pump Inhibitors : Increase REZUROCK dosage to 200 mg twice daily. (7.1 , 2.3 )
- BCRP Substrates: Avoid concomitant use with drugs that are BCRP substrates where possible. If used together, monitor patients more frequently for adverse reactions and decrease the substrates dosage(s) in accordance with the respective Prescribing Information. (7.2 )
- OATP1B1 Substrates: If used together, monitor patients more frequently for adverse reactions and decrease the substrates dosage(s) in accordance with the respective Prescribing Information. (7.2 )
- Certain CYP1A2, CYP3A, P-gp or UGT1A1 Substrates : Avoid concomitant use with these substrates for which minimal concentration changes may lead to serious toxicities. If concomitant use cannot be avoided, decrease the substrates dosage(s) in accordance with the respective Prescribing Information. (7.2 )
Effect of Other Drugs on REZUROCK
Proton Pump Inhibitors
Belumosudil exhibits pH-dependent solubility. Concomitant use of REZUROCK with proton pump inhibitors decreases belumosudil exposure [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ] , which may reduce the efficacy of REZUROCK. Increase the dosage of REZUROCK when used concomitantly with proton pump inhibitors [see Dosage and Administration (2.3) ].
Strong CYP3A Inducers
Belumosudil is a CYP3A substrate. Concomitant use of REZUROCK with strong CYP3A inducers decreases belumosudil exposure [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ] , which may reduce the efficacy of REZUROCK. Increase the dosage of REZUROCK when used concomitantly with strong CYP3A inducers [see Dosage and Administration (2.3) ].
Effect of REZUROCK on Other Drugs
BCRP and OATP1B1 Substrates
Avoid concomitant use with drugs that are BCRP substrates where possible. If used together, monitor patients more frequently for adverse reactions and decrease the BCRP substrates dosage(s) in accordance with the respective Prescribing Information.
Belumosudil is a BCRP inhibitor. Concomitant use of REZUROCK with BCRP substrates increases their plasma concentrations [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ] , which may increase the risk of adverse reactions related to these substrates.
Belumosudil is an OATP1B1 inhibitor. Concomitant use of REZUROCK with OATP1B1 substrates may increase their plasma concentrations. Monitor patients more frequently for adverse reactions of these substrates and decrease the OATP1B1 substrates dosage(s) in accordance with the respective Prescribing Information [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ] .
Certain CYP1A2 Substrates
Avoid concomitant use of REZUROCK with drugs that are sensitive CYP1A2 substrates, for which minimal concentration changes may lead to serious toxicities. If concomitant use cannot be avoided, decrease the CYP1A2 substrate dosage(s) in accordance with the respective Prescribing Information.
Belumosudil is a CYP1A2 inhibitor. Concomitant use of REZUROCK with sensitive CYP1A2 substrates (e.g., caffeine) is predicted to increase CYP1A2 substrate exposure [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ] , which may increase the risk of adverse reactions related to these substrates.
Certain CYP3A Substrates
Avoid concomitant use of REZUROCK with drugs that are sensitive CYP3A substrates, for which minimal concentration changes may lead to serious toxicities. If concomitant use cannot be avoided, decrease the CYP3A substrate dosage(s) in accordance with the respective Prescribing Information.
Belumosudil is a CYP3A inhibitor. Concomitant use of REZUROCK with sensitive CYP3A substrates (e.g., midazolam) is predicted to increase CYP3A substrate exposure [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ] , which may increase the risk of adverse reactions related to these substrates.
Certain UGT1A1 Substrates
Avoid concomitant use of REZUROCK with drugs that are UGT1A1 substrates, for which minimal concentration changes may lead to serious toxicities. If concomitant use cannot be avoided, decrease the UGT1A1 substrates dosage(s) in accordance with the respective Prescribing Information.
Belumosudil is a UGT1A1 inhibitor. Concomitant use of REZUROCK with a UGT1A1 substrate decreased plasma concentrations of the glucuronide metabolite of the UGT1A1 substrate [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ]. Concomitant use of belumosudil with other UGT1A1 substrates may increase their plasma concentrations, which may increase the risk of adverse reactions related to these substrates.
Certain P-gp Substrates
Avoid concomitant use of REZUROCK with drugs that are P-gp substrates, for which minimal concentration changes may lead to serious toxicities. If concomitant use cannot be avoided, decrease the P-gp substrates dosage(s) in accordance with the respective Prescribing Information.
Belumosudil is a P-gp inhibitor. Concomitant use of REZUROCK with P-gp substrates increased their plasma concentrations [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ] , which may increase the risk of adverse reactions related to these substrates.
DESCRIPTION
Belumosudil is a kinase inhibitor. The active pharmaceutical ingredient is belumosudil mesylate with the molecular formula C 27 H 28 N 6 O 5 S and the molecular weight is 548.62 g/mol. The chemical name for belumosudil mesylate is 2-{3-[4-(1 H -indazol-5-ylamino)-2-quinazolinyl]phenoxy}- N -(propan-2-yl) acetamide methanesulfonate (1:1). The chemical structure is as follows:
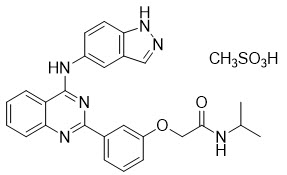
Belumosudil mesylate is a yellow powder that is practically insoluble in water, slightly soluble in methanol and DMF and soluble in DMSO.
REZUROCK tablets are for oral administration. Each tablet contains 200 mg of the free base equivalent to 242.5 mg of belumosudil mesylate. The tablet also contains the following inactive ingredients: colloidal silicon dioxide, croscarmellose sodium, hypromellose, magnesium stearate, and microcrystalline cellulose.
The tablet film consists of polyethylene glycol, polyvinyl alcohol, talc, titanium dioxide and yellow iron oxide.
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Mechanism of Action
Belumosudil is an inhibitor of rho-associated, coiled-coil containing protein kinase (ROCK) which inhibits ROCK2 and ROCK1 with IC 50 values of approximately 100 nM and 3 µM, respectively. Belumosudil down-regulated proinflammatory responses via regulation of STAT3/STAT5 phosphorylation and shifting Th17/Treg balance in ex-vivo or in vitro -human T cell assays. Belumosudil also inhibited aberrant pro-fibrotic signaling, in vitro . In vivo , belumosudil demonstrated activity in animal models of chronic GVHD.
Pharmacodynamics
Belumosudil exposure-response relationships and the time course of pharmacodynamic response are not established.
Cardiac Electrophysiology
At 2.4 times the maximum exposure for approved recommended dose, REZUROCK does not prolong the QT interval to any clinically relevant extent.
Pharmacokinetics
The following pharmacokinetic parameters are presented for chronic GVHD patients administered belumosudil 200 mg once daily, unless otherwise specified. The mean (% coefficient of variation, %CV) steady-state AUC and C max of belumosudil was 22,700 (48%) h∙ng/mL and 2390 (44%) ng/mL, respectively. Belumosudil C max and AUC increased in an approximately proportional manner over a dosage range of 200 and 400 mg (1 to 2 times once daily recommended dosage). The accumulation ratio of belumosudil was 1.4.
Absorption
Median T max of belumosudil at steady state was 1.26 to 2.53 hours following administration of 200 mg once daily or twice daily in patients. The mean (%CV) bioavailability was 64% (17%) following a single belumosudil dose in healthy subjects.
Effect of Food
Belumosudil C max and AUC increased 2.2 times and 2 times, respectively, following administration of a single belumosudil dose with a high-fat and high-calorie meal (800 to 1,000 calories with approximately 50% of total caloric content of the meal from fat) compared to the fasted state in healthy subjects. Median T max was delayed 0.5 hours.
Distribution
The geometric mean volume of distribution after a single dose of belumosudil in healthy subjects was 184 L (geo CV% 67.7%).
Belumosudil binding to human serum albumin and human α 1 -acid glycoprotein was 99.9% and 98.6%, respectively, in vitro .
Elimination
The mean (%CV) elimination half-life of belumosudil was 19 hours (39%), and clearance was 9.83 L/hours (46%) in patients.
Metabolism
Belumosudil is primarily metabolized by CYP3A and to a lesser extent by CYP2C8, CYP2D6, and UGT1A9, in vitro .
Excretion
Following a single oral dose of radiolabeled belumosudil in healthy subjects, 85% of radioactivity was recovered in feces (30% as unchanged) and less than 5% in urine.
Specific Populations
No clinically significant differences in belumosudil pharmacokinetics were observed with regard to age (18 to 77 years), sex, weight (38.6 to 143 kg), or mild to moderate renal impairment (eGFR ≥60 and <90 mL/min/1.72m 2 to eGFR ≥30 and <60 mL/min/1.72m 2 ). The effect of severe renal impairment on the pharmacokinetics of belumosudil has not been studied.
Patients with Hepatic Impairment
Following a single 200 mg dose of belumosudil, changes in belumosudil exposure in subjects with varying degrees of hepatic impairment based on Child-Pugh score without liver GVHD relative to subjects with normal hepatic function is shown in Table 4.
| Hepatic Impairment Category | Changes in Belumosudil Exposure in Subjects with Hepatic Impairment Compared to Subjects with Normal Hepatic Function | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total (Free + Bound) Concentrations | Free Concentrations | |||
| C max | AUC | C max | AUC | |
| Mild (Child-Pugh A) | 1.2-fold increase | 1.4-fold increase | 14% decrease | 19% decrease |
| Moderate (Child-Pugh B) | 6% decrease | 1.5-fold increase | 12% decrease | 1.4-fold increase |
| Severe (Child-Pugh C) | 1.3-fold increase | 4.2-fold increase | 5.4-fold increase | 16-fold increase |
Drug Interaction Studies
Clinical Studies and Model-Informed Approaches
Proton Pump Inhibitors : Concomitant use of rabeprazole decreased belumosudil C max by 87% and AUC by 80%, and omeprazole decreased belumosudil C max by 68% and AUC by 47% in healthy subjects.
Strong Cytochrome P450 (CYP) 3A Inhibitors : There was no clinically meaningful effect on belumosudil exposure when used concomitantly with itraconazole (strong CYP3A inhibitor) in healthy subjects.
Strong CYP3A Inducers : Concomitant use of rifampin (strong CYP3A inducer) decreased belumosudil C max by 59% and AUC by 72% in healthy subjects.
Moderate CYP3A Inducers : Concomitant use of efavirenz (moderate CYP3A inducer) is predicted to decrease belumosudil C max by 19% and AUC by 35% in healthy subjects.
CYP1A2 Substrates: Concomitant use of belumosudil is predicted to increase caffeine (sensitive CYP1A2 substrate) C max and AUC approximately 1.1- and 1.6-fold, respectively.
CYP3A Substrates: Concomitant use of belumosudil is predicted to increase midazolam (sensitive CYP3A substrate) C max and AUC approximately 1.3- and 1.7-fold, respectively.
UGT1A1 Substrates: Concomitant use of belumosudil did not have clinically significant effect on the exposure of raltegravir (UGT1A1 substrate), but decreased raltegravir glucuronide (metabolite formed via the UGT1A1 pathway) C max by 42% and AUC by 40%.
BCRP/OATP1B1 Substrates : Concomitant use of belumosudil increased rosuvastatin (BCRP and OATP1B1 substrate) C max and AUC by 3.6- and 4.6-fold, respectively .
P-glycoprotein (P-gp) Substrates: Concomitant use of belumosudil increased dabigatran (P-gp substrate) C max and AUC by 2-fold.
Other drugs : Concomitant use of belumosudil is not predicted to have clinically significant effects on the exposure of ( S )-warfarin (CYP2C9 substrate), omeprazole (CYP2C19 substrate), and CYP2C8 substrates that are not an OATP1B1 substrate.
In Vitro Studies
UDP-Glucuronosyltransferase (UGT) : Belumosudil is an inhibitor of UGT1A9.
Transporter Systems : Belumosudil is a substrate of P-gp.
NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenesis
Belumosudil did not result in any carcinogenic effect in a 6-month CByB6F1-Tg (HRAS)2Jic hemizygous mouse study at oral doses up to 15 mg/kg/day in female and 30 mg/kg/day in male mice.
Mutagenesis
Belumosudil was not genotoxic in an in vitro bacterial mutagenicity (Ames) assay, in vitro chromosome aberration assay in human peripheral blood lymphocytes (HPBL) or an in vivo rat bone marrow micronucleus assay.
Impairment of Fertility
In a combined male and female rat fertility and early embryonic development study, belumosudil-treated male animals were mated with untreated females, or untreated males were mated with belumosudil-treated females. Belumosudil was administered orally at doses of 50, 150 or 275 mg/kg/day to male rats 70 days prior to and throughout the mating period, and to female rats 14 days prior to mating and up to Gestation Day 7. At the dose of 275 mg/kg/day, adverse findings in female rats (treated with belumosudil or untreated but mated with treated males) regarding early embryonic development included increased pre- or post-implantation loss and decreased number of viable embryos. Administration of belumosudil to male rats at a dose of 275 mg/kg/day resulted in abnormal sperm findings (reduced motility, reduced count, and increased percentage of abnormal sperm), and testes/epididymis organ changes (reduced weight and degeneration). Fertility was reduced in both treated males or females at the 275 mg/kg/day dose and reached statistical significance in males. Adverse changes in male and female reproductive organs also occurred in general 3-month and 6-month toxicology studies. In males, findings included spermatozoa degeneration at a belumosudil dose of 50 mg/kg/day in rats and 35 mg/kg/day in dogs. The exposure (AUC) at the doses of 50 mg/kg/day in male rats and 35 mg/kg/day in male dogs is approximately equivalent to the clinical exposure at the recommended dose of 200 mg/day. Changes were reversible in dogs but not fully reversible in rats. In female rats, changes included decreased follicular development in ovaries and lower uterine weights that correlated with uterine/cervical hypoplasia at 275 mg/kg/day [corresponding to 9 times exposure in patients at the recommended dose of 200 mg/day]. Changes were fully reversed during the 4-week recovery period.
CLINICAL STUDIES
Chronic Graft versus Host Disease
Study KD025-213 (NCT03640481) was a randomized, open-label, multicenter study of REZUROCK for treatment of patients with chronic GVHD who had received 2 to 5 prior lines of systemic therapy and required additional treatment. Patients were excluded from the studies if platelets were <50 × 10 9 /L; absolute neutrophil count <1.5 × 10 9 /L; AST or ALT >3 × ULN; total bilirubin >1.5 × ULN; QTc(F) >480 ms; eGFR <30 mL/min/1.73 m 2 ; or FEV1 ≤39%. There were 66 patients treated with REZUROCK 200 mg taken orally once daily. Concomitant treatment with supportive care therapies for chronic GVHD was permitted. Concomitant treatment with GVHD prophylaxis and standard care systemic chronic GVHD therapies was permitted as long as the subject has been on a stable dose for at least 2 weeks prior to study. Initiation of new systemic chronic GVHD therapy while on study was not permitted.
Demographics and baseline characteristics are summarized in Table 5.
| REZUROCK 200 mg once daily (N=65) | |
|---|---|
| Age, Median, Years (minimum, maximum) | 53 (21, 77) |
| Age ≥65 Years, n (%) | 17 (26) |
| Male, n (%) | 42 (65) |
| Race, n (%) | |
| White | 54 (83) |
| Black | 6 (9) |
| Other or Not Reported | 5 (8) |
| Median (range) time (months) from Chronic GVHD Diagnosis | 25.3 (1.9, 162.4) |
| ≥4 Organs Involved, n (%) | 31 (48) |
| Median (range) Number of Prior Lines of Therapy | 3 (2, 6) |
| Number of Prior Lines of Therapy, n (%) | |
| 2 | 23 (35) |
| 3 | 12 (19) |
| 4 | 15 (23) |
| ≥5 | 15 (23) |
| Prior chronic GVHD treatment with ibrutinib, n (%) | 21 (32) |
| Prior chronic GVHD treatment with ruxolitinib, n (%) | 20 (31) |
| Refractory to Last Therapy, n (% Denominator excludes patients with unknown status ) | 43/55 (78) |
| Severe chronic GVHD, n (%) | 46 (71) |
| Median (range) Global Severity Rating | 7 (2, 9) |
| Median (range) Lee Symptom Scale Score at baseline | 27 (7, 56) |
| Median (range) Corticosteroid dose at baseline (PE/kg) Prednisone equivalents/kilogram | 0.19 (0.03, 0.95) |
The efficacy of REZUROCK was based on overall response rate (ORR) through Cycle 7 Day 1 where overall response included complete response or partial response according to the 2014 NIH Response Criteria. The ORR results are presented in Table 6. The ORR was 75% (95% CI: 63, 85). The median duration of response, calculated from first response to progression, death, or new systemic therapies for chronic GVHD, was 1.9 months (95% CI: 1.2, 2.9). The median time to first response was 1.8 months (95% CI: 1.0, 1.9). In patients who achieved response, no death or new systemic therapy initiation occurred in 62% (95% CI: 46, 74) of patients for at least 12 months since response.
| REZUROCK 200 mg once daily (N=65) | |
|---|---|
| Overall Response Rate (ORR) | 49 (75%) |
| 95% Confidence Interval Estimated using Clopper-Pearson method | (63%, 85%) |
| Complete Response | 4 (6%) |
| Partial Response | 45 (69%) |
ORR results were supported by exploratory analyses of patient-reported symptom bother which showed at least a 7-point decrease in the Lee Symptom Scale summary score through Cycle 7 Day 1 in 52% (95% CI: 40, 65) of patients.
HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
REZUROCK 200 mg tablets are supplied as pale yellow film-coated oblong tablets containing 200 mg of belumosudil (equivalent to 242.5 mg belumosudil mesylate). Each tablet is debossed with "KDM" on one side and "200" on the other side and is packaged as follows:
- 200 mg tablets in 30 count bottle: NDC 79802-200-30
Store at room temperature, 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F); excursions permitted from 15°C to 30°C (59°F to 86°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature].
Dispense to patient in original container only. Store in original container to protect from moisture. Replace cap securely each time after opening. Do not discard desiccant.
Mechanism of Action
Belumosudil is an inhibitor of rho-associated, coiled-coil containing protein kinase (ROCK) which inhibits ROCK2 and ROCK1 with IC 50 values of approximately 100 nM and 3 µM, respectively. Belumosudil down-regulated proinflammatory responses via regulation of STAT3/STAT5 phosphorylation and shifting Th17/Treg balance in ex-vivo or in vitro -human T cell assays. Belumosudil also inhibited aberrant pro-fibrotic signaling, in vitro . In vivo , belumosudil demonstrated activity in animal models of chronic GVHD.