Sotylize prior authorization resources
Most recent state uniform prior authorization forms
Dosage & administration
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- Initiate therapy at 80 mg twice daily. Increase the dose as needed in increments of 80 mg/day, every 3 days to a maximum 320 mg total daily dose (2.2 )
- If creatinine clearance is between 60 and 40 mL/min, administer once daily, if less than 40 mL/min, sotalol is not recommended (2.1 )
- Pediatrics: Dosage depends on age (2.4 )
General Safety Measures of Oral Sotalol Therapy
Withdraw other antiarrhythmic therapy before starting SOTYLIZE and monitor for a minimum of 2 to 3 plasma half-lives prior to initiating SOTYLIZE therapy if the patient's clinical condition permits [see Drug Interactions (7) ] .
Hospitalize patients being initiated or re-initiated on sotalol for at least 3 days or until steady-state drug levels are achieved in a facility that can provide cardiac resuscitation and continuous electrocardiographic monitoring. Initiate oral sotalol therapy in the presence of personnel trained in the management of serious arrhythmias. Perform a baseline ECG to determine the QT interval and measure and normalize serum potassium and magnesium levels before initiating therapy. Measure serum creatinine and calculate an estimated creatinine clearance in order to establish the appropriate dosing interval. Monitor QTc 2 to 4 hours after each uptitration in dose.
Discharge patients on sotalol therapy from an in-patient setting with an adequate supply of sotalol to allow uninterrupted therapy until the patient can fill a sotalol prescription.
Advise patients who miss a dose to take the next dose at the usual time. Do not double the dose or shorten the dosing interval.
Adult Dose for Ventricular Arrhythmia
The recommended initial dose is 80 mg twice daily. This dose may be increased in increments of 80 mg per day every 3 days provided the QTc <500 msec [see Warning and Precautions (5.1) ] . Continually monitor patients until steady state blood levels are achieved. In most patients, a therapeutic response is obtained at a total daily dose of 160 to 320 mg/day, given in two or three divided doses. Oral doses as high as 480 to 640 mg once or twice a day have been utilized in patients with refractory life-threatening arrhythmias.
Adult Dose for Prevention of Recurrence of AFIB/AFL
The recommended initial dose is 80 mg twice daily. This dose may be increased in increments of 80 mg per day every 3 days provided the QTc ˂500 msec [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) ] . Continually monitor patients until steady state blood levels are achieved. Most patients will have a satisfactory response with 120 mg twice daily. Initiation of sotalol in patients with QTc ˃450 msec is contraindicated [see Contraindication (4) ] .
Pediatric Dose for Ventricular Arrhythmias or AFIB/AFL
Use the same precautionary measures for children as you would use for adults when initiating and re-initiating sotalol treatment.
For Children Aged About 2 Years and Older
For children aged about 2 years and older with normal renal function, doses normalized for body surface area are appropriate for both initial and incremental dosing. Since the Class III potency in children is not very different from that in adults, reaching plasma concentrations that occur within the adult dose range is an appropriate guide [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.1 , 12.3) ].
For initiation of treatment, 1.2 mg/kg three times a day (3.6 mg/kg total daily dose) is approximately equivalent to the initial 160 mg total daily dose for adults. Subsequent titration to a maximum of 2.4 mg/kg three times a day (approximately equivalent to the 360 mg total daily dose for adults) can then occur. Titration should be guided by clinical response, heart rate, and QTc, with increased dosing being preferably conducted in-hospital. Allow at least 36 hours between dose increments to attain steady-state plasma concentrations of sotalol in patients with age-adjusted normal renal function.
For Children Aged About 2 Years or Younger
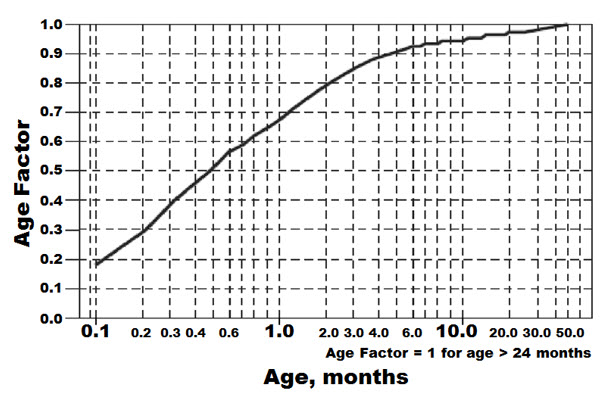
For children aged 2 years or younger, the pediatric dosage should be reduced by a factor that depends upon age, as shown in the following graph (age plotted on a logarithmic scale in months):
| For a child aged 1 month, multiply the starting dose by 0.7; the initial starting dose would be (1.2 mg/kg × 0.7)=0.8 mg/kg, administered three times daily. For a child aged about 1 week, multiply the initial starting dose by 0.3; the starting dose would be (1.2 mg/kg × 0.3)=0.4 mg/kg. Use similar calculations for dose titration. |
 |
Dosage for Patients with Renal Impairment
Adults
In any age group with decreased renal function, sotalol doses should be lowered or the intervals between doses increased. It will take much longer to reach steady-state with any dose and/or frequency of administration. Closely monitor heart rate and QTc.
Dose escalations in renal impairment should be done after administration of at least 5 doses at appropriate intervals (Table 1). Sotalol is partly removed by dialysis; specific advice is unavailable on dosing patients on dialysis.
Administer the initial dose of 80 mg and subsequent doses at the intervals listed in Table 1.
| Creatinine Clearance mL/min | Dosing Interval (hours) |
|---|---|
| > 60 | 12 |
| 30-59 | 24 |
| 10-29 | 36-48 |
| <10 | Dose should be individualized |

By using PrescriberAI, you agree to the AI Terms of Use.
Sotylize prescribing information
WARNING: LIFE-THREATENING PROARRHYTHMIA
To minimize the risk of drug-induced arrhythmia, initiate or re-initiate oral sotalol in a facility that can provide cardiac resuscitation and continuous electrocardiographic monitoring.
Sotalol can cause life-threatening ventricular tachycardia associated with QT interval prolongation.
If the QT interval prolongs to 500 msec or greater, reduce the dose, lengthen the dosing interval, or discontinue the drug.
Calculate creatinine clearance to determine appropriate dosing [see Dosage and Administration (2.5) ] .
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
SOTYLIZE is an antiarrhythmic indicated for:
- The treatment of life-threatening ventricular arrhythmias (1.1 )
- The maintenance of normal sinus rhythm in patients with highly symptomatic atrial fibrillation/flutter (AFIB/AFL) (1.2 )
Limitations of Use
Life-Threatening Ventricular Arrhythmia
SOTYLIZE is indicated for the treatment of documented, life-threatening ventricular arrhythmias, such as sustained ventricular tachycardia.
Limitation of Use
SOTYLIZE has not been shown to enhance survival in patients with life-threatening ventricular arrhythmias.
Delay in Recurrence of Atrial Fibrillation/Atrial Flutter (AFIB/AFL)
SOTYLIZE is indicated for the maintenance of normal sinus rhythm [delay in time to recurrence of atrial fibrillation/atrial flutter (AFIB/AFL)] in patients with highly symptomatic AFIB/AFL who are currently in sinus rhythm.
Limitation of Use
Because sotalol can cause life-threatening ventricular arrhythmias, reserve its use for patients in whom AFIB/AFL is highly symptomatic. Patients with paroxysmal AFIB that is easily reversed (by Valsalva maneuver, for example) should usually not be given SOTYLIZE .
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- Initiate therapy at 80 mg twice daily. Increase the dose as needed in increments of 80 mg/day, every 3 days to a maximum 320 mg total daily dose (2.2 )
- If creatinine clearance is between 60 and 40 mL/min, administer once daily, if less than 40 mL/min, sotalol is not recommended (2.1 )
- Pediatrics: Dosage depends on age (2.4 )
General Safety Measures of Oral Sotalol Therapy
Withdraw other antiarrhythmic therapy before starting SOTYLIZE and monitor for a minimum of 2 to 3 plasma half-lives prior to initiating SOTYLIZE therapy if the patient's clinical condition permits [see Drug Interactions (7) ] .
Hospitalize patients being initiated or re-initiated on sotalol for at least 3 days or until steady-state drug levels are achieved in a facility that can provide cardiac resuscitation and continuous electrocardiographic monitoring. Initiate oral sotalol therapy in the presence of personnel trained in the management of serious arrhythmias. Perform a baseline ECG to determine the QT interval and measure and normalize serum potassium and magnesium levels before initiating therapy. Measure serum creatinine and calculate an estimated creatinine clearance in order to establish the appropriate dosing interval. Monitor QTc 2 to 4 hours after each uptitration in dose.
Discharge patients on sotalol therapy from an in-patient setting with an adequate supply of sotalol to allow uninterrupted therapy until the patient can fill a sotalol prescription.
Advise patients who miss a dose to take the next dose at the usual time. Do not double the dose or shorten the dosing interval.
Adult Dose for Ventricular Arrhythmia
The recommended initial dose is 80 mg twice daily. This dose may be increased in increments of 80 mg per day every 3 days provided the QTc <500 msec [see Warning and Precautions (5.1) ] . Continually monitor patients until steady state blood levels are achieved. In most patients, a therapeutic response is obtained at a total daily dose of 160 to 320 mg/day, given in two or three divided doses. Oral doses as high as 480 to 640 mg once or twice a day have been utilized in patients with refractory life-threatening arrhythmias.
Adult Dose for Prevention of Recurrence of AFIB/AFL
The recommended initial dose is 80 mg twice daily. This dose may be increased in increments of 80 mg per day every 3 days provided the QTc ˂500 msec [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) ] . Continually monitor patients until steady state blood levels are achieved. Most patients will have a satisfactory response with 120 mg twice daily. Initiation of sotalol in patients with QTc ˃450 msec is contraindicated [see Contraindication (4) ] .
Pediatric Dose for Ventricular Arrhythmias or AFIB/AFL
Use the same precautionary measures for children as you would use for adults when initiating and re-initiating sotalol treatment.
For Children Aged About 2 Years and Older
For children aged about 2 years and older with normal renal function, doses normalized for body surface area are appropriate for both initial and incremental dosing. Since the Class III potency in children is not very different from that in adults, reaching plasma concentrations that occur within the adult dose range is an appropriate guide [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.1 , 12.3) ].
For initiation of treatment, 1.2 mg/kg three times a day (3.6 mg/kg total daily dose) is approximately equivalent to the initial 160 mg total daily dose for adults. Subsequent titration to a maximum of 2.4 mg/kg three times a day (approximately equivalent to the 360 mg total daily dose for adults) can then occur. Titration should be guided by clinical response, heart rate, and QTc, with increased dosing being preferably conducted in-hospital. Allow at least 36 hours between dose increments to attain steady-state plasma concentrations of sotalol in patients with age-adjusted normal renal function.
For Children Aged About 2 Years or Younger
For children aged 2 years or younger, the pediatric dosage should be reduced by a factor that depends upon age, as shown in the following graph (age plotted on a logarithmic scale in months):
| For a child aged 1 month, multiply the starting dose by 0.7; the initial starting dose would be (1.2 mg/kg × 0.7)=0.8 mg/kg, administered three times daily. For a child aged about 1 week, multiply the initial starting dose by 0.3; the starting dose would be (1.2 mg/kg × 0.3)=0.4 mg/kg. Use similar calculations for dose titration. |
 |
Dosage for Patients with Renal Impairment
Adults
In any age group with decreased renal function, sotalol doses should be lowered or the intervals between doses increased. It will take much longer to reach steady-state with any dose and/or frequency of administration. Closely monitor heart rate and QTc.
Dose escalations in renal impairment should be done after administration of at least 5 doses at appropriate intervals (Table 1). Sotalol is partly removed by dialysis; specific advice is unavailable on dosing patients on dialysis.
Administer the initial dose of 80 mg and subsequent doses at the intervals listed in Table 1.
| Creatinine Clearance mL/min | Dosing Interval (hours) |
|---|---|
| > 60 | 12 |
| 30-59 | 24 |
| 10-29 | 36-48 |
| <10 | Dose should be individualized |
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Oral solution: 5 mg/mL, in 250 mL or 480 mL bottles.
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
- Lactation: Do not breastfeed (8.2 )
Pregnancy
Risk Summary
Both the untreated underlying condition in pregnancy and the use of sotalol in pregnancy cause adverse outcomes to the mother and fetus/neonate ( see Clinical Considerations ). In animal reproduction studies in rats, early resorptions were increased at 15 times the maximum recommended human dose (MRHD). In rabbits an increase in fetal death was observed at 2 times the MRHD administered as single dose. Sotalol did not reveal any teratogenic potential in rats or rabbits at 15 and 2 times the MRHD respectively ( see Data ).
All pregnancies have a background risk of birth defect, loss, or other adverse outcomes. The estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population is unknown. In the United States (U.S.) general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2 to 4% and 15 to 20%, respectively.
Clinical Considerations
The incidence of VT is increased and may be more symptomatic during pregnancy. Most tachycardia episodes are initiated by ectopic beats and the occurrence of arrhythmia episodes may, therefore, increase during pregnancy. Breakthrough arrhythmias may also occur during pregnancy, as therapeutic treatment levels may be difficult to maintain due to the increased volume of distribution and increased drug metabolism inherent in the pregnant state.
Fetal/Neonatal Adverse Reactions
Sotalol has been shown to cross the placenta and is found in amniotic fluid. From published observational studies, the potential fetal adverse effects of sotalol use during pregnancy are growth restriction, transient fetal bradycardia, hyperbilirubinemia, hypoglycemia, uterine contractions, and possible intrauterine death. Sotalol may have a greater effect on QT prolongation in the immature heart than in the adult heart, and therefore, conveys an increased risk of serious fetal arrhythmia and/or possible intrauterine death. Monitor newborns for symptoms and adverse reactions associated with beta-blockers.
Labor or Delivery
Generally, risk of arrhythmias increases during labor and delivery process; therefore, considering the proarrhythmia potential of the drug, patients treated with sotalol should be monitored continuously during labor and delivery.
Data
Animal Data
Reproduction studies in rats and rabbits administered sotalol during organogenesis at 15 times and 2 times the MRHD as mg/m 2 , respectively, did not reveal any teratogenic potential associated with sotalol.
In pregnant rats, sotalol doses administered during organogenesis at approximately 15 times the MRHD as mg/m 2 , increased the number of early resorptions, while no increase in early resorptions was noted at 2 times the MRHD as mg/m 2 .
In reproductive studies in rabbits, a sotalol dose (160 mg/kg/day) at 5 times the MRHD as mg/m 2 produced a slight increase in fetal death, and maternal toxicity. However, one study from published data reported an increase in fetal deaths in rabbits receiving a single dose (50 mg/kg) at 2 times the MRHD as mg/m 2 on gestation day 14.
Lactation
Risk Summary
Limited available data from published literature report that sotalol is present in human milk. The estimated daily infant dose of sotalol received from breastmilk is 0.8-3.4 mg/kg, estimated at 22 to 25.5% of the maternal weight-adjusted dosage of SOTYLIZE ( see Data ). The amount of drug in breast milk is similar to the neonatal therapeutic dosage. Therefore, there is potential for bradycardia and other symptoms from beta-blockers such as dry mouth, skin or eyes, diarrhea or constipation in the breastfed infant. There is no information regarding the effects of sotalol on milk production. Because of the potential serious adverse reactions to the breastfed child and high level of sotalol in breast milk, advise women not to breastfeed while on treatment with SOTYLIZE.
Data
Sotalol is present in human milk in high levels. A prospective study evaluated 20 paired samples of breast milk and maternal blood from 5 mothers who elected to breastfeed. Breast milk samples had a mean sotalol concentration of 10.5 g µg/mL (± 1.1 µg/mL; range: 4.8 to 20.2 µg/mL compared to a simultaneous mean maternal plasma concentration of 2.3 µg/mL (± 0.3 µg/mL; range: 0.8 to 5.0 µg/mL). The mean milk plasma ratio was 5:4:1 (range: 2.2 to 8.8.). The estimated daily infant dose was 0.8 -3.4 mg/kg, estimated at 22 to 25.5% of the maternal weight-adjusted dosage of sotalol. This is similar to recommended therapeutic dose in neonates. None of the mothers reported any adverse reactions in the breastfed infant.
Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
Infertility
Based on the published literature, beta-blockers (including sotalol) may cause erectile dysfunction.
Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of sotalol in children have not been established. However, the Class III electrophysiologic and beta-blocking effects, the pharmacokinetics, and the relationship between the effects (QTc interval and resting heart rate) and drug concentrations have been evaluated in children aged between 3 days and 12 years old [see Dosage and Administration (2.2) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.2) ] .
Associated side effects of sotalol use in pediatric patients are those typical of a beta-blocking agent, and lead to discontinuation of the drug in 3 to 6% of patients. As in adults, the Class III antiarrhythmic action of sotalol in pediatric patients is associated with a significant proarrhythmic potential for adverse effects. In pediatric patients, the incidence of proarrhythmic side effects of sotalol varies from 0 to 22%; however, sotalol-induced Torsade de Pointes tachycardias are observed less frequently in the pediatric population.
Proarrhythmic effects of sotalol in pediatric patients included increased ventricular ectopy and exacerbation of bradycardia, the latter predominantly in patients with sinus node dysfunction following surgery for congenital cardiac defects. Bradycardia may require emergency pacemaker implantation. Close in-patient monitoring is recommended for several days.
Renal Impairment
Sotalol is mainly eliminated via the kidneys. Adjust dosing intervals based on creatinine clearance [see Dosage and Administration (2.5) ] .
CONTRAINDICATIONS
For the treatment of AFIB/AFL or ventricular arrhythmias, SOTYLIZE is contraindicated in patients with:
- Baseline QT interval ˃450 msec
- Sinus bradycardia, sick sinus syndrome, second and third degree AV block, unless a functioning pacemaker is present
- Congenital or acquired long QT syndromes
- Cardiogenic shock or decompensated heart failure
- Serum potassium <4 mEq/L
- Bronchial asthma or related bronchospastic conditions
- Hypersensitivity to sotalol
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- QT prolongation, bradycardia, AV block, hypotension, worsening heart failure: Reduce dose as needed (5.1 )
- Acute exacerbation of coronary artery disease upon cessation of therapy: Do not abruptly discontinue (5.5 )
- Correct any electrolyte disturbances (5.5 )
- May mask symptoms of hypoglycemia and alter glucose levels; monitor (5.7 )
QT Prolongation and Proarrhythmia
SOTYLIZE can cause serious and potentially fatal ventricular arrhythmias such as sustained VT/VF, primarily Torsade de Pointes (TdP) type ventricular tachycardia, a polymorphic ventricular tachycardia associated with QT interval prolongation. Factors such as reduced creatinine clearance, female sex, higher doses, reduced heart rate, and history of sustained VT/VF or heart failure increases the risk of TdP. The risk of TdP can be reduced by adjustment of the sotalol dose according to creatinine clearance and by monitoring the ECG for excessive increases in the QT interval [see Dosage and Administration (2.1) ] .
Correct hypokalemia or hypomagnesemia prior to initiating SOTYLIZE, as these conditions can exaggerate the degree of QT prolongation, and increase the potential for Torsade de Pointes. Special attention should be given to electrolyte and acid-base balance in patients experiencing severe or prolonged diarrhea or patients receiving concomitant diuretic drugs.
Proarrhythmic events must be anticipated not only on initiating therapy, but with every upward dose adjustment [see Dosage and Administration (2.1) ].
Avoid use with other drugs known to cause QT prolongation [see Drug Interactions (7.1) ].
Bradycardia/Heart Block/Sick Sinus Syndrome
Sinus bradycardia (heart rate less than 50 bpm) occurred in 13% of patients receiving sotalol in clinical trials, and led to discontinuation in about 3% of patients. Bradycardia itself increases the risk of Torsade de Pointes. Sinus pause, sinus arrest and sinus node dysfunction occur in less than 1% of patients. The incidence of 2 nd - or 3 rd -degree AV block is approximately 1%.
SOTYLIZE is contraindicated in patients with sick sinus syndrome because it may cause sinus bradycardia, sinus pauses or sinus arrest.
Hypotension
Sotalol produces significant reductions in both systolic and diastolic blood pressures and may result in hypotension. Monitor hemodynamics in patients with marginal cardiac compensation.
Heart Failure
New onset or worsening heart failure may occur during initiation or uptitration of sotalol because of its beta-blocking effects. Monitor for signs and symptoms of heart failure and discontinue treatment if symptoms occur.
Cardiac Ischemia after Abrupt Discontinuation
Following abrupt cessation of therapy with beta-adrenergic blockers, exacerbations of angina pectoris and myocardial infarction may occur. When discontinuing chronically administered SOTYLIZE, particularly in patients with ischemic heart disease, gradually reduce the dosage over a period of 1 to 2 weeks, if possible, and monitor the patient. If angina markedly worsens or acute coronary ischemia develops, treat appropriately and consider use of an alternative beta-blocker. Warn patients not to interrupt therapy without their physician's advice. Because coronary artery disease is common, but may be unrecognized, the abrupt discontinuation of sotalol may unmask latent coronary insufficiency.
Bronchospasm
Patients with bronchospastic diseases (for example chronic bronchitis and emphysema) should not receive beta-blockers. If SOTYLIZE is to be administered, use the smallest effective dose, to minimize inhibition of bronchodilation produced by endogenous or exogenous catecholamine stimulation of beta-2-receptors.
Diabetes
Beta-blockers may prevent early warning signs of hypoglycemia, such as tachycardia, and increase the risk for severe or prolonged hypoglycemia at any time during treatment, especially in patients with diabetes mellitus or children and patients who are fasting (i.e., surgery, not eating regularly, or are vomiting). Monitor blood sugar, as appropriate.
Thyroid Abnormalities
Avoid abrupt withdrawal of beta-blockers in patients with thyroid disease because it may lead to an exacerbation of symptoms of hyperthyroidism, including thyroid storm. Beta-blockers may mask certain clinical signs (for example, tachycardia) of hyperthyroidism.
Anaphylaxis
While taking beta-blockers, patients with a history of anaphylactic reaction to a variety of allergens may have a more severe reaction on repeated challenge, either accidental, diagnostic, or therapeutic. Such patients may be unresponsive to the usual doses of epinephrine used to treat the allergic reaction.
Major Surgery
Chronically administered beta-blocking therapy should not be routinely withdrawn prior to major surgery; however, the impaired ability of the heart to respond to reflex adrenergic stimuli may augment the risks of general anesthesia and surgical procedures.
ADVERSE REACTIONS
Most common adverse reactions (≥2%) for SOTYLIZE are: fatigue 4%, bradycardia (less than 50 bpm) 3%, dyspnea 3%, proarrhythmia 3%, asthenia 2%, and dizziness 2%.(6 )
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Azurity Pharmaceuticals, Inc. at 1-800-461-7449 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
Adverse reactions that are clearly related to sotalol are those which are typical of its Class II (beta-blocking) and Class III (cardiac action potential duration prolongation) effects and are dose related.
Ventricular Arrhythmias
Serious Adverse Reactions
SOTYLIZE can cause serious and potentially fatal ventricular arrhythmias such as sustained VT/VF, primarily Torsade de Pointes (TdP). [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) ]. The effect on QT and the risk of Torsade de Pointes are both dose related.
Pediatric Patients
In an unblinded multicenter trial of 25 pediatric patients aged ≤ 1 month to 12 years with SVT and/or VT receiving daily doses of 30, 90, and 210 mg/m 2 with dosing every 8 hours for a total of 9 doses, no Torsade de Pointes or other serious new arrhythmias were observed. The clinical trial safety profile in pediatric patients was similar to that in adult patients. Both the Class III and beta-blocking effects of sotalol were linearly related to the plasma concentration [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.2) ].
Atrial Fibrillation/Atrial Flutter
Placebo-controlled Clinical Trials
In a pooled clinical trial population consisting of 4 placebo-controlled studies with 275 patients with atrial fibrillation (AFIB/atrial flutter (AFL) treated with 160 to 320 mg of oral sotalol, the following adverse events presented in Table 2 occurred in at least 2% of placebo-treated patients and at a lesser rate than oral sotalol-treated patients. The data are presented by incidence reactions in the oral sotalol and placebo groups by body system and daily dose.
| Placebo | Oral Sotalol Total Daily Dose | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Adverse Reaction | N=282 (%) | 160-240 N=153 (%) | >240-320 N=122 (%) |
| Bradycardia | 3 | 13 | 12 |
| Diarrhea | 2 | 5 | 6 |
| Nausea/Vomiting | 5 | 8 | 6 |
| Fatigue | 9 | 20 | 19 |
| Hyperhidrosis | 3 | 5 | 5 |
| Weakness | 3 | 5 | 5 |
| Dizziness | 12 | 16 | 13 |
| Headache | 5 | 3 | 12 |
| Dyspnea | 7 | 9 | 10 |
Overall, discontinuation because of unacceptable adverse events was necessary in 17% of the patients and occurred in 10% of patients less than two weeks after starting treatment. The most common adverse reactions leading to discontinuation of oral sotalol were: fatigue 4.6%, bradycardia 2.4%, proarrhythmia 2.2%, dyspnea 2%, and QT interval prolongation 1.4%.
Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during post-approval use of sotalol. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to estimate reliably their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure:
emotional liability, slightly clouded sensorium, incoordination, vertigo, paralysis, thrombocytopenia, eosinophilia, leukopenia, photosensitivity reaction, fever, pulmonary edema, hyperlipidemia, myalgia, pruritus, alopecia.
DRUG INTERACTIONS
- Class I or III Antiarrhythmics or other drugs that prolong the QT interval: Avoid concomitant use (7.1 )
- Digoxin, calcium channel blocker: increased risk of bradycardia, hypotension, heart failure (7.2 )
- Dosage of insulin or antidiabetic drugs may need adjustment (7.4 )
- Aluminum or magnesium-based antacids reduce sotalol exposure (7.7 )
Antiarrhythmics and Other QT Prolonging Drugs
Discontinue Class I or Class III antiarrhythmic agents for at least three half-lives prior to dosing with sotalol. Class Ia antiarrhythmic drugs such as disopyramide, quinidine and procainamide and other Class III drugs (for example, amiodarone) are not recommended as concomitant therapy with sotalol because of their potential to prolong refractoriness [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) ] .
Negative Chronotropes
Digitalis glycosides, diltiazem, verapamil, and beta-blockers slow atrioventricular conduction and decrease heart rate. Concomitant use with negative chronotropes can increase the risk of bradycardia or hypotension .
Catecholamine-Depleting Agents
Concomitant use of catecholamine-depleting drugs, such as reserpine and guanethidine, with a beta-blocker may produce an excessive reduction of resting sympathetic nervous tone. Monitor such patients for hypotension and/or marked bradycardia which may produce syncope.
Insulin and Oral Antidiabetics
Hyperglycemia may occur, and the dosage of insulin or antidiabetic drugs may require adjustment [see Warnings and Precautions 5.7 ]
Beta-2-Receptor Stimulants
Beta-agonists such as albuterol, terbutaline and isoproterenol may have to be administered in increased dosages when used concomitantly with sotalol.
Clonidine
Concomitant use with sotalol increases the risk of bradycardia and AV block. Because beta-blockers may potentiate the rebound hypertension sometimes observed after clonidine discontinuation, withdraw sotalol several days before the gradual withdrawal of clonidine to reduce the risk of rebound hypertension.
Antacids
Avoid administration of oral sotalol within 2 hours of antacids containing aluminum oxide and magnesium hydroxide.
Drug/Laboratory Test Interactions
The presence of sotalol in the urine may result in falsely elevated levels of urinary metanephrine when measured by flourimetric or photometric methods.
DESCRIPTION
SOTYLIZE is an aqueous solution containing sotalol hydrochloride.
Sotalol hydrochloride is a white, crystalline solid with a molecular weight of 308.8. It is hydrophilic, soluble in water, propylene glycol and ethanol, but is only slightly soluble in chloroform. Chemically, sotalol hydrochloride is d,l- N -[4-[1-hydroxy-2-[(1-methylethyl) amino]ethyl]phenyl]methane-sulfonamide monohydrochloride. The molecular formula is C 12 H 20 N 2 O 3 S HCl and is represented by the following structural formula:
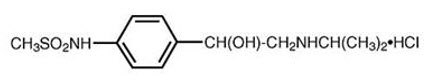
SOTYLIZE is a grape-flavored aqueous solution. Each mL contains 5 mg sotalol HCl. Inactive ingredients are sodium citrate, citric acid, sucralose, sodium benzoate and purified water.
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Mechanism of Action
Sotalol has both beta-adrenoreceptor blocking (Vaughan Williams Class II) and cardiac action potential duration prolongation (Vaughan Williams Class III) antiarrhythmic properties. The two isomers of sotalol have similar Class III antiarrhythmic effects, while the l-isomer is responsible for virtually all of the beta-blocking activity. The beta-blocking effect of sotalol is non-cardioselective, half maximal at an oral dose of about 80 mg/day and maximal at doses between 320 and 640 mg/day. Sotalol does not have partial agonist or membrane stabilizing activity. Although significant beta-blocker occurs at oral doses as low as 25 mg, significant Class III effects are seen only at daily doses of 160 mg and above.
In children, a Class III electrophysiological effect can be seen at daily doses of 210 mg/m 2 body surface area (BSA). A reduction of the resting heart rate due to the beta-blocking effect of sotalol is observed at daily doses ≥90 mg/m 2 in children.
Pharmacodynamics
Cardiac Electrophysiological Effects
Sotalol hydrochloride prolongs the plateau phase of the cardiac action potential in the isolated myocyte, as well as in isolated tissue preparations of ventricular or atrial muscle (Class III activity). In intact animals it slows heart rate, decreases AV nodal conduction and increases the refractory periods of atrial and ventricular muscle and conduction tissue.
In human, the Class II (beta-blockers) electrophysiological effects of sotalol are manifested by increased sinus cycle length (slowed heart rate), decreased AV nodal conduction and increased AV nodal refractoriness. The Class III electrophysiological effects in man include prolongation of the atrial and ventricular monophasic action potentials, and effective refractory period prolongation of atrial muscle, ventricular muscle, and atrio-ventricular accessory pathways (where present) in both the anterograde and retrograde directions. With oral doses of 160 to 640 mg/day, the surface ECG shows dose-related mean increases of 40 to100 msec in QT and 10 to40 msec in QTc [see Warning and Precautions (5.1] ) . No significant alteration in QRS interval was observed.
In a small study (n=25) of patients with implanted defibrillators treated concurrently with sotalol, the average defibrillatory threshold was 6 joules (range 2 to15 joules) compared to a mean of 16 joules for a non-randomized comparative group primarily receiving amiodarone.
Twenty-five children in an unblinded, multicenter trial with supraventricular (SVT) and/or ventricular (VT) tachyarrhythmias, aged between 3 days and 12 years (mostly neonates and infants), received an ascending titration regimen with daily doses of 30, 90 and 210 mg/m 2 with dosing every 8 hours for a total of 9 doses. During steady-state, the respective average increases above baseline of the QT c interval, in msec (%), were 2, 14, and 29 msec at the 3 dose levels. The respective mean maximum increases above baseline of the QTc interval were 23, 36, and 55 msec at the 3 dose levels. The steady-state percent increases in the RR interval were 3, 9 and 12%. The smallest children (BSA<0.33m 2 ) showed a tendency for larger Class III effects (∆QTc) and an increased frequency of prolongations of the QTc interval as compared with larger children (BSA≥0.33m 2 ). The beta-blocking effects also tended to be greater in the smaller children (BSA<0.33m 2 ). Both the Class III and beta-blocking effects of sotalol were linearly related with the plasma concentrations.
Hemodynamics
In a study of systemic hemodynamic function measured invasively in 12 patients with a mean LV ejection fraction of 37% and ventricular tachycardia (9 sustained and 3 non-sustained), a median dose of 160 mg twice daily of sotalol produced a 28% reduction in heart rate and a 24% decrease in cardiac index at 2 hours post-dosing at steady-state. Concurrently, systemic vascular resistance and stroke volume showed non-significant increases of 25% and 8%, respectively. One patient was discontinued because of worsening congestive heart failure. Pulmonary capillary wedge pressure increased significantly from 6.4 mmHg to 11.8 mmHg in the 11 patients who completed the study. Mean arterial pressure, mean pulmonary artery pressure and stroke work index did not significantly change. Exercise and isoproterenol induced tachycardia are antagonized by sotalol, and total peripheral resistance increases by a small amount.
In hypertensive patients, sotalol produces significant reductions in both systolic and diastolic blood pressures. Although sotalol is usually well-tolerated hemodynamically, deterioration in cardiac performance may occur in patients with marginal cardiac compensation [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3) ].
Pharmacokinetics
The pharmacokinetics of the d- and l-enantiomers of sotalol are essentially identical.
Absorption
In healthy subjects, the oral bioavailability of sotalol is 90 to100%. After oral administration, peak plasma concentrations are reached in 2.5 to 4 hours, and steady-state plasma concentrations are attained within 2 to3 days (that is, after 5-6 doses when administered twice daily). Over the oral dosage range 160 to640 mg/day, sotalol displays dose proportionality with respect to plasma concentrations. When administered with a standard meal, the absorption of sotalol was reduced by approximately 20% compared to administration in fasting state.
Distribution
Sotalol does not bind to plasma proteins. Distribution occurs to a central (plasma) and to a peripheral compartment. Sotalol crosses the blood brain barrier poorly.
Metabolism
Sotalol is not metabolized and is not expected to inhibit or induce any CYP450 enzymes.
Excretion
Excretion of sotalol is predominantly via the kidney in the unchanged form, and therefore, lower doses are necessary in conditions of renal impairment [ see Dosage and Administration (2.5) ]. The mean elimination half-life of sotalol is 12 hours. Dosing every 12 hours results in trough plasma concentrations which are approximately one-half of those at peak.
Specific Populations
Pediatric: The combined analysis of a single-dose and a multiple-dose study with 59 children, aged between 3 days and 12 years, showed the pharmacokinetics of sotalol to be first order. A daily dose of 30 mg/m 2 of sotalol was administered in the single dose study and daily doses of 30, 90 and 210 mg/m 2 were administered every 8 hours in the multi-dose study. After rapid absorption with peak levels occurring on average between 2-3 hours following administration, sotalol was eliminated with a mean half-life of 9.5 hours. Steady-state was reached after 1 to 2 days. The average peak to trough concentration ratio was 2. Body surface area was the most important covariate and more relevant than age for the pharmacokinetics of sotalol. The smallest children (BSA <0.33 m 2 ) exhibited a greater drug exposure (+59%) than the larger children who showed a uniform drug concentration profile. The intersubject variation for oral clearance was 22%.
Geriatric: Age does not significantly alter the pharmacokinetics of SOTYLIZE, but impaired renal function in geriatric patients can increase the terminal elimination half-life, resulting in increased drug accumulation.
Renal Impairment: Sotalol is mainly eliminated via the kidneys through glomerular filtration and to a small degree by tubular secretion. There is a direct relationship between renal function, as measured by serum creatinine or creatinine clearance, and the elimination rate of sotalol. The half-life of sotalol is prolonged (up to 69 hours) in anuric patients. Adjust doses or dosing intervals based on creatinine clearance [see Dosage and Administration (2.5) ].
Hepatic Impairment: Patients with hepatic impairment show no alteration in clearance of sotalol.
Drug-Drug Interactions
Antacids: Administration of oral sotalol within 2 hours of antacids may result in a reduction in Cmax and AUC of 26% and 20%, respectively, and consequently in a 25% reduction in the bradycardic effect at rest. Administration of the antacid two hours after oral sotalol has no effect on the pharmacokinetics or pharmacodynamics of sotalol.
No pharmacokinetic interactions were observed with hydrochlorothiazide or warfarin.
NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Calculations of safety margins are for the maximum recommended human dose (MRHD) of 640 mg/day of sotalol, administered for life-threatening ventricular arrhythmias in a 60-kg human.
No evidence of carcinogenic potential was observed in rats during a 24-month study at 137 to275 mg/kg/day (approximately 30 times the maximum recommended human oral dose (MRHD) as mg/kg or 5 times the MRHD as mg/m 2 ) or in mice, during a 24-month study at 4141 to 7122 mg/kg/day (approximately 450 to 750 times the MRHD as mg/kg or 36 to 63 times the MRHD as mg/m 2 ).
Sotalol has not been evaluated in any specific assay of mutagenicity or clastogenicity.
Animal Toxicology and/or Pharmacology
No significant reduction in fertility occurred in rats at oral doses of 1000 mg/kg/day (approximately 94 times the MRHD as mg/kg or 15 times the MRHD as mg/m 2 ) prior to mating, except for a small reduction in the number of offspring per litter.
CLINICAL STUDIES
Ventricular Arrhythmias
In patients with life-threatening arrhythmias [sustained ventricular tachycardia/fibrillation (VT/VF)], sotalol was studied acutely [by suppression of programmed electrical stimulation (PES) induced VT and by suppression of Holter monitor evidence of sustained VT] and, in acute responders, chronically.
In a double-blind, randomized comparison of sotalol and procainamide in 104 patients given intravenously (total of 2 mg/kg sotalol vs. 19 mg/kg of procainamide over 90 minutes), sotalol suppressed PES induction in 30% of patients vs. 20% for procainamide (p=0.2).
In a randomized clinical trial (Electrophysiologic Study Versus Electrocardiographic Monitoring [ESVEM] Trial) in 486 patients comparing the choice of antiarrhythmic therapy by PES suppression vs. Holter monitor selection (in each case followed by treadmill exercise testing) in patients with a history of sustained VT/VF who were also inducible by PES, the effectiveness acutely and chronically of sotalol hydrochloride was compared with 6 other drugs (procainamide, quinidine, mexiletine, propafenone, imipramine, and pirmenol). The Overall response, limited to first randomized drug, was 39% for sotalol and 30% for the pooled other drugs. Acute response rate for first drug randomized using suppression of PES induction was 36% for sotalol vs. a mean of 13% for the other drugs. Using the Holter monitoring endpoint (complete suppression of sustained VT, 90% suppression of NSVT, 80% suppression of PVC pairs, and at least 70% suppression of PVCs), sotalol yielded 41% response vs. 45% for the other drugs combined. Among responders placed on long-term therapy identified acutely as effective (by either PES or Holter), sotalol, when compared to the pool of other drugs, had the lowest two-year mortality (13% vs. 22%), the lowest two-year VT recurrence rate (30% vs. 60%), and the lowest withdrawal rate (38% vs. about 75 to 80%). The most commonly used doses of orally administered sotalol in this trial were 320 to480 mg/day (66% of patients), with 16% receiving 240 mg/day or less and 18% receiving 640 mg or more.
It cannot be determined, however, in the absence of a controlled comparison of sotalol vs. no pharmacologic treatment (for example, in patients with implanted defibrillators) whether sotalol response causes improved survival or identifies a population with a good prognosis.
Sotalol has not been shown to enhance survival in patients with ventricular arrythmias.
Supraventricular Arrhythmias
Sotalol has been studied in patients with symptomatic AFIB/AFL in two principal studies, one in patients with primarily paroxysmal AFIB/AFL, the other in patients with primarily chronic AFIB.
In one study, a U.S. multicenter, randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind, dose-response trial of patients with symptomatic primarily paroxysmal AFIB/AFL, three fixed dose levels of sotalol (80 mg, 120 mg and 160 mg) twice daily and placebo were compared in 253 patients. In patients with reduced creatinine clearance (40 to 60 mL/min) the same doses were given once daily. Patients were excluded for the following reasons: QT >450 msec; creatinine clearance <40 mL/min; intolerance to beta-blockers; bradycardia-tachycardia syndrome in the absence of an implanted pacemaker; AFIB/AFL was asymptomatic or was associated with syncope, embolic CVA or TIA; acute myocardial infarction within the previous 2 months; congestive heart failure; bronchial asthma or other contraindications to beta-blocker therapy; receiving potassium losing diuretics without potassium replacement or without concurrent use of ACE-inhibitors; uncorrected hypokalemia (serum potassium <3.5 mEq/L) or hypomagnesemia (serum magnesium <1.5 mEq/L); received chronic oral amiodarone therapy for >1 month within previous 12 weeks; congenital or acquired long QT syndromes; history of Torsade de Pointes with other antiarrhythmic agents which increase the duration of ventricular repolarization; sinus rate <50 bpm during waking hours; unstable angina pectoris; receiving treatment with other drugs that prolong the QT interval; and AFIB/AFL associated with the Wolff-Parkinson-White (WPW) syndrome. If the QT interval increased to ≥520 msec (or JT ≥430 msec if QRS >100 msec) the drug was discontinued. The patient population in this trial was 64% male, and the mean age was 62 years. No structural heart disease was present in 43% of the patients. Doses were administered once daily in 20% of the patients because of reduced creatinine clearance.
Sotalol was shown to prolong the time to the first symptomatic, ECG-documented recurrence of AFIB/AFL, as well as to reduce the risk of such recurrence at both 6 and 12 months. The 120 mg dose was more effective than 80 mg, but 160 mg did not appear to have an added benefit. Note that these doses were given twice or once daily, depending on renal function. The results are shown in Figure 1, Table 3 and Table 4.
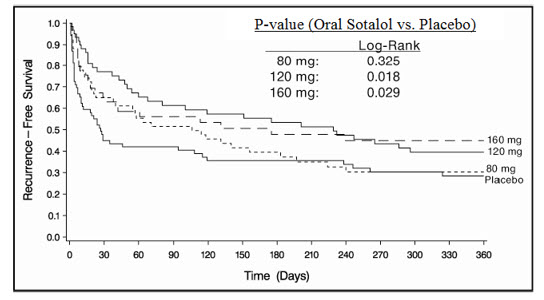 |
| Placebo | Sotalol Dose | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 80 mg | 120 mg | 160 mg | ||
| Note that columns do not add up to 100% due to discontinuations (D/C) for "other" reasons. | ||||
| Randomized | 69 | 59 | 63 | 62 |
| On treatment in NSR at 12 months without recurrence Symptomatic AFIB/AFL | 23% | 22% | 29% | 23% |
| Recurrence Efficacy endpoint of Study 1; study treatment stopped. | 67% | 58% | 49% | 42% |
| D/C for AEs | 6% | 12% | 18% | 29% |
| Placebo n=69 | Oral Sotalol Dose | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 80 mg n=59 | 120 mg n=63 | 160 mg n=62 | ||
| p-value vs. placebo | 0.325 | 0.018 | 0.029 | |
| Relative Risk (RR) to placebo | 0.81 | 0.59 | 0.59 | |
| Median time to recurrence (days) | 27 | 106 | 229 | 175 |
Discontinuation because of adverse events was dose related.
In a second multicenter, randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind study of 6 months duration in 232 patients with chronic AFIB, oral sotalol was titrated over a dose range from 80 mg/day to 320 mg/day. The patient population of this trial was 70% male with a mean age of 65 years. Structural heart disease was present in 49% of the patients. All patients had chronic AFIB for >2 weeks but <1 year at entry with a mean duration of 4.1 months. Patients were excluded if they had significant electrolyte imbalance, QTc >460 msec, QRS >140 msec, any degree of AV block or functioning pacemaker, uncompensated cardiac failure, asthma, significant renal disease (estimated creatinine clearance <50 mL/min), heart rate <50 bpm, myocardial infarction or open heart surgery in past 2 months, unstable angina, infective endocarditis, active pericarditis or myocarditis, ≥ 3 DC cardioversions in the past, medications that prolonged QT interval, and previous amiodarone treatment.
After successful cardioversion patients were randomized to receive placebo (n=114) or sotalol (n=118), at a starting dose of 80 mg twice daily. If the initial dose was not tolerated it was decreased to 80 mg once daily, but if it was tolerated it was increased to 160 mg twice daily. During the maintenance period 67% of treated patients received a dose of 160 mg twice daily, and the remainder received doses of 80 mg once daily (17%) and 80 mg twice daily (16%).
Tables 5 and 6 show the results of the trial. There was a longer time to ECG-documented recurrence of AFIB and a reduced risk of recurrence at 6 months compared to placebo.
| Placebo n=114 | Oral Sotalol n=118 | |
|---|---|---|
| On treatment in NSR at 6 months without recurrence Symptomatic or asymptomatic AFIB/AFL | 29% | 45% |
| Recurrence Efficacy endpoint of Study 2; study treatment stopped. | 67% | 49% |
| D/C for AEs | 3% | 6% |
| Death | 1% |
| Placebo | Oral Sotalol | Relative Risk | P-value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Median time to recurrence (days) | 44 | >180 | 0.55 | 0.002 |
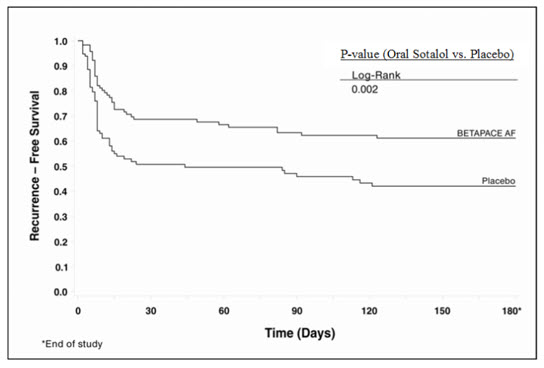 |
HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
SOTYLIZE (sotalol hydrochloride) is supplied as follows:
- NDC 24338-530-25, 5 mg/mL: 250 mL bottle
- NDC 24338-530-48, 5 mg/mL: 480 mL bottle
Store at 20°C to 25°C (68°F -77°F); excursions permitted between 15°C and 30°C (59°F-86°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature].
Mechanism of Action
Sotalol has both beta-adrenoreceptor blocking (Vaughan Williams Class II) and cardiac action potential duration prolongation (Vaughan Williams Class III) antiarrhythmic properties. The two isomers of sotalol have similar Class III antiarrhythmic effects, while the l-isomer is responsible for virtually all of the beta-blocking activity. The beta-blocking effect of sotalol is non-cardioselective, half maximal at an oral dose of about 80 mg/day and maximal at doses between 320 and 640 mg/day. Sotalol does not have partial agonist or membrane stabilizing activity. Although significant beta-blocker occurs at oral doses as low as 25 mg, significant Class III effects are seen only at daily doses of 160 mg and above.
In children, a Class III electrophysiological effect can be seen at daily doses of 210 mg/m 2 body surface area (BSA). A reduction of the resting heart rate due to the beta-blocking effect of sotalol is observed at daily doses ≥90 mg/m 2 in children.