Get your patient on Stelara (Ustekinumab)
Stelara prior authorization resources
Most recent state uniform prior authorization forms
Brand Resources
Stelara patient education
Patient toolkit
Dosage & administration
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Adult Patients with Plaque Psoriasis Subcutaneous Recommended Dosage (2.1 ) :
| Weight Range (kilograms) | Dosage |
|---|---|
| less than or equal to 100 kg | 45 mg administered subcutaneously initially and 4 weeks later, followed by 45 mg administered subcutaneously every 12 weeks |
| greater than 100 kg | 90 mg administered subcutaneously initially and 4 weeks later, followed by 90 mg administered subcutaneously every 12 weeks |
Pediatric Patients 6 Years of Age and Older with Plaque Psoriasis Subcutaneous Recommended Dosage (2.1 ) : Weight-based dosing is recommended at the initial dose, 4 weeks later, then every 12 weeks thereafter.
| Weight Range (kilograms) | Dose |
|---|---|
| less than 60 kg | 0.75 mg/kg |
| 60 kg to 100 kg | 45 mg |
| greater than 100 kg | 90 mg |
Psoriatic Arthritis Adult Subcutaneous Recommended Dosage (2.2 ):
- The recommended dosage is 45 mg administered subcutaneously initially and 4 weeks later, followed by 45 mg administered subcutaneously every 12 weeks.
- For patients with co-existent moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis weighing greater than 100 kg, the recommended dosage is 90 mg administered subcutaneously initially and 4 weeks later, followed by 90 mg administered subcutaneously every 12 weeks.
Psoriatic Arthritis Pediatric 6 years of Age and Older Subcutaneous Recommended Dosage (2.2 ): Weight-based dosing is recommended at the initial dose, 4 weeks later, then every 12 weeks thereafter.
| Weight Range (kilograms) | Dose |
|---|---|
| less than 60 kg | 0.75 mg/kg |
| 60 kg or more | 45 mg |
| greater than 100 kg with co-existent moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis | 90 mg |
Crohn's Disease and Ulcerative Colitis Initial Adult Intravenous Recommended Dose (2.3 ) :
A single intravenous infusion using weight-based dosing:
| Weight Range (kilograms) | Recommended Dose |
|---|---|
| up to 55 kg | 260 mg (2 vials) |
| greater than 55 kg to 85 kg | 390 mg (3 vials) |
| greater than 85 kg | 520 mg (4 vials) |
Crohn's Disease and Ulcerative Colitis Maintenance Adult Subcutaneous Recommended Dosage (2.3 ) :
A subcutaneous 90 mg dose 8 weeks after the initial intravenous dose, then every 8 weeks thereafter.
Recommended Dosage in Plaque Psoriasis
Subcutaneous Adult Dosage Regimen
- For patients weighing 100 kg or less, the recommended dosage is 45 mg initially and 4 weeks later, followed by 45 mg every 12 weeks.
- For patients weighing more than 100 kg, the recommended dosage is 90 mg initially and 4 weeks later, followed by 90 mg every 12 weeks.
In subjects weighing more than 100 kg, 45 mg was also shown to be efficacious. However, 90 mg resulted in greater efficacy in these subjects [see Clinical Studies (14) ] .
Subcutaneous Pediatric Dosage Regimen
Administer STELARA subcutaneously at Weeks 0 and 4, then every 12 weeks thereafter.
The recommended dose of STELARA for pediatric patients 6 years of age and older with plaque psoriasis based on body weight is shown below (Table 1).
| Body Weight of Patient at the Time of Dosing | Recommended Dose |
|---|---|
| less than 60 kg | 0.75 mg/kg |
| 60 kg to 100 kg | 45 mg |
| more than 100 kg | 90 mg |
For pediatric patients weighing less than 60 kg, the administration volume for the recommended dose (0.75 mg/kg) is shown in Table 2; withdraw the appropriate volume from the vial.
| Body Weight (kg) at the time of dosing | Dose (mg) | Volume of injection (mL) |
|---|---|---|
| 15 | 11.3 | 0.12 |
| 16 | 12 | 0.13 |
| 17 | 12.8 | 0.14 |
| 18 | 13.5 | 0.15 |
| 19 | 14.3 | 0.16 |
| 20 | 15 | 0.17 |
| 21 | 15.8 | 0.17 |
| 22 | 16.5 | 0.18 |
| 23 | 17.3 | 0.19 |
| 24 | 18 | 0.20 |
| 25 | 18.8 | 0.21 |
| 26 | 19.5 | 0.22 |
| 27 | 20.3 | 0.22 |
| 28 | 21 | 0.23 |
| 29 | 21.8 | 0.24 |
| 30 | 22.5 | 0.25 |
| 31 | 23.3 | 0.26 |
| 32 | 24 | 0.27 |
| 33 | 24.8 | 0.27 |
| 34 | 25.5 | 0.28 |
| 35 | 26.3 | 0.29 |
| 36 | 27 | 0.3 |
| 37 | 27.8 | 0.31 |
| 38 | 28.5 | 0.32 |
| 39 | 29.3 | 0.32 |
| 40 | 30 | 0.33 |
| 41 | 30.8 | 0.34 |
| 42 | 31.5 | 0.35 |
| 43 | 32.3 | 0.36 |
| 44 | 33 | 0.37 |
| 45 | 33.8 | 0.37 |
| 46 | 34.5 | 0.38 |
| 47 | 35.3 | 0.39 |
| 48 | 36 | 0.4 |
| 49 | 36.8 | 0.41 |
| 50 | 37.5 | 0.42 |
| 51 | 38.3 | 0.42 |
| 52 | 39 | 0.43 |
| 53 | 39.8 | 0.44 |
| 54 | 40.5 | 0.45 |
| 55 | 41.3 | 0.46 |
| 56 | 42 | 0.46 |
| 57 | 42.8 | 0.47 |
| 58 | 43.5 | 0.48 |
| 59 | 44.3 | 0.49 |
Recommended Dosage in Psoriatic Arthritis
Subcutaneous Adult Dosage Regimen
- The recommended dosage is 45 mg initially and 4 weeks later, followed by 45 mg every 12 weeks.
- For patients with co-existent moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis weighing more than 100 kg, the recommended dosage is 90 mg initially and 4 weeks later, followed by 90 mg every 12 weeks.
Subcutaneous Pediatric Dosage Regimen
Administer STELARA subcutaneously at Weeks 0 and 4, then every 12 weeks thereafter.
The recommended dose of STELARA for pediatric patients 6 years of age and older with psoriatic arthritis, based on body weight, is shown below (Table 3).
| Body Weight of Patient at the Time of Dosing | Recommended Dose |
|---|---|
| less than 60 kg For pediatric patients weighing less than 60 kg, the administration volume for the recommended dose (0.75 mg/kg) is shown in Table 2; withdraw the appropriate volume from the vial. | 0.75 mg/kg |
| 60 kg or more | 45 mg |
| greater than 100 kg with co-existent moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis | 90 mg |
Recommended Dosage in Crohn's Disease and Ulcerative Colitis
Intravenous Induction Adult Dosage Regimen
A single intravenous infusion dose of STELARA using the weight-based dosage regimen specified in Table 4 [see Instructions for dilution of STELARA 130 mg vial for intravenous infusion (2.5) ] .
| Body Weight of Patient at the time of dosing | Dose | Number of 130 mg/26 mL (5 mg/mL) STELARA vials |
|---|---|---|
| 55 kg or less | 260 mg | 2 |
| more than 55 kg to 85 kg | 390 mg | 3 |
| more than 85 kg | 520 mg | 4 |
Subcutaneous Maintenance Adult Dosage Regimen
The recommended maintenance dosage is a subcutaneous 90 mg dose administered 8 weeks after the initial intravenous dose, then every 8 weeks thereafter.
General Considerations for Administration
- STELARA is intended for use under the guidance and supervision of a healthcare provider . STELARA should only be administered to patients who will be closely monitored and have regular follow-up visits with a healthcare provider. The appropriate dose should be determined by a healthcare provider using the patient's current weight at the time of dosing. In pediatric patients, it is recommended that STELARA be administered by a healthcare provider. If a healthcare provider determines that it is appropriate, a patient may self-inject or a caregiver may inject STELARA after proper training in subcutaneous injection technique. Instruct patients to follow the directions provided in the Instructions for Use [see Instructions for Use] .
- The needle cover on the prefilled syringe contains dry natural rubber (a derivative of latex). The needle cover should not be handled by persons sensitive to latex.
- It is recommended that each injection be administered at a different anatomic location (such as upper arms, gluteal regions, thighs, or any quadrant of abdomen) than the previous injection, and not into areas where the skin is tender, bruised, erythematous, or indurated. When using the vial, a 1 mL syringe with a 27 gauge, ½ inch needle is recommended.
- Prior to administration, visually inspect STELARA for particulate matter and discoloration. STELARA is a colorless to light yellow solution and may contain a few small translucent or white particles. Do not use STELARA if it is discolored or cloudy, or if other particulate matter is present. STELARA does not contain preservatives; therefore, discard any unused product remaining in the vial and/or syringe.
Preparation and Administration of STELARA 130 mg/26 mL (5 mg/mL) Vial for Intravenous Infusion (Crohn's Disease and Ulcerative Colitis)
STELARA solution for intravenous infusion must be diluted, prepared, and infused by a healthcare professional using aseptic technique.
- Calculate the dose and the number of STELARA vials needed based on patient weight (Table 4). Each 26 mL vial of STELARA contains 130 mg of ustekinumab.
- Withdraw, and then discard a volume of the 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP from the 250 mL infusion bag equal to the volume of STELARA to be added (discard 26 mL sodium chloride for each vial of STELARA needed, for 2 vials- discard 52 mL, for 3 vials- discard 78 mL, 4 vials- discard 104 mL). Alternatively, a 250 mL infusion bag containing 0.45% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP may be used.
- Withdraw 26 mL of STELARA from each vial needed and add it to the 250 mL infusion bag. The final volume in the infusion bag should be 250 mL. Gently mix.
- Visually inspect the diluted solution before infusion. Do not use if visibly opaque particles, discoloration or foreign particles are observed.
- Infuse the diluted solution over a period of at least one hour. Once diluted, the infusion should be completely administered within eight hours of the dilution in the infusion bag.
- Use only an infusion set with an in-line, sterile, non-pyrogenic, low protein-binding filter (pore size 0.2 micrometer).
- Do not infuse STELARA concomitantly in the same intravenous line with other agents.
- STELARA does not contain preservatives. Each vial is for a one-time use in only one patient. Discard any remaining solution. Dispose any unused medicinal product in accordance with local requirements.
Storage
If necessary, the diluted infusion solution may be kept at room temperature up to 25 °C (77 °F) for up to 7 hours. Storage time at room temperature begins once the diluted solution has been prepared. The infusion should be completed within 8 hours after the dilution in the infusion bag (cumulative time after preparation including the storage and the infusion period). Do not freeze. Discard any unused portion of the infusion solution.

By using PrescriberAI, you agree to the AI Terms of Use.
Stelara prescribing information
| Warnings and Precautions Serious Hypersensitivity Reactions (5.5 ) | 11/2025 |
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
STELARA is a human interleukin-12 and -23 antagonist indicated for the treatment of:
Adult patients with:
- moderate to severe plaque psoriasis (PsO) who are candidates for phototherapy or systemic therapy. (1.1 )
- active psoriatic arthritis (PsA) . (1.2 )
- moderately to severely active Crohn's disease (CD) . (1.3 )
- moderately to severely active ulcerative colitis. (1.4 )
Pediatric patients 6 years and older with:
Plaque Psoriasis (PsO)
STELARA is indicated for the treatment of adults and pediatric patients 6 years of age and older with moderate to severe plaque psoriasis who are candidates for phototherapy or systemic therapy.
Psoriatic Arthritis (PsA)
STELARA is indicated for the treatment of adults and pediatric patients 6 years of age and older with active psoriatic arthritis.
Crohn's Disease (CD)
STELARA is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with moderately to severely active Crohn's disease.
Ulcerative Colitis
STELARA is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with moderately to severely active ulcerative colitis.
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Adult Patients with Plaque Psoriasis Subcutaneous Recommended Dosage (2.1 ) :
| Weight Range (kilograms) | Dosage |
|---|---|
| less than or equal to 100 kg | 45 mg administered subcutaneously initially and 4 weeks later, followed by 45 mg administered subcutaneously every 12 weeks |
| greater than 100 kg | 90 mg administered subcutaneously initially and 4 weeks later, followed by 90 mg administered subcutaneously every 12 weeks |
Pediatric Patients 6 Years of Age and Older with Plaque Psoriasis Subcutaneous Recommended Dosage (2.1 ) : Weight-based dosing is recommended at the initial dose, 4 weeks later, then every 12 weeks thereafter.
| Weight Range (kilograms) | Dose |
|---|---|
| less than 60 kg | 0.75 mg/kg |
| 60 kg to 100 kg | 45 mg |
| greater than 100 kg | 90 mg |
Psoriatic Arthritis Adult Subcutaneous Recommended Dosage (2.2 ):
- The recommended dosage is 45 mg administered subcutaneously initially and 4 weeks later, followed by 45 mg administered subcutaneously every 12 weeks.
- For patients with co-existent moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis weighing greater than 100 kg, the recommended dosage is 90 mg administered subcutaneously initially and 4 weeks later, followed by 90 mg administered subcutaneously every 12 weeks.
Psoriatic Arthritis Pediatric 6 years of Age and Older Subcutaneous Recommended Dosage (2.2 ): Weight-based dosing is recommended at the initial dose, 4 weeks later, then every 12 weeks thereafter.
| Weight Range (kilograms) | Dose |
|---|---|
| less than 60 kg | 0.75 mg/kg |
| 60 kg or more | 45 mg |
| greater than 100 kg with co-existent moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis | 90 mg |
Crohn's Disease and Ulcerative Colitis Initial Adult Intravenous Recommended Dose (2.3 ) :
A single intravenous infusion using weight-based dosing:
| Weight Range (kilograms) | Recommended Dose |
|---|---|
| up to 55 kg | 260 mg (2 vials) |
| greater than 55 kg to 85 kg | 390 mg (3 vials) |
| greater than 85 kg | 520 mg (4 vials) |
Crohn's Disease and Ulcerative Colitis Maintenance Adult Subcutaneous Recommended Dosage (2.3 ) :
A subcutaneous 90 mg dose 8 weeks after the initial intravenous dose, then every 8 weeks thereafter.
Recommended Dosage in Plaque Psoriasis
Subcutaneous Adult Dosage Regimen
- For patients weighing 100 kg or less, the recommended dosage is 45 mg initially and 4 weeks later, followed by 45 mg every 12 weeks.
- For patients weighing more than 100 kg, the recommended dosage is 90 mg initially and 4 weeks later, followed by 90 mg every 12 weeks.
In subjects weighing more than 100 kg, 45 mg was also shown to be efficacious. However, 90 mg resulted in greater efficacy in these subjects [see Clinical Studies (14) ] .
Subcutaneous Pediatric Dosage Regimen
Administer STELARA subcutaneously at Weeks 0 and 4, then every 12 weeks thereafter.
The recommended dose of STELARA for pediatric patients 6 years of age and older with plaque psoriasis based on body weight is shown below (Table 1).
| Body Weight of Patient at the Time of Dosing | Recommended Dose |
|---|---|
| less than 60 kg | 0.75 mg/kg |
| 60 kg to 100 kg | 45 mg |
| more than 100 kg | 90 mg |
For pediatric patients weighing less than 60 kg, the administration volume for the recommended dose (0.75 mg/kg) is shown in Table 2; withdraw the appropriate volume from the vial.
| Body Weight (kg) at the time of dosing | Dose (mg) | Volume of injection (mL) |
|---|---|---|
| 15 | 11.3 | 0.12 |
| 16 | 12 | 0.13 |
| 17 | 12.8 | 0.14 |
| 18 | 13.5 | 0.15 |
| 19 | 14.3 | 0.16 |
| 20 | 15 | 0.17 |
| 21 | 15.8 | 0.17 |
| 22 | 16.5 | 0.18 |
| 23 | 17.3 | 0.19 |
| 24 | 18 | 0.20 |
| 25 | 18.8 | 0.21 |
| 26 | 19.5 | 0.22 |
| 27 | 20.3 | 0.22 |
| 28 | 21 | 0.23 |
| 29 | 21.8 | 0.24 |
| 30 | 22.5 | 0.25 |
| 31 | 23.3 | 0.26 |
| 32 | 24 | 0.27 |
| 33 | 24.8 | 0.27 |
| 34 | 25.5 | 0.28 |
| 35 | 26.3 | 0.29 |
| 36 | 27 | 0.3 |
| 37 | 27.8 | 0.31 |
| 38 | 28.5 | 0.32 |
| 39 | 29.3 | 0.32 |
| 40 | 30 | 0.33 |
| 41 | 30.8 | 0.34 |
| 42 | 31.5 | 0.35 |
| 43 | 32.3 | 0.36 |
| 44 | 33 | 0.37 |
| 45 | 33.8 | 0.37 |
| 46 | 34.5 | 0.38 |
| 47 | 35.3 | 0.39 |
| 48 | 36 | 0.4 |
| 49 | 36.8 | 0.41 |
| 50 | 37.5 | 0.42 |
| 51 | 38.3 | 0.42 |
| 52 | 39 | 0.43 |
| 53 | 39.8 | 0.44 |
| 54 | 40.5 | 0.45 |
| 55 | 41.3 | 0.46 |
| 56 | 42 | 0.46 |
| 57 | 42.8 | 0.47 |
| 58 | 43.5 | 0.48 |
| 59 | 44.3 | 0.49 |
Recommended Dosage in Psoriatic Arthritis
Subcutaneous Adult Dosage Regimen
- The recommended dosage is 45 mg initially and 4 weeks later, followed by 45 mg every 12 weeks.
- For patients with co-existent moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis weighing more than 100 kg, the recommended dosage is 90 mg initially and 4 weeks later, followed by 90 mg every 12 weeks.
Subcutaneous Pediatric Dosage Regimen
Administer STELARA subcutaneously at Weeks 0 and 4, then every 12 weeks thereafter.
The recommended dose of STELARA for pediatric patients 6 years of age and older with psoriatic arthritis, based on body weight, is shown below (Table 3).
| Body Weight of Patient at the Time of Dosing | Recommended Dose |
|---|---|
| less than 60 kg For pediatric patients weighing less than 60 kg, the administration volume for the recommended dose (0.75 mg/kg) is shown in Table 2; withdraw the appropriate volume from the vial. | 0.75 mg/kg |
| 60 kg or more | 45 mg |
| greater than 100 kg with co-existent moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis | 90 mg |
Recommended Dosage in Crohn's Disease and Ulcerative Colitis
Intravenous Induction Adult Dosage Regimen
A single intravenous infusion dose of STELARA using the weight-based dosage regimen specified in Table 4 [see Instructions for dilution of STELARA 130 mg vial for intravenous infusion (2.5) ] .
| Body Weight of Patient at the time of dosing | Dose | Number of 130 mg/26 mL (5 mg/mL) STELARA vials |
|---|---|---|
| 55 kg or less | 260 mg | 2 |
| more than 55 kg to 85 kg | 390 mg | 3 |
| more than 85 kg | 520 mg | 4 |
Subcutaneous Maintenance Adult Dosage Regimen
The recommended maintenance dosage is a subcutaneous 90 mg dose administered 8 weeks after the initial intravenous dose, then every 8 weeks thereafter.
General Considerations for Administration
- STELARA is intended for use under the guidance and supervision of a healthcare provider . STELARA should only be administered to patients who will be closely monitored and have regular follow-up visits with a healthcare provider. The appropriate dose should be determined by a healthcare provider using the patient's current weight at the time of dosing. In pediatric patients, it is recommended that STELARA be administered by a healthcare provider. If a healthcare provider determines that it is appropriate, a patient may self-inject or a caregiver may inject STELARA after proper training in subcutaneous injection technique. Instruct patients to follow the directions provided in the Instructions for Use [see Instructions for Use] .
- The needle cover on the prefilled syringe contains dry natural rubber (a derivative of latex). The needle cover should not be handled by persons sensitive to latex.
- It is recommended that each injection be administered at a different anatomic location (such as upper arms, gluteal regions, thighs, or any quadrant of abdomen) than the previous injection, and not into areas where the skin is tender, bruised, erythematous, or indurated. When using the vial, a 1 mL syringe with a 27 gauge, ½ inch needle is recommended.
- Prior to administration, visually inspect STELARA for particulate matter and discoloration. STELARA is a colorless to light yellow solution and may contain a few small translucent or white particles. Do not use STELARA if it is discolored or cloudy, or if other particulate matter is present. STELARA does not contain preservatives; therefore, discard any unused product remaining in the vial and/or syringe.
Preparation and Administration of STELARA 130 mg/26 mL (5 mg/mL) Vial for Intravenous Infusion (Crohn's Disease and Ulcerative Colitis)
STELARA solution for intravenous infusion must be diluted, prepared, and infused by a healthcare professional using aseptic technique.
- Calculate the dose and the number of STELARA vials needed based on patient weight (Table 4). Each 26 mL vial of STELARA contains 130 mg of ustekinumab.
- Withdraw, and then discard a volume of the 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP from the 250 mL infusion bag equal to the volume of STELARA to be added (discard 26 mL sodium chloride for each vial of STELARA needed, for 2 vials- discard 52 mL, for 3 vials- discard 78 mL, 4 vials- discard 104 mL). Alternatively, a 250 mL infusion bag containing 0.45% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP may be used.
- Withdraw 26 mL of STELARA from each vial needed and add it to the 250 mL infusion bag. The final volume in the infusion bag should be 250 mL. Gently mix.
- Visually inspect the diluted solution before infusion. Do not use if visibly opaque particles, discoloration or foreign particles are observed.
- Infuse the diluted solution over a period of at least one hour. Once diluted, the infusion should be completely administered within eight hours of the dilution in the infusion bag.
- Use only an infusion set with an in-line, sterile, non-pyrogenic, low protein-binding filter (pore size 0.2 micrometer).
- Do not infuse STELARA concomitantly in the same intravenous line with other agents.
- STELARA does not contain preservatives. Each vial is for a one-time use in only one patient. Discard any remaining solution. Dispose any unused medicinal product in accordance with local requirements.
Storage
If necessary, the diluted infusion solution may be kept at room temperature up to 25 °C (77 °F) for up to 7 hours. Storage time at room temperature begins once the diluted solution has been prepared. The infusion should be completed within 8 hours after the dilution in the infusion bag (cumulative time after preparation including the storage and the infusion period). Do not freeze. Discard any unused portion of the infusion solution.
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
STELARA (ustekinumab) is a colorless to light yellow solution and may contain a few small translucent or white particles.
Subcutaneous Injection
- Injection: 45 mg/0.5 mL or 90 mg/mL solution in a single-dose prefilled syringe
- Injection: 45 mg/0.5 mL solution in a single-dose vial
Intravenous Infusion
- Injection: 130 mg/26 mL (5 mg/mL) solution in a single-dose vial
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
Pregnancy
Risk Summary
Available data from the Organization of Teratology Information Specialists (OTIS)/MotherToBaby STELARA Pregnancy Registry, published literature and pharmacovigilance in pregnant women have not identified a STELARA-associated risk of major birth defects, miscarriage or other adverse maternal or fetal outcomes (see Data ) . There are risks to the mother and the fetus associated with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) in pregnancy. In animal reproductive and developmental toxicity studies, no adverse developmental effects were observed in offspring after administration of ustekinumab to pregnant monkeys at exposures greater than 100 times the maximum recommended human dose (MRHD).
All pregnancies have a background risk of birth defect, loss, or other adverse outcomes. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage of clinically recognized pregnancies is 2% to 4% and 15% to 20%, respectively.
Clinical Considerations
Disease-associated Maternal and Embryo/Fetal Risk
Published data suggest that the risk of adverse pregnancy outcomes in women with IBD is associated with increased disease activity. Adverse pregnancy outcomes include preterm delivery (before 37 weeks of gestation), low birth weight (less than 2500 g) infants, and small for gestational age at birth.
Fetal/Neonatal Adverse Reactions
Transport of endogenous IgG antibodies across the placenta increases as pregnancy progresses, and peaks during the third trimester. Therefore, STELARA may be present in infants exposed in utero . The potential clinical impact of ustekinumab exposure in infants exposed in utero should be considered.
Data
Human Data
An observational pregnancy registry conducted by (OTIS)/MotherToBaby in the U.S. and Canada (enrollment between 2013 and 2019) assessed the risk of major birth defects, pattern of major and minor anomalies in live-born infants, miscarriage, and adverse infant outcomes in women with STELARA exposure. In the registry study, there were 101 participants and 107 pregnancies with exposure to STELARA (88 prospective; 19 retrospective). Most participants had a primary indication of CD (65.4%) or psoriasis (30.8%). The pregnancy registry did not identify a STELARA -associated risk of major birth defects, pattern of major or minor anomalies, increased risk of miscarriage or adverse infant outcomes. Methodological limitations of the registry include small sample size, lack of an internal comparison group, a mix of prospective and retrospective reports, and unmeasured confounders. The conclusions from the pregnancy registry were consistent with the published literature and pharmacovigilance.
Animal Data
Ustekinumab was tested in two embryo-fetal development toxicity studies in cynomolgus monkeys. No teratogenic or other adverse developmental effects were observed in fetuses from pregnant monkeys that were administered ustekinumab subcutaneously twice weekly or intravenously weekly during the period of organogenesis. Serum concentrations of ustekinumab in pregnant monkeys were greater than 100 times the serum concentration in patients treated subcutaneously with 90 mg of ustekinumab weekly for 4 weeks.
In a combined embryo-fetal development and pre- and post-natal development toxicity study, pregnant cynomolgus monkeys were administered subcutaneous doses of ustekinumab twice weekly at exposures greater than 100 times the MRHD from the beginning of organogenesis to Day 33 after delivery. Neonatal deaths occurred in the offspring of one monkey administered ustekinumab at 22.5 mg/kg and one monkey dosed at 45 mg/kg. No ustekinumab-related-effects on functional, morphological, or immunological development were observed in the neonates from birth through six months of age.
Lactation
Risk Summary
Limited data from published literature suggests that ustekinumab is present in human breast milk. There are no available data on the effects of ustekinumab on milk production. The effects of local gastrointestinal exposure and limited systemic exposure in the breastfed infant to ustekinumab are unknown. No adverse effects on the breastfed infant causally related to ustekinumab have been identified in the published literature or postmarketing experience.
The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother's clinical need for STELARA and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed child from STELARA or from the underlying maternal condition.
Pediatric Use
Plaque Psoriasis
The safety and effectiveness of STELARA have been established for the treatment of moderate to severe plaque psoriasis in pediatric patients 6 years of age and older who are candidates for phototherapy or systemic therapy.
Use of STELARA in pediatric patients 12 to less than 17 years of age is supported by evidence from a multicenter, randomized, 60 week trial (Ps STUDY 3) that included a 12 week, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel group portion, in 110 pediatric subjects 12 years of age and older [see Adverse Reactions (6.1) , Clinical Studies (14.2) ] .
Use of STELARA in pediatric patients 6 to 11 years of age is supported by evidence from an open-label, single-arm, efficacy, safety, and pharmacokinetics trial (Ps STUDY 4) in 44 subjects [see Adverse Reactions (6.1) , Pharmacokinetics (12.3) ] .
The safety and effectiveness of STELARA have not been established in pediatric patients less than 6 years of age with plaque psoriasis.
Psoriatic Arthritis
The safety and effectiveness of STELARA have been established for treatment of psoriatic arthritis in pediatric patients 6 years of age and older.
Use of STELARA in these age groups is supported by evidence from adequate and well controlled trials of STELARA in adult subjects with psoriasis and PsA, pharmacokinetic data from adult subjects with psoriasis, adult subjects with PsA and pediatric subjects with psoriasis, and safety data from two clinical trials in 44 pediatric subjects 6 to 11 years old with psoriasis and 110 pediatric subjects 12 years of age and older with psoriasis. The observed pre-dose (trough) concentrations are generally comparable between adult subjects with psoriasis, adult subjects with PsA and pediatric subjects with psoriasis, and the PK exposure is expected to be comparable between adult and pediatric subjects with PsA [see Adverse Reactions (6.1) , Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) , and Clinical Studies (14.1 , 14.2 , 14.3) ].
The safety and effectiveness of STELARA have not been established in pediatric patients less than 6 years old with psoriatic arthritis.
Crohn's Disease and Ulcerative Colitis
The safety and effectiveness of STELARA have not been established in pediatric patients with Crohn's disease or ulcerative colitis.
Geriatric Use
Of the 6709 subjects exposed to STELARA, a total of 340 were 65 years of age or older (183 subjects with plaque psoriasis, 65 subjects with psoriatic arthritis, 58 subjects with Crohn's disease, and 34 subjects with ulcerative colitis), and 40 subjects were 75 years of age or older. Clinical trials of STELARA did not include sufficient numbers of subjects 65 years of age and older to determine whether they respond differently from younger adult subjects.
CONTRAINDICATIONS
STELARA is contraindicated in patients with clinically significant hypersensitivity to ustekinumab or to any of the excipients in STELARA [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5) ].
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- Infections : Serious infections have occurred. Avoid starting STELARA during any clinically important active infection. If a serious infection or clinically significant infection develops, discontinue STELARA until the infection resolves. (5.1 )
- Theoretical Risk for Particular Infections : Serious infections from mycobacteria, salmonella, and Bacillus Calmette-Guerin (BCG) vaccinations have been reported in patients genetically deficient in IL-12/IL-23. Consider diagnostic tests for these infections as dictated by clinical circumstances. (5.2 )
- Tuberculosis (TB) : Evaluate patients for TB prior to initiating treatment with STELARA. Initiate treatment of latent TB before administering STELARA. (5.3 )
- Malignancies : STELARA may increase risk of malignancy. The safety of STELARA in patients with a history of or a known malignancy has not been evaluated. (5.4 )
- Serious Hypersensitivity Reactions : If a severe or other clinically significant hypersensitivity reaction occurs, discontinue STELARA immediately and initiate appropriate medical treatment. (5.5 )
- Posterior Reversible Encephalopathy Syndrome (PRES) : If PRES is suspected, treat promptly, and discontinue STELARA. (5.6 )
- Immunizations: Avoid use of live vaccines in patients during treatment with STELARA . (5.7 )
- Noninfectious Pneumonia : Cases of interstitial pneumonia, eosinophilic pneumonia, and cryptogenic organizing pneumonia have been reported during post-approval use of STELARA. If diagnosis is confirmed, discontinue STELARA and institute appropriate treatment. (5.8 )
Infections
STELARA may increase the risk of infections and reactivation of latent infections. Serious bacterial, mycobacterial, fungal, and viral infections were observed in patients receiving STELARA [see Adverse Reactions (6.1 , 6.3) ] .
Serious infections requiring hospitalization, or otherwise clinically significant infections, reported in clinical trials included the following:
- Plaque Psoriasis : diverticulitis, cellulitis, pneumonia, appendicitis, cholecystitis, sepsis, osteomyelitis, viral infections, gastroenteritis, and urinary tract infections.
- Psoriatic arthritis : cholecystitis.
- Crohn's disease : anal abscess, gastroenteritis, ophthalmic herpes zoster, pneumonia, and listeria meningitis.
- Ulcerative colitis : gastroenteritis, ophthalmic herpes zoster, pneumonia, and listeriosis.
Avoid initiating treatment with STELARA in patients with any clinically important active infection until the infection resolves or is adequately treated. Consider the risks and benefits of treatment prior to initiating use of STELARA in patients with a chronic infection or a history of recurrent infection.
Instruct patients to seek medical advice if signs or symptoms suggestive of an infection occur while on treatment with STELARA and discontinue STELARA for serious or clinically significant infections until the infection resolves or is adequately treated.
Theoretical Risk for Vulnerability to Particular Infections
Individuals genetically deficient in IL-12/IL-23 are particularly vulnerable to disseminated infections from mycobacteria (including nontuberculous, environmental mycobacteria), salmonella (including nontyphi strains), and Bacillus Calmette-Guerin (BCG) vaccinations. Serious infections and fatal outcomes have been reported in such patients.
It is not known whether patients with pharmacologic blockade of IL-12/IL-23 from treatment with STELARA may be susceptible to these types of infections. Consider appropriate diagnostic testing, (e.g., tissue culture, stool culture, as dictated by clinical circumstances).
Pre-treatment Evaluation for Tuberculosis
Evaluate patients for tuberculosis infection prior to initiating treatment with STELARA.
Avoid administering STELARA to patients with active tuberculosis infection. Initiate treatment of latent tuberculosis prior to administering STELARA. Consider anti-tuberculosis therapy prior to initiation of STELARA in patients with a past history of latent or active tuberculosis in whom an adequate course of treatment cannot be confirmed. Closely monitor patients receiving STELARA for signs and symptoms of active tuberculosis during and after treatment.
Malignancies
STELARA is an immunosuppressant and may increase the risk of malignancy. Malignancies were reported among subjects who received STELARA in clinical trials [see Adverse Reactions (6.1) ] . In rodent models, inhibition of IL-12/IL-23p40 increased the risk of malignancy [see Nonclinical Toxicology (13) ] .
The safety of STELARA has not been evaluated in patients who have a history of malignancy or who have a known malignancy.
There have been post-marketing reports of the rapid appearance of multiple cutaneous squamous cell carcinomas in patients receiving STELARA who had pre-existing risk factors for developing non-melanoma skin cancer. Monitor all patients receiving STELARA for the appearance of non-melanoma skin cancer. Closely follow patients greater than 60 years of age, those with a medical history of prolonged immunosuppressant therapy and those with a history of PUVA treatment [see Adverse Reactions (6.1) ] .
Serious Hypersensitivity Reactions
Serious hypersensitivity reactions, including anaphylaxis and angioedema, have been reported with STELARA in clinical trials and postmarketing. Some serious hypersensitivity reactions have occurred during the first intravenous dose of STELARA [see Adverse Reactions (6.1 , 6.3) ].
If a severe or clinically significant hypersensitivity reaction occurs, discontinue STELARA immediately and initiate appropriate medical treatment [see Contraindications (4) ].
Posterior Reversible Encephalopathy Syndrome (PRES)
Two cases of posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome (PRES), also known as Reversible Posterior Leukoencephalopathy Syndrome (RPLS), were reported in clinical trials. Cases have also been reported in postmarketing experience in patients with psoriasis, psoriatic arthritis, and Crohn's disease. Clinical presentation included headaches, seizures, confusion, visual disturbances, and imaging changes consistent with PRES a few days to several months after ustekinumab initiation. A few cases reported latency of a year or longer. Patients recovered with supportive care following withdrawal of ustekinumab.
Monitor all patients treated with STELARA for signs and symptoms of PRES. If PRES is suspected, promptly administer appropriate treatment and discontinue STELARA.
Immunizations
Prior to initiating therapy with STELARA, patients should receive all age-appropriate immunizations as recommended by current immunization guidelines. Patients being treated with STELARA should avoid receiving live vaccines. Avoid administering BCG vaccines during treatment with STELARA or for one year prior to initiating treatment or one year following discontinuation of treatment. Caution is advised when administering live vaccines to household contacts of patients receiving STELARA because of the potential risk for shedding from the household contact and transmission to patient.
Non-live vaccinations received during a course of STELARA may not elicit an immune response sufficient to prevent disease.
Noninfectious Pneumonia
Cases of interstitial pneumonia, eosinophilic pneumonia, and cryptogenic organizing pneumonia have been reported during post-approval use of STELARA. Clinical presentations included cough, dyspnea, and interstitial infiltrates following one to three doses. Serious outcomes have included respiratory failure and prolonged hospitalization. Patients improved with discontinuation of therapy and in certain cases administration of corticosteroids. If diagnosis is confirmed, discontinue STELARA and institute appropriate treatment [see Postmarketing Experience (6.3) ] .
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following serious adverse reactions are discussed elsewhere in the label:
- Infections [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) ]
- Malignancies [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4) ]
- Serious Hypersensitivity Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5) ]
- Posterior Reversible Encephalopathy Syndrome (PRES) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6) ]
- Noninfectious Pneumonia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8) ]
Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
Adult Subjects with Plaque Psoriasis
The safety data reflect exposure to STELARA in 3117 adult subjects with plaque psoriasis, including 2414 exposed for at least 6 months, 1855 exposed for at least one year, 1653 exposed for at least two years, 1569 exposed for at least three years, 1482 exposed for at least four years and 838 exposed for at least five years.
Table 5 summarizes the adverse reactions that occurred at a rate of at least 1% with higher rates in the STELARA groups during the placebo-controlled period of Ps STUDY 1 and Ps STUDY 2 [see Clinical Studies (14) ] .
| STELARA | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Placebo | 45 mg | 90 mg | |
| Subjects treated | 665 | 664 | 666 |
| Nasopharyngitis | 51 (8%) | 56 (8%) | 49 (7%) |
| Upper respiratory tract infection | 30 (5%) | 36 (5%) | 28 (4%) |
| Headache | 23 (3%) | 33 (5%) | 32 (5%) |
| Fatigue | 14 (2%) | 18 (3%) | 17 (3%) |
| Back pain | 8 (1%) | 9 (1%) | 14 (2%) |
| Dizziness | 8 (1%) | 8 (1%) | 14 (2%) |
| Pharyngolaryngeal pain | 7 (1%) | 9 (1%) | 12 (2%) |
| Pruritus | 9 (1%) | 10 (2%) | 9 (1%) |
| Injection site erythema | 3 (<1%) | 6 (1%) | 13 (2%) |
| Myalgia | 4 (1%) | 7 (1%) | 8 (1%) |
| Depression | 3 (<1%) | 8 (1%) | 4 (1%) |
Adverse reactions that occurred at rates less than 1% in the controlled period of Ps STUDIES 1 and 2 through week 12 included: cellulitis, herpes zoster, diverticulitis, and certain injection site reactions (pain, swelling, pruritus, induration, hemorrhage, bruising, and irritation).
One case of PRES occurred during clinical trials in adult subjects with plaque psoriasis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6) ] .
Infections
In the placebo-controlled period of clinical trials of subjects with plaque psoriasis (average follow-up of 12.6 weeks for subjects receiving placebo and 13.4 weeks for STELARA-treated subjects), 27% of STELARA-treated subjects reported infections (1.39 per patient-years of follow-up) compared with 24% of subjects receiving placebo (1.21 per patient-years of follow-up). Serious infections occurred in 0.3% of STELARA-treated subjects (0.01 per patient-years of follow-up) and in 0.4% of subjects receiving placebo (0.02 per patient-year of follow-up) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) ] .
In the controlled and non-controlled portions of clinical trials in subjects with plaque psoriasis (median follow-up of 3.2 years), representing 8998 patient-years of exposure, 72.3% of STELARA-treated subjects reported infections (0.87 per patient-years of follow-up). Serious infections were reported in 2.8% of subjects (0.01 per patient-years of follow-up).
Malignancies
In the controlled and non-controlled portions of clinical trials in subjects with plaque psoriasis (median follow-up of 3.2 years, representing 8998 patient-years of exposure), 1.7% of STELARA-treated subjects reported malignancies excluding non-melanoma skin cancers (0.60 per hundred patient-years of follow-up). Non-melanoma skin cancer was reported in 1.5% of STELARA-treated subjects (0.52 per hundred patient-years of follow-up) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4) ] . The most frequently observed malignancies other than non-melanoma skin cancer during the clinical trials were: prostate, melanoma, colorectal and breast. Malignancies other than non-melanoma skin cancer in STELARA-treated subjects during the controlled and uncontrolled portions of trials were similar in type and number to what would be expected in the general U.S. population according to the SEER database (adjusted for age, gender and race). 1
Pediatric Subjects with Plaque Psoriasis
The safety of STELARA was assessed in two trials of pediatric subjects with moderate to severe plaque psoriasis. Ps STUDY 3 evaluated safety for up to 60 weeks in 110 pediatric subjects 12 to 17 years old. Ps STUDY 4 evaluated safety for up to 56 weeks in 44 pediatric subjects 6 to 11 years old. The safety profile in pediatric subjects was similar to the safety profile from trials in adults with plaque psoriasis.
Psoriatic Arthritis
The safety of STELARA was assessed in 927 subjects in two randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trials in adults with active psoriatic arthritis (PsA). The overall safety profile of STELARA in subjects with PsA was consistent with the safety profile seen in clinical trials in adult subjects with plaque psoriasis. A higher incidence of arthralgia, nausea, and dental infections was observed in STELARA-treated subjects when compared with placebo-treated subjects (3% vs. 1% for arthralgia and 3% vs. 1% for nausea; 1% vs. 0.6% for dental infections) in the placebo-controlled portions of the PsA clinical trials.
Crohn's Disease
The safety of STELARA was assessed in 1407 subjects with moderately to severely active Crohn's disease (Crohn's Disease Activity Index [CDAI] greater than or equal to 220 and less than or equal to 450) in three randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group, multicenter trials. These 1407 subjects included 40 subjects who received a prior investigational intravenous ustekinumab formulation but were not included in the efficacy analyses. In trials CD-1 and CD-2 there were 470 subjects who received STELARA 6 mg/kg as a weight-based single intravenous induction dose and 466 who received placebo [see Dosage and Administration (2.3) ] . Subjects who were responders in either trial CD-1 or CD-2 were randomized to receive a subcutaneous maintenance regimen of either 90 mg STELARA every 8 weeks, or placebo for 44 weeks in trial CD-3. Subjects in these 3 trials may have received other concomitant therapies including aminosalicylates, immunomodulatory agents [azathioprine (AZA), 6-mercaptopurine (6-MP), methotrexate (MTX)], oral corticosteroids (prednisone or budesonide), and/or antibiotics for their Crohn's disease [see Clinical Studies (14.4) ] .
The overall safety profile of STELARA was consistent with the safety profile seen in the clinical trials in adult subjects with plaque psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis. Common adverse reactions in trials CD-1 and CD-2 and in trial CD-3 are listed in Tables 6 and 7, respectively.
| Placebo | STELARA 6 mg/kg single intravenous induction dose | |
|---|---|---|
| N=466 | N=470 | |
| Vomiting | 3% | 4% |
Other less common adverse reactions reported in subjects in trials CD-1 and CD-2 included asthenia (1% vs 0.4%), acne (1% vs 0.4%), and pruritus (2% vs 0.4%).
| Placebo | STELARA 90 mg subcutaneous maintenance dose every 8 weeks | |
|---|---|---|
| N=133 | N=131 | |
| Nasopharyngitis | 8% | 11% |
| Injection site erythema | 0 | 5% |
| Vulvovaginal candidiasis/mycotic infection | 1% | 5% |
| Bronchitis | 3% | 5% |
| Pruritus | 2% | 4% |
| Urinary tract infection | 2% | 4% |
| Sinusitis | 2% | 3% |
Infections
In subjects with Crohn's disease, serious or other clinically significant infections included anal abscess, gastroenteritis, and pneumonia. In addition, listeria meningitis and ophthalmic herpes zoster were reported in one subject each [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) ] .
Malignancies
With up to one year of treatment in the Crohn's disease clinical trials, 0.2% of STELARA-treated subjects (0.36 events per hundred patient-years) and 0.2% of placebo-treated subjects (0.58 events per hundred patient-years) developed non-melanoma skin cancer. Malignancies other than non-melanoma skin cancers occurred in 0.2% of STELARA-treated subjects (0.27 events per hundred patient-years) and in none of the placebo-treated subjects.
Hypersensitivity Reactions Including Anaphylaxis
In CD trials, two subjects reported hypersensitivity reactions following STELARA administration. One subject experienced signs and symptoms consistent with anaphylaxis (tightness of the throat, shortness of breath, and flushing) after a single subcutaneous administration (0.1% of subjects receiving subcutaneous STELARA). In addition, one subject experienced signs and symptoms consistent with or related to a hypersensitivity reaction (chest discomfort, flushing, urticaria, and increased body temperature) after the initial intravenous STELARA dose (0.08% of subjects receiving intravenous STELARA). These subjects were treated with oral antihistamines or corticosteroids and in both cases symptoms resolved within an hour [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5) ] .
Ulcerative Colitis
The safety of STELARA was evaluated in two randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trials (UC-1 [IV induction] and UC-2 [SC maintenance]) in 960 adult subjects with moderately to severely active ulcerative colitis [see Clinical Studies (14.5) ] . The overall safety profile of STELARA in subjects with ulcerative colitis was consistent with the safety profile seen across all approved indications. Adverse reactions reported in at least 3% of STELARA-treated subjects and at a higher rate than placebo were:
- Induction (UC-1): nasopharyngitis (7% vs 4%).
- Maintenance (UC-2): nasopharyngitis (24% vs 20%), headache (10% vs 4%), abdominal pain (7% vs 3%), influenza (6% vs 5%), fever (5% vs. 4%), diarrhea (4% vs 1%), sinusitis (4% vs 1%), fatigue (4% vs 2%), and nausea (3% vs 2%).
Infections
In subjects with ulcerative colitis, serious or other clinically significant infections included gastroenteritis and pneumonia. In addition, listeriosis and ophthalmic herpes zoster were reported in one subject each [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) ] .
Malignancies
With up to one year of treatment in the ulcerative colitis clinical trials, 0.4% of STELARA-treated subjects (0.48 events per hundred patient-years) and 0.0% of subjects receiving placebo (0.00 events per hundred patient-years) developed non-melanoma skin cancer. Malignancies other than non-melanoma skin cancers occurred in 0.5% of STELARA-treated subjects (0.64 events per hundred patient-years) and 0.2% of subjects receiving placebo (0.40 events per hundred patient-years).
Immunogenicity
The observed incidence of anti-drug antibodies is highly dependent on the sensitivity and specificity of the assay. Differences in assay methods preclude meaningful comparisons of the incidence of anti-drug antibodies in the studies described below with the incidence of anti-drug antibodies in studies of other ustekinumab products.
Approximately 6 to 12.4% of subjects treated with STELARA in clinical trials in subjects with plaque psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis developed antibodies to ustekinumab, which were generally low-titer. In clinical trials in subjects with plaque psoriasis, antibodies to ustekinumab were associated with reduced or undetectable serum ustekinumab concentrations and reduced efficacy. In trials in subjects with plaque psoriasis, the majority of subjects who were positive for antibodies to ustekinumab had neutralizing antibodies.
In clinical trials in subjects with Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis, 2.9% and 4.6% of subjects, respectively, developed antibodies to ustekinumab when treated with STELARA for approximately one year. No apparent association between the development of antibodies to ustekinumab and the development of injection site reactions was seen.
Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been reported during post-approval use of STELARA. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to STELARA exposure.
Immune system disorders: Hypersensitivity reactions (e.g., anaphylaxis, angioedema, dyspnea, rash, urticaria), including a fatal case that presented with chest tightness and dyspnea during infusion of the first dose .
Infections and infestations: Lower respiratory tract infection (including opportunistic fungal infections and tuberculosis).
Neurological disorders: Posterior Reversible Encephalopathy Syndrome (PRES) .
Respiratory, thoracic, and mediastinal disorders: Interstitial pneumonia, eosinophilic pneumonia, and cryptogenic organizing pneumonia.
Skin reactions : Pustular psoriasis, erythrodermic psoriasis, hypersensitivity vasculitis.
DRUG INTERACTIONS
Concomitant Therapies
In trials in subjects with plaque psoriasis the safety of STELARA in combination with immunosuppressive agents or phototherapy has not been evaluated . In trials in subjects with psoriatic arthritis, concomitant MTX use did not appear to influence the safety or efficacy of STELARA. In trials in subjects with Crohn's disease (CD-1 and CD-2) and ulcerative colitis (UC-1), immunomodulators (6-MP, AZA, MTX) were used concomitantly in approximately 30% of subjects and corticosteroids were used concomitantly in approximately 40% and 50% of Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis subjects, respectively. Use of these concomitant therapies did not appear to influence the overall safety or efficacy of STELARA.
CYP450 Substrates
The formation of CYP450 enzymes can be suppressed by increased levels of certain cytokines (e.g., IL-1, IL-6, TNFα, IFN) during chronic inflammation. Thus, use of STELARA, an antagonist of IL-12 and IL-23, could normalize the formation of CYP450 enzymes. Upon initiation or discontinuation of STELARA in patients who are receiving concomitant CYP450 substrates, particularly those with a narrow therapeutic index, consider monitoring for therapeutic effect or drug concentration and adjust the individual dosage of the CYP substrate as needed. See the prescribing information of specific CYP substrates.
A CYP-mediated drug interaction effect was not observed in subjects with Crohn’s disease [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ] .
Allergen Immunotherapy
STELARA has not been evaluated in patients who have undergone allergy immunotherapy. STELARA may decrease the protective effect of allergen immunotherapy (decrease tolerance) which may increase the risk of an allergic reaction to a dose of allergen immunotherapy. Therefore, caution should be exercised in patients receiving or who have received allergen immunotherapy, particularly for anaphylaxis.
DESCRIPTION
Ustekinumab, a human IgG1κ monoclonal antibody, is a human interleukin-12 and -23 antagonist. Using DNA recombinant technology, ustekinumab is produced in a murine cell line (Sp2/0). The manufacturing process contains steps for the clearance of viruses. Ustekinumab is comprised of 1326 amino acids and has an estimated molecular mass that ranges from 148,079 to 149,690 Daltons.
STELARA ® (ustekinumab) injection is a sterile, preservative-free, colorless to light yellow solution and may contain a few small translucent or white particles with pH of 5.7– 6.3.
STELARA for Subcutaneous Use
Available as 45 mg of ustekinumab in 0.5 mL and 90 mg of ustekinumab in 1 mL, supplied as a sterile solution in a single-dose prefilled syringe with a 27 gauge fixed ½ inch needle and as 45 mg of ustekinumab in 0.5 mL in a single-dose Type I glass vial with a coated stopper. The syringe is fitted with a passive needle guard and a needle cover that contains dry natural rubber (a derivative of latex).
Each 0.5 mL prefilled syringe or vial delivers 45 mg ustekinumab, L-histidine and L-histidine monohydrochloride monohydrate (0.5 mg), Polysorbate 80 (0.02 mg), and sucrose (38 mg).
Each 1 mL prefilled syringe delivers 90 mg ustekinumab, L-histidine and L-histidine monohydrochloride monohydrate (1 mg), Polysorbate 80 (0.04 mg), and sucrose (76 mg).
STELARA for Intravenous Infusion
Available as 130 mg of ustekinumab in 26 mL, supplied as a single-dose Type I glass vial with a coated stopper.
Each 26 mL vial delivers 130 mg ustekinumab, EDTA disodium salt dihydrate (0.52 mg), L-histidine (20 mg), L-histidine hydrochloride monohydrate (27 mg), L-methionine (10.4 mg), Polysorbate 80 (10.4 mg), and sucrose (2210 mg).
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Mechanism of Action
Ustekinumab is a human IgG1қ monoclonal antibody that binds with specificity to the p40 protein subunit used by both the IL-12 and IL-23 cytokines. IL-12 and IL-23 are naturally occurring cytokines that are involved in inflammatory and immune responses, such as natural killer cell activation and CD4+ T-cell differentiation and activation. In in vitro models, ustekinumab was shown to disrupt IL-12 and IL-23 mediated signaling and cytokine cascades by disrupting the interaction of these cytokines with a shared cell-surface receptor chain, IL-12Rβ1. The cytokines IL-12 and IL-23 have been implicated as important contributors to the chronic inflammation that is a hallmark of Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis. In animal models of colitis, genetic absence or antibody blockade of the p40 subunit of IL-12 and IL-23, the target of ustekinumab, was shown to be protective.
Pharmacodynamics
Plaque Psoriasis
In a small exploratory trial, a decrease was observed in the expression of mRNA of its molecular targets IL-12 and IL-23 in lesional skin biopsies measured at baseline and up to two weeks post-treatment in subjects with plaque psoriasis.
Ulcerative Colitis
In both trial UC-1 (induction) and trial UC-2 (maintenance), a positive relationship was observed between exposure and rates of clinical remission, clinical response, and endoscopic improvement. The response rate approached a plateau at the ustekinumab exposures associated with the recommended dosing regimen for maintenance treatment [see Clinical Studies (14.5) ] .
Pharmacokinetics
Absorption
In adult subjects with plaque psoriasis, the median time to reach the maximum serum concentration (T max ) was 13.5 days and 7 days, respectively, after a single subcutaneous administration of 45 mg (N=22) and 90 mg (N=24) of ustekinumab. In healthy subjects (N=30), the median T max value (8.5 days) following a single subcutaneous administration of 90 mg of ustekinumab was comparable to that observed in subjects with plaque psoriasis.
Following multiple subcutaneous doses of STELARA in adult subjects with plaque psoriasis, steady-state serum concentrations of ustekinumab were achieved by Week 28. The mean (±SD) steady-state trough serum ustekinumab concentrations were 0.69 ± 0.69 mcg/mL for subjects less than or equal to 100 kg receiving a 45 mg dose and 0.74 ± 0.78 mcg/mL for subjects greater than 100 kg receiving a 90 mg dose. There was no apparent accumulation in serum ustekinumab concentration over time when given subcutaneously every 12 weeks.
Following the recommended intravenous induction dose, mean ±SD peak serum ustekinumab concentration was 125.2 ± 33.6 mcg/mL in subjects with Crohn's disease, and 129.1 ± 27.6 mcg/mL in subjects with ulcerative colitis. Starting at Week 8, the recommended subcutaneous maintenance dosing of 90 mg ustekinumab was administered every 8 weeks. Steady state ustekinumab concentration was achieved by the start of the second maintenance dose. There was no apparent accumulation in ustekinumab concentration over time when given subcutaneously every 8 weeks. Mean ±SD steady-state trough concentration was 2.5 ± 2.1 mcg/mL in subjects with Crohn's disease, and 3.3 ± 2.3 mcg/mL in subjects with ulcerative colitis for 90 mg ustekinumab administered every 8 weeks.
Distribution
Population pharmacokinetic analyses showed that the volume of distribution of ustekinumab in the central compartment was 2.7 L (95% CI: 2.69, 2.78) in subjects with Crohn's disease and 3.0 L (95% CI: 2.96, 3.07) in subjects with ulcerative colitis. The total volume of distribution at steady-state was 4.6 L in subjects with Crohn's disease and 4.4 L in subjects with ulcerative colitis.
Elimination
The mean (±SD) half-life ranged from 14.9 ± 4.6 to 45.6 ± 80.2 days across all trials in subjects with plaque psoriasis following subcutaneous administration. Population pharmacokinetic analyses showed that the clearance of ustekinumab was 0.19 L/day (95% CI: 0.185, 0.197) in subjects with Crohn's disease and 0.19 L/day (95% CI: 0.179, 0.192) in subjects with ulcerative colitis with an estimated median terminal half-life of approximately 19 days for both IBD (Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis) populations.
These results indicate the pharmacokinetics of ustekinumab were similar between subjects with Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis.
Metabolism
The metabolic pathway of ustekinumab has not been characterized. As a human IgG1κ monoclonal antibody, ustekinumab is expected to be degraded into small peptides and amino acids via catabolic pathways in the same manner as endogenous IgG.
Specific Populations
Weight
When given the same dose, subjects with plaque psoriasis or psoriatic arthritis weighing more than 100 kg had lower median serum ustekinumab concentrations compared with those subjects weighing 100 kg or less. The median trough serum concentrations of ustekinumab in subjects of higher weight (greater than 100 kg) in the 90 mg group were comparable to those in subjects of lower weight (100 kg or less) in the 45 mg group.
Age: Geriatric Population
A population pharmacokinetic analysis (N=106/1937 subjects with plaque psoriasis greater than or equal to 65 years old) was performed to evaluate the effect of age on the pharmacokinetics of ustekinumab. There were no apparent changes in pharmacokinetic parameters (clearance and volume of distribution) in subjects older than 65 years old.
Age: Pediatric Population
Following multiple recommended doses of STELARA in pediatric subjects 6 years of age and older with plaque psoriasis, steady-state serum concentrations of ustekinumab were achieved by Week 28. At Week 28, the mean ±SD steady-state trough serum ustekinumab concentrations were 0.36 ± 0.26 mcg/mL and 0.54 ± 0.43 mcg/mL, respectively, in pediatric subjects 6 to 11 years of age and pediatric subjects 12 years of age and older.
Overall, the observed steady-state ustekinumab trough concentrations in pediatric subjects with plaque psoriasis were within the range of those observed for adult subjects with plaque psoriasis and adult subjects with PsA after administration of STELARA.
Drug Interaction Studies
The effects of IL-12 or IL-23 on the regulation of CYP450 enzymes were evaluated in an in vitro study using human hepatocytes, which showed that IL-12 and/or IL-23 at levels of 10 ng/mL did not alter human CYP450 enzyme activities (CYP1A2, 2B6, 2C9, 2C19, 2D6, or 3A4).
No clinically significant changes in exposure of caffeine (CYP1A2 substrate), warfarin (CYP2C9 substrate), omeprazole (CYP2C19 substrate), dextromethorphan (CYP2D6 substrate), or midazolam (CYP3A substrate) were observed when used concomitantly with ustekinumab at the approved recommended dosage in subjects with Crohn’s disease [see Drug Interactions (7.2) ] .
Population pharmacokinetic analyses indicated that the clearance of ustekinumab was not impacted by concomitant MTX, NSAIDs, and oral corticosteroids, or prior exposure to a TNF blocker in subjects with psoriatic arthritis.
In subjects with Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis, population pharmacokinetic analyses did not indicate changes in ustekinumab clearance with concomitant use of corticosteroids or immunomodulators (AZA, 6-MP, or MTX); and serum ustekinumab concentrations were not impacted by concomitant use of these medications.
NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Animal studies have not been conducted to evaluate the carcinogenic or mutagenic potential of STELARA. Published literature showed that administration of murine IL-12 caused an anti-tumor effect in mice that contained transplanted tumors and IL-12/IL-23p40 knockout mice or mice treated with anti-IL-12/IL-23p40 antibody had decreased host defense to tumors. Mice genetically manipulated to be deficient in both IL-12 and IL-23 or IL-12 alone developed UV-induced skin cancers earlier and more frequently compared to wild-type mice. The relevance of these experimental findings in mouse models for malignancy risk in humans is unknown.
No effects on fertility were observed in male cynomolgus monkeys that were administered ustekinumab at subcutaneous doses up to 45 mg/kg twice weekly (45 times the MRHD on a mg/kg basis) prior to and during the mating period. However, fertility and pregnancy outcomes were not evaluated in mated females.
No effects on fertility were observed in female mice that were administered an analogous IL-12/IL-23p40 antibody by subcutaneous administration at doses up to 50 mg/kg, twice weekly, prior to and during early pregnancy.
Animal Toxicology and/or Pharmacology
In a 26-week toxicology study, one out of 10 monkeys subcutaneously administered 45 mg/kg ustekinumab twice weekly for 26 weeks had a bacterial infection.
CLINICAL STUDIES
Adult Subjects with Plaque Psoriasis
Two multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trials (Ps STUDY 1 and Ps STUDY 2) enrolled a total of 1996 subjects 18 years of age and older with plaque psoriasis who had a minimum body surface area involvement of 10%, and Psoriasis Area and Severity Index (PASI) score ≥12, and who were candidates for phototherapy or systemic therapy. Subjects with guttate, erythrodermic, or pustular psoriasis were excluded from the trials.
Ps STUDY 1 enrolled 766 subjects and Ps STUDY 2 enrolled 1230 subjects. The trials had the same design through Week 28. In both trials, subjects were randomized in equal proportion to placebo, 45 mg or 90 mg of STELARA. Subjects randomized to STELARA received 45 mg or 90 mg doses, regardless of weight, at Weeks 0, 4, and 16. Subjects randomized to receive placebo at Weeks 0 and 4 crossed over to receive STELARA (either 45 mg or 90 mg) at Weeks 12 and 16.
In both trials, subjects in all treatment groups had a median baseline PASI score ranging from approximately 17 to 18. Baseline PGA score was marked or severe in 44% of subjects in Ps STUDY 1 and 40% of subjects in Ps STUDY 2. Approximately two-thirds of all subjects had received prior phototherapy, 69% had received either prior conventional systemic or biologic therapy for the treatment of psoriasis, with 56% receiving prior conventional systemic therapy and 43% receiving prior biologic therapy. A total of 28% of subjects had a history of psoriatic arthritis.
In both trials, the endpoints were the proportion of subjects who achieved at least a 75% reduction in PASI score (PASI 75) from baseline to Week 12 and treatment success (cleared or minimal) on the Physician's Global Assessment (PGA). The PGA is a 6-category scale ranging from 0 (cleared) to 5 (severe) that indicates the physician's overall assessment of psoriasis focusing on plaque thickness/induration, erythema, and scaling.
Clinical Response
The results of Ps STUDY 1 and Ps STUDY 2 are presented in Table 8 below.
| Ps STUDY 1 | Ps STUDY 2 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| STELARA | STELARA | |||||
| Placebo | 45 mg | 90 mg | Placebo | 45 mg | 90 mg | |
| Subjects randomized | 255 | 255 | 256 | 410 | 409 | 411 |
| PASI 75 response | 8 (3%) | 171 (67%) | 170 (66%) | 15 (4%) | 273 (67%) | 311 (76%) |
| PGA of Cleared or Minimal | 10 (4%) | 151 (59%) | 156 (61%) | 18 (4%) | 277 (68%) | 300 (73%) |
Examination of age, gender, and race subgroups did not identify differences in response to STELARA among these subgroups.
In subjects who weighed 100 kg or less, response rates were comparable with both the 45 mg and 90 mg doses; however, in subjects who weighed greater than 100 kg, higher response rates were seen with 90 mg dosing compared with 45 mg dosing (Table 9 below).
| Ps STUDY 1 | Ps STUDY 2 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| STELARA | STELARA | |||||
| Placebo | 45 mg | 90 mg | Placebo | 45 mg | 90 mg | |
| Subjects randomized | 255 | 255 | 256 | 410 | 409 | 411 |
| PASI 75 response Subjects were dosed with trial medication at Weeks 0 and 4. | ||||||
| ≤100 kg | 4% | 74% | 65% | 4% | 73% | 78% |
| 6/166 | 124/168 | 107/164 | 12/290 | 218/297 | 225/289 | |
| >100 kg | 2% | 54% | 68% | 3% | 49% | 71% |
| 2/89 | 47/87 | 63/92 | 3/120 | 55/112 | 86/121 | |
| PGA of Cleared or Minimal | ||||||
| ≤100 kg | 4% | 64% | 63% | 5% | 74% | 75% |
| 7/166 | 108/168 | 103/164 | 14/290 | 220/297 | 216/289 | |
| >100 kg | 3% | 49% | 58% | 3% | 51% | 69% |
| 3/89 | 43/87 | 53/92 | 4/120 | 57/112 | 84/121 | |
Subjects in Ps STUDY 1 who were PASI 75 responders at both Weeks 28 and 40 were re-randomized at Week 40 to either continued dosing of STELARA (STELARA at Week 40) or to withdrawal of therapy (placebo at Week 40). At Week 52, 89% (144/162) of subjects re-randomized to STELARA treatment were PASI 75 responders compared with 63% (100/159) of subjects re-randomized to placebo (treatment withdrawal after Week 28 dose). The median time to loss of PASI 75 response among the subjects randomized to treatment withdrawal was 16 weeks.
Pediatric Subjects with Plaque Psoriasis
A multicenter, randomized, double blind, placebo-controlled trial (Ps STUDY 3) enrolled 110 pediatric subjects 12 years of age and older with a minimum BSA involvement of 10%, a PASI score greater than or equal to 12, and a PGA score greater than or equal to 3, who were candidates for phototherapy or systemic therapy and whose disease was inadequately controlled by topical therapy.
Subjects were randomized to receive placebo (n = 37), the recommended dose of STELARA (n = 36), or one-half the recommended dose of STELARA (n = 37) by subcutaneous injection at Weeks 0 and 4 followed by dosing every 12 weeks (q12w). The recommended dose of STELARA was 0.75 mg/kg for subjects weighing less than 60 kg, 45 mg for subjects weighing 60 kg to 100 kg, and 90 mg for subjects weighing greater than 100 kg. At Week 12, subjects who received placebo were crossed over to receive STELARA at the recommended dose or one-half the recommended dose.
Of the pediatric subjects, approximately 63% had prior exposure to phototherapy or conventional systemic therapy and approximately 11% had prior exposure to biologics.
The endpoints were the proportion of subjects who achieved a PGA score of cleared (0) or minimal (1), PASI 75, and PASI 90 at Week 12. Subjects were followed for up to 60 weeks following first administration of trial agent.
Clinical Response
The efficacy results at Week 12 for Ps STUDY 3 are presented in Table 10.
| Ps STUDY 3 | ||
|---|---|---|
| Placebo n (%) | STELARA Using the weight-based dosage regimen specified in Table 1 and Table 2. n (%) | |
| N | 37 | 36 |
| PGA | ||
| PGA of cleared (0) or minimal (1) | 2 (5.4%) | 25 (69.4%) |
| PASI | ||
| PASI 75 responders | 4 (10.8%) | 29 (80.6%) |
| PASI 90 responders | 2 (5.4%) | 22 (61.1%) |
Psoriatic Arthritis
The safety and efficacy of STELARA was assessed in 927 subjects (PsA STUDY 1, n=615; PsA STUDY 2, n=312), in two randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trials in adult subjects 18 years of age and older with active PsA (≥5 swollen joints and ≥5 tender joints) despite nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory (NSAID) or disease modifying antirheumatic (DMARD) therapy. Subjects in these trials had a diagnosis of PsA for at least 6 months. Subjects with each subtype of PsA were enrolled, including polyarticular arthritis with the absence of rheumatoid nodules (39%), spondylitis with peripheral arthritis (28%), asymmetric peripheral arthritis (21%), distal interphalangeal involvement (12%) and arthritis mutilans (0.5%). Over 70% and 40% of the patients, respectively, had enthesitis and dactylitis at baseline.
Subjects were randomized to receive treatment with STELARA 45 mg, 90 mg, or placebo subcutaneously at Weeks 0 and 4 followed by every 12 weeks (q12w) dosing. Approximately 50% of subjects continued on stable doses of MTX (≤25 mg/week). The primary endpoint was the percentage of subjects achieving ACR 20 response at Week 24.
In PsA STUDY 1 and PsA STUDY 2, 80% and 86% of the subjects, respectively, had been previously treated with DMARDs. In PsA STUDY 1, previous treatment with anti-tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α agent was not allowed. In PsA STUDY 2, 58% (n=180) of the subjects had been previously treated with TNF blocker, of whom over 70% had discontinued their TNF blocker treatment for lack of efficacy or intolerance at any time.
Clinical Response
In both trials, a greater proportion of subjects achieved ACR 20, ACR 50 and PASI 75 response in the STELARA 45 mg and 90 mg groups compared to placebo at Week 24 (see Table 11 ). ACR 70 responses were also higher in the STELARA 45 mg and 90 mg groups, although the difference was only numerical (p=NS) in STUDY 2. Responses were consistent in subjects treated with STELARA alone or in combination with methotrexate. Responses were similar in subjects regardless of prior TNFα exposure.
| PsA STUDY 1 | PsA STUDY 2 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| STELARA | STELARA | |||||
| Placebo | 45 mg | 90 mg | Placebo | 45 mg | 90 mg | |
| Number of subjects randomized | 206 | 205 | 204 | 104 | 103 | 105 |
| ACR 20 response, N (%) | 47 (23%) | 87 (42%) | 101 (50%) | 21 (20%) | 45 (44%) | 46 (44%) |
| ACR 50 response, N (%) | 18 (9%) | 51 (25%) | 57 (28%) | 7 (7%) | 18 (17%) | 24 (23%) |
| ACR 70 response, N (%) | 5 (2%) | 25 (12%) | 29 (14%) | 3 (3%) | 7 (7%) | 9 (9%) |
| Number of subjects with ≥ 3% BSA Number of subjects with ≥ 3% BSA psoriasis skin involvement at baseline | 146 | 145 | 149 | 80 | 80 | 81 |
| PASI 75 response, N (%) | 16 (11%) | 83 (57%) | 93 (62%) | 4 (5%) | 41 (51%) | 45 (56%) |
The percent of subjects achieving ACR 20 responses by visit is shown in Figure 1.
| Figure 1: Percent of subjects achieving ACR 20 response through Week 24 |
|---|
| PsA STUDY 1 |
 |
The results of the components of the ACR response criteria are shown in Table 12.
| PsA STUDY 1 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| STELARA | |||
| Placebo (N = 206) | 45 mg (N = 205) | 90 mg (N = 204) | |
| Number of swollen joints Number of swollen joints counted (0–66) | |||
| Baseline | 15 | 12 | 13 |
| Mean Change at Week 24 | -3 | -5 | -6 |
| Number of tender joints Number of tender joints counted (0–68) | |||
| Baseline | 25 | 22 | 23 |
| Mean Change at Week 24 | -4 | -8 | -9 |
| Subject's assessment of pain Visual analogue scale; 0= best, 10=worst. | |||
| Baseline | 6.1 | 6.2 | 6.6 |
| Mean Change at Week 24 | -0.5 | -2.0 | -2.6 |
| Subject global assessment | |||
| Baseline | 6.1 | 6.3 | 6.4 |
| Mean Change at Week 24 | -0.5 | -2.0 | -2.5 |
| Physician global assessment | |||
| Baseline | 5.8 | 5.7 | 6.1 |
| Mean Change at Week 24 | -1.4 | -2.6 | -3.1 |
| Disability index (HAQ) Disability Index of the Health Assessment Questionnaire; 0 = best, 3 = worst, measures the patient's ability to perform the following: dress/groom, arise, eat, walk, reach, grip, maintain hygiene, and maintain daily activity. | |||
| Baseline | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.2 |
| Mean Change at Week 24 | -0.1 | -0.3 | -0.4 |
| CRP (mg/dL) CRP: (Normal Range 0.0–1.0 mg/dL) | |||
| Baseline | 1.6 | 1.7 | 1.8 |
| Mean Change at Week 24 | 0.01 | -0.5 | -0.8 |
An improvement in enthesitis and dactylitis scores was observed in each STELARA group compared with placebo at Week 24.
Physical Function
STELARA-treated subjects showed improvement in physical function compared to subjects receiving placebo as assessed by HAQ-DI at Week 24. In both trials, the proportion of HAQ-DI responders (≥0.3 improvement in HAQ-DI score) was greater in the STELARA 45 mg and 90 mg groups compared to placebo at Week 24.
Crohn's Disease
STELARA was evaluated in three randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trials in adult subjects with moderately to severely active Crohn's disease (Crohn's Disease Activity Index [CDAI] score of 220 to 450). There were two 8-week intravenous induction trials(CD-1 and CD-2) followed by a 44-week subcutaneous randomized withdrawal maintenance trial (CD-3) representing 52 weeks of therapy. Subjects in CD-1 had failed or were intolerant to treatment with one or more TNF blockers, while subjects in CD-2 had failed or were intolerant to treatment with immunomodulators or corticosteroids, but never failed treatment with a TNF blocker.
Trials CD-1 and CD-2
In trials CD-1 and CD-2, 1409 subjects were randomized, of whom 1368 (CD-1, n=741; CD-2, n=627) were included in the final efficacy analysis. Induction of clinical response (defined as a reduction in CDAI score of greater than or equal to 100 points or CDAI score of less than 150) at Week 6 and clinical remission (defined as a CDAI score of less than 150) at Week 8 were evaluated. In both trials, subjects were randomized to receive a single intravenous administration of STELARA at either approximately 6 mg/kg, placebo (see Table 4 ), or 130 mg (a lower dose than recommended).
In trial CD-1, subjects had failed or were intolerant to prior treatment with a TNF blocker: 29% subjects had an inadequate initial response (primary non-responders), 69% responded but subsequently lost response (secondary non-responders) and 36% were intolerant to a TNF blocker. Of these subjects, 48% failed or were intolerant to one TNF blocker and 52% had failed 2 or 3 prior TNF blockers. At baseline and throughout the trial, approximately 46% of the subjects were receiving corticosteroids and 31% of the subjects were receiving immunomodulators (AZA, 6-MP, MTX). The median baseline CDAI score was 319 in the STELARA approximately 6 mg/kg group and 313 in the placebo group.
In trial CD-2, subjects had failed or were intolerant to prior treatment with corticosteroids (81% of subjects), at least one immunomodulator (6-MP, AZA, MTX; 68% of subjects), or both (49% of subjects). Additionally, 69% never received a TNF blocker and 31% previously received but had not failed a TNF blocker. At baseline, and throughout the trial, approximately 39% of the subjects were receiving corticosteroids and 35% of the subjects were receiving immunomodulators (AZA, 6-MP, MTX). The median baseline CDAI score was 286 in the STELARA and 290 in the placebo group.
In these induction trials, a greater proportion of subjects treated with STELARA (at the recommended dose of approximately 6 mg/kg dose) achieved clinical response at Week 6 and clinical remission at Week 8 compared to placebo (see Table 13 for clinical response and remission rates). Clinical response and remission were significant as early as Week 3 in STELARA-treated subjects and continued to improve through Week 8.
| CD-1 n = 741 | CD-2 n = 627 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Placebo N = 247 | STELARA Infusion dose of STELARA using the weight-based dosage regimen specified in Table 4. N = 249 | Treatment difference and 95% CI | Placebo N = 209 | STELARA N = 209 | Treatment difference and 95% CI | |
| Clinical remission is defined as CDAI score < 150; Clinical response is defined as reduction in CDAI score by at least 100 points or being in clinical remission: 70 point response is defined as reduction in CDAI score by at least 70 points | ||||||
| Clinical Response (100 point), Week 6 | 53 (21%) | 84 (34%) 0.001≤ p < 0.01 | 12% (4%, 20%) | 60 (29%) | 116 (56%) p < 0.001 | 27% (18%, 36%) |
| Clinical Remission, Week 8 | 18 (7%) | 52 (21%) | 14% (8%, 20%) | 41 (20%) | 84 (40%) | 21% (12%, 29%) |
| Clinical Response (100 point), Week 8 | 50 (20%) | 94 (38%) | 18% (10%, 25%) | 67 (32%) | 121 (58%) | 26% (17%, 35%) |
| 70 Point Response, Week 6 | 75 (30%) | 109 (44%) | 13% (5%, 22%) | 81 (39%) | 135 (65%) | 26% (17%, 35%) |
| 70 Point Response, Week 3 | 67 (27%) | 101 (41%) | 13% (5%, 22%) | 66 (32%) | 106 (51%) | 19% (10%, 28%) |
Trial CD-3
The maintenance trial (CD-3), evaluated 388 subjects who achieved clinical response (≥100 point reduction in CDAI score) at Week 8 with either induction dose of STELARA in trials CD-1 or CD-2. Subjects were randomized to receive a subcutaneous maintenance regimen of either 90 mg STELARA every 8 weeks or placebo for 44 weeks (see Table 14 ).
| Placebo The placebo group consisted of subjects who were in response to STELARA and were randomized to receive placebo at the start of maintenance therapy. | 90 mg STELARA every 8 weeks | Treatment difference and 95% CI | |
|---|---|---|---|
| N = 131 Subjects who achieved clinical response to STELARA at the end of the induction trial. | N = 128 | ||
| Clinical remission is defined as CDAI score < 150; Clinical response is defined as reduction in CDAI of at least 100 points or being in clinical remission | |||
| Clinical Remission | 47 (36%) | 68 (53%) p < 0.01 | 17% (5%, 29%) |
| Clinical Response | 58 (44%) | 76 (59%) 0.01≤ p < 0.05 | 15% (3%, 27%) |
| Clinical Remission in patients in remission at the start of maintenance therapy Subjects in remission at the end of maintenance therapy who were in remission at the start of maintenance therapy. This does not account for any other time point during maintenance therapy. | 36/79 (46%) | 52/78 (67%) | 21% (6%, 36%) |
At Week 44, 47% of subjects who received STELARA were corticosteroid-free and in clinical remission, compared to 30% of subjects in the placebo group.
At Week 0 of trial CD-3, 34/56 (61%) STELARA-treated subjects who previously failed or were intolerant to TNF blocker therapies were in clinical remission and 23/56 (41%) of these subjects were in clinical remission at Week 44. In the placebo arm, 27/61 (44%) subjects were in clinical remission at Week 0 while 16/61 (26%) of these subjects were in remission at Week 44.
At Week 0 of trial CD-3, 46/72 (64%) STELARA-treated subjects who had previously failed immunomodulator therapy or corticosteroids (but not TNF blockers) were in clinical remission and 45/72 (63%) of these subjects were in clinical remission at Week 44. In the placebo arm, 50/70 (71%) of these subjects were in clinical remission at Week 0 while 31/70 (44%) were in remission at Week 44. In the subset of these subjects who were also naïve to TNF blockers, 34/52 (65%) of STELARA-treated subjects were in clinical remission at Week 44 as compared to 25/51 (49%) in the placebo arm.
Subjects who were not in clinical response 8 weeks after STELARA induction were not included in the primary efficacy analyses for trial CD-3; however, these subjects were eligible to receive a 90 mg subcutaneous injection of STELARA upon entry into trial CD-3. Of these subjects, 102/219 (47%) achieved clinical response eight weeks later and were followed for the duration of the trial.
Ulcerative Colitis
STELARA was evaluated in two randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trials [UC-1 and UC-2 (NCT02407236)] in adult subjects with moderately to severely active ulcerative colitis who had an inadequate response to or failed to tolerate a biologic (i.e., TNF blocker and/or vedolizumab), corticosteroids, and/or 6-MP or AZA therapy. The 8-week intravenous induction trial (UC-1) was followed by the 44-week subcutaneous randomized withdrawal maintenance trial (UC-2) for a total of 52 weeks of therapy.
Disease assessment was based on the Mayo score, which ranged from 0 to 12 and has four subscores that were each scored from 0 (normal) to 3 (most severe): stool frequency, rectal bleeding, findings on centrally-reviewed endoscopy, and physician global assessment. Moderately to severely active ulcerative colitis was defined at baseline (Week 0) as Mayo score of 6 to 12, including a Mayo endoscopy subscore ≥2. An endoscopy score of 2 was defined by marked erythema, absent vascular pattern, friability, erosions; and a score of 3 was defined by spontaneous bleeding, ulceration. At baseline, subjects had a median Mayo score of 9, with 84% of subjects having moderate disease (Mayo score 6–10) and 15% having severe disease (Mayo score 11–12).
Subjects in these trials may have received other concomitant therapies including aminosalicylates, immunomodulatory agents (AZA, 6-MP, or MTX), and oral corticosteroids (prednisone).
Trial UC-1
In UC-1, 961 subjects were randomized at Week 0 to a single intravenous administration of STELARA of approximately 6 mg/kg, 130 mg (a lower dose than recommended), or placebo. Subjects enrolled in UC-1 had to have failed therapy with corticosteroids, immunomodulators or at least one biologic. A total of 51% had failed at least one biologic and 17% had failed both a TNF blocker and an integrin receptor blocker. Of the total population, 46% had failed corticosteroids or immunomodulators but were biologic-naïve and an additional 3% had previously received but had not failed a biologic. At induction baseline and throughout the trial, approximately 52% subjects were receiving oral corticosteroids, 28% subjects were receiving immunomodulators (AZA, 6-MP, or MTX) and 69% subjects were receiving aminosalicylates.
The primary endpoint was clinical remission at Week 8. Clinical remission with a definition of: Mayo stool frequency subscore of 0 or 1, Mayo rectal bleeding subscore of 0 (no rectal bleeding), and Mayo endoscopy subscore of 0 or 1 (Mayo endoscopy subscore of 0 defined as normal or inactive disease and Mayo subscore of 1 defined as presence of erythema, decreased vascular pattern and no friability) is provided in Table 15.
The secondary endpoints were clinical response, endoscopic improvement, and histologic-endoscopic mucosal improvement. Clinical response with a definition of (≥ 2 points and ≥ 30% decrease in modified Mayo score, defined as 3-component Mayo score without the Physician's Global Assessment, with either a decrease from baseline in the rectal bleeding subscore ≥1 or a rectal bleeding subscore of 0 or 1), endoscopic improvement with a definition of Mayo endoscopy subscore of 0 or 1, and histologic-endoscopic mucosal improvement with a definition of combined endoscopic improvement and histologic improvement of the colon tissue [neutrophil infiltration in <5% of crypts, no crypt destruction, and no erosions, ulcerations, or granulation tissue] are provided in Table 15.
In UC-1, a significantly greater proportion of subjects treated with STELARA (at the recommended dose of approximately 6 mg/kg dose) were in clinical remission and response and achieved endoscopic improvement and histologic-endoscopic mucosal improvement compared to placebo (see Table 15 ).
| Endpoint | Placebo N = 319 | STELARA Infusion dose of STELARA using the weight-based dosage regimen specified in Table 4. N = 322 | Treatment difference and 97.5% CI Adjusted treatment difference (97.5% CI) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | % | N | % | ||
| Clinical Remission Clinical remission was defined as Mayo stool frequency subscore of 0 or 1, Mayo rectal bleeding subscore of 0, and Mayo endoscopy subscore of 0 or 1 (modified so that 1 does not include friability). | 22 | 7% | 62 | 19% | 12% (7%, 18%) p < 0.001 |
| Bio-naïve An additional 7 subjects on placebo and 9 subjects on STELARA (6 mg/kg) had been exposed to, but had not failed, biologics. | 14/151 | 9% | 36/147 | 24% | |
| Prior biologic failure | 7/161 | 4% | 24/166 | 14% | |
| Endoscopic Improvement Endoscopic improvement was defined as Mayo endoscopy subscore of 0 or 1 (modified so that 1 does not include friability). | 40 | 13% | 80 | 25% | 12% (6%, 19%) |
| Bio-naïve | 28/151 | 19% | 43/147 | 29% | |
| Prior biologic failure | 11/161 | 7% | 34/166 | 20% | |
| Clinical Response Clinical response was defined as a decrease from baseline in the modified Mayo score by ≥30% and ≥2 points, with either a decrease from baseline in the rectal bleeding subscore ≥1 or a rectal bleeding subscore of 0 or 1. | 99 | 31% | 186 | 58% | 27% (18%, 35%) |
| Bio-naïve | 55/151 | 36% | 94/147 | 64% | |
| Prior biologic failure | 42/161 | 26% | 86/166 | 52% | |
| Histologic-Endoscopic Mucosal Improvement Histologic-endoscopic mucosal improvement was defined as combined endoscopic improvement (Mayo endoscopy subscore of 0 or 1) and histologic improvement of the colon tissue (neutrophil infiltration in <5% of crypts, no crypt destruction, and no erosions, ulcerations, or granulation tissue). | 26 | 8% | 54 | 17% | 9% (3%, 14%) |
| Bio-naïve | 19/151 | 13% | 30/147 | 20% | |
| Prior biologic failure | 6/161 | 4% | 21/166 | 13% | |
The relationship of histologic-endoscopic mucosal improvement, as defined in UC-1, at Week 8 to disease progression and long-term outcomes was not evaluated during UC-1.
Rectal Bleeding and Stool Frequency Subscores
Decreases in rectal bleeding and stool frequency subscores were observed as early as Week 2 in STELARA-treated subjects.
Trial UC-2
The maintenance trial (UC-2) evaluated 523 subjects who achieved clinical response 8 weeks following the intravenous administration of either induction dose of STELARA in UC-1. These subjects were randomized to receive a subcutaneous maintenance regimen of either 90 mg STELARA every 8 weeks, or every 12 weeks (a lower dose than recommended), or placebo for 44 weeks.
The primary endpoint was the proportion of subjects in clinical remission at Week 44. The secondary endpoints included the proportion of subjects maintaining clinical response at Week 44, the proportion of subjects with endoscopic improvement at Week 44, the proportion of subjects with corticosteroid-free clinical remission at Week 44, and the proportion of subjects maintaining clinical remission at Week 44 among subjects who achieved clinical remission 8 weeks after induction.
Results of the primary and secondary endpoints at Week 44 in subjects treated with STELARA at the recommended dosage (90 mg every 8 weeks) compared to the placebo are shown in Table 16.
| Endpoint | Placebo The placebo group consisted of subjects who were in response to STELARA and were randomized to receive placebo at the start of maintenance therapy. N = 175 Clinical response was defined as a decrease from baseline in the modified Mayo score by ≥30% and ≥2 points, with either a decrease from baseline in the rectal bleeding subscore ≥1 or a rectal bleeding subscore of 0 or 1. | 90 mg STELARA every 8 weeks N = 176 | Treatment difference and 95% CI | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | % | N | % | ||
| Clinical Remission Clinical remission was defined as Mayo stool frequency subscore of 0 or 1, Mayo rectal bleeding subscore of 0, and Mayo endoscopy subscore of 0 or 1 (modified so that 1 does not include friability). | 46 | 26% | 79 | 45% | 19% (9%, 28%) p =<0.001 |
| Bio-naïve An additional 3 subjects on placebo and 6 subjects on STELARA had been exposed to, but had not failed, biologics. | 30/84 | 36% | 39/79 | 49% | |
| Prior biologic failure | 16/88 | 18% | 37/91 | 41% | |
| Maintenance of Clinical Response at Week 44 | 84 | 48% | 130 | 74% | 26% (16%, 36%) |
| Bio-naïve | 49/84 | 58% | 62/79 | 78% | |
| Prior biologic failure | 35/88 | 40% | 64/91 | 70% | |
| Endoscopic Improvement Endoscopic improvement was defined as Mayo endoscopy subscore of 0 or 1 (modified so that 1 does not include friability). | 47 | 27% | 83 | 47% | 20% (11%, 30%) |
| Bio-naïve | 29/84 | 35% | 42/79 | 53% | |
| Prior biologic failure | 18/88 | 20% | 38/91 | 42% | |
| Corticosteroid-free Clinical Remission Corticosteroid-free clinical remission was defined as subjects in clinical remission and not receiving corticosteroids at Week 44. | 45 | 26% | 76 | 43% | 17% (8%, 27%) |
| Bio-naïve | 30/84 | 36% | 38/79 | 48% | |
| Prior biologic failure | 15/88 | 17% | 35/91 | 38% | |
| Maintenance of Clinical Remission at Week 44 in subjects who achieved clinical remission 8 weeks after induction | 18/50 | 36% | 27/41 | 66% | 31% (12%, 50%) p=0.004 |
| Bio-naïve | 12/27 | 44% | 14/20 | 70% | |
| Prior biologic failure | 6/23 | 26% | 12/18 | 67% | |
Other Endpoints
Week 16 Responders to Ustekinumab Induction
Subjects who were not in clinical response 8 weeks after induction with STELARA in UC-1 were not included in the primary efficacy analyses for trial UC-2; however, these subjects were eligible to receive a 90 mg subcutaneous injection of STELARA at Week 8. Of these subjects, 55/101 (54%) achieved clinical response eight weeks later (Week 16) and received STELARA 90 mg subcutaneously every 8 weeks during the UC-2 trial. At Week 44, there were 97/157 (62%) subjects who maintained clinical response and there were 51/157 (32%) who achieved clinical remission.
Histologic-Endoscopic Mucosal Improvement at Week 44
The proportion of subjects achieving histologic-endoscopic mucosal improvement during maintenance treatment in UC-2 was 75/172 (44%) among subjects on STELARA and 40/172 (23%) in subjects on placebo at Week 44. The relationship of histologic-endoscopic mucosal improvement, as defined in UC-2, at Week 44 to progression of disease or long-term outcomes was not evaluated in UC-2.
Endoscopic Normalization
Normalization of endoscopic appearance of the mucosa was defined as a Mayo endoscopic subscore of 0. At Week 8 in UC-1, endoscopic normalization was achieved in 25/322 (8%) of subjects treated with STELARA and 12/319 (4%) of subjects in the placebo group. At Week 44 of UC-2, endoscopic normalization was achieved in 51/176 (29%) of subjects treated with STELARA and in 32/175 (18%) of subjects in placebo group.
HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
STELARA ® (ustekinumab) injection is a sterile, preservative-free, colorless to light yellow solution and may contain a few small translucent or white particles. It is supplied as individually packaged, single-dose prefilled syringes or single-dose vials.
For Subcutaneous Use
Prefilled Syringes
- 45 mg/0.5 mL (NDC 57894-060-03)
- 90 mg/mL (NDC 57894-061-03)
Each prefilled syringe is equipped with a 27 -gauge fixed ½ inch needle, a needle safety guard, and a needle cover that contains dry natural rubber.
Single-dose Vial
- 45 mg/0.5 mL (NDC 57894-060-02)
For Intravenous Infusion
Single-dose Vial
- 130 mg/26 mL (5 mg/mL) (NDC 57894-054-27)
Storage and Stability
Store STELARA vials and prefilled syringes refrigerated between 2 °C to 8 °C (36 °F to 46 °F). Store STELARA vials upright. Keep the product in the original carton to protect from light until the time of use. Do not freeze. Do not shake.
If needed, individual prefilled syringes may be stored at room temperature up to 30 °C (86 °F) for a maximum single period of up to 30 days in the original carton to protect from light. Record the date when the prefilled syringe is first removed from the refrigerator on the carton in the space provided. Once a syringe has been stored at room temperature, do not return to the refrigerator. Discard the syringe if not used within 30 days at room temperature storage. Do not use STELARA after the expiration date on the carton or on the prefilled syringe.
INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE STELARA ( stel ar a ) (ustekinumab) injection, for subcutaneous use
This Instructions for Use contains information on how to inject STELARA using a prefilled syringe.
Read this Instructions for Use before you start using STELARA. A healthcare provider should show you how to prepare and give an injection of STELARA the right way.
If you cannot give the injection:
- ask your healthcare provider to help you, or
- ask someone who has been trained by a healthcare provider to give your injections.
Do not try to inject STELARA until you have been shown how to inject STELARA by a healthcare provider.
Important information You Need to Know Before Injecting STELARA:
- For subcutaneous use only (inject directly under the skin).
- Before you start, check the carton to make sure that it is the right dose. You will have either 45 mg or 90 mg as prescribed by the healthcare provider.
- If the dose is 45 mg, you will receive one 45 mg prefilled syringe.
- If the dose is 90 mg, you will receive either one 90 mg prefilled syringe or two 45 mg prefilled syringes. If you receive two 45 mg prefilled syringes for a 90 mg dose, you will need to give two injections, one right after the other.
- Check the expiration date on the prefilled syringe and carton. If the expiration date has passed or if the prefilled syringe has been kept at room temperature up to 86°F (30°C) for longer than a maximum single period of 30 days or if the prefilled syringe has been stored above 86°F (30°C), do not use it. If the expiration date has passed or if the prefilled syringe has been stored above 86°F (30°C) or at room temperature for longer than 30 days, call the healthcare provider or pharmacist, or call 1-800-526-7736 for help.
- Make sure the syringe is not damaged.
- The needle cover on the prefilled syringe contains latex. Do not handle the needle cover on the STELARA prefilled syringe if you are allergic to latex.
- Check the prefilled syringe for any particles or discoloration. The liquid in the prefilled syringe should look clear and colorless to light yellow with a few small clear or white particles.
- Do not use if it is frozen, discolored, cloudy or has large particles. Get a new prefilled syringe.
- Do not shake the prefilled syringe at any time. Shaking the prefilled syringe may damage the STELARA medicine. If the prefilled syringe has been shaken, do not use it. Get a new prefilled syringe.
- To reduce the risk of accidental needle sticks, each prefilled syringe has a needle guard that is automatically activated to cover the needle after you have given the injection. Do not pull back on the plunger at any time.
Storing STELARA prefilled syringes
- Store STELARA prefilled syringes in the refrigerator between 36°F to 46°F (2°C to 8°C).
- Store STELARA prefilled syringes in the original carton to protect from light.
- Do not freeze STELARA prefilled syringes.
- If needed, STELARA prefilled syringe may be stored at room temperature up to 86°F (30°C) for a maximum single period of up to 30 days in the original carton to protect from light.
- Record the date when the prefilled syringe is removed from the refrigerator on the carton in the space provided.
- After a prefilled syringe has been stored at room temperature, do not return it to the refrigerator.
- Throw away (discard) the prefilled syringe if it is not used within 30 days at room temperature storage.
Keep STELARA and all medicines out of the reach of children.
Gather the supplies you will need to prepare and to give the injection. (See Figure A )
You will need:
- antiseptic wipes
- cotton balls or gauze pads
- adhesive bandage
- your prescribed dose of STELARA (See Figure B )
- FDA-cleared sharps disposal container. See " Step 4: Disposing of the syringes "
Figure A

Figure B
To prevent early activation of the needle safety guard, do not touch the NEEDLE GUARD ACTIVATION CLIPS at any time during use.

Step 1: Preparing the injection
- Choose a well-lit, clean, flat work surface.
- Wash your hands well with soap and warm water.
- Hold the prefilled syringe with the covered needle pointing upward.
Step 2: Preparing the injection site
- Choose an injection site around the stomach area (abdomen), buttocks, upper legs (thighs). If a caregiver is giving the injection, the outer area of the upper arms may also be used. (See Figure C )
- Use a different injection site for each injection. Do not give an injection in an area of the skin that is tender, bruised, red or hard.
- Clean the skin with an antiseptic wipe where you plan to give the injection.
- Do not touch this area again before giving the injection. Let the skin dry before injecting.
- Do not fan or blow on the clean area.
Figure C

•Areas in gray are recommended injection sites.
Step 3: Injecting STELARA
- Remove the needle cover when you are ready to inject STELARA.
- Do not touch the plunger or plunger head while removing the needle cover.
- Hold the body of the prefilled syringe with one hand and pull the needle cover straight off. (see Figure D )
- Put the needle cover in the trash.
- You may also see a drop of liquid at the end of the needle. This is normal.
- Do not touch the needle or let it touch anything.
- Do not use the prefilled syringe if it is dropped without the needle cover in place.
Figure D
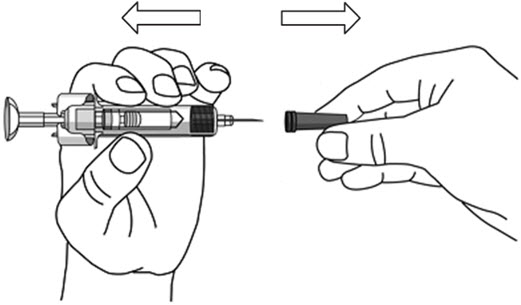
- Hold the body of the prefilled syringe in one hand between the thumb and index fingers. (See Figure E )
Figure E
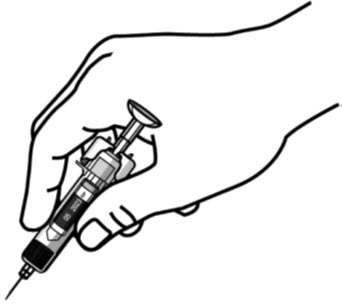
- Do not pull back on the plunger at any time.
- Use the other hand to gently pinch the cleaned area of skin. Hold firmly.
- Use a quick, dart-like motion to insert the needle into the pinched skin at about a 45-degree angle. (See Figure F )
Figure F
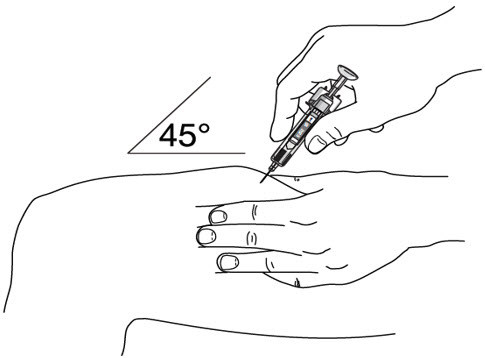
- Inject all of the liquid by using your thumb to push in the plunger until the plunger head is completely between the needle guard wings. (See Figure G )
Figure G
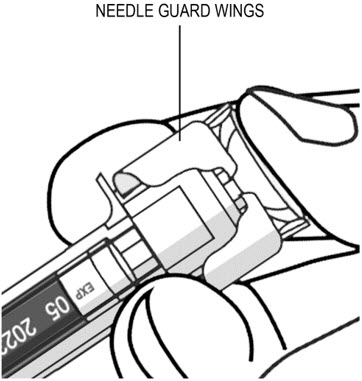
- When the plunger is pushed as far as it will go, keep pressure on the plunger head. Take the needle out of the skin and then let go of the skin.
- Slowly take your thumb off the plunger head. This will let the empty syringe move up until the entire needle is covered by the needle guard. (See Figure H )
Figure H
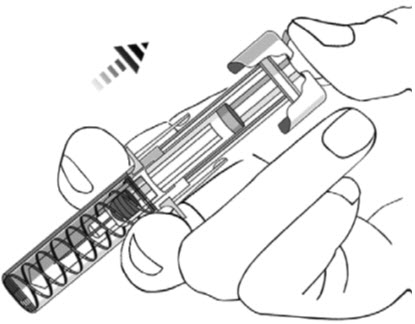
- When the needle is pulled out of the skin, there may be a little bleeding at the injection site. This is normal. You can press a cotton ball or gauze pad to the injection site if needed. Do not rub the injection site. You may cover the injection site with a small adhesive bandage, if necessary.
If the dose is 90 mg, you will receive either one 90 mg prefilled syringe or two 45 mg prefilled syringes. If you receive two 45 mg prefilled syringes for a 90 mg dose, you will need to give a second injection right after the first. Repeat Steps 1 to 3 for the second injection using a new syringe. Choose a different site for the second injection.
Step 4: Disposing of the syringes.
- Put the syringe in a FDA-cleared sharps disposal container right away after use. Do not throw away (dispose of) syringes in your household trash.
- If you do not have a FDA-cleared sharps disposal container, you may use a household container that is:
- made of heavy-duty plastic
- can be closed with a tight-fitting, puncture-resistant lid, without sharps being able to come out.
- upright and stable during use,
- leak-resistant,
- and properly labeled to warn of hazardous waste inside the container.
- When your sharps disposal container is almost full, you will need to follow your community guidelines for the right way to dispose of your sharps disposal container. There may be local or state laws about how to throw away syringes and needles. For more information about safe sharps disposal, and for specific information about sharps disposal in the state that you live in, go to the FDA's website at: http://www.fda.gov/safesharpsdisposal.
- Do not dispose of your sharps disposal container in your household trash unless your community guidelines permit this. Do not recycle your sharps disposal container.
- If you have any questions, talk to your healthcare provider or pharmacist.
Prefilled Syringe Manufactured by: Janssen Biotech, Inc., Horsham, PA 19044, USA License No. 1864 at Baxter Pharmaceutical Solutions, Bloomington, IN 47403 and at Cilag AG, Schaffhausen, Switzerland
This Instructions for Use has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
Revised: 06/2025
© Johnson & Johnson and its affiliates 2025
Mechanism of Action
Ustekinumab is a human IgG1қ monoclonal antibody that binds with specificity to the p40 protein subunit used by both the IL-12 and IL-23 cytokines. IL-12 and IL-23 are naturally occurring cytokines that are involved in inflammatory and immune responses, such as natural killer cell activation and CD4+ T-cell differentiation and activation. In in vitro models, ustekinumab was shown to disrupt IL-12 and IL-23 mediated signaling and cytokine cascades by disrupting the interaction of these cytokines with a shared cell-surface receptor chain, IL-12Rβ1. The cytokines IL-12 and IL-23 have been implicated as important contributors to the chronic inflammation that is a hallmark of Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis. In animal models of colitis, genetic absence or antibody blockade of the p40 subunit of IL-12 and IL-23, the target of ustekinumab, was shown to be protective.