Trijardy XR prior authorization resources
Most recent state uniform prior authorization forms
Brand Resources
Trijardy XR patient education
Patient toolkit
Dosage & administration
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- Assess renal function before initiating and as clinically indicated. Assess volume status and correct volume depletion before initiating. (2.1 )
- Individualize the starting dosage based on the patient's current regimen and renal function. (2.2 , 2.3 )
- Initiation is not recommended in patients with an eGFR less than 45 mL/min/1.73 m 2 , due to the metformin HCl component. (2.3 )
- The maximum recommended dosage of TRIJARDY XR is 25 mg empagliflozin, 5 mg linagliptin and 2,000 mg metformin HCl. (2.2 )
- Take once daily with a meal in the morning. (2.2 )
- Swallow whole; do not split, crush, dissolve, or chew. (2.2 )
- TRIJARDY XR may need to be discontinued at time of, or prior to, iodinated contrast imaging procedures. (2.4 )
- Withhold TRIJARDY XR for at least 3 days, if possible, prior to surgery or procedures associated with prolonged fasting. (2.5 )
Testing Prior to Initiation of TRIJARDY XR
- Assess renal function before initiating TRIJARDY XR and as clinically indicated [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1 , 5.4) ] .
- Assess volume status. In patients with volume depletion, correct this condition before initiating TRIJARDY XR [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4) and Use in Specific Populations (8.5 , 8.6) ].
Recommended Dosage and Administration
- Individualize the starting dosage of TRIJARDY XR based on the patient's current regimen:
- In patients on metformin HCl, with or without linagliptin, switch to TRIJARDY XR containing a similar total daily dosage of metformin HCl and a total daily dosage of empagliflozin 10 mg and linagliptin 5 mg;
- In patients on metformin HCl and any regimen containing empagliflozin, with or without linagliptin, switch to TRIJARDY XR containing a similar total daily dosage of metformin HCl, the same total daily dosage of empagliflozin and linagliptin 5 mg.
- Monitor effectiveness and tolerability, and adjust dosing as appropriate, not to exceed the maximum recommended daily dosage of empagliflozin 25 mg, linagliptin 5 mg and metformin HCl 2,000 mg .
- Take TRIJARDY XR orally, once daily with a meal in the morning.
- Take TRIJARDY XR 10 mg/5 mg/1,000 mg or TRIJARDY XR 25 mg/5 mg/1,000 mg as a single tablet once daily.
- Take TRIJARDY XR 5 mg/2.5 mg/1,000 mg or TRIJARDY XR 12.5 mg/2.5 mg/1,000 mg as two tablets together once daily.
- Swallow TRIJARDY XR tablets whole. Do not split, crush, dissolve, or chew.
Dosage Recommendations in Patients with Renal Impairment
- Initiation of TRIJARDY XR is not recommended in patients with an eGFR less than 45 mL/min/1.73 m 2 , due to the metformin HCl component.
- TRIJARDY XR is contraindicated in patients with an eGFR less than 30 mL/min/1.73 m 2 [see Contraindications (4) , Warnings and Precautions (5.1 , 5.4) , and Use in Specific Populations (8.6) ] .
Discontinuation for Iodinated Contrast Imaging Procedures
Discontinue TRIJARDY XR at the time of, or prior to, an iodinated contrast imaging procedure in patients with an eGFR less than 60 mL/min/1.73 m 2 ; in patients with a history of liver disease, alcoholism or heart failure; or in patients who will be administered intra-arterial iodinated contrast. Re-evaluate eGFR 48 hours after the imaging procedure; restart TRIJARDY XR if renal function is stable [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) ] .
Temporary Interruption for Surgery
Withhold TRIJARDY XR for at least 3 days, if possible, prior to surgery or procedures associated with prolonged fasting. Resume TRIJARDY XR when the patient is clinically stable and has resumed oral intake [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.2) ].
Recommendations Regarding Missed Dose
- If a dose is missed, instruct patients to take the dose as soon as possible.
- Advise patients not to double up the next dose.

By using PrescriberAI, you agree to the AI Terms of Use.
Trijardy XR prescribing information
WARNING: LACTIC ACIDOSIS
Postmarketing cases of metformin-associated lactic acidosis have resulted in death, hypothermia, hypotension, and resistant bradyarrhythmias. The onset of metformin-associated lactic acidosis is often subtle, accompanied only by nonspecific symptoms such as malaise, myalgias, respiratory distress, somnolence, and abdominal pain. Metformin-associated lactic acidosis was characterized by elevated blood lactate levels (>5 mmol/Liter), anion gap acidosis (without evidence of ketonuria or ketonemia), an increased lactate/pyruvate ratio; and metformin plasma levels generally >5 mcg/mL [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) ] .
Risk factors for metformin-associated lactic acidosis include renal impairment, concomitant use of certain drugs (e.g., carbonic anhydrase inhibitors such as topiramate), age 65 years old or greater, having a radiological study with contrast, surgery and other procedures, hypoxic states (e.g., acute congestive heart failure), excessive alcohol intake, and hepatic impairment.
Steps to reduce the risk of and manage metformin-associated lactic acidosis in these high risk groups are provided in the full prescribing information [see Dosage and Administration (2.3) , Contraindications (4) , Warnings and Precautions (5.1) , Drug Interactions (7) , and Use in Specific Populations (8.6 , 8.7) ].
If metformin-associated lactic acidosis is suspected, immediately discontinue TRIJARDY XR and institute general supportive measures in a hospital setting. Prompt hemodialysis is recommended [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) ].
| Warnings and Precautions (5.5 ) | 10/2025 |
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
TRIJARDY XR is a combination of empagliflozin, linagliptin, and metformin hydrochloride (HCl) indicated as an adjunct to diet and exercise to improve glycemic control in adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus .
Empagliflozin is indicated to reduce the risk of cardiovascular (CV) death in adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus and established CV disease [see Clinical Studies (14.2) ] .
Limitations of Use
TRIJARDY XR is not recommended for use to improve glycemic control in patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus. It may increase the risk of diabetic ketoacidosis in these patients [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) ] .
TRIJARDY XR has not been studied in patients with a history of pancreatitis. It is unknown whether patients with a history of pancreatitis are at an increased risk for the development of pancreatitis while using TRIJARDY XR [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3) ].
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- Assess renal function before initiating and as clinically indicated. Assess volume status and correct volume depletion before initiating. (2.1 )
- Individualize the starting dosage based on the patient's current regimen and renal function. (2.2 , 2.3 )
- Initiation is not recommended in patients with an eGFR less than 45 mL/min/1.73 m 2 , due to the metformin HCl component. (2.3 )
- The maximum recommended dosage of TRIJARDY XR is 25 mg empagliflozin, 5 mg linagliptin and 2,000 mg metformin HCl. (2.2 )
- Take once daily with a meal in the morning. (2.2 )
- Swallow whole; do not split, crush, dissolve, or chew. (2.2 )
- TRIJARDY XR may need to be discontinued at time of, or prior to, iodinated contrast imaging procedures. (2.4 )
- Withhold TRIJARDY XR for at least 3 days, if possible, prior to surgery or procedures associated with prolonged fasting. (2.5 )
Testing Prior to Initiation of TRIJARDY XR
- Assess renal function before initiating TRIJARDY XR and as clinically indicated [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1 , 5.4) ] .
- Assess volume status. In patients with volume depletion, correct this condition before initiating TRIJARDY XR [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4) and Use in Specific Populations (8.5 , 8.6) ].
Recommended Dosage and Administration
- Individualize the starting dosage of TRIJARDY XR based on the patient's current regimen:
- In patients on metformin HCl, with or without linagliptin, switch to TRIJARDY XR containing a similar total daily dosage of metformin HCl and a total daily dosage of empagliflozin 10 mg and linagliptin 5 mg;
- In patients on metformin HCl and any regimen containing empagliflozin, with or without linagliptin, switch to TRIJARDY XR containing a similar total daily dosage of metformin HCl, the same total daily dosage of empagliflozin and linagliptin 5 mg.
- Monitor effectiveness and tolerability, and adjust dosing as appropriate, not to exceed the maximum recommended daily dosage of empagliflozin 25 mg, linagliptin 5 mg and metformin HCl 2,000 mg .
- Take TRIJARDY XR orally, once daily with a meal in the morning.
- Take TRIJARDY XR 10 mg/5 mg/1,000 mg or TRIJARDY XR 25 mg/5 mg/1,000 mg as a single tablet once daily.
- Take TRIJARDY XR 5 mg/2.5 mg/1,000 mg or TRIJARDY XR 12.5 mg/2.5 mg/1,000 mg as two tablets together once daily.
- Swallow TRIJARDY XR tablets whole. Do not split, crush, dissolve, or chew.
Dosage Recommendations in Patients with Renal Impairment
- Initiation of TRIJARDY XR is not recommended in patients with an eGFR less than 45 mL/min/1.73 m 2 , due to the metformin HCl component.
- TRIJARDY XR is contraindicated in patients with an eGFR less than 30 mL/min/1.73 m 2 [see Contraindications (4) , Warnings and Precautions (5.1 , 5.4) , and Use in Specific Populations (8.6) ] .
Discontinuation for Iodinated Contrast Imaging Procedures
Discontinue TRIJARDY XR at the time of, or prior to, an iodinated contrast imaging procedure in patients with an eGFR less than 60 mL/min/1.73 m 2 ; in patients with a history of liver disease, alcoholism or heart failure; or in patients who will be administered intra-arterial iodinated contrast. Re-evaluate eGFR 48 hours after the imaging procedure; restart TRIJARDY XR if renal function is stable [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) ] .
Temporary Interruption for Surgery
Withhold TRIJARDY XR for at least 3 days, if possible, prior to surgery or procedures associated with prolonged fasting. Resume TRIJARDY XR when the patient is clinically stable and has resumed oral intake [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.2) ].
Recommendations Regarding Missed Dose
- If a dose is missed, instruct patients to take the dose as soon as possible.
- Advise patients not to double up the next dose.
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
TRIJARDY XR Tablets:
| Empagliflozin Strength | Linagliptin Strength | Metformin HCl Extended-Release Strength | Color/Shape | Tablet Markings |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 mg | 2.5 mg | 1,000 mg | grey, oval-shaped, film-coated tablet | Printed on one side in white ink with the Boehringer Ingelheim company symbol and "395" on the top line and "5/2.5" on the bottom line. |
| 10 mg | 5 mg | 1,000 mg | tan, oval-shaped, film-coated tablet | Printed on one side in white ink with the Boehringer Ingelheim company symbol and "380" on the top line and "10/5" on the bottom line. |
| 12.5 mg | 2.5 mg | 1,000 mg | red, oval-shaped, film-coated tablet | Printed on one side in white ink with the Boehringer Ingelheim company symbol and "385" on the top line and "12.5/2.5" on the bottom line. |
| 25 mg | 5 mg | 1,000 mg | brown, oval-shaped, film-coated tablet | Printed on one side in white ink with the Boehringer Ingelheim company symbol and "390" on the top line and "25/5" on the bottom line. |
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
- Pregnancy: Advise females of the potential risk to a fetus especially during the second and third trimesters. (8.1 )
- Lactation: Not recommended when breastfeeding. (8.2 )
- Females and Males of Reproductive Potential: Advise premenopausal females of the potential for an unintended pregnancy. (8.3 )
- Geriatric Patients: Higher incidence of adverse reactions related to volume depletion and reduced renal function. (8.5 )
- Renal Impairment: Higher incidence of adverse reactions related to reduced renal function. (8.6 )
- Hepatic Impairment: Avoid use in patients with hepatic impairment. (8.7 )
Pregnancy
Risk Summary
Based on animal data showing adverse renal effects from empagliflozin, TRIJARDY XR is not recommended during the second and third trimesters of pregnancy.
The limited available data with TRIJARDY XR, linagliptin, or empagliflozin in pregnant women are not sufficient to determine a drug-associated risk for major birth defects and miscarriage. Published studies with metformin HCl use during pregnancy have not reported a clear association with metformin HCl and major birth defect or miscarriage risk (see Data ) . There are risks to the mother and fetus associated with poorly controlled diabetes in pregnancy (see Clinical Considerations ).
In animal studies, empagliflozin, a component of TRIJARDY XR, resulted in adverse renal changes in rats when administered during a period of renal development corresponding to the late second and third trimesters of human pregnancy. Doses approximately 13-times the maximum clinical dose caused renal pelvic and tubule dilatations that were reversible. No adverse developmental effects were observed when linagliptin or metformin HCl were administered to pregnant rats or rabbits (see Data ).
The estimated background risk of major birth defects is 6% to 10% in women with pre-gestational diabetes with a HbA1c >7 and has been reported to be as high as 20% to 25% in women with HbA1c >10. The estimated background risk of miscarriage for the indicated population is unknown. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2% to 4% and 15% to 20%, respectively.
Clinical Considerations
Disease-associated maternal and/or embryo/fetal risk
Poorly controlled diabetes in pregnancy increases the maternal risk for diabetic ketoacidosis, pre-eclampsia, spontaneous abortions, preterm delivery, and delivery complications. Poorly controlled diabetes increases the fetal risk for major birth defects, stillbirth, and macrosomia related morbidity.
Data
Human Data
Published data from postmarketing studies have not reported a clear association with metformin HCl and major birth defects, miscarriage, or adverse maternal or fetal outcomes when metformin HCl was used during pregnancy. However, these studies cannot definitely establish the absence of any metformin-associated risk because of methodological limitations, including small sample size and inconsistent comparator groups.
Animal Data
Empagliflozin: Empagliflozin dosed directly to juvenile rats from postnatal day (PND) 21 until PND 90 at doses of 1, 10, 30, and 100 mg/kg/day caused increased kidney weights and renal tubular and pelvic dilatation at 100 mg/kg/day, which approximates 13-times the maximum clinical dose of 25 mg, based on AUC. These findings were not observed after a 13-week, drug-free recovery period. These outcomes occurred with drug exposure during periods of renal development in rats that correspond to the late second and third trimester of human renal development.
In embryo-fetal development studies in rats and rabbits, empagliflozin was administered for intervals coinciding with the first trimester period of organogenesis in humans. Doses up to 300 mg/kg/day, which approximates 48-times (rats) and 128-times (rabbits) the maximum clinical dose of 25 mg (based on AUC), did not result in adverse developmental effects. In rats, at higher doses of empagliflozin causing maternal toxicity, malformations of limb bones increased in fetuses at 700 mg/kg/day or 154-times the 25 mg maximum clinical dose. Empagliflozin crosses the placenta and reaches fetal tissues in rats. In the rabbit, higher doses of empagliflozin resulted in maternal and fetal toxicity at 700 mg/kg/day, or 139-times the 25 mg maximum clinical dose.
In pre- and postnatal development studies in pregnant rats, empagliflozin was administered from gestation day 6 through to lactation day 20 (weaning) at up to 100 mg/kg/day (approximately 16-times the 25 mg maximum clinical dose) without maternal toxicity. Reduced body weight was observed in the offspring at greater than or equal to 30 mg/kg/day (approximately 4-times the 25 mg maximum clinical dose).
Linagliptin: No adverse developmental outcome was observed when linagliptin was administered to pregnant Wistar Han rats and Himalayan rabbits during the period of organogenesis at doses up to 240 mg/kg/day and 150 mg/kg/day, respectively. These doses represent approximately 943-times (rats) and 1,943-times (rabbits) the 5 mg maximum clinical dose, based on exposure. No adverse functional, behavioral, or reproductive outcome was observed in offspring following administration of linagliptin to Wistar Han rats from gestation day 6 to lactation day 21 at a dose 49-times the maximum recommended human dose, based on exposure.
Linagliptin crosses the placenta into the fetus following oral dosing in pregnant rats and rabbits.
Metformin HCl: Metformin HCl did not cause adverse developmental effects when administered to pregnant Sprague Dawley rats and rabbits at doses up to 600 mg/kg/day during the period of organogenesis. This represents an exposure of approximately 2- and 6-times a clinical dose of 2,000 mg, based on body surface area (mg/m 2 ) for rats and rabbits, respectively.
Lactation
Risk Summary
There is limited information regarding the presence of TRIJARDY XR, or its components (empagliflozin, linagliptin, or metformin HCl) in human milk, the effects on the breastfed infant, or the effects on milk production. Limited published studies report that metformin is present in human milk (see Data ) . Empagliflozin and linagliptin are present in rat milk (see Data ) . Since human kidney maturation occurs in utero and during the first 2 years of life when lactational exposure may occur, there may be risk to the developing human kidney.
Because of the potential for serious adverse reactions in a breastfed infant, including the potential for empagliflozin to affect postnatal renal development, advise patients that use of TRIJARDY XR is not recommended while breastfeeding .
Data
Published clinical lactation studies report that metformin is present in human milk which resulted in infant doses approximately 0.11% to 1% of the maternal weight-adjusted dosage and a milk/plasma ratio ranging between 0.13 and 1. However, the studies were not designed to definitely establish the risk of use of metformin HCl during lactation because of small sample size and limited adverse event data collected in infants.
Empagliflozin was present at a low level in rat fetal tissues after a single oral dose to the dams at gestation day 18. In rat milk, the mean milk to plasma ratio ranged from 0.634 to 5, and was greater than one from 2 to 24 hours post-dose. The mean maximal milk to plasma ratio of 5 occurred at 8 hours post-dose, suggesting accumulation of empagliflozin in the milk. Juvenile rats directly exposed to empagliflozin showed a risk to the developing kidney (renal pelvic and tubular dilatations) during maturation.
Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
Discuss the potential for unintended pregnancy with premenopausal women as therapy with metformin HCl may result in ovulation in some anovulatory women.
Pediatric Use
Safety and effectiveness of TRIJARDY XR have not been established in pediatric patients.
Geriatric Use
Assess renal function more frequently in TRIJARDY XR-treated geriatric patients because there is a greater risk of empagliflozin-associated intravascular volume contraction and symptomatic hypotension in geriatric patients and there is a greater risk of metformin-associated lactic acidosis in geriatric patients [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1 , 5.4) ].
The recommended dosage for the metformin HCl component of TRIJARDY XR in geriatric patients should usually start at the lower end of the dosage range.
Of the 273 patients treated with the combination of empagliflozin, linagliptin, and metformin HCl to improve glycemic control in adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus, 58 were 65 years of age and older, while 8 were 75 years of age and older. Clinical trials of TRIJARDY XR did not include sufficient numbers of geriatric patients to determine whether they respond differently from younger adult patients.
Empagliflozin
In empagliflozin type 2 diabetes mellitus trials, 2,721 empagliflozin-treated patients were 65 years of age and older and 491 patients were 75 years of age and older. In these trials, volume depletion-related adverse reactions occurred in 2.1%, 2.3%, and 4.4% of patients 75 years of age and older in the placebo, empagliflozin 10 mg, and empagliflozin 25 mg once daily groups, respectively; and urinary tract infections occurred in 10.5%, 15.7%, and 15.1% of patients 75 years of age and older in the placebo, empagliflozin 10 mg, and empagliflozin 25 mg once daily groups, respectively.
Linagliptin
In linagliptin trials, 1,085 linagliptin-treated patients were 65 years of age and older and 131 patients were 75 years of age and older. In these linagliptin trials, no overall differences in safety or effectiveness of linagliptin were observed between geriatric patients and younger adult patients.
Metformin HCl
Clinical trials of metformin HCl did not include sufficient numbers of patients 65 years of age and older to determine whether they respond differently from younger adult patients.
Renal Impairment
TRIJARDY XR should not be initiated in patients with an eGFR less than 45 mL/min/1.73 m 2 due to the metformin HCl component and is contraindicated in patients with severe renal impairment (eGFR less than 30 mL/min/1.73 m 2 ).
Empagliflozin
The glucose lowering benefit of empagliflozin 25 mg decreased in patients with worsening renal function. The risks of renal impairment [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4) ] , volume depletion adverse reactions and urinary tract infection-related adverse reactions increased with worsening renal function.
Metformin HCl
Metformin is substantially excreted by the kidney, and the risk of metformin accumulation and lactic acidosis increases with the degree of renal impairment [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) ] .
Hepatic Impairment
Use of metformin HCl in patients with hepatic impairment has been associated with some cases of lactic acidosis. TRIJARDY XR is not recommended in patients with hepatic impairment [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) ].
CONTRAINDICATIONS
TRIJARDY XR is contraindicated in patients with:
- severe renal impairment (eGFR less than 30 mL/min/1.73 m 2 ) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1 , 5.4) and Use in Specific Populations (8.6) ].
- acute or chronic metabolic acidosis, including diabetic ketoacidosis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) ].
- hypersensitivity to empagliflozin, linagliptin, metformin HCl or any of the excipients in TRIJARDY XR, reactions such as anaphylaxis, angioedema, exfoliative skin conditions, urticaria, or bronchial hyperreactivity have occurred [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8) and Adverse Reactions (6) ] .
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- Diabetic Ketoacidosis in Patients with Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus and Other Ketoacidosis: Consider ketone monitoring in patients at risk of ketoacidosis, as indicated. Assess for ketoacidosis regardless of presenting blood glucose levels and discontinue TRIJARDY XR if ketoacidosis is suspected. Monitor patients for resolution of ketoacidosis before restarting. (5.2 )
- Pancreatitis: There have been reports of acute pancreatitis, including fatal pancreatitis. If pancreatitis is suspected, promptly discontinue TRIJARDY XR. (5.3 )
- Volume Depletion: Before initiating TRIJARDY XR, assess volume status and renal function in patients with impaired renal function, elderly patients, or patients on loop diuretics. Monitor for signs and symptoms during therapy. (5.4 )
- Genitourinary Infections, including Urosepsis, Pyelonephritis, Necrotizing Fasciitis of the Perineum (Fournier's Gangrene), and Genital Mycotic Infections: Monitor patients for signs and symptoms of genitourinary infections and treat promptly, if indicated. Immediately evaluate patients presenting with pain or tenderness, erythema, or swelling in the genital or perineal area, along with fever or malaise, for necrotizing fasciitis and if suspected, discontinue TRIJARDY XR, and promptly institute appropriate medical and/or surgical intervention. (5.5 )
- Hypoglycemia: Consider lowering the dosage of insulin secretagogue or insulin to reduce the risk of hypoglycemia when initiating TRIJARDY XR. (5.6 )
- Lower Limb Amputation: Monitor patients for infections or ulcers of lower limbs, and institute appropriate treatment. (5.7 )
- Hypersensitivity Reactions: Serious hypersensitivity reactions (e.g., anaphylaxis, angioedema, and exfoliative skin conditions) have occurred with empagliflozin and linagliptin. If hypersensitivity reactions occur, discontinue TRIJARDY XR, treat promptly, and monitor until signs and symptoms resolve. (5.8 )
- Vitamin B 12 Deficiency: Metformin may lower vitamin B 12 levels. Measure hematologic parameters annually and vitamin B 12 at 2 to 3 year intervals and manage any abnormalities. (5.9 )
- Arthralgia: Severe and disabling arthralgia has been reported in patients taking linagliptin. Consider as a possible cause for severe joint pain and discontinue TRIJARDY XR if appropriate. (5.10 )
- Bullous Pemphigoid: There have been reports of bullous pemphigoid requiring hospitalization. Tell patients to report development of blisters or erosions. If bullous pemphigoid is suspected, discontinue TRIJARDY XR. (5.11 )
- Heart Failure: Heart failure has been observed with two other members of the DPP-4 inhibitor class. Consider risks and benefits of TRIJARDY XR in patients who have known risk factors for heart failure. Monitor for signs and symptoms. (5.12 )
Lactic Acidosis
There have been postmarketing cases of metformin-associated lactic acidosis, including fatal cases. These cases had a subtle onset and were accompanied by nonspecific symptoms such as malaise, myalgias, abdominal pain, respiratory distress, or increased somnolence; however, hypothermia, hypotension, and resistant bradyarrhythmias have occurred with severe acidosis. Metformin-associated lactic acidosis was characterized by elevated blood lactate concentrations (>5 mmol/Liter), anion gap acidosis (without evidence of ketonuria or ketonemia), and an increased lactate:pyruvate ratio; metformin plasma levels generally >5 mcg/mL. Metformin decreases liver uptake of lactate increasing lactate blood levels, which may increase the risk of lactic acidosis, especially in patients at risk.
If metformin-associated lactic acidosis is suspected, general supportive measures should be instituted promptly in a hospital setting, along with immediate discontinuation of TRIJARDY XR. In TRIJARDY XR-treated patients with a diagnosis or strong suspicion of lactic acidosis, prompt hemodialysis is recommended to correct the acidosis and remove accumulated metformin (metformin is dialyzable, with a clearance of up to 170 mL/minute under good hemodynamic conditions). Hemodialysis has often resulted in reversal of symptoms and recovery .
Educate patients and their families about the symptoms of lactic acidosis and if these symptoms occur instruct them to discontinue TRIJARDY XR and report these symptoms to their healthcare provider.
For each of the known and possible risk factors for metformin-associated lactic acidosis, recommendations to reduce the risk of and manage metformin-associated lactic acidosis are provided below:
Renal Impairment: The postmarketing metformin-associated lactic acidosis cases primarily occurred in patients with significant renal impairment. The risk of metformin accumulation and metformin-associated lactic acidosis increases with the severity of renal impairment because metformin is substantially excreted by the kidney. Clinical recommendations based upon the patient's renal function include [see Dosage and Administration (2.3) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ] :
- Before initiating TRIJARDY XR, obtain an estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR).
- TRIJARDY XR is contraindicated in patients with an eGFR below 30 mL/min/1.73 m 2 [see Contraindications (4) ].
- Obtain an eGFR at least annually in all patients taking TRIJARDY XR. In patients at increased risk for the development of renal impairment (e.g., the elderly), renal function should be assessed more frequently.
Drug Interactions: The concomitant use of TRIJARDY XR with specific drugs may increase the risk of metformin-associated lactic acidosis: those that impair renal function, result in significant hemodynamic change, interfere with acid-base balance or increase metformin accumulation [see Drug Interactions (7) ] . Therefore, consider more frequent monitoring of patients.
Age 65 or Greater: The risk of metformin-associated lactic acidosis increases with the patient's age because elderly patients have a greater likelihood of having hepatic, renal, or cardiac impairment than younger patients. Assess renal function more frequently in elderly patients [see Use in Specific Populations (8.5) ] .
Radiological Studies with Contrast: Administration of intravascular iodinated contrast agents in metformin-treated patients has led to an acute decrease in renal function and the occurrence of lactic acidosis. Stop TRIJARDY XR at the time of, or prior to, an iodinated contrast imaging procedure in patients with an eGFR less than 60 mL/min/1.73 m 2 ; in patients with a history of hepatic impairment, alcoholism, or heart failure; or in patients who will be administered intra-arterial iodinated contrast. Re-evaluate eGFR 48 hours after the imaging procedure, and restart TRIJARDY XR if renal function is stable.
Surgery and Other Procedures: Withholding of food and fluids during surgical or other procedures may increase the risk for volume depletion, hypotension and renal impairment. TRIJARDY XR should be temporarily discontinued while patients have restricted food and fluid intake.
Hypoxic States: Several of the postmarketing cases of metformin-associated lactic acidosis occurred in the setting of acute congestive heart failure (particularly when accompanied by hypoperfusion and hypoxemia). Cardiovascular collapse (shock), acute myocardial infarction, sepsis, and other conditions associated with hypoxemia have been associated with lactic acidosis and may also cause prerenal azotemia. When such events occur, discontinue TRIJARDY XR.
Excessive Alcohol Intake: Alcohol potentiates the effect of metformin on lactate metabolism and this may increase the risk of metformin-associated lactic acidosis. Warn patients against excessive alcohol intake while receiving TRIJARDY XR.
Hepatic Impairment: Patients with hepatic impairment have developed cases of metformin-associated lactic acidosis. This may be due to impaired lactate clearance resulting in higher lactate blood levels. Therefore, avoid use of TRIJARDY XR in patients with clinical or laboratory evidence of hepatic disease.
Diabetic Ketoacidosis in Patients with Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus and Other Ketoacidosis
In patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus, empagliflozin, a component of TRIJARDY XR, significantly increases the risk of diabetic ketoacidosis, a life-threatening event, beyond the background rate. In placebo-controlled trials of patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus, the risk of ketoacidosis was markedly increased in patients who received sodium glucose co-transporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors compared to patients who received placebo and fatal ketoacidosis has occurred with empagliflozin. TRIJARDY XR is not indicated for glycemic control in patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus.
Type 2 diabetes mellitus and pancreatic disorders (e.g., history of pancreatitis or pancreatic surgery) are also risk factors for ketoacidosis. There have been postmarketing reports of fatal events of ketoacidosis in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus using SGLT2 inhibitors, including empagliflozin.
Precipitating conditions for diabetic ketoacidosis or other ketoacidosis include under-insulinization due to insulin dose reduction or missed insulin doses, acute febrile illness, reduced caloric intake, ketogenic diet, surgery, volume depletion, and alcohol abuse.
Signs and symptoms are consistent with dehydration and severe metabolic acidosis and include nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, generalized malaise, and shortness of breath. Blood glucose levels at presentation may be below those typically expected for diabetic ketoacidosis (e.g., less than 250 mg/dL). Ketoacidosis and glucosuria may persist longer than typically expected. Urinary glucose excretion persists for 3 days after discontinuing TRIJARDY XR [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.2) ] ; however, there have been postmarketing reports of ketoacidosis and/or glucosuria lasting greater than 6 days and some up to 2 weeks after discontinuation of SGLT2 inhibitors.
Consider ketone monitoring in patients at risk for ketoacidosis if indicated by the clinical situation. Assess for ketoacidosis regardless of presenting blood glucose levels in patients who present with signs and symptoms consistent with severe metabolic acidosis. If ketoacidosis is suspected, discontinue TRIJARDY XR, promptly evaluate, and treat ketoacidosis, if confirmed. Monitor patients for resolution of ketoacidosis before restarting TRIJARDY XR.
Withhold TRIJARDY XR, if possible, in temporary clinical situations that could predispose patients to ketoacidosis. Resume TRIJARDY XR when the patient is clinically stable and has resumed oral intake [see Dosage and Administration (2.5) ].
Educate all patients on the signs and symptoms of ketoacidosis and instruct patients to discontinue TRIJARDY XR and seek medical attention immediately if signs and symptoms occur.
Pancreatitis
Acute pancreatitis, including fatal pancreatitis, has been reported in patients treated with linagliptin. In the CARMELINA trial [see Clinical Studies (14.3) ] , acute pancreatitis was reported in 9 (0.3%) patients treated with linagliptin and in 5 (0.1%) patients treated with placebo. Two patients treated with linagliptin in the CARMELINA trial had acute pancreatitis with a fatal outcome. There have been postmarketing reports of acute pancreatitis, including fatal pancreatitis, in patients treated with linagliptin.
Take careful notice of potential signs and symptoms of pancreatitis. If pancreatitis is suspected, promptly discontinue TRIJARDY XR and initiate appropriate management. It is unknown whether patients with a history of pancreatitis are at increased risk for the development of pancreatitis while using TRIJARDY XR.
Volume Depletion
Empagliflozin can cause intravascular volume depletion which may sometimes manifest as symptomatic hypotension or acute transient changes in creatinine [see Adverse Reactions (6.1) ]. There have been post-marketing reports of acute kidney injury, some requiring hospitalization and dialysis, in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus receiving SGLT2 inhibitors, including empagliflozin. Patients with impaired renal function (eGFR less than 60 mL/min/1.73 m 2 ), elderly patients, or patients on loop diuretics may be at increased risk for volume depletion or hypotension. Before initiating TRIJARDY XR in patients with one or more of these characteristics, assess volume status and renal function. In patients with volume depletion, correct this condition before initiating TRIJARDY XR. Monitor for signs and symptoms of volume depletion, and renal function after initiating therapy.
Genitourinary Infections, including Urosepsis, Pyelonephritis, Necrotizing Fasciitis of the Perineum (Fournier's Gangrene), and Genital Mycotic Infections
Empagliflozin increases urinary glucose excretion [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.2) ] and increases the risk of genitourinary infections including urinary tract infections and genital mycotic infections in both male and female patients [see Adverse Reactions (6.1) ] .
Serious genitourinary infections, including urosepsis, pyelonephritis, and necrotizing fasciitis of the perineum (Fournier's gangrene, a rare life-threatening infection requiring urgent surgical intervention), have occurred in patients with and without diabetes mellitus receiving SGLT2 inhibitors, including empagliflozin [see Adverse Reactions (6.2) ]. Cases have required hospitalization. In patients with Fournier's gangrene, serious outcomes have included multiple surgeries and death. TRIJARDY XR is only indicated for use in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Patients with history of chronic or recurrent genitourinary infections are more likely to develop genitourinary infections when using TRIJARDY XR. Monitor patients for signs and symptoms of genitourinary infections and treat promptly, if indicated.
Immediately evaluate patients presenting with pain or tenderness, erythema, or swelling in the genital or perineal area, along with fever or malaise, for necrotizing fasciitis. If suspected, discontinue TRIJARDY XR and promptly institute appropriate medical and/or surgical intervention.
Hypoglycemia with Concomitant Use with Insulin and Insulin Secretagogues
Insulin and insulin secretagogues are known to cause hypoglycemia. The risk of hypoglycemia is increased when TRIJARDY XR is used in combination with an insulin secretagogue (e.g., sulfonylurea) or insulin. Therefore, a lower dosage of the insulin secretagogue or insulin may be required to reduce the risk of hypoglycemia when used in combination with TRIJARDY XR.
Lower Limb Amputation
In some clinical studies with SGLT2 inhibitors an imbalance in the incidence of lower limb amputation has been observed. Across four empagliflozin outcome trials, lower limb amputation event rates were 4.3 and 5.0 events per 1,000 patient-years in the placebo group and the empagliflozin 10 mg or 25 mg dose group, respectively, with a HR of 1.05 (95 % CI) (0.81, 1.36).
In a long-term cardio-renal outcome trial, in patients with chronic kidney disease, the occurrence of lower limb amputations was reported with event rates of 2.9, and 4.3 events per 1,000 patient-years in the placebo, and empagliflozin 10 mg treatment arms, respectively. Amputation of the toe and mid-foot were most frequent (21 out of 28 empagliflozin 10 mg treated patients with lower limb amputations), and some involving above and below the knee. Some patients had multiple amputations. TRIJARDY XR is not indicated for the treatment of chronic kidney disease.
Peripheral artery disease, and diabetic foot infection (including osteomyelitis), were the most common precipitating medical events leading to the need for an amputation. The risk of amputation was highest in patients with a baseline history of diabetic foot, peripheral artery disease (including previous amputation) or diabetes.
Counsel patients about the importance of routine preventative foot care. Monitor patients receiving TRIJARDY XR for signs and symptoms of diabetic foot infection (including osteomyelitis), new pain or tenderness, sores or ulcers involving the lower limbs, and institute appropriate treatment.
Hypersensitivity Reactions
There have been postmarketing reports of serious hypersensitivity reactions in patients treated with linagliptin. These reactions include anaphylaxis, angioedema, and exfoliative skin conditions. Onset of these reactions occurred predominantly within the first 3 months after initiation of treatment with linagliptin, with some reports occurring after the first dose.
Angioedema has also been reported with other dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) inhibitors. Use caution in a patient with a history of angioedema to another DPP-4 inhibitor because it is unknown whether such patients will be predisposed to angioedema with TRIJARDY XR.
There have been postmarketing reports of serious hypersensitivity reactions (e.g., angioedema) in patients treated with empagliflozin.
If a hypersensitivity reaction occurs, discontinue TRIJARDY XR, treat promptly per standard of care, and monitor until signs and symptoms resolve. TRIJARDY XR is contraindicated in patients with hypersensitivity to linagliptin, empagliflozin or any of the excipients in TRIJARDY XR [see Contraindications (4) ] .
Vitamin B 12 Deficiency
In metformin HCl clinical trials of 29-week duration, a decrease to subnormal levels of previously normal serum vitamin B 12 levels was observed in approximately 7% of metformin-treated patients. Such decrease, possibly due to interference with B 12 absorption from the B 12 -intrinsic factor complex, may be associated with anemia but appears to be rapidly reversible with discontinuation of metformin or vitamin B 12 supplementation. Certain individuals (those with inadequate vitamin B 12 or calcium intake or absorption) appear to be predisposed to developing subnormal vitamin B 12 levels. Measure hematologic parameters on an annual basis and vitamin B 12 at 2 to 3 year intervals in patients on TRIJARDY XR and manage any abnormalities [see Adverse Reactions (6.1) ].
Severe and Disabling Arthralgia
There have been postmarketing reports of severe and disabling arthralgia in patients taking linagliptin. The time to onset of symptoms following initiation of drug therapy varied from one day to years. Patients experienced relief of symptoms upon discontinuation of the medication. A subset of patients experienced a recurrence of symptoms when restarting the same drug or a different DPP-4 inhibitor. Consider DPP-4 inhibitors as a possible cause for severe joint pain and discontinue drug if appropriate.
Bullous Pemphigoid
Bullous pemphigoid was reported in 7 (0.2%) patients treated with linagliptin compared to none in patients treated with placebo in the CARMELINA trial [see Clinical Studies (14.3) ] , and 3 of these patients were hospitalized due to bullous pemphigoid. Postmarketing cases of bullous pemphigoid requiring hospitalization have been reported with DPP-4 inhibitor use. In reported cases, patients typically recovered with topical or systemic immunosuppressive treatment and discontinuation of the DPP-4 inhibitor. Tell patients to report development of blisters or erosions while receiving TRIJARDY XR. If bullous pemphigoid is suspected, TRIJARDY XR should be discontinued and referral to a dermatologist should be considered for diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
Heart Failure
An association between DPP-4 inhibitor treatment and heart failure has been observed in cardiovascular outcomes trials for two other members of the DPP-4 inhibitor class. These trials evaluated patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease.
Consider the risks and benefits of TRIJARDY XR prior to initiating treatment in patients at risk for heart failure, such as those with a prior history of heart failure and a history of renal impairment, and observe these patients for signs and symptoms of heart failure during therapy. Advise patients of the characteristic symptoms of heart failure and to immediately report such symptoms. If heart failure develops, evaluate and manage according to current standards of care and consider discontinuation of TRIJARDY XR.
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following important adverse reactions are described below and elsewhere in the labeling:
- Lactic Acidosis [see Boxed Warning and Warnings and Precautions (5.1) ]
- Diabetic Ketoacidosis in Patients with Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus and Other Ketoacidosis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) ]
- Pancreatitis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3) ]
- Volume Depletion [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4) ]
- Genitourinary Infections, including Urosepsis, Pyelonephritis, Necrotizing Fasciitis of the Perineum (Fournier's Gangrene), and Genital Mycotic Infections [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5) ]
- Hypoglycemia with Concomitant Use with Insulin and Insulin Secretagogues [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6) ]
- Lower Limb Amputation [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7) ]
- Hypersensitivity Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8) ]
- Vitamin B 12 Deficiency [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9) ]
- Severe and Disabling Arthralgia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.10) ]
- Bullous Pemphigoid [see Warnings and Precautions (5.11) ]
- Heart Failure [see Warnings and Precautions (5.12) ]
Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
Empagliflozin, Linagliptin and Metformin HCl
The safety of concomitantly administered empagliflozin (daily dosage 10 mg or 25 mg), linagliptin (daily dosage 5 mg) and metformin HCl has been evaluated in a total of 686 patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus treated for up to 52 weeks in an active-controlled clinical trial. The most common adverse reactions are shown in Table 1.
| Adverse Reactions | Empagliflozin 10 mg + Linagliptin 5 mg + Metformin HCl (%) n=136 | Empagliflozin 25 mg + Linagliptin 5 mg + Metformin HCl (%) n=137 |
|---|---|---|
| a Predefined grouping, including, but not limited to, urinary tract infection, asymptomatic bacteriuria, cystitis | ||
| Upper respiratory tract infection | 10.3 | 8.0 |
| Urinary tract infection a | 9.6 | 10.2 |
| Nasopharyngitis | 8.1 | 5.8 |
| Diarrhea | 6.6 | 2.2 |
| Constipation | 5.1 | 5.8 |
| Headache | 5.1 | 5.1 |
| Gastroenteritis | 2.9 | 5.8 |
Hypoglycemia
The incidence of hypoglycemia (defined as plasma or capillary glucose of less than 54 mg/dL) was 0.7% in patients receiving empagliflozin 10 mg/linagliptin 5 mg/metformin HCl and 0.7% in patients receiving empagliflozin 25 mg/linagliptin 5 mg/metformin HCl. Events of severe hypoglycemia (requiring assistance regardless of blood glucose) did not occur in this trial.
Empagliflozin
Adverse reactions that occurred in ≥2% of patients receiving empagliflozin and more commonly than in patients given placebo included (10 mg, 25 mg, and placebo): urinary tract infection (9.3%, 7.6%, and 7.6%), female genital mycotic infections (5.4%, 6.4%, and 1.5%), upper respiratory tract infection (3.1%, 4.0%, and 3.8%), increased urination (3.4%, 3.2%, and 1.0%), dyslipidemia (3.9%, 2.9%, and 3.4%), arthralgia (2.4%, 2.3%, and 2.2%), male genital mycotic infections (3.1%, 1.6%, and 0.4%), and nausea (2.3%, 1.1%, and 1.4%).
Thirst (including polydipsia) was reported in 0%, 1.7%, and 1.5% for placebo, empagliflozin 10 mg, and empagliflozin 25 mg, respectively.
Empagliflozin causes an osmotic diuresis, which may lead to intravascular volume contraction and adverse reactions related to volume depletion. Events related to volume depletion (hypotension and syncope) were reported in 3 patients (1.1%) treated with empagliflozin, linagliptin and metformin HCl combination therapy.
Linagliptin
Adverse reactions reported in ≥2% of patients treated with linagliptin 5 mg and more commonly than in patients treated with placebo included: nasopharyngitis (7.0% and 6.1%), diarrhea (3.3% and 3.0%), and cough (2.1% and 1.4%).
Other adverse reactions reported in clinical trials with treatment of linagliptin monotherapy were hypersensitivity (e.g., urticaria, angioedema, localized skin exfoliation, or bronchial hyperreactivity) and myalgia.
In the clinical trial program, pancreatitis was reported in 15.2 cases per 10,000 patient-year exposure while being treated with linagliptin, compared with 3.7 cases per 10,000 patient-year exposure while being treated with comparator (placebo and active comparator, sulfonylurea). Three additional cases of pancreatitis were reported following the last administered dose of linagliptin.
Metformin HCl
The most common (>5%) adverse reactions due to initiation of metformin HCl therapy are diarrhea, nausea/vomiting, flatulence, abdominal discomfort, indigestion, asthenia, and headache.
In a 24-week clinical trial in which extended-release metformin HCl or placebo was added to glyburide therapy, the most common (>5% and greater than placebo) adverse reactions in the combined treatment group were hypoglycemia (13.7% vs 4.9%), diarrhea (12.5% vs 5.6%), and nausea (6.7% vs 4.2%).
Other Adverse Reactions in Clinical Trials with Empagliflozin in Adults
- Genital Mycotic Infections : In the pool of five placebo-controlled clinical trials, the incidence of genital mycotic infections (e.g., vaginal mycotic infection, vaginal infection, genital infection fungal, vulvovaginal candidiasis, and vulvitis) was increased in patients treated with empagliflozin compared to placebo, occurring in 0.9%, 4.1%, and 3.7% of patients randomized to placebo, empagliflozin 10 mg, and empagliflozin 25 mg, respectively. Discontinuation from trial due to genital infection occurred in 0% of placebo-treated patients and 0.2% of patients treated with either empagliflozin 10 mg or 25 mg. Genital mycotic infections occurred more frequently in female than male patients. Phimosis occurred more frequently in male patients treated with empagliflozin 10 mg (less than 0.1%) and empagliflozin 25 mg (0.1%) than placebo (0%).
- Urinary Tract Infections : In the pool of five placebo-controlled clinical trials, the incidence of urinary tract infections (e.g., urinary tract infection, asymptomatic bacteriuria, and cystitis) was increased in patients treated with empagliflozin compared to placebo. Patients with a history of chronic or recurrent urinary tract infections were more likely to experience a urinary tract infection. The rate of treatment discontinuation due to urinary tract infections was 0.1%, 0.2%, and 0.1% for placebo, empagliflozin 10 mg, and empagliflozin 25 mg, respectively. Urinary tract infections occurred more frequently in female patients. The incidence of urinary tract infections in female patients randomized to placebo, empagliflozin 10 mg, and empagliflozin 25 mg was 16.6%, 18.4%, and 17.0%, respectively. The incidence of urinary tract infections in male patients randomized to placebo, empagliflozin 10 mg, and empagliflozin 25 mg was 3.2%, 3.6%, and 4.1%, respectively [see Use in Specific Populations (8.5) ] .
- Lower Limb Amputations : Across four empagliflozin outcome trials, lower limb amputation event rates were 4.3 and 5.0 events per 1,000 patient-years in the placebo group and the empagliflozin 10 mg or 25 mg dose group, respectively, with a HR of 1.05 (95% CI) (0.81, 1.36). In a long-term cardio-renal outcome trial with empagliflozin, in patients with chronic kidney disease, the occurrence of lower limb amputations was reported with event rates of 2.9, and 4.3 events per 1,000 patient-years in the placebo, and empagliflozin 10 mg treatment arms, respectively. TRIJARDY XR is not indicated for the treatment of chronic kidney disease.
Laboratory Test Abnormalities in Clinical Trials of Empagliflozin, Linagliptin, or Metformin HCl
Empagliflozin
Increases in Serum Creatinine and Decreases in eGFR: Initiation of empagliflozin causes an increase in serum creatinine and decrease in eGFR within weeks of starting therapy and then these changes stabilize. In a trial of patients with moderate renal impairment, larger mean changes were observed. In a long-term CV outcomes trial, the increase in serum creatinine and decrease in eGFR generally did not exceed 0.1 mg/dL and -9.0 mL/min/1.73 m 2 , respectively, at Week 4, and reversed after treatment discontinuation, suggesting acute hemodynamic changes may play a role in the renal function changes observed with empagliflozin.
Increase in Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol (LDL-C): Dose-related increases in low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) were observed in patients treated with empagliflozin. LDL-C increased by 2.3%, 4.6%, and 6.5% in patients treated with placebo, empagliflozin 10 mg, and empagliflozin 25 mg, respectively. The range of mean baseline LDL-C levels was 90.3 to 90.6 mg/dL across treatment groups.
Increase in Hematocrit: Median hematocrit decreased by 1.3% in placebo and increased by 2.8% in empagliflozin 10 mg and 2.8% in empagliflozin 25 mg-treated patients. At the end of treatment, 0.6%, 2.7%, and 3.5% of patients with hematocrits initially within the reference range had values above the upper limit of the reference range with placebo, empagliflozin 10 mg, and empagliflozin 25 mg, respectively.
Linagliptin
Increase in Uric Acid: Changes in laboratory values that occurred more frequently in the linagliptin group and ≥1% more than in the placebo group were increases in uric acid (1.3% in the placebo group, 2.7% in the linagliptin group).
Increase in Lipase: In a placebo-controlled clinical trial with linagliptin in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients with micro- or macroalbuminuria, a mean increase of 30% in lipase concentrations from baseline to 24 weeks was observed in the linagliptin arm, compared to a mean decrease of 2% in the placebo arm. Lipase levels above 3 times upper limit of normal were seen in 8.2% compared to 1.7% patients in the linagliptin and placebo arms, respectively.
Increase in Amylase: In a CV safety trial comparing linagliptin versus glimepiride in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus, amylase levels above 3 times upper limit of normal were seen in 1.0% compared to 0.5% of patients in the linagliptin and glimepiride arms, respectively.
The clinical significance of elevations in lipase and amylase with linagliptin is unknown in the absence of other signs and symptoms of pancreatitis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3) ] .
Metformin HCl
Decrease in Vitamin B 12 : In metformin HCl clinical trials of 29-week duration, a decrease to subnormal levels of previously normal serum vitamin B 12 levels was observed in approximately 7% of patients.
Postmarketing Experience
Additional adverse reactions have been identified during postapproval use of linagliptin, empagliflozin, or metformin HCl. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is generally not possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
- Gastrointestinal Disorders: Acute pancreatitis, including fatal pancreatitis [see Indications and Usage (1) ] , mouth ulceration, stomatitis
- Immune System Disorders: Hypersensitivity reactions including anaphylaxis, angioedema, and exfoliative skin conditions
- Infections: Necrotizing fasciitis of the perineum (Fournier's gangrene), urosepsis and pyelonephritis
- Metabolism and Nutrition Disorders: Ketoacidosis
- Musculoskeletal and Connective Tissue Disorders: Rhabdomyolysis, severe and disabling arthralgia
- Renal and Urinary Disorders: Acute kidney injury
- Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue Disorders: Bullous pemphigoid, skin reactions (e.g., rash, urticaria)
- Hepatobiliary Disorders: Cholestatic, hepatocellular, and mixed hepatocellular liver injury
DRUG INTERACTIONS
Table 2 describes clinically relevant interactions with TRIJARDY XR.
| Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors | |
| Clinical Impact | Topiramate or other carbonic anhydrase inhibitors (e.g., zonisamide, acetazolamide or dichlorphenamide) frequently causes a decrease in serum bicarbonate and induce non-anion gap, hyperchloremic metabolic acidosis. Concomitant use of these drugs with TRIJARDY XR may increase the risk of lactic acidosis. |
| Intervention | Consider more frequent monitoring of these patients. |
| Drugs that Reduce Metformin Clearance | |
| Clinical Impact | Concomitant use of drugs that interfere with common renal tubular transport systems involved in the renal elimination of metformin (e.g., organic cationic transporter-2 [OCT2] / multidrug and toxin extrusion [MATE] inhibitors such as ranolazine, vandetanib, dolutegravir, and cimetidine) could increase systemic exposure to metformin and may increase the risk for lactic acidosis [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ] . |
| Intervention | Consider the benefits and risks of concomitant use. |
| Alcohol | |
| Clinical Impact | Alcohol is known to potentiate the effect of metformin on lactate metabolism. |
| Intervention | Warn patients against excessive alcohol intake while receiving TRIJARDY XR. |
| Diuretics | |
| Clinical Impact | Coadministration of empagliflozin with diuretics resulted in increased urine volume and frequency of voids, which might enhance the potential for volume depletion. |
| Intervention | Before initiating TRIJARDY XR, assess volume status and renal function. In patients with volume depletion, correct this condition before initiating TRIJARDY XR. Monitor for signs and symptoms of volume depletion, and renal function after initiating therapy. |
| Insulin or Insulin Secretagogues | |
| Clinical Impact | The risk of hypoglycemia is increased when TRIJARDY XR is used in combination with an insulin secretagogue (e.g., sulfonylurea) or insulin. |
| Intervention | Coadministration of TRIJARDY XR with an insulin secretagogue (e.g., sulfonylurea) or insulin may require lower dosages of the insulin secretagogue or insulin to reduce the risk of hypoglycemia. |
| Drugs Affecting Glycemic Control | |
| Clinical Impact | Certain drugs tend to produce hyperglycemia and may lead to loss of glycemic control. These drugs include the thiazides and other diuretics, corticosteroids, phenothiazines, thyroid products, estrogens, oral contraceptives, phenytoin, nicotinic acid, sympathomimetics, calcium channel blocking drugs, and isoniazid. |
| Intervention | When such drugs are administered to a patient receiving TRIJARDY XR, the patient should be closely observed to maintain adequate glycemic control. When such drugs are withdrawn from a patient receiving TRIJARDY XR, the patient should be observed closely for hypoglycemia. |
| Lithium | |
| Clinical Impact | Concomitant use of an SGLT2 inhibitor with lithium may decrease serum lithium concentrations. |
| Intervention | Monitor serum lithium concentration more frequently during TRIJARDY XR initiation and dosage changes. |
| Inducers of P-glycoprotein or CYP3A4 Enzymes | |
| Clinical Impact | Rifampin decreased linagliptin exposure, suggesting that the efficacy of linagliptin may be reduced when administered in combination with a strong P-gp or CYP3A4 inducer. |
| Intervention | Use of alternative treatments is strongly recommended when linagliptin is to be administered with a strong P-gp or CYP3A4 inducer. |
| Positive Urine Glucose Test | |
| Clinical Impact | SGLT2 inhibitors increase urinary glucose excretion and will lead to positive urine glucose tests. |
| Intervention | Monitoring glycemic control with urine glucose tests is not recommended in patients taking SGLT2 inhibitors. Use alternative methods to monitor glycemic control. |
| Interference with 1,5-anhydroglucitol (1,5-AG) Assay | |
| Clinical Impact | Measurements of 1,5-AG are unreliable in assessing glycemic control in patients taking SGLT2 inhibitors. |
| Intervention | Monitoring glycemic control with 1,5-AG assay is not recommended. Use alternative methods to monitor glycemic control. |
DESCRIPTION
TRIJARDY XR tablets for oral use contain: empagliflozin, linagliptin, and metformin HCl.
Empagliflozin
Empagliflozin is an inhibitor of the SGLT2.
The chemical name of empagliflozin is D-Glucitol,1,5-anhydro-1-C-[4-chloro-3-[[4-[[(3S)-tetrahydro-3-furanyl]oxy]phenyl]methyl]phenyl]-, (1S).
The molecular formula is C 23 H 27 ClO 7 and the molecular weight is 450.91. The structural formula is:
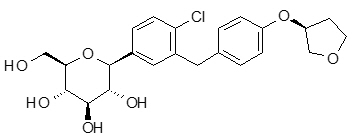
Empagliflozin is a white to yellowish, non-hygroscopic powder. It is very slightly soluble in water, sparingly soluble in methanol, slightly soluble in ethanol and acetonitrile, soluble in 50% acetonitrile/water, and practically insoluble in toluene.
Linagliptin
Linagliptin is an inhibitor of the DPP-4 enzyme.
The chemical name of linagliptin is 1H-Purine-2,6-dione, 8-[(3R)-3-amino-1-piperidinyl]-7-(2-butyn-1-yl)-3,7-dihydro-3-methyl-1-[(4-methyl-2-quinazolinyl)methyl]-
The molecular formula is C 25 H 28 N 8 O 2 and the molecular weight is 472.54. The structural formula is:
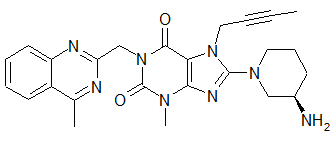
Linagliptin is a white to yellowish, not or only slightly hygroscopic solid substance. It is very slightly soluble in water. Linagliptin is soluble in methanol, sparingly soluble in ethanol, very slightly soluble in isopropanol, and very slightly soluble in acetone.
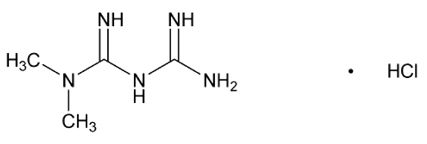
Metformin HCl
Metformin HCl ( N,N -dimethylimidodicarbonimidic diamide hydrochloride) is a biguanide. Metformin HCl is a white to off-white crystalline compound with a molecular formula of C 4 H 11 N 5 ∙HCl and a molecular weight of 165.63. Metformin HCl is freely soluble in water and is practically insoluble in acetone, ether, and chloroform. The pKa of metformin is 12.4. The pH of a 1% aqueous solution of metformin hydrochloride is 6.68. The structural formula is:
TRIJARDY XR
Each film-coated tablet of TRIJARDY XR consists of an extended-release metformin HCl core tablet that is coated with the immediate-release drug substances: empagliflozin and linagliptin.
TRIJARDY XR tablets for oral administration are available in four strengths containing:
- 5 mg empagliflozin, 2.5 mg linagliptin, and 1,000 mg metformin HCl (equivalent to 779.86 mg of metformin)
- 10 mg empagliflozin, 5 mg linagliptin, and 1,000 mg metformin HCl (equivalent to 779.86 mg of metformin)
- 12.5 mg empagliflozin, 2.5 mg linagliptin, and 1,000 mg metformin HCl (equivalent to 779.86 mg of metformin)
- 25 mg empagliflozin, 5 mg linagliptin, and 1,000 mg metformin HCl (equivalent to 779.86 mg of metformin)
Each film-coated tablet of TRIJARDY XR contains the following inactive ingredients: Tablet Core: hypromellose, magnesium stearate, and polyethylene oxide. Film Coatings and Printing Ink: ammonium hydroxide, arginine, carnauba wax, ferric oxide yellow and ferric oxide red (10 mg/5 mg/1,000 mg), ferrosoferric oxide and ferric oxide red (12.5 mg/2.5 mg/1,000 mg), ferrosoferric oxide and ferric oxide yellow (5 mg/2.5 mg/1,000 mg and 25 mg/5 mg/1,000 mg), hydroxypropyl cellulose, hypromellose, isopropyl alcohol, n-butyl alcohol, polyethylene glycol, propylene glycol, purified water, shellac glaze, talc, and titanium dioxide.
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Mechanism of Action
TRIJARDY XR
TRIJARDY XR contains: empagliflozin, a SGLT2 inhibitor, linagliptin, a DPP-4 inhibitor, and metformin HCl, a biguanide.
Empagliflozin
Empagliflozin is an inhibitor of SGLT2, the predominant transporter responsible for reabsorption of glucose from the glomerular filtrate back into the circulation. By inhibiting SGLT2, empagliflozin reduces renal reabsorption of filtered glucose and lowers the renal threshold for glucose, and thereby increases urinary glucose excretion.
Linagliptin
Linagliptin is an inhibitor of DPP-4, an enzyme that degrades the incretin hormones glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) and glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP). Thus, linagliptin increases the concentrations of active incretin hormones, stimulating the release of insulin in a glucose-dependent manner and decreasing the levels of glucagon in the circulation. Both incretin hormones are involved in the physiological regulation of glucose homeostasis. Incretin hormones are secreted at a low basal level throughout the day and levels rise immediately after meal intake. GLP-1 and GIP increase insulin biosynthesis and secretion from pancreatic beta cells in the presence of normal and elevated blood glucose levels. Furthermore, GLP-1 also reduces glucagon secretion from pancreatic alpha cells, resulting in a reduction in hepatic glucose output.
Metformin HCl
Metformin HCl is an antihyperglycemic agent which improves glucose tolerance in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus, lowering both basal and postprandial plasma glucose. Metformin HCl decreases hepatic glucose production, decreases intestinal absorption of glucose, and improves insulin sensitivity by increasing peripheral glucose uptake and utilization. With metformin HCl therapy, insulin secretion remains unchanged while fasting insulin levels and day-long plasma insulin response may decrease.
Pharmacodynamics
Empagliflozin
Urinary Glucose Excretion
In patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus, urinary glucose excretion increased immediately following a dose of empagliflozin and was maintained at the end of a 4-week treatment period averaging at approximately 64 grams per day with 10 mg empagliflozin and 78 grams per day with 25 mg empagliflozin once daily. Data from single oral doses of empagliflozin in healthy subjects indicate that, on average, the elevation in urinary glucose excretion approaches baseline by about 3 days for the 10 mg and 25 mg doses.
Urinary Volume
In a 5-day study, mean 24-hour urine volume increase from baseline was 341 mL on Day 1 and 135 mL on Day 5 of empagliflozin 25 mg once daily treatment.
Cardiac Electrophysiology
In a randomized, placebo-controlled, active-comparator, crossover study, 30 healthy subjects were administered a single oral dose of empagliflozin 25 mg, empagliflozin 200 mg (8 times the maximum recommended dose), moxifloxacin, and placebo. No increase in QTc was observed with either 25 mg or 200 mg empagliflozin.
Linagliptin
Linagliptin binds to DPP-4 in a reversible manner and increases the concentrations of incretin hormones. Linagliptin glucose-dependently increases insulin secretion and lowers glucagon secretion, thus resulting in a better regulation of the glucose homeostasis. Linagliptin binds selectively to DPP-4 and selectively inhibits DPP-4, but not DPP-8 or DPP-9 activity in vitro at concentrations approximating therapeutic exposures.
Cardiac Electrophysiology
In a randomized, placebo-controlled, active-comparator, 4-way crossover study, 36 healthy subjects were administered a single oral dose of linagliptin 5 mg, linagliptin 100 mg (20 times the recommended dose), moxifloxacin, and placebo. No increase in QTc was observed with either the recommended dose of 5 mg or the 100 mg dose. At the 100 mg dose, peak linagliptin plasma concentrations were approximately 38-fold higher than the peak concentrations following a 5-mg dose.
Pharmacokinetics
TRIJARDY XR
Administration of TRIJARDY XR with food resulted in no change in overall exposure of empagliflozin or linagliptin. For metformin HCl extended-release, high-fat meals increased systemic exposure (as measured by area-under-the-curve [AUC]) by approximately 70% relative to fasting, while C max is not affected. Meals prolonged T max by approximately 3 hours.
Empagliflozin
The pharmacokinetics of empagliflozin has been characterized in healthy volunteers and patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and no clinically relevant differences were noted between the two populations. The steady-state mean plasma AUC and C max were 1,870 nmol∙h/L and 259 nmol/L, respectively, with 10 mg empagliflozin once daily treatment, and 4,740 nmol∙h/L and 687 nmol/L, respectively, with 25 mg empagliflozin once daily treatment. Systemic exposure of empagliflozin increased in a dose-proportional manner in the therapeutic dose range. Empagliflozin does not appear to have time-dependent pharmacokinetic characteristics. Following once-daily dosing, up to 22% accumulation, with respect to plasma AUC, was observed at steady-state.
Absorption
After oral administration, peak plasma concentrations of empagliflozin were reached at 1.5 hours post-dose. Administration of 25 mg empagliflozin after intake of a high-fat and high-calorie meal resulted in slightly lower exposure; AUC decreased by approximately 16% and C max decreased by approximately 37%, compared to fasted condition. The observed effect of food on empagliflozin pharmacokinetics was not considered clinically relevant and empagliflozin may be administered with or without food.
Distribution
The apparent steady-state volume of distribution was estimated to be 73.8 L based on a population pharmacokinetic analysis. Following administration of an oral [ 14 C]-empagliflozin solution to healthy subjects, the red blood cell partitioning was approximately 36.8% and plasma protein binding was 86.2%.
Elimination
The apparent terminal elimination half-life of empagliflozin was estimated to be 12.4 h and apparent oral clearance was 10.6 L/h based on the population pharmacokinetic analysis.
Metabolism
No major metabolites of empagliflozin were detected in human plasma and the most abundant metabolites were three glucuronide conjugates (2-O-, 3-O-, and 6-O-glucuronide). Systemic exposure of each metabolite was less than 10% of total drug-related material. In vitro studies suggested that the primary route of metabolism of empagliflozin in humans is glucuronidation by the uridine 5'-diphospho-glucuronosyltransferases UGT2B7, UGT1A3, UGT1A8, and UGT1A9.
Excretion
Following administration of an oral [ 14 C]-empagliflozin solution to healthy subjects, approximately 95.6% of the drug-related radioactivity was eliminated in feces (41.2%) or urine (54.4%). The majority of drug-related radioactivity recovered in feces was unchanged parent drug and approximately half of drug-related radioactivity excreted in urine was unchanged parent drug.
Linagliptin
Absorption
The absolute bioavailability of linagliptin is approximately 30%. A high-fat meal reduced C max by 15% and increased AUC by 4%; this effect is not clinically relevant. Linagliptin may be administered with or without food.
Distribution
The mean apparent volume of distribution at steady-state following a single intravenous dose of linagliptin 5 mg to healthy subjects is approximately 1,110 L, indicating that linagliptin extensively distributes to the tissues. Plasma protein binding of linagliptin is concentration-dependent, decreasing from about 99% at 1 nmol/L to 75% to 89% at ≥30 nmol/L, reflecting saturation of binding to DPP-4 with increasing concentration of linagliptin. At high concentrations, where DPP-4 is fully saturated, 70% to 80% of linagliptin remains bound to plasma proteins and 20% to 30% is unbound in plasma. Plasma binding is not altered in patients with renal or hepatic impairment.
Elimination
Linagliptin has a terminal half-life of about 200 hours at steady-state, though the accumulation half-life is about 11 hours. Renal clearance at steady-state was approximately 70 mL/min.
Metabolism
Following oral administration, the majority (about 90%) of linagliptin is excreted unchanged, indicating that metabolism represents a minor elimination pathway. A small fraction of absorbed linagliptin is metabolized to a pharmacologically inactive metabolite, which shows a steady-state exposure of 13.3% relative to linagliptin.
Excretion
Following administration of an oral [ 14 C]-linagliptin dose to healthy subjects, approximately 85% of the administered radioactivity was eliminated via the enterohepatic system (80%) or urine (5%) within 4 days of dosing.
Metformin HCl extended-release
Absorption
Following a single oral dose of 1,000 mg (2 × 500 mg tablets) metformin HCl extended-release after a meal, the time to reach maximum plasma metformin concentration (T max ) is achieved at approximately 7 to 8 hours. In both single- and multiple-dose studies in healthy subjects, once daily 1,000 mg (2 × 500 mg tablets) dosing provides equivalent systemic exposure, as measured by AUC, and up to 35% higher C max of metformin relative to the immediate-release given as 500 mg twice daily.
Single oral doses of metformin HCl extended-release from 500 mg to 2,500 mg resulted in less than proportional increase in both AUC and C max . Low-fat and high-fat meals increased the systemic exposure (as measured by AUC) from metformin extended-release tablets by about 38% and 73%, respectively, relative to fasting. Both meals prolonged metformin T max by approximately 3 hours but C max , was not affected.
Distribution
The apparent volume of distribution (V/F) of metformin following single oral doses of immediate-release metformin HCl tablets 850 mg averaged 654±358 L. Metformin is negligibly bound to plasma proteins. Metformin partitions into erythrocytes, most likely as a function of time.
Elimination
Metformin has a plasma elimination half-life of approximately 6.2 hours. In blood, the elimination half-life is approximately 17.6 hours, suggesting that the erythrocyte mass may be a compartment of distribution.
Metabolism
Intravenous single-dose studies in normal subjects demonstrate that metformin does not undergo hepatic metabolism (no metabolites have been identified in humans) nor biliary excretion.
Excretion
Following oral administration, approximately 90% of the absorbed drug is excreted via the renal route within the first 24 hours. Renal clearance is approximately 3.5 times greater than creatinine clearance, which indicates that tubular secretion is the major route of metformin elimination.
Specific Populations
Geriatric Patients
Empagliflozin : Age did not have a clinically meaningful impact on the pharmacokinetics of empagliflozin based on a population pharmacokinetic analysis [see Use in Specific Populations (8.5) ] .
Metformin HCl : Limited data from controlled pharmacokinetic studies of metformin HCl in healthy elderly subjects suggest that total plasma clearance of metformin is decreased, the half-life is prolonged, and C max is increased, compared with healthy young subjects. From these data, it appears that the change in metformin pharmacokinetics with aging is primarily accounted for by a change in renal function.
Effects of Age, Body Mass Index, Gender, and Race
Empagliflozin : Age, body mass index (BMI), gender and race (Asians versus primarily Whites) do not have a clinically meaningful effect on pharmacokinetics of empagliflozin.
Linagliptin : Based on the population PK analysis, age, body mass index (BMI), gender and race do not have a clinically meaningful effect on pharmacokinetics of linagliptin [see Use in Specific Populations (8.5) ] .
Metformin HCl : Metformin pharmacokinetic parameters did not differ significantly between normal subjects and patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus when analyzed according to gender. Similarly, in controlled clinical studies in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus, the antihyperglycemic effect of metformin HCl was comparable in males and females.
No studies of metformin pharmacokinetic parameters according to race have been performed. In controlled clinical studies of metformin HCl in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus, the antihyperglycemic effect was comparable in Whites (n=249), Blacks or African Americans (n=51), and Hispanics or Latinos (n=24).
Patients with Renal Impairment
TRIJARDY XR : Studies characterizing the pharmacokinetics of empagliflozin, linagliptin, and metformin HCl after administration of TRIJARDY XR in renally impaired patients have not been performed.
Empagliflozin : In patients with mild (eGFR: 60 to less than 90 mL/min/1.73 m 2 ), moderate (eGFR: 30 to less than 60 mL/min/1.73 m 2 ), and severe (eGFR: less than 30 mL/min/1.73 m 2 ) renal impairment and patients on dialysis due to kidney failure, AUC of empagliflozin increased by approximately 18%, 20%, 66%, and 48%, respectively, compared to subjects with normal renal function. Peak plasma levels of empagliflozin were similar in patients with moderate renal impairment and patients on dialysis due to kidney failure compared to subjects with normal renal function. Peak plasma levels of empagliflozin were roughly 20% higher in patients with mild and severe renal impairment, as compared to subjects with normal renal function. Population pharmacokinetic analysis showed that the apparent oral clearance of empagliflozin decreased, with a decrease in eGFR leading to an increase in drug exposure. However, the fraction of empagliflozin that was excreted unchanged in urine, and urinary glucose excretion, declined with decrease in eGFR.
Linagliptin : An open-label pharmacokinetic study evaluated the pharmacokinetics of linagliptin 5 mg in male and female patients with varying degrees of chronic renal impairment. The study included 6 healthy subjects with normal renal function (creatinine clearance [CrCl] ≥80 mL/min), 6 patients with mild renal impairment (CrCl 50 to <80 mL/min), 6 patients with moderate renal impairment (CrCl 30 to <50 mL/min), 10 patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and severe renal impairment (CrCl <30 mL/min), and 11 patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and normal renal function. Creatinine clearance was measured by 24-hour urinary creatinine clearance measurements or estimated from serum creatinine based on the Cockcroft-Gault formula.
Under steady-state conditions, linagliptin exposure in patients with mild renal impairment was comparable to healthy subjects.
In patients with moderate renal impairment under steady-state conditions, mean exposure of linagliptin increased (AUC τ,ss by 71% and C max by 46%), compared with healthy subjects. This increase was not associated with a prolonged accumulation half-life, terminal half-life, or an increased accumulation factor. Renal excretion of linagliptin was below 5% of the administered dose and was not affected by decreased renal function. Patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and severe renal impairment showed steady-state exposure approximately 40% higher than that of patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and normal renal function (increase in AUC τ,ss by 42% and C max by 35%). For both type 2 diabetes mellitus groups, renal excretion was below 7% of the administered dose.
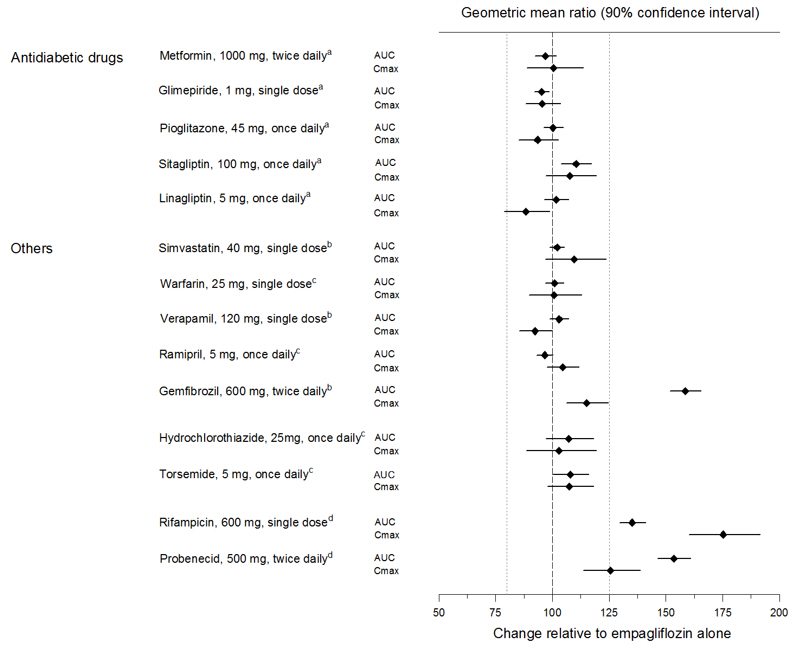
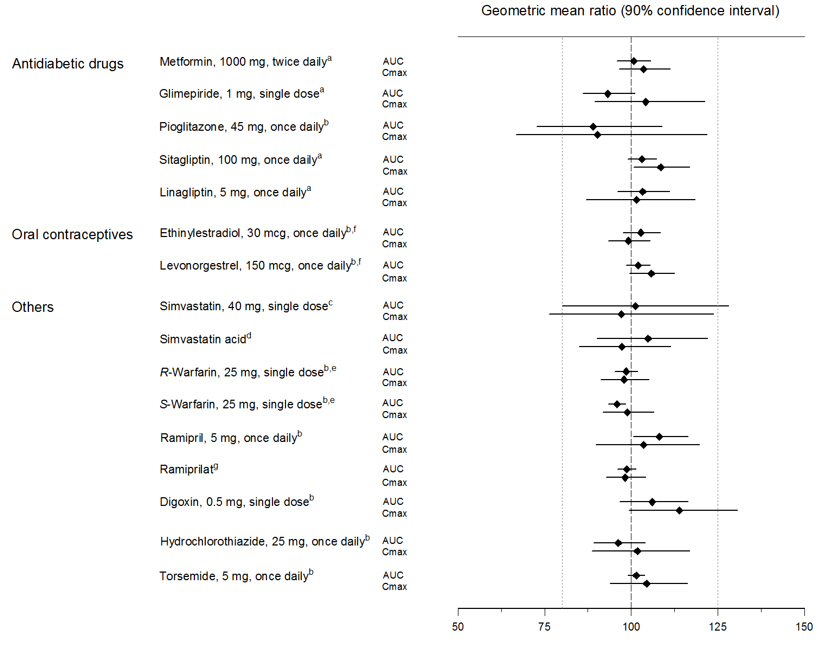
These findings were further supported by the results of population pharmacokinetic analyses.
Metformin HCl : In patients with decreased renal function, the plasma and blood half-life of metformin is prolonged and the renal clearance is decreased [see Contraindications (4) and Warnings and Precautions (5.1) ] .
Patients with Hepatic Impairment
TRIJARDY XR : Studies characterizing the pharmacokinetics of empagliflozin, linagliptin, and metformin after administration of TRIJARDY XR in hepatically impaired patients have not been performed.
Empagliflozin : In patients with mild, moderate, and severe hepatic impairment according to the Child-Pugh classification, AUC of empagliflozin increased by approximately 23%, 47%, and 75% and C max increased by approximately 4%, 23%, and 48%, respectively, compared to subjects with normal hepatic function.
Linagliptin : In patients with mild hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh class A) steady-state exposure (AUC τ,ss ) of linagliptin was approximately 25% lower and C max,ss was approximately 36% lower than in healthy subjects. In patients with moderate hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh class B), AUC ss of linagliptin was about 14% lower and C max,ss was approximately 8% lower than in healthy subjects. Patients with severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh class C) had comparable exposure of linagliptin in terms of AUC 0-24 and approximately 23% lower C max compared with healthy subjects. Reductions in the pharmacokinetic parameters seen in patients with hepatic impairment did not result in reductions in DPP-4 inhibition.
Metformin HCl : No pharmacokinetic studies of metformin have been conducted in patients with hepatic impairment.
Drug Interaction Studies
Pharmacokinetic drug interaction studies with TRIJARDY XR have not been performed; however, such studies have been conducted with the individual components of TRIJARDY XR (empagliflozin, linagliptin, and metformin HCl).
Empagliflozin
In vitro Assessment of Drug Interactions
Empagliflozin does not inhibit, inactivate, or induce CYP450 isoforms. In vitro data suggest that the primary route of metabolism of empagliflozin in humans is glucuronidation by the uridine 5'-diphospho-glucuronosyltransferases UGT1A3, UGT1A8, UGT1A9 and UGT2B7. Empagliflozin does not inhibit UGT1A1, UGT1A3, UGT1A8, UGT1A9, or UGT2B7. Therefore, no effect of empagliflozin is anticipated on concomitantly administered drugs that are substrates of the major CYP450 isoforms or UGT1A1, UGT1A3, UGT1A8, UGT1A9, or UGT2B7. The effect of UGT induction (e.g., induction by rifampicin or any other UGT enzyme inducer) on empagliflozin exposure has not been evaluated.
Empagliflozin is a substrate for P-glycoprotein (P-gp) and breast cancer resistance protein (BCRP), but it does not inhibit these efflux transporters at therapeutic doses. Based on in vitro studies, empagliflozin is considered unlikely to cause interactions with drugs that are P-gp substrates. Empagliflozin is a substrate of the human uptake transporters OAT3, OATP1B1, and OATP1B3, but not OAT1 and OCT2. Empagliflozin does not inhibit any of these human uptake transporters at clinically relevant plasma concentrations and, therefore, no effect of empagliflozin is anticipated on concomitantly administered drugs that are substrates of these uptake transporters.
In vivo Assessment of Drug Interactions
Empagliflozin pharmacokinetics were similar with and without coadministration of metformin HCl, glimepiride, pioglitazone, sitagliptin, linagliptin, warfarin, verapamil, ramipril, and simvastatin in healthy volunteers and with or without coadministration of hydrochlorothiazide and torsemide in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (see Figure 1 ). In subjects with normal renal function, coadministration of empagliflozin with probenecid resulted in a 30% decrease in the fraction of empagliflozin excreted in urine without any effect on 24-hour urinary glucose excretion. The relevance of this observation to patients with renal impairment is unknown.
| a empagliflozin, 50 mg, once daily; b empagliflozin, 25 mg, single dose; c empagliflozin, 25 mg, once daily; d empagliflozin, 10 mg, single dose |
Figure 1 Effect of Various Medications on the Pharmacokinetics of Empagliflozin as Displayed as 90% Confidence Interval of Geometric Mean AUC and C max Ratios [reference lines indicate 100% (80% - 125%)] |
|
Empagliflozin had no clinically relevant effect on the pharmacokinetics of metformin, glimepiride, pioglitazone, sitagliptin, linagliptin, warfarin, digoxin, ramipril, simvastatin, hydrochlorothiazide, torsemide, and oral contraceptives when coadministered in healthy volunteers (see Figure 2 ).
| a empagliflozin, 50 mg, once daily; b empagliflozin, 25 mg, once daily; c empagliflozin, 25 mg, single dose; d administered as simvastatin; e administered as warfarin racemic mixture; f administered as Microgynon ® ; g administered as ramipril |
Figure 2 Effect of Empagliflozin on the Pharmacokinetics of Various Medications as Displayed as 90% Confidence Interval of Geometric Mean AUC and C max Ratios [reference lines indicate 100% (80% - 125%)] |
|
Linagliptin
In vitro Assessment of Drug Interactions
Linagliptin is a weak to moderate inhibitor of CYP isozyme CYP3A4 but does not inhibit other CYP isozymes and is not an inducer of CYP isozymes, including CYP1A2, 2A6, 2B6, 2C8, 2C9, 2C19, 2D6, 2E1, and 4A11.
Linagliptin is a P-glycoprotein (P-gp) substrate and inhibits P-gp mediated transport of digoxin at high concentrations. Based on these results, and in vivo drug interaction studies, linagliptin is considered unlikely to cause interactions with other P-gp substrates at therapeutic concentrations.
In vivo Assessment of Drug Interactions
Strong inducers of CYP3A4 or P-gp (e.g., rifampin) decrease exposure to linagliptin to subtherapeutic and likely ineffective concentrations [see Drug Interactions (7) ] . In vivo studies indicated evidence of a low propensity for causing drug interactions with substrates of CYP3A4, CYP2C9, CYP2C8, P-gp and organic cationic transporter (OCT).
Table 3 describes the effect of coadministered drugs on systemic exposure of linagliptin.
| Coadministered Drug | Dosing of Coadministered Drug a | Dosing of Linagliptin a | Geometric Mean Ratio (ratio with/without coadministered drug) No effect=1.0 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AUC d | C max | |||
| a Multiple dose (steady-state) unless otherwise noted | ||||
| b For information regarding clinical recommendations [see Drug Interactions (7) ] . | ||||
| c Single dose | ||||
| d AUC = AUC (0 to 24 hours) for single dose treatments and AUC = AUC (TAU) for multiple-dose treatments | ||||
| QD = once daily | ||||
| BID = twice daily | ||||
| TID = three times daily | ||||
| Metformin | 850 mg TID | 10 mg QD | 1.20 | 1.03 |
| Glyburide | 1.75 mg c | 5 mg QD | 1.02 | 1.01 |
| Pioglitazone | 45 mg QD | 10 mg QD | 1.13 | 1.07 |
| Ritonavir | 200 mg BID | 5 mg c | 2.01 | 2.96 |
| Rifampin b | 600 mg QD | 5 mg QD | 0.60 | 0.56 |
Table 4 describes the effect of linagliptin on systemic exposure of coadministered drugs.
| Coadministered Drug | Dosing of Coadministered Drug a | Dosing of Linagliptin a | Geometric Mean Ratio (ratio with/without coadministered drug) No effect=1.0 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AUC c | C max | ||||
| a Multiple dose (steady-state) unless otherwise noted | |||||
| b Single dose | |||||
| c AUC = AUC (INF) for single dose treatments and AUC = AUC (TAU) for multiple-dose treatments | |||||
| d AUC = AUC (0-168) and C max = E max for pharmacodynamic end points | |||||
| INR = International Normalized Ratio | |||||
| PT = Prothrombin Time | |||||
| QD = once daily | |||||
| TID = three times daily | |||||
| Metformin | 850 mg TID | 10 mg QD | metformin | 1.01 | 0.89 |
| Glyburide | 1.75 mg b | 5 mg QD | glyburide | 0.86 | 0.86 |
| Pioglitazone | 45 mg QD | 10 mg QD | pioglitazone metabolite M-III metabolite M-IV | 0.94 0.98 1.04 | 0.86 0.96 1.05 |
| Digoxin | 0.25 mg QD | 5 mg QD | digoxin | 1.02 | 0.94 |
| Simvastatin | 40 mg QD | 10 mg QD | simvastatin simvastatin acid | 1.34 1.33 | 1.10 1.21 |
| Warfarin | 10 mg b | 5 mg QD | R-warfarin S-warfarin INR PT | 0.99 1.03 0.93 d 1.03 d | 1.00 1.01 1.04 d 1.15 d |
| Ethinylestradiol and levonorgestrel | ethinylestradiol 0.03 mg and levonorgestrel 0.150 mg QD | 5 mg QD | ethinylestradiol levonorgestrel | 1.01 1.09 | 1.08 1.13 |
Metformin HCl
Table 5 describes the effect of coadministered drugs on plasma metformin systemic exposure.
| Coadministered Drug | Dosing of Coadministered Drug• | Dosing of Metformin HCl• | Geometric Mean Ratio (ratio with/without coadministered drug) No effect=1.0 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AUC † | C max | ||||
| •All metformin and coadministered drugs were given as single doses | |||||
| †AUC = AUC (INF) | |||||
| ≠Metformin HCl extended-release tablets 500 mg | |||||
| ‡Ratio of arithmetic means | |||||
| ••At steady-state with topiramate 100 mg every 12 hours and metformin 500 mg every 12 hours; AUC = AUC (0-12 hours) | |||||
| Glyburide | 5 mg | 500 mg≠ | metformin | 0.98‡ | 0.99‡ |
| Furosemide | 40 mg | 850 mg | metformin | 1.09‡ | 1.22‡ |
| Nifedipine | 10 mg | 850 mg | metformin | 1.16 | 1.21 |
| Propranolol | 40 mg | 850 mg | metformin | 0.90 | 0.94 |
| Ibuprofen | 400 mg | 850 mg | metformin | 1.05‡ | 1.07‡ |
| Cationic drugs eliminated by renal tubular secretion may reduce metformin elimination [see Drug Interactions (7) ]. | |||||
| Cimetidine | 400 mg | 850 mg | metformin | 1.40 | 1.61 |
| Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors may cause metabolic acidosis [see Drug Interactions (7) ] . | |||||
| Topiramate•• | 100 mg | 500 mg | metformin | 1.25 | 1.17 |
Table 6 describes the effect of metformin on coadministered drug systemic exposure.
| Coadministered Drug | Dosing of Coadministered Drug• | Dosing of Metformin HCl• | Geometric Mean Ratio (ratio with/without metformin) No effect=1.0 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AUC † | C max | ||||
| •All metformin and coadministered drugs were given as single doses | |||||
| †AUC = AUC (INF) unless otherwise noted | |||||
| §AUC (0-24 hours) reported | |||||
| ‡Ratio of arithmetic means, p-value of difference <0.05 | |||||
| ¶Ratio of arithmetic means | |||||
| Glyburide | 5 mg | 500 mg§ | glyburide | 0.78‡ | 0.63‡ |
| Furosemide | 40 mg | 850 mg | furosemide | 0.87‡ | 0.69‡ |
| Nifedipine | 10 mg | 850 mg | nifedipine | 1.10§ | 1.08 |
| Propranolol | 40 mg | 850 mg | propranolol | 1.01§ | 0.94 |
| Ibuprofen | 400 mg | 850 mg | ibuprofen | 0.97¶ | 1.01¶ |
| Cimetidine | 400 mg | 850 mg | cimetidine | 0.95§ | 1.01 |
NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
TRIJARDY XR
No carcinogenicity, mutagenicity, or impairment of fertility studies have been conducted with the combination of empagliflozin, linagliptin, and metformin HCl.
Empagliflozin
Carcinogenesis was evaluated in 2-year studies conducted in CD-1 mice and Wistar rats. Empagliflozin did not increase the incidence of tumors in female rats dosed at 100, 300, or 700 mg/kg/day (up to 72 times the exposure from the maximum clinical dose of 25 mg). In male rats, hemangiomas of the mesenteric lymph node were increased significantly at 700 mg/kg/day or approximately 42 times the exposure from a 25 mg clinical dose. Empagliflozin did not increase the incidence of tumors in female mice dosed at 100, 300, or 1,000 mg/kg/day (up to 62 times the exposure from a 25 mg clinical dose). Renal tubule adenomas and carcinomas were observed in male mice at 1,000 mg/kg/day, which is approximately 45 times the exposure of the maximum clinical dose of 25 mg. These tumors may be associated with a metabolic pathway predominantly present in the male mouse kidney.
Empagliflozin was not mutagenic or clastogenic with or without metabolic activation in the in vitro Ames bacterial mutagenicity assay, the in vitro L5178Y tk +/- mouse lymphoma cell assay, and an in vivo micronucleus assay in rats.
Empagliflozin had no effects on mating, fertility or early embryonic development in treated male or female rats, up to the high dose of 700 mg/kg/day (approximately 155 times the 25 mg clinical dose in males and females, respectively).
Linagliptin
Linagliptin did not increase the incidence of tumors in male and female rats in a 2-year study at doses of 6, 18, and 60 mg/kg. The highest dose of 60 mg/kg is approximately 418 times the clinical dose of 5 mg/day based on AUC exposure. Linagliptin did not increase the incidence of tumors in mice in a 2-year study at doses up to 80 mg/kg (males) and 25 mg/kg (females), or approximately 35 and 270 times the clinical dose based on AUC exposure. Higher doses of linagliptin in female mice (80 mg/kg) increased the incidence of lymphoma at approximately 215 times the clinical dose based on AUC exposure.
Linagliptin was not mutagenic or clastogenic with or without metabolic activation in the Ames bacterial mutagenicity assay, a chromosomal aberration test in human lymphocytes, and an in vivo micronucleus assay.
In fertility studies in rats, linagliptin had no adverse effects on early embryonic development, mating, fertility, or bearing live young up to the highest dose of 240 mg/kg (approximately 943 times the clinical dose based on AUC exposure).
Metformin HCl
Long-term carcinogenicity studies have been performed in Sprague Dawley rats at doses of 150, 300, and 450 mg/kg/day in males and 150, 450, 900, and 1,200 mg/kg/day in females. These doses are approximately 2, 4, and 8 times in males, and 3, 7, 12, and 16 times in females of the maximum recommended human daily dose of 2,000 mg/kg/day based on body surface area comparisons. No evidence of carcinogenicity with metformin was found in either male or female rats. A carcinogenicity study was also performed in Tg.AC transgenic mice at doses of up to 2,000 mg/kg/day applied dermally. No evidence of carcinogenicity was observed in male or female mice.
Genotoxicity assessments in the Ames test, gene mutation test (mouse lymphoma cells), chromosomal aberrations test (human lymphocytes) and in vivo mouse micronucleus tests were negative.
Fertility of male or female rats was not affected by metformin when administered at doses up to 600 mg/kg/day, which is approximately 3 times the maximum recommended human daily dose based on body surface area comparisons.
CLINICAL STUDIES
Empagliflozin and Linagliptin Add-on Combination Therapy with Metformin for Glycemic Control
A total of 686 patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus participated in a double-blind, active-controlled trial to evaluate the efficacy of empagliflozin 10 mg or 25 mg in combination with linagliptin 5 mg, compared to the individual components.
Patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus inadequately controlled on at least 1,500 mg of metformin HCl per day entered a single-blind placebo run-in period for 2 weeks. At the end of the run-in period, patients who remained inadequately controlled and had an HbA1c between 7% and 10.5% were randomized 1:1:1:1:1 to one of 5 active-treatment arms of empagliflozin 10 mg or 25 mg, linagliptin 5 mg, or linagliptin 5 mg in combination with 10 mg or 25 mg empagliflozin as a fixed dose combination tablet.
At Week 24, empagliflozin 10 mg or 25 mg used in combination with linagliptin 5 mg provided statistically significant improvement in HbA1c (p-value <0.0001) and FPG (p-value <0.001) compared to the individual components in patients who had been inadequately controlled on metformin HCl (see Table 7 , Figure 3 ). Treatment with empagliflozin 10 mg or 25 mg used in combination with linagliptin 5 mg also resulted in a statistically significant reduction in body weight compared to linagliptin 5 mg (p-value <0.0001). There was no statistically significant difference compared to empagliflozin alone.
| Empagliflozin 10 mg/ Linagliptin 5 mg | Empagliflozin 25 mg/ Linagliptin 5 mg | Empagliflozin 10 mg | Empagliflozin 25 mg | Linagliptin 5 mg | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| a Full analysis population (observed case) using MMRM. MMRM model included treatment, renal function, region, visit, visit by treatment interaction, and baseline HbA1c. | |||||
| b Patients with HbA1c above 7% at baseline: empagliflozin 25 mg/linagliptin 5 mg, n=123; empagliflozin 10 mg/linagliptin 5 mg, n=128; empagliflozin 25 mg, n=132; empagliflozin 10 mg, n=125; linagliptin 5 mg, n=119. Non-completers were considered failures (NCF). | |||||
| c Full analysis population using last observation carried forward. ANCOVA model included treatment, renal function, region, baseline weight, and baseline HbA1c. | |||||
| d p<0.001 for FPG; p<0.0001 for HbA1c and body weight | |||||
| HbA1c (%) | |||||
| Number of patients | n=135 | n=133 | n=137 | n=139 | n=128 |
| Baseline (mean) | 8.0 | 7.9 | 8.0 | 8.0 | 8.0 |
| Change from baseline (adjusted mean) | -1.1 | -1.2 | -0.7 | -0.6 | -0.7 |
| Comparison vs empagliflozin 25 mg or 10 mg (adjusted mean) (95% CI) a | -0.4 (-0.6, -0.2) d | -0.6 (-0.7, -0.4) d | -- | -- | -- |
| Comparison vs linagliptin 5 mg (adjusted mean) (95% CI) a | -0.4 (-0.6, -0.2) d | -0.5 (-0.7, -0.3) d | -- | -- | -- |
| Patients [n (%)] achieving HbA1c <7% b | 74 (58) | 76 (62) | 35 (28) | 43 (33) | 43 (36) |
| FPG (mg/dL) | |||||
| Number of patients | n=133 | n=131 | n=136 | n=137 | n=125 |
| Baseline (mean) | 157 | 155 | 162 | 160 | 156 |
| Change from baseline (adjusted mean) | -33 | -36 | -21 | -21 | -13 |
| Comparison vs empagliflozin 25 mg or 10 mg (adjusted mean) (95% CI) a | -12 (-18, -5) d | -15 (-22, -9) d | -- | -- | -- |
| Comparison vs linagliptin 5 mg (adjusted mean) (95% CI) a | -20 (-27, -13) d | -23 (-29, -16) d | -- | -- | -- |
| Body Weight | |||||
| Number of patients | n=135 | n=134 | n=137 | n=140 | n=128 |
| Baseline (mean) in kg | 87 | 85 | 86 | 88 | 85 |
| % change from baseline (adjusted mean) | -3.1 | -3.4 | -3.0 | -3.5 | -0.7 |
| Comparison vs empagliflozin 25 mg or 10 mg (adjusted mean) (95% CI) c | 0.0 (-0.9, 0.8) | 0.1 (-0.8, 0.9) | -- | -- | -- |
| Comparison vs linagliptin 5 mg (adjusted mean) (95% CI) c | -2.4 (-3.3, -1.5) d | -2.7 (-3.6, -1.8) d | -- | -- | -- |
Figure 3 Adjusted Mean HbA1c Change at Each Time Point (Completers) and at Week 24 (mITT population)
Empagliflozin Cardiovascular Outcomes in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease
EMPA-REG OUTCOME was a multicenter, multinational, randomized, double-blind parallel group trial that compared the risk of experiencing a major adverse cardiovascular event (MACE) between empagliflozin and placebo when these were added to and used concomitantly with standard of care treatments for diabetes mellitus and atherosclerotic CV disease. Concomitant antidiabetic medications were kept stable for the first 12 weeks of the trial. Thereafter, antidiabetic and atherosclerotic therapies could be adjusted, at the discretion of investigators, to ensure participants were treated according to the standard care for these diseases.
A total of 7,020 patients were treated (empagliflozin 10 mg = 2,345; empagliflozin 25 mg = 2,342; placebo = 2,333) and followed for a median of 3.1 years. Approximately 72% of the trial population was White, 22% was Asian, and 5% was Black or African American. The mean age was 63 years and approximately 72% were male.
All patients in the trial had inadequately controlled type 2 diabetes mellitus at baseline (HbA1c greater than or equal to 7%). The mean HbA1c at baseline was 8.1% and 57% of participants had diabetes mellitus for more than 10 years. Approximately 31%, 22% and 20% reported a past history of neuropathy, retinopathy and nephropathy to investigators, respectively and the mean eGFR was 74 mL/min/1.73 m 2 . At baseline, patients were treated with one (~30%) or more (~70%) antidiabetic medications including metformin HCl (74%), insulin (48%), sulfonylurea (43%) and dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor (11%).
All patients had established atherosclerotic CV disease at baseline including one (82%) or more (18%) of the following: a documented history of coronary artery disease (76%), stroke (23%) or peripheral artery disease (21%). At baseline, the mean systolic blood pressure was 136 mmHg, the mean diastolic blood pressure was 76 mmHg, the mean LDL was 86 mg/dL, the mean HDL was 44 mg/dL, and the mean urinary albumin to creatinine ratio (UACR) was 175 mg/g. At baseline, approximately 81% of patients were treated with renin angiotensin system inhibitors, 65% with beta-blockers, 43% with diuretics, 77% with statins, and 86% with antiplatelet agents (mostly aspirin).
The primary endpoint in EMPA-REG OUTCOME was the time to first occurrence of a Major Adverse Cardiac Event (MACE). A major adverse cardiac event was defined as occurrence of either a CV death or a non-fatal myocardial infarction (MI) or a non-fatal stroke. The statistical analysis plan had pre-specified that the 10 and 25 mg doses would be combined. A Cox proportional hazards model was used to test for non-inferiority against the pre-specified risk margin of 1.3 for the hazard ratio of MACE and superiority on MACE if non-inferiority was demonstrated. Type-1 error was controlled across multiples tests using a hierarchical testing strategy.
Empagliflozin significantly reduced the risk of first occurrence of primary composite endpoint of CV death, non-fatal myocardial infarction, or non-fatal stroke (HR: 0.86; 95% CI: 0.74, 0.99). The treatment effect was due to a significant reduction in the risk of CV death in subjects randomized to empagliflozin (HR: 0.62; 95% CI: 0.49, 0.77), with no change in the risk of non-fatal myocardial infarction or non-fatal stroke (see Table 8 and Figures 4 and 5 ). Results for the 10 mg and 25 mg empagliflozin dosages were consistent with results for the combined dose groups.
| Placebo N=2,333 | Empagliflozin N=4,687 | Hazard ratio vs placebo (95% CI) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| a Treated set (patients who had received at least one dose of trial drug) | |||
| b p−value for superiority (2−sided) 0.04 | |||
| c Total number of events | |||
| Composite of CV death, non-fatal myocardial infarction, non-fatal stroke (time to first occurrence) b | 282 (12.1%) | 490 (10.5%) | 0.86 (0.74, 0.99) |
| Non-fatal myocardial infarction c | 121 (5.2%) | 213 (4.5%) | 0.87 (0.70, 1.09) |
| Non-fatal stroke c | 60 (2.6%) | 150 (3.2%) | 1.24 (0.92, 1.67) |
| CV death c | 137 (5.9%) | 172 (3.7%) | 0.62 (0.49, 0.77) |
Figure 4 Estimated Cumulative Incidence of First MACE
Figure 5 Estimated Cumulative Incidence of CV Death
The efficacy of empagliflozin on CV death was generally consistent across major demographic and disease subgroups.
Vital status was obtained for 99.2% of subjects in the trial. A total of 463 deaths were recorded during the EMPA-REG OUTCOME trial. Most of these deaths were categorized as CV deaths. The non-CV deaths were only a small proportion of deaths and were balanced between the treatment groups (2.1% in patients treated with empagliflozin, and 2.4% of patients treated with placebo).
Linagliptin Cardiovascular Safety Trials in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
CARMELINA
The CV risk of linagliptin was evaluated in CARMELINA (NCT01897532), a multinational, multi-center, placebo-controlled, double-blind, parallel group trial comparing linagliptin (N=3,494) to placebo (N=3,485) in adult patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and a history of established macrovascular and/or renal disease. The trial compared the risk of major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) between linagliptin and placebo when these were added to standard of care treatments for diabetes mellitus and other CV risk factors. The trial was event driven, the median duration of follow-up was 2.2 years and vital status was obtained for 99.7% of patients.
Patients were eligible to enter the trial if they were adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus, with HbA1c of 6.5% to 10%, and had either albuminuria and previous macrovascular disease (39% of enrolled population), or evidence of impaired renal function by eGFR and Urinary Albumin Creatinine Ratio (UACR) criteria (42% of enrolled population), or both (18% of enrolled population).
At baseline the mean age was 66 years, and the population was 63% male, 80% White, 9% Asian, 6% Black or African American and 36% were of Hispanic or Latino ethnicity. Mean HbA1c was 8.0% and mean duration of type 2 diabetes mellitus was 15 years. The trial population included 17% patients ≥75 years of age and 62% patients with renal impairment defined as eGFR <60 mL/min/1.73 m 2 . The mean eGFR was 55 mL/min/1.73 m 2 and 27% of patients had mild renal impairment (eGFR 60 to 90 mL/min/1.73 m 2 ), 47% of patients had moderate renal impairment (eGFR 30 to <60 mL/min/1.73 m 2 ) and 15% of patients had severe renal impairment (eGFR <30 mL/min/1.73 m 2 ). Patients were taking at least one antidiabetic drug (97%), and the most common were insulin and analogues (57%), metformin HCl (54%) and sulfonylurea (32%). Patients were also taking antihypertensives (96%), lipid lowering drugs (76%) with 72% on statin, and aspirin (62%).
The primary endpoint, MACE, was the time to first occurrence of one of three composite outcomes which included CV death, non-fatal myocardial infarction or non-fatal stroke. The trial was designed as a non-inferiority trial with a pre-specified risk margin of 1.3 for the hazard ratio of MACE. A total of 434 patients on linagliptin and 420 patients on placebo experienced MACE. The incidence rate of MACE in both treatment arms: 56.3 MACE per 1,000 patient-years on placebo vs. 57.7 MACE per 1,000 patient-years on linagliptin. The estimated hazard ratio for MACE associated with linagliptin relative to placebo was 1.02 with a 95% confidence interval of (0.89, 1.17). The upper bound of this confidence interval, 1.17, excluded the risk margin of 1.3.
CAROLINA
The CV risk of linagliptin was evaluated in CAROLINA, a multi-center, multinational, randomized, double-blind parallel group trial comparing linagliptin (N=3,023) to glimepiride (N=3,010) in adult patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and a history of established CV disease and/or multiple CV risk factors. The trial compared the risk of major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) between linagliptin and glimepiride when these were added to standard of care treatments for diabetes mellitus and other CV risk factors. The trial was event driven, the median duration of follow-up was 6.23 years and vital status was obtained for 99.3% of patients.
Patients were eligible to enter the trial if they were adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus with insufficient glycemic control (defined as HbA1c of 6.5% to 8.5% or 6.5% to 7.5% depending on treatment-naïve, on monotherapy or on combination therapy), and were defined to be at high CV risk with previous vascular disease, evidence of vascular related end-organ damage, age ≥70 years, and/or two CV risk factors (duration of diabetes mellitus >10 years, systolic blood pressure >140 mmHg, current smoker, LDL cholesterol ≥135 mg/dL).
At baseline the mean age was 64 years and the population was 60% male, 73% White, 18% Asian, 5% Black or African American, and 17% were of Hispanic or Latino ethnicity. The mean HbA1c was 7.15% and mean duration of type 2 diabetes mellitus was 7.6 years. The trial population included 34% patients ≥70 years of age and 19% patients with renal impairment defined as eGFR <60 mL/min/1.73 m 2 . The mean eGFR was 77 mL/min/1.73 m 2 . Patients were taking at least one antidiabetic drug (91%) and the most common were metformin HCl (83%) and sulfonylurea (28%). Patients were also taking antihypertensives (89%), lipid lowering drugs (70%) with 65% on statin, and aspirin (47%).
The primary endpoint, MACE, was the time to first occurrence of one of three composite outcomes which included CV death, non-fatal myocardial infarction or non-fatal stroke. The trial was designed as a non-inferiority trial with a pre-specified risk margin of 1.3 for the hazard ratio of MACE. A total of 356 patients on linagliptin and 362 patients on glimepiride experienced MACE. The incidence rate of MACE in both treatment arms: 20.7 MACE per 1,000 patient-years on linagliptin vs. 21.2 MACE per 1,000 patient-years on glimepiride. The estimated hazard ratio for MACE associated with linagliptin relative to glimepiride was 0.98 with a 95% confidence interval of (0.84, 1.14). The upper bound of this confidence interval, 1.14, excluded the risk margin of 1.3.
HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
TRIJARDY XR tablets are available as follows:
| Tablet Strength | Color/Shape | Tablet Markings | Package Size | NDC Number |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 mg Empagliflozin 2.5 mg Linagliptin 1,000 mg Metformin HCl Extended-Release | grey, oval-shaped, film-coated tablet | Printed on one side in white ink with the Boehringer Ingelheim company symbol and "395" on the top line and "5/2.5" on the bottom line. | Bottles of 60 Bottles of 180 | 0597-0395-82 0597-0395-23 |
| 10 mg Empagliflozin 5 mg Linagliptin 1,000 mg Metformin HCl Extended-Release | tan, oval-shaped, film-coated tablet | Printed on one side in white ink with the Boehringer Ingelheim company symbol and "380" on the top line and "10/5" on the bottom line. | Bottles of 30 Bottles of 90 | 0597-0380-13 0597-0380-68 |
| 12.5 mg Empagliflozin 2.5 mg Linagliptin 1,000 mg Metformin HCl Extended-Release | red, oval-shaped, film-coated tablet | Printed on one side in white ink with the Boehringer Ingelheim company symbol and "385" on the top line and "12.5/2.5" on the bottom line. | Bottles of 60 Bottles of 180 | 0597-0385-77 0597-0385-86 |
| 25 mg Empagliflozin 5 mg Linagliptin 1,000 mg Metformin HCl Extended-Release | brown, oval-shaped, film-coated tablet | Printed on one side in white ink with the Boehringer Ingelheim company symbol and "390" on the top line and "25/5" on the bottom line. | Bottles of 30 Bottles of 90 | 0597-0390-71 0597-0390-13 |
Storage
Store at 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F); excursions permitted to 15°C to 30°C (59°F to 86°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature]. Protect from exposure to high humidity.
Mechanism of Action
TRIJARDY XR
TRIJARDY XR contains: empagliflozin, a SGLT2 inhibitor, linagliptin, a DPP-4 inhibitor, and metformin HCl, a biguanide.
Empagliflozin
Empagliflozin is an inhibitor of SGLT2, the predominant transporter responsible for reabsorption of glucose from the glomerular filtrate back into the circulation. By inhibiting SGLT2, empagliflozin reduces renal reabsorption of filtered glucose and lowers the renal threshold for glucose, and thereby increases urinary glucose excretion.
Linagliptin
Linagliptin is an inhibitor of DPP-4, an enzyme that degrades the incretin hormones glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) and glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP). Thus, linagliptin increases the concentrations of active incretin hormones, stimulating the release of insulin in a glucose-dependent manner and decreasing the levels of glucagon in the circulation. Both incretin hormones are involved in the physiological regulation of glucose homeostasis. Incretin hormones are secreted at a low basal level throughout the day and levels rise immediately after meal intake. GLP-1 and GIP increase insulin biosynthesis and secretion from pancreatic beta cells in the presence of normal and elevated blood glucose levels. Furthermore, GLP-1 also reduces glucagon secretion from pancreatic alpha cells, resulting in a reduction in hepatic glucose output.
Metformin HCl
Metformin HCl is an antihyperglycemic agent which improves glucose tolerance in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus, lowering both basal and postprandial plasma glucose. Metformin HCl decreases hepatic glucose production, decreases intestinal absorption of glucose, and improves insulin sensitivity by increasing peripheral glucose uptake and utilization. With metformin HCl therapy, insulin secretion remains unchanged while fasting insulin levels and day-long plasma insulin response may decrease.