Get your patient on Ubrelvy (Ubrogepant)
Ubrelvy prior authorization resources
Most recent state uniform prior authorization forms
Brand Resources
Ubrelvy patient education
Patient toolkit
Dosage & administration
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- The recommended dose is 50 mg or 100 mg taken orally, as needed. (2.1 )
- If needed, a second dose may be administered at least 2 hours after the initial dose. (2.1 )
- The maximum dose in a 24-hour period is 200 mg. (2.1 )
- Severe Hepatic or Severe Renal Impairment: Recommended dose is 50 mg; if needed, a second 50 mg dose may be taken at least 2 hours after the initial dose. (2.2 , 8.6 , 8.7 )
2.1 Recommended Dosage
The recommended dose of UBRELVY is 50 mg or 100 mg taken orally with or without food.
If needed, a second dose may be taken at least 2 hours after the initial dose. The maximum dose in a 24-hour period is 200 mg. The safety of treating more than 8 migraines in a 30-day period has not been established.
2.2 Dosage Modification s
Dosing modifications for concomitant use of specific drugs and for patients with hepatic or renal impairment are provided in Table 1.
| Dosage Modifications | Initi a l Dose | Second Dose a (if needed) |
| Concomitant Drug [see Drug Interactions (7 )] | ||
| Moderate CYP3A4 Inhibitors (7.1 ) | 50 mg | Avoid within 24 hours |
| Weak CYP3A4 Inhibitors (7.1 ) | 50 mg | 50 mg |
| Strong CYP3A4 Inducers (7.2 ) | Avoid concomitant use | |
| Weak & Moderate CYP3A4 Inducers (7.2 ) | 100 mg | 100 mg |
| BCRP and/or P-gp only Inhibitors (7.3 ) | 50 mg | 50 mg |
| Spec i fic Populations [see Use in Specific Populations (8 )] | ||
| Severe Hepatic Impairment (Child-Pugh Class C) (8.6 ) | 50 mg | 50 mg |
| Severe Renal Impairment (CLcr 15-29 mL/min) (8.7 ) | 50 mg | 50 mg |
| End-Stage Renal Disease (CLcr <15 mL/min) (8.7 ) | Avoid use | |
| a Second dose may be taken at least 2 hours after the initial dose | ||

By using PrescriberAI, you agree to the AI Terms of Use.
Ubrelvy prescribing information
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
UBRELVY is indicated for the acute treatment of migraine with or without aura in adults.
Limitations of Use
UBRELVY is not indicated for the preventive treatment of migraine.
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- The recommended dose is 50 mg or 100 mg taken orally, as needed. (2.1 )
- If needed, a second dose may be administered at least 2 hours after the initial dose. (2.1 )
- The maximum dose in a 24-hour period is 200 mg. (2.1 )
- Severe Hepatic or Severe Renal Impairment: Recommended dose is 50 mg; if needed, a second 50 mg dose may be taken at least 2 hours after the initial dose. (2.2 , 8.6 , 8.7 )
2.1 Recommended Dosage
The recommended dose of UBRELVY is 50 mg or 100 mg taken orally with or without food.
If needed, a second dose may be taken at least 2 hours after the initial dose. The maximum dose in a 24-hour period is 200 mg. The safety of treating more than 8 migraines in a 30-day period has not been established.
2.2 Dosage Modification s
Dosing modifications for concomitant use of specific drugs and for patients with hepatic or renal impairment are provided in Table 1.
| Dosage Modifications | Initi a l Dose | Second Dose a (if needed) |
| Concomitant Drug [see Drug Interactions (7 )] | ||
| Moderate CYP3A4 Inhibitors (7.1 ) | 50 mg | Avoid within 24 hours |
| Weak CYP3A4 Inhibitors (7.1 ) | 50 mg | 50 mg |
| Strong CYP3A4 Inducers (7.2 ) | Avoid concomitant use | |
| Weak & Moderate CYP3A4 Inducers (7.2 ) | 100 mg | 100 mg |
| BCRP and/or P-gp only Inhibitors (7.3 ) | 50 mg | 50 mg |
| Spec i fic Populations [see Use in Specific Populations (8 )] | ||
| Severe Hepatic Impairment (Child-Pugh Class C) (8.6 ) | 50 mg | 50 mg |
| Severe Renal Impairment (CLcr 15-29 mL/min) (8.7 ) | 50 mg | 50 mg |
| End-Stage Renal Disease (CLcr <15 mL/min) (8.7 ) | Avoid use | |
| a Second dose may be taken at least 2 hours after the initial dose | ||
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
UBRELVY 50 mg is supplied as white to off-white, capsule-shaped, biconvex tablets debossed with “U50” on one side.
UBRELVY 100 mg is supplied as white to off-white, capsule-shaped, biconvex tablets debossed with “U100” on one side.
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Pregnancy Exposure Registry
There is a pregnancy exposure registry that monitors outcomes in women who become pregnant while taking UBRELVY. Patients should be encouraged to enroll by calling 1-833-277-0206 or visiting http://empresspregnancyregistry.com .
Risk Summary
There are no adequate data on the developmental risk associated with the use of UBRELVY in pregnant women. In animal studies, adverse effects on embryofetal development were observed following administration of ubrogepant during pregnancy (increased embryofetal mortality in rabbits) or during pregnancy and lactation (decreased body weight in offspring in rats) at doses greater than those used clinically and which were associated with maternal toxicity ( see Data ) .
In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriages in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2-4% and 15-20%, respectively. The estimated rate of major birth defects (2.2% -2.9%) and miscarriage (17%) among deliveries to women with migraine are similar to rates reported in women without migraine.
Clinical Considerations
Disease-Associated Maternal and/or Embryo/Fetal Risk
Published data have suggested that women with migraine may be at increased risk of preeclampsia and gestational hypertension during pregnancy.
Data
Animal Data
Oral administration of ubrogepant (0, 1.5, 5, 25, 125 mg/kg/day) to pregnant rats during the period of organogenesis resulted in no adverse effects on embryofetal development. Plasma exposure (AUC) at the highest dose tested is approximately 45 times that in humans at the maximum recommended human dose (MRHD) of 200 mg/day.
In pregnant rabbits, ubrogepant (0, 15, 45, 75, or 250 mg/kg/day) was administered orally throughout organogenesis in two separate studies. In both studies, the highest dose tested (250 mg/kg/day) was associated with maternal toxicity. In the first study, ubrogepant produced abortion and increased embryofetal mortality in surviving litters at the high dose (250 mg/kg/day). In the second study, excessive maternal toxicity at the high dose (250 mg/kg/day) resulted in early termination and lack of fetal data for that dose group. Plasma exposure (AUC) at the highest no-effect dose (75 mg/kg/day) for adverse effects on embryofetal development in rabbit is approximately 8 times that in humans at the MRHD.
Oral administration of ubrogepant (0, 25, 60, or 160 mg/kg/day) to rats throughout gestation and lactation resulted in decreased body weight in offspring at birth and during the lactation period at the mid and high doses, which were associated with maternal toxicity. Plasma exposure (AUC) at the no-effect dose for adverse effects on pre- and postnatal development in rats (25 mg/kg/day) is approximately 15 times that in humans at the MRHD.
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
Data from a lactation study in twelve healthy adult females indicate that ubrogepant is excreted in breast milk in low amounts. The estimated relative infant dose is approximately 0.15% of the maternal weight-adjusted dose, and the milk-to-plasma ratio is 0.23 (see Data ) . There are no data on the effects of ubrogepant on the breastfed infant or the effects on milk production. The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother’s clinical need for UBRELVY and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed infant from UBRELVY or from the underlying maternal condition.
Data
A study was conducted in twelve healthy adult lactating females who were between 24 and 34 years of age and between 1 month and 6 months postpartum. Each subject was administered a single oral dose of ubrogepant 100 mg. Maternal plasma and breast milk were collected for 24 hours after dosing. Using a 150 mL/kg/day estimated infant milk intake, the mean estimated relative infant dose was approximately 0.15% of the maternal weight-adjusted dose. The mean milk-to-plasma ratio was 0.23. All subjects had detectable levels of ubrogepant in breast milk during the study; by 16 to 24 hours after dosing, 17% of females in the study had detectable levels of ubrogepant in breast milk. The mean cumulative amount of ubrogepant excreted in breast milk over 24 hours was less than 0.02 mg of a 100 mg dose.
8.4 Pediatric Use
Safety and effectiveness in pediatric patients have not been established.
8.5 Geriatric Use
In pharmacokinetic studies, no clinically significant pharmacokinetic differences were observed between elderly and younger subjects. Clinical studies of UBRELVY did not include sufficient numbers of patients aged 65 years and over to determine whether they respond differently from younger patients. In general, dose selection for an elderly patient should be cautious, usually starting at the low end of the dosing range.
8.6 Hepatic Impairment
In patients with pre-existing mild (Child-Pugh Class A), moderate (Child-Pugh Class B), or severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh Class C), ubrogepant exposure was increased by 7%, 50%, and 115%, respectively . No dose adjustment is recommended for patients with mild or moderate hepatic impairment. Dose adjustment for UBRELVY is recommended for patients with severe hepatic impairment [ s ee Dosage and Administration (2.2 ) ] .
8.7 Renal Impairment
The renal route of elimination plays a minor role in the clearance of ubrogepant [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3 )] . No dose adjustment is recommended for patients with mild or moderate renal impairment. Dose adjustment is recommended for patients with severe renal impairment (CLcr 15-29 mL/min) [see Dosage and Administration (2.2 ) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3 )] . Avoid use of UBRELVY in patients with end-stage renal disease (ESRD) (CLcr <15 mL/min).
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
UBRELVY is contraindicated:
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- Hypersensitivity Reactions: If a serious hypersensitivity reaction occurs, discontinue UBRELVY and initiate appropriate therapy. Severe hypersensitivity reactions have included anaphylaxis and dyspnea. These reactions can occur within minutes, hours, or days after administration. (5.1 )
- Hypertension: New-onset or worsening of pre-existing hypertension may occur. (5.2 )
- Raynaud’s phenomenon: New-onset or worsening of pre-existing Raynaud’s phenomenon may occur. (5.3 )
5 .1 Hypersensitivity Reactions
Hypersensitivity reactions, including anaphylaxis, dyspnea, facial or throat edema, rash, urticaria, and pruritus, have been reported with use of UBRELVY. Hypersensitivity reactions can occur minutes, hours, or days after administration. Most reactions occurred within hours after dosing and were not serious, and some reactions led to discontinuation. If a serious or severe hypersensitivity reaction occurs, discontinue UBRELVY and institute appropriate therapy [see Contraindications (4 ) and Adverse Reactions (6.2 )] .
5.000000000000000e+00 2 Hyper tension
Development of hypertension and worsening of pre-existing hypertension have been reported following the use of CGRP antagonists, including UBRELVY, in the postmarketing setting. Some of the patients who developed new-onset hypertension had risk factors for hypertension. There were cases requiring initiation of pharmacological treatment for hypertension and, in some cases, hospitalization. Hypertension may occur at any time during treatment, but was most frequently reported within 7 days of therapy initiation. The CGRP antagonist was discontinued in many of the reported cases.
Monitor patients treated with UBRELVY for new-onset hypertension, or worsening of pre-existing hypertension, and consider whether discontinuation of UBRELVY is warranted if evaluation fails to establish an alternative etiology or blood pressure is inadequately controlled.
5.000000000000000e+00 3 Raynaud’s Phenomenon
Development of Raynaud’s phenomenon and recurrence or worsening of pre-existing Raynaud’s phenomenon have been reported in the postmarketing setting following the use of CGRP antagonists, including UBRELVY. In reported cases with small molecule CGRP antagonists, symptom onset occurred a median of 1.5 days following dosing. Many of the cases reported serious outcomes, including hospitalizations and disability, generally related to debilitating pain. In most reported cases, discontinuation of the CGRP antagonist resulted in resolution of symptoms.
UBRELVY should be discontinued if signs or symptoms of Raynaud’s phenomenon develop, and patients should be evaluated by a healthcare provider if symptoms do not resolve. Patients with a history of Raynaud’s phenomenon should be monitored for, and informed about the possibility of, worsening or recurrence of signs and symptoms.
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following clinically significant adverse reactions are described elsewhere in labeling:
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
The safety of UBRELVY was evaluated in 3,624 subjects who received at least one dose of UBRELVY. In two randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, Phase 3 trials in adult patients with migraine (Studies 1 and 2), a total of 1,439 patients received UBRELVY 50 mg or 100 mg [see Clinical Studies (14 )] . Of the UBRELVY-treated patients in these 2 studies, approximately 89% were female, 82% were White, 15% were Black, and 17% were of Hispanic or Latino ethnicity. The mean age at study entry was 41 years (range of 18-75 years).
Long-term safety was assessed in 813 patients, dosing intermittently for up to 1 year in an open-label extension study. Patients were permitted to treat up to 8 migraines per month with UBRELVY. Of these 813 patients, 421 patients were exposed to 50 mg or 100 mg for at least 6 months, and 364 patients were exposed to these doses for at least one year, all of whom treated at least two migraine attacks per month, on average. In that study, 2.5% of patients were withdrawn from UBRELVY because of an adverse reaction. The most common adverse reaction resulting in discontinuation in the long-term safety study was nausea.
Adverse reactions in Studies 1 and 2 are shown in Table 2.
| Placebo (N= 984) % | UBRELVY 50 mg (N=954) % | UBRELVY 100 mg (N=485) % | |
| Nausea | 2 | 2 | 4 |
| Somnolence• | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| Dry Mouth | 1 | <1 | 2 |
•Somnolence includes the adverse reaction-related terms sedation and fatigue.
6 . 2 Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during post-approval use of UBRELVY. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Immune System Disorders: Hypersensitivity (e.g., anaphylaxis, dyspnea, facial or throat edema, rash, urticaria, and pruritus) [see Contraindications (4 ) and Warnings and Precautions (5.1 )]
Vascular Disorders: Hypertension [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2 )] , Raynaud’s phenomenon [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3 )]
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 CYP3A4 I nhibitors
Co-administration of UBRELVY with ketoconazole, a strong CYP3A4 inhibitor, resulted in a significant increase in exposure of ubrogepant [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3 ) ] . UBRELVY should not be used with strong CYP3A4 inhibitors (e.g., ketoconazole, itraconazole, clarithromycin) [see Contraindication s (4 )] .
Co-administration of UBRELVY with verapamil, a moderate CYP3A4 inhibitor, resulted in an increase in ubrogepant exposure [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3 ) ] . Dose adjustment is recommended with concomitant use of UBRELVY and moderate CYP3A4 inhibitors (e.g., cyclosporine, ciprofloxacin, fluconazole, fluvoxamine, grapefruit juice) [see Dosage and Administration (2.2 )] .
No dedicated drug interaction study was conducted with ubrogepant and weak CYP3A4 inhibitors. Dose adjustment is recommended with concomitant use of UBRELVY with weak CYP3A4 inhibitors [see Dosage and Administration (2.2 )] .
7.2 CYP3A4 I nducers
Co-administration of UBRELVY with rifampin, a strong CYP3A4 inducer, resulted in a significant reduction in ubrogepant exposure [ s ee Clinical Pharmacology (12.3 ) ] . In patients taking strong CYP3A4 inducers (e.g., phenytoin, barbiturates, rifampin, St. John’s Wort), loss of ubrogepant efficacy is expected, and concomitant use should be avoided.
Co-administration of UBRELVY with moderate or weak CYP3A4 inducers was not evaluated in a clinical study. Dose adjustment is recommended with concomitant use of UBRELVY and moderate or weak CYP3A4 inducers [see Dosage and Administration (2.2 )] .
7 .3 BCRP and / or P-gp Only Inhibitors
Ubrogepant is a substrate of BCRP and P-gp efflux transporters. Use of BCRP and/or P-gp only inhibitors (e.g., quinidine, carvedilol, eltrombopag, curcumin) may increase the exposure of ubrogepant [ s ee Clinical Pharmacology (12.3 ) ] . Clinical drug interaction studies with inhibitors of these transporters were not conducted. Dose adjustment is recommended with BCRP and/or P-gp only inhibitors [see Dosage and Administration (2.2 ) ] .
11 DESCRIPTION
The active ingredient of UBRELVY is ubrogepant, a calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) receptor antagonist. The chemical name of ubrogepant is (3' S )- N -((3 S ,5 S ,6 R )-6-methyl-2-oxo-5-phenyl-1-(2,2,2-trifluoroethyl)piperidin-3-yl)-2'-oxo-1',2',5,7-tetrahydrospiro[cyclopenta[ b ]pyridine-6,3'-pyrrolo[2,3- b ]pyridine]-3-carboxamide and has the following structural formula:
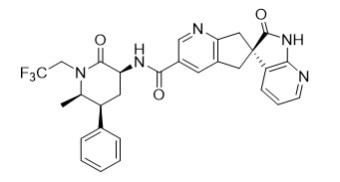
The molecular formula is C 29 H 26 F 3 N 5 O 3 and molecular weight is 549.6. Ubrogepant is a white to off-white powder. It is freely soluble in ethanol, methanol, acetone, and acetonitrile; and is practically insoluble in water.
UBRELVY is available as tablets for oral administration containing 50 mg or 100 mg ubrogepant. The inactive ingredients include colloidal silicon dioxide, croscarmellose sodium, mannitol, microcrystalline cellulose, polyvinylpyrrolidone vinyl acetate copolymer, sodium chloride, sodium stearyl fumarate, and vitamin E polyethylene glycol succinate.
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Ubrogepant is a calcitonin gene-related peptide receptor antagonist.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
Cardiac Electrophysiology
At a dose 2 times the maximum recommended daily dose, UBRELVY does not prolong the QT interval to any clinically relevant extent.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Absorption
Following oral administration of UBRELVY, ubrogepant is absorbed with peak plasma concentrations at approximately 1.5 hours. Ubrogepant displays dose-proportional pharmacokinetics within the recommended dose range [see Dosage and Administration (2.1 )] .
Effect of Food
When UBRELVY was administered with a high-fat meal, the time to maximum ubrogepant plasma concentration was delayed by 2 hours and resulted in a 22% reduction in C max with no change in AUC. UBRELVY was administered without regard to food in clinical efficacy studies [see Dosage and Administration (2.1 )] .
Distribution
Plasma protein binding of ubrogepant is 87% in vitro. The mean apparent central volume of distribution of ubrogepant (V/F) after single dose oral administration is approximately 350 L.
Elimination
Metabolism
Ubrogepant is eliminated mainly through metabolism, primarily by CYP3A4. The parent compound (ubrogepant), and 2 glucuronide conjugate metabolites were the most prevalent circulating components in human plasma. The glucuronide metabolites are not expected to contribute to the pharmacological activity of ubrogepant since they were reported as about 6000-fold less potent in the CGRP receptor binding assay.
Excretion
The elimination half-life of ubrogepant is approximately 5-7 hours. The mean apparent oral clearance (CL/F) of ubrogepant is approximately 87 L/hr. Ubrogepant is excreted mostly via the biliary/fecal route, while the renal route is a minor route of elimination. Following single oral dose administration of [ 14 C]-ubrogepant to healthy male subjects, 42% and 6% of the dose was recovered as unchanged ubrogepant in feces and urine, respectively.
Specific Populations
Patients with Renal Impairment
Population pharmacokinetic analysis based on pooled data from clinical studies was used to evaluate the effect of renal impairment characterized based on estimated creatinine clearance (CLcr) using the Cockcroft-Gault (C-G) equation. Renal impairment did not reveal a significant difference in the pharmacokinetics of ubrogepant in patients with mild or moderate renal impairment (CLcr 30-89 mL/min) relative to those with normal renal function (CLcr >90 mL/min). Patients with severe renal impairment or ESRD (eGFR <30 mL/min) have not been studied. Dose adjustment in patients with severe renal impairment (CLcr 15-29 mL/min) is recommended based on ADME information and a conservative assumption that severe renal impairment is unlikely to cause more than a two-fold increase in exposure of ubrogepant [see Dosage and Administration (2.2 )] . No dosing recommendations can be made for patients with ESRD (CLcr<15 mL/min).
Patients with Hepatic Impairment
In patients with pre-existing mild (Child-Pugh Class A), moderate (Child-Pugh Class B), or severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh Class C), ubrogepant exposure was increased by 7%, 50%, and 115%, respectively. Patients with severe hepatic impairment require dose adjustments [see Dosage and Administration (2.2 )] .
Other Specific Populations
Based on a population pharmacokinetic analysis, age, sex, race, and body weight did not have a significant effect on the pharmacokinetics (C max and AUC) of ubrogepant. Therefore, no dose adjustments are warranted based on these factors.
Drug Interactions
In Vitro Studies
Enzymes
Ubrogepant is not an inhibitor of CYP1A2, 2B6, or 3A4. Ubrogepant is a weak inhibitor of CYP2C8, 2C9, 2D6, 2C19, MAO-A, and UGT1A1. The in vitro inhibition potential is not expected to be clinically significant. Ubrogepant is not an inducer of CYP1A2, 2B6, or 3A4 at clinically relevant concentrations.
Transporters
Ubrogepant is a substrate of BCRP and P-gp transporters in-vitro; therefore, use of inhibitors of BCRP and/or P-gp may increase the exposure of ubrogepant. Dose adjustment for concomitant use of UBRELVY with inhibitors of BCRP and/or P-gp is recommended based on ADME and clinical interaction studies with CYP3A4/P-gp inhibitors that show the highest predicted potential increase in exposure of ubrogepant is not expected to be more than two-fold [see Dosage and Administration (2.2 ) and Drug Interactions (7.3 ) ] .
Ubrogepant is a weak substrate of OATP1B1, OATP1B3, and OAT1, but not a substrate of OAT3. It is not an inhibitor of P-gp, BCRP, BSEP, MRP3, MRP4, OAT1, OAT3, or NTCP transporters, but is a weak inhibitor of OATP1B1, OATP1B3, and OCT2 transporters. Dose adjustments are needed only for P-gp, or BCRP inhibitors. No clinical drug interactions are expected for UBRELVY with other transporters.
In V iv o Studies
CYP3A4 Inhibitors [see Dosage and Administration (2.2 ), Contraindications (4 ), and Dr ug Interactions (7.1 ) ] :
Co-administration of UBRELVY with ketoconazole, a strong CYP3A4 inhibitor, resulted in a 9.7-fold and 5.3-fold increase in AUC inf and C max of ubrogepant, respectively . Co-administration of UBRELVY with verapamil, a moderate CYP3A4 inhibitor, resulted in about 3.5-fold and 2.8-fold increase in AUC inf and C max of ubrogepant, respectively. No dedicated drug interaction study was conducted to assess concomitant use with weak CYP3A4 inhibitors. The conservative prediction of the maximal potential increase in ubrogepant exposure with weak CYP3A4 inhibitors is not expected to be more than 2-fold.
CYP3A4 Inducers [see Dosage and Administration (2.2 ) and Drug Interactions (7.2 ) ] :
Co-administration of UBRELVY with rifampin, a strong CYP3A4 inducer, resulted in an 80% reduction in ubrogepant exposure. No dedicated drug interaction studies were conducted to assess concomitant use with weak or moderate CYP3A4 inducers. Dose adjustment for concomitant use of UBRELVY with weak or moderate CYP3A4 inducers is recommended based on a conservative prediction of 50% reduction in exposure of ubrogepant.
Other Drug-Drug Interaction Evaluations:
No significant pharmacokinetic interactions were observed for either ubrogepant or co-administered drugs when UBRELVY was administered with oral contraceptives (containing norgestimate and ethinyl estradiol), acetaminophen, naproxen, sumatriptan, esomeprazole, erenumab, galcanezumab, or atogepant.
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenicity
Two-year oral carcinogenicity studies of ubrogepant were conducted in mice (0, 5, 15, or 50 mg/kg/day) and rats (0, 10, 30, or 100 mg/kg in males; 0, 10, 30, or 150 mg/kg in females). There was no evidence of drug-related tumors in either species. The highest dose tested in mice is similar to the maximum recommended human dose (200 mg/day) on a body surface area (mg/m 2 ) basis. Plasma exposure (AUC) at the highest dose tested in rats is approximately 25 times that in humans at the maximum recommended human dose (MRHD) of 200 mg/day.
Mutagenicity
Ubrogepant was negative in in vitro (Ames, chromosomal aberration test in Chinese Hamster Ovary cells) and in vivo (rat bone marrow micronucleus) assays.
Impairment of Fertility
Oral administration of ubrogepant (0, 20, 80, or 160 mg/kg/day) to male and female rats (mated with drug-naïve females and males, respectively) resulted in no adverse effects on fertility or reproductive performance. Plasma exposures (AUC) at the highest dose tested are approximately 30 times that in humans at the MRHD.
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
The efficacy of UBRELVY for the acute treatment of migraine was demonstrated in two randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trials [Study 1 (NCT02828020) and Study 2 (NCT02867709)]. Study 1 randomized patients to placebo (n=559) or UBRELVY 50 mg (n=556) or 100 mg (n=557) and Study 2 randomized patients to placebo (n=563) or UBRELVY 50 mg (n=562). In all studies, patients were instructed to treat a migraine with moderate to severe headache pain intensity. A second dose of study medication (UBRELVY or placebo), or the patient’s usual acute treatment for migraine, was allowed between 2 to 48 hours after the initial treatment for a non-responding or recurrent migraine headache. Up to 23% of patients were taking preventive medications for migraine at baseline. None of these patients were on concomitant preventive medication that act on the CGRP pathway.
The primary efficacy analyses were conducted in patients who treated a migraine with moderate to severe pain. The efficacy of UBRELVY was established by an effect on pain freedom at 2 hours post-dose and most bothersome symptom (MBS) freedom at 2 hours post-dose, compared to placebo, for Studies 1 and 2. Pain freedom was defined as a reduction of moderate or severe headache pain to no pain, and MBS freedom was defined as the absence of the self-identified MBS (i.e., photophobia, phonophobia, or nausea). Among patients who selected an MBS, the most commonly selected was photophobia (56%), followed by phonophobia (24%), and nausea (19%).
In both studies, the percentage of patients achieving headache pain freedom and MBS freedom 2 hours post-dose was significantly greater among patients receiving UBRELVY compared to those receiving placebo (see Table 3 ). Table 3 also presents the results of the analyses of the percentage of patients achieving pain relief at 2 hours (defined as a reduction in migraine pain from moderate or severe to mild or none) post-dose and the percentage of patients achieving sustained pain freedom between 2 to 24 hours post-dose.
The incidence of photophobia and phonophobia was reduced following administration of UBRELVY at both doses (50 mg and 100 mg) as compared to placebo.
| Study 1 | Study 2 | ||||
| UBRELVY 50 mg | UBRELVY 100 mg | Placebo | UBRELVY 50 mg | Placebo | |
| Pain Free at 2 hours | |||||
| N | 422 | 448 | 456 | 464 | 456 |
| % Responders | 19.2 | 21.2 | 11.8 | 21.8 | 14.3 |
| Difference from placebo (%) | 7.4 | 9.4 | 7.5 | ||
| p value | 0.002 | <0.001 | 0.007 | ||
| Most Bothersome Symptom Free at 2 hours | |||||
| N | 420 | 448 | 454 | 463 | 456 |
| % Responders | 38.6 | 37.7 | 27.8 | 38.9 | 27.4 |
| Difference from placebo (%) | 10.8 | 9.9 | 11.5 | ||
| p value | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | ||
| P ain R elief at 2 hours | |||||
| N | 422 | 448 | 456 | 464 | 456 |
| % Responders | 60.7 | 61.4 | 49.1 | 62.7 | 48.2 |
| p value | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | ||
| Sustained Pain Freedom 2-24 hours | |||||
| N | 418 | 441 | 452 | 457 | 451 |
| % Responders | 12.7 | 15.4 | 8.6 | 14.4 | 8.2 |
| p value | •NS | 0.002 | 0.005 | ||
• Not statistically significant (NS)
Figure 1 presents the percentage of patients achieving migraine pain freedom within 2 hours following treatment in Studies 1 and 2.
Figure 1: Percentage of Patients Achieving Pain Freedom within 2 Hours in Pooled Studies 1 and 2
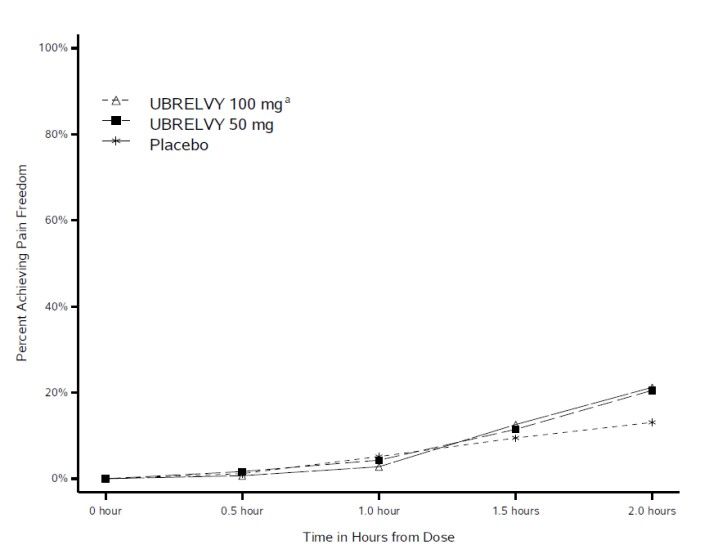
a The 100 mg arm was only included in Study 1.
Figure 2 presents the percentage of patients achieving MBS freedom within 2 hours in Studies 1 and 2.
Figure 2: Percentage of Patients Achieving MBS Freedom within 2 Hours in Pooled Studies 1 and 2
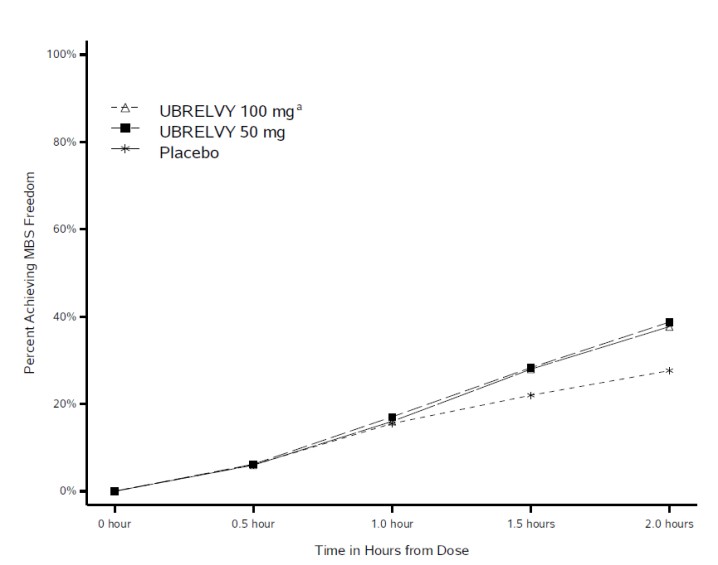
a The 100 mg arm was only included in Study 1.
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
16.1 How Supplied
UBRELVY 50 mg is supplied as white to off-white, capsule-shaped, biconvex tablets debossed with “U50” on one side in unit-dose packets (each packet contains 1 tablet):
- Box of 10 Packets, NDC: 0023-6498-10
- Box of 16 Packets, NDC: 0023-6498-16
- Box of 30 Packets, NDC: 0023-6498-30
UBRELVY 100 mg is supplied as white to off-white capsule-shaped, biconvex tablets debossed with “U100” on one side in unit-dose packets (each packet contains 1 tablet):
- Box of 10 Packets, NDC: 0023-6501-10
- Box of 16 Packets, NDC: 0023-6501-16
- Box of 30 Packets, NDC: 0023-6501-30
16.2 Storage and Handling
Store between 20°C and 25°C (68°F and 77°F): excursions permitted between 15°C and 30°C (59°F and 86°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature ] .
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Ubrogepant is a calcitonin gene-related peptide receptor antagonist.