Get your patient on Yervoy (Ipilimumab)
Yervoy prior authorization resources
Most recent state uniform prior authorization forms
Brand Resources
Dosage & administration
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- Administer by intravenous infusion after dilution based upon recommended infusion rate for each indication. (2)
- Unresectable or Metastatic Melanoma :
- YERVOY 3 mg/kg every 3 weeks for a maximum of 4 doses. (2.2)
- YERVOY 3 mg/kg immediately following nivolumab 1 mg/kg on the same day, every 3 weeks for 4 doses. After completing 4 doses of the combination, administer nivolumab as a single agent as recommended in the Full Prescribing Information for nivolumab. (2.2)
- Adjuvant Treatment of Melanoma : YERVOY 3 mg/kg every 3 weeks for 4 doses, followed by 3 mg/kg every 12 weeks for up to 4 additional doses. (2.2)
- Advanced Renal Cell Carcinoma : YERVOY 1 mg/kg immediately following nivolumab 3 mg/kg on the same day, every 3 weeks for 4 doses. After completing 4 doses of the combination, administer nivolumab as a single agent as recommended in Full Prescribing Information for nivolumab. (2.2)
- Treatment of microsatellite instability-high (MSI-H) or mismatch repair deficient (dMMR) colorectal cancer in combination with nivolumab :
- Adult and pediatric patients weighing 40 kg or greater: YERVOY 1 mg/kg immediately following nivolumab 240 mg on the same day every 3 weeks for a maximum of 4 doses. After completing the combination, administer nivolumab as a single agent as recommended in Full Prescribing Information for nivolumab. (2.2)
- Pediatric patients weighing less than 40 kg: YERVOY 1 mg/kg immediately following nivolumab 3 mg/kg on the same day every 3 weeks for a maximum of 4 doses. After completing the combination, administer nivolumab as a single agent as recommended in Full Prescribing Information for nivolumab. (2.2 )
- Hepatocellular Carcinoma : YERVOY 3 mg/kg intravenously over 30 minutes immediately following nivolumab 1 mg/kg intravenously over 30 minutes on the same day, every 3 weeks for up to 4 doses. After completing up to 4 doses of the combination, administer nivolumab as a single agent as recommended in Full Prescribing Information for nivolumab. (2.2)
- Metastatic non-small cell lung cancer :
- Malignant pleural mesothelioma : YERVOY 1 mg/kg every 6 weeks with nivolumab 360 mg every 3 weeks. (2.2)
- Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma: YERVOY 1 mg/kg every 6 weeks with nivolumab 3 mg/kg every 2 weeks or 360 mg every 3 weeks. (2.2)
- See full Prescribing Information for preparation and administration instructions and dosage modifications for adverse reactions.
Patient Selection
Information on FDA-approved tests for patient selection is available at:
Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
- Select patients with metastatic NSCLC for treatment with YERVOY in combination with nivolumab based on PD-L1 expression [see Clinical Studies (14.6) ] .
Esophageal Cancer
- Select patients with unresectable or advanced or metastatic ESCC for treatment with YERVOY in combination with nivolumab based on PD-L1 expression [see Clinical Studies (14.8) ] .
- An FDA-approved companion diagnostic for the detection of PD-L1 expression in patients with advanced or metastatic ESCC is not available.
Recommended Dosage
The recommended dosages of YERVOY as a single agent are presented in Table 1.
Administer YERVOY as a 30-minute intravenous infusion [see Preparation and Administration (2.4) ] .
Indication | Recommended YERVOY Dosage | Duration of Therapy |
Unresectable or metastatic melanoma | 3 mg/kg every 3 weeks | Maximum of 4 doses |
Adjuvant treatment of melanoma | 3 mg/kg every 3 weeks followed by 3 mg/kg every 12 weeks | Every 3 weeks up to a maximum of 4 doses Every 12 weeks for up to 4 additional doses |
The recommended dosages of YERVOY in combination with other therapeutic agents are presented in Table 2. Administer YERVOY on the same day as other therapeutic agents.
Refer to the respective Prescribing Information for each therapeutic agent administered in combination with YERVOY for recommended dosage information, as appropriate.
| • Refer to the Prescribing Information for the agents administered in combination with YERVOY for recommended dosing information, as appropriate. † Refer to the Prescribing Information for nivolumab for dosage information after completing use in combination with YERVOY. | ||
Indication | Recommended YERVOY Dosage | Duration of Therapy |
Unresectable or metastatic melanoma | 3 mg/kg every 3 weeks with nivolumab 1 mg/kg | In combination with nivolumab for a maximum of 4 doses or until unacceptable toxicity, whichever occurs earlier. After completing 4 doses of combination therapy, administer nivolumab as a single agent until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity.† |
Advanced renal cell carcinoma | 1 mg/kg every 3 weeks with nivolumab 3 mg/kg | In combination with nivolumab After completing 4 doses of combination therapy, administer nivolumab as single agent until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity. † |
Microsatellite instability-high (MSI‑H) or mismatch repair deficient (dMMR) metastatic colorectal cancer | Adult patients and pediatric patients age 12 years and older and weighing 40 kg or more: 1 mg/kg every 3 weeks with nivolumab 240 mg | In combination with nivolumab After completing 4 doses of combination therapy, administer nivolumab as single agent until disease progression, unacceptable toxicity , or up to 2 years . † |
Pediatric patients age 12 years and older and weighing less than 40 kg: 1 mg/kg every 3 weeks | ||
Hepatocellular carcinoma | 3 mg/kg every 3 weeks with nivolumab 1 mg/kg | In combination with nivolumab After completing a maximum of 4 doses of combination therapy, administer nivolumab as single agent until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity. † |
Metastatic non-small cell lung cancer expressing PD‑L1 | 1 mg/kg every 6 weeks with nivolumab 360 mg every 3 weeks | In combination with nivolumab until disease progression, unacceptable toxicity, or up to 2 years in patients without disease progression. † |
Metastatic or recurrent non-small cell lung cancer | 1 mg/kg every 6 weeks with nivolumab 360 mg every 3 weeks and histology-based platinum‑doublet chemotherapy every 3 weeks | In combination with nivolumab until disease progression, unacceptable toxicity, or up to 2 years in patients without disease progression. † |
2 cycles of histology-based platinum-doublet chemotherapy | ||
Malignant pleural mesothelioma | 1 mg/kg every 6 weeks with nivolumab 360 mg every 3 weeks | In combination with nivolumab until disease progression, unacceptable toxicity, or up to 2 years in patients without disease progression. † |
Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma | 1 mg/kg every 6 weeks with nivolumab 3 mg/kg every 2 weeks or 360 mg every 3 weeks | In combination with nivolumab until disease progression, unacceptable toxicity, or up to 2 years. |
Recommended Dosage Modifications for Adverse Reactions
No dose reduction for YERVOY is recommended. In general, withhold YERVOY for severe (Grade 3) immune-mediated adverse reactions. Permanently discontinue YERVOY for life-threatening (Grade 4) immune-mediated adverse reactions, recurrent severe (Grade 3) immune-mediated reactions that require systemic immunosuppressive treatment, persistent moderate (Grade 2) or severe (Grade 3) reactions lasting 12 weeks or longer after last YERVOY dose (excluding endocrinopathy), or an inability to reduce corticosteroid dose to 10 mg or less of prednisone or equivalent per day within 12 weeks of initiating steroids. Dosage modifications for YERVOY or YERVOY in combination with nivolumab for adverse reactions that require management different from these general guidelines are summarized in Table 3.
When YERVOY is administered in combination with nivolumab, withhold or permanently discontinue both YERVOY and nivolumab for toxicity.
| ALT = alanine aminotransferase, AST = aspartate aminotransferase, DRESS = Drug Rash with Eosinophilia and Systemic Symptoms, SJS = Stevens Johnson Syndrome, TEN = toxic epidermal necrolysis, ULN = upper limit of normal • Based on Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (CTCAE), Version 4.03 a Resume in patients with complete or partial resolution (Grade 0 or 1) after corticosteroid taper. Permanently discontinue if no complete or partial resolution within 12 weeks of last dose or inability to reduce prednisone to 10 mg per day (or equivalent) or less within 12 weeks of initiating steroids. b If AST/ALT are less than or equal to ULN at baseline, withhold or permanently discontinue YERVOY based on recommendations for hepatitis with no liver involvement. c This guidance is only applicable to HCC patients who are being treated with YERVOY in combination with nivolumab. d Depending on clinical severity, consider withholding for Grade 2 endocrinopathy until symptom improvement with hormone replacement. Resume once acute symptoms have resolved. | ||
Adverse Reaction | Severity• | Dosage Modifications |
Immune-Mediated Adverse Reactions [See Warnings and Precautions (5.1) ] | ||
Colitis | Grade 2 | Withhold a |
Grade 3 or 4 | Permanently discontinue | |
Hepatitis with no tumor involvement of the liver or Hepatitis with tumor involvement of the liver/non-HCC | AST or ALT increases to more than 3 times and up to 5 times the ULN or Total bilirubin increases to more than 1.5 times and up to 3 times the ULN | Withhold a |
AST or ALT more than 5 times the ULN or Total bilirubin more than 3 times the ULN | Permanently discontinue | |
Hepatitis with tumor involvement of the liver b /HCC c | Baseline AST/ALT is more than 1 and up to 3 times ULN and increases to more than 5 and up to 10 times ULN or Baseline AST/ALT is more than 3 and up to 5 times ULN and increases to more than 8 and up to 10 times ULN. | Withhold a |
AST/ALT increases to more than 10 times ULN or Total bilirubin increases to more than 3 times ULN. | Permanently discontinue | |
Exfoliative Dermatologic Conditions | Suspected SJS, TEN, or DRESS | Withhold |
Confirmed SJS, TEN, or DRESS | Permanently discontinue | |
Endocrinopathies d | Grades 3 or 4 | Withhold until clinically stable or permanently discontinue depending on severity |
Pneumonitis | Grade 2 | Withhold a |
Grade 3 or 4 | Permanently discontinue | |
Nephritis with Renal Dysfunction | Grade 2 or 3 increased blood creatinine | Withhold a |
Grade 4 increased blood creatinine | Permanently discontinue | |
Neurological Toxicities | Grade 2 | Withhold a |
Grade 3 or 4 | Permanently discontinue | |
Myocarditis | Grade 2, 3 or 4 | Permanently discontinue |
Ophthalmologic | Grade 2, 3, or 4 that does not improve to Grade 1 within 2 weeks while receiving topical therapy or that requires systemic treatment | Permanently discontinue |
Other Adverse Reactions | ||
Infusion-Related Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) ] | Grade 1 or 2 | Interrupt or slow the rate of infusion |
Grade 3 or 4 | Permanently discontinue | |
Preparation and Administration
- Do not shake product.
- Visually inspect for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration. Discard vial if solution is cloudy, there is pronounced discoloration (solution may have pale-yellow color), or there is foreign particulate matter other than translucent-to-white, amorphous particles.
Preparation of Solution
- Allow the vial(s) to stand at room temperature for approximately 5 minutes prior to preparation of infusion.
- Withdraw the required volume of YERVOY and transfer into an intravenous bag.
- Dilute with 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP or 5% Dextrose Injection, USP to a final concentration ranging from 1 mg/mL to 2 mg/mL . Mix diluted solution by gentle inversion.
- After preparation, store the diluted solution either refrigerated at 2°C to 8°C (36°F to 46°F) or at room temperature of 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F) for no more than 24 hours from the time of preparation to the time of infusion.
- Discard partially used or empty vials of YERVOY.
Administration
- Do not co-administer other drugs through the same intravenous line.
- Flush the intravenous line with 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP or 5% Dextrose Injection, USP after each dose.
- Administer diluted YERVOY solution by intravenous infusion over 30 minutes through an intravenous line containing a sterile, non-pyrogenic, low-protein -binding in-line filter.
- When administered in combination with nivolumab, infuse nivolumab first followed by YERVOY on the same day.
- When administered with nivolumab and platinum-doublet chemotherapy, infuse nivolumab first followed by YERVOY and then platinum-doublet chemotherapy on the same day.
- Use separate infusion bags and filters for each infusion.

Yervoy prescribing information
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
YERVOY is a human cytotoxic T-lymphocyte antigen 4 (CTLA-4)-blocking antibody indicated for:
Melanoma
- Treatment of unresectable or metastatic melanoma in adults and pediatric patients 12 years and older as a single agent or in combination with nivolumab. (1.1)
- Adjuvant treatment of adult patients with cutaneous melanoma with pathologic involvement of regional lymph nodes of more than 1 mm who have undergone complete resection, including total lymphadenectomy. (1.2)
Renal Cell Carcinoma (RCC)
- Treatment of adult patients with intermediate or poor risk advanced renal cell carcinoma, as first-line treatment in combination with nivolumab. (1.3)
Colorectal Cancer
- Treatment of adults and pediatric patients 12 years and older with unresectable or metastatic microsatellite instability-high (MSI-H) or mismatch repair deficient (dMMR) colorectal cancer (CRC) in combination with nivolumab. (1.4)
Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- adult patients with unresectable or metastatic hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) as first-line treatment in combination with nivolumab. (1.5 )
- in combination with nivolumab in adult patients with unresectable or metastatic HCC who have been previously treated with sorafenib. (1.5)
Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC)
- Treatment of adult patients with metastatic non-small cell lung cancer expressing PD-L1 (≥1%) as determined by an FDA-approved test, with no EGFR or ALK genomic tumor aberrations, as first-line treatment in combination with nivolumab. (1.6)
- Treatment of adult patients with metastatic or recurrent non-small cell lung cancer with no EGFR or ALK genomic tumor aberrations as first-line treatment, in combination with nivolumab and 2 cycles of platinum-doublet chemotherapy. (1.6)
Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma
- Treatment of adult patients with unresectable malignant pleural mesothelioma, as first-line treatment in combination with nivolumab. (1.7)
Esophageal Cancer
- Treatment of adult patients with unresectable advanced or metastatic esophageal squamous cell carcinoma, as first line treatment in combination with nivolumab whose tumors express PD-L1 (≥1). (1.8)
Unresectable or Metastatic Melanoma
YERVOY, as a single agent or in combination with nivolumab, is indicated for the treatment of unresectable or metastatic melanoma in adult and pediatric patients 12 years and older.
Adjuvant Treatment of Melanoma
YERVOY is indicated for the adjuvant treatment of adult patients with cutaneous melanoma with pathologic involvement of regional lymph nodes of more than 1 mm who have undergone complete resection, including total lymphadenectomy.
Advanced Renal Cell Carcinoma
YERVOY, in combination with nivolumab, is indicated for the first-line treatment of adult patients with intermediate or poor risk advanced renal cell carcinoma (RCC).
Microsatellite Instability-High or Mismatch Repair Deficient Metastatic Colorectal Cancer
- YERVOY, in combination with nivolumab, is indicated for the treatment of adult and pediatric patients 12 years and older with unresectable or metastatic microsatellite instability-high (MSI-H) or mismatch repair deficient (dMMR) colorectal cancer ( CRC ).
Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- YERVOY, in combination with nivolumab, is indicated for the first-line treatment of adult patients with unresectable or metastatic hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC).
- YERVOY, in combination with nivolumab, is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with unresectable or metastatic HCC who have been previously treated with sorafenib.
Metastatic Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
YERVOY, in combination with nivolumab, is indicated for the first-line treatment of adult patients with metastatic non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) whose tumors express PD-L1 (≥1%) as determined by an FDA-approved test [see Dosage and Administration (2.1) ] , with no EGFR or ALK genomic tumor aberrations.
YERVOY, in combination with nivolumab and 2 cycles of platinum-doublet chemotherapy, is indicated for the first-line treatment of adult patients with metastatic or recurrent NSCLC, with no EGFR or ALK genomic tumor aberrations.
Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma
YERVOY, in combination with nivolumab, is indicated for the first-line treatment of adult patients with unresectable malignant pleural mesothelioma.
Esophageal Cancer
YERVOY, in combination with nivolumab, is indicated for the first-line treatment of adult patients with unresectable advanced or metastatic esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) whose tumors express PD-L1 (≥1) [see Dosage and Administration (2.1) ] .
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- Administer by intravenous infusion after dilution based upon recommended infusion rate for each indication. (2)
- Unresectable or Metastatic Melanoma :
- YERVOY 3 mg/kg every 3 weeks for a maximum of 4 doses. (2.2)
- YERVOY 3 mg/kg immediately following nivolumab 1 mg/kg on the same day, every 3 weeks for 4 doses. After completing 4 doses of the combination, administer nivolumab as a single agent as recommended in the Full Prescribing Information for nivolumab. (2.2)
- Adjuvant Treatment of Melanoma : YERVOY 3 mg/kg every 3 weeks for 4 doses, followed by 3 mg/kg every 12 weeks for up to 4 additional doses. (2.2)
- Advanced Renal Cell Carcinoma : YERVOY 1 mg/kg immediately following nivolumab 3 mg/kg on the same day, every 3 weeks for 4 doses. After completing 4 doses of the combination, administer nivolumab as a single agent as recommended in Full Prescribing Information for nivolumab. (2.2)
- Treatment of microsatellite instability-high (MSI-H) or mismatch repair deficient (dMMR) colorectal cancer in combination with nivolumab :
- Adult and pediatric patients weighing 40 kg or greater: YERVOY 1 mg/kg immediately following nivolumab 240 mg on the same day every 3 weeks for a maximum of 4 doses. After completing the combination, administer nivolumab as a single agent as recommended in Full Prescribing Information for nivolumab. (2.2)
- Pediatric patients weighing less than 40 kg: YERVOY 1 mg/kg immediately following nivolumab 3 mg/kg on the same day every 3 weeks for a maximum of 4 doses. After completing the combination, administer nivolumab as a single agent as recommended in Full Prescribing Information for nivolumab. (2.2 )
- Hepatocellular Carcinoma : YERVOY 3 mg/kg intravenously over 30 minutes immediately following nivolumab 1 mg/kg intravenously over 30 minutes on the same day, every 3 weeks for up to 4 doses. After completing up to 4 doses of the combination, administer nivolumab as a single agent as recommended in Full Prescribing Information for nivolumab. (2.2)
- Metastatic non-small cell lung cancer :
- Malignant pleural mesothelioma : YERVOY 1 mg/kg every 6 weeks with nivolumab 360 mg every 3 weeks. (2.2)
- Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma: YERVOY 1 mg/kg every 6 weeks with nivolumab 3 mg/kg every 2 weeks or 360 mg every 3 weeks. (2.2)
- See full Prescribing Information for preparation and administration instructions and dosage modifications for adverse reactions.
Patient Selection
Information on FDA-approved tests for patient selection is available at:
Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
- Select patients with metastatic NSCLC for treatment with YERVOY in combination with nivolumab based on PD-L1 expression [see Clinical Studies (14.6) ] .
Esophageal Cancer
- Select patients with unresectable or advanced or metastatic ESCC for treatment with YERVOY in combination with nivolumab based on PD-L1 expression [see Clinical Studies (14.8) ] .
- An FDA-approved companion diagnostic for the detection of PD-L1 expression in patients with advanced or metastatic ESCC is not available.
Recommended Dosage
The recommended dosages of YERVOY as a single agent are presented in Table 1.
Administer YERVOY as a 30-minute intravenous infusion [see Preparation and Administration (2.4) ] .
Indication | Recommended YERVOY Dosage | Duration of Therapy |
Unresectable or metastatic melanoma | 3 mg/kg every 3 weeks | Maximum of 4 doses |
Adjuvant treatment of melanoma | 3 mg/kg every 3 weeks followed by 3 mg/kg every 12 weeks | Every 3 weeks up to a maximum of 4 doses Every 12 weeks for up to 4 additional doses |
The recommended dosages of YERVOY in combination with other therapeutic agents are presented in Table 2. Administer YERVOY on the same day as other therapeutic agents.
Refer to the respective Prescribing Information for each therapeutic agent administered in combination with YERVOY for recommended dosage information, as appropriate.
| • Refer to the Prescribing Information for the agents administered in combination with YERVOY for recommended dosing information, as appropriate. † Refer to the Prescribing Information for nivolumab for dosage information after completing use in combination with YERVOY. | ||
Indication | Recommended YERVOY Dosage | Duration of Therapy |
Unresectable or metastatic melanoma | 3 mg/kg every 3 weeks with nivolumab 1 mg/kg | In combination with nivolumab for a maximum of 4 doses or until unacceptable toxicity, whichever occurs earlier. After completing 4 doses of combination therapy, administer nivolumab as a single agent until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity.† |
Advanced renal cell carcinoma | 1 mg/kg every 3 weeks with nivolumab 3 mg/kg | In combination with nivolumab for a maximum of 4 doses. After completing 4 doses of combination therapy, administer nivolumab as single agent until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity. † |
Microsatellite instability-high (MSI‑H) or mismatch repair deficient (dMMR) metastatic colorectal cancer | Adult patients and pediatric patients age 12 years and older and weighing 40 kg or more: 1 mg/kg every 3 weeks with nivolumab 240 mg | In combination with nivolumab for a maximum of 4 doses . † After completing 4 doses of combination therapy, administer nivolumab as single agent until disease progression, unacceptable toxicity , or up to 2 years . † |
Pediatric patients age 12 years and older and weighing less than 40 kg: 1 mg/kg every 3 weeks with nivolumab 3 mg/kg | ||
Hepatocellular carcinoma | 3 mg/kg every 3 weeks with nivolumab 1 mg/kg | In combination with nivolumab for a maximum of 4 doses. After completing a maximum of 4 doses of combination therapy, administer nivolumab as single agent until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity. † |
Metastatic non-small cell lung cancer expressing PD‑L1 | 1 mg/kg every 6 weeks with nivolumab 360 mg every 3 weeks | In combination with nivolumab until disease progression, unacceptable toxicity, or up to 2 years in patients without disease progression. † |
Metastatic or recurrent non-small cell lung cancer | 1 mg/kg every 6 weeks with nivolumab 360 mg every 3 weeks and histology-based platinum‑doublet chemotherapy every 3 weeks | In combination with nivolumab until disease progression, unacceptable toxicity, or up to 2 years in patients without disease progression. † |
2 cycles of histology-based platinum-doublet chemotherapy | ||
Malignant pleural mesothelioma | 1 mg/kg every 6 weeks with nivolumab 360 mg every 3 weeks | In combination with nivolumab until disease progression, unacceptable toxicity, or up to 2 years in patients without disease progression. † |
Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma | 1 mg/kg every 6 weeks with nivolumab 3 mg/kg every 2 weeks or 360 mg every 3 weeks | In combination with nivolumab until disease progression, unacceptable toxicity, or up to 2 years. |
Recommended Dosage Modifications for Adverse Reactions
No dose reduction for YERVOY is recommended. In general, withhold YERVOY for severe (Grade 3) immune-mediated adverse reactions. Permanently discontinue YERVOY for life-threatening (Grade 4) immune-mediated adverse reactions, recurrent severe (Grade 3) immune-mediated reactions that require systemic immunosuppressive treatment, persistent moderate (Grade 2) or severe (Grade 3) reactions lasting 12 weeks or longer after last YERVOY dose (excluding endocrinopathy), or an inability to reduce corticosteroid dose to 10 mg or less of prednisone or equivalent per day within 12 weeks of initiating steroids. Dosage modifications for YERVOY or YERVOY in combination with nivolumab for adverse reactions that require management different from these general guidelines are summarized in Table 3.
When YERVOY is administered in combination with nivolumab, withhold or permanently discontinue both YERVOY and nivolumab for toxicity.
| ALT = alanine aminotransferase, AST = aspartate aminotransferase, DRESS = Drug Rash with Eosinophilia and Systemic Symptoms, SJS = Stevens Johnson Syndrome, TEN = toxic epidermal necrolysis, ULN = upper limit of normal • Based on Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (CTCAE), Version 4.03 a Resume in patients with complete or partial resolution (Grade 0 or 1) after corticosteroid taper. Permanently discontinue if no complete or partial resolution within 12 weeks of last dose or inability to reduce prednisone to 10 mg per day (or equivalent) or less within 12 weeks of initiating steroids. b If AST/ALT are less than or equal to ULN at baseline, withhold or permanently discontinue YERVOY based on recommendations for hepatitis with no liver involvement. c This guidance is only applicable to HCC patients who are being treated with YERVOY in combination with nivolumab. d Depending on clinical severity, consider withholding for Grade 2 endocrinopathy until symptom improvement with hormone replacement. Resume once acute symptoms have resolved. | ||
Adverse Reaction | Severity• | Dosage Modifications |
Immune-Mediated Adverse Reactions [See Warnings and Precautions (5.1) ] | ||
Colitis | Grade 2 | Withhold a |
Grade 3 or 4 | Permanently discontinue | |
Hepatitis with no tumor involvement of the liver or Hepatitis with tumor involvement of the liver/non-HCC | AST or ALT increases to more than 3 times and up to 5 times the ULN or Total bilirubin increases to more than 1.5 times and up to 3 times the ULN | Withhold a |
AST or ALT more than 5 times the ULN or Total bilirubin more than 3 times the ULN | Permanently discontinue | |
Hepatitis with tumor involvement of the liver b /HCC c | Baseline AST/ALT is more than 1 and up to 3 times ULN and increases to more than 5 and up to 10 times ULN or Baseline AST/ALT is more than 3 and up to 5 times ULN and increases to more than 8 and up to 10 times ULN. | Withhold a |
AST/ALT increases to more than 10 times ULN or Total bilirubin increases to more than 3 times ULN. | Permanently discontinue | |
Exfoliative Dermatologic Conditions | Suspected SJS, TEN, or DRESS | Withhold |
Confirmed SJS, TEN, or DRESS | Permanently discontinue | |
Endocrinopathies d | Grades 3 or 4 | Withhold until clinically stable or permanently discontinue depending on severity |
Pneumonitis | Grade 2 | Withhold a |
Grade 3 or 4 | Permanently discontinue | |
Nephritis with Renal Dysfunction | Grade 2 or 3 increased blood creatinine | Withhold a |
Grade 4 increased blood creatinine | Permanently discontinue | |
Neurological Toxicities | Grade 2 | Withhold a |
Grade 3 or 4 | Permanently discontinue | |
Myocarditis | Grade 2, 3 or 4 | Permanently discontinue |
Ophthalmologic | Grade 2, 3, or 4 that does not improve to Grade 1 within 2 weeks while receiving topical therapy or that requires systemic treatment | Permanently discontinue |
Other Adverse Reactions | ||
Infusion-Related Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) ] | Grade 1 or 2 | Interrupt or slow the rate of infusion |
Grade 3 or 4 | Permanently discontinue | |
Preparation and Administration
- Do not shake product.
- Visually inspect for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration. Discard vial if solution is cloudy, there is pronounced discoloration (solution may have pale-yellow color), or there is foreign particulate matter other than translucent-to-white, amorphous particles.
Preparation of Solution
- Allow the vial(s) to stand at room temperature for approximately 5 minutes prior to preparation of infusion.
- Withdraw the required volume of YERVOY and transfer into an intravenous bag.
- Dilute with 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP or 5% Dextrose Injection, USP to a final concentration ranging from 1 mg/mL to 2 mg/mL . Mix diluted solution by gentle inversion.
- After preparation, store the diluted solution either refrigerated at 2°C to 8°C (36°F to 46°F) or at room temperature of 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F) for no more than 24 hours from the time of preparation to the time of infusion.
- Discard partially used or empty vials of YERVOY.
Administration
- Do not co-administer other drugs through the same intravenous line.
- Flush the intravenous line with 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP or 5% Dextrose Injection, USP after each dose.
- Administer diluted YERVOY solution by intravenous infusion over 30 minutes through an intravenous line containing a sterile, non-pyrogenic, low-protein -binding in-line filter.
- When administered in combination with nivolumab, infuse nivolumab first followed by YERVOY on the same day.
- When administered with nivolumab and platinum-doublet chemotherapy, infuse nivolumab first followed by YERVOY and then platinum-doublet chemotherapy on the same day.
- Use separate infusion bags and filters for each infusion.
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Injection: 50 mg/10 mL (5 mg/mL) and 200 mg/40 mL (5 mg/mL) as a clear to slightly opalescent, colorless to pale-yellow solution in a single-dose vial.
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
- Lactation : Advise not to breastfeed. (8.2 )
Pregnancy
Risk Summary
Based on findings from animal studies and its mechanism of action [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.1) ] , YERVOY can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. There is insufficient human data for YERVOY exposure in pregnant women. In animal reproduction studies, administration of ipilimumab to cynomolgus monkeys from the onset of organogenesis through delivery resulted in higher incidences of abortion, stillbirth, premature delivery (with corresponding lower birth weight), and higher incidences of infant mortality in a dose-related manner (see Data ) . The effects of ipilimumab are likely to be greater during the second and third trimesters of pregnancy. Human IgG1 is known to cross the placental barrier and ipilimumab is an IgG1; therefore, ipilimumab has the potential to be transmitted from the mother to the developing fetus. Advise pregnant women of the potential risk to a fetus. Report pregnancies to Bristol-Myers Squibb at 1-844-593-7869.
In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2% to 4% and 15% to 20%, respectively.
Data
Animal Data
In a combined study of embryo-fetal and peri-postnatal development, pregnant cynomolgus monkeys received ipilimumab every 3 weeks from the onset of organogenesis in the first trimester through parturition. No treatment-related adverse effects on reproduction were detected during the first two trimesters of pregnancy. Beginning in the third trimester, administration of ipilimumab at doses resulting in exposures approximately 2.6 to 7.2 times the human exposure at a dose of 3 mg/kg resulted in dose-related increases in abortion, stillbirth, premature delivery (with corresponding lower birth weight), and an increased incidence of infant mortality. In addition, developmental abnormalities were identified in the urogenital system of 2 infant monkeys exposed in utero to 30 mg/kg of ipilimumab (7.2 times the humans exposure based on area under the curve at a dose of 3 mg/kg). One female infant monkey had unilateral renal agenesis of the left kidney and ureter, and 1 male infant monkey had an imperforate urethra with associated urinary obstruction and subcutaneous scrotal edema.
Genetically engineered mice heterozygous for CTLA-4 (CTLA-4+/−), the target for ipilimumab, appeared healthy and gave birth to healthy CTLA-4+/− heterozygous offspring. Mated CTLA-4+/− heterozygous mice also produced offspring deficient in CTLA-4 (homozygous negative, CTLA-4−/−). The CTLA-4−/− homozygous negative offspring appeared healthy at birth, exhibited signs of multiorgan lymphoproliferative disease by 2 weeks of age, and all died by 3 to 4 weeks of age with massive lymphoproliferation and multiorgan tissue destruction.
Lactation
Risk Summary
There are no data on the presence of YERVOY in human milk or its effects on the breastfed child or milk production. In monkeys, ipilimumab was present in milk (see Data ) . Because of the potential for serious adverse reactions in breastfed children, advise women not to breastfeed during treatment with YERVOY and for 3 months following the last dose.
Data
In monkeys treated at dose levels resulting in exposures 2.6 and 7.2 times higher than those in humans at a 3 mg/kg dose, ipilimumab was present in milk at concentrations of 0.1 mcg/mL and 0.4 mcg/mL, representing a ratio of up to 0.3% of the steady-state serum concentration of the drug.
Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
Pregnancy Testing
Verify pregnancy status in females of reproductive potential prior to initiating YERVOY [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1) ] .
Contraception
YERVOY can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1) ] . Advise females of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with YERVOY and for 3 months following the last dose.
Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of YERVOY have been established in pediatric patients aged 12 years and older for the following indications: as a single agent and in combination with nivolumab for unresectable or metastatic melanoma, in combination with nivolumab for the treatment of MSI-H or dMMR unresectable and metastatic CRC, and in combination with nivolumab for MSI-H or dMMR mCRC that has progressed following treatment with a fluoropyrimidine, oxaliplatin, and irinotecan. Use of YERVOY for these indications is supported by evidence from adequate and well-controlled studies in adults with melanoma or MSI-H or dMMR mCRC and additional pharmacokinetic data in pediatric patients. Ipilimumab exposures in pediatric patients 12 years and older are comparable to that of adults, and the courses of melanoma and MSI-H or dMMR mCRC are similar in pediatric patients aged 12 years and older to that of adults to allow extrapolation of safety and efficacy [see Adverse Reactions (6.1) , Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) , Clinical Studies (14.4) ] .
The safety and effectiveness of YERVOY have not been established in pediatric patients younger than 12 years old with unresectable or metastatic melanoma or MSI-H or dMMR mCRC.
The safety and effectiveness of YERVOY have not been established in pediatric patients for the adjuvant treatment of melanoma or for the treatment of advanced renal cell carcinoma, hepatocellular carcinoma, metastatic non-small cell lung cancer, malignant pleural mesothelioma and esophageal cancer.
In a dose-finding trial (NCT01445379), 33 patients aged 2 to 21 years (median 13 years) with relapsed or refractory solid tumors were evaluated including unresectable stage IIIc or stage IV melanoma (12), progressive or refractory sarcomas (17), renal or bladder carcinoma (3), and neuroblastoma (1). No responses in the patients with non-melanoma solid tumors and no new safety signals were observed in pediatric patients in this study.
Geriatric Use
Single Agent
Of the 511 patients treated with YERVOY in Study MDX010-20 (unresectable or metastatic melanoma), 28% were 65 years and over. No overall differences in safety or effectiveness were observed between these patients and younger patients.
In Combination with Nivolumab
Of the 314 patients randomized to YERVOY administered with nivolumab in CHECKMATE-067, 41% were 65 years or older and 11% were 75 years or older. No overall differences in safety or effectiveness were reported between elderly patients and younger patients.
Of the 576 patients randomized to YERVOY 1 mg/kg every 6 weeks with nivolumab 3 mg/kg every 2 weeks in CHECKMATE-227 (NSCLC), 48% were 65 years or older and 10% were 75 years or older. No overall difference in safety was reported between older patients and younger patients; however, there was a higher discontinuation rate due to adverse reactions in patients aged 75 years or older (29%) relative to all patients who received YERVOY with nivolumab (18%). Of the 396 patients in the primary efficacy population (PD-L1 ≥1%) randomized to YERVOY 1 mg/kg every 6 weeks with nivolumab 3 mg/kg every 2 weeks in CHECKMATE-227, the hazard ratio for overall survival was 0.70 (95% CI: 0.55, 0.89) in the 199 patients younger than 65 years compared to 0.91 (95% CI: 0.72, 1.15) in the 197 patients 65 years or older [see Clinical Studies (14.6) ] .
Of the 303 patients randomized to YERVOY 1 mg/kg every 6 weeks in combination with nivolumab 3 mg/kg every 2 weeks in CHECKMATE-743 (malignant pleural mesothelioma), 77% were 65 years old or older and 26% were 75 years or older. No overall difference in safety was reported between older patients and younger patients; however, there were higher rates of serious adverse reactions and discontinuation rate due to adverse reactions in patients aged 75 years or older (68% and 35%, respectively) relative to all patients who received YERVOY with nivolumab (54% and 28%, respectively). For patients aged 75 years or older who received chemotherapy, the rate of serious adverse reactions was 34% and discontinuation due to adverse reactions was 26% relative to 28% and 19% respectively for all patients. The hazard ratio for overall survival was 0.76 (95% CI: 0.52, 1.11) in the 71 patients younger than 65 years compared to 0.74 (95% CI: 0.59, 0.93) in the 232 patients 65 years or older randomized to YERVOY in combination with nivolumab.
Of the 550 patients randomized to YERVOY 1 mg/kg with nivolumab in CHECKMATE-214 (renal cell carcinoma), 38% were 65 years or older and 8% were 75 years or older. No overall difference in safety was observed between these patients and younger patients. In geriatric patients with intermediate or poor risk, no overall difference in effectiveness was observed.
Of the 354 patients with dMMR or MSI-H metastatic CRC (mCRC) who were randomized to YERVOY in combination with nivolumab, 44% were 65 years or older and 14% were 75 years or older. Of the 353 patients randomized to nivolumab, as a single agent, 45% were 65 years or older and 13% were 75 years or older. There was a higher incidence of any Grade 3 or 4 adverse reactions (55%) in patients aged 65 years or older receiving YERVOY in combination with nivolumab compared to those younger than 65 receiving the combination (42%). There was a higher incidence of adverse reactions leading to discontinuation in patients aged 65 years or older receiving YERVOY in combination with nivolumab (23%) compared to those younger than 65 receiving the combination (15%). No overall differences in effectiveness were reported between elderly patients and younger patients receiving YERVOY in combination with nivolumab [see Clinical Studies (14.4) ] .
Of the 335 patients with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma who were randomized to YERVOY in combination with nivolumab, 52% were 65 years or older and 14% were 75 years or older. No overall difference in safety was reported between elderly patients and younger patients.
Of the 49 patients who received YERVOY 3 mg/kg with nivolumab in Cohort 4 of CHECKMATE-040 (previously treated hepatocellular carcinoma), 29% were between 65 years and 74 years of age and 8% were 75 years or older. Clinical studies of YERVOY in combination with nivolumab did not include sufficient numbers of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma aged 65 and over to determine whether they respond differently from younger patients.
Of the 325 patients who received YERVOY 1 mg/kg every 6 weeks in combination with nivolumab 3 mg/kg every 2 weeks in CHECKMATE-648 (ESCC), 43% were 65 years old or older and 7% were 75 years or older. No overall difference in safety was reported between older patients and younger patients; however, there was a higher discontinuation rate due to adverse reactions in patients aged 75 years or older (38%) relative to all patients who received YERVOY with nivolumab (23%). For patients aged 75 years or older who received chemotherapy, the discontinuation rate due to adverse reactions was 33% relative to 23% for all patients.
Study CA184-029 (adjuvant treatment of melanoma) and CHECKMATE-142 (metastatic colorectal cancer) did not include sufficient numbers of patients aged 65 years and older to determine whether they respond differently from younger patients.
In Combination with Nivolumab and Platinum-Doublet Chemotherapy
Of the 361 patients randomized to YERVOY 1 mg/kg every 6 weeks in combination with nivolumab 360 mg every 3 weeks and platinum-doublet chemotherapy every 3 weeks (for 2 cycles) in CHECKMATE-9LA (NSCLC), 51% were 65 years or older and 10% were 75 years or older. No overall difference in safety was reported between older patients and younger patients; however, there was a higher discontinuation rate due to adverse reactions in patients aged 75 years or older (43%) relative to all patients who received YERVOY with nivolumab and chemotherapy (24%). For patients aged 75 years or older who received chemotherapy only, the discontinuation rate due to adverse reactions was 16% relative to all patients who had a discontinuation rate of 13%. Based on an updated analysis for overall survival, of the 361 patients randomized to YERVOY in combination with nivolumab and platinum-doublet chemotherapy in CHECKMATE-9LA, the hazard ratio for overall survival was 0.61 (95% CI: 0.47, 0.80) in the 176 patients younger than 65 years compared to 0.73 (95% CI: 0.56, 0.95) in the 185 patients 65 years or older.
CONTRAINDICATIONS
None.
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
Severe and Fatal Immune-Mediated Adverse Reactions
YERVOY is a fully human monoclonal antibody that blocks T-cell inhibitory signals induced by the CTLA-4 pathway, thereby removing inhibition of the immune response with the potential for induction of immune-mediated adverse reactions. Immune-mediated adverse reactions listed herein may not be inclusive of all possible severe and fatal immune-mediated reactions.
Immune-mediated adverse reactions, which may be severe or fatal, can occur in any organ system or tissue. Immune-mediated adverse reactions can occur at any time after starting YERVOY. While immune-mediated adverse reactions usually manifest during treatment, immune-mediated adverse reactions can also manifest after discontinuation of YERVOY.
Early identification and management are essential to ensure safe use of YERVOY. Monitor for signs and symptoms that may be clinical manifestations of underlying immune-mediated adverse reactions. Evaluate clinical chemistries including liver enzymes, creatinine, adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) level, and thyroid function at baseline and before each dose. Institute medical management promptly, including specialty consultation as appropriate.
Withhold or permanently discontinue YERVOY depending on severity [see Dosage and Administration (2.3) ]. In general, if YERVOY requires interruption or discontinuation, administer systemic corticosteroid therapy (1 to 2 mg/kg/day prednisone or equivalent) until improvement to Grade 1 or less. Upon improvement to Grade 1 or less, initiate corticosteroid taper and continue to taper over at least 1 month. Consider administration of other systemic immunosuppressants in patients whose immune-mediated adverse reactions are not controlled with corticosteroid therapy.
Immune-Mediated Colitis
YERVOY can cause immune-mediated colitis, which may be fatal. Cytomegalovirus (CMV) infection/reactivation has been reported in patients with corticosteroid-refractory immune-mediated colitis. In cases of corticosteroid-refractory colitis, consider repeating infectious workup to exclude alternative etiologies.
YERVOY 3 mg/kg as a Single Agent
Immune-mediated colitis occurred in 12% (62/511) of patients who received YERVOY 3 mg/kg as a single agent, including Grade 3-5 (7%) and Grade 2 (5%). Colitis led to permanent discontinuation of YERVOY in 4.3% and withholding of at least one dose of YERVOY in 0.2% of patients.
Systemic corticosteroids were required in 74% (46/62) of patients with immune-mediated colitis. Five patients required coadministration of another immunosuppressant with corticosteroids. Colitis resolved in 76% of the 62 patients. One patient was withheld one or more doses of YERVOY for colitis, and no patient received additional treatment after symptom improvement.
YERVOY 1 mg/kg with 3 mg/kg Nivolumab
Immune-mediated colitis occurred in 9% (60/666) of patients who received YERVOY 1 mg/kg with nivolumab for the treatment of RCC or mCRC, including Grade 3 (4.4%), and Grade 2 (3.7%). Colitis led to permanent discontinuation of YERVOY and nivolumab in 3.2% and withholding of YERVOY and nivolumab in 2.7% of patients.
In patients who received YERVOY 1 mg/kg with nivolumab, use of systemic corticosteroids was one of the diagnostic criteria required to identify immune-mediated colitis. Systemic corticosteroids were therefore required in 100% (60/60) of patients with immune-mediated colitis. Approximately 23% of patients required coadministration of another immunosuppressant with corticosteroids. Colitis resolved in 95% of the 60 patients. Of the 18 patients in whom YERVOY or nivolumab was withheld for colitis, 16 received additional treatment after symptom improvement; of these, 10 had recurrence of colitis.
YERVOY 3 mg/kg with 1 mg/kg Nivolumab
Immune-mediated colitis occurred in 25% (115/456) of patients with melanoma or HCC receiving YERVOY 3 mg/kg with nivolumab 1 mg/kg every 3 weeks, including Grade 4 (0.4%), Grade 3 (14%), and Grade 2 (8%) adverse reactions. Colitis led to permanent discontinuation of YERVOY with nivolumab in 14% and withholding of treatment in 4.4% of patients.
Systemic corticosteroids were required in 100% (115/115) of patients with colitis. Approximately 23% of patients required addition of infliximab to high-dose corticosteroids. Colitis resolved in 93% of 115 patients. Of the 20 patients in whom YERVOY with nivolumab was withheld for colitis, 16 reinitiated treatment after symptom improvement, and 9 had recurrence of colitis.
Immune-Mediated Hepatitis
YERVOY 3 mg/kg as a Single Agent
Immune-mediated hepatitis occurred in 4.1% (21/511) of patients who received YERVOY 3 mg/kg as a single agent, including Grade 3-5 (1.6%) and Grade 2 (2.5%). Hepatitis led to permanent discontinuation of YERVOY in 0.4% of patients and withholding of at least one dose of YERVOY in none of the patients.
Systemic corticosteroids were required in 29% (6/21) of patients with immune-mediated hepatitis. No patients required the coadministration of another immunosuppressant with corticosteroids. Hepatitis resolved in 86% of the 21 patients.
YERVOY 3 mg/kg with Vemurafenib
The safety and effectiveness of YERVOY in combination with vemurafenib have not been established [see Indications and Usage (1) ] . In a dose-finding trial, Grade 3 increases in transaminases with or without concomitant increases in total bilirubin occurred in 6 of 10 patients who received concurrent YERVOY (3 mg/kg) and vemurafenib (960 mg or 720 mg twice daily).
YERVOY 1 mg/kg with 3 mg/kg Nivolumab
Immune-mediated hepatitis occurred in 7% (48/666) of patients who received YERVOY 1 mg/kg with nivolumab for the treatment of RCC or mCRC, including Grade 4 (1.2%), Grade 3 (4.9%), and Grade 2 (0.4%). Hepatitis led to permanent discontinuation of YERVOY and nivolumab in 3.6% and withholding of YERVOY and nivolumab in 2.6% of patients.
In patients who received YERVOY 1 mg/kg with nivolumab, use of systemic corticosteroids was one of the diagnostic criteria required to identify immune-mediated hepatitis. Systemic corticosteroids were therefore required in 100% (48/48) of patients with immune-mediated hepatitis. Approximately 19% of patients required coadministration of another immunosuppressant with corticosteroids. Hepatitis resolved in 88% of the 48 patients. Of the 17 patients in whom YERVOY or nivolumab was withheld for hepatitis, 14 received additional treatment after symptom improvement; of these, 10 had recurrence of hepatitis.
YERVOY 3 mg/kg with 1 mg/kg Nivolumab
Immune-mediated hepatitis occurred in 15% (70/456) of patients with melanoma or HCC receiving YERVOY 3 mg/kg with nivolumab 1 mg/kg every 3 weeks, including Grade 4 (2.4%), Grade 3 (11%), and Grade 2 (1.8%) adverse reactions. Immune-mediated hepatitis led to permanent discontinuation of YERVOY with nivolumab in 8% and withholding of treatment in 3.5% of patients.
Systemic corticosteroids were required in 100% (70/70) of patients with hepatitis. Approximately 9% of patients with immune-mediated hepatitis required addition of mycophenolic acid to high-dose corticosteroids. Hepatitis resolved in 91% of the 70 patients. Of the 16 patients in whom YERVOY with nivolumab was withheld for hepatitis, 14 reinitiated treatment after symptom improvement, and 8 had recurrence of hepatitis.
Immune-Mediated Dermatologic Adverse Reactions
YERVOY can cause immune-mediated rash or dermatitis, including bullous and exfoliative dermatitis, Stevens Johnson Syndrome, toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN), and DRESS (Drug Rash with Eosinophilia and Systemic Symptoms). Topical emollients and/or topical corticosteroids may be adequate to treat mild to moderate non-bullous/exfoliative rashes. Withhold or permanently discontinue YERVOY depending on severity [see Dosage and Administration (2.3) ] .
YERVOY 3 mg/kg as a Single Agent
Immune-mediated rash occurred in 15% (76/511) of patients who received YERVOY 3 mg/kg as a single agent, including Grade 3-5 (2.5%) and Grade 2 (12%). Rash led to permanent discontinuation of YERVOY in 0.2% and withholding of at least one dose of YERVOY in 1.4% of patients.
Systemic corticosteroids were required in 43% (33/76) of patients with immune-mediated rash. Rash resolved in 71% of the 76 patients. Of the 7 patients in whom YERVOY was withheld for rash, 3 received additional treatment after symptom improvement; of these, 1 had recurrence of rash.
YERVOY 1 mg/kg with 3 mg/kg Nivolumab
Immune-mediated rash occurred in 16% (108/666) of patients who received YERVOY 1 mg/kg with nivolumab for the treatment of RCC or mCRC, including Grade 3 (3.5%) and Grade 2 (4.2%). Rash led to permanent discontinuation of YERVOY and nivolumab in 0.5% of patients and withholding of YERVOY and nivolumab in 2.0% of patients.
In patients who received YERVOY 1 mg/kg with nivolumab, use of systemic corticosteroids was one of the diagnostic criteria required to identify immune-mediated rash. Systemic corticosteroids were therefore required in 100% (108/108) of patients. Rash resolved in 75% of 108 patients. Of the 13 patients in whom YERVOY or nivolumab was withheld for rash, 11 received additional treatment after symptom improvement; of these, 5 had recurrence of rash.
YERVOY 3 mg/kg with 1 mg/kg Nivolumab
Immune-mediated rash occurred in 28% (127/456) of patients with melanoma or HCC receiving YERVOY 3 mg/kg with nivolumab 1 mg/kg every 3 weeks, including Grade 3 (4.8%) and Grade 2 (10%) adverse reactions. Immune-mediated rash led to permanent discontinuation of YERVOY with nivolumab in 0.4% and withholding of treatment in 3.9% of patients.
Systemic corticosteroids were required in 100% (127/127) of patients with immune-mediated rash. Rash resolved in 84% of the 127 of patients. Of the 18 patients in whom YERVOY with nivolumab was withheld for rash, 15 reinitiated treatment after symptom improvement, and 8 had recurrence of rash.
Immune-Mediated Endocrinopathies
YERVOY 3 mg/kg as a Single Agent
Grade 2-5 immune-mediated endocrinopathies occurred in 4% (21/511) of patients who received YERVOY 3 mg/kg as a single agent.
Severe to life-threatening (Grade 3-4) endocrinopathies occurred in 9 patients (1.8%). All 9 of these patients had hypopituitarism with some patients having additional concomitant endocrinopathies, such as adrenal insufficiency, hypogonadism, and hypothyroidism. Six of the 9 patients were hospitalized for severe endocrinopathies.
Moderate (Grade 2) endocrinopathy occurred in 12 patients (2.3%), including hypothyroidism, adrenal insufficiency, hypopituitarism, hyperthyroidism and Cushing’s syndrome.
Of the 21 patients with moderate to life-threatening endocrinopathy, 17 required long-term hormone replacement therapy, including adrenal hormones (n=10) and thyroid hormones (n=13).
YERVOY 1 mg/kg with 3 mg/kg Nivolumab
Hypophysitis:
YERVOY can cause immune-mediated hypophysitis. Hypophysitis can present with acute symptoms associated with mass effect such as headache, photophobia, or visual field cuts. Hypophysitis can cause hypopituitarism. Initiate hormone replacement as clinically indicated. Withhold or permanently discontinue YERVOY depending on severity [see Dosage and Administration (2.3) ].
Hypophysitis occurred in 4.4% (29/666) of patients who received YERVOY 1 mg/kg with nivolumab for the treatment of RCC or mCRC, including Grade 4 (0.3%), Grade 3 (2.4%), and Grade 2 (0.9%). Hypophysitis led to permanent discontinuation of YERVOY and nivolumab in 1.2% and withholding of YERVOY with nivolumab in 2.1% of patients. Approximately 72% of patients with hypophysitis received hormone replacement therapy. Systemic corticosteroids were required in 72% (21/29) of patients with immune-mediated hypophysitis. Hypophysitis resolved in 59% of the 29 patients. Of the 14 patients in whom YERVOY or nivolumab was withheld for hypophysitis, 11 received additional treatment after symptom improvement; of these, 2 had recurrence of hypophysitis.
Adrenal Insufficiency:
Adrenal insufficiency occurred in 7% (48/666) of patients who received YERVOY 1 mg/kg with nivolumab for the treatment of RCC or mCRC, including Grade 4 (0.3%), Grade 3 (2.5%), and Grade 2 (4.1%). Adrenal insufficiency led to permanent discontinuation of YERVOY with nivolumab in 1.2% and withholding of YERVOY with nivolumab in 2.1% of patients. Approximately 94% of patients with adrenal insufficiency received hormone replacement therapy. Systemic corticosteroids were required in 94% (45/48) of patients with adrenal insufficiency. Adrenal insufficiency resolved in 29% of the 48 patients. Of the 14 patients in whom YERVOY or nivolumab was withheld for adrenal insufficiency, 11 received additional treatment after symptom improvement; of these, 2 had recurrence of adrenal insufficiency.
Hyperthyroidism:
Hyperthyroidism occurred in 12% (80/666) of patients who received YERVOY 1 mg/kg with nivolumab for the treatment of RCC or mCRC, including Grade 3 (0.6%) and Grade 2 (4.5%). No patients discontinued YERVOY for hyperthyroidism. Hyperthyroidism led to withholding of YERVOY with nivolumab in 2.3% of patients. Approximately 19% received a thyroid synthesis inhibitor. Systemic corticosteroids were required in 20% (16/80) of patients with hyperthyroidism. Hyperthyroidism resolved in 85% of the 80 patients. Of the 15 patients in whom YERVOY or nivolumab was withheld for hyperthyroidism, 11 received additional treatment after symptom improvement; of these, 3 had recurrence of hyperthyroidism.
Hypothyroidism:
Hypothyroidism occurred in 18% (122/666) of patients who received YERVOY 1 mg/kg with nivolumab for the treatment of RCC or mCRC, including Grade 3 (0.6%) and Grade 2 (11%). Hypothyroidism led to permanent discontinuation of YERVOY with nivolumab in 0.2% and withholding of YERVOY with nivolumab in 1.4% of patients. Approximately 82% received thyroid hormone replacement. Systemic corticosteroids were required in 7% (9/122) of patients with hypothyroidism. Hypothyroidism resolved in 27% of the 122 patients. Of the 9 patients in whom YERVOY or nivolumab was withheld for hypothyroidism, 5 received additional treatment after symptom improvement; of these, one patient had recurrence of hypothyroidism.
Thyroiditis:
Thyroiditis occurred in 2.7% (22/666) of patients who received YERVOY 1 mg/kg with nivolumab for the treatment of RCC or mCRC, including Grade 3 (4.5%) and Grade 2 (2.2%). Thyroiditis led to permanent discontinuation of YERVOY with nivolumab in 0.2% and withholding of YERVOY with nivolumab in 0.8% of patients. Systemic corticosteroids were required in 18% (4/22) of patients with thyroiditis. Thyroiditis resolved in 64% of the 22 patients. Of the 5 patients in whom YERVOY or nivolumab was withheld for thyroiditis, 5 received additional treatment after symptom improvement; of these, no patients had recurrence of thyroiditis.
Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus:
Diabetes occurred in 2.7% (15/666) of patients who received YERVOY 1 mg/kg with nivolumab for the treatment of RCC or mCRC, including Grade 4 (0.6%), Grade 3 (0.3%), and Grade 2 (0.9%). Diabetes led to the permanent discontinuation of YERVOY with nivolumab in 0.5% and withholding of YERVOY with nivolumab in 0.5% of patients. Systemic corticosteroids were required in 7% (1/15) of patients with diabetes. Diabetes resolved in 27% of the 15 patients. Of the 3 patients in whom YERVOY or nivolumab was withheld for diabetes, 2 received additional treatment after symptom improvement; of these, none had recurrence of diabetes.
YERVOY 3 mg/kg with 1 mg/kg Nivolumab
Hypophysitis:
Hypophysitis occurred in 9% (42/456) of patients with melanoma or HCC receiving YERVOY 3 mg/kg with nivolumab 1 mg/kg every 3 weeks, including Grade 3 (2.4%) and Grade 2 (6%) adverse reactions. Hypophysitis led to permanent discontinuation of YERVOY with nivolumab in 0.9% and withholding of treatment in 4.2% of patients.
Approximately 86% of patients with hypophysitis received hormone replacement therapy. Systemic corticosteroids were required in 88% (37/42) of patients with hypophysitis. Hypophysitis resolved in 38% of the 42 patients. Of the 19 patients in whom YERVOY with nivolumab was withheld for hypophysitis, 9 reinitiated treatment after symptom improvement, and 1 had recurrence of hypophysitis.
Adrenal Insufficiency:
Adrenal insufficiency occurred in 8% (35/456) of patients with melanoma or HCC receiving YERVOY 3 mg/kg with nivolumab 1 mg/kg every 3 weeks, including Grade 4 (0.2%), Grade 3 (2.4%), and Grade 2 (4.2%) adverse reactions. Adrenal insufficiency led to permanent discontinuation of YERVOY with nivolumab in 0.4% of patients and withholding of treatment in 2.0% of patients.
Approximately 71% (25/35) of patients with adrenal insufficiency received hormone replacement therapy, including systemic corticosteroids. Adrenal insufficiency resolved in 37% of the 35 patients. Of the 9 patients in whom YERVOY with nivolumab was withheld for adrenal insufficiency, 7 reinitiated treatment after symptom improvement, and all required hormone replacement therapy for their ongoing adrenal insufficiency.
Hypothyroidism:
Hypothyroidism occurred in 20% (91/456) of patients with melanoma or HCC receiving YERVOY 3 mg/kg with nivolumab 1 mg/kg every 3 weeks, including Grade 3 (0.4%) and Grade 2 (11%) adverse reactions. Hypothyroidism led to permanent discontinuation of YERVOY with nivolumab in 0.9% of patients and withholding of treatment in 0.9% of patients.
Approximately 89% of patients with hypothyroidism received levothyroxine. Systemic corticosteroids were required in 2.2% (2/91) of patients with hypothyroidism. Hypothyroidism resolved in 41% of the 91 patients. Of the 4 patients in whom YERVOY with nivolumab was withheld for hypothyroidism, 2 reinitiated treatment after symptom improvement, and none had recurrence of hypothyroidism.
Hyperthyroidism:
Hyperthyroidism occurred in 9% (42/456) of patients with melanoma or HCC receiving YERVOY 3 mg/kg with nivolumab 1 mg/kg every 3 weeks, including Grade 3 (0.9%) and Grade 2 (4.2%) adverse reactions. Hyperthyroidism led to permanent discontinuation of YERVOY with nivolumab in no patients and withholding of treatment in 2.4% of patients.
Approximately 26% of patients with hyperthyroidism received methimazole and 21% received carbimazole. Systemic corticosteroids were required in 17% (7/42) of patients. Hyperthyroidism resolved in 91% of the 42 patients. Of the 11 patients in whom YERVOY with nivolumab was withheld for hyperthyroidism, 8 reinitiated treatment after symptom improvement, and 1 had recurrence of hyperthyroidism.
Immune-Mediated Pneumonitis
YERVOY 1 mg/kg with 3 mg/kg Nivolumab
Immune-mediated pneumonitis occurred in 3.9% (26/666) of patients who received YERVOY 1 mg/kg with nivolumab for the treatment of RCC or mCRC, including Grade 3 (1.4%) and Grade 2 (2.6%). Pneumonitis led to permanent discontinuation of YERVOY and nivolumab in 1.8% and withholding of YERVOY and nivolumab in 1.5% of patients.
In patients who received YERVOY 1 mg/kg with nivolumab, use of systemic corticosteroids was one of the diagnostic criteria required to identify immune-mediated pneumonitis. Systemic corticosteroids were therefore required in 100% (26/26) of patients with immune-mediated pneumonitis. Approximately 8% required coadministration of another immunosuppressant with corticosteroids. Pneumonitis resolved in 92% of the 26 patients. Of the 10 patients in whom YERVOY or nivolumab was withheld for pneumonitis, 10 received additional treatment after symptom improvement; of these, 4 had recurrence of pneumonitis.
In NSCLC, immune-mediated pneumonitis occurred in 9% (50/576) of patients receiving YERVOY 1 mg/kg every 6 weeks with nivolumab 3 mg/kg every 2 weeks, including Grade 4 (0.5%), Grade 3 (3.5%), and Grade 2 (4.0%) immune-mediated pneumonitis. Four patients (0.7%) died due to pneumonitis. The median duration was 1.5 months (range: 5 days to 25+ months). Immune-mediated pneumonitis led to permanent discontinuation of YERVOY with nivolumab in 5% of patients and withholding of YERVOY with nivolumab in 3.6% of patients.
Systemic corticosteroids were required in 100% of patients with pneumonitis followed by a corticosteroid taper. Pneumonitis resolved in 72% of the patients. Approximately 13% (2/16) of patients had recurrence of pneumonitis after re-initiation of YERVOY with nivolumab.
YERVOY 3 mg/kg with 1 mg/kg Nivolumab
Immune-mediated pneumonitis occurred in 7% (31/456) of patients who received YERVOY 3 mg/kg with nivolumab for the treatment of HCC or melanoma, including Grade 4 (0.2%), Grade 3 (2.0%), and Grade 2 (4.4%). Immune-mediated pneumonitis led to permanent discontinuation or withholding of treatment in 2.9% and 3.9% of patients, respectively.
Systemic corticosteroids were required in 100% of patients with pneumonitis. Pneumonitis resolved in 94% of the patients. Of the 13 patients in whom YERVOY or nivolumab was withheld for pneumonitis, 13 received additional treatment after symptom improvement, and 4 had recurrence of pneumonitis.
Immune-Mediated Nephritis with Renal Dysfunction
YERVOY 1 mg/kg with 3 mg/kg Nivolumab
Immune-mediated nephritis with renal dysfunction occurred in 4.1% (27/666) of patients who received YERVOY 1 mg/kg with nivolumab for the treatment of RCC or mCRC, including Grade 4 (0.6%), Grade 3 (1.1%), and Grade 2 (2.2%). Nephritis with renal dysfunction led to permanent discontinuation of YERVOY and nivolumab in 1.2% and withholding of nivolumab and YERVOY in 1.8% of patients.
In patients who received YERVOY 1 mg/kg with nivolumab, use of systemic corticosteroids was one of the diagnostic criteria required to identify immune-mediated nephritis with renal dysfunction. Systemic corticosteroids were therefore required in 100% (27/27) of patients with immune-mediated nephritis with renal dysfunction. Nephritis with renal dysfunction resolved in 67% of the 27 patients. Of the 12 patients in whom YERVOY or nivolumab was withheld for nephritis, 10 received additional treatment after symptom improvement; of these, 4 had recurrence of nephritis.
Other Immune-Mediated Adverse Reactions
Across clinical trials of YERVOY administered as a single agent or in combination with nivolumab, the following clinically significant immune-mediated adverse reactions, some with fatal outcome, occurred in <1% of patients unless otherwise specified, as shown below:
Nervous System: Autoimmune neuropathy (2%), meningitis, encephalitis, myelitis and demyelination, myasthenic syndrome/myasthenia gravis, Guillain-Barré syndrome, nerve paresis, motor dysfunction
Cardiovascular: Angiopathy, myocarditis, pericarditis, temporal arteritis, vasculitis
Ocular: Blepharitis, episcleritis, iritis, orbital myositis, scleritis, uveitis. Some cases can be associated with retinal detachment. If uveitis occurs in combination with other immune-mediated adverse reactions, consider a Vogt-Koyanagi-Harada-like syndrome, which has been observed in patients receiving YERVOY and may require treatment with systemic corticosteroids to reduce the risk of permanent vision loss.
Gastrointestinal: Duodenitis, gastritis, pancreatitis (1.3%)
Musculoskeletal and Connective Tissue: Arthritis, myositis, polymyalgia rheumatica, polymyositis, rhabdomyolysis
Other (hematologic/immune): Aplastic anemia, conjunctivitis, cytopenias (2.5%), eosinophilia (2.1%), erythema multiforme, histiocytic necrotizing lymphadenitis (Kikuchi lymphadenitis), hypersensitivity vasculitis, meningitis, neurosensory hypoacusis, psoriasis, sarcoidosis, systemic inflammatory response syndrome, and solid organ transplant rejection.
Infusion-Related Reactions
Severe infusion-related reactions can occur with YERVOY. Discontinue YERVOY in patients with severe or life-threatening infusion reactions. Interrupt or slow the rate of infusion in patients with mild or moderate infusion reactions [see Dosage and Administration (2.3) ] . Infusion-related reactions occurred in 0.6% (3/511) of patients who received single-agent YERVOY 3 mg/kg for the unresectable or metastatic treatment of melanoma. Infusion-related reactions occurred in 5% (33/666) of patients who received YERVOY 1 mg/kg with nivolumab for the treatment of RCC or CRC. Infusion-related reactions occurred in 8% (4/49) of patients who received YERVOY 3 mg/kg with nivolumab for the treatment of HCC. Infusion-related reactions occurred in 12% (37/300) of patients with malignant pleural mesothelioma who received YERVOY 1 mg/kg every 6 weeks with nivolumab 3 mg/kg every 2 weeks.
Complications of Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplant after YERVOY
Fatal or serious graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) can occur in patients who receive YERVOY either before or after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT). These complications may occur despite intervening therapy between CTLA-4 receptor blocking antibody and allogeneic HSCT.
Follow patients closely for evidence of GVHD and intervene promptly [see Adverse Reactions (6.2) ] . Consider the benefit versus risks of treatment with YERVOY after allogeneic HSCT.
Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
Based on its mechanism of action and findings from animal studies, YERVOY can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. In animal reproduction studies, administration of ipilimumab to cynomolgus monkeys from the onset of organogenesis through delivery resulted in higher incidences of abortion, stillbirth, premature delivery (with corresponding lower birth weight) and higher incidences of infant mortality in a dose-related manner. The effects of ipilimumab are likely to be greater during the second and third trimesters of pregnancy. Advise pregnant women of the potential risk to a fetus. Advise females of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with YERVOY and for 3 months after the last dose [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1 , 8.3 )] .
Risks Associated When Administered in Combination with Nivolumab
YERVOY is indicated for use in combination with nivolumab for patients with advanced RCC, MSI-H or dMMR mCRC, HCC, and NSCLC. Refer to the nivolumab Full Prescribing Information for additional risk information that applies to the combination use treatment.
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following clinically significant adverse reactions are described elsewhere in the labeling:
- Severe and fatal immune-mediated adverse reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) ] .
- Infusion-related reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) ] .
Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared with rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in clinical practice.
The data described in the Warnings and Precautions section reflect exposure to YERVOY 3 mg/kg as a single agent (or in combination with an investigational gp100 peptide vaccine) in 511 patients in Study MDX010-20; YERVOY 1 mg/kg administered with nivolumab 3 mg/kg in 1,362 patients in CHECKMATE-214, CHECKMATE-142, CHECKMATE-227, and CHECKMATE-743; YERVOY 3 mg/kg administered with nivolumab 1 mg/kg in 456 patients enrolled in CHECKMATE-067, CHECKMATE-040, and another randomized trial; and to YERVOY 1 mg/kg, administered in combination with nivolumab and platinum-doublet chemotherapy in CHECKMATE-9LA.
Unresectable or Metastatic Melanoma
The safety of YERVOY was evaluated in 643 previously treated patients with unresectable or metastatic melanoma in Study MDX010-20 [see Clinical Studies (14.1) ] . Study MDX010-20 excluded patients with active autoimmune disease or those receiving systemic immunosuppression for organ transplantation. Patients received YERVOY 3 mg/kg by intravenous infusion for 4 doses as a single agent (n=131), YERVOY with an investigational gp100 peptide vaccine (n=380), or gp100 peptide vaccine as a single agent (n=132). Patients in the trial received a median of 4 doses (range: 1 to 4 doses).
The trial population characteristics were: median age 57 years (range: 19 to 90), 59% male, 94% White, and baseline ECOG performance status 0 (56%).
YERVOY was discontinued for adverse reactions in 10% of patients. Table 4 presents adverse reactions from Study MDX010-20.
Adverse Reactions | YERVOY 3 mg/kg n=131 | YERVOY 3 mg/kg and gp100 n=380 | gp100 n=132 | |||
All Grades (%) | Grade 3 to 5 (%) | All Grades (%) | Grade 3 to 5 (%) | All Grades (%) | Grade 3 to 5 (%) | |
General and Administration-Site Conditions | ||||||
Fatigue | 41 | 7 | 34 | 5 | 31 | 3 |
Gastrointestinal | ||||||
Diarrhea | 32 | 5 | 37 | 4 | 20 | 1 |
Colitis | 8 | 5 | 5 | 3 | 2 | 0 |
Dermatologic | ||||||
Pruritus | 31 | 0 | 21 | <1 | 11 | 0 |
Rash | 29 | 2 | 25 | 2 | 8 | 0 |
Unresectable or Metastatic Melanoma: In Combination with Nivolumab
The safety of YERVOY, administered with nivolumab or as a single agent, was evaluated in CHECKMATE-067, a randomized (1:1:1), double-blind trial in 937 patients with previously untreated, unresectable or metastatic melanoma [see Clinical Studies (14.1) ]. The trial excluded patients with autoimmune disease, a medical condition requiring systemic treatment with corticosteroids (more than 10 mg daily prednisone equivalent) or other immunosuppressive medication within 14 days of the start of study therapy, a positive test result for hepatitis B or C, or a history of HIV.
Patients were randomized to receive:
- YERVOY 3 mg/kg by intravenous infusion over 90 minutes with nivolumab 1 mg/kg by intravenous infusion every 3 weeks for 4 doses followed by nivolumab as a single agent at a dose of 3 mg/kg by intravenous infusion every 2 weeks (YERVOY and nivolumab arm; n=313), or
- Nivolumab 3 mg/kg by intravenous infusion every 2 weeks (nivolumab arm; n=313), or
- YERVOY 3 mg/kg by intravenous infusion over 90 minutes every 3 weeks for up to 4 doses (YERVOY arm; n=311).
The median duration of exposure to nivolumab was 2.8 months (range: 1 day to 36.4 months) for the YERVOY and nivolumab arm. In the YERVOY and nivolumab arm, 39% were exposed to nivolumab for ≥6 months and 30% exposed for >1 year.
Serious adverse reactions (74%), adverse reactions leading to permanent discontinuation (47%) or to dosing delays (58%), and Grade 3 or 4 adverse reactions (72%) occurred in patients treated with YERVOY and nivolumab.
The most frequent (≥10%) serious adverse reactions in the YERVOY and nivolumab arm were diarrhea (13%), colitis (10%), and pyrexia (10%). The most frequent adverse reactions leading to discontinuation of both drugs in the YERVOY and nivolumab arm were colitis (10%), diarrhea (8%), increased ALT (4.8%), increased AST (4.5%), and pneumonitis (1.9%).
The most common (≥20%) adverse reactions in the YERVOY and nivolumab arm were fatigue, diarrhea, rash, nausea, pyrexia, pruritus, musculoskeletal pain, vomiting, decreased appetite, cough, headache, dyspnea, upper respiratory tract infection, arthralgia, and increased transaminases.
Tables 5 and 6 summarize the incidence of adverse reactions and laboratory abnormalities, respectively, in CHECKMATE-067.
| Toxicity was graded per NCI CTCAE v4. a Includes asthenia and fatigue. b Includes pustular rash, dermatitis, acneiform dermatitis, allergic dermatitis, atopic dermatitis, bullous dermatitis, exfoliative dermatitis, psoriasiform dermatitis, drug eruption, exfoliative rash, erythematous rash, generalized rash, macular rash, maculopapular rash, morbilliform rash, papular rash, papulosquamous rash, and pruritic rash. c Includes back pain, bone pain, musculoskeletal chest pain, musculoskeletal discomfort, myalgia, neck pain, pain in extremity, and spinal pain. d Includes upper respiratory tract infection, nasopharyngitis, pharyngitis, and rhinitis. e Includes hypertension and blood pressure increased. | ||||||
Adverse Reaction | YERVOY and Nivolumab (n=313) | Nivolumab (n=313) | YERVOY (n=311) | |||
All Grades (%) | Grades 3-4 (%) | All Grades (%) | Grades 3-4 (%) | All Grades (%) | Grades 3-4 (%) | |
General | ||||||
Fatigue a | 62 | 7 | 59 | 1.6 | 51 | 4.2 |
Pyrexia | 40 | 1.6 | 16 | 0 | 18 | 0.6 |
Gastrointestinal | ||||||
Diarrhea | 54 | 11 | 36 | 5 | 47 | 7 |
Nausea | 44 | 3.8 | 30 | 0.6 | 31 | 1.9 |
Vomiting | 31 | 3.8 | 20 | 1.0 | 17 | 1.6 |
Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue | ||||||
Rash b | 53 | 6 | 40 | 1.9 | 42 | 3.5 |
Vitiligo | 9 | 0 | 10 | 0.3 | 5 | 0 |
Musculoskeletal and Connective Tissue | ||||||
Musculoskeletal pain c | 32 | 2.6 | 42 | 3.8 | 36 | 1.9 |
Arthralgia | 21 | 0.3 | 21 | 1.0 | 16 | 0.3 |
Metabolism and Nutrition | ||||||
Decreased appetite | 29 | 1.9 | 22 | 0 | 24 | 1.3 |
Respiratory, Thoracic and Mediastinal | ||||||
Cough/productive cough | 27 | 0.3 | 28 | 0.6 | 22 | 0 |
Dyspnea/exertional dyspnea | 24 | 2.9 | 18 | 1.3 | 17 | 0.6 |
Infections | ||||||
Upper respiratory tract infection d | 23 | 0 | 22 | 0.3 | 17 | 0 |
Endocrine | ||||||
Hypothyroidism | 19 | 0.6 | 11 | 0 | 5 | 0 |
Hyperthyroidism | 11 | 1.3 | 6 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
Investigations | ||||||
Decreased weight | 12 | 0 | 7 | 0 | 7 | 0.3 |
Vascular | ||||||
Hypertension e | 7 | 2.2 | 11 | 5 | 9 | 2.3 |
Clinically important adverse reactions in <10% of patients who received YERVOY with nivolumab:
Gastrointestinal Disorders: stomatitis, intestinal perforation
Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue Disorders: vitiligo
Musculoskeletal and Connective Tissue Disorders: myopathy, Sjogren’s syndrome, spondyloarthropathy, myositis (including polymyositis)
Nervous System Disorders: neuritis, peroneal nerve palsy
| a Each test incidence is based on the number of patients who had both baseline and at least one on-study laboratory measurement available: YERVOY and nivolumab (range: 75 to 297); nivolumab (range: 81 to 306); YERVOY (range: 61 to 301) | ||||||
Laboratory Abnormality | YERVOY and Nivolumab | Nivolumab | YERVOY | |||
All Grades (%) | Grade 3-4 (%) | All Grades (%) | Grade 3-4 (%) | All Grades (%) | Grade 3-4 (%) | |
Chemistry | ||||||
Increased ALT | 55 | 16 | 25 | 3.0 | 29 | 2.7 |
Hyperglycemia | 53 | 5 | 46 | 7 | 26 | 0 |
Increased AST | 52 | 13 | 29 | 3.7 | 29 | 1.7 |
Hyponatremia | 45 | 10 | 22 | 3.3 | 26 | 7 |
Increased lipase | 43 | 22 | 32 | 12 | 24 | 7 |
Increased alkaline phosphatase | 41 | 6 | 27 | 2.0 | 23 | 2.0 |
Hypocalcemia | 31 | 1.1 | 15 | 0.7 | 20 | 0.7 |
Increased amylase | 27 | 10 | 19 | 2.7 | 15 | 1.6 |
Increased creatinine | 26 | 2.7 | 19 | 0.7 | 17 | 1.3 |
Hematology | ||||||
Anemia | 52 | 2.7 | 41 | 2.6 | 41 | 6 |
Lymphopenia | 39 | 5 | 41 | 4.9 | 29 | 4.0 |
Adjuvant Treatment of Melanoma
The safety of YERVOY was evaluated in Study E1609, an open-label, multicenter, randomized trial for the adjuvant treatment of patients with completely resected node positive cutaneous melanoma [see Clinical Studies (14.2) ] . Patients received YERVOY 3 mg/kg intravenously every 3 weeks for 4 doses followed by 3 mg/kg every 12 weeks for up to 4 additional doses, or high-dose interferon-α2b (HDI). Among patients who received YERVOY, 55% were exposed for 6 months or longer and 42% were exposed for greater than 1 year.
Fatal adverse reactions occurred in 1.4% of patients who received YERVOY, including gastric perforation (0.2%), and cardiac arrest (0.2%). Permanent discontinuation of YERVOY due to an adverse reaction occurred in 35% of patients.
The most common adverse reactions (≥20%) in the YERVOY arm were fatigue, diarrhea, rash, pruritus, nausea, and headache. Table 7 summarizes adverse reactions in E1609.
| Adverse Reaction | YERVOY 3 mg/kg n=516 | HDI n=520 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| All Grades (%) | Grade 3 to 4 (%) | All Grades (%) | Grade 3 to 4 (%) | |
General disorders and administration site conditions | ||||
Fatigue | 56 | 3 | 87 | 22 |
Decreased appetite | 14 | 0.6 | 53 | 2.1 |
Pyrexia | 10 | 0 | 31 | 0.8 |
Gastrointestinal | ||||
Diarrhea | 49 | 10 | 34 | 0.8 |
Nausea | 29 | 1.2 | 66 | 4.2 |
Abdominal Pain | 19 | 1 | 9 | 0.4 |
Vomiting | 11 | 0.6 | 26 | 2.3 |
Colitis | 10 | 8 | 1 | 0.4 |
Dermatologic | ||||
Rash | 46 | 4 | 18 | 1 |
Pruritus | 41 | 2 | 15 | 0 |
Nervous System Disorders | ||||
Headache | 25 | 2 | 45 | 3 |
Endocrine | ||||
Endocrine disorders, other | 19 | 4.1 | 2 | 0 |
Hypothyroidism | 11 | 0.6 | 10 | 0.2 |
Adrenal insufficiency | 10 | 2 | 0.6 | 0 |
Other Clinical Experience
Across clinical studies in which patients received YERVOY as a single agent at doses ranging from 0.3 to 10 mg/kg, the following adverse reactions were also reported (incidence <1% unless otherwise noted): urticaria (2%), large intestinal ulcer, esophagitis, acute respiratory distress syndrome, renal failure, and infusion reaction.
Advanced Renal Cell Carcinoma: In Combination with Nivolumab
The safety of YERVOY in combination with nivolumab was evaluated in 1082 patients with previously untreated advanced RCC in CHECKMATE-214 [see Clinical Studies (14.3) ] . Patients received YERVOY 1 mg/kg with nivolumab 3 mg/kg intravenously every 3 weeks for 4 doses followed by nivolumab as a single agent at a dose of 3 mg/kg every 2 weeks (n=547) or sunitinib 50 mg orally daily for first 4 weeks of each 6-week cycle (n=535). The median duration of treatment was 7.9 months (range: 1 day to 21.4+ months) in YERVOY and nivolumab arm. In this trial, 57% of patients in the YERVOY and nivolumab arm were exposed to treatment for greater than 6 months and 38% of patients were exposed to treatment for greater than 1 year.
Serious adverse reactions occurred in 59% of patients receiving YERVOY with nivolumab. The most frequent serious adverse reactions reported in ≥2% of patients treated with YERVOY and nivolumab were diarrhea, pyrexia, pneumonia, pneumonitis, hypophysitis, acute kidney injury, dyspnea, adrenal insufficiency, and colitis.
In patients who received YERVOY with nivolumab, study therapy was discontinued for adverse reactions in 31% and delayed for adverse reactions in 54%.
The most common adverse reactions (≥20%) in the YERVOY and nivolumab arm were fatigue, rash, diarrhea, musculoskeletal pain, pruritus, nausea, cough, pyrexia, arthralgia, vomiting, dyspnea, and decreased appetite. Table 8 summarizes adverse reactions in CHECKMATE-214.
| Toxicity was graded per NCI CTCAE v4. a Includes asthenia. b Includes peripheral edema, peripheral swelling. c Includes dermatitis described as acneiform, bullous, and exfoliative, drug eruption, rash described as exfoliative, erythematous, follicular, generalized, macular, maculopapular, papular, pruritic, and pustular, fixed-drug eruption. d Includes back pain, bone pain, musculoskeletal chest pain, musculoskeletal discomfort, myalgia, neck pain, pain in extremity, spinal pain. | ||||
Adverse Reaction | YERVOY 1 mg/kg and Nivolumab n=547 | Sunitinib n=535 | ||
Grades 1-4 (%) | Grades 3-4 (%) | Grades 1-4 (%) | Grades 3-4 (%) | |
General and Administration Site Conditions | ||||
Fatigue a | 58 | 8 | 69 | 13 |
Pyrexia | 25 | 0.7 | 17 | 0.6 |
Edema b | 16 | 0.5 | 17 | 0.6 |
Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue | ||||
Rash c | 39 | 3.7 | 25 | 1.1 |
Pruritus/generalized pruritus | 33 | 0.5 | 11 | 0 |
Gastrointestinal | ||||
Diarrhea | 38 | 4.6 | 58 | 6 |
Nausea | 30 | 2.0 | 43 | 1.5 |
Vomiting | 20 | 0.9 | 28 | 2.1 |
Abdominal pain | 19 | 1.6 | 24 | 1.9 |
Constipation | 17 | 0.4 | 18 | 0 |
Musculoskeletal and Connective Tissue | ||||
Musculoskeletal pain d | 37 | 4.0 | 40 | 2.6 |
Arthralgia | 23 | 1.3 | 16 | 0 |
Respiratory, Thoracic, and Mediastinal | ||||
Cough/productive cough | 28 | 0.2 | 25 | 0.4 |
Dyspnea/exertional dyspnea | 20 | 2.4 | 21 | 2.1 |
Metabolism and Nutrition | ||||
Decreased appetite | 21 | 1.8 | 29 | 0.9 |
Nervous System | ||||
Headache | 19 | 0.9 | 23 | 0.9 |
Endocrine | ||||
Hypothyroidism | 18 | 0.4 | 27 | 0.2 |
Table 9 summarizes the laboratory abnormalities in CHECKMATE-214.
| a Each test incidence is based on the number of patients who had both baseline and at least one on-study laboratory measurement available: nivolumab and YERVOY group (range: 490 to 538 patients) and sunitinib group (range: 485 to 523 patients). | ||||
Laboratory Abnormality | YERVOY 1 mg/kg and Nivolumab a | Sunitinib a | ||
Grades 1-4 (%) | Grades 3-4 (%) | Grades 1-4 (%) | Grades 3-4 (%) | |
Chemistry | ||||
Increased lipase | 48 | 20 | 51 | 20 |
Increased creatinine | 42 | 2.1 | 46 | 1.7 |
Increased ALT | 41 | 7 | 44 | 2.7 |
Increased AST | 40 | 4.8 | 60 | 2.1 |
Increased amylase | 39 | 12 | 33 | 7 |
Hyponatremia | 39 | 10 | 36 | 7 |
Increased alkaline phosphatase | 29 | 2.0 | 32 | 1.0 |
Hyperkalemia | 29 | 2.4 | 28 | 2.9 |
Hypocalcemia | 21 | 0.4 | 35 | 0.6 |
Hypomagnesemia | 16 | 0.4 | 26 | 1.6 |
Hematology | ||||
Anemia | 43 | 3.0 | 64 | 9 |
Lymphopenia | 36 | 5 | 63 | 14 |
In addition, among patients with TSH ≤ ULN at baseline, a lower proportion of patients experienced a treatment-emergent elevation of TSH > ULN in the YERVOY with nivolumab group compared to the sunitinib group (31% and 61%, respectively).
MSI-H or dMMR Metastatic Colorectal Cancer
Treatment of MSI -H or dMMR mCRC: In Combination with Nivolumab
The safety of YERVOY in combination with nivolumab was evaluated in CHECKMATE-8HW, a randomized, open-label, three arm trial in immunotherapy naïve patients with MSI-H or dMMR mCRC [see Clinical Studies (14.4) ] . Patients received one of the following:
- YERVOY 1 mg/kg every 3 weeks and nivolumab 240 mg every 3 weeks for a maximum of 4 doses, then nivolumab 480 mg every 4 weeks.
- Nivolumab 240 mg every 2 weeks for 6 doses, then nivolumab 480 mg every 4 weeks.
- Investigator’s choice chemotherapy: mFOLFOX or FOLFIRI [see Clinical Studies (14.4) ] .
In the YERVOY and nivolumab arm, the median duration of exposure to YERVOY was 2.1 months (range 1 day to 3.7 months); patients received a median of 4 doses (range 1-4). The median duration of treatment in the YERVOY and nivolumab arm was 20.5 months (range: 1 day to 35.9 months); 70% were exposed to treatment for >6 months, and 63% were exposed for >1 year. The median duration of treatment was 16.4 months (range: 1 day to 36 months) in the nivolumab-only arm; 64% were exposed to treatment for >6 months, and 54% were exposed for >1 year.
Serious adverse reactions occurred in 46% of patients receiving YERVOY in combination with nivolumab, and 39% of patients receiving nivolumab alone. The most frequent serious adverse reactions reported in ≥1% of patients who received YERVOY with nivolumab were adrenal insufficiency (2.8%), hypophysitis (2.8%), diarrhea (2.0%), abdominal pain (2.0%), small intestinal obstruction (2.0%), pneumonia (1.7%), acute kidney injury (1.4%), immune-mediated enterocolitis (1.4%), pneumonitis (1.4%), colitis (1.1%), large intestinal obstruction (1.1%), and urinary tract infection (1.1%). The most frequent serious adverse reactions reported in >1% of patients who received OPDIVO, as a single agent, were intestinal obstruction (2.3%), acute kidney injury (1.7%), COVID-19 (1.7%), abdominal pain (1.4%), diarrhea (1.4%), ileus (1.4%), subileus (1.4%), pulmonary embolism (1.4%), adrenal insufficiency (1.1%) and pneumonia (1.1%).
Fatal adverse reactions occurred in 2 (0.6%) patients who received YERVOY in combination with nivolumab; these included myocarditis, and pneumonitis (1 each).
YERVOY and/or nivolumab were permanently discontinued in 19% of patients receiving the combination. The most frequent adverse reactions (>1%) leading to permanent discontinuation were adrenal insufficiency (1.4%), immune-mediated enterocolitis (1.1%), and pneumonitis (1.1%). Nivolumab was permanently discontinued in 13% of patients receiving single agent nivolumab. Adverse reactions leading to the delay of YERVOY and/or nivolumab occurred in 48% of patients receiving the combination; single agent nivolumab was delayed in 37% of patients due to adverse reactions.
The most common adverse reactions reported in ≥20% of patients treated with YERVOY in combination with nivolumab were fatigue, diarrhea, pruritus, abdominal pain, musculoskeletal pain, and nausea. The most common adverse reactions reported in ≥20% of patients treated with nivolumab as a single agent, were fatigue, diarrhea, abdominal pain, pruritus, and musculoskeletal pain.
Tables 10 and 11 summarize the adverse reactions and selected laboratory abnormalities, for YERVOY in combination with nivolumab and nivolumab arms respectively, in CHECKMATE-8HW.
| Toxicity was graded per NCI CTCAE v5. | ||||
| a Includes colitis, diarrhea, enterocolitis, immune-mediated enterocolitis | ||||
Adverse Reaction | YERVOY and Nivolumab (n=352) | Nivolumab (n=351) | ||
All Grades (%) | Grades 3 or 4 (%) | All Grades (%) | Grades 3 or 4 (%) | |
Gastrointestinal | ||||
Diarrheaa | 35 | 4.5 | 30 | 3.4 |
Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue | ||||
Pruritus | 30 | 0 | 23 | 0 |
Musculoskeletal and Connective Tissue | ||||
Arthralgia | 20 | 0.6 | 15 | 0.6 |
Endocrine | ||||
Hypothyroidism | 18 | 0.6 | 10 | 0 |
Hyperthyroidism | 12 | 0 | 5 | 0 |
| a Each test incidence is based on the number of patients who had both baseline and at least one on-study laboratory measurement available: YERVOY and nivolumab group (range: 108 to 343 patients) or nivolumab group (range: 102 to 348 patients). | ||||
Laboratory Abnormality a | YERVOY and Nivolumab (n=352) | Nivolumab (n=351) | ||
All Grades (%) | Grades 3-or 4 (%) | All Grades (%) | Grades 3 or -4 (%) | |
Hematology | ||||
Lymphocytes decreased | 30 | 5 | 37 | 4 |
Neutrophils decreased | 21 | 1.7 | 12 | 0.6 |
Chemistry | ||||
Lipase increased | 44 | 10 | 32 | 11 |
Amylase increased | 41 | 4.6 | 33 | 5 |
ALT increased | 39 | 3.5 | 32 | 1.4 |
AST increased | 38 | 3.2 | 29 | 1.4 |
Sodium decreased | 36 | 3.2 | 30 | 2.3 |
Creatinine increased | 32 | 2 | 25 | 1.4 |
Potassium increased | 29 | 1.2 | 35 | 0.9 |
Glucose decreased | 17 | 0 | 12 | 0 |
Hepatocellular Carcinoma: In Combination with Nivolumab
Unresectable or Metastatic Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC)
The safety of YERVOY in combination with nivolumab was evaluated in CHECKMATE-9DW, a randomized, open-label trial in adult patients with unresectable or metastatic HCC [see Clinical Studies (14.5) ] . Patients received YERVOY in combination with nivolumab (n=332) or investigator’s choice of lenvatinib (n=275) or sorafenib (n=50) at the following dosage:
- YERVOY 3 mg/kg administered intravenously over 30 minutes in combination with nivolumab 1 mg/kg administered intravenously over 30 minutes every 3 weeks, for a maximum of 4 doses, followed by single agent nivolumab at 480 mg administered intravenously over 30 minutes every 4 weeks, or
- Investigator’s choice:
- Lenvatinib 8 mg orally daily (if body weight <60 kg) or 12 mg orally daily (if body weight ≥60 kg), or
- Sorafenib 400 mg orally twice daily
In the YERVOY and nivolumab arm, the median duration of exposure to nivolumab was 4.7 months (range: <0.1 to 24.4 months), 45% were exposed for >6 months and 30% were exposed for >1 year.
Serious adverse reactions occurred in 53% of patients treated with YERVOY in combination with nivolumab. The most frequent non-liver-related serious adverse reactions reported in ≥2% were diarrhea/colitis (4.5%), gastrointestinal hemorrhage (3%), and rash (2.4%).
Liver-related serious adverse reactions occurred in 17% of patients treated with YERVOY in combination with nivolumab, including Grade 3-4 events in 16% of patients. The most frequently reported all grade liver-related serious adverse reactions occurring in ≥1% of patients were immune-mediated hepatitis (3%), increased AST/ALT (3%), hepatic failure (2.4%), ascites (2.4%), and hepatotoxicity (1.2%).
Fatal adverse reactions occurred in 12 (3.6%) patients who received YERVOY in combination with nivolumab; these included 4 (1.2%) patients who died due to immune-mediated or autoimmune hepatitis and 4 (1.2%) patients who died of hepatic failure.
Permanent discontinuation due to an adverse reaction occurred in 27% of patients treated with YERVOY in combination with nivolumab. Adverse reactions leading to permanent discontinuation in >1% of patients included immune-mediated hepatitis (1.8%), diarrhea/colitis (1.8%), and hepatic failure (1.2%).
Dosage interruptions due to an adverse reaction occurred in 62% of patients treated with YERVOY in combination with nivolumab. Adverse reactions which required dosage interruption in >5% of patients included increased AST (13%), increased ALT (11%), and diarrhea/colitis (8%).
The most common (>20%) adverse reactions were rash, pruritus, fatigue, and diarrhea.
Tables 12 and 13 summarize the adverse reactions and laboratory abnormalities, respectively, in CHECKMATE-9DW.
| Toxicity was graded per NCI CTCAE v5 | ||||
| a Represents a composite of multiple related terms. | ||||
Adverse Reaction | YERVOY and Nivolumab (n=332) | Lenvatinib or Sorafenib (n=325) | ||
All Grades (%) | Grades 3-4 (%) | All Grades (%) | Grades 3-4 (%) | |
Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue | ||||
Rash a | 36 | 3.6 | 15 | 1.2 |
Pruritus | 34 | 1.5 | 7 | 0.3 |
General | ||||
Fatigue a | 33 | 2.4 | 39 | 4 |
Pyrexia a | 15 | 0.6 | 9 | 1.5 |
Edema a | 13 | 1.2 | 13 | 1.5 |
Gastrointestinal | ||||
Diarrhea | 25 | 6 | 39 | 3.4 |
Abdominal pain a | 14 | 1.2 | 27 | 2.5 |
Nausea | 10 | 0.3 | 16 | 0.9 |
Musculoskeletal and Connective Tissue | ||||
Musculoskeletal pain a | 17 | 0.6 | 23 | 0.3 |
Arthralgia | 12 | 0.3 | 13 | 0.6 |
Metabolism and Nutrition | ||||
Decreased appetite | 16 | 1.2 | 28 | 1.8 |
Endocrine | ||||
Hypothyroidism a | 14 | 0 | 27 | 0 |
Hyperthyroidism | 11 | 0.6 | 1.5 | 0 |
Respiratory, Thoracic and Mediastinal | ||||
Cough a | 13 | 0 | 8 | 0 |
Clinically important adverse reactions reported in <10% of patients who received YERVOY with nivolumab were hyperglycemia (8%), adrenal insufficiency (4.2%), pneumonitis (2.7%), and pancreatitis (2.4%).
| a Each test incidence is based on the number of patients who had both baseline and at least one on-study laboratory measurement available: YERVOY and nivolumab group (range: 168 to 331 patients) and lenvatinib or sorafenib group (range: 145 to 315 patients). | |||||
Laboratory Abnormality | YERVOY and Nivolumab (n=332) | Lenvatinib or Sorafenib (n=325) | |||
Grades 1-4 (%) | Grades 3-4 (%) | Grades 1-4 (%) | Grades 3-4 (%) | ||
Chemistry | |||||
Increased AST | 62 | 29 | 51 | 14 | |
Increased ALT | 61 | 17 | 46 | 9 | |
Increased lipase | 58 | 16 | 39 | 5 | |
Decreased albumin | 48 | 0.9 | 57 | 0.6 | |
Hyponatremia | 45 | 6 | 42 | 3.8 | |
Hyperglycemia | 44 | 15 | 32 | 2.1 | |
Increased bilirubin | 44 | 10 | 44 | 8 | |
Increased amylase | 41 | 6 | 26 | 1 | |
Increased alkaline phosphatase | 36 | 1.2 | 38 | 5 | |
Hypocalcemia | 29 | 0.9 | 46 | 0 | |
Increased creatinine | 26 | 2.4 | 23 | 0.6 | |
Hypokalemia | 21 | 2.1 | 20 | 2.6 | |
Hematology | |||||
Anemia | 44 | 5 | 40 | 3.8 | |
Lymphopenia | 40 | 6.1 | 40 | 8 | |
Thrombocytopenia | 27 | 4 | 44 | 4.8 | |
Neutropenia | 24 | 4 | 32 | 3.5 | |
Previously Treated Hepatocellular Carcinoma
The safety of YERVOY 3 mg/kg in combination with nivolumab 1 mg/kg was evaluated in a subgroup of 49 patients with HCC and Child-Pugh Class A cirrhosis who progressed on or were intolerant to sorafenib enrolled in Cohort 4 of CHECKMATE-040. YERVOY and nivolumab were administered every 3 weeks for four doses, followed by single-agent nivolumab 240 mg every 2 weeks until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity.
During the YERVOY and nivolumab combination period, 33 of 49 (67%) patients received all four planned doses of YERVOY and nivolumab. During the entire treatment period, the median duration of exposure to YERVOY was 2.1 months (range: 0 to 4.5 months) and to nivolumab was 5.1 months (range: 0 to 35+ months). Forty-seven percent of patients were exposed to treatment for >6 months, and 35% of patients were exposed to treatment for >1 year. Serious adverse reactions occurred in 59% of patients. Treatment was discontinued in 29% of patients and delayed in 65% of patients for an adverse reaction.
Serious adverse reactions reported in ≥4% of patients were pyrexia, diarrhea, anemia, increased AST, adrenal insufficiency, ascites, esophageal varices hemorrhage, hyponatremia, increased blood bilirubin, and pneumonitis.
Table 14 summarizes the adverse reactions and Table 15 summarizes the laboratory abnormalities of YERVOY in combination with nivolumab in CHECKMATE-040.
Adverse Reaction | YERVOY and Nivolumab (n=49) | |
All Grades (%) | Grades 3-4 (%) | |
Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue | ||
Rash | 53 | 8 |
Pruritus | 53 | 4 |
Musculoskeletal and Connective Tissue | ||
Musculoskeletal pain | 41 | 2 |
Arthralgia | 10 | 0 |
Gastrointestinal | ||
Diarrhea | 39 | 4 |
Abdominal pain | 22 | 6 |
Nausea | 20 | 0 |
Ascites | 14 | 6 |
Constipation | 14 | 0 |
Dry mouth | 12 | 0 |
Dyspepsia | 12 | 2 |
Vomiting | 12 | 2 |
Stomatitis | 10 | 0 |
Respiratory, Thoracic and Mediastinal | ||
Cough | 37 | 0 |
Dyspnea | 14 | 0 |
Pneumonitis | 10 | 2 |
Metabolism and Nutrition | ||
Decreased appetite | 35 | 2 |
General | ||
Fatigue | 27 | 2 |
Pyrexia | 27 | 0 |
Malaise | 18 | 2 |
Edema | 16 | 2 |
Influenza-like illness | 14 | 0 |
Chills | 10 | 0 |
Nervous System | ||
Headache | 22 | 0 |
Dizziness | 20 | 0 |
Endocrine | ||
Hypothyroidism | 20 | 0 |
Adrenal insufficiency | 18 | 4 |
Investigations | ||
Weight decreased | 20 | 0 |
Psychiatric | ||
Insomnia | 18 | 0 |
Blood and Lymphatic System | ||
Anemia | 10 | 4 |
Infections | ||
Influenza | 10 | 2 |
Vascular | ||
Hypotension | 10 | 0 |
Clinically important adverse reactions reported in <10% of patients receiving YERVOY with nivolumab were hyperglycemia (8%), colitis (4%), and increased blood creatine phosphokinase (2%).
Laboratory Abnormality | YERVOY and Nivolumab (n=47) | |
All Grades (%) | Grades 3-4 (%) | |
Hematology | ||
Lymphopenia | 53 | 13 |
Anemia | 43 | 4.3 |
Neutropenia | 43 | 9 |
Leukopenia | 40 | 2.1 |
Thrombocytopenia | 34 | 4.3 |
Chemistry | ||
Increased AST | 66 | 40 |
Increased ALT | 66 | 21 |
Increased bilirubin | 55 | 11 |
Increased lipase | 51 | 26 |
Hyponatremia | 49 | 32 |
Hypocalcemia | 47 | 0 |
Increased alkaline phosphatase | 40 | 4.3 |
Increased amylase | 38 | 15 |
Hypokalemia | 26 | 2.1 |
Hyperkalemia | 23 | 4.3 |
Increased creatinine | 21 | 0 |
Hypomagnesemia | 11 | 0 |
In patients who received YERVOY with nivolumab, virologic breakthrough occurred in 4 of 28 (14%) patients and 2 of 4 (50%) patients with active HBV or HCV at baseline, respectively. HBV virologic breakthrough was defined as at least a 1 log increase in HBV DNA for those patients with detectable HBV DNA at baseline. HCV virologic breakthrough was defined as a 1 log increase in HCV RNA from baseline.
First-line Treatment of Metastatic NSCLC: In Combination with Nivolumab
The safety of YERVOY in combination with nivolumab was evaluated in CHECKMATE-227, a randomized, multicenter, multi-cohort, open-label trial in patients with previously untreated metastatic or recurrent NSCLC with no EGFR or ALK genomic tumor aberrations [see Clinical Studies (14.6) ] . The trial excluded patients with untreated brain metastases, carcinomatous meningitis, active autoimmune disease, or medical conditions requiring systemic immunosuppression. Patients received YERVOY 1 mg/kg by intravenous infusion over 30 minutes every 6 weeks and nivolumab 3 mg/kg by intravenous infusion over 30 minutes every 2 weeks or platinum-doublet chemotherapy every 3 weeks for 4 cycles. The median duration of therapy in YERVOY and nivolumab-treated patients was 4.2 months (range: 1 day to 25.5 months): 39% of patients received YERVOY and nivolumab for >6 months and 23% of patients received YERVOY and nivolumab for >1 year. The population characteristics were: median age 64 years (range: 26 to 87); 48% were ≥65 years of age, 76% White, and 67% male. Baseline ECOG performance status was 0 (35%) or 1 (65%), 85% were former/current smokers, 11% had brain metastases, 28% had squamous histology and 72% had non-squamous histology.
Serious adverse reactions occurred in 58% of patients. YERVOY and nivolumab were discontinued for adverse reactions in 24% of patients and 53% had at least one dose withheld for an adverse reaction.
The most frequent (≥2%) serious adverse reactions were pneumonia, diarrhea/colitis, pneumonitis, hepatitis, pulmonary embolism, adrenal insufficiency, and hypophysitis. Fatal adverse reactions occurred in 1.7% of patients; these included events of pneumonitis (4 patients), myocarditis, acute kidney injury, shock, hyperglycemia, multi-system organ failure, and renal failure. The most common (≥20%) adverse reactions were fatigue, rash, decreased appetite, musculoskeletal pain, diarrhea/colitis, dyspnea, cough, hepatitis, nausea, and pruritus.
Tables 16 and 17 summarize selected adverse reactions and laboratory abnormalities, respectively, in CHECKMATE-227.
| a Includes fatigue and asthenia. b Includes eyelid edema, face edema, generalized edema, localized edema, edema, edema peripheral, and periorbital edema. c Includes autoimmune dermatitis, dermatitis, dermatitis acneiform, dermatitis allergic, dermatitis atopic, dermatitis bullous, dermatitis contact, dermatitis exfoliative, dermatitis psoriasiform, granulomatous dermatitis, rash generalized, drug eruption, dyshidrotic eczema, eczema, exfoliative rash, nodular rash, rash, rash erythematous, rash generalized, rash macular, rash maculo-papular, rash papular, rash pruritic, rash pustular, toxic skin eruption. d Includes pruritus and pruritus generalized. e Includes back pain, bone pain, musculoskeletal chest pain, musculoskeletal discomfort, musculoskeletal pain, myalgia, and pain in extremity. f Includes colitis, colitis microscopic, colitis ulcerative, diarrhea, enteritis infectious, enterocolitis, enterocolitis infectious, and enterocolitis viral. g Includes abdominal discomfort, abdominal pain, abdominal pain lower, abdominal pain upper, and abdominal tenderness. h Includes dyspnea and dyspnea exertional. i Includes cough and productive cough. j Includes alanine aminotransferase increased, aspartate aminotransferase increased, autoimmune hepatitis, blood bilirubin increased, hepatic enzyme increased, hepatic failure, hepatic function abnormal, hepatitis, hepatitis E, hepatocellular injury, hepatotoxicity, hyperbilirubinemia, immune-mediated hepatitis, liver function test abnormal, liver function test increased, transaminases increased. k Includes autoimmune thyroiditis, blood thyroid stimulating hormone increased, hypothyroidism, primary hypothyroidism, thyroiditis, and tri-iodothyronine free decreased. l Contains blood thyroid stimulating hormone decreased, hyperthyroidism, and tri-iodothyronine free increased. m Includes lower respiratory tract infection, lower respiratory tract infection bacterial, lung infection, pneumonia, pneumonia adenoviral, pneumonia aspiration, pneumonia bacterial, pneumonia klebsiella, pneumonia influenzal, pneumonia viral, atypical pneumonia, organizing pneumonia. | ||||
Adverse Reaction | YERVOY and Nivolumab (n=576) | Platinum-Doublet Chemotherapy (n=570) | ||
All Grades (%) | Grades 3-4 (%) | All Grades (%) | Grades 3-4 (%) | |
General | ||||
Fatigue a | 44 | 6 | 42 | 4.4 |
Pyrexia | 18 | 0.5 | 11 | 0.4 |
Edema b | 14 | 0.2 | 12 | 0.5 |
Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue | ||||
Rash c | 34 | 4.7 | 10 | 0.4 |
Pruritus d | 21 | 0.5 | 3.3 | 0 |
Metabolism and Nutrition | ||||
Decreased appetite | 31 | 2.3 | 26 | 1.4 |
Musculoskeletal and Connective Tissue | ||||
Musculoskeletal pain e | 27 | 1.9 | 16 | 0.7 |
Arthralgia | 13 | 0.9 | 2.5 | 0.2 |
Gastrointestinal | ||||
Diarrhea/colitis f | 26 | 3.6 | 16 | 0.9 |
Nausea | 21 | 1.0 | 42 | 2.5 |
Constipation | 18 | 0.3 | 27 | 0.5 |
Vomiting | 13 | 1.0 | 18 | 2.3 |
Abdominal pain g | 10 | 0.2 | 9 | 0.7 |
Respiratory, Thoracic, and Mediastinal | ||||
Dyspnea h | 26 | 4.3 | 16 | 2.1 |
Cough i | 23 | 0.2 | 13 | 0 |
Hepatobiliary | ||||
Hepatitis j | 21 | 9 | 10 | 1.2 |
Endocrine | ||||
Hypothyroidism k | 16 | 0.5 | 1.2 | 0 |
Hyperthyroidism l | 10 | 0 | 0.5 | 0 |
Infections and Infestations | ||||
Pneumonia m | 13 | 7 | 8 | 4.0 |
Nervous System | ||||
Headache | 11 | 0.5 | 6 | 0 |
Other clinically important adverse reactions in CHECKMATE-227 were:
Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue: urticaria, alopecia, erythema multiforme, vitiligo
Gastrointestinal: stomatitis, pancreatitis, gastritis
Musculoskeletal and Connective Tissue: arthritis, polymyalgia rheumatica, rhabdomyolysis
Nervous System: peripheral neuropathy, autoimmune encephalitis
Blood and Lymphatic System: eosinophilia
Eye Disorders: blurred vision, uveitis
Cardiac: atrial fibrillation, myocarditis
| a Each test incidence is based on the number of patients who had both baseline and at least one on-study laboratory measurement available: YERVOY and nivolumab group (range: 494 to 556 patients) and chemotherapy group (range: 469 to 542 patients). | ||||
Laboratory Abnormality | YERVOY and Nivolumab | Platinum-doublet Chemotherapy | ||
Grades 1-4 (%) | Grades 3-4 (%) | Grades 1-4 (%) | Grades 3-4 (%) | |
Hematology | ||||
Anemia | 46 | 3.6 | 78 | 14 |
Lymphopenia | 46 | 5 | 60 | 15 |
Chemistry | ||||
Hyponatremia | 41 | 12 | 26 | 4.9 |
Increased AST | 39 | 5 | 26 | 0.4 |
Increased ALT | 36 | 7 | 27 | 0.7 |
Increased lipase | 35 | 14 | 14 | 3.4 |
Increased alkaline phosphatase | 34 | 3.8 | 20 | 0.2 |
Increased amylase | 28 | 9 | 18 | 1.9 |
Hypocalcemia | 28 | 1.7 | 17 | 1.3 |
Hyperkalemia | 27 | 3.4 | 22 | 0.4 |
Increased creatinine | 22 | 0.9 | 17 | 0.2 |
First-line Treatment of Metastatic or Recurrent NSCLC: In Combination with Nivolumab and Platinum-Doublet Chemotherapy
The safety of YERVOY in combination with nivolumab and platinum-doublet chemotherapy was evaluated in CHECKMATE-9LA [see Clinical Studies (14.6) ] . Patients received either YERVOY 1 mg/kg administered every 6 weeks in combination with nivolumab 360 mg administered every 3 weeks and platinum-doublet chemotherapy administered every 3 weeks for 2 cycles; or platinum-doublet chemotherapy administered every 3 weeks for 4 cycles. The median duration of therapy in YERVOY in combination with nivolumab and platinum-doublet chemotherapy was 6 months (range: 1 day to 19 months): 50% of patients received YERVOY and nivolumab for >6 months and 13% of patients received YERVOY and nivolumab for >1 year.
Serious adverse reactions occurred in 57% of patients who were treated with YERVOY in combination with nivolumab and platinum-doublet chemotherapy. The most frequent (>2%) serious adverse reactions were pneumonia, diarrhea, febrile neutropenia, anemia, acute kidney injury, musculoskeletal pain, dyspnea, pneumonitis, and respiratory failure. Fatal adverse reactions occurred in 7 (2%) patients, and included hepatic toxicity, acute renal failure, sepsis, pneumonitis, diarrhea with hypokalemia, and massive hemoptysis in the setting of thrombocytopenia.
Study therapy with YERVOY in combination with nivolumab and platinum-doublet chemotherapy was permanently discontinued for adverse reactions in 24% of patients and 56% had at least one treatment withheld for an adverse reaction. The most common (>20%) adverse reactions were fatigue, musculoskeletal pain, nausea, diarrhea, rash, decreased appetite, constipation, and pruritus.
Tables 18 and 19 summarize selected adverse reactions and laboratory abnormalities, respectively, in CHECKMATE-9LA.
| Toxicity was graded per NCI CTCAE v4. a Includes fatigue and asthenia. b Includes myalgia, back pain, pain in extremity, musculoskeletal pain, bone pain, flank pain, muscle spasms, musculoskeletal chest pain, musculoskeletal disorder, osteitis, musculoskeletal stiffness, non-cardiac chest pain, arthralgia, arthritis, arthropathy, joint effusion, psoriatic arthropathy, synovitis. c Includes colitis, ulcerative colitis, diarrhea, and enterocolitis. d Includes abdominal discomfort, abdominal pain, lower abdominal pain, upper abdominal pain, and gastrointestinal pain. e Includes acne, dermatitis, acneiform dermatitis, allergic dermatitis, atopic dermatitis, bullous dermatitis, generalized exfoliative dermatitis, eczema, keratoderma blennorrhagica, palmar-plantar erythrodysesthesia syndrome, rash, erythematous rash, generalized rash, macular rash, maculo-papular rash, morbilliform rash, papular rash, pruritic rash, skin exfoliation, skin reaction, skin toxicity, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, urticaria. f Includes pruritus and generalized pruritus. g Includes cough, productive cough, and upper-airway cough syndrome. h Includes dyspnea, dyspnea at rest, and exertional dyspnea. i Includes autoimmune thyroiditis, increased blood thyroid stimulating hormone, hypothyroidism, thyroiditis, and decreased free tri-iodothyronine. j Includes dizziness, vertigo and positional vertigo | ||||
Adverse Reaction | YERVOY and Nivolumab and Platinum-Doublet Chemotherapy (n=358) | Platinum-Doublet Chemotherapy (n=349) | ||
All Grades (%) | Grades 3-4 (%) | All Grades (%) | Grades 3-4 (%) | |
General | ||||
Fatigue a | 49 | 5 | 40 | 4.9 |
Pyrexia | 14 | 0.6 | 10 | 0.6 |
Musculoskeletal and Connective Tissue | ||||
Musculoskeletal pain b | 39 | 4.5 | 27 | 2.0 |
Gastrointestinal | ||||
Nausea | 32 | 1.7 | 41 | 0.9 |
Diarrhea c | 31 | 6 | 18 | 1.7 |
Constipation | 21 | 0.6 | 23 | 0.6 |
Vomiting | 18 | 2.0 | 17 | 1.4 |
Abdominal pain d | 12 | 0.6 | 11 | 0.9 |
Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue | ||||
Rash e | 30 | 4.7 | 10 | 0.3 |
Pruritus f | 21 | 0.8 | 2.9 | 0 |
Alopecia | 11 | 0.8 | 10 | 0.6 |
Metabolism and Nutrition | ||||
Decreased appetite | 28 | 2.0 | 22 | 1.7 |
Respiratory, Thoracic and Mediastinal | ||||
Cough g | 19 | 0.6 | 15 | 0.9 |
Dyspnea h | 18 | 4.7 | 14 | 3.2 |
Endocrine | ||||
Hypothyroidism i | 19 | 0.3 | 3.4 | 0 |
Nervous System | ||||
Headache | 11 | 0.6 | 7 | 0 |
Dizziness j | 11 | 0.6 | 6 | 0 |
| a Each test incidence is based on the number of patients who had both baseline and at least one on-study laboratory measurement available: YERVOY and nivolumab and platinum-doublet chemotherapy group (range: 197 to 347 patients) and platinum-doublet chemotherapy group (range: 191 to 335 patients). | ||||
Laboratory Abnormality | YERVOY and Nivolumab and Platinum-Doublet Chemotherapy | Platinum-Doublet Chemotherapy | ||
Grades 1-4 (%) | Grades 3-4 (%) | Grades 1-4 (%) | Grades 3-4 (%) | |
Hematology | ||||
Anemia | 70 | 9 | 74 | 16 |
Lymphopenia | 41 | 6 | 40 | 11 |
Neutropenia | 40 | 15 | 42 | 15 |
Leukopenia | 36 | 10 | 40 | 9 |
Thrombocytopenia | 23 | 4.3 | 24 | 5 |
Chemistry | ||||
Hyperglycemia | 45 | 7 | 42 | 2.6 |
Hyponatremia | 37 | 10 | 27 | 7 |
Increased ALT | 34 | 4.3 | 24 | 1.2 |
Increased lipase | 31 | 12 | 10 | 2.2 |
Increased alkaline phosphatase | 31 | 1.2 | 26 | 0.3 |
Increased amylase | 30 | 7 | 19 | 1.3 |
Increased AST | 30 | 3.5 | 22 | 0.3 |
Hypomagnesemia | 29 | 1.2 | 33 | 0.6 |
Hypocalcemia | 26 | 1.4 | 22 | 1.8 |
Increased creatinine | 26 | 1.2 | 23 | 0.6 |
Hyperkalemia | 22 | 1.7 | 21 | 2.1 |
First-line Treatment of Unresectable Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma: In Combination with Nivolumab
The safety of YERVOY in combination with nivolumab was evaluated in CHECKMATE-743, a randomized, open-label trial in patients with previously untreated unresectable malignant pleural mesothelioma [see Clinical Studies (14.7) ] . Patients received either YERVOY 1 mg/kg over 30 minutes by intravenous infusion every 6 weeks and nivolumab 3 mg/kg over 30 minutes by intravenous infusion every 2 weeks for up to 2 years; or platinum-doublet chemotherapy for up to 6 cycles. The median duration of therapy in YERVOY and nivolumab-treated patients was 5.6 months (range: 0 to 26.2 months); 48% of patients received YERVOY and nivolumab for >6 months and 24% of patients received YERVOY and nivolumab for >1 year.
Serious adverse reactions occurred in 54% of patients who were treated with YERVOY in combination with nivolumab. The most frequent (≥2%) serious adverse reactions were pneumonia, pyrexia, diarrhea, pneumonitis, pleural effusion, dyspnea, acute kidney injury, infusion-related reaction, musculoskeletal pain, and pulmonary embolism. Fatal adverse reactions occurred in 4 (1.3%) patients and included pneumonitis, acute heart failure, sepsis, and encephalitis.
Both YERVOY and nivolumab were permanently discontinued due to adverse reactions in 23% of patients and 52% had at least one dose withheld due to an adverse reaction. An additional 4.7% of patients permanently discontinued YERVOY alone due to adverse reactions.
The most common (≥20%) adverse reactions were fatigue, musculoskeletal pain, rash, diarrhea, dyspnea, nausea, decreased appetite, cough, and pruritus.
Tables 20 and 21 summarize adverse reactions and laboratory abnormalities, respectively, in CHECKMATE-743.
| a Includes fatigue and asthenia. b Includes pyrexia and tumor-associated fever. c Includes edema, generalized edema, peripheral edema, and peripheral swelling. d Includes musculoskeletal pain, back pain, bone pain, flank pain, involuntary muscle contractions, muscle spasms, muscle twitching, musculoskeletal chest pain, musculoskeletal stiffness, myalgia, neck pain, non-cardiac chest pain, pain in extremity, polymyalgia rheumatica, and spinal pain. e Includes rash, acne, acneiform dermatitis, allergic dermatitis, atopic dermatitis, autoimmune dermatitis, bullous dermatitis, contact dermatitis, dermatitis, drug eruption, dyshidrotic eczema, eczema, erythematous rash, exfoliative rash, generalized exfoliative dermatitis, generalized rash, granulomatous dermatitis, keratoderma blennorrhagica, macular rash, maculopapular rash, morbilliform rash, nodular rash, papular rash, psoriasiform dermatitis, pruritic rash, pustular rash, skin exfoliation, skin reaction, skin toxicity, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, toxic skin eruption, and urticaria. f Includes pruritus, allergic pruritus, and generalized pruritus. g Includes diarrhea, colitis, enteritis, infectious enteritis, enterocolitis, infectious enterocolitis, microscopic colitis, ulcerative colitis, and viral enterocolitis. h Includes abdominal pain, abdominal discomfort, abdominal tenderness, gastrointestinal pain, lower abdominal pain, and upper abdominal pain. i Includes dyspnea, dyspnea at rest, and exertional dyspnea. j Includes cough, productive cough, and upper-airway cough syndrome. k Includes hypothyroidism, autoimmune thyroiditis, decreased free tri-iodothyronine, increased blood thyroid stimulating hormone, primary hypothyroidism, thyroiditis, and autoimmune hypothyroidism. l Includes upper respiratory tract infection, nasopharyngitis, pharyngitis, and rhinitis. m Includes pneumonia, lower respiratory tract infection, lung infection, aspiration pneumonia, and Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia. | ||||
Adverse Reaction | YERVOY and Nivolumab (n=300) | Chemotherapy (n=284) | ||
All Grades (%) | Grades 3-4 (%) | All Grades (%) | Grades 3-4 (%) | |
General | ||||
Fatigue a | 43 | 4.3 | 45 | 6 |
Pyrexia b | 18 | 1.3 | 4.6 | 0.7 |
Edema c | 17 | 0 | 8 | 0 |
Musculoskeletal and Connective Tissue | ||||
Musculoskeletal pain d | 38 | 3.3 | 17 | 1.1 |
Arthralgia | 13 | 1.0 | 1.1 | 0 |
Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue | ||||
Rash e | 34 | 2.7 | 11 | 0.4 |
Pruritus f | 21 | 1.0 | 1.4 | 0 |
Gastrointestinal | ||||
Diarrhea g | 32 | 6 | 12 | 1.1 |
Nausea | 24 | 0.7 | 43 | 2.5 |
Constipation | 19 | 0.3 | 30 | 0.7 |
Abdominal pain h | 15 | 1 | 10 | 0.7 |
Vomiting | 14 | 0 | 18 | 2.1 |
Respiratory, Thoracic, and Mediastinal | ||||
Dyspnea i | 27 | 2.3 | 16 | 3.2 |
Cough j | 23 | 0.7 | 9 | 0 |
Metabolism and Nutrition | ||||
Decreased appetite | 24 | 1.0 | 25 | 1.4 |
Endocrine | ||||
Hypothyroidism k | 15 | 0 | 1.4 | 0 |
Infections and Infestations | ||||
Upper respiratory tract infection l | 12 | 0.3 | 7 | 0 |
Pneumonia m | 10 | 4.0 | 4.2 | 2.1 |
| a Each test incidence is based on the number of patients who had both baseline and at least one on-study laboratory measurement available: YERVOY and nivolumab group (range: 109 to 297 patients) and chemotherapy group (range: 90 to 276 patients). | ||||
Laboratory Abnormality | YERVOY and Nivolumab | Chemotherapy | ||
Grades 1-4 (%) | Grades 3-4 (%) | Grades 1-4 (%) | Grades 3-4 (%) | |
Chemistry | ||||
Hyperglycemia | 53 | 3.7 | 34 | 1.1 |
Increased AST | 38 | 7 | 17 | 0 |
Increased ALT | 37 | 7 | 15 | 0.4 |
Increased lipase | 34 | 13 | 9 | 0.8 |
Hyponatremia | 32 | 8 | 21 | 2.9 |
Increased alkaline phosphatase | 31 | 3.1 | 12 | 0 |
Hyperkalemia | 30 | 4.1 | 16 | 0.7 |
Hypocalcemia | 28 | 0 | 16 | 0 |
Increased amylase | 26 | 5 | 13 | 0.9 |
Increased creatinine | 20 | 0.3 | 20 | 0.4 |
Hematology | ||||
Lymphopenia | 43 | 8 | 57 | 14 |
Anemia | 43 | 2.4 | 75 | 15 |
First-line Treatment of Unresectable Advanced or Metastatic ESCC: In Combination with Nivolumab
The safety of YERVOY in combination with nivolumab was evaluated in CHECKMATE-648, a randomized, active-controlled, multicenter, open-label trial in patients with previously untreated unresectable advanced, recurrent or metastatic ESCC [see Clinical Studies (14.8) ]. Patients received one of the following treatments:
- YERVOY 1 mg/kg every 6 weeks in combination with nivolumab 3 mg/kg every 2 weeks.
- 5-FU (fluorouracil) 800 mg/m 2 /day intravenously on days 1 through 5 (for 5 days), and cisplatin 80 mg/m 2 intravenously on day 1 (of a 4-week cycle).
Among patients who received YERVOY and nivolumab, the median duration of exposure was 2.8 months (range: 0 to 24 months).
Serious adverse reactions occurred in 69% of patients receiving YERVOY in combination with nivolumab.
The most frequent serious adverse reactions reported in ≥2% of patients who received YERVOY with nivolumab were pneumonia (10%), pyrexia (4.3%), pneumonitis (4.0%), aspiration pneumonia (3.7%), dysphagia (3.7%), hepatic function abnormal (2.8%), decreased appetite (2.8%), adrenal insufficiency (2.5%), and dehydration (2.5%).
Fatal adverse reactions occurred in 5 (1.6%) patients who received YERVOY in combination with nivolumab; these included pneumonitis, interstitial lung disease, pulmonary embolism, and acute respiratory distress syndrome.
YERVOY and/or nivolumab were discontinued in 23% of patients and delayed in 46% of patients for an adverse reaction.
The most common adverse reactions reported in ≥20% of patients treated with YERVOY in combination with nivolumab were rash, fatigue, pyrexia, nausea, diarrhea, and constipation.
Tables 22 and 23 summarize the adverse reactions and laboratory abnormalities, respectively, in CHECKMATE-648.
| Adverse Reaction | YERVOY and Nivolumab (n=322) | Cisplatin and 5-FU (n=304) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| All Grades (%) | Grades 3-4 (%) | All Grades (%) | Grades 3-4 (%) | |
| Toxicity was graded per NCI CTCAE v4. a Includes dermatitis, dermatitis acneiform, dermatitis allergic, dermatitis bullous, drug eruption, exfoliative rash, rash erythematous, rash follicular, rash macular, rash maculo-papular, rash papular, and rash pruritic. b Includes tumor associated fever. c Includes asthenia and malaise. d Includes aphthous ulcer, mouth ulceration, and mucosal inflammation. e Includes abdominal discomfort, abdominal pain lower, and abdominal pain upper. f Includes back pain, bone pain, musculoskeletal chest pain, myalgia, neck pain, pain in extremity, and spinal pain. g Includes organizing pneumonia, pneumonia bacterial, and pneumonia pseudomonal. h Includes productive cough. | ||||
Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue | ||||
Rash a | 31 | 3.1 | 7 | 0 |
Pruritis | 17 | 0.9 | 3.6 | 0 |
General | ||||
Fatigue c | 28 | 2.5 | 41 | 4.9 |
Pyrexia b | 23 | 0.9 | 12 | 0.3 |
Gastrointestinal | ||||
Nausea | 22 | 0.6 | 56 | 2.6 |
Diarrhea | 22 | 1.9 | 20 | 2.0 |
Constipation | 20 | 0.3 | 43 | 1.0 |
Vomiting | 15 | 1.6 | 19 | 3.0 |
Dysphagia | 12 | 5 | 12 | 4.9 |
Stomatitis d | 11 | 0.6 | 35 | 3.0 |
Abdominal pain e | 10 | 0.9 | 11 | 0.7 |
Metabolism and Nutrition | ||||
Decreased appetite | 17 | 4.0 | 50 | 6 |
Musculoskeletal and Connective Tissue | ||||
Musculoskeletal pain f | 14 | 0.6 | 8 | 0.3 |
Infections and Infestations | ||||
Pneumonia g | 14 | 8 | 10 | 2.6 |
Endocrine | ||||
Hypothyroidism | 14 | 0 | 0.3 | 0 |
Respiratory, Thoracic and Mediastinal | ||||
Cough h | 13 | 0.3 | 13 | 0.3 |
Investigations | ||||
Weight decreased | 12 | 1.9 | 11 | 1.0 |
| Laboratory Abnormality | YERVOY and Nivolumab (n=322) | Cisplatin and 5-FU (n=304) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Grades 1-4 (%) | Grades 3-4 (%) | Grades 1-4 (%) | Grades 3-4 (%) | |
| a Each test incidence is based on the number of patients who had both baseline and at least one on-study laboratory measurement available: YERVOY and nivolumab group (range: 59 to 307 patients) or Cisplatin and 5-FU group (range: 56 to 283 patients). | ||||
Hematology | ||||
Anemia | 52 | 7 | 66 | 14 |
Lymphopenia | 50 | 13 | 44 | 8 |
Neutropenia | 13 | 1.3 | 48 | 13 |
Thrombocytopenia | 12 | 1.0 | 29 | 2.8 |
Chemistry | ||||
Hyponatremia | 45 | 11 | 40 | 8 |
Hyperglycemia | 43 | 4.3 | 36 | 0.8 |
Increased AST | 39 | 6 | 11 | 1.4 |
Increased ALT | 33 | 6 | 8 | 0.7 |
Hypocalcemia | 32 | 0 | 23 | 0.7 |
Increased alkaline phosphatase | 31 | 3.3 | 15 | 0 |
Hyperkalemia | 23 | 1.6 | 24 | 0.7 |
Hypokalemia | 19 | 5 | 17 | 6 |
Hypercalcemia | 15 | 2.0 | 8 | 0 |
Hypoglycemia | 15 | 1.2 | 7 | 0 |
Increased creatinine | 15 | 0.7 | 31 | 0.7 |
Hypomagnesemia | 15 | 0 | 25 | 1.8 |
Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during post-approval use of YERVOY. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Blood and lymphatic system disorders: hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (HLH)
Immune System: graft-versus-host disease, solid organ transplant rejection
Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue: Drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS syndrome)
DESCRIPTION
Ipilimumab is a human cytotoxic T-lymphocyte antigen 4 (CTLA-4)-blocking antibody. Ipilimumab is a recombinant IgG1 kappa immunoglobulin with an approximate molecular weight of 148 kDa. Ipilimumab is produced in mammalian (Chinese hamster ovary) cell culture.
YERVOY (ipilimumab) injection, for intravenous use is a sterile, preservative-free, clear to slightly opalescent, colorless to pale-yellow solution, which may contain a small amount of visible translucent-to-white, amorphous ipilimumab particulates. It is supplied in single-dose vials of 50 mg/10 mL or 200 mg/40 mL. Each milliliter contains 5 mg of ipilimumab and the following inactive ingredients: diethylene triamine pentaacetic acid (DTPA) (0.04 mg), mannitol (10 mg), polysorbate 80 (vegetable origin) (0.1 mg), sodium chloride (5.85 mg), tris hydrochloride (3.15 mg), and Water for Injection, USP at a pH of 7.
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Mechanism of Action
CTLA-4 is a negative regulator of T-cell activity. Ipilimumab is a monoclonal antibody that binds to CTLA-4 and blocks the interaction of CTLA-4 with its ligands, CD80/CD86. Blockade of CTLA-4 has been shown to augment T-cell activation and proliferation, including the activation and proliferation of tumor infiltrating T-effector cells. Inhibition of CTLA-4 signaling can also reduce T-regulatory cell function, which may contribute to a general increase in T-cell responsiveness, including the anti-tumor immune response.
Pharmacokinetics
The pharmacokinetics (PK) of ipilimumab was studied in 785 patients with unresectable or metastatic melanoma who received doses of 0.3, 3, or 10 mg/kg once every 3 weeks for 4 doses. The PK of ipilimumab is linear in the dose range of 0.3 mg/kg to 10 mg/kg. Following administration of YERVOY every 3 weeks, the systemic accumulation was 1.5-fold or less. Steady-state concentrations of ipilimumab were reached by the third dose; the mean minimum concentration (C min ) at steady state was 19.4 mcg/mL at 3 mg/kg and 58.1 mcg/mL at 10 mg/kg every 3 weeks.
Elimination
The mean (percent coefficient of variation) terminal half-life (t 1/2 ) was 15.4 days (34%) and then mean (percent coefficient of variation) clearance (CL) was 16.8 mL/h (38%).
The CL of ipilimumab was unchanged in presence of anti-ipilimumab antibodies.
Specific Populations
The CL of ipilimumab increased with increasing body weight supporting the recommended body weight (mg/kg) based dosing. The following factors had no clinically important effect on the CL of ipilimumab: age (range: 23 to 88 years), sex, performance status, renal impairment (glomerular filtration rate ≥15 mL/min/1.73 m 2 ), mild hepatic impairment (total bilirubin [TB] >1 to 1.5 times the upper limit of normal [ULN] or AST > ULN), previous cancer therapy, and baseline lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) levels. The effect of race was not examined due to limited data available in non-White racial groups. YERVOY has not been studied in patients with moderate (TB >1.5 to 3 times ULN and any AST) or severe (TB >3 times ULN and any AST) hepatic impairment.
Pediatric Patients
The exposures of ipilimumab in pediatric patients 12 years and older are comparable to those in adult patients at the recommended dosage.
Drug Interaction Studies
Ipilimumab with Nivolumab
When YERVOY 1 mg/kg was administered with nivolumab 3 mg/kg every 3 weeks, the CL of ipilimumab was unchanged compared to when YERVOY was administered alone.
When YERVOY 3 mg/kg every 3 weeks was administered in combination with nivolumab 1 mg/kg every 3 weeks, the CL of ipilimumab was unchanged compared to ipilimumab administered alone and the CL of nivolumab was increased by 29% compared to nivolumab administered alone.
When YERVOY 1 mg/kg every 6 weeks was administered in combination with nivolumab 3 mg/kg every 2 weeks, the CL of ipilimumab increased by 30% compared to YERVOY administered alone and the CL of nivolumab was unchanged compared to nivolumab administered alone.
When YERVOY 1 mg/kg every 6 weeks was administered in combination with nivolumab 360 mg every 3 weeks and chemotherapy, the CL of ipilimumab increased by 22% compared to YERVOY administered alone and the CL of nivolumab was unchanged compared to nivolumab administered alone.
Immunogenicity
The observed incidence of anti-drug antibodies (ADA) is highly dependent on the sensitivity and specificity of the assay. Differences in assay methods preclude meaningful comparisons of the incidence of ADA in the studies described below with the incidence of ADA in other studies, including those of YERVOY or of other ipilimumab products.
Eleven (1.1%) of 1024 evaluable patients with unresectable or metastatic melanoma tested positive for treatment-emergent binding antibodies against ipilimumab in an electrochemiluminescent (ECL) based assay. This assay had substantial limitations in detecting anti-ipilimumab antibodies in the presence of ipilimumab. Seven (4.9%) of 144 patients receiving ipilimumab developed anti-ipilimumab antibodies and 7 (4.5%) of 156 patients receiving placebo for the adjuvant treatment of melanoma tested positive for anti-ipilimumab antibodies using an ECL assay with improved drug tolerance. No patients tested positive for neutralizing antibodies. No infusion-related reactions occurred in patients who tested positive for anti-ipilimumab antibodies.
Of the 499 patients evaluable for anti-ipilimumab antibodies in CHECKMATE-214 and CHECKMATE-142, 27 (5.4%) were positive for anti-ipilimumab antibodies; there were no patients with neutralizing antibodies against ipilimumab. There was no evidence of increased incidence of infusion reactions to YERVOY in patients with anti-ipilimumab antibodies.
Of 483 patients evaluable for anti-ipilimumab antibodies in CHECKMATE-227 Part 1, 8.5% were positive for treatment-emergent anti-ipilimumab antibodies. No patients had neutralizing antibodies against ipilimumab. In Part 1 of the same study, of 491 patients evaluable for anti-nivolumab antibodies, 36.7% were positive for anti-nivolumab antibodies and 1.4% had neutralizing antibodies against nivolumab.
Of 305 patients evaluable for anti-ipilimumab antibodies in CHECKMATE-9LA, 8% were positive for anti-ipilimumab antibodies and 1.6% were positive for anti-ipilimumab neutralizing antibodies. There was no evidence of increased incidence of infusion reactions to YERVOY in patients with anti-ipilimumab antibodies. Of 308 patients evaluable for anti-nivolumab antibodies in CHECKMATE-9LA, 34% were positive for anti-nivolumab antibodies and 2.6% had neutralizing antibodies against nivolumab.
Of 271 patients evaluable for anti-ipilimumab antibodies in CHECKMATE-743, 13.7% were positive for anti-ipilimumab antibodies and 0.4% were positive for anti-ipilimumab neutralizing antibodies. Of 269 patients evaluable for anti-nivolumab antibodies in CHECKMATE-743, 25.7% were positive for anti-nivolumab antibodies and 0.7% had neutralizing antibodies against nivolumab.
Anti-drug antibody and neutralizing antibody responses were monitored throughout the treatment period where the benefit to risk ratio was assessed. Incidence of anti-drug antibodies and neutralizing antibodies are presented in Table 24.
| a Details of each treatment regimen are described in Section 14 [see Clinical Studies (14) ]. | |||
| b NAb incidence is reported among the subset of patients positive for ADA. | |||
| ADA = treatment-emergent anti-ipilimumab antibodies, NAb = neutralizing antibodies, HCC = hepatocellular carcinoma, RCC = renal cell carcinoma, CRC = colorectal cancer, NSCLC = non-small cell lung cancer. | |||
Treatment Regimen a | Indication(s) | ADA | NAb b |
YERVOY as a single agent | Melanoma | 1.1% (11/1024) | 0 (0/11) |
Adjuvant Melanoma | 4.9 (7/144) | 0 (0/7) | |
YERVOY with nivolumab for 4 doses followed by nivolumab as a single agent | Melanoma | 8.4% (33/391) | 3% (1/33) |
HCC | 5.3% (13/244) | 0 (0/13) | |
RCC and CRC | 5.4% (27/499) | 0% (0/27) | |
YERVOY with nivolumab | Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma | 13.7% (37/271) | 2.7% (1/37) |
NSCLC | 8.5% (41/483) | 0 (0/41) | |
YERVOY with nivolumab and 2 cycles of platinum-doublet chemotherapy | NSCLC | 7.5% (23/305) | 21.7% (5/23) |
Effects of Anti-Drug Antibodies
Presence of treatment-emergent anti-ipilimumab antibodies did not affect ipilimumab clearance after administration of ipilimumab as monotherapy or in combination with nivolumab. These anti-drug antibody-associated pharmacokinetic changes were not considered to be clinically significant. There was no identified clinically significant effect of anti-drug antibodies on incidence of infusion-related reactions. In hepatocellular carcinoma, there was no identified clinically significant effect of anti-drug antibodies on efficacy for ipilimumab in combination with nivolumab. For other indications, the effects of anti-drug antibodies on effectiveness have not been fully characterized.
NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
The carcinogenic potential of ipilimumab has not been evaluated in long-term animal studies, and the genotoxic potential of ipilimumab has not been evaluated.
Fertility studies have not been performed with ipilimumab.
CLINICAL STUDIES
Unresectable or Metastatic Melanoma
The efficacy of YERVOY was investigated in a Study MDX010-20, a randomized (3:1:1), double-blind, double-dummy trial (NCT00094653) that included patients with unresectable or metastatic melanoma previously treated with one or more of the following: aldesleukin, dacarbazine, temozolomide, fotemustine, or carboplatin. The trial enrolled only patients with HLA-A2•0201 genotype; this HLA genotype facilitates the immune presentation of the investigational peptide vaccine. The trial excluded patients with active autoimmune disease or those receiving systemic immunosuppression for organ transplantation. Patients were randomized to YERVOY administered at a dose of 3 mg/kg as an intravenous infusion every 3 weeks for 4 doses with an investigational peptide vaccine with incomplete Freund’s adjuvant - gp100 administered at a dose of 2 mg peptide by deep subcutaneous injection every 3 weeks for 4 doses; gp100 administered at a dose of 2 mg by deep subcutaneous injection every 3 weeks for 4 doses as a single agent with a placebo; or YERVOY administered at a dose of 3 mg/kg by intravenous infusion every 3 weeks for 4 doses with a placebo. The major efficacy outcome measure was overall survival (OS) in the YERVOY and gp100 arm compared to that in the single-agent gp100 arm. Secondary efficacy outcome measures were OS in the YERVOY and gp100 arm compared to the YERVOY arm, OS in the YERVOY arm compared to the gp100 arm, best overall response rate (BORR) as assessed by the investigator at week 24 between each of the trial arms, and duration of response. Assessment of tumor response was conducted at weeks 12 and 24, and every 3 months thereafter. Patients with evidence of objective tumor response at 12 or 24 weeks had assessment for confirmation of durability of response at 16 or 28 weeks, respectively.
A total of 676 patients were randomized, 403 to YERVOY and gp100 arm, 137 to YERVOY single agent arm and 136 to gp100 single agent arm. Of the randomized patients, 61%, 59%, and 54% in the YERVOY and gp100, YERVOY, and gp100 arms, respectively, were male. Twenty-nine percent were ≥65 years of age, the median age was 57 years, 71% had M1c stage, 12% had a history of previously treated brain metastasis, 98% had ECOG performance status of 0 and 1, 23% had received aldesleukin, and 38% had elevated LDH level. Sixty-one percent of patients randomized to either YERVOY-containing arm received all 4 planned doses. The median duration of follow-up was 8.9 months.
The efficacy results are shown in Table 25 and Figure 1.
| a Not adjusted for multiple comparisons. b Not Reached | |||
YERVOY 3 mg/kg n=137 | YERVOY 3 mg/kg and gp100 n=403 | gp100 n=136 | |
Overall Survival | |||
Median in months (95% CI) | 10 (8.0, 13.8) | 10 (8.5, 11.5) | 6 (5.5, 8.7) |
Hazard ratio (vs. gp100) (95% CI) | 0.66 (0.51, 0.87) | 0.68 (0.55, 0.85) | |
p-value | p=0.0026 a | p=0.0004 | |
Hazard ratio (vs. YERVOY) (95% CI) | 1.04 (0.83, 1.30) | ||
Best Overall Response Rate (BORR) (95% CI) | 10.9% (6.3%, 17.4%) | 5.7% (3.7%, 8.4%) | 1.5% (0.2%, 5.2%) |
Median duration of response in months | NR b | 11.5 | NR b |
Figure 1: Kaplan-Meier Curves for Overall Survival in Study MDX010-20
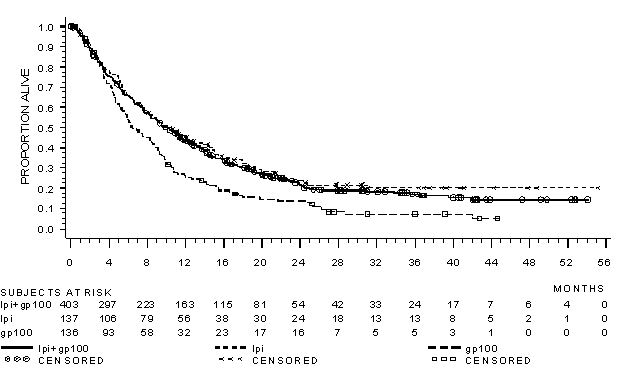
Previously Untreated Metastatic Melanoma: In Combination with Nivolumab
CHECKMATE-067 (NCT01844505) was a multicenter, randomized (1:1:1), double-blind trial in which 945 patients with previously untreated, unresectable or metastatic melanoma were randomized to one of the following arms: YERVOY and nivolumab, nivolumab, or YERVOY. Patients were required to have completed adjuvant or neoadjuvant treatment at least 6 weeks prior to randomization and have no prior treatment with anti-CTLA-4 antibody and no evidence of active brain metastasis, ocular melanoma, autoimmune disease, or medical conditions requiring systemic immunosuppression.
Patients were randomized to receive:
- YERVOY 3 mg/kg with nivolumab 1 mg/kg intravenously every 3 weeks for 4 doses, followed by nivolumab as a single agent at a dose of 3 mg/kg by intravenous infusion every 2 weeks (YERVOY and nivolumab arm),
- Nivolumab 3 mg/kg by intravenous infusion every 2 weeks (nivolumab arm), or
- YERVOY 3 mg/kg intravenously every 3 weeks for 4 doses followed by placebo every 2 weeks (YERVOY arm)
Randomization was stratified by PD-L1 expression (≥5% vs. <5% tumor cell membrane expression) as determined by a clinical trial assay, BRAF V600 mutation status, and M stage per the AJCC staging system (M0, M1a, M1b vs. M1c). Tumor assessments were conducted 12 weeks after randomization then every 6 weeks for the first year, and every 12 weeks thereafter. The major efficacy outcome measures were investigator-assessed PFS per RECIST v1.1 and OS. Additional efficacy outcome measures were confirmed ORR and duration of response.
The trial population characteristics were: median age 61 years (range: 18 to 90); 65% male; 97% White; ECOG performance score 0 (73%) or 1 (27%). Disease characteristics were: AJCC Stage IV disease (93%); M1c disease (58%); elevated LDH (36%); history of brain metastases (4%); BRAF V600 mutation-positive melanoma (32%); PD-L1 ≥5% tumor cell membrane expression as determined by the clinical trials assay (46%); and prior adjuvant therapy (22%).
CHECKMATE-067 demonstrated statistically significant improvements in OS and PFS for patients randomized to either nivolumab-containing arm as compared with the YERVOY arm. The trial was not designed to assess whether adding YERVOY to nivolumab improves PFS or OS compared to nivolumab as a single agent. Efficacy results are shown in Table 26 and Figure 2.
| a OS results are based on final OS analysis with 28 months of minimum follow-up; PFS (co-primary endpoint) and ORR (secondary endpoint) results were based on primary analysis with 9 months of minimum follow-up. b Based on a stratified proportional hazards model. c Based on stratified log-rank test. d If the maximum of the two OS p-values is less than 0.04 (a significance level assigned by the Hochberg procedure), then both p-values are considered significant. e p-value is compared with 0.005 of the allocated alpha for final PFS treatment comparisons. f Based on the stratified Cochran-Mantel-Haenszel test. + Censored observation | |||
YERVOY and Nivolumab (n=314) | Nivolumab (n=316) | YERVOY (n=315) | |
Overall Survival a | |||
Deaths (%) | 128 (41) | 142 (45) | 197 (63) |
Hazard ratio b (vs. YERVOY) (95% CI) | 0.55 (0.44, 0.69) | 0.63 (0.50, 0.78) | |
p-value c, d | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | |
Progression-free Survival a | |||
Disease progression or death | 151 (48%) | 174 (55%) | 234 (74%) |
Median (months) (95% CI) | 11.5 (8.9, 16.7) | 6.9 (4.3, 9.5) | 2.9 (2.8, 3.4) |
Hazard ratio b (vs. YERVOY) (95% CI) | 0.42 (0.34, 0.51) | 0.57 (0.47, 0.69) | |
p-value c, e | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | |
Confirmed Overall Response Rate a | 50% | 40% | 14% |
(95% CI) | (44, 55) | (34, 46) | (10, 18) |
p-value f | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | |
Complete response | 8.9% | 8.5% | 1.9% |
Partial response | 41% | 31% | 12% |
Duration of Response | |||
Proportion ≥6 months in duration | 76% | 74% | 63% |
Range (months) | 1.2+ to 15.8+ | 1.3+ to 14.6+ | 1.0+ to 13.8+ |
Figure 2: Overall Survival - CHECKMATE-067
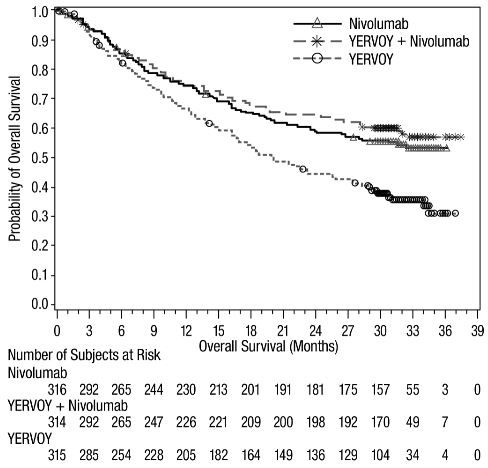
Based on a minimum follow-up of 48 months, the median OS was not reached (95% CI: 38.2, NR) in the YERVOY and nivolumab arm. The median OS was 36.9 months (95% CI: 28.3, NR) in the nivolumab arm and 19.9 months (95% CI: 16.9, 24.6) in the YERVOY arm.
Based on a minimum follow-up of 28 months, the median PFS was 11.7 months (95% CI: 8.9, 21.9) in the YERVOY and nivolumab arm, 6.9 months (95% CI: 4.3, 9.5) in the nivolumab arm, and 2.9 months (95% CI: 2.8, 3.2) in the YERVOY arm. Based on a minimum follow-up of 28 months, the proportion of responses lasting ≥24 months was 55% in the YERVOY and nivolumab arm, 56% in the nivolumab arm, and 39% in the YERVOY arm.
Adjuvant Treatment of Melanoma
The efficacy of YERVOY was evaluated in Study E1609 (NCT01274338), an open-label, multicenter, randomized trial for the adjuvant treatment of cutaneous melanoma in patients with completely resected node positive disease (either clinically detectable or any size with ulceration or mitosis ≥1/mm 2 ), in transit metastasis, satellites, or metastatic disease. The trial excluded patients with a history of prior therapy for melanoma and autoimmune disease requiring steroid treatment. Patients were randomized to receive one of the following regimens:
- YERVOY 3 mg/kg intravenously every 3 weeks for 4 doses, followed by the same dose every 12 weeks for up to 4 additional doses,
- High-dose interferon α-2b (HDI) intravenously at 20 million units/m 2 per day, 5 days per week, for 4 weeks (induction), followed by 10 million units/m 2 per day SC every other day, 3 days per week, for 48 weeks (maintenance), or
- YERVOY 10 mg/kg intravenously every 3 weeks for 4 doses, followed by the same dose every 12 weeks for up to 4 additional doses.
Randomization was stratified by AJCC 7th edition stage (IIIB, IIIC, M1a, or M1b). Tumor assessments were conducted every 3 months in patients <2 years from study entry, then every 6 months in patients 2-5 years from study entry, and every 12 months in patients >5 years from study entry for up to 20 years. Treatment continued for a maximum of 60 weeks with ipilimumab or 52 weeks with HDI, or until unacceptable toxic effects, disease progression, or withdrawal of consent. The major efficacy outcome measures were investigator-assessed recurrence-free survival (RFS) by imaging (for CNS lesions) or imaging and positive cytology or histology (for non-CNS lesions) and overall survival (OS). Only the efficacy results for the recommended starting dose of 3 mg/kg YERVOY are described below.
A total of 1051 patients were randomized to YERVOY 3 mg/kg (n=523) and HDI (n=528). The median age was 54 years (range: 18 to 83), 62% were male, 97% were white, 0.3% were Asian, and 0.4% were Black. Regarding disease stage, 53% had Stage IIIB, 40% had Stage IIIC (with no in-transit metastases), and 7% had Stage IV disease.
The efficacy results are in Table 27 and Figure 3.
| a Two-sided p-value from log-rank test stratified by AJCC stage. | ||
YERVOY 3 mg/kg n=523 | HDI n=528 | |
Overall Survival | ||
Number of deaths (%) | 130 (25) | 134 (25) |
Hazard ratio (95% CI) | 0.78 (0.61, 0.99) | |
p-value (stratified log-rank a ) | 0.044 | |
5-year OS Rates (95% CI) | 72 (68, 76) | 67 (62, 71) |
Recurrence-Free Survival | ||
Number of events (%) | 246 (47) | 232 (44) |
Median in years (95% CI) | 4.5 (2.7, NA) | 2.5 (1.8, 3.5) |
Hazard ratio (95% CI) | 0.85 (0.71, 1.02) | |
Figure 3: Kaplan-Meier Curves for Overall Survival with Ipilimumab 3 mg/kg vs. HDI in Study E1609

Advanced Renal Cell Carcinoma
The efficacy of YERVOY with nivolumab was evaluated in CHECKMATE-214 (NCT02231749), a randomized (1:1), open-label study in patients with previously untreated advanced RCC. Patients were included regardless of their PD-L1 status. CHECKMATE-214 excluded patients with any history of or concurrent brain metastases, active autoimmune disease, or medical conditions requiring systemic immunosuppression. Patients were randomized to nivolumab 3 mg/kg and YERVOY 1 mg/kg administered intravenously every 3 weeks for 4 doses followed by nivolumab 3 mg/kg every two weeks or to sunitinib administered orally 50 mg daily for the first 4 weeks of each 6-week cycle. Treatment continued until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity. Patients were stratified by International Metastatic RCC Database Consortium (IMDC) prognostic score and region. The major efficacy outcome measures were OS, PFS (IRRC-assessed), and confirmed ORR (IRRC-assessed) in intermediate/poor risk patients. Intermediate/poor risk patients had at least 1 or more of 6 prognostic risk factors as per the IMDC criteria: less than one year from time of initial RCC diagnosis to randomization, Karnofsky performance status (KPS) <80%, hemoglobin less than the lower limit of normal, corrected calcium >10 mg/dL, platelet count >ULN, and absolute neutrophil count >ULN.
A total of 847 patients were randomized, 425 to YERVOY with nivolumab and 422 to sunitinib. The median age was 61 years (range: 21 to 85) with 38% ≥65 years of age and 8% ≥75 years of age. The majority of patients were male (73%) and White (87%) and 26% and 74% of patients had a baseline KPS of 70% to 80% and 90% to 100%, respectively.
Efficacy results from CHECKMATE-214 are presented in Table 28 and Figure 4. In intermediate/poor risk patients, the trial demonstrated statistically significant improvement in OS and ORR for patients randomized to YERVOY and nivolumab arm as compared with sunitinib arm. OS benefit was observed regardless of PD-L1 expression level. The trial did not demonstrate a statistically significant improvement in PFS.
| a Based on a stratified proportional hazards model. b Based on a stratified log-rank test. c p-value is compared to alpha 0.002 in order to achieve statistical significance. d Based on the stratified DerSimonian-Laird test. e p-value is compared to alpha 0.001 in order to achieve statistical significance. f Not Significant at alpha level of 0.009. | ||
Efficacy Parameter | Intermediate/Poor-Risk | |
YERVOY 1 mg/kg and Nivolumab n=425 | Sunitinib n=422 | |
Overall Survival | ||
Number of deaths | 140 (32.9%) | 188 (44.5%) |
Median in months | NE | 25.9 |
Hazard ratio (99.8% CI) a | 0.63 (0.44, 0.89) | |
p-value b,c | <0.0001 | |
Confirmed Objective Response Rate (95% CI) | 41.6% (36.9%, 46.5%) | 26.5% (22.4%, 31.0%) |
Complete Response | 40 (9.4%) | 5 (1.2%) |
Partial Response | 137 (32.2%) | 107 (25.4%) |
Median duration of response in months (95% CI) | NE (21.8, NE) | 18.2 (14.8, NE) |
p-value d,e | <0.0001 | |
Progression-free Survival | ||
Number of events (progression or death) | 228 (53.6%) | 228 (54.0%) |
Median in months | 11.6 | 8.4 |
Hazard ratio (99.1% CI) a | 0.82 (0.64, 1.05) | |
p-value b | NS f | |
Figure 4: Kaplan-Meier Curves for Overall Survival (Intermediate/Poor Risk Population) in CHECKMATE-214
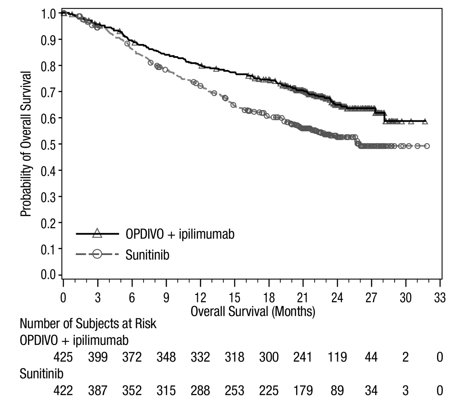
CHECKMATE-214 also randomized 249 favorable risk patients as per IMDC criteria to nivolumab and YERVOY (n=125) or to sunitinib (n=124). These patients were not evaluated as part of the efficacy analysis population. OS in favorable risk patients receiving nivolumab and YERVOY compared to sunitinib has a hazard ratio of 1.45 (95% CI: 0.75, 2.81). The efficacy of nivolumab and YERVOY in previously untreated renal cell carcinoma with favorable risk disease has not been established.
Microsatellite Instability-High or Mismatch Repair Deficient Metastatic Colorectal Cancer
Treatment of MSI-H or dMMR mCRC In Combination with Nivolumab
CHECKMATE-8HW (NCT03143153) was a randomized, 3-arm, open-label trial in immunotherapy-naive patients across all lines of therapy with unresectable or metastatic CRC with known tumor MSI-H or dMMR (MSI-H/dMMR) status as determined in accordance with local standard of practice using PCR, NGS or IHC, assays. Central assessment of MSI-H status using PCR (Idylla MSI) test and dMMR status using IHC (Omnis MMR) test was conducted retrospectively on patient tumor specimens used for local MSI-H/dMMR status determination. Patients with confirmed MSI-H/dMMR status by either central test comprised the primary study population.
The trial excluded patients with brain metastasis that were symptomatic, had active autoimmune disease, used systemic corticosteroids or immunosuppressants, or had been treated with checkpoint inhibitors.
Patients were randomized to receive one of the following treatments:
- YERVOY 1 mg/kg every 3 weeks and nivolumab 240 mg every 3 weeks for a maximum of 4 doses, then nivolumab 480 mg every 4 weeks
- Nivolumab 240 mg every 2 weeks for 6 doses, then nivolumab 480 mg every 4 weeks.
- Investigator’s choice chemotherapy
- mFOLFOX6 (oxaliplatin, leucovorin, and FU) with or without either bevacizumab or cetuximab: Oxaliplatin 85 mg/m 2 , leucovorin 400 mg/m 2 , and FU 400 mg/m 2 bolus followed by FU 2400 mg/m 2 over 46 hours every 2 weeks. Bevacizumab 5 mg/kg or cetuximab 500 mg/m 2 administered prior to mFOLFOX6 every 2 weeks.
- FOLFIRI (irinotecan, leucovorin, and FU) with or without either bevacizumab or cetuximab: Irinotecan 180 mg/m 2 , leucovorin 400 mg/m 2 , and FU 400 mg/m 2 bolus and FU 2400 mg/m 2 over 46 hours every 2 weeks. Bevacizumab 5 mg/kg on or cetuximab 500 mg/m 2 administered prior to FOLFIRI every 2 weeks.
Randomization was stratified by tumor location (right vs left) and by prior lines of therapy (0, 1, 2L+). Patients randomized to the chemotherapy arm could receive YERVOY plus nivolumab combination upon progression assessed by BICR.
Study treatment was administered until disease progression, unacceptable toxicity, or for up to 2 years for patients who received YERVOY plus nivolumab or nivolumab monotherapy. Patients who discontinued combination therapy because of an adverse reaction attributed to YERVOY were permitted to continue nivolumab as a single agent. Nivolumab with or without YERVOY could be administered beyond RECIST 1.1-assessed progressive disease if there was a clinical benefit as determined by investigator and therapy was tolerated. Tumor assessments per RECIST v1.1 were conducted every 6 weeks for the first 24 weeks, then every 8 weeks thereafter up until week 96, then every 16 weeks thereafter up until week 144, and then every 24 weeks.
The evaluation of efficacy relied on the comparison of patients with centrally confirmed MSI-H/dMMR mCRC randomized to YERVOY in combination with nivolumab versus chemotherapy in the first-line (1L) setting and the comparison of patients with centrally confirmed MSI-H/dMMR mCRC randomized to YERVOY in combination with nivolumab vs nivolumab in all lines setting.
The major efficacy outcome measure was BICR-assessed PFS per RECIST 1.1. Additional efficacy measures included ORR and duration of response assessed by BICR and OS.
The baseline characteristics of the total of 839 patients randomized were: the median age was 63 years (range: 20 to 87), with 46% ≥65 years of age and 14% ≥75 years of age; 50% were male and 87% were White, 9.3% were Asian, 1.5% Black or African American, and 2.3% other race; 9.2% were Hispanic or Latino, 50% Not Hispanic or Latino, 41% ethnicity unknown. Baseline ECOG performance status was 0 (52%) and (48%); number of prior lines of therapy was 0 (56%) and 1 (24%), and ≥2 (19%); tumor location was right-sided or left-sided for 69% and 31% of patients. The baseline characteristics in patients with centrally confirmed MSI-H/dMMR is consistent with all randomized patients.
First Line YERVOY in combination with nivolumab
Among 303 patients in the first-line setting were randomly assigned to YERVOY in combination with nivolumab (202) and to chemotherapy (101), 171 and 84 patients had centrally confirmed MSI-H/dMMR status in YERVOY in combination with nivolumab arm and chemotherapy arm, respectively.
In the 1L setting, 200 of 202 patients assigned to receive YERVOY in combination with nivolumab and 88 of 101 patients assigned to received chemotherapy received at least 1 dose of study treatment. Among the 88 patients who received chemotherapy, 58% and 42% of patients received oxaliplatin-containing regimens and irinotecan-containing regimens, respectively, and 66 (75%) patients received a targeted agent, either bevacizumab (64%) or cetuximab (11%).
The BICR-assessed PFS efficacy results for patients with centrally confirmed MSI-H/dMMR randomized to the YERVOY and nivolumab arm compared with chemotherapy in the 1L setting are presented in Table 29 and Figure 5. The comparative results of ORR and OS between arms were not available at the time of the PFS analysis due to statistical testing strategy.
| NR: Not Reached; NE: Not Estimable. | ||
| Minimum follow-up was 6.1 months at data cutoff date 12Oct2023. | ||
| a Based on log-rank test stratified by the same factors as used in the Cox proportional hazards model. The p-value threshold for statistical significance was 0.0209. | ||
| b Based on Kaplan-Meier estimates. | ||
| c HR from a Cox proportional hazards model stratified by tumor sidedness (left vs right) per IRT | ||
YERVOY and Nivolumab (n=171) | Chemotherapy (n=84) | |
Progression-free Survival | ||
Disease progression or death (%) | 48 (28) | 52 (62) |
Median in months b (95% CI) | NR (38.4, NE) | 5.8 (4.4, 7.8) |
Hazard ratio c (95% CI) | 0.21 (0.14, 0.32) | |
p-value a | <0.0001 | |
Figure 5: Progression-free Survival, (First line YERVOY + nivolumab vs Chemotherapy)- CHECKMATE-8HW
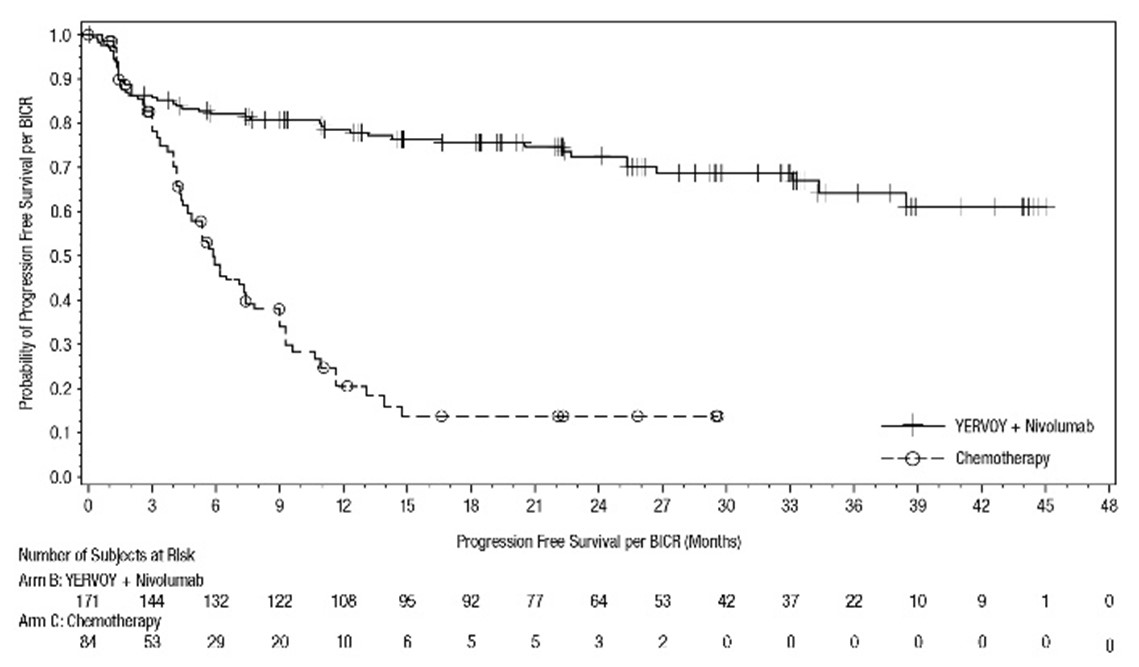
All Lines YERVOY in combination with nivolumab
Among 707 patients across all treatment lines who were randomly assigned to YERVOY in combination with nivolumab (354) and to nivolumab (353) single agent, 296 and 286 patients had centrally confirmed MSI-H/dMMR status in the YERVOY in combination with nivolumab arm and in the nivolumab arm, respectively. Patients receiving at least 1 dose of study treatment included 352 of 354 patients randomized to OPDIVO in combination with ipilimumab, and 351 of 353 patients randomized to single agent OPDIVO.
The BICR-assessed PFS and ORR efficacy results for patients with centrally confirmed MSI-H/dMMR randomized to the YERVOY in combination with nivolumab compared with nivolumab single agent across all treatment lines setting are presented in Table 30 and Figure 6. At the time of PFS analysis OS between arms were not available due to statistical testing strategy.
| NR: Not Reached; NE: Not Estimable. | ||
| Minimum follow-up was 16.7 months at data cutoff date 28Aug2024. | ||
| a Based on log-rank test stratified by the same factors as used in the Cox proportional hazards model. The p-value threshold for statistical significance was 0.0095. | ||
| b Based on Kaplan-Meier estimates. | ||
| c HR from a Cox proportional hazards model stratified by tumor sidedness (left vs right) and prior lines of therapy (0, 1, ≥2) per IRT. | ||
| d Based on Cochran-Mantel-Haenszel test stratified by the same factors as used in the Cox proportional hazards model. The p-value threshold for statistical significance was 0.006. | ||
YERVOY and Nivolumab (n=296) | Nivolumab (n=286) | |
Progression-free Survival | ||
Disease progression or death n (%) | 101 (34) | 136 (48) |
Median (months) b (95% CI) | NR (53.82, NE) | 39.3 (22.1, NE) |
Hazard ratio c (95% CI) | 0.62 (0.48, 0.81) | |
p-value a | 0.0003 | |
Objective Response Rate (ORR) | ||
Response Rate, n (%) (95% CI) | 209 (71%) (65, 76) | 165 (58%) (52, 63) |
Complete Response Rate, n (%) | 90 (30%) | 80 (28%) |
Partial Response, n (%) | 119 (40%) | 65 (30%) |
p-value d | 0.0011 | |
Figure 6: Progression-free Survival (All lines (YERVOY + Nivolumab vs Nivolumab)- CHECKMATE-8HW
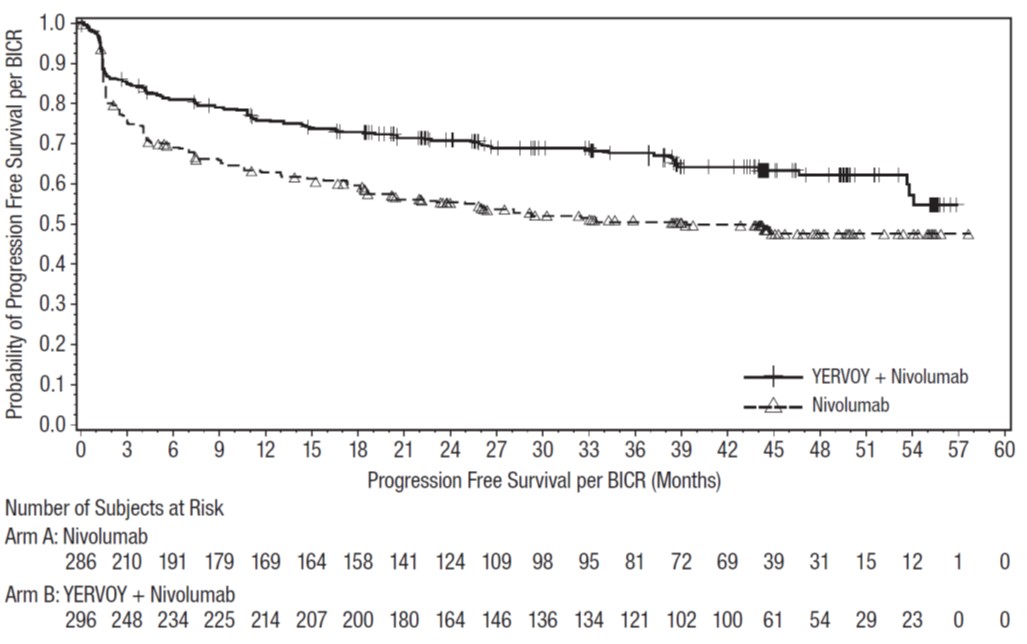
Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Treatment of Unresectable or Metastatic Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC)
CHECKMATE-9DW (NCT04039607) was a randomized (1:1), open-label trial in adults (18 years of age or older) with unresectable or metastatic HCC. Patients had histologically confirmed HCC, Child Pugh Class A, ECOG performance status 0 or 1, and no prior systemic therapy for advanced disease. Esophagogastroduodenoscopy was not mandated prior to enrollment. The trial excluded patients with active autoimmune disease, brain or leptomeningeal metastases, a history of hepatic encephalopathy (within 12 months of randomization), a platelet count <60,000, clinically significant ascites, medical conditions requiring systemic immunosuppression, infection with HIV, or active co-infection with hepatitis B virus (HBV) and hepatitis C virus (HCV) or HBV and hepatitis D virus (HDV).
Patients were randomized to receive either:
- YERVOY 3 mg/kg administered intravenously over 30 minutes in combination with nivolumab 1 mg/kg administered intravenously over 30 minutes every 3 weeks, for a maximum of 4 doses, followed by single agent nivolumab at 480 mg administered intravenously over 30 minutes every 4 weeks, or
- Investigator’s choice:
- Lenvatinib 8 mg orally daily (if body weight <60 kg) or 12 mg orally daily (if body weight ≥60 kg), or
- Sorafenib 400 mg orally twice daily
Randomization was stratified by etiology (HBV vs. HCV vs. non-viral), macrovascular invasion and/or extrahepatic spread (present or absent), and alpha-fetoprotein levels (≥400 or <400 ng/mL). Study treatment for YERVOY in combination with nivolumab continued until disease progression, unacceptable toxicity, or up to 2 years. Patients who discontinued combination therapy because of an adverse reaction attributed to YERVOY were permitted to continue nivolumab as a single agent. Treatment beyond RECIST 1.1 defined disease progression was permitted if the patient was clinically stable and considered to be deriving clinical benefit by the investigator. Tumor assessments were performed at baseline, after randomization at week 9 and week 16, then every 8 weeks up to 48 weeks, and then every 12 weeks thereafter until disease progression, treatment discontinuation, or initiation of subsequent therapy. The primary efficacy outcome measure was OS in all randomized patients. Additional efficacy measures included BICR-assessed ORR and DOR based on RECIST 1.1 criteria.
A total of 668 patients were randomized to receive YERVOY in combination with nivolumab (n=335) or investigator’s choice (n=333) of lenvatinib or sorafenib. In the investigator arm, 85% and 15% of treated patients received lenvatinib or sorafenib, respectively. The trial population characteristics were: median age was 66 years (range: 20 to 89), with 53% ≥65 years old; 82% male; 53% White, 44% Asian, 2.2% Black; 12% Hispanic or Latino, 48% Not Hispanic or Latino, 40% not reported. Baseline ECOG performance status was 0 (71%) or 1 (29%). Thirty-four percent (34%) of patients had HBV infection, 28% had HCV infection, and 36% had no evidence of HBV or HCV infection.
Nineteen percent (19%) of patients had alcoholic liver disease and 11% had non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. The majority of patients had BCLC stage C (73%) disease at baseline, 19% had stage B, and 6% had stage A. Patients with Child-Pugh scores of 5, 6, and 7 were 77%, 20%, and 3%, respectively; 1 patient with Child Pugh 8 was enrolled. A total of 54% of patients had extrahepatic spread; 25% had macrovascular invasion; and 33% had AFP levels ≥400 µg/L.
CHECKMATE-9DW demonstrated a statistically significant improvement in OS and ORR. The minimum follow-up was 26.8 months. Efficacy results are shown in Table 31 and Figure 7.
| a Based on stratified Cox proportional hazard model. | ||
| b Based on a 2-sided stratified log-rank test. Boundary for statistical significance: p-value ≤0.0257 | ||
| c Assessed by BICR using RECIST 1.1 | ||
| d Based on a 2-sided stratified Cochran-Mantel-Haenszel test. Boundary for statistical significance: p-value ≤0.025 | ||
| e NR: Not Reached | ||
| + Censored observation | ||
YERVOY and Nivolumab (n=335) | Lenvatinib or Sorafenib (n=333) | |
Overall Survival | ||
Deaths (%) | 194 (58%) | 228 (68%) |
Median (months) (95% CI) | 23.7 (18.8, 29.4) | 20.6 (17.5, 22.5) |
Hazard ratio (95% CI) a | 0.79 (0.65, 0.96) | |
p-value b | 0.0180 | |
Overall Response Rate, n (%) c | 121 (36.1) | 44 (13.2) |
(95% CI) | (31.0, 41.5) | (9.8, 17.3) |
p-value d | <0.0001 | |
Complete response (%) | 23 (6.9) | 6 (1.8) |
Partial response (%) | 98 (29.3) | 38 (11.4) |
Duration of Response (months) c | ||
Median (95% CI) | 30.4 (21.2, NR e ) | 12.9 (10.2, 31.2) |
Range | 1.5+, 36.9+ | 2.1+, 32.5+ |
Figure 7: Overall Survival - CHECKMATE-9DW
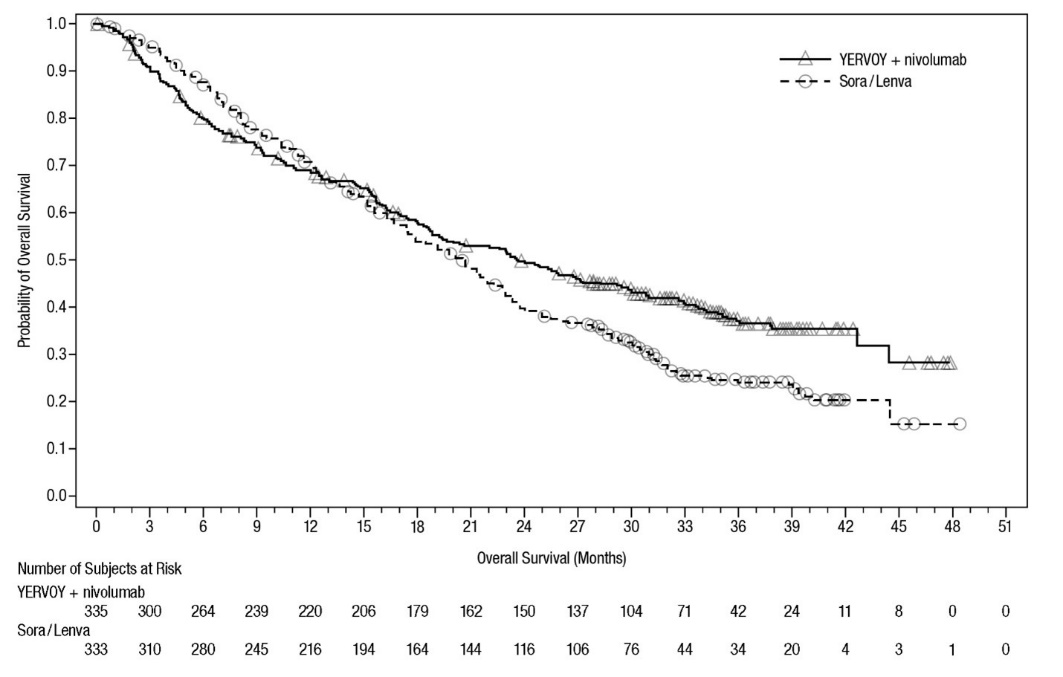
Previously Treated Hepatocellular Carcinoma
CHECKMATE-040 (NCT01658878) was a multicenter, multiple cohort, open-label trial conducted in patients with HCC who progressed on or were intolerant to sorafenib. Additional eligibility criteria included histologic confirmation of HCC and Child-Pugh Class A cirrhosis. The trial excluded patients with active autoimmune disease, brain metastasis, a history of hepatic encephalopathy, clinically significant ascites, infection with HIV, or active co-infection with hepatitis B virus (HBV) and hepatitis C virus (HCV) or HBV and hepatitis D virus (HDV); however, patients with only active HBV or HCV were eligible.
The efficacy of YERVOY 3 mg/kg in combination with nivolumab 1 mg/kg was evaluated in Cohort 4 of CHECKMATE-040. A total of 49 patients received the combination regimen, which was administered every 3 weeks for four doses, followed by single-agent nivolumab at 240 mg every 2 weeks until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity.
The median age was 60 years (range: 18 to 80); 88% were male; 74% were Asian, and 25% were White. Baseline ECOG performance status was 0 (61%) or 1 (39%). Fifty-seven percent (57%) of patients had active HBV infection, 8% had active HCV infection, and 35% had no evidence of active HBV or HCV. The etiology for HCC was alcoholic liver disease in 16% and non-alcoholic liver disease in 6% of patients. Child-Pugh class and score was A5 for 82% and A6 for 18%; 80% of patients had extrahepatic spread; 35% had vascular invasion; and 51% had alfa-fetoprotein (AFP) levels ≥400 µg/L. Prior treatment history included surgery (74%), radiotherapy (29%), or local treatment (59%). All patients had received prior sorafenib, of whom 10% were unable to tolerate sorafenib; 29% of patients had received 2 or more prior systemic therapies.
Efficacy results are shown in Table 32.
| a Confirmed by BICR. b Confidence interval is based on the Clopper and Pearson method. | |
YERVOY and Nivolumab (Cohort 4) (n=49) | |
Overall Response Rate per BICR, a n (%), RECIST v1.1 | 16 (33%) |
(95% CI) b | (20, 48) |
Complete response | 4 (8%) |
Partial response | 12 (24%) |
Duration of Response per BICR, a RECIST v1.1 | n=16 |
Range (months) | 4.6, 30.5+ |
Percent with duration ≥6 months | 88% |
Percent with duration ≥12 months | 56% |
Percent with duration ≥24 months | 31% |
Overall Response Rate per BICR, a n (%), mRECIST | 17 (35%) |
(95% CI) b | (22, 50) |
Complete response | 6 (12%) |
Partial response | 11 (22%) |
Metastatic Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
First-line Treatment of Metastatic Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC) Expressing PD-L1 (≥1%): In Combination with Nivolumab
CHECKMATE-227 (NCT02477826) was a randomized, open-label, multi-part trial in patients with metastatic or recurrent NSCLC. The study included patients (18 years of age or older) with histologically confirmed Stage IV or recurrent NSCLC (per the 7th International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer [ASLC] classification), ECOG performance status 0 or 1, and no prior anticancer therapy. Patients were enrolled regardless of their tumor PD-L1 status. Patients with known EGFR mutations or ALK translocations sensitive to available targeted inhibitor therapy, untreated brain metastases, carcinomatous meningitis, active autoimmune disease, or medical conditions requiring systemic immunosuppression were excluded from the study. Patients with treated brain metastases were eligible if neurologically returned to baseline at least 2 weeks prior to enrolment, and either off corticosteroids, or on a stable or decreasing dose of <10 mg daily prednisone equivalents.
Primary efficacy results were based on Part 1a of the study, which was limited to patients with PD-L1 tumor expression ≥1%. Tumor specimens were evaluated prospectively using the PD-L1 IHC 28-8 pharmDx assay at a central laboratory. Randomization was stratified by tumor histology (non-squamous versus squamous). The evaluation of efficacy relied on the comparison between:
- YERVOY 1 mg/kg administered intravenously over 30 minutes every 6 weeks in combination with nivolumab 3 mg/kg administered intravenously over 30 minutes every 2 weeks; or
- Platinum-doublet chemotherapy
Chemotherapy regimens consisted of pemetrexed (500 mg/m 2 ) and cisplatin (75 mg/m 2 ) or pemetrexed (500 mg/m 2 ) and carboplatin (AUC 5 or 6) for non-squamous NSCLC or gemcitabine (1000 or 1250 mg/m 2 ) and cisplatin (75 mg/m 2 ) or gemcitabine (1000 mg/m 2 ) and carboplatin (AUC 5) (gemcitabine was administered on Days 1 and 8 of each cycle) for squamous NSCLC.
Study treatment continued until disease progression, unacceptable toxicity, or for up to 24 months. Treatment continued beyond disease progression if a patient was clinically stable and was considered to be deriving clinical benefit by the investigator. Patients who discontinued combination therapy because of an adverse event attributed to YERVOY were permitted to continue nivolumab as a single agent. Tumor assessments were performed every 6 weeks from the first dose of study treatment for the first 12 months, then every 12 weeks until disease progression or study treatment was discontinued. The primary efficacy outcome measure was OS. Additional efficacy outcome measures included PFS, ORR, and duration of response as assessed by BICR.
In Part 1a, a total of 793 patients were randomized to receive either YERVOY in combination with nivolumab (n=396) or platinum-doublet chemotherapy (n=397). The median age was 64 years (range: 26 to 87) with 49% of patients ≥65 years and 10% of patients ≥75 years, 76% White, and 65% male. Baseline ECOG performance status was 0 (34%) or 1 (65%), 50% with PD-L1 ≥50%, 29% with squamous and 71% with non-squamous histology, 10% had brain metastases, and 85% were former/current smokers.
The study demonstrated a statistically significant improvement in OS for PD-L1 ≥1% patients randomized to the YERVOY and nivolumab arm compared to platinum-doublet chemotherapy arm. The OS results are presented in Table 33 and Figure 8.
| a Kaplan-Meier estimate. b Based on a stratified Cox proportional hazard model. | ||
YERVOY and Nivolumab (n=396) | Platinum-Doublet Chemotherapy (n=397) | |
Overall Survival | ||
Events (%) | 258 (65%) | 298 (75%) |
Median (months) a (95% CI) | 17.1 (15, 20.1) | 14.9 (12.7, 16.7) |
Hazard ratio (95% CI) b | 0.79 (0.67, 0.94) | |
Stratified log-rank p-value | 0.0066 | |
Figure 8: Overall Survival (PD-L1 ≥1%) - CHECKMATE-227
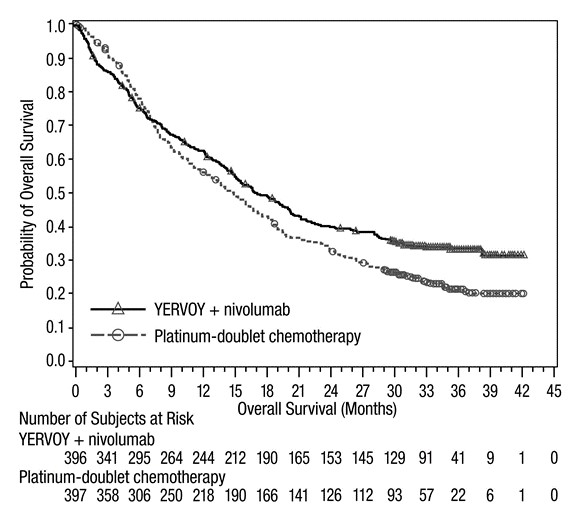
BICR-assessed PFS showed a HR of 0.82 (95% CI: 0.69, 0.97), with a median PFS of 5.1 months (95% CI: 4.1, 6.3) in the YERVOY and nivolumab arm and 5.6 months (95% CI: 4.6, 5.8) in the platinum-doublet chemotherapy arm. The BICR-assessed confirmed ORR was 36% (95% CI: 31, 41) in the YERVOY and nivolumab arm and 30% (95% CI: 26, 35) in the platinum-doublet chemotherapy arm. Median duration of response observed in the YERVOY and nivolumab arm was 23.2 months and 6.2 months in the platinum-doublet chemotherapy arm.
First-line Treatment of Metastatic or Recurrent NSCLC: In Combination with Nivolumab and Platinum-Doublet Chemotherapy
CHECKMATE-9LA (NCT03215706) was a randomized, open-label trial in patients with metastatic or recurrent NSCLC. The trial included patients (18 years of age or older) with histologically confirmed Stage IV or recurrent NSCLC (per the 7th International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer classification [IASLC]), ECOG performance status 0 or 1, and no prior anticancer therapy (including EGFR and ALK inhibitors) for metastatic disease. Patients were enrolled regardless of their tumor PD-L1 status. Patients with known EGFR mutations or ALK translocations sensitive to available targeted inhibitor therapy, untreated brain metastases, carcinomatous meningitis, active autoimmune disease, or medical conditions requiring systemic immunosuppression were excluded from the study. Patients with stable brain metastases were eligible for enrollment.
Patients were randomized 1:1 to receive either:
- YERVOY 1 mg/kg administered intravenously over 30 minutes every 6 weeks, nivolumab 360 mg administered intravenously over 30 minutes every 3 weeks, and platinum-doublet chemotherapy administered intravenously every 3 weeks for 2 cycles, or
- platinum-doublet chemotherapy administered every 3 weeks for 4 cycles.
Platinum-doublet chemotherapy consisted of either carboplatin (AUC 5 or 6) and pemetrexed 500 mg/m 2 , or cisplatin 75 mg/m 2 and pemetrexed 500 mg/m 2 for non-squamous NSCLC; or carboplatin (AUC 6) and paclitaxel 200 mg/m 2 for squamous NSCLC. Patients with non-squamous NSCLC in the control arm could receive optional pemetrexed maintenance therapy. Stratification factors for randomization were tumor PD-L1 expression level (≥1% versus <1% or non-quantifiable), histology (squamous versus non-squamous), and sex (male versus female). Study treatment continued until disease progression, unacceptable toxicity, or for up to 2 years. Treatment could continue beyond disease progression if a patient was clinically stable and was considered to be deriving clinical benefit by the investigator. Patients who discontinued combination therapy because of an adverse reaction attributed to YERVOY were permitted to continue nivolumab as a single agent as part of the study. Tumor assessments were performed every 6 weeks from the first dose of study treatment for the first 12 months, then every 12 weeks until disease progression or study treatment was discontinued. The primary efficacy outcome measure was OS. Additional efficacy outcome measures included PFS, ORR, and duration of response as assessed by BICR.
A total of 719 patients were randomized to receive either YERVOY in combination with nivolumab and platinum-doublet chemotherapy (n=361) or platinum-doublet chemotherapy (n=358). The median age was 65 years (range: 26 to 86) with 51% of patients ≥65 years and 10% of patients ≥75 years. The majority of patients were White (89%) and male (70%). Baseline ECOG performance status was 0 (31%) or 1 (68%), 57% had tumors with PD-L1 expression ≥1% and 37% had tumors with PD-L1 expression that was <1%, 32% had tumors with squamous histology and 68% had tumors with non-squamous histology, 17% had CNS metastases, and 86% were former or current smokers.
The study demonstrated a statistically significant benefit in OS, PFS, and ORR. Efficacy results from the prespecified interim analysis when 351 events were observed (87% of the planned number of events for final analysis) are presented in Table 34.
| a Based on a stratified Cox proportional hazard model. b p-value is compared with the allocated alpha of 0.033 for this interim analysis. c p-value is compared with the allocated alpha of 0.0252 for this interim analysis. d Kaplan-Meier estimate. e Confidence interval based on the Clopper and Pearson Method. f p-value is compared with the allocated alpha of 0.025 for this interim analysis. | ||
YERVOY and Nivolumab and Platinum-Doublet Chemotherapy (n=361) | Platinum-Doublet Chemotherapy (n=358) | |
Overall Survival | ||
Events (%) | 156 (43.2) | 195 (54.5) |
Median (months) (95% CI) | 14.1 (13.2, 16.2) | 10.7 (9.5, 12.5) |
Hazard ratio (96.71% CI) a | 0.69 (0.55, 0.87) | |
Stratified log-rank p-value b | 0.0006 | |
Progression-free Survival per BICR | ||
Events (%) | 232 (64.3) | 249 (69.6) |
Hazard ratio (97.48% CI) a | 0.70 (0.57, 0.86) | |
Stratified log-rank p-value c | 0.0001 | |
Median (months) d (95% CI) | 6.8 (5.6, 7.7) | 5.0 (4.3, 5.6) |
Overall Response Rate per BICR (%) | 38 | 25 |
(95% CI) e | (33, 43) | (21, 30) |
Stratified CMH test p-value f | 0.0003 | |
Duration of Response per BICR | ||
Median (months) (95% CI) d | 10.0 (8.2, 13.0) | 5.1 (4.3, 7.0) |
With an additional 4.6 months of follow-up the hazard ratio for overall survival was 0.66 (95% CI: 0.55, 0.80) and median survival was 15.6 months (95% CI: 13.9, 20.0) and 10.9 months (95% CI: 9.5, 12.5) for patients receiving YERVOY and nivolumab and platinum-doublet chemotherapy or platinum-doublet chemotherapy, respectively (Figure 9).
Figure 9: Overall Survival - CHECKMATE-9LA
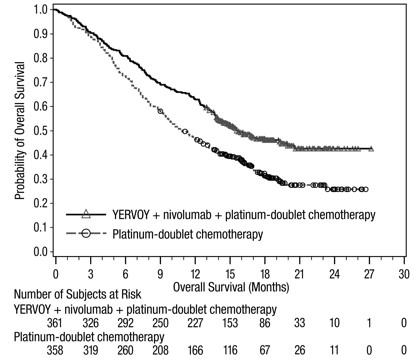
Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma
CHECKMATE-743 (NCT02899299) was a randomized, open-label trial in patients with unresectable malignant pleural mesothelioma. The trial included patients with histologically confirmed and previously untreated malignant pleural mesothelioma with no palliative radiotherapy within 14 days of initiation of therapy. Patients with interstitial lung disease, active autoimmune disease, medical conditions requiring systemic immunosuppression, or active brain metastasis were excluded from the trial. Patients were randomized 1:1 to receive either:
- YERVOY 1 mg/kg over 30 minutes by intravenous infusion every 6 weeks and nivolumab 3 mg/kg over 30 minutes by intravenous infusion every 2 weeks for up to 2 years, or
- cisplatin 75 mg/m 2 and pemetrexed 500 mg/m 2 , or carboplatin 5 AUC and pemetrexed 500 mg/m 2 administered every 3 weeks for 6 cycles.
Stratification factors for randomization were tumor histology (epithelioid vs. sarcomatoid or mixed histology subtypes) and sex (male vs. female). Study treatment continued for up to 2 years, or until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity. Patients who discontinued combination therapy because of an adverse reaction attributed to YERVOY were permitted to continue nivolumab as a single agent. Treatment could continue beyond disease progression if a patient was clinically stable and was considered to be deriving clinical benefit by the investigator. Tumor assessments were performed every 6 weeks from the first dose of study treatment for the first 12 months, then every 12 weeks until disease progression or study treatment was discontinued. The primary efficacy outcome measure was OS. Additional efficacy outcome measures included PFS, ORR, and duration of response as assessed by BICR utilizing modified RECIST criteria.
A total of 605 patients were randomized to receive either YERVOY in combination with nivolumab (n=303) or chemotherapy (n=302). The median age was 69 years (range: 25 to 89), with 72% of patients ≥65 years and 26% ≥75 years; 85% were White, 11% were Asian, and 77% were male. Baseline ECOG performance status was 0 (40%) or 1 (60%), 35% had Stage III and 51% had Stage IV disease, 75% had epithelioid and 25% had non-epithelioid histology, 75% had tumors with PD-L1 expression ≥1%, and 22% had tumors with PD-L1 expression <1%.
The trial demonstrated a statistically significant improvement in OS for patients randomized to YERVOY in combination with nivolumab compared to chemotherapy. Efficacy results from the prespecified interim analysis are presented in Table 35 and Figure 10.
| a At the time of the interim analysis, 419 deaths (89% of the deaths needed for the final analysis) had occurred. b Kaplan-Meier estimate. c Stratified Cox proportional hazard model. d p-value is compared with the allocated alpha of 0.0345 for this interim analysis. e Based on confirmed response by BICR. | ||
YERVOY and Nivolumab (n=303) | Chemotherapy (n=302) | |
Overall Survival a | ||
Events (%) | 200 (66) | 219 (73) |
Median (months) b (95% CI) | 18.1 (16.8, 21.5) | 14.1 (12.5, 16.2) |
Hazard ratio (95% CI) c | 0.74 (0.61, 0.89) | |
Stratified log-rank p-value d | 0.002 | |
Progression-free Survival | ||
Events (%) | 218 (72) | 209 (69) |
Hazard ratio (95% CI) c | 1.0 (0.82, 1.21) | |
Median (months) b (95% CI) | 6.8 (5.6, 7.4) | 7.2 (6.9, 8.1) |
Overall Response Rate e | 40% | 43% |
(95% CI) | (34, 45) | (37, 49) |
Duration of Response | ||
Median (months) a (95% CI) | 11.0 (8.1, 16.5) | 6.7 (5.3, 7.1) |
Figure 10: Overall Survival - CHECKMATE-743
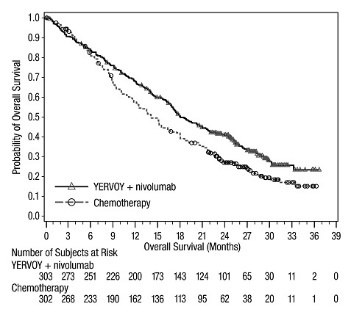
In a prespecified exploratory analysis based on histology, in the subgroup of patients with epithelioid histology, the hazard ratio (HR) for OS was 0.85 (95% CI: 0.68, 1.06), with median OS of 18.7 months in the YERVOY and nivolumab arm and 16.2 months in the chemotherapy arm. In the subgroup of patients with non-epithelioid histology, the HR for OS was 0.46 (95% CI: 0.31, 0.70), with median OS of 16.9 months in the YERVOY and nivolumab arm and 8.8 months in the chemotherapy arm.
Esophageal Cancer
CHECKMATE-648 (NCT03143153) was a randomized, active-controlled, open-label trial in patients with previously untreated unresectable advanced, recurrent or metastatic ESCC (squamous or adenosquamous histology). The trial enrolled patients whose tumor was evaluable for tumor cell (TC) PD-L1 expression [also called PD-L1 tumor proportion score (TPS)], which was evaluated using the PD-L1 IHC 28-8 pharmDx assay at a central laboratory. Patients were not amenable to chemoradiation or surgery with curative intent. A retrospective scoring of a patient’s tumor PD-L1 status using Combined Positive Score (CPS) was also conducted using the PD-L1-stained tumor specimens used for randomization. Prior treatment with curative intent was allowed if completed more than six months prior to trial enrollment. The trial excluded patients with brain metastasis that were symptomatic, had active autoimmune disease, used systemic corticosteroids or immunosuppressants, or patients at high risk of bleeding or fistula due to apparent invasion of tumor to organs adjacent to the esophageal tumor. Patients were randomized to receive one of the following treatments:
- YERVOY 1 mg/kg every 6 weeks in combination with nivolumab 3 mg/kg every 2 weeks.
- Fluorouracil 800 mg/m 2 /day intravenously on days 1 through 5 (for 5 days), and cisplatin 80 mg/m 2 intravenously on day 1 (of a 4-week cycle).
Patients were treated until disease progression, unacceptable toxicity, or up to 2 years. Patients who discontinued combination therapy because of an adverse reaction attributed to YERVOY were permitted to continue nivolumab as a single agent.
Randomization was stratified by TC PD-L1 expression (≥1% vs. <1% or indeterminate), region (East Asia vs. Rest of Asia vs. Rest of World), ECOG performance status (0 vs. 1), and number of organs with metastases (≤1 vs. ≥2). The major efficacy outcome measures were OS and BICR-assessed PFS in patients with TC PD-L1 expression ≥1%. Additional efficacy measures included OS in all randomized patients, BICR-assessed PFS in all randomized patients, and ORR assessed by BICR in TC PD-L1 expression ≥1% and in all randomized patients. The tumor assessments per RECIST v1.1 were conducted every 6 weeks up to and including week 48, then every 12 weeks thereafter.
A total of 649 patients were randomized in Arms A and C of the CHECKMATE-648 study, among whom 644 and 601 patients had quantifiable TC PD-L1 expression and CPS at baseline, respectively; 84% (546/649) had tumors with PD-L1 CPS ≥1. The trial population characteristics in patients with PD-L1 CPS ≥1 were: median age 63 years (range: 26 to 81), 45% were ≥65 years of age, 84% were male, 71% were Asian, 25% were White, and 1.6% were Black or African American. Patients had histological confirmation of squamous cell carcinoma (99%) or adenosquamous cell carcinoma (1.3%) in the esophagus. Baseline ECOG performance status was 0 (46%) or 1 (54%).
A statistically significant improvement in OS was demonstrated in patients randomized to YERVOY in combination with nivolumab compared with chemotherapy; however, an exploratory analysis of OS in patients with PD-L1 CPS <1 showed a HR of 1.0 (95% CI 0.52, 1.94), including that the improvement in the ITT population was primarily attributed to the results observed in the subgroup of patients with PD-L1 CPS ≥1. Efficacy results are shown in Table 36 and Figures 11 and 12.
| a Assessed by BICR. b Based on stratified Cox proportional hazard model. Hazard ratios are reported for each nivolumab- containing arm compared to chemotherapy within each analysis population. c Based on a stratified 2-sided log-rank test. S1 Significant p-value compared to stopping boundary of 0.014. NS: Not Statistically significant, NT: Not evaluated for statistical significance as per pre-specified hierarchical testing procedure. | ||||
YERVOY and Nivolumab (n=158) | Cisplatin and Fluorouracil (n=157) | YERVOY and Nivolumab (n=266) | Cisplatin and Fluorouracil (n=280) | |
TC PD-L1 expression ≥1% | PD-L1 CPS ≥1 | |||
Overall Survival | ||||
Deaths (%) | 106 (67) | 121 (77) | 179 (67) | 205 (73) |
Median (months) (95% CI) | 13.7 (11.2, 17.0) | 9.1 (7.7, 10) | 12.7 (10.9, 15.5) | 9.8 (8.8, 11.6) |
Hazard ratio (95% CI) b | 0.64 (0.49, 0.84) | 0.76 (0.62, 0.93) | ||
p-value c | 0.0010 S1 | |||
Progression-free Survival a | ||||
Disease progression or death (%) | 123 (78) | 100 (64) | 206 (77) | 184 (66) |
Median (months) (95% CI) | 4.0 (2.4, 4.9) | 4.4 (2.9, 5.8) | 2.8 (2.6, 4.2) | 5.6 (4.2, 5.9) |
Hazard ratio (95% CI) b | 1.02 (0.78, 1.34) | 1.2 (1.0, 1.5) | ||
p-value c | NS | |||
Overall Response Rate, n (%) a, NT | 56 (35.4) | 31 (19.7) | 74 (28) | 76 (27) |
(95% CI) | (28.0, 43.4) | (13.8, 26.8) | (22.5, 33.6) | (22.0, 32.8) |
Complete response (%) | 28 (17.7) | 8 (5.1) | 32 (12.0) | 18 (6.4) |
Partial response (%) | 28 (17.7) | 23 (14.6) | 42 (15.8) | 58 (20.7) |
Median (95% CI) | 11.8 (7.1, 27.4) | 5.7 (4.4, 8.7) | 11.8 (7.1, 23.6) | 6.9 (5.7, 8.2) |
Range | 1.4+, 34.5+ | 1.4+, 31.8+ | 1.4+, 34.5+ | 1.4+, 31.8+ |
Figure 11: Overall Survival - CHECKMATE-648 | |
(A) OS in TC PD-L1 ≥1% | (B) OS in PD-L1 CPS ≥1 |
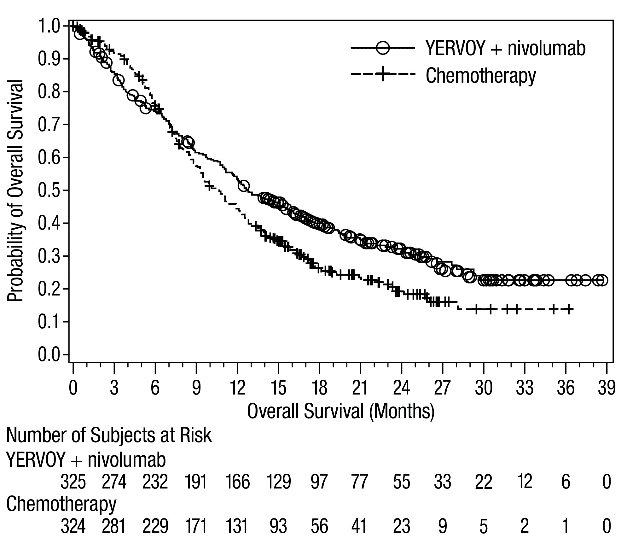 | 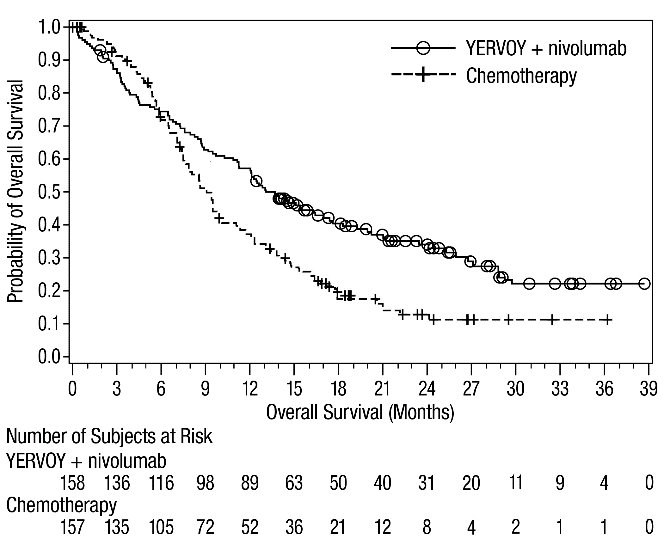 |
Figure 12: Progression-free Survival – CHECKMATE-648 | |
(A) PFS in TC PD-L1 ≥1% | (B) PFS in PD-L1 CPS ≥1 |
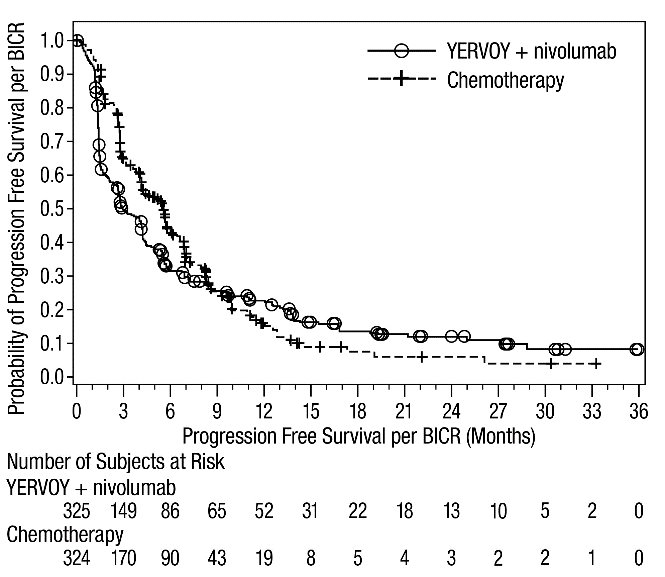 |  |
HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
YERVOY (ipilimumab) injection is a sterile, preservative-free, clear to slightly opalescent, colorless to pale-yellow solution. YERVOY is available as follows:
Carton Contents | NDC |
One 50 mg/10 mL (5 mg/mL), single-dose vial | NDC 0003-2327-11 |
One 200 mg/40 mL (5 mg/mL), single-dose vial | NDC 0003-2328-22 |
Store YERVOY under refrigeration at 2°C to 8°C (36°F to 46°F). Protect YERVOY from light by storing in the original carton until time of use. Do not freeze or shake.
Mechanism of Action
CTLA-4 is a negative regulator of T-cell activity. Ipilimumab is a monoclonal antibody that binds to CTLA-4 and blocks the interaction of CTLA-4 with its ligands, CD80/CD86. Blockade of CTLA-4 has been shown to augment T-cell activation and proliferation, including the activation and proliferation of tumor infiltrating T-effector cells. Inhibition of CTLA-4 signaling can also reduce T-regulatory cell function, which may contribute to a general increase in T-cell responsiveness, including the anti-tumor immune response.