Abiraterone Acetate
Abiraterone Acetate Prescribing Information
Dosage and Administration, Important Administration Instructions (2.3) 08/2021
Warnings and Precautions, Hypoglycemia (5.6) 10/2020
Abiraterone acetate tablets are indicated in combination with prednisone for the treatment of patients with
- Metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (CRPC)
- Metastatic high-risk castration-sensitive prostate cancer (CSPC)
Abiraterone acetate 250 mg tablets, USP are white to off-white, oval, biconvex uncoated tablets. Engraved "A250" on one side, "APO" on the other side.
None.
The following are discussed in more detail in other sections of the labeling:
- Hypokalemia, Fluid Retention, and Cardiovascular Adverse Reactions due to Mineralocorticoid Excess [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
- Adrenocortical Insufficiency [see.]
5.2 Adrenocortical InsufficiencyAdrenal insufficiency occurred in 0.3% of 2230 patients taking abiraterone acetate and in 0.1% of 1763 patients taking placebo in the combined data of the randomized, placebo-controlled clinical studies. Adrenocortical insufficiency was reported in patients receiving abiraterone acetate in combination with prednisone, following interruption of daily steroids and/or with concurrent infection or stress.Monitor patients for symptoms and signs of adrenocortical insufficiency, particularly if patients are withdrawn from prednisone, have prednisone dose reductions, or experience unusual stress. Symptoms and signs of adrenocortical insufficiency may be masked by adverse reactions associated with mineralocorticoid excess seen in patients treated with abiraterone acetate. If clinically indicated, perform appropriate tests to confirm the diagnosis of adrenocortical insufficiency. Increased dosage of corticosteroids may be indicated before, during and after stressful situations[see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]. - Hepatotoxicity [see.]
5.3 HepatotoxicityIn postmarketing experience, there have been abiraterone acetate-associated severe hepatic toxicity, including fulminant hepatitis, acute liver failure and deaths[see Adverse Reactions (6.2)].In the combined data of randomized clinical trials, grade 3 to 4 ALT or AST increases (at least 5 X ULN) were reported in 6% of 2230 patients who received abiraterone acetate, typically during the first 3 months after starting treatment. Patients whose baseline ALT or AST were elevated were more likely to experience liver test elevation than those beginning with normal values. Treatment discontinuation due to ALT and AST increases or abnormal hepatic function occurred in 1.1% of 2230 patients taking abiraterone acetate. In these clinical trials, no deaths clearly related to abiraterone acetate were reported due to hepatotoxicity events.Measure serum transaminases (ALT and AST) and bilirubin levels prior to starting treatment with abiraterone acetate, every two weeks for the first three months of treatment and monthly thereafter. In patients with baseline moderate hepatic impairment receiving a reduced abiraterone acetate dose of 250 mg, measure ALT, AST, and bilirubin prior to the start of treatment, every week for the first month, every two weeks for the following two months of treatment and monthly thereafter. Promptly measure serum total bilirubin, AST, and ALT if clinical symptoms or signs suggestive of hepatotoxicity develop. Elevations of AST, ALT, or bilirubin from the patient’s baseline should prompt more frequent monitoring. If at any time AST or ALT rise above five times the ULN, or the bilirubin rises above three times the ULN, interrupt abiraterone acetate treatment and closely monitor liver function.
Re-treatment with abiraterone acetate at a reduced dose level may take place only after return of liver function tests to the patient’s baseline or to AST and ALT less than or equal to 2.5 X ULN and total bilirubin less than or equal to 1.5 X ULN
[see Dosage and Administration ].Permanently discontinue abiraterone acetate tablets for patients who develop a concurrent elevation of ALT greater than 3 x ULN and total bilirubin greater than 2 x ULN in the absence of biliary obstruction or other causes responsible for the concurrent elevation
[see Dosage and Administration ].The safety of abiraterone acetate re-treatment of patients who develop AST or ALT greater than or equal to 20 X ULN and/or bilirubin greater than or equal to 10 X ULN is unknown.
- Increased Fractures and Mortality in Combination with Radium Ra 223 Dichloride [see Warnings and Precautions ()].
5.4 Increased Fractures and Mortality in Combination with Radium Ra 223 DichlorideAbiraterone acetate plus prednisone/prednisolone is not recommended for use in combination with radium Ra 223 dichloride outside of clinical trials.
The clinical efficacy and safety of concurrent initiation of abiraterone acetate plus prednisone/prednisolone and radium Ra 223 dichloride was assessed in a randomized, placebo-controlled multicenter study (ERA-223 trial) in 806 patients with asymptomatic or mildly symptomatic castration-resistant prostate cancer with bone metastases. The study was unblinded early based on an Independent Data Monitoring Committee recommendation.
At the primary analysis, increased incidences of fractures (28.6% vs 11.4%) and deaths (38.5% vs 35.5%) have been observed in patients who received abiraterone acetate plus prednisone/prednisolone in combination with radium Ra 223 dichloride compared to patients who received placebo in combination with abiraterone acetate plus prednisone/prednisolone.
Abiraterone acetate, USP the active ingredient of abiraterone acetate tablets, USP is the acetyl ester of abiraterone. Abiraterone is an inhibitor of CYP17 (17α-hydroxylase/C17,20-lyase). Each abiraterone acetate tablet, USP contains 250 mg of abiraterone acetate, USP. Abiraterone acetate, USP is designated chemically as (3β)-17-(3-pyridinyl) androsta-5,16-dien-3-yl acetate and its structure is:
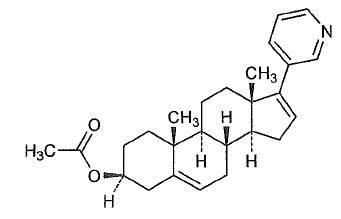
Abiraterone acetate, USP is a white to off-white, non-hygroscopic, crystalline powder. Its molecular formula is C26H33NO2 and it has a molecular weight of 391.55 g/mol. Abiraterone acetate, USP is a lipophilic compound with an octanol-water partition coefficient of 5.12 (Log P) and is practically insoluble in water. The pKa of the aromatic nitrogen is 5.19.
Abiraterone acetate tablets are available in 250 mg uncoated tablets with the following inactive ingredients: colloidal silicon dioxide, crospovidone, lactose monohydrate, magnesium stearate, and sodium lauryl sulfate.