Get your patient on Dupixent (Dupilumab)
Dupixent prior authorization resources
Most recent state uniform prior authorization forms
Brand Resources
Patient education
Administration guides
Patient education materials
Treatment initiation and patient onboarding
Patient support program
Dosing resources
Clinical information
Insurance resources
Prior authorization & coverage support
Reimbursement information
Financial assistance & copay programs
Specialty pharmacy coordination
Legal resources
Other resources
Dosage & administration
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
DUPIXENT is administered by subcutaneous injection. (2.1 )
Atopic Dermatitis
Dosage in Adults (2.3 ):
- Recommended dosage is an initial dose of 600 mg (two 300 mg injections), followed by 300 mg given every 2 weeks (Q2W).
Dosage in Pediatric Patients 6 Months to 5 Years of Age (2.3 ):
| Body Weight | Initial and Subsequent Dosage |
|---|---|
| 5 to less than 15 kg | 200 mg (one 200 mg injection) every 4 weeks (Q4W) |
| 15 to less than 30 kg | 300 mg (one 300 mg injection) every 4 weeks (Q4W) |
Dosage in Pediatric Patients 6 Years of Age and Older (2.3 ):
| Body Weight | Initial Loading Dose | Subsequent Dosage Q2W – every 2 weeks; Q4W – every 4 weeks |
|---|---|---|
| 15 to less than 30 kg | 600 mg (two 300 mg injections) | 300 mg Q4W |
| 30 to less than 60 kg | 400 mg (two 200 mg injections) | 200 mg Q2W |
| 60 kg or more | 600 mg (two 300 mg injections) | 300 mg Q2W |
Asthma
Dosage in Adult and Pediatric Patients 12 Years and Older (2.4 ):
| Initial Loading Dose | Subsequent Dosage |
|---|---|
| 400 mg (two 200 mg injections) | 200 mg every 2 weeks (Q2W) |
| Or | |
| 600 mg (two 300 mg injections) | 300 mg every 2 weeks (Q2W) |
| Dosage for patients with oral corticosteroid-dependent asthma or with co-morbid moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis or adults with co-morbid chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps | |
| 600 mg (two 300 mg injections) | 300 mg every 2 weeks (Q2W) |
Dosage in Pediatric Patients 6 to 11 Years of Age (2.4 ):
| Body Weight | Initial Dose and Subsequent Dosage |
|---|---|
| 15 to less than 30 kg | 300 mg every 4 weeks (Q4W) |
| ≥30 kg | 200 mg every 2 weeks (Q2W) |
For pediatric patients 6 to 11 years old with asthma and co-morbid moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis, follow the recommended dosage as per Table 2 which includes an initial loading dose. (2.3 )
Chronic Rhinosinusitis with Nasal Polyps (2.5 ):
- Recommended dosage for adult and pediatric patients 12 years of age and older is 300 mg given every 2 weeks (Q2W).
Eosinophilic Esophagitis (2.6 ):
| Body Weight | Recommended Dosage in Adult and Pediatric Patients 1 Year and Older, Weighing At Least 15 kg |
|---|---|
| 15 to less than 30 kg | 200 mg every 2 weeks (Q2W) |
| 30 to less than 40 kg | 300 mg every 2 weeks (Q2W) |
| 40 kg or more | 300 mg every week (QW) |
Prurigo Nodularis (2.7 ):
- Recommended dosage for adult patients is an initial dose of 600 mg (two 300 mg injections), followed by 300 mg given every 2 weeks (Q2W).
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (2.8 ):
- Recommended dosage for adult patients is 300 mg given every 2 weeks (Q2W).
Chronic Spontaneous Urticaria
Dosage in Adults (2.9 ):
- Recommended dosage is an initial dose of 600 mg (two 300 mg injections), followed by 300 mg given every 2 weeks (Q2W).
Dosage in Pediatric Patients 12 to 17 Years of Age (2.9 ):
| Body Weight | Initial Loading Dose | Subsequent Dosage |
|---|---|---|
| 30 to less than 60 kg | 400 mg (two 200 mg injections) | 200 mg Q2W |
| 60 kg or more | 600 mg (two 300 mg injections) | 300 mg Q2W |
Bullous Pemphigoid (2.10 ):
Recommended dosage for adult patients is an initial dose of 600 mg (two 300 mg injections), followed by 300 mg given every other week (Q2W). Use DUPIXENT in combination with a tapering course of oral corticosteroids.
Important Administration Instructions
DUPIXENT is administered by subcutaneous injection.
DUPIXENT is intended for use under the guidance of a healthcare provider. Provide proper training to patients and/or caregivers on the preparation and administration of DUPIXENT prior to use according to the "Instructions for Use".
Use of Pre-filled Pen or Pre-filled Syringe
The DUPIXENT pre-filled pen is for use in adult and pediatric patients aged 2 years and older.
The DUPIXENT pre-filled syringe is for use in adult and pediatric patients aged 6 months and older.
A caregiver or patient 12 years of age and older may inject DUPIXENT using the pre-filled syringe or pre-filled pen. In pediatric patients 12 years of age and older, administer DUPIXENT under the supervision of an adult. In pediatric patients 6 months to less than 12 years of age, administer DUPIXENT by a caregiver.
Administration Instructions
For patients with AD, asthma, PN, CSU, and BP taking an initial 600 mg dose, administer each of the two DUPIXENT 300 mg injections at different injection sites.
For patients with AD, asthma, and CSU taking an initial 400 mg dose, administer each of the two DUPIXENT 200 mg injections at different injection sites.
Administer subcutaneous injection into the thigh or abdomen, except for the 2 inches (5 cm) around the navel. The upper arm can also be used if a caregiver administers the injection.
Rotate the injection site with each injection. DO NOT inject DUPIXENT into skin that is tender, damaged, bruised, or scarred.
The DUPIXENT "Instructions for Use" contains more detailed instructions on the preparation and administration of DUPIXENT [see Instructions for Use] .
Vaccination Prior to Treatment
Consider completing all age-appropriate vaccinations as recommended by current immunization guidelines prior to initiating treatment with DUPIXENT [see Warnings and Precautions (5.10) ] .
Recommended Dosage for Atopic Dermatitis
Dosage in Adults
The recommended dosage of DUPIXENT for adult patients is an initial dose of 600 mg (two 300 mg injections), followed by 300 mg given every 2 weeks (Q2W).
Dosage in Pediatric Patients 6 Months to 5 Years of Age
The recommended dosage of DUPIXENT for pediatric patients 6 months to 5 years of age is specified in Table 1.
| Body Weight | Initial For pediatric patients 6 months to 5 years of age with AD, no initial loading dose is recommended. and Subsequent Dosage |
|---|---|
| 5 to less than 15 kg | 200 mg (one 200 mg injection) every 4 weeks (Q4W) |
| 15 to less than 30 kg | 300 mg (one 300 mg injection) every 4 weeks (Q4W) |
Dosage in Pediatric Patients 6 Years of Age and Older
The recommended dosage of DUPIXENT for pediatric patients 6 years of age and older is specified in Table 2.
| Body Weight | Initial Loading Dose | Subsequent Dosage |
|---|---|---|
| 15 to less than 30 kg | 600 mg (two 300 mg injections) | 300 mg every 4 weeks (Q4W) |
| 30 to less than 60 kg | 400 mg (two 200 mg injections) | 200 mg every 2 weeks (Q2W) |
| 60 kg or more | 600 mg (two 300 mg injections) | 300 mg every 2 weeks (Q2W) |
Concomitant Topical Therapies
DUPIXENT can be used with or without topical corticosteroids. Topical calcineurin inhibitors may be used, but should be reserved for problem areas only, such as the face, neck, intertriginous and genital areas.
Recommended Dosage for Asthma
Dosage in Adult and Pediatric Patients 12 Years and Older
The recommended dosage of DUPIXENT for adult and pediatric patients 12 years of age and older is specified in Table 3.
| Initial Loading Dose | Subsequent Dosage |
|---|---|
| 400 mg (two 200 mg injections) | 200 mg every 2 weeks (Q2W) |
| Or | |
| 600 mg (two 300 mg injections) | 300 mg every 2 weeks (Q2W) |
| Dosage for patients with oral corticosteroid-dependent asthma or with co-morbid moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis or adults with co-morbid chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps | |
| 600 mg (two 300 mg injections) | 300 mg every 2 weeks (Q2W) |
Dosage in Pediatric Patients 6 to 11 Years of Age
The recommended dosage of DUPIXENT for pediatric patients 6 to 11 years of age is specified in Table 4.
| Body Weight | Initial For pediatric patients 6 to 11 years of age with asthma, no initial loading dose is recommended. and Subsequent Dosage |
|---|---|
| 15 to less than 30 kg | 300 mg every 4 weeks (Q4W) |
| ≥30 kg | 200 mg every 2 weeks (Q2W) |
For pediatric patients 6 to 11 years of age with asthma and co-morbid moderate-to-severe AD, follow the recommended dosage as per Table 2 which includes an initial loading dose [see Dosage and Administration (2.3) ] .
Recommended Dosage for Chronic Rhinosinusitis with Nasal Polyps
The recommended dosage of DUPIXENT for adult and pediatric patients 12 years of age and older is 300 mg given every 2 weeks (Q2W).
Recommended Dosage for Eosinophilic Esophagitis
The recommended dosage of DUPIXENT for adult and pediatric patients 1 year of age and older, weighing at least 15 kg, is specified in Table 5.
| Body Weight | Recommended Dosage |
|---|---|
| 15 to less than 30 kg | 200 mg every 2 weeks (Q2W) |
| 30 to less than 40 kg | 300 mg every 2 weeks (Q2W) |
| 40 kg or more | 300 mg every week (QW) |
Recommended Dosage for Prurigo Nodularis
The recommended dosage of DUPIXENT for adult patients is an initial dose of 600 mg (two 300 mg injections) followed by 300 mg given every 2 weeks (Q2W).
Recommended Dosage for Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
The recommended dosage of DUPIXENT for adult patients is 300 mg given every 2 weeks (Q2W).
Recommended Dosage for Chronic Spontaneous Urticaria
Dosage in Adults
The recommended dosage of DUPIXENT for adult patients is an initial dose of 600 mg (two 300 mg injections), followed by 300 mg given every 2 weeks (Q2W).
Dosage in Pediatric Patients 12 to 17 Years of Age
The recommended dosage of DUPIXENT for pediatric patients 12 to 17 years of age is specified in Table 6.
| Body Weight | Initial Loading Dose | Subsequent Dosage |
|---|---|---|
| 30 to less than 60 kg | 400 mg (two 200 mg injections) | 200 mg every 2 weeks (Q2W) |
| 60 kg or more | 600 mg (two 300 mg injections) | 300 mg every 2 weeks (Q2W) |
Recommended Dosage for Bullous Pemphigoid
The recommended dosage of DUPIXENT for adult patients is an initial dose of 600 mg (two 300 mg injections) followed by 300 mg given every other week (Q2W).
Concomitant Oral Corticosteroids:
Use DUPIXENT in combination with a tapering course of oral corticosteroids. Once disease control has occurred, gradually taper corticosteroids after which continue DUPIXENT as monotherapy. In case of relapse, corticosteroids may be added if medically advisable.
Missed Doses
If a weekly dose is missed, administer the dose as soon as possible, and start a new weekly schedule from the date of the last administered dose.
If an every 2 week dose is missed, administer the injection within 7 days from the missed dose and then resume the patient's original schedule. If the missed dose is not administered within 7 days, administer the dose, starting a new schedule based on this date.
If an every 4 week dose is missed, administer the injection within 7 days from the missed dose and then resume the patient's original schedule. If the missed dose is not administered within 7 days, administer the dose, starting a new schedule based on this date.
Preparation for Use
Before injection, remove DUPIXENT from the refrigerator and allow DUPIXENT to reach room temperature (45 minutes for the 300 mg/2 mL pre-filled syringe or pre-filled pen, and 30 minutes for the 200 mg/1.14 mL pre-filled syringe or pre-filled pen) without removing the needle cap. After removal from the refrigerator, DUPIXENT must be used within 14 days or discarded.
Inspect DUPIXENT visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration. DUPIXENT is a clear to slightly opalescent, colorless to pale yellow solution. Do not use if the liquid contains visible particulate matter, is discolored or cloudy (other than clear to slightly opalescent, colorless to pale yellow). DUPIXENT does not contain preservatives; therefore, discard any unused product remaining in the pre-filled syringe or pre-filled pen.

By using PrescriberAI, you agree to the AI Terms of Use.
Dupixent prescribing information
| Indications and Usage, Chronic Rhinosinusitis with Nasal Polyps (1.3 ) | 09/2024 |
| Indications and Usage, Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (1.6 ) | 09/2024 |
| Indications and Usage, Chronic Spontaneous Urticaria (1.7 ) | 04/2025 |
| Indications and Usage, Bullous Pemphigoid (1.8 ) | 06/2025 |
| Dosage and Administration, Chronic Rhinosinusitis with Nasal Polyps (2.5 ) | 09/2024 |
| Dosage and Administration, Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (2.8 ) | 09/2024 |
| Dosage and Administration, Chronic Spontaneous Urticaria (2.9 ) | 04/2025 |
| Dosage and Administration, Bullous Pemphigoid (2.10 ) | 06/2025 |
| Dosage and Administration, Missed Doses (2.11 ) | 06/2025 |
| Warnings and Precautions, Hypersensitivity (5.1 ) | 06/2025 |
| Warnings and Precautions, Conjunctivitis and Keratitis (5.2 ) | 06/2025 |
| Warnings and Precautions (5.2 , 5.3 , 5.7 , 5.8 ) | 04/2025 |
| Warnings and Precautions (5.2 , 5.4 ) | 09/2024 |
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
DUPIXENT is an interleukin-4 receptor alpha antagonist indicated:
Atopic Dermatitis
for the treatment of adult and pediatric patients aged 6 months and older with moderate-to-severe AD whose disease is not adequately controlled with topical prescription therapies or when those therapies are not advisable. DUPIXENT can be used with or without topical corticosteroids. (1.1 )
Asthma
as an add-on maintenance treatment of adult and pediatric patients aged 6 years and older with moderate-to-severe asthma characterized by an eosinophilic phenotype or with oral corticosteroid dependent asthma. (1.2 ) Limitations of Use: Not for the relief of acute bronchospasm or status asthmaticus. (1.2 )
Chronic Rhinosinusitis with Nasal Polyps
as an add-on maintenance treatment in adult and pediatric patients aged 12 years and older with inadequately controlled chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps (CRSwNP). (1.3 )
Eosinophilic Esophagitis
for the treatment of adult and pediatric patients aged 1 year and older, weighing at least 15 kg, with eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE). (1.4 )
Prurigo Nodularis
for the treatment of adult patients with prurigo nodularis (PN). (1.5 )
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
as an add-on maintenance treatment of adult patients with inadequately controlled chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and an eosinophilic phenotype. (1.6 ) Limitations of Use: Not for the relief of acute bronchospasm. (1.6 )
Chronic Spontaneous Urticaria
for the treatment of adult and pediatric patients aged 12 years and older with chronic spontaneous urticaria (CSU) who remain symptomatic despite H1 antihistamine treatment. (1.7 )
Limitations of Use: Not indicated for other forms of urticaria. (1.7 )
Bullous Pemphigoid
for the treatment of adult patients with bullous pemphigoid (BP). (1.8 )
Atopic Dermatitis
DUPIXENT is indicated for the treatment of adult and pediatric patients aged 6 months and older with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis (AD) whose disease is not adequately controlled with topical prescription therapies or when those therapies are not advisable. DUPIXENT can be used with or without topical corticosteroids.
Asthma
DUPIXENT is indicated as an add-on maintenance treatment of adult and pediatric patients aged 6 years and older with moderate-to-severe asthma characterized by an eosinophilic phenotype or with oral corticosteroid dependent asthma.
Limitations of Use
DUPIXENT is not indicated for the relief of acute bronchospasm or status asthmaticus.
Chronic Rhinosinusitis with Nasal Polyps
DUPIXENT is indicated as an add-on maintenance treatment in adult and pediatric patients aged 12 years and older with inadequately controlled chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps (CRSwNP).
Eosinophilic Esophagitis
DUPIXENT is indicated for the treatment of adult and pediatric patients aged 1 year and older, weighing at least 15 kg, with eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE).
Prurigo Nodularis
DUPIXENT is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with prurigo nodularis (PN).
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
DUPIXENT is indicated as an add-on maintenance treatment of adult patients with inadequately controlled chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and an eosinophilic phenotype.
Limitations of Use
DUPIXENT is not indicated for the relief of acute bronchospasm.
Chronic Spontaneous Urticaria
DUPIXENT is indicated for the treatment of adult and pediatric patients aged 12 years and older with chronic spontaneous urticaria (CSU) who remain symptomatic despite H1 antihistamine treatment.
Limitations of Use:
DUPIXENT is not indicated for treatment of other forms of urticaria.
Bullous Pemphigoid
DUPIXENT is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with bullous pemphigoid (BP).
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
DUPIXENT is administered by subcutaneous injection. (2.1 )
Atopic Dermatitis Dosage in Adults (2.3 ):
- Recommended dosage is an initial dose of 600 mg (two 300 mg injections), followed by 300 mg given every 2 weeks (Q2W).
Dosage in Pediatric Patients 6 Months to 5 Years of Age (2.3 ):
| Body Weight | Initial and Subsequent Dosage |
|---|---|
| 5 to less than 15 kg | 200 mg (one 200 mg injection) every 4 weeks (Q4W) |
| 15 to less than 30 kg | 300 mg (one 300 mg injection) every 4 weeks (Q4W) |
Dosage in Pediatric Patients 6 Years of Age and Older (2.3 ):
| Body Weight | Initial Loading Dose | Subsequent Dosage Q2W – every 2 weeks; Q4W – every 4 weeks |
|---|---|---|
| 15 to less than 30 kg | 600 mg (two 300 mg injections) | 300 mg Q4W |
| 30 to less than 60 kg | 400 mg (two 200 mg injections) | 200 mg Q2W |
| 60 kg or more | 600 mg (two 300 mg injections) | 300 mg Q2W |
Asthma Dosage in Adult and Pediatric Patients 12 Years and Older (2.4 ):
| Initial Loading Dose | Subsequent Dosage |
|---|---|
| 400 mg (two 200 mg injections) | 200 mg every 2 weeks (Q2W) |
| Or | |
| 600 mg (two 300 mg injections) | 300 mg every 2 weeks (Q2W) |
| Dosage for patients with oral corticosteroid-dependent asthma or with co-morbid moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis or adults with co-morbid chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps | |
| 600 mg (two 300 mg injections) | 300 mg every 2 weeks (Q2W) |
Dosage in Pediatric Patients 6 to 11 Years of Age (2.4 ):
| Body Weight | Initial Dose and Subsequent Dosage |
|---|---|
| 15 to less than 30 kg | 300 mg every 4 weeks (Q4W) |
| ≥30 kg | 200 mg every 2 weeks (Q2W) |
For pediatric patients 6 to 11 years old with asthma and co-morbid moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis, follow the recommended dosage as per Table 2 which includes an initial loading dose. (2.3 )
Chronic Rhinosinusitis with Nasal Polyps (2.5 ):
- Recommended dosage for adult and pediatric patients 12 years of age and older is 300 mg given every 2 weeks (Q2W).
Eosinophilic Esophagitis (2.6 ):
| Body Weight | Recommended Dosage in Adult and Pediatric Patients 1 Year and Older, Weighing At Least 15 kg |
|---|---|
| 15 to less than 30 kg | 200 mg every 2 weeks (Q2W) |
| 30 to less than 40 kg | 300 mg every 2 weeks (Q2W) |
| 40 kg or more | 300 mg every week (QW) |
Prurigo Nodularis (2.7 ):
- Recommended dosage for adult patients is an initial dose of 600 mg (two 300 mg injections), followed by 300 mg given every 2 weeks (Q2W).
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (2.8 ):
- Recommended dosage for adult patients is 300 mg given every 2 weeks (Q2W).
Chronic Spontaneous Urticaria Dosage in Adults (2.9 ):
- Recommended dosage is an initial dose of 600 mg (two 300 mg injections), followed by 300 mg given every 2 weeks (Q2W).
Dosage in Pediatric Patients 12 to 17 Years of Age (2.9 ):
| Body Weight | Initial Loading Dose | Subsequent Dosage |
|---|---|---|
| 30 to less than 60 kg | 400 mg (two 200 mg injections) | 200 mg Q2W |
| 60 kg or more | 600 mg (two 300 mg injections) | 300 mg Q2W |
Bullous Pemphigoid (2.10 ):
Recommended dosage for adult patients is an initial dose of 600 mg (two 300 mg injections), followed by 300 mg given every other week (Q2W). Use DUPIXENT in combination with a tapering course of oral corticosteroids.
Important Administration Instructions
DUPIXENT is administered by subcutaneous injection.
DUPIXENT is intended for use under the guidance of a healthcare provider. Provide proper training to patients and/or caregivers on the preparation and administration of DUPIXENT prior to use according to the "Instructions for Use".
Use of Pre-filled Pen or Pre-filled Syringe
The DUPIXENT pre-filled pen is for use in adult and pediatric patients aged 2 years and older.
The DUPIXENT pre-filled syringe is for use in adult and pediatric patients aged 6 months and older.
A caregiver or patient 12 years of age and older may inject DUPIXENT using the pre-filled syringe or pre-filled pen. In pediatric patients 12 years of age and older, administer DUPIXENT under the supervision of an adult. In pediatric patients 6 months to less than 12 years of age, administer DUPIXENT by a caregiver.
Administration Instructions
For patients with AD, asthma, PN, CSU, and BP taking an initial 600 mg dose, administer each of the two DUPIXENT 300 mg injections at different injection sites.
For patients with AD, asthma, and CSU taking an initial 400 mg dose, administer each of the two DUPIXENT 200 mg injections at different injection sites.
Administer subcutaneous injection into the thigh or abdomen, except for the 2 inches (5 cm) around the navel. The upper arm can also be used if a caregiver administers the injection.
Rotate the injection site with each injection. DO NOT inject DUPIXENT into skin that is tender, damaged, bruised, or scarred.
The DUPIXENT "Instructions for Use" contains more detailed instructions on the preparation and administration of DUPIXENT [see Instructions for Use] .
Vaccination Prior to Treatment
Consider completing all age-appropriate vaccinations as recommended by current immunization guidelines prior to initiating treatment with DUPIXENT [see Warnings and Precautions (5.10) ] .
Recommended Dosage for Atopic Dermatitis
Dosage in Adults
The recommended dosage of DUPIXENT for adult patients is an initial dose of 600 mg (two 300 mg injections), followed by 300 mg given every 2 weeks (Q2W).
Dosage in Pediatric Patients 6 Months to 5 Years of Age
The recommended dosage of DUPIXENT for pediatric patients 6 months to 5 years of age is specified in Table 1.
| Body Weight | Initial For pediatric patients 6 months to 5 years of age with AD, no initial loading dose is recommended. and Subsequent Dosage |
|---|---|
| 5 to less than 15 kg | 200 mg (one 200 mg injection) every 4 weeks (Q4W) |
| 15 to less than 30 kg | 300 mg (one 300 mg injection) every 4 weeks (Q4W) |
Dosage in Pediatric Patients 6 Years of Age and Older
The recommended dosage of DUPIXENT for pediatric patients 6 years of age and older is specified in Table 2.
| Body Weight | Initial Loading Dose | Subsequent Dosage |
|---|---|---|
| 15 to less than 30 kg | 600 mg (two 300 mg injections) | 300 mg every 4 weeks (Q4W) |
| 30 to less than 60 kg | 400 mg (two 200 mg injections) | 200 mg every 2 weeks (Q2W) |
| 60 kg or more | 600 mg (two 300 mg injections) | 300 mg every 2 weeks (Q2W) |
Concomitant Topical Therapies
DUPIXENT can be used with or without topical corticosteroids. Topical calcineurin inhibitors may be used, but should be reserved for problem areas only, such as the face, neck, intertriginous and genital areas.
Recommended Dosage for Asthma
Dosage in Adult and Pediatric Patients 12 Years and Older
The recommended dosage of DUPIXENT for adult and pediatric patients 12 years of age and older is specified in Table 3.
| Initial Loading Dose | Subsequent Dosage |
|---|---|
| 400 mg (two 200 mg injections) | 200 mg every 2 weeks (Q2W) |
| Or | |
| 600 mg (two 300 mg injections) | 300 mg every 2 weeks (Q2W) |
| Dosage for patients with oral corticosteroid-dependent asthma or with co-morbid moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis or adults with co-morbid chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps | |
| 600 mg (two 300 mg injections) | 300 mg every 2 weeks (Q2W) |
Dosage in Pediatric Patients 6 to 11 Years of Age
The recommended dosage of DUPIXENT for pediatric patients 6 to 11 years of age is specified in Table 4.
| Body Weight | Initial For pediatric patients 6 to 11 years of age with asthma, no initial loading dose is recommended. and Subsequent Dosage |
|---|---|
| 15 to less than 30 kg | 300 mg every 4 weeks (Q4W) |
| ≥30 kg | 200 mg every 2 weeks (Q2W) |
For pediatric patients 6 to 11 years of age with asthma and co-morbid moderate-to-severe AD, follow the recommended dosage as per Table 2 which includes an initial loading dose [see Dosage and Administration (2.3) ] .
Recommended Dosage for Chronic Rhinosinusitis with Nasal Polyps
The recommended dosage of DUPIXENT for adult and pediatric patients 12 years of age and older is 300 mg given every 2 weeks (Q2W).
Recommended Dosage for Eosinophilic Esophagitis
The recommended dosage of DUPIXENT for adult and pediatric patients 1 year of age and older, weighing at least 15 kg, is specified in Table 5.
| Body Weight | Recommended Dosage |
|---|---|
| 15 to less than 30 kg | 200 mg every 2 weeks (Q2W) |
| 30 to less than 40 kg | 300 mg every 2 weeks (Q2W) |
| 40 kg or more | 300 mg every week (QW) |
Recommended Dosage for Prurigo Nodularis
The recommended dosage of DUPIXENT for adult patients is an initial dose of 600 mg (two 300 mg injections) followed by 300 mg given every 2 weeks (Q2W).
Recommended Dosage for Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
The recommended dosage of DUPIXENT for adult patients is 300 mg given every 2 weeks (Q2W).
Recommended Dosage for Chronic Spontaneous Urticaria
Dosage in Adults
The recommended dosage of DUPIXENT for adult patients is an initial dose of 600 mg (two 300 mg injections), followed by 300 mg given every 2 weeks (Q2W).
Dosage in Pediatric Patients 12 to 17 Years of Age
The recommended dosage of DUPIXENT for pediatric patients 12 to 17 years of age is specified in Table 6.
| Body Weight | Initial Loading Dose | Subsequent Dosage |
|---|---|---|
| 30 to less than 60 kg | 400 mg (two 200 mg injections) | 200 mg every 2 weeks (Q2W) |
| 60 kg or more | 600 mg (two 300 mg injections) | 300 mg every 2 weeks (Q2W) |
Recommended Dosage for Bullous Pemphigoid
The recommended dosage of DUPIXENT for adult patients is an initial dose of 600 mg (two 300 mg injections) followed by 300 mg given every other week (Q2W).
Concomitant Oral Corticosteroids:
Use DUPIXENT in combination with a tapering course of oral corticosteroids. Once disease control has occurred, gradually taper corticosteroids after which continue DUPIXENT as monotherapy. In case of relapse, corticosteroids may be added if medically advisable.
Missed Doses
If a weekly dose is missed, administer the dose as soon as possible, and start a new weekly schedule from the date of the last administered dose.
If an every 2 week dose is missed, administer the injection within 7 days from the missed dose and then resume the patient's original schedule. If the missed dose is not administered within 7 days, administer the dose, starting a new schedule based on this date.
If an every 4 week dose is missed, administer the injection within 7 days from the missed dose and then resume the patient's original schedule. If the missed dose is not administered within 7 days, administer the dose, starting a new schedule based on this date.
Preparation for Use
Before injection, remove DUPIXENT from the refrigerator and allow DUPIXENT to reach room temperature (45 minutes for the 300 mg/2 mL pre-filled syringe or pre-filled pen, and 30 minutes for the 200 mg/1.14 mL pre-filled syringe or pre-filled pen) without removing the needle cap. After removal from the refrigerator, DUPIXENT must be used within 14 days or discarded.
Inspect DUPIXENT visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration. DUPIXENT is a clear to slightly opalescent, colorless to pale yellow solution. Do not use if the liquid contains visible particulate matter, is discolored or cloudy (other than clear to slightly opalescent, colorless to pale yellow). DUPIXENT does not contain preservatives; therefore, discard any unused product remaining in the pre-filled syringe or pre-filled pen.
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
DUPIXENT is a clear to slightly opalescent, colorless to pale yellow solution in a:
Single-dose pre-filled syringe with needle shield as:
- Injection: 300 mg/2 mL (150 mg/mL)
- Injection: 200 mg/1.14 mL (175 mg/mL)
Single-dose pre-filled pen as:
- Injection: 300 mg/2 mL (150 mg/mL)
- Injection: 200 mg/1.14 mL (175 mg/mL)
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
Pregnancy
Pregnancy Exposure Registry
There is a pregnancy exposure registry that monitors pregnancy outcomes in women exposed to DUPIXENT during pregnancy.
Healthcare providers and patients may call 1-877-311-8972 or go to https://mothertobaby.org/ongoing-study/dupixent/ to enroll in or to obtain information about the registry.
Risk Summary
Available data from case reports and case series with DUPIXENT use in pregnant women have not identified a drug-associated risk of major birth defects, miscarriage, or adverse maternal or fetal outcomes. Human IgG antibodies are known to cross the placental barrier; therefore, DUPIXENT may be transmitted from the mother to the developing fetus. There are adverse effects on maternal and fetal outcomes associated with asthma in pregnancy ( see Clinical Considerations ). In an enhanced pre- and post-natal developmental study, no adverse developmental effects were observed in offspring born to pregnant monkeys after subcutaneous administration of a homologous antibody against interleukin-4-receptor alpha (IL-4Rα) during organogenesis through parturition at doses up to 10-times the maximum recommended human dose (MRHD) ( see Data ) .
The background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated populations are unknown. All pregnancies have a background risk of birth defect, loss or other adverse outcomes. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2% to 4% and 15% to 20%, respectively.
Clinical Considerations
Disease-Associated Maternal and/or Embryo-fetal Risk
In women with poorly or moderately controlled asthma, evidence demonstrates that there is an increased risk of preeclampsia in the mother and prematurity, low birth weight, and small for gestational age in the neonate. The level of asthma control should be closely monitored in pregnant women and treatment adjusted as necessary to maintain optimal control.
Fetal/Neonatal Adverse Reactions
Transport of endogenous IgG antibodies across the placenta increases as pregnancy progresses, and peaks during the third trimester. Therefore, DUPIXENT may be present in infants exposed in utero . The potential clinical impact of dupilumab exposure in infants exposed in utero should be considered.
Data
Animal Data
In an enhanced pre- and post-natal development toxicity study, pregnant cynomolgus monkeys were administered weekly subcutaneous doses of homologous antibody against IL-4Rα up to 10 times the MRHD (on a mg/kg basis of 100 mg/kg/week) from the beginning of organogenesis to parturition. No treatment-related adverse effects on embryo-fetal toxicity or malformations, or on morphological, functional, or immunological development were observed in the infants from birth through 6 months of age.
Lactation
Risk Summary
There are no data on the presence of dupilumab in human milk, the effects on the breastfed infant, or the effects on milk production. Maternal IgG is known to be present in human milk. The effects of local gastrointestinal exposure and limited systemic exposure to dupilumab on the breastfed infant are unknown. The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother's clinical need for DUPIXENT and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed child from DUPIXENT or from the underlying maternal condition.
Pediatric Use
Atopic Dermatitis
The safety and effectiveness of DUPIXENT have been established in pediatric patients 6 months of age and older with moderate-to-severe AD, whose disease is not adequately controlled with topical prescription therapies or when those therapies are not advisable.
Use of DUPIXENT in this age group is supported by data from the following clinical trials:
- AD-1526 which included 251 pediatric subjects 12 years of age and older with moderate-to-severe AD. Of the 251 subjects, 82 were treated with DUPIXENT 200 mg Q2W (<60 kg) or 300 mg Q2W (≥60 kg) and 85 were treated with matching placebo
- AD-1652 which included 367 pediatric subjects 6 to 11 years of age with severe AD. Of the 367 subjects, 120 were treated with DUPIXENT 300 mg Q4W + TCS (15 to <30 kg) or 200 mg Q2W + TCS (≥30 kg) and 123 were treated with matching placebo + TCS
- AD-1539 which included 162 pediatric subjects 6 months to 5 years of age with moderate-to-severe AD. Of the 162 subjects, 83 were treated with DUPIXENT 200 mg Q4W + TCS (5 to <15 kg) or 300 mg Q4W + TCS (15 to <30 kg) and 79 subjects were assigned to be treated with matching placebo + TCS
- AD-1434, an open-label extension study that enrolled 275 pediatric subjects 12 years of age and older treated with DUPIXENT ± TCS, 368 pediatric subjects 6 to 11 years of age treated with DUPIXENT ± TCS, and 180 pediatric subjects 6 months to 5 years of age treated with DUPIXENT ± TCS
- Liberty-AD-HAFT which included 27 pediatric subjects 12 years of age and older with atopic dermatitis with moderate-to-severe hand and/or foot involvement treated with DUPIXENT (N=14) or matching placebo (N=13)
The safety and effectiveness were generally consistent between pediatric and adult patients. In addition, hand-foot-and-mouth disease was reported in 9 (5%) pediatric subjects and skin papilloma was reported in 4 (2%) pediatric subjects 6 months to 5 years of age treated with DUPIXENT ± TCS in AD-1434. These cases did not lead to study drug discontinuation [see Adverse Reactions (6.1) and Clinical Studies (14.1) ] .
Safety and effectiveness of DUPIXENT have not been established in pediatric patients younger than 6 months of age with AD.
Asthma
The safety and effectiveness of DUPIXENT for an add-on maintenance treatment in patients with moderate-to-severe asthma characterized by an eosinophilic phenotype or with oral corticosteroid dependent asthma have been established in pediatric patients 6 years of age and older. Use of DUPIXENT for this indication is supported by evidence from adequate and well-controlled studies in adult and pediatric patients 6 years and older [see Clinical Studies (14.2)] .
Pediatric Subjects 12 to 17 Years of Age :
A total of 107 pediatric subjects 12 to 17 years of age with moderate-to-severe asthma were enrolled in QUEST and received either 200 mg (N=21) or 300 mg (N=18) DUPIXENT (or matching placebo either 200 mg [N=34] or 300 mg [N=34]) Q2W. Asthma exacerbations and lung function were assessed in both pediatric subjects 12 to 17 years of age and adults. For both the 200 mg and 300 mg Q2W doses, improvements in FEV 1 (LS mean change from baseline at Week 12) were observed (0.36 L and 0.27 L, respectively). For the 200 mg Q2W dose, subjects had a reduction in the rate of severe exacerbations that was consistent with adults. Dupilumab exposure was higher in pediatric subjects 12 to 17 years of age than that in adults at the respective dose level which was mainly accounted for by difference in body weight [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ] .
The adverse event profile in pediatric subjects 12 to 17 years of age was generally similar to the adults [see Adverse Reactions (6.1) ] .
Pediatric Subjects 6 to 11 Years of Age :
A total of 408 pediatric subjects 6 to 11 years of age with moderate-to-severe asthma were enrolled in VOYAGE, which evaluated doses of 100 mg Q2W or 200 mg Q2W. Improvement in asthma exacerbations and lung function were demonstrated [see Clinical Studies (14.2) ] . The effectiveness of DUPIXENT 300 mg Q4W in subjects 6 to 11 years of age with body weight 15 to <30 kg was extrapolated from efficacy of 100 mg Q2W in VOYAGE with support from population pharmacokinetic analyses showing higher drug exposure levels with 300 mg Q4W [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ] . Subjects who completed the treatment period of the VOYAGE study could participate in the open-label extension study (LTS14424). Eighteen subjects (≥15 to <30 kg) out of 365 subjects were exposed to 300 mg Q4W in this study, and the safety profile in these eighteen subjects was consistent with that seen in VOYAGE. Additional safety for DUPIXENT 300 mg Q4W is based upon available safety information from the pediatric AD indication [see Adverse Reactions (6.1) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ] .
Safety and effectiveness of DUPIXENT have not been established in pediatric patients younger than 6 years of age with asthma.
CRSwNP
The safety and effectiveness of DUPIXENT for add-on maintenance treatment in patients with inadequately controlled chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps (CRSwNP) have been established in pediatric patients aged 12 years and older. Use of DUPIXENT for this indication is supported by evidence from adequate and well-controlled studies of DUPIXENT as add-on maintenance treatment in adults with inadequately controlled CRSwNP (SINUS-24 and SINUS-52) with the following additional data:
- Pharmacokinetic (PK) data from adult and pediatric patients aged 12 years and older with moderate-to-severe asthma and adult patients with inadequately controlled CRSwNP
- Safety data in pediatric patients aged 12 years and older with moderate-to-severe asthma [see Adverse Reactions (6.1) , Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) , and Clinical Studies (14.3) ]
Safety and effectiveness of DUPIXENT have not been established in pediatric patients younger than 12 years of age with CRSwNP.
EoE
The safety and effectiveness of DUPIXENT for the treatment of EoE have been established in pediatric subjects 1 year of age and older, weighing at least 15 kg. Use of DUPIXENT in this population is supported by an adequate well-controlled study in adults and 72 pediatric subjects 12 to 17 years of age (Study EoE-1), a clinical study in 61 pediatric subjects 1 to 11 years of age (Study EoE-2), and pharmacokinetic data in adult and pediatric subjects 1 to 17 years of age. The safety of DUPIXENT in pediatric subjects 1 to 17 years of age was similar to adults [see Adverse Reactions (6.1) , Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) , and Clinical Studies (14.4) ] .
Safety and effectiveness of DUPIXENT have not been established in pediatric patients younger than 1 year of age, or weighing less than 15 kg, with EoE.
Prurigo Nodularis
Safety and effectiveness of DUPIXENT have not been established in pediatric patients with PN.
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
The safety and effectiveness of DUPIXENT have not been established in pediatric patients with COPD. COPD is largely a disease of adult patients.
Chronic Spontaneous Urticaria
The safety and effectiveness of DUPIXENT for the treatment of CSU in patients who remain symptomatic despite H1 antihistamine treatment have been established in pediatric patients 12 years of age and older. The use of DUPIXENT in this indication is supported by evidence from two adequate and well-controlled studies in adults with additional pharmacokinetic data in 6 pediatric patients 12 years of age and older, and safety data in pediatric patients in other indications [see Dosage and Administration (2.9) , Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) , and Clinical Studies (14.7) ] .
Safety and effectiveness of DUPIXENT have not been established in pediatric patients younger than 12 years of age, and/or weighing less than 30 kg, with CSU.
Bullous Pemphigoid
The safety and effectiveness of DUPIXENT have not been established in pediatric patients with BP. BP is largely a disease of adult patients.
Geriatric Use
Of the 1539 subjects with AD exposed to DUPIXENT in a dose-ranging study and placebo-controlled trials, 70 subjects were 65 years or older. Clinical trials of DUPIXENT in AD did not include sufficient numbers of subjects aged 65 years and older to determine whether they respond differently from younger subjects.
Of the 1977 subjects with asthma exposed to DUPIXENT, a total of 240 subjects were 65 years or older. Efficacy and safety in this age group was similar to the overall study population.
Of the 440 subjects with CRSwNP exposed to DUPIXENT, a total of 79 subjects were 65 years or older. Efficacy and safety in this age group were similar to the overall study population.
Clinical studies of DUPIXENT in EoE did not include sufficient numbers of subjects aged 65 years and older to determine whether they respond differently from younger adult subjects.
Of the 152 subjects with PN exposed to DUPIXENT, a total of 37 were 65 years or older including 8 subjects 75 years or older. Clinical trials did not include a sufficient number of subjects 65 years of age and older to determine whether they respond differently from younger adult subjects.
Of the 1874 subjects with COPD randomized in clinical trials of DUPIXENT, a total of 1072 were 65 years or older, while 244 subjects were 75 years or older. No overall differences in safety or effectiveness of DUPIXENT have been observed between subjects 65 years of age and older and younger adult subjects.
Of the 198 subjects with CSU exposed to DUPIXENT, a total of 30 subjects were 65 years or older, including 7 subjects 75 years or older. Efficacy and safety in subjects 65 years or older were similar to the overall study population.
Of the 53 subjects with BP exposed to DUPIXENT, a total of 40 were 65 years or older, including 22 subjects 75 years or older. Ten percent of subjects aged 65 years and older treated with DUPIXENT had an adverse reaction of vision blurred compared to zero in younger adult subjects.
CONTRAINDICATIONS
DUPIXENT is contraindicated in patients who have known hypersensitivity to dupilumab or any excipients of DUPIXENT [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) ] .
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- Hypersensitivity: Hypersensitivity reactions including anaphylaxis, acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis (AGEP), serum sickness, angioedema, urticaria, rash, erythema nodosum, and erythema multiforme have occurred. Discontinue DUPIXENT in the event of a hypersensitivity reaction. (5.1 )
- Conjunctivitis and Keratitis: Advise patients to report new onset or worsening eye symptoms to their healthcare provider. Consider ophthalmological examination, as appropriate. (5.2 )
- Eosinophilic Conditions: Be alert to vasculitic rash, worsening pulmonary symptoms, cardiac complications, kidney injury and/or neuropathy, especially upon reduction of oral corticosteroids. (5.3 )
- Reduction of Corticosteroid Dosage: Do not discontinue systemic, topical, or inhaled corticosteroids abruptly upon initiation of DUPIXENT. Decrease steroids gradually, if appropriate. (5.5 )
- Psoriasis: Advise patients to report new-onset psoriasis symptoms to their healthcare provider. If symptoms persist or worsen, consider dermatologic evaluation and/or discontinuation of DUPIXENT. (5.7 )
- Arthralgia and Psoriatic Arthritis: Advise patients to report new onset joint symptoms to their healthcare provider. If symptoms persist or worsen, consider rheumatological evaluation and/or discontinuation of DUPIXENT. (5.8 )
- Parasitic (Helminth) Infections: Treat pre-existing helminth infections before initiating DUPIXENT. If patients become infected while receiving DUPIXENT and do not respond to anti-helminth treatment, discontinue DUPIXENT until the infection resolves. (5.9)
- Vaccinations: Avoid use of live vaccines. (5.10 )
Hypersensitivity
Hypersensitivity reactions, including anaphylaxis, acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis (AGEP), serum sickness or serum sickness-like reactions, angioedema, generalized urticaria, rash, erythema nodosum and erythema multiforme have been reported. A case of AGEP was reported in an adult subject who participated in the bullous pemphigoid development program. If a clinically significant hypersensitivity reaction occurs, institute appropriate therapy and discontinue DUPIXENT [see Adverse Reactions (6.1 , 6.2) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.6) ] .
Conjunctivitis and Keratitis
Conjunctivitis and keratitis adverse reactions have been reported in clinical trials [see Adverse Reactions (6.1) ] .
Conjunctivitis and keratitis occurred more frequently in AD subjects who received DUPIXENT compared to those who received placebo. Conjunctivitis was the most frequently reported eye disorder. Most subjects with conjunctivitis or keratitis recovered or were recovering during the treatment period.
Among subjects with asthma, the frequencies of conjunctivitis and keratitis were similar between DUPIXENT and placebo.
In adult subjects with CRSwNP, the frequency of conjunctivitis was 2% in the DUPIXENT group compared to 1% in the placebo group in the 24-week safety pool; these subjects recovered. There were no cases of keratitis reported in the CRSwNP development program.
Among subjects with EoE, there were no reports of conjunctivitis and keratitis in the DUPIXENT group in placebo-controlled trials.
In subjects with PN, the frequency of conjunctivitis was 4% in the DUPIXENT group compared to 1% in the placebo group; these subjects recovered or were recovering during the treatment period. There were no cases of keratitis reported in the PN development program.
Among subjects with COPD, the frequency of conjunctivitis and keratitis was 1.4% and 0.1% in the DUPIXENT group and 1% and 0% in the placebo group, respectively.
In subjects with CSU, the frequency of conjunctivitis was similar between DUPIXENT and placebo. There were no cases of keratitis reported in the CSU development program.
Among subjects with BP, the frequency of conjunctivitis and keratitis was 7.5% and 3.8% in the DUPIXENT group and 0% and 0% in the placebo group, respectively.
Conjunctivitis and keratitis adverse events have also been reported with DUPIXENT in postmarketing settings, predominantly in AD patients. Some patients reported visual disturbances (e.g., blurred vision) associated with conjunctivitis or keratitis.
Advise patients or their caregivers to report new onset or worsening eye symptoms to their healthcare provider. Consider ophthalmological examination for patients who develop conjunctivitis that does not resolve following standard treatment or signs and symptoms suggestive of keratitis, as appropriate.
Eosinophilic Conditions
Patients being treated for asthma may present with clinical features of eosinophilic pneumonia or eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis (EGPA). These events may be associated with the reduction of oral corticosteroid therapy. Healthcare providers should be alert to vasculitic rash, worsening pulmonary symptoms, cardiac complications, kidney injury, and/or neuropathy presenting in their patients with eosinophilia. Cases of eosinophilic pneumonia were reported in adults who participated in the asthma development program. Cases of EGPA have been reported with DUPIXENT in adults who participated in the asthma development program as well as in adults with co-morbid asthma in the CRSwNP development program. Advise patients to report signs of eosinophilic pneumonia and EGPA to their healthcare provider. Consider withholding DUPIXENT if eosinophilic pneumonia or EGPA are suspected.
Acute Symptoms of Asthma or Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease or Acute Deteriorating Disease
DUPIXENT should not be used to treat acute symptoms or acute exacerbations of asthma or COPD. Do not use DUPIXENT to treat acute bronchospasm or status asthmaticus. Patients should seek medical advice if their asthma or COPD remains uncontrolled or worsens after initiation of treatment with DUPIXENT.
Risk Associated with Abrupt Reduction of Corticosteroid Dosage
Do not discontinue systemic, topical, or inhaled corticosteroids abruptly upon initiation of therapy with DUPIXENT. Reductions in corticosteroid dose, if appropriate, should be gradual and performed under the direct supervision of a healthcare provider. Reduction in corticosteroid dose may be associated with systemic withdrawal symptoms and/or unmask conditions previously suppressed by systemic corticosteroid therapy.
Patients with Co-morbid Asthma
Advise patients with co-morbid asthma not to adjust or stop their asthma treatments without consultation with their physicians.
Psoriasis
Cases of new-onset psoriasis have been reported with the use of DUPIXENT for the treatment of atopic dermatitis and asthma, including in patients without a family history of psoriasis. In postmarketing reports, onset of psoriasis varied from weeks to months after the first dose of DUPIXENT and resulted in partial or complete resolution of psoriasis with discontinuation of dupilumab, with or without use of supplemental treatment for psoriasis (topical or systemic). Those who continued on dupilumab received supplemental treatment for psoriasis to improve associated symptoms. Advise patients to report new-onset psoriasis symptoms to their healthcare provider. If symptoms persist or worsen, consider dermatologic evaluation and/or discontinuation of DUPIXENT.
Arthralgia and Psoriatic Arthritis
Arthralgia has been reported with the use of DUPIXENT with some patients reporting gait disturbances or decreased mobility associated with joint symptoms; some cases resulted in hospitalization [see Adverse Reactions (6.1) ] . In postmarketing reports, onset of arthralgia was variable, ranging from days to months after the first dose of DUPIXENT.
Cases of new-onset psoriatic arthritis requiring systemic treatment have been reported with the use of DUPIXENT.
Some patients' symptoms resolved while continuing treatment with DUPIXENT, and other patients recovered or were recovering following discontinuation of DUPIXENT.
Advise patients to report new onset or worsening joint symptoms to their healthcare provider. If symptoms persist or worsen, consider rheumatological evaluation and/or discontinuation of DUPIXENT.
Parasitic (Helminth) Infections
Patients with known helminth infections were excluded from participation in clinical studies. It is unknown if DUPIXENT will influence the immune response against helminth infections.
Treat patients with pre-existing helminth infections before initiating therapy with DUPIXENT. If patients become infected while receiving treatment with DUPIXENT and do not respond to anti-helminth treatment, discontinue treatment with DUPIXENT until the infection resolves. Adverse reactions of helminth infections (5 cases of enterobiasis and 1 case of ascariasis) were reported in pediatric subjects 6 to 11 years old who participated in the pediatric asthma development program [see Adverse Reactions (6.1) ] .
Vaccinations
Consider completing all age-appropriate vaccinations as recommended by current immunization guidelines prior to initiating treatment with DUPIXENT. Avoid use of live vaccines during treatment with DUPIXENT. It is unknown if administration of live vaccines during DUPIXENT treatment will impact the safety or effectiveness of these vaccines. Limited data are available regarding coadministration of DUPIXENT with non-live vaccines [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.2) ] .
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following clinically significant adverse reactions are described elsewhere in the labeling:
- Hypersensitivity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) ]
- Conjunctivitis and Keratitis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) ]
- Psoriasis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7) ]
- Arthralgia and Psoriatic Arthritis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8) ]
- Parasitic (Helminth) Infections [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9) ]
Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
Atopic Dermatitis
Adults with Atopic Dermatitis
Three randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicenter trials (SOLO 1, SOLO 2, and CHRONOS) and one dose-ranging trial (AD-1021) evaluated the safety of DUPIXENT in subjects with moderate-to-severe AD [see Clinical Studies (14) ] . In terms of co-morbid conditions, 48% of the subjects had asthma, 49% had allergic rhinitis, 37% had food allergy, and 27% had allergic conjunctivitis. In these 4 trials, 1472 subjects were treated with subcutaneous injections of DUPIXENT, with or without concomitant topical corticosteroids (TCS).
A total of 739 subjects were treated with DUPIXENT for at least 1 year in the development program for moderate-to-severe AD.
SOLO 1, SOLO 2, and AD-1021 compared the safety of DUPIXENT monotherapy to placebo through Week 16. CHRONOS compared the safety of DUPIXENT + TCS to placebo + TCS through Week 52.
AD-1225 is a multicenter, open-label extension (OLE) trial which assessed the long-term safety of repeat doses of DUPIXENT through 260 weeks of treatment in adults with moderate-to-severe AD who had previously participated in controlled trials of DUPIXENT or had been screened for SOLO 1 or SOLO 2. The safety data in AD-1225 reflect exposure to DUPIXENT 200 mg QW, 300 mg QW and 300 mg Q2W in 2677 subjects, including 2254 exposed for at least 52 weeks, 1224 exposed for at least 100 weeks, 561 exposed for at least 148 weeks and 179 exposed for at least 260 weeks.
Weeks 0 to 16 (SOLO 1, SOLO 2, CHRONOS, and AD-1021)
In DUPIXENT monotherapy trials (SOLO 1, SOLO 2, and AD-1021) through Week 16, the proportion of subjects who discontinued treatment because of adverse events was 1.9% in both the DUPIXENT 300 mg Q2W and placebo groups. Table 7 summarizes the adverse reactions that occurred at a rate of at least 1% in the DUPIXENT 300 mg Q2W monotherapy groups, and in the DUPIXENT + TCS group, all at a higher rate than in their respective comparator groups during the first 16 weeks of treatment.
| Adverse Reaction | DUPIXENT Monotherapy Pooled analysis of SOLO 1, SOLO 2, and AD-1021. | DUPIXENT + TCS Analysis of CHRONOS where subjects were on background TCS therapy. | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DUPIXENT 300 mg Q2W DUPIXENT 600 mg at Week 0, followed by 300 mg every 2 weeks. | Placebo | DUPIXENT 300 mg Q2W+ TCS | Placebo + TCS | |
| N=529 n (%) | N=517 n (%) | N=110 n (%) | N=315 n (%) | |
| Injection site reaction | 51 (10) | 28 (5) | 11 (10) | 18 (6) |
| Conjunctivitis Conjunctivitis cluster includes conjunctivitis, allergic conjunctivitis, bacterial conjunctivitis, viral conjunctivitis, giant papillary conjunctivitis, eye irritation, and eye inflammation. | 51 (10) | 12 (2) | 10 (9) | 15 (5) |
| Blepharitis | 2 (<1) | 1 (<1) | 5 (5) | 2 (1) |
| Oral herpes | 20 (4) | 8 (2) | 3 (3) | 5 (2) |
| Keratitis Keratitis cluster includes keratitis, ulcerative keratitis, allergic keratitis, atopic keratoconjunctivitis, and ophthalmic herpes simplex. | 1 (<1) | 0 | 4 (4) | 0 |
| Eye pruritus | 3 (1) | 1 (<1) | 2 (2) | 2 (1) |
| Other herpes simplex virus infection Other herpes simplex virus infection cluster includes herpes simplex, genital herpes, herpes simplex otitis externa, and herpes virus infection, but excludes eczema herpeticum. | 10 (2) | 6 (1) | 1 (1) | 1 (<1) |
| Dry eye | 1 (<1) | 0 | 2 (2) | 1 (<1) |
Safety through Week 52 (CHRONOS)
In the DUPIXENT with concomitant TCS trial (CHRONOS) through Week 52, the proportion of subjects who discontinued treatment because of adverse events was 1.8% in DUPIXENT 300 mg Q2W + TCS group and 7.6% in the placebo + TCS group. Two subjects discontinued DUPIXENT because of adverse reactions: atopic dermatitis (1 subject) and exfoliative dermatitis (1 subject).
The safety profile of DUPIXENT + TCS through Week 52 was generally consistent with the safety profile observed at Week 16.
Safety through 260 Weeks (AD-1225)
The long-term safety profile observed in this trial through 260 weeks was generally consistent with the safety profile of DUPIXENT observed in controlled studies.
Pediatric Subjects 12 Years of Age and Older with Atopic Dermatitis
The safety of DUPIXENT was assessed in a trial of 250 pediatric subjects 12 years of age and older with moderate-to-severe AD (AD-1526). The safety profile of DUPIXENT in these subjects through Week 16 was similar to the safety profile seen in adults with AD.
The long-term safety of DUPIXENT was assessed in an open-label extension study in pediatric subjects 12 years of age and older with moderate-to-severe AD (AD-1434). The safety profile of DUPIXENT in subjects followed through Week 52 was similar to the safety profile observed at Week 16 in AD-1526. The long-term safety profile of DUPIXENT observed in pediatric subjects 12 years of age and older was consistent with that seen in adults with AD.
Pediatric Subjects 6 to 11 Years of Age with Atopic Dermatitis
The safety of DUPIXENT with concomitant TCS was assessed in a trial of 367 pediatric subjects 6 to 11 years of age with severe AD (AD-1652). The safety profile of DUPIXENT + TCS in these subjects through Week 16 was similar to the safety profile from trials in adult and pediatric subjects 12 years of age and older with AD.
The long-term safety of DUPIXENT ± TCS was assessed in an open-label extension study of 368 pediatric subjects 6 to 11 years of age with AD (AD-1434). Among subjects who entered this study, 110 (30%) had moderate and 72 (20%) had severe AD at the time of enrollment in AD-1434. The safety profile of DUPIXENT ± TCS in subjects followed through Week 52 was similar to the safety profile observed through Week 16 in AD-1652. The long-term safety profile of DUPIXENT ± TCS observed in pediatric subjects 6 to 11 years of age was consistent with that seen in adult and pediatric subjects 12 years of age and older with AD.
Pediatric Subjects 6 Months to 5 Years of Age with Atopic Dermatitis
The safety of DUPIXENT with concomitant TCS was assessed in a trial of 161 pediatric subjects 6 months to 5 years of age with moderate-to-severe AD (AD-1539). The safety profile of DUPIXENT + TCS in these subjects through Week 16 was similar to the safety profile from trials in adults and pediatric subjects 6 years of age and older with AD.
The long-term safety of DUPIXENT ± TCS was assessed in an open-label extension study of 180 pediatric subjects 6 months to 5 years of age with AD (AD-1434). The majority of subjects were treated with DUPIXENT 300 mg every 4 weeks. The safety profile of DUPIXENT ± TCS in subjects followed through Week 52 was similar to the safety profile observed through Week 16 in AD-1539. The long-term safety profile of DUPIXENT ± TCS observed in pediatric subjects 6 months to 5 years of age was consistent with that seen in adults and pediatric subjects 6 years of age and older with AD. In addition, hand-foot-and-mouth disease was reported in 9 (5%) pediatric subjects and skin papilloma was reported in 4 (2%) pediatric subjects treated with DUPIXENT ± TCS. These cases did not lead to study drug discontinuation.
Atopic Dermatitis with Hand and/or Foot Involvement
The safety of DUPIXENT was assessed in a 16-week, multicenter, randomized, double-blind, parallel-group, placebo-controlled trial (Liberty-AD-HAFT) in 133 adult and pediatric subjects 12 to 17 years of age with atopic dermatitis with moderate-to-severe hand and/or foot involvement [see Clinical Studies (14) ] . In this trial 67 subjects received DUPIXENT, and 66 subjects received placebo. DUPIXENT-treated subjects received the recommended dosage based on their age and body weight [see Dosage and Administration (2.3) ] . The safety profile of DUPIXENT in these subjects through Week 16 was consistent with the safety profile from studies in adult and pediatric subjects 6 months of age and older with moderate-to-severe AD.
Asthma
Adults and Pediatric Subjects 12 Years of Age and Older with Asthma
A total of 2888 adult and pediatric subjects 12 to 17 years of age with moderate-to-severe asthma (AS) were evaluated in 3 randomized, placebo-controlled, multicenter trials of 24 to 52 weeks duration (DRI12544, QUEST, and VENTURE). Of these, 2678 had a history of 1 or more severe exacerbations in the year prior to enrollment despite regular use of medium to high-dose inhaled corticosteroids plus an additional controller(s) (DRI12544 and QUEST). A total of 210 subjects with oral corticosteroid-dependent asthma receiving high-dose inhaled corticosteroids plus up to two additional controllers were enrolled (VENTURE). The safety population (DRI12544 and QUEST) was 12-87 years of age, of which 63% were female, and 82% were White. DUPIXENT 200 mg or 300 mg was administered subcutaneously Q2W, following an initial dose of 400 mg or 600 mg, respectively.
In DRI12544 and QUEST, the proportion of subjects who discontinued treatment due to adverse events was 4% of the placebo group, 3% of the DUPIXENT 200 mg Q2W group, and 6% of the DUPIXENT 300 mg Q2W group.
Table 8 summarizes the adverse reactions that occurred at a rate of at least 1% in subjects treated with DUPIXENT and at a higher rate than in their respective comparator groups in DRI12544 and QUEST.
| Adverse Reaction | DRI12544 and QUEST | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| DUPIXENT 200 mg Q2W | DUPIXENT 300 mg Q2W | Placebo | |
| N=779 n (%) | N=788 n (%) | N=792 n (%) | |
| Injection site reactions Injection site reactions cluster includes erythema, edema, pruritus, pain, and inflammation. | 111 (14%) | 144 (18%) | 50 (6%) |
| Oropharyngeal pain | 13 (2%) | 19 (2%) | 7 (1%) |
| Eosinophilia Eosinophilia = blood eosinophils ≥3,000 cells/mcL or deemed by the investigator to be an adverse event. None met the criteria for serious eosinophilic conditions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3) ] . | 17 (2%) | 16 (2%) | 2 (<1%) |
Injection site reactions were most common with the loading (initial) dose.
The safety profile of DUPIXENT through Week 52 was generally consistent with the safety profile observed at Week 24.
Pediatric Subjects 6 to 11 Years of Age with Asthma
The safety of DUPIXENT was assessed in 405 pediatric subjects 6 to 11 years of age with moderate-to-severe asthma (VOYAGE). The safety profile of DUPIXENT in these subjects through Week 52 was similar to the safety profile from studies in adult and pediatric subjects 12 years of age and older with moderate-to-severe asthma with the addition of helminth infections. Helminth infections were reported in 2.2% (6 subjects) in the DUPIXENT group and 0.7% (1 subject) in the placebo group. The majority of cases were enterobiasis, reported in 1.8% (5 subjects) in the DUPIXENT group and none in the placebo group. There was one case of ascariasis in the DUPIXENT group. All helminth infection cases were mild to moderate and subjects recovered with anti-helminth treatment without DUPIXENT treatment discontinuation.
Chronic Rhinosinusitis with Nasal Polyps
A total of 722 adult subjects with chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps (CRSwNP) were evaluated in 2 randomized, placebo-controlled, multicenter trials of 24 to 52 weeks duration (SINUS-24 and SINUS-52). The safety pool consisted of data from the first 24 weeks of treatment from both studies.
In the safety pool, the proportion of adult subjects who discontinued treatment due to adverse events was 5% of the placebo group and 2% of the DUPIXENT 300 mg Q2W group.
Table 9 summarizes the adverse reactions that occurred at a rate of at least 1% in adult subjects treated with DUPIXENT and at a higher rate than in their respective comparator group in SINUS-24 and SINUS-52.
| Adverse Reaction | SINUS-24 and SINUS-52 | |
|---|---|---|
| DUPIXENT 300 mg Q2W | Placebo | |
| N=440 n (%) | N=282 n (%) | |
| Injection site reactions Injection site reactions cluster includes injection site reaction, pain, bruising and swelling. | 28 (6%) | 12 (4%) |
| Conjunctivitis Conjunctivitis cluster includes conjunctivitis, allergic conjunctivitis, bacterial conjunctivitis, viral conjunctivitis, giant papillary conjunctivitis, eye irritation, and eye inflammation. | 7 (2%) | 2 (1%) |
| Arthralgia | 14 (3%) | 5 (2%) |
| Gastritis | 7 (2%) | 2 (1%) |
| Insomnia | 6 (1%) | 0 (<1%) |
| Eosinophilia | 5 (1%) | 1 (<1%) |
| Toothache | 5 (1%) | 1 (<1%) |
The safety profile of DUPIXENT through Week 52 was generally consistent with the safety profile observed at Week 24.
Eosinophilic Esophagitis
Adults and Pediatric Subjects 12 Years of Age and Older with EoE
A total of 239 adult and pediatric subjects 12 years of age and older, weighing at least 40 kg, with EoE were evaluated in a randomized, double-blind, parallel-group, multicenter, placebo-controlled trial, including two 24-week treatment periods (Study EoE-1 Parts A and B) and received either DUPIXENT 300 mg QW or placebo [see Clinical Studies (14.4) ] .
The proportion of subjects who discontinued treatment due to adverse events was 2% of the placebo group and 2% of the DUPIXENT 300 mg QW group.
Table 10 summarizes the adverse reactions that occurred at a rate of at least 2% in subjects treated with DUPIXENT and at a higher rate than in their respective comparator group in Parts A and B.
| Study EoE-1 Parts A and B | ||
|---|---|---|
| Adverse Reaction | DUPIXENT 300 mg QW N=122 n (%) | Placebo N=117 n (%) |
| Injection site reactions Injection site reactions are composed of several terms including, but not limited to, injection site swelling, pain, and bruising. | 46 (38%) | 39 (33%) |
| Upper respiratory tract infections Upper respiratory tract infections are composed of several terms including, but not limited to, COVID-19, sinusitis, and upper respiratory tract infection. | 22 (18%) | 12 (10%) |
| Arthralgia | 3 (2%) | 1 (1%) |
| Herpes viral infections Herpes viral infections are composed of oral herpes and herpes simplex. | 3 (2%) | 1 (1%) |
The safety profile of DUPIXENT in 72 pediatric subjects 12 to 17 years of age, weighing at least 40 kg, and adults in Parts A and B was similar.
Pediatric Subjects 1 to 11 Years of Age, Weighing at least 15 kg, with EoE
A total of 61 pediatric subjects 1 to 11 years of age, weighing at least 15 kg, with EoE were evaluated in a randomized, blinded, parallel-group, multicenter trial, including an initial 16-week placebo-controlled treatment period (Study EoE-2 Part A) and a 36-week extended active treatment period (Study EoE-2 Part B). Subjects in Part A received a weight-based dosing regimen of DUPIXENT or placebo [see Clinical Studies (14.4) ] . All subjects in Part B completed Part A and received active treatment with weight-based dosing regimens of DUPIXENT in Part B (N=47).
The safety profile of DUPIXENT through Week 16 of Study EoE-2 Part A was generally similar to the safety profile in adult and pediatric subjects 12 years of age and older with EoE. In Part B, a helminth infection was reported in one DUPIXENT-treated subject.
Prurigo Nodularis
A total of 309 adult subjects with prurigo nodularis (PN) were evaluated in two 24-week randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicenter trials (PRIME and PRIME2) [see Clinical Studies (14.5) ] . The safety pool included data from the 24-week treatment and 12-week follow-up periods from both trials.
The proportion of subjects who discontinued treatment due to adverse events was 3% of the placebo group and 0% of the DUPIXENT 300 mg Q2W group.
Subjects with co-morbid conditions included 43% of subjects with a history of atopy (defined as having a medical history of AD, allergic rhinitis/rhino conjunctivitis, asthma, or food allergy), 8% of subjects with a history of hypothyroidism and 9% of subjects with a history of diabetes mellitus type 2.
Table 11 summarizes the adverse reactions that occurred at a rate of at least 2% in subjects treated with DUPIXENT and at a higher rate than in their respective comparator group in PRIME and PRIME2.
| Adverse Reaction | PRIME and PRIME2 | |
|---|---|---|
| DUPIXENT 300 mg Q2W | Placebo | |
| N=152 n (%) | N=157 n (%) | |
| Nasopharyngitis Nasopharyngitis includes pharyngitis | 8 (5%) | 3 (2%) |
| Conjunctivitis Conjunctivitis includes conjunctivitis and allergic conjunctivitis. | 6 (4%) | 2 (1%) |
| Herpes Infection Herpes infection includes oral herpes, genital herpes simplex, herpes zoster and ophthalmic herpes zoster | 5 (3%) | 0% |
| Dizziness Dizziness includes dizziness postural, vertigo and vertigo positional | 5 (3%) | 2 (1%) |
| Myalgia Myalgia includes musculoskeletal pain and musculoskeletal chest pain | 5 (3%) | 2 (1%) |
| Diarrhea | 4 (3%) | 1 (1%) |
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
A total of 1874 adult subjects with inadequately controlled chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and an eosinophilic phenotype were evaluated in two randomized, double-blind, multicenter, parallel-group, placebo-controlled trials with a 52-week treatment period (BOREAS and NOTUS) [see Clinical Studies (14.6) ] . Of those randomized, 1872 subjects received at least one dose of DUPIXENT 300 mg or placebo subcutaneously every 2 weeks (Q2W). The safety of DUPIXENT was assessed in the pooled safety population from BOREAS and NOTUS, which consisted of 938 adult subjects treated with DUPIXENT. Of the subjects treated with DUPIXENT, 98% utilized inhaled triple therapy at baseline (comprising of an inhaled corticosteroid, long-acting beta-agonist, and long-acting muscarinic antagonist), and 97% had chronic bronchitis.
Table 12 summarizes the adverse reactions that occurred in at least 2% of subjects treated with DUPIXENT and at a higher rate than placebo in BOREAS and NOTUS trials.
| Adverse Reaction | BOREAS and NOTUS | |
|---|---|---|
| DUPIXENT 300 mg Q2W | Placebo | |
| N=938 n (%) | N=934 n (%) | |
| Viral Infection Consists of multiple similar terms. | 133 (14.2) | 115 (12.3) |
| Headache | 73 (7.8) | 62 (6.6) |
| Nasopharyngitis | 73 (7.8) | 69 (7.4) |
| Back Pain | 42 (4.5) | 29 (3.1) |
| Diarrhea | 35 (3.7) | 30 (3.2) |
| Arthralgia | 29 (3.1) | 25 (2.7) |
| Urinary Tract Infection | 28 (3.0) | 18 (1.9) |
| Local Administration Reaction | 26 (2.8) | 6 (0.6) |
| Injection Site Reaction | 11 (1.2) | 2 (0.2) |
| Rhinitis | 24 (2.6) | 17 (1.8) |
| Eosinophilia Eosinophilia was defined as blood eosinophils ≥3,000 cells/mcL or deemed by the investigator to be an adverse event. None met the criteria for serious eosinophilic conditions. | 22 (2.3) | 7 (0.7) |
| Toothache | 20 (2.1) | 11 (1.2) |
| Gastritis | 19 (2) | 7 (0.7) |
Less Common Adverse Reaction in Subjects with COPD: Cholecystitis
In adult subjects with COPD, cholecystitis was reported in 6 subjects (0.6%) in the DUPIXENT group compared to 1 subject (0.1%) in the placebo group. Among these subjects, serious cholecystitis was reported in 4 (0.4%) of the DUPIXENT group compared with 0% of the placebo group.
Chronic Spontaneous Urticaria
The pooled safety data below reflects the safety of DUPIXENT in adult and pediatric subjects 12 years of age and older with chronic spontaneous urticaria (CSU) who remain symptomatic despite H1 antihistamine treatment. A total of 392 adult and pediatric subjects 12 years of age and older with CSU were evaluated for safety in three randomized, double-blind, parallel-group, multicenter, placebo-controlled, studies, Study A, B, and C, conducted under a master protocol (CUPID) for 36 weeks [see Clinical Studies (14.7) ] . The pooled safety population received an initial dose of DUPIXENT 600 mg or 400 mg, followed by DUPIXENT 300 mg or 200 mg, respectively, or matching placebo, administered subcutaneously every 2 weeks (Q2W) [see Dosage and Administration (2.9) ] .
Table 13 summarizes the adverse reactions that occurred in at least 2% in subjects treated with DUPIXENT and at a higher rate than placebo in CUPID Study A, B and C (pooled safety population).
| Adverse Reaction | CUPID Study A, B, and C | |
|---|---|---|
| DUPIXENT 200 mg Q2W or 300 mg Q2W | Placebo | |
| N=195 n (%) | N=197 n (%) | |
| Injection site reactions Injection site reactions cluster includes injection site dermatitis, injection site erythema, injection site hematoma, injection site induration, injection site pain, injection site pruritus, injection site reaction, injection site swelling | 20 (10.3) | 16 (8.1) |
Bullous Pemphigoid
The safety of DUPIXENT was evaluated in a 52-week, randomized, double-blind, parallel-group, multicenter, placebo-controlled trial (ADEPT) in a total of 106 adult subjects with moderate-to-severe bullous pemphigoid (BP) [see Clinical Studies (14.8) ] . Of the 106 randomized subjects, all received at least one dose of DUPIXENT or placebo with a course of oral corticosteroids (OCS) with a prespecified taper. At the time of analysis, 87 subjects had completed Week 36 and 65 subjects had completed Week 52.
Table 14 summarizes the adverse reactions that occurred in at least 2% of subjects treated with DUPIXENT and at a higher rate than placebo in the ADEPT trial.
| Adverse Reaction | ADEPT | |
|---|---|---|
| DUPIXENT 300 mg Q2W + OCS | Placebo+ OCS | |
| N=53 n (%) | N=53 n (%) | |
| Arthralgia | 5 (9%) | 3 (6%) |
| Conjunctivitis | 4 (8%) | 0% |
| Vision blurred | 4 (8%) | 0% |
| Herpes viral infections Herpes viral infections include herpes simplex and herpes zoster | 3 (6%) | 0% |
| Keratitis | 2 (4%) | 0% |
A case of AGEP was reported in 1 subject with BP treated with DUPIXENT compared with 0 subjects in the placebo group.
Specific Adverse Reactions for AD, Asthma, CRSwNP, EoE, PN, COPD, CSU and BP
Conjunctivitis and Keratitis
In adult subjects with AD, conjunctivitis was reported in 10% (34 per 100 patient-years) in the 300 mg Q2W dose group and in 2% of the placebo group (8 per 100 patient-years) during the 16-week treatment period of the monotherapy trials (SOLO 1, SOLO 2, and AD-1021). During the 52-week treatment period of concomitant therapy AD trial (CHRONOS), conjunctivitis was reported in 16% of the DUPIXENT 300 mg Q2W + TCS group (20 per 100 patient-years) and in 9% of the placebo + TCS group (10 per 100 patient-years). During the long-term OLE trial with data through 260 weeks (AD-1225), conjunctivitis was reported in 21% of the DUPIXENT group (12 per 100 patient-years).
In DUPIXENT AD monotherapy trials (SOLO 1, SOLO 2, and AD-1021) through Week 16, keratitis was reported in <1% of the DUPIXENT group (1 per 100 patient-years) and in 0% of the placebo group (0 per 100 patient-years). In the 52-week DUPIXENT + topical corticosteroids (TCS) AD trial (CHRONOS), keratitis was reported in 4% of the DUPIXENT + TCS group (4 per 100 patient-years) and in 2% of the placebo + TCS group (2 per 100 patient-years). Conjunctivitis and keratitis occurred more frequently in AD subjects who received DUPIXENT. Conjunctivitis was the most frequently reported eye disorder. During the long-term OLE trial with data through 260 weeks (AD-1225), keratitis was reported in 3% of the DUPIXENT group (1 per 100 patient-years). Most subjects with conjunctivitis or keratitis recovered or were recovering during the treatment period.
Among subjects with asthma, the frequency of conjunctivitis and keratitis was similar between DUPIXENT and placebo.
In adult subjects with CRSwNP, the frequency of conjunctivitis was 2% in the DUPIXENT group compared to 1% in the placebo group in the 24-week safety pool; these subjects recovered.
In the 52-week CRSwNP study (SINUS-52), the frequency of conjunctivitis was 3% in the DUPIXENT adult subjects and 1% in the placebo subjects; all of these subjects recovered. There were no cases of keratitis reported in the CRSwNP development program.
Among subjects with EoE, there were no reports of conjunctivitis and keratitis in the DUPIXENT group in placebo-controlled trials. In the 36-week active treatment extension period of Study EoE-2 Part B, conjunctivitis was reported in 4% of DUPIXENT-treated pediatric subjects with EoE.
Among subjects with PN, the frequency of conjunctivitis was 4% in the DUPIXENT group compared to 1% in the placebo group; all of these subjects recovered or were recovering during the treatment period. There were no cases of keratitis reported in the PN development program.
Among subjects with COPD, the frequency of conjunctivitis and keratitis was 1.4% and 0.1% in the DUPIXENT group and 1% and 0% in the placebo group, respectively.
Among subjects with CSU in the pooled safety population, the frequency of conjunctivitis was similar between DUPIXENT and placebo. There were no cases of keratitis reported in the CSU development program.
Among subjects with BP, the frequency of conjunctivitis and keratitis was 8% and 4% in the DUPIXENT group and 0% and 0% in the placebo group, respectively.
Eczema Herpeticum and Herpes Zoster
The rate of eczema herpeticum was similar in the placebo and DUPIXENT groups in the AD trials. The rates remained stable through 260 weeks in the long-term OLE trial (AD-1225).
Herpes zoster was reported in <1% of the DUPIXENT groups (1 per 100 patient-years) and in <1% of the placebo group (1 per 100 patient-years) in the 16-week AD monotherapy trials. In the 52-week DUPIXENT + TCS AD trial, herpes zoster was reported in 1% of the DUPIXENT + TCS group (1 per 100 patient-years) and 2% of the placebo + TCS group (2 per 100 patient-years). During the long-term OLE trial with data through 260 weeks (AD-1225), 2.0% of DUPIXENT-treated subjects reported herpes zoster (0.94 per 100 patient-years of follow up). Among asthma subjects the frequency of herpes zoster was similar between DUPIXENT and placebo. Among subjects with CRSwNP or EoE there were no reported cases of herpes zoster or eczema herpeticum.
Among subjects with PN, herpes zoster and ophthalmic herpes zoster were each reported in <1% of the DUPIXENT group (1 per 100 patient-years) and 0% of the placebo group.
Among subjects with COPD, herpes zoster was reported in 0.9% of the DUPIXENT group and 0.2% of the placebo group. Ophthalmic herpes zoster was reported in 0.1% of the DUPIXENT group and 0.2% of the placebo group.
Among subjects with CSU in the pooled safety population, herpes zoster was reported in <1% of the DUPIXENT and placebo groups (1 per 100 patient-years). There were no cases of eczema herpeticum reported in the CSU development program.
Among subjects with BP, herpes zoster was reported in 4% of the DUPIXENT group and 0% of the placebo group.
Hypersensitivity Reactions
Hypersensitivity reactions were reported in <1% of DUPIXENT-treated subjects. These included anaphylaxis, AGEP, serum sickness or serum sickness-like reactions, generalized urticaria, rash, erythema nodosum, and erythema multiforme [see Contraindications (4) , and Clinical Pharmacology (12.6) ] .
Eosinophils
DUPIXENT-treated subjects with AD, asthma, CRSwNP, and COPD had a greater initial increase from baseline in blood eosinophil count compared to subjects receiving placebo. In adult subjects with AD (SOLO 1, SOLO 2, and AD-1021), the mean and median increases in blood eosinophils from baseline to Week 4 were 100 and 0 cells/mcL, respectively. In pediatric subjects less than 6 years old with AD, the mean and median increases from baseline to week 4 were 478 and 90 cells/mcL, respectively.
In adult and pediatric subjects 12 years of age and older with asthma (DRI12544 and QUEST), the mean and median increases in blood eosinophils from baseline to Week 4 were 130 and 10 cells/mcL, respectively. In subjects 6 to 11 years of age with asthma (VOYAGE), the mean and median increases in blood eosinophils from baseline to Week 12 were 124 and 0 cells/mcL, respectively.
In adult subjects with CRSwNP (SINUS-24 and SINUS-52), the mean and median increases in blood eosinophils from baseline to Week 16 were 150 and 50 cells/mcL, respectively.
In subjects with COPD (BOREAS and NOTUS), the mean and median increases in blood eosinophils from baseline to Week 8 were 60 and 0 cells/mcL, respectively.
An increase from baseline in blood eosinophil count was not observed in adult and pediatric subjects 12 years of age and older with EoE treated with DUPIXENT as compared to placebo (Study EoE-1). In pediatric subjects 1 to 11 years of age with EoE (Study EoE-2 Part A), blood eosinophil counts were generally consistent with those observed in Study EoE-1.
In adult and pediatric subjects with CSU (CUPID Study A, Study B, and Study C) treated with DUPIXENT, an increase from baseline in blood eosinophil count was not observed compared to placebo at Week 12.
In subjects with PN (PRIME and PRIME2), the mean and median decrease in blood eosinophils from baseline to Week 4 were 9 and 10 cells/mcL, respectively.
In DUPIXENT-treated subjects with BP in ADEPT, all of whom received background oral corticosteroid (OCS) treatment, the mean and median decrease in blood eosinophils from baseline to Week 4 were 1022 and 485 cells/mcL, respectively.
In the trials for the COPD indication, treatment-emergent eosinophilia (≥500 cells/mcL) was higher in DUPIXENT (41.7%) than in the placebo group (39.4%); none of the cases were associated with clinical symptoms, and treatment-emergent eosinophilia (≥1000 cells/mcL) was higher in DUPIXENT (13.6%) than in the placebo group (8.1%).
Across the trials for AD, asthma, CRSwNP, and CSU indications, the incidence of treatment-emergent eosinophilia (≥500 cells/mcL) was similar in DUPIXENT and placebo groups.
In the trials for the PN indication, the incidence of treatment-emergent eosinophilia (≥500 cells/mcL) was lower in DUPIXENT than in the placebo group.
In the trial for the BP indication, the incidence of treatment-emergent eosinophilia (≥500 cells/mcL) was higher in DUPIXENT (21%) than in the placebo group (11%).
Treatment-emergent eosinophilia (≥5,000 cells/mcL) was observed in <3% of DUPIXENT-treated subjects and <0.5% in subjects receiving placebo (SOLO 1, SOLO 2, and AD-1021; DRI12544, QUEST, and VOYAGE; SINUS-24 and SINUS-52; PRIME and PRIME2; BOREAS and NOTUS; CUPID Study A, B, and C). Blood eosinophil counts declined to near baseline or remained below baseline levels (PRIME and PRIME2; BOREAS and NOTUS; ADEPT) during treatment. In trial AD-1539, treatment-emergent eosinophilia (≥5,000 cells/mcL) was reported in 8% of DUPIXENT-treated subjects and 0% in subjects receiving placebo [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3) ] .
Cardiovascular Thromboembolic Events
In the 1-year placebo-controlled trial in adult and pediatric subjects 12 years of age and older with asthma (QUEST), cardiovascular thromboembolic events (cardiovascular deaths, non-fatal myocardial infarctions, and non-fatal strokes) were reported in 1 (0.2%) of the DUPIXENT 200 mg Q2W group, 4 (0.6%) of the DUPIXENT 300 mg Q2W group, and 2 (0.3%) of the placebo group.
In the 1-year placebo-controlled trial in subjects with AD (CHRONOS), cardiovascular thromboembolic events (cardiovascular deaths, non-fatal myocardial infarctions, and non-fatal strokes) were reported in 1 (0.9%) of the DUPIXENT + TCS 300 mg Q2W group, 0 (0.0%) of the DUPIXENT + TCS 300 mg QW group, and 1 (0.3%) of the placebo + TCS group.
In the 24-week placebo-controlled trial in adult subjects with CRSwNP (SINUS-24), cardiovascular thromboembolic events (cardiovascular deaths, non-fatal myocardial infarctions, and non-fatal strokes) were reported in 1 (0.7%) of the DUPIXENT group and 0 (0.0%) of the placebo group.
In the 1-year placebo-controlled trial in adult subjects with CRSwNP (SINUS-52), there were no cases of cardiovascular thromboembolic events (cardiovascular deaths, non-fatal myocardial infarctions, and non-fatal strokes) reported in any treatment arm.
In the 24-week placebo-controlled trial in subjects with EoE (Study EoE-1 Parts A and B), there were no cases of cardiovascular thromboembolic events (cardiovascular deaths, non-fatal myocardial infarctions, and non-fatal strokes) reported in any treatment arm.
In the 24-week placebo-controlled trial in subjects with CSU (CUPID Study A, B, and C), there were no cases of cardiovascular thromboembolic events (cardiovascular deaths, non-fatal myocardial infarctions, and non-fatal strokes) reported in any treatment arm.
Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during post-approval use of DUPIXENT. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
- Immune system disorders: angioedema
- Musculoskeletal system disorders: psoriatic arthritis
- Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders: Facial skin reactions, including erythema, rash, scaling, edema, papules, pruritus, burning, and pain; new-onset psoriasis, vasculitis
DESCRIPTION
Dupilumab, an interleukin-4 receptor alpha antagonist, is a human monoclonal antibody of the IgG4 subclass that binds to the IL-4Rα subunit and inhibits IL-4 and IL-13 signaling. Dupilumab has an approximate molecular weight of 147 kDa.
Dupilumab is produced by recombinant DNA technology in Chinese Hamster Ovary cell suspension culture.
DUPIXENT (dupilumab) Injection is supplied as a sterile, preservative-free, clear to slightly opalescent, colorless to pale yellow solution for subcutaneous injection. DUPIXENT is provided as either a single-dose pre-filled syringe with needle shield or a single-dose pre-filled pen in a siliconized Type-1 clear glass syringe. The needle cap is not made with natural rubber latex.
Each 300 mg pre-filled syringe or pre-filled pen delivers 300 mg dupilumab in 2 mL which also contains L-arginine hydrochloride (10.5 mg), L-histidine (6.2 mg), polysorbate 80 (4 mg), sodium acetate (2 mg), sucrose (100 mg), and water for injection, pH 5.9.
Each 200 mg pre-filled syringe or pre-filled pen delivers 200 mg dupilumab in 1.14 mL which also contains L-arginine hydrochloride (12 mg), L-histidine (3.5 mg), polysorbate 80 (2.3 mg), sodium acetate (1.2 mg), sucrose (57 mg), and water for injection, pH 5.9.
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Mechanism of Action
Dupilumab is a human monoclonal IgG4 antibody that inhibits interleukin-4 (IL-4) and interleukin-13 (IL-13) signaling by specifically binding to the IL-4Rα subunit shared by the IL-4 and IL-13 receptor complexes. Dupilumab inhibits IL-4 signaling via the Type I receptor and both IL-4 and IL-13 signaling through the Type II receptor.
Inflammation driven by IL-4 and IL-13 is an important component in the pathogenesis of asthma, AD, CRSwNP, EoE, PN, COPD, CSU, and BP. Multiple cell types that express IL-4Rα (e.g., mast cells, basophils, eosinophils, macrophages, lymphocytes, epithelial cells, goblet cells) and inflammatory mediators (e.g., histamine, eicosanoids, leukotrienes, cytokines, chemokines) are involved in inflammation. Blocking IL-4Rα with dupilumab inhibits IL-4 and IL-13 cytokine-induced inflammatory responses, including the release of proinflammatory cytokines, chemokines, nitric oxide, and IgE. The mechanism of dupilumab action has not been definitively established.
Pharmacodynamics
Consistent with inhibition of IL-4 and IL-13 signaling, dupilumab treatment decreased certain biomarkers of inflammation. In asthma subjects, fractional exhaled nitric oxide (FeNO) and circulating concentrations of eotaxin-3, total IgE, allergen specific IgE, TARC, and periostin were decreased relative to placebo. Reductions in these biomarkers were comparable for the 300 mg Q2W and 200 mg Q2W regimens. These markers were near maximal suppression after 2 weeks of treatment, except for IgE which declined more slowly. These effects were sustained throughout treatment. The median percent reduction from baseline in total IgE concentrations with dupilumab treatments was 52% at Week 24 (DRI12544) and 70% at Week 52 (QUEST). For FeNO, the mean percent reduction from baseline at Week 2 was 35% and 24% in DRI12544 and QUEST, respectively, and in the overall safety population, the mean FeNO level decreased to 20 ppb.
A continuous decline in total IgE in serum was observed in CSU trials.
Antibody Response to Non-Live Vaccines During DUPIXENT Treatment
In a clinical study, adult subjects with AD were treated once weekly for 16 weeks with 300 mg of DUPIXENT (twice the recommended dosing frequency). After 12 weeks of administration, subjects received a Tdap vaccine and a meningococcal polysaccharide vaccine. Antibody responses to tetanus toxoid and serogroup C meningococcal polysaccharide were assessed 4 weeks later. Antibody responses to both tetanus toxoid and serogroup C meningococcal polysaccharide were similar in DUPIXENT-treated and placebo-treated subjects. Antibody responses to the other active components of both vaccines were not assessed. Antibody responses to other non-live vaccines were also not assessed.
Pharmacokinetics
The pharmacokinetics of dupilumab is similar in subjects with AD, asthma, CRSwNP, EoE, PN, COPD, CSU, and BP.
Absorption
Following an initial subcutaneous (SC) dose of 600 mg, 400 mg, or 300 mg, dupilumab reached peak mean ± SD concentrations (C max ) of 70.1±24.1 mcg/mL, 41.8±12.4 mcg/mL, or 30.5±9.39 mcg/mL, respectively, by approximately 1 week post dose. Steady-state concentrations were achieved by Week 16 following the administration of 600 mg starting dose and 300 mg dose either weekly or Q2W, or 400 mg starting dose and 200 mg dose Q2W, or 300 mg Q2W without a loading dose. Across clinical trials, the mean ± SD steady-state trough concentrations ranged from 55.3±34.3 mcg/mL to 80.2±35.3 mcg/mL for 300 mg administered Q2W, from 173±75.9 mcg/mL to 195±71.7 mcg/mL for 300 mg administered weekly, and from 29.2±18.7 to 36.5±22.2 mcg/mL for 200 mg administered Q2W.
The bioavailability of dupilumab following a SC dose is similar between AD, asthma, CRSwNP, EoE, PN, COPD, CSU, and BP subjects, ranging between 61% and 66%.
Distribution
The estimated total volume of distribution was approximately 4.8±1.3 L.
Elimination
The metabolic pathway of dupilumab has not been characterized. As a human monoclonal IgG4 antibody, dupilumab is expected to be degraded into small peptides and amino acids via catabolic pathways in the same manner as endogenous IgG. After the last steady-state dose of 300 mg QW, 300 mg Q2W, 200 mg Q2W, 300 mg Q4W, or 200 mg Q4W dupilumab, the median times to non-detectable concentration (<78 ng/mL) ranged from 9 to 13 weeks in adults and pediatric subjects 12 years of age and older. Population pharmacokinetic analyses indicate the median times to non-detectable concentration are approximately 1.5 times (up to 19 weeks) and 2.5 times (up to 32 weeks) longer in pediatric subjects 6 to 11 years of age and pediatric subjects 6 months to 5 years of age, respectively.
Dose Linearity
Dupilumab exhibited nonlinear target-mediated pharmacokinetics with exposures increasing in a greater than dose-proportional manner. The systemic exposure increased by 30-fold when the dose increased 8-fold following a single dose of dupilumab from 75 mg to 600 mg (i.e., 0.25-times to 2-times the recommended dose).
Weight
Dupilumab trough concentrations were lower in subjects with higher body weight.
Immunogenicity
Development of antibodies to dupilumab was associated with lower serum dupilumab concentrations. A few subjects who had high antibody titers also had no detectable serum dupilumab concentrations.
Specific Populations
Age
Based on population pharmacokinetic analysis, age did not affect dupilumab clearance in adults and in pediatric subjects 6 to 17 years of age. In pediatric subjects 6 months to 5 years of age, clearance increased with age.
Geriatric Patients
No overall differences in the pharmacokinetics of dupilumab were observed between elderly and younger adult subjects.
Pediatric Patients
Atopic Dermatitis
For pediatric subjects 12 years of age and older with AD receiving every 2 week dosing (Q2W) with either 200 mg (<60 kg) or 300 mg (≥60 kg), the mean ± SD steady-state trough concentration of dupilumab was 54.5±27.0 mcg/mL.
For pediatric subjects 6 to 11 years of age with AD receiving every 2 week dosing (Q2W) with 200 mg (≥30 kg) or every 4 week dosing (Q4W) with 300 mg (<30 kg), mean ± SD steady-state trough concentration was 86.0±34.6 mcg/mL and 98.7±33.2 mcg/mL, respectively.
For pediatric subjects 6 months to 5 years of age with AD receiving every 4 week dosing (Q4W) with 300 mg (≥15 to <30 kg) or 200 mg (≥5 to <15 kg), the mean ± SD steady-state trough concentration was 110±42.8 mcg/mL and 109±50.8 mcg/mL, respectively.
Asthma
A total of 107 pediatric subjects 12 to 17 years of age with asthma were enrolled in QUEST. The mean ± SD steady-state trough concentrations of dupilumab were 107±51.6 mcg/mL and 46.7±26.9 mcg/mL, respectively, for 300 mg or 200 mg administered Q2W.
In VOYAGE, dupilumab pharmacokinetics was investigated in 270 subjects with moderate-to-severe asthma following subcutaneous administration of either 100 mg Q2W (for 91 pediatric subjects weighing <30 kg) or 200 mg Q2W (for 179 pediatric subjects weighing ≥30 kg). The mean ± SD steady-state trough concentration was 58.4±28.0 mcg/mL and 85.1±44.9 mcg/mL, respectively. Simulation of a 300 mg Q4W subcutaneous dose in pediatric subjects 6 to 11 years of age with body weight of ≥15 to <30 kg resulted in predicted steady-state trough concentrations (98.7±41.0 mcg/mL) and average concentrations higher than the observed trough concentrations and average concentrations of 100 mg Q2W (<30 kg).
CRSwNP
Clinical studies have not been conducted in pediatric patients aged 12 years and older with CRSwNP. Dupilumab exposures are expected to be comparable between adults and pediatric patients aged 12 years and older at the recommended dosage for CRSwNP (300 mg every 2 weeks).
Eosinophilic Esophagitis
In Study EoE-1, dupilumab pharmacokinetics were investigated in 35 pediatric subjects 12 to 17 years of age, weighing at least 40 kg, with EoE, receiving 300 mg QW. The mean ± SD steady-state trough concentration of dupilumab was 227±95.3 mcg/mL.
In Study EoE-2 Part A, dupilumab pharmacokinetics were investigated in 20 pediatric subjects 1 to 11 years of age with EoE receiving the following weight-based dosing regimens: ≥15 to <30 kg (200 mg Q2W) and ≥30 to <40 kg (300 mg Q2W). At Week 16, the mean ± SD steady-state trough concentration of dupilumab was 174±66.2 mcg/mL.
The systemic exposure in pediatric subjects 1 to 11 years of age with a body weight ≥40 kg receiving 300 mg QW is expected to be comparable to adult and pediatric subjects 12 years and older with a body weight ≥40 kg. The systemic exposure in pediatric subjects 12 to 17 years of age with a body weight <40 kg receiving 300 mg Q2W is expected to be comparable to pediatric subjects 6 to 11 years of age.
Chronic Spontaneous Urticaria
A total of 12 pediatric subjects 12 to 17 years of age with CSU were enrolled in CUPID. The observed steady-state trough concentrations of 6 pediatric subjects 12 to 17 years of age with CSU who received DUPIXENT 300 mg Q2W or 200 mg Q2W were within the range of steady-state trough concentrations in adult subjects with CSU who received DUPIXENT 300 mg Q2W.
Drug Interaction Studies
An effect of dupilumab on the PK of co-administered medications is not expected. Based on the population analysis, commonly co-administered medications had no effect on DUPIXENT pharmacokinetics in subjects with moderate-to-severe asthma.
Cytochrome P450 Substrates
The effects of dupilumab on the pharmacokinetics of midazolam (metabolized by CYP3A4), warfarin (metabolized by CYP2C9), omeprazole (metabolized by CYP2C19), metoprolol (metabolized by CYP2D6), and caffeine (metabolized by CYP1A2) were evaluated in a study with 12-13 evaluable subjects with AD (a SC loading dose of 600 mg followed by 300 mg SC weekly for six weeks). No clinically significant changes in AUC were observed. The largest effect was observed for metoprolol (CYP2D6) with an increase in AUC of 29%.
Immunogenicity
The observed incidence of anti-drug antibodies is highly dependent on the sensitivity and specificity of the assay. Differences in assay methods preclude meaningful comparisons of the incidence of anti-drug antibodies in the trials described below with the incidence of anti-drug antibodies in other trials, including those of DUPIXENT or of other dupilumab products.
The anti-drug antibody (ADA) and neutralizing antibody (NAb) incidence rates in subjects treated with DUPIXENT are presented in Table 15.
| Indication and Population | Dose and Duration of Treatment | Anti-drug Antibody (ADA) | Neutralizing Antibody NAb Neutralizing potential is assessed only for ADA-positive samples. The NAb incidence is reported as a percentage of subjects with treatment emergent ADA. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Treatment-Emergent ADA Treatment-emergent ADA: A negative result or missing result at baseline with at least 1 positive post-baseline result in the ADA assay. | Persistent ADA Persistent ADA: A treatment-emergent ADA positive response with 2 or more consecutive ADA positive samples separated by a greater than 12-week period (>84 days), with no ADA negative result in between. | |||
| Atopic Dermatitis | ||||
| Adult | 300 mg Q2W for 52 weeks | 6/105 (6%) | 2/105 (2%) | 1/6 (17%) |
| 12 to 17 years of age | 300 mg or 200 mg Q2W for 16 weeks | 13/81 (16%) | 2/81 (3%) | 4/13 (31%) |
| 6 to 11 years of age | 200 mg Q2W or 300 mg Q4W for 16 weeks | 3/171 (2%) | 0/171 (0%) | 1/3 (33%) |
| 6 months to 5 years of age | 200 mg Q4W, or 300 mg Q4W for 16 weeks | 1/74 (1%) | 0/74 (0%) | 0/1 (0%) |
| Asthma | ||||
| Adult and 12 years of age or older | 300 mg Q2W for 52 weeks | 32/626 (5%) | 13/626 (2%) | 14/32 (44%) |
| 200 mg Q2W for 52 weeks | 58/625 (9%) | 26/625 (4%) | 27/58 (47%) | |
| 6 to 11 years of age | 100 mg Q2W or 200 mg Q2W up to 52 weeks | 17/269 (6%) | 9/269 (3%) | 6/17 (35%) |
| Chronic Rhinosinusitis with Nasal Polyps | ||||
| Adult | 300 mg Q2W for 52 weeks | 8/148 (5%) | 3/148 (2%) | 5/8 (63%) |
| Eosinophilic Esophagitis | ||||
| Adult and 12 years of age or older | 300 mg QW for 52 weeks | 1/108 (1%) | 0/108 (0%) | 0/1 (0%) |
| 1 to 11 years of age | 200 mg Q2W or 300 mg Q2W for 52 weeks Immunogenicity was reported on pooled data for pediatric subjects 1 to 11 years of age with EoE receiving SC dupilumab 100 mg Q2W (in subjects weighing ≥5 kg to <15kg), 200 mg Q2W (in subjects weighing ≥15 kg to <30 kg), 300 mg Q2W (in subjects weighing ≥30 kg to <60 kg), and 300 mg QW (in subjects weighing ≥60 kg). | 1/37 (3%) | 0/37 (0%) | 0/1 (0%) One subject 1 to 11 years of age with EoE with pre-existing immunoreactivity that was positive for neutralizing antibodies was excluded from the NAb positive subjects. |
| Prurigo Nodularis | ||||
| Adult | 300 mg Q2W for 24 weeks | 11/143 (8%) | 2/143 (1%) | 4/11 (36%) |
| Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease | ||||
| Adult | 300 mg Q2W for 52 weeks | 77/922 (8%) | 24/922 (3%) | 28/77 (36%) |
| Chronic Spontaneous Urticaria | ||||
| Adult and 12 years of age or older | 200 mg Q2W or 300 mg Q2W through 24 weeks | 9/193 (5%) | 1/193 (1%) | 2/9 (22%) |
| Bullous Pemphigoid | ||||
| Adult | 300 mg Q2W up to 52 weeks | 2/52 (4%) | 0/52 (0%) | 2/2 (100%) |
Two adult subjects with AD who experienced high titer antibody responses developed serum sickness or serum sickness-like reactions during DUPIXENT therapy [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) ] .
The antibody titers detected in subjects who received DUPIXENT were mostly low. In subjects who received DUPIXENT, development of high titer antibodies to DUPIXENT was associated with lower serum dupilumab concentrations [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) ] .
NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Animal studies have not been conducted to evaluate the carcinogenic or mutagenic potential of dupilumab.
No effects on fertility parameters such as reproductive organs, menstrual cycle length, or sperm analysis were observed in sexually mature mice that were subcutaneously administered a homologous antibody against IL-4Rα at doses up to 200 mg/kg/week.
CLINICAL STUDIES
Atopic Dermatitis
Adults with Atopic Dermatitis
Three randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trials (SOLO 1 (NCT02277743), SOLO 2 (NCT02277769), and CHRONOS (NCT02260986)) enrolled a total of 2119 adult subjects with moderate-to-severe AD not adequately controlled by topical medication(s). Disease severity was defined by an Investigator's Global Assessment (IGA) score ≥3 in the overall assessment of AD lesions on a severity scale of 0 to 4, an Eczema Area and Severity Index (EASI) score ≥16 on a scale of 0 to 72, and a minimum body surface area involvement of ≥10%. At baseline, the mean age of subjects was 38 years; 59% of subjects were male, 67% were White, 24% were Asian, and 6% were Black; 52% of subjects had a baseline IGA score of 3 (moderate AD), and 48% of subjects had a baseline IGA of 4 (severe AD). The baseline mean EASI score was 33 and the baseline weekly averaged Peak Pruritus Numeric Rating Scale (NRS) was 7 on a scale of 0-10.
In all three trials, subjects in the DUPIXENT group received subcutaneous injections of DUPIXENT 600 mg at Week 0, followed by 300 mg every 2 weeks (Q2W). In the monotherapy trials (SOLO 1 and SOLO 2), subjects received DUPIXENT or placebo for 16 weeks.
In the concomitant therapy trial (CHRONOS), subjects received DUPIXENT or placebo with concomitant topical corticosteroids (TCS) and as needed topical calcineurin inhibitors for problem areas only, such as the face, neck, intertriginous and genital areas for 52 weeks.
All three trials assessed the primary endpoint, the change from baseline to Week 16 in the proportion of subjects with an IGA 0 (clear) or 1 (almost clear) and at least a 2-point improvement. Other endpoints included the proportion of subjects with EASI-75 (improvement of at least 75% in EASI score from baseline), and reduction in itch as defined by at least a 4-point improvement in the Peak Pruritus NRS from baseline to Week 16.
Clinical Response at Week 16 (SOLO 1, SOLO 2, and CHRONOS)
The results of the DUPIXENT monotherapy trials (SOLO 1 and SOLO 2) and the DUPIXENT with concomitant TCS trial (CHRONOS) are presented in Table 16.
| SOLO 1 | SOLO 2 | CHRONOS | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DUPIXENT 300 mg Q2W | Placebo | DUPIXENT 300 mg Q2W | Placebo | DUPIXENT 300 mg Q2W + TCS | Placebo + TCS | |
| Number of subjects randomized (FAS) Full Analysis Set (FAS) includes all subjects randomized. | 224 | 224 | 233 | 236 | 106 | 315 |
| IGA 0 or 1 Responder was defined as a subject with an IGA 0 or 1 ("clear" or "almost clear") and a reduction of ≥2 points on a 0-4 IGA scale. , Subjects who received rescue treatment or with missing data were considered as non-responders. | 38% | 10% | 36% | 9% | 39% | 12% |
| EASI-75 | 51% | 15% | 44% | 12% | 69% | 23% |
| EASI-90 | 36% | 8% | 30% | 7% | 40% | 11% |
| Number of subjects with baseline Peak Pruritus NRS score ≥4 | 213 | 212 | 225 | 221 | 102 | 299 |
| Peak Pruritus NRS (≥4-point improvement) | 41% | 12% | 36% | 10% | 59% | 20% |
| Figure 1: Proportion of Adult Subjects with Moderate-to-Severe AD with ≥4-point Improvement on the Peak Pruritus NRS in SOLO 1 In the primary analyses of the efficacy endpoints, subjects who received rescue treatment or with missing data were considered non-responders. and SOLO 2Studies (FAS) Full Analysis Set (FAS) includes all subjects randomized. | |
|---|---|
| SOLO 1 | SOLO 2 |
 | |
In CHRONOS, of the 421 subjects, 353 had been on study for 52 weeks at the time of data analysis. Of these 353 subjects, responders at Week 52 represent a mixture of subjects who maintained their efficacy from Week 16 (e.g., 53% of DUPIXENT IGA 0 or 1 responders at Week 16 remained responders at Week 52) and subjects who were non-responders at Week 16 who later responded to treatment (e.g., 24% of DUPIXENT IGA 0 or 1 non-responders at Week 16 became responders at Week 52). Results of supportive analyses of the 353 subjects in the DUPIXENT with concomitant TCS trial (CHRONOS) are presented in Table 17.
| DUPIXENT 300 mg Q2W + TCS | Placebo + TCS | |
|---|---|---|
| Number of Subjects In CHRONOS, of the 421 randomized and treated subjects, 68 subjects (16%) had not been on study for 52 weeks at the time of data analysis. | 89 | 264 |
| Responder Responder was defined as a subject with an IGA 0 or 1 ("clear" or "almost clear") and a reduction of ≥2 points on a 0-4 IGA scale. , Subjects who received rescue treatment or with missing data were considered as non-responders. at Week 16 and 52 | 22% | 7% |
| Responder at Week 16 but Non-responder at Week 52 | 20% | 7% |
| Non-responder at Week 16 and Responder at Week 52 | 13% | 6% |
| Non-responder at Week 16 and 52 | 44% | 80% |
| Overall Responder , Rate at Week 52 | 36% | 13% |
Treatment effects in subgroups (weight, age, gender, race, and prior treatment, including immunosuppressants) in SOLO 1, SOLO 2, and CHRONOS were generally consistent with the results in the overall study population.
In SOLO 1, SOLO 2, and CHRONOS, a third randomized treatment arm of DUPIXENT 300 mg QW did not demonstrate additional treatment benefit over DUPIXENT 300 mg Q2W.
Subjects in SOLO 1 and SOLO 2 who had an IGA 0 or 1 with a reduction of ≥2 points were re-randomized into SOLO CONTINUE (NCT02395133). SOLO CONTINUE evaluated multiple DUPIXENT monotherapy dose regimens for maintaining treatment response. The study included subjects randomized to continue with DUPIXENT 300 mg Q2W (62 subjects) or switch to placebo (31 subjects) for 36 weeks. IGA 0 or 1 responses at Week 36 were as follows: 33 (53%) in the Q2W group and 3 (10%) in the placebo group.
Pediatric Subjects 12 Years of Age and Older with Atopic Dermatitis
The efficacy of DUPIXENT monotherapy in pediatric subjects 12 years of age and older was evaluated in a multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial (AD-1526; NCT03054428) in 251 pediatric subjects 12 to 17 years of age, with moderate-to-severe AD defined by an IGA score ≥3 (scale of 0 to 4), an EASI score ≥16 (scale of 0 to 72), and a minimum BSA involvement of ≥10%. Eligible subjects enrolled into this trial had previous inadequate response to topical medication.
Subjects in the DUPIXENT group with baseline weight of <60 kg received an initial dose of 400 mg at Week 0, followed by 200 mg Q2W for 16 weeks. Subjects with baseline weight of ≥60 kg received an initial dose of 600 mg at Week 0, followed by 300 mg Q2W for 16 weeks. Subjects were permitted to receive rescue treatment at the discretion of the investigator. Subjects who received rescue treatment were considered non-responders.
In AD-1526, the mean age was 14.5 years, the median weight was 59.4 kg, 41% of subjects were female, 63% were White, 15% were Asian, and 12% were Black. At baseline, 46% of subjects had an IGA score of 3 (moderate AD), 54% had an IGA score of 4 (severe AD), the mean BSA involvement was 57%, and 42% had received prior systemic immunosuppressants. Also, at baseline, the mean EASI score was 36, and the weekly averaged Peak Pruritus NRS was 8 on a scale of 0-10. Overall, 92% of subjects had at least one co-morbid allergic condition; 66% had allergic rhinitis, 54% had asthma, and 61% had food allergies.
The primary endpoint was the proportion of subjects with an IGA 0 (clear) or 1 (almost clear) and at least a 2-point improvement from baseline to Week 16. Other evaluated outcomes included the proportion of subjects with EASI-75 or EASI-90 (improvement of at least 75% or 90% in EASI from baseline, respectively), and reduction in itch as measured by the Peak Pruritus NRS (≥4-point improvement).
The efficacy results at Week 16 for AD-1526 are presented in Table 18.
| DUPIXENT At Week 0, subjects received 400 mg (baseline weight <60 kg) or 600 mg (baseline weight ≥60 kg) of DUPIXENT. 200 mg (<60 kg) or 300 mg (≥60 kg) Q2W N=82 | Placebo N=85 | |
|---|---|---|
| IGA 0 or 1 Responder was defined as a subject with an IGA 0 or 1 ("clear" or "almost clear") and a reduction of ≥2 points on a 0-4 IGA scale. , Subjects who received rescue treatment or with missing data were considered as non-responders (59% and 21% in the placebo and DUPIXENT arms, respectively). | 24% | 2% |
| EASI-75 | 42% | 8% |
| EASI-90 | 23% | 2% |
| Peak Pruritus NRS (≥4-point improvement) | 37% | 5% |
A greater proportion of subjects randomized to DUPIXENT achieved an improvement in the Peak Pruritus NRS compared to placebo (defined as ≥4-point improvement at Week 4). See Figure 2 .
| Figure 2: Proportion of Pediatric Subjects 12 Years of Age and Older with Moderate-to-Severe AD with ≥4-point Improvement on the Peak Pruritus NRS in AD-1526 In the primary analyses of the efficacy endpoints, subjects who received rescue treatment or with missing data were considered non-responders. (FAS) Full Analysis Set (FAS) includes all subjects randomized. |
|---|
 |
Pediatric Subjects 6 to 11 Years of Age with Atopic Dermatitis
The efficacy and safety of DUPIXENT use concomitantly with TCS in pediatric subjects was evaluated in a multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial (AD-1652; NCT03345914) in 367 subjects 6 to 11 years of age, with AD defined by an IGA score of 4 (scale of 0 to 4), an EASI score ≥21 (scale of 0 to 72), and a minimum BSA involvement of ≥15%. Eligible subjects enrolled into this trial had previous inadequate response to topical medication. Enrollment was stratified by baseline weight (<30 kg; ≥30 kg).
Subjects in the DUPIXENT Q4W + TCS group received an initial dose of 600 mg on Day 1, followed by 300 mg Q4W from Week 4 to Week 12, regardless of weight. Subjects in the DUPIXENT Q2W + TCS group with baseline weight of <30 kg received an initial dose of 200 mg on Day 1, followed by 100 mg Q2W from Week 2 to Week 14, and subjects with baseline weight of ≥30 kg received an initial dose of 400 mg on Day 1, followed by 200 mg Q2W from Week 2 to Week 14. Subjects were permitted to receive rescue treatment at the discretion of the investigator. Subjects who received rescue treatment were considered non-responders.
In AD-1652, the mean age was 8.5 years, the median weight was 29.8 kg, 50% of subjects were female, 69% were White, 17% were Black, and 8% were Asian. At baseline, the mean BSA involvement was 58%, and 17% had received prior systemic non-steroidal immunosuppressants. Also, at baseline the mean EASI score was 37.9, and the weekly average of daily worst itch score was 7.8 on a scale of 0-10. Overall, 92% of subjects had at least one co-morbid allergic condition; 64% had food allergies, 63% had other allergies, 60% had allergic rhinitis, and 47% had asthma.
The primary endpoint was the proportion of subjects with an IGA 0 (clear) or 1 (almost clear) at Week 16. Other evaluated outcomes included the proportion of subjects with EASI-75 or EASI-90 (improvement of at least 75% or 90% in EASI from baseline, respectively), and reduction in itch as measured by the Peak Pruritus NRS (≥4-point improvement).
Table 19 presents the results by baseline weight strata for the approved dose regimens.
| DUPIXENT 300 mg Q4W At Day 1, subjects received 600 mg of DUPIXENT. + TCS | Placebo + TCS | DUPIXENT 200 mg Q2W At Day 1, subjects received 200 mg (baseline weight <30 kg) or 400 mg (baseline weight ≥30 kg) of DUPIXENT. + TCS | Placebo + TCS | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (N=61) | (N=61) | (N=59) | (N=62) | |
| <30 kg | <30 kg | ≥30 kg | ≥30 kg | |
| IGA 0 or 1 Responder was defined as a subject with an IGA 0 or 1 ("clear" or "almost clear"). , Subjects who received rescue treatment or with missing data were considered as non-responders. | 30% | 13% | 39% | 10% |
| EASI-75 | 75% | 28% | 75% | 26% |
| EASI-90 | 46% | 7% | 36% | 8% |
| Peak Pruritus NRS (≥4-point improvement) | 54% | 12% | 61% | 13% |
A greater proportion of subjects randomized to DUPIXENT + TCS achieved an improvement in the Peak Pruritus NRS compared to placebo + TCS (defined as ≥4-point improvement at Week 16). See Figure 3 .
| Figure 3: Proportion of Pediatric Subjects 6 to 11 Years of Age with AD with ≥4-point Improvement on the Peak Pruritus NRS at Week 16 in AD-1652 In the primary analyses of the efficacy endpoints, subjects who received rescue treatment or with missing data were considered non-responders. (FAS) Full Analysis Set (FAS) includes all subjects randomized. |
|---|
 |
Pediatric Subjects 6 Months to 5 Years of Age with Atopic Dermatitis
The efficacy and safety of DUPIXENT use concomitantly with TCS in pediatric subjects was evaluated in a multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial (AD-1539; NCT03346434) in 162 subjects 6 months to 5 years of age, with moderate-to-severe AD defined by an IGA score ≥3 (scale of 0 to 4), an EASI score ≥16 (scale of 0 to 72), and a minimum BSA involvement of ≥10%. Eligible subjects enrolled into this trial had previous inadequate response to topical medication. Enrollment was stratified by baseline weight (≥5 to <15 kg and ≥15 to <30 kg).
Subjects in the DUPIXENT Q4W + TCS group with baseline weight of ≥5 to <15 kg received an initial dose of 200 mg on Day 1, followed by 200 mg Q4W from Week 4 to Week 12, and subjects with baseline weight of ≥15 to <30 kg received an initial dose of 300 mg on Day 1, followed by 300 mg Q4W from Week 4 to Week 12. Subjects were permitted to receive rescue treatment at the discretion of the investigator. Subjects who received rescue treatment were considered non-responders.
In AD-1539, the mean age was 3.8 years, the median weight was 16.5 kg, 39% of subjects were female, 69% were White, 19% were Black, and 6% were Asian. At baseline, the mean BSA involvement was 58%, and 29% of subjects had received prior systemic immunosuppressants. Also, at baseline the mean EASI score was 34.1, and the weekly average of daily worst scratch/itch score was 7.6 on a scale of 0-10. Overall, 81.4% of subjects had at least one co-morbid allergic condition; 68.3% had food allergies, 52.8% had other allergies, 44.1% had allergic rhinitis, and 25.5% had asthma.
The primary endpoint was the proportion of subjects with an IGA 0 (clear) or 1 (almost clear) at Week 16. Other evaluated outcomes included the proportion of subjects with EASI-75 or EASI-90 (improvement of at least 75% or 90% in EASI from baseline, respectively), and reduction in itch as measured by the Worst Scratch/Itch NRS (≥4-point improvement).
The efficacy results at Week 16 for AD-1539 are presented in Table 20.
| DUPIXENT + TCS 200 mg (5 to <15 kg) or 300 mg (15 to <30 kg) Q4W At Day 1, subjects received 200 mg (5 to <15 kg) or 300 mg (15 to <30 kg) of DUPIXENT. | Placebo + TCS | Difference vs. Placebo (95 % CI) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| (N=83) | (N=79) | ||
| CI = confidence interval | |||
| IGA 0 or 1 Responder was defined as a subject with an IGA 0 or 1 ("clear" or "almost clear"). , Subjects who received rescue treatment (63% and 19% in the placebo and DUPIXENT arms, respectively) or with missing data were considered as non-responders. | 28% | 4% | 24% (13%, 34%) |
| EASI-75 | 53% | 11% | 42% (29%, 55%) |
| EASI-90 | 25% | 3% | 23% (12%, 33%) |
| Worst Scratch/Itch NRS (≥4-point improvement) | 48% | 9% | 39% (26%, 52%) |
Atopic Dermatitis with Hand and/or Foot Involvement
The efficacy and safety of DUPIXENT was evaluated in a 16-week, multicenter, randomized, double-blind, parallel-group, placebo-controlled trial (Liberty-AD-HAFT; NCT04417894) in 133 adult and pediatric subjects 12 to 17 years of age with atopic dermatitis with moderate-to-severe hand and/or foot involvement, defined by an established diagnosis of atopic dermatitis and screening to rule out irritant and allergic contact dermatitis through history and appropriate patch testing, and by an IGA (hand and foot) score ≥3 (scale of 0 to 4) and a hand and foot Peak Pruritus Numeric Rating Scale (NRS) score for maximum itch intensity ≥4 (scale of 0 to 10). Fifty-three (53) percent (N=70/133) of the subjects also had moderate-to-severe AD outside of the hands or feet (IGA global ≥3). Eligible subjects had previous inadequate response or intolerance to treatment of hand and/or foot dermatitis with topical AD medications. In this trial 67 subjects received DUPIXENT, and 66 subjects received placebo. DUPIXENT-treated subjects received the recommended dosage based on their age and body weight [see Dosage and Administration (2.3) ] . Subjects were not allowed concomitant use of topical treatments for AD on the hands and feet during the trial, but were allowed the use of topical treatments for AD on other parts of the body with certain restrictions.
In Liberty-AD-HAFT, 38% of subjects were male, 80% were White, 13% were Asian, and 5% were Black or African American. For ethnicity, 4% were identified as Hispanic or Latino and 96% were identified as not Hispanic or Latino. Seventy-two (72) percent (N=96/133) of subjects had a baseline IGA (hand and foot) score of 3 (atopic dermatitis with moderate hand and/or foot involvement), and 28% (N=37/133) of subjects had a baseline IGA (hand and foot) score of 4 (atopic dermatitis with severe hand and/or foot involvement). The baseline weekly averaged hand and foot Peak Pruritus NRS score was 7.1.
The primary endpoint was the proportion of subjects with an IGA hand and foot score of 0 (clear) or 1 (almost clear) at Week 16. The key secondary endpoint was reduction of itch as measured by the hand and foot Peak Pruritus NRS (≥4-point improvement).
The efficacy results at Week 16 for Liberty-AD-HAFT are presented in Table 21.
| DUPIXENT 200/300 mg Q2W Adults received a loading dose of DUPIXENT 600 mg SC followed by 300 mg SC Q2W. Pediatric subjects 12 to 17 years of age received a loading dose of DUPIXENT 600 mg SC followed by 300 mg SC Q2W (for body weight ≥60 kg) or a loading dose of DUPIXENT 400 mg SC followed by 200 mg SC Q2W (for body weight <60 kg). | Placebo | Difference vs. Placebo (95 % CI) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| (N=67) | (N=66) | ||
| CI = confidence interval | |||
| IGA (hand and foot) 0 or 1 Responder was defined as a subject with an IGA 0 or 1 ("clear" or "almost clear"). , Subjects who received rescue treatment (21% and 3% in the placebo and DUPIXENT arms, respectively) or with missing data were considered as non-responders. | 40% | 17% | 24% (9%, 38%) |
| Improvement (reduction) of weekly averaged hand and foot Peak Pruritus NRS ≥4 | 52% | 14% | 39% (24%, 53%) |
Asthma
The asthma development program for patients aged 12 years and older included three randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group, multicenter trials (DRI12544 (NCT01854047), QUEST (NCT02414854), and VENTURE (NCT02528214)) of 24 to 52 weeks in treatment duration which enrolled a total of 2888 subjects. Subjects enrolled in DRI12544 and QUEST were required to have a history of 1 or more asthma exacerbations that required treatment with systemic corticosteroids or emergency department visit or hospitalization for the treatment of asthma in the year prior to trial entry. Subjects enrolled in VENTURE required dependence on daily oral corticosteroids in addition to regular use of high-dose inhaled corticosteroids plus an additional controller(s). In all 3 trials, subjects were enrolled without requiring a minimum baseline blood eosinophil count. In QUEST and VENTURE, subjects with screening blood eosinophil level of >1500 cells/mcL (<1.3%) were excluded. DUPIXENT was administered as add-on to background asthma treatment. Subjects continued background asthma therapy throughout the duration of the studies, except in VENTURE in which OCS dose was tapered as described below.
DRI12544
DRI12544 was a 24-week dose-ranging study which included 776 adult subjects (18 years of age and older). DUPIXENT compared with placebo was evaluated in adult subjects with moderate-to-severe asthma on a medium or high-dose inhaled corticosteroid and a long acting beta agonist. Subjects were randomized to receive either 200 mg (N=150) or 300 mg (N=157) DUPIXENT every 2 weeks (Q2W) or 200 mg (N=154) or 300 mg (N=157) DUPIXENT every 4 weeks following an initial dose of 400 mg, 600 mg or placebo (N=158), respectively. The primary endpoint was mean change from baseline to Week 12 in FEV 1 (L) in subjects with baseline blood eosinophils ≥300 cells/mcL. Other endpoints included percent change from baseline in FEV 1 and annualized rate of severe asthma exacerbation events during the 24-week placebo-controlled treatment period. Results were evaluated in the overall population and subgroups based on baseline blood eosinophil count (≥300 cells/mcL and <300 cells/mcL). Additional secondary endpoints included responder rates in the patient reported Asthma Control Questionnaire (ACQ-5) and Asthma Quality of Life Questionnaire, Standardized Version (AQLQ(S)) scores.
QUEST
QUEST was a 52-week study which included 1902 adult and pediatric subjects (12 years of age and older). DUPIXENT compared with placebo was evaluated in 107 pediatric subjects 12 to 17 years of age and 1795 adult subjects with moderate-to-severe asthma on a medium or high-dose inhaled corticosteroid (ICS) and a minimum of one and up to two additional controller medications. Subjects were randomized to receive either 200 mg (N=631) or 300 mg (N=633) DUPIXENT Q2W (or matching placebo for either 200 mg [N=317] or 300 mg [N=321] Q2W) following an initial dose of 400 mg, 600 mg or placebo, respectively. The primary endpoints were the annualized rate of severe exacerbation events during the 52-week placebo-controlled period and change from baseline in pre-bronchodilator FEV 1 at Week 12 in the overall population (unrestricted by minimum baseline blood eosinophils count). Additional secondary endpoints included annualized severe exacerbation rates and FEV 1 in subjects with different baseline levels of blood eosinophils as well as responder rates in the ACQ-5 and AQLQ(S) scores.
VENTURE
VENTURE was a 24-week oral corticosteroid-reduction study in 210 adult and pediatric subjects 15 years of age and older with asthma who required daily oral corticosteroids in addition to regular use of high dose inhaled corticosteroids plus an additional controller. After optimizing the OCS dose during the screening period, subjects received 300 mg DUPIXENT (N=103) or placebo (N=107) once Q2W for 24 weeks following an initial dose of 600 mg or placebo. Subjects continued to receive their existing asthma medicine during the study; however, their OCS dose was reduced every 4 weeks during the OCS reduction phase (Week 4-20), as long as asthma control was maintained. The primary endpoint was the percent reduction of oral corticosteroid dose at Weeks 20 to 24 compared with the baseline dose, while maintaining asthma control in the overall population (unrestricted by minimum baseline blood eosinophils count). Additional secondary endpoints included the annualized rate of severe exacerbation events during treatment period and responder rate in the ACQ-5 and AQLQ(S) scores.
The demographics and baseline characteristics of these 3 trials are provided in Table 22 below.
| Parameter | DRI12544 (N=776) | QUEST (N=1902) | VENTURE (N=210) |
|---|---|---|---|
| ICS = inhaled corticosteroid; FEV 1 = Forced expiratory volume in 1 second; AD = atopic dermatitis; NP = nasal polyps; AR = allergic rhinitis; FeNO = fraction of exhaled nitric oxide | |||
| Mean age (years) (SD) | 49 (13) | 48 (15) | 51 (13) |
| % Female | 63 | 63 | 61 |
| % White | 78 | 83 | 94 |
| Duration of Asthma (years), mean (± SD) | 22 (15) | 21 (15) | 20 (14) |
| Never smoked (%) | 77 | 81 | 81 |
| Mean exacerbations in previous year (± SD) | 2.2 (2.1) | 2.1 (2.2) | 2.1 (2.2) |
| High dose ICS use (%) | 50 | 52 | 89 |
| Pre-dose FEV 1 (L) at baseline (± SD) | 1.84 (0.54) | 1.78 (0.60) | 1.58 (0.57) |
| Mean percent predicted FEV 1 at baseline (%) (± SD) | 61 (11) | 58 (14) | 52 (15) |
| % Reversibility (± SD) | 27 (15) | 26 (22) | 19 (23) |
| Atopic Medical History % Overall (AD %, NP %, AR %) | 73 (8, 11, 62) | 78 (10, 13, 69) | 72 (8, 21, 56) |
| Mean FeNO ppb (± SD) | 39 (35) | 35 (33) | 38 (31) |
| Mean total IgE IU/mL ( ± SD) | 435 (754) | 432 (747) | 431 (776) |
| Mean baseline blood Eosinophil count (± SD) cells/mcL | 350 (430) | 360 (370) | 350 (310) |
Exacerbations in Subjects with Asthma
DRI12544 and QUEST evaluated the frequency of severe asthma exacerbations defined as deterioration of asthma requiring the use of systemic corticosteroids for at least 3 days or hospitalization or emergency room visit due to asthma that required systemic corticosteroids. In the primary analysis population (subjects with baseline blood eosinophil count of ≥300 cells/mcL in DRI12544 and the overall population in QUEST), subjects receiving either DUPIXENT 200 mg or 300 mg Q2W had significant reductions in the rate of asthma exacerbations compared to placebo. In the overall population in QUEST, the rate of severe exacerbations was 0.46 and 0.52 for DUPIXENT 200 mg Q2W and 300 mg Q2W, respectively, compared to matched placebo rates of 0.87 and 0.97. The rate ratio of severe exacerbations compared to placebo was 0.52 (95% CI: 0.41, 0.66) and 0.54 (95% CI: 0.43, 0.68) for DUPIXENT 200 mg Q2W and 300 mg Q2W, respectively. Results in subjects with baseline blood eosinophil counts ≥300 cells/mcL in DRI12544 and QUEST are shown in Table 23.
Response rates by baseline blood eosinophils and baseline FeNO for QUEST are shown for the overall population in Figure 4 and Figure 5, respectively. Elevation of FeNO can be a marker of the eosinophilic asthma phenotype when supported by clinical data. Pre-specified subgroup analyses of DRI12544 and QUEST demonstrated that there were greater reductions in severe exacerbations in subjects with higher baseline blood eosinophil levels (≥150 cells/mcL) or FeNO (≥25 ppb). In QUEST, reductions in exacerbations were significant in the subgroup of subjects with baseline blood eosinophils ≥150 cells/mcL. In subjects with baseline blood eosinophil count <150 cells/mcL and FeNO <25 ppb, similar severe exacerbation rates were observed between DUPIXENT and placebo.
In QUEST, the estimated rate ratio of exacerbations leading to hospitalizations and/or emergency room visits versus placebo was 0.53 (95% CI: 0.28, 1.03) and 0.74 (95% CI: 0.32, 1.70) with DUPIXENT 200 mg or 300 mg Q2W, respectively.
| Trial | Treatment | Baseline Blood EOS ≥300 cells/mcL (primary analysis population, DRI12544) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | Rate (95% CI) | Rate Ratio (95% CI) | ||
| DRI12544 | DUPIXENT 200 mg Q2W | 65 | 0.30 (0.13, 0.68) | 0.29 (0.11, 0.76) |
| DUPIXENT 300 mg Q2W | 64 | 0.20 (0.08, 0.52) | 0.19 (0.07, 0.56) | |
| Placebo | 68 | 1.04 (0.57, 1.90) | ||
| QUEST | DUPIXENT 200 mg Q2W | 264 | 0.37 (0.29, 0.48) | 0.34 (0.24, 0.48) |
| Placebo | 148 | 1.08 (0.85, 1.38) | ||
| DUPIXENT 300 mg Q2W | 277 | 0.40 (0.32, 0.51) | 0.33 (0.23, 0.45) | |
| Placebo | 142 | 1.24 (0.97, 1.57) | ||
Figure 4: Relative Risk in Annualized Event Rate of Severe Exacerbations across Baseline Blood Eosinophil Count (cells/mcL) in Subjects with Moderate-to-Severe Asthma (QUEST)

Figure 5: Relative Risk in Annualized Event Rate of Severe Exacerbations across Baseline FeNO Group (ppb) in Subjects with Moderate-to-Severe Asthma (QUEST)

The time to first exacerbation was longer for the subjects receiving DUPIXENT compared to placebo in QUEST (Figure 6).
| Figure 6: Kaplan Meier Incidence Curve for Time to First Severe Exacerbation in Subjects with Moderate-to-Severe Asthma with Baseline Blood Eosinophils ≥300 cells/mcL (QUEST) At the time of the database lock, not all subjects had completed Week 52 |
|---|
 |
Lung Function in Subjects with Asthma
Significant increases in pre-bronchodilator FEV 1 were observed at Week 12 for DRI12544 and QUEST in the primary analysis populations (subjects with baseline blood eosinophil count of ≥300 cells/mcL in DRI12544 and the overall population in QUEST). In the overall population in QUEST, the FEV 1 LS mean change from baseline was 0.32 L (21%) and 0.34 L (23%) for DUPIXENT 200 mg Q2W and 300 mg Q2W, respectively, compared to matched placebo means of 0.18 L (12%) and 0.21 L (14%). The mean treatment difference versus placebo was 0.14 L (95% CI: 0.08, 0.19) and 0.13 L (95% CI: 0.08, 0.18) for DUPIXENT 200 mg Q2W and 300 mg Q2W, respectively. Results in subjects with baseline blood eosinophil counts ≥300 cells/mcL in DRI12544 and QUEST are shown in Table 24.
Improvements in FEV 1 by baseline blood eosinophils and baseline FeNO for QUEST are shown in Figure 7 and 8, respectively. Subgroup analysis of DRI12544 and QUEST demonstrated greater improvement in subjects with higher baseline blood eosinophils (≥150 cells/mcL) or FeNO (≥25 ppb). In subjects with baseline blood eosinophil count <150 cells/mcL and FeNO <25 ppb, similar differences in FEV 1 were observed between DUPIXENT and placebo.
Mean changes in FEV 1 over time in QUEST are shown in Figure 9.
| Trial | Treatment | Baseline Blood EOS ≥300 cells/mcL (primary analysis population, DRI12544) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | LS Mean Change from baseline L (%) | LS Mean Difference vs. placebo (95% CI) | ||
| DRI12544 | DUPIXENT 200 mg Q2W | 65 | 0.43 (25.9) | 0.26 (0.11, 0.40) |
| DUPIXENT 300 mg Q2W | 64 | 0.39 (25.8) | 0.21 (0.06, 0.36) | |
| Placebo | 68 | 0.18 (10.2) | ||
| QUEST | DUPIXENT 200 mg Q2W | 264 | 0.43 (29.0) | 0.21 (0.13, 0.29) |
| Placebo | 148 | 0.21 (15.6) | ||
| DUPIXENT 300 mg Q2W | 277 | 0.47 (32.5) | 0.24 (0.16, 0.32) | |
| Placebo | 142 | 0.22 (14.4) | ||
Figure 7: LS Mean Difference in Change from Baseline vs Placebo to Week 12 in Pre-Bronchodilator FEV 1 across Baseline Blood Eosinophil Counts (cells/mcL) in Subjects with Moderate-to-Severe Asthma (QUEST)

Figure 8: LS Mean Difference in Change from Baseline vs Placebo to Week 12 in Pre-bronchodilator FEV 1 across Baseline FeNO (ppb) in Subjects with Moderate-to-Severe Asthma (QUEST)

Figure 9: Mean Change from Baseline in Pre-Bronchodilator FEV 1 (L) Over Time in Subjects with Moderate-to-Severe Asthma with Baseline Blood Eosinophils ≥300 cells/mcL (QUEST)

Additional Secondary Endpoints in Asthma Trial (QUEST)
ACQ-5 and AQLQ(S) were assessed in QUEST at 52 weeks. The responder rate was defined as an improvement in score of 0.5 or more (scale range 0-6 for ACQ-5 and 1-7 for AQLQ(S)).
- The ACQ-5 responder rate for DUPIXENT 200 mg and 300 mg Q2W in the overall population was 69% vs 62% placebo (odds ratio 1.37; 95% CI: 1.01, 1.86) and 69% vs 63% placebo (odds ratio 1.28; 95% CI: 0.94, 1.73), respectively; and the AQLQ(S) responder rates were 62% vs 54% placebo (odds ratio 1.61; 95% CI: 1.17, 2.21) and 62% vs 57% placebo (odds ratio 1.33; 95% CI: 0.98, 1.81), respectively.
- The ACQ-5 responder rate for DUPIXENT 200 mg and 300 mg Q2W in subjects with baseline blood eosinophils ≥300 cells/mcL was 75% vs 67% placebo (odds ratio: 1.46; 95% CI: 0.90, 2.35) and 71% vs 64% placebo (odds ratio: 1.39; 95% CI: 0.88, 2.19), respectively; and the AQLQ(S) responder rates were 71% vs 55% placebo (odds ratio: 2.02; 95% CI: 1.24, 3.32) and 65% vs 55% placebo (odds ratio: 1.79; 95% CI: 1.13, 2.85), respectively.
Oral Corticosteroid Reduction in Asthma Trial (VENTURE)
VENTURE evaluated the effect of DUPIXENT on reducing the use of maintenance oral corticosteroids. The baseline mean oral corticosteroid dose was 12 mg in the placebo group and 11 mg in the group receiving DUPIXENT. The primary endpoint was the percent reduction from baseline of the final oral corticosteroid dose at Week 24 while maintaining asthma control.
Compared with placebo, subjects receiving DUPIXENT achieved greater reductions in daily maintenance oral corticosteroid dose, while maintaining asthma control. The mean percent reduction in daily OCS dose from baseline was 70% (median 100%) in subjects receiving DUPIXENT (95% CI: 60%, 80%) compared to 42% (median 50%) in subjects receiving placebo (95% CI: 33%, 51%). Reductions of 50% or higher in the OCS dose were observed in 82 (80%) subjects receiving DUPIXENT compared to 57 (53%) in those receiving placebo. The proportion of subjects with a mean final dose less than 5 mg at Week 24 was 72% for DUPIXENT and 37% for placebo (odds ratio 4.48 95% CI: 2.39, 8.39). A total of 54 (52%) subjects receiving DUPIXENT versus 31 (29%) subjects in the placebo group had a 100% reduction in their OCS dose.
In this 24-week trial, asthma exacerbations (defined as a temporary increase in oral corticosteroid dose for at least 3 days) were lower in subjects receiving DUPIXENT compared with those receiving placebo (annualized rate 0.65 and 1.60 for the DUPIXENT and placebo group, respectively; rate ratio 0.41 [95% CI 0.26, 0.63]) and improvement in pre-bronchodilator FEV 1 from baseline to Week 24 was greater in subjects receiving DUPIXENT compared with those receiving placebo (LS mean difference for DUPIXENT versus placebo of 0.22 L [95% CI: 0.09 to 0.34 L]). Effects on lung function and on oral steroid and exacerbation reduction were similar irrespective of baseline blood eosinophil levels. The ACQ-5 and AQLQ(S) were also assessed in VENTURE and showed improvements similar to those in QUEST.
Pediatric Subjects 6 to 11 Years of Age with Asthma
The efficacy and safety of DUPIXENT in pediatric subjects was evaluated in a 52-week multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study (VOYAGE; NCT02948959) in 408 subjects 6 to 11 years of age, with moderate-to-severe asthma on a medium or high-dose ICS and a second controller medication or high-dose ICS alone. Subjects were required to have a history of 1 or more asthma exacerbation(s) that required treatment with systemic corticosteroids or emergency department visit or hospitalization for the treatment of asthma in the year prior to trial entry. Subjects were randomized to DUPIXENT (N=273) or matching placebo (N=135) every 2 weeks based on body weight <30 kg (100 mg Q2W) or ≥30 kg (200 mg Q2W). The effectiveness of DUPIXENT 300 mg Q4W was extrapolated from efficacy of 100 mg Q2W in VOYAGE with support from population pharmacokinetic analyses showing higher drug exposure levels with 300 mg Q4W [see Pediatric Use (8.4) and Pharmacokinetics (12.3) ] .
The primary endpoint was the annualized rate of severe asthma exacerbation events during the 52-week placebo-controlled period. Severe asthma exacerbations were defined as deterioration of asthma requiring the use of systemic corticosteroids for at least 3 days or hospitalization or emergency room visit due to asthma that required systemic corticosteroids. The key secondary endpoint was the change from baseline in pre-bronchodilator FEV 1 percent predicted at Week 12. Additional secondary endpoints included mean change from baseline and responder rates in the ACQ-7-IA (Asthma Control Questionnaire-7-Interviewer Administered) and PAQLQ(S)-IA (Pediatric Asthma Quality of Life Questionnaire with Standardized Activities Interviewer Administered) scores.
The demographics and baseline characteristics for VOYAGE are provided in Table 25 below.
| Parameter | VOYAGE (N=408) |
|---|---|
| ICS = inhaled corticosteroid; FEV 1 = Forced expiratory volume in 1 second; AD = atopic dermatitis; AR = allergic rhinitis; FeNO = fraction of exhaled nitric oxide | |
| Mean age (years) (SD) | 9 (2) |
| % Female | 36 |
| % White | 88 |
| Mean body weight (kg) | 36 |
| Mean exacerbations in previous year (± SD) | 2.4 (2.2) |
| High dose ICS use (%) | 44 |
| Pre-dose FEV 1 (L) at baseline (± SD) | 1.48 (0.41) |
| Mean percent predicted FEV 1 (%) (±SD) | 78 (15) |
| Mean % Reversibility (± SD) | 20 (21) |
| Atopic Medical History % Overall (AD %, AR %) | 92 (36, 82) |
| Mean FeNO ppb (± SD) | 28 (24) |
| % subjects with FeNO ppb ≥20 | 50 |
| Median total IgE IU/mL (±SD) | 792 (1093) |
| Mean baseline Eosinophil count (± SD) cells/mcL | 502 (395) |
DUPIXENT significantly reduced the annualized rate of severe asthma exacerbation events during the 52-week treatment period compared to placebo in populations with an eosinophilic phenotype as indicated by elevated blood eosinophils and/or the population with elevated FeNO. Subgroup analyses for results of DUPIXENT treatment based upon either baseline eosinophil level or baseline FeNO level were similar to the pediatric (12 to 17 years of age) and adult trials and are described for the adult and pediatric (12 to 17 years of age) asthma population above. In subjects with baseline blood eosinophil count <150 cells/mcL and FeNO <20 ppb, similar severe asthma exacerbation rates were observed between DUPIXENT and placebo.
Significant improvements in percent predicted pre-bronchodilator FEV 1 were observed at Week 12. Significant improvements in percent predicted FEV 1 were observed as early as Week 2 and were maintained through Week 52 in VOYAGE (Figure 10).
The efficacy results for VOYAGE are presented in Table 26.
| Treatment | EOS ≥300 cells/mcL This reflects the prespecified primary analysis population for VOYAGE in the United States. | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Annualized Severe Exacerbations Rate over 52 Weeks | |||
| N | Rate (95% CI) | Rate Ratio (95% CI) | |
| DUPIXENT 100 mg Q2W The effectiveness of DUPIXENT 300 mg Q4W was extrapolated from efficacy of 100 mg Q2W. (<30 kg)/ 200 mg Q2W (≥30 kg) | 175 | 0.24 (0.16, 0.35) | 0.35 (0.22, 0.56) |
| Placebo | 84 | 0.67 (0.47, 0.95) | |
| Mean Change from Baseline in Percent Predicted FEV 1 at Week 12 | |||
| N | LS mean Δ from Baseline | LS mean difference vs. Placebo (95% CI) | |
| DUPIXENT 100 mg Q2W(<30 kg)/ 200 mg Q2W (≥30 kg) | 168 | 10.15 | 5.32 (1.76, 8.88) |
| Placebo | 80 | 4.83 | |
Figure 10: Mean Change from Baseline in Percent Predicted Pre-bronchodilator FEV 1 (L) Over Time in Pediatric Subjects 6 to 11 Years of Age in VOYAGE (Baseline Blood Eosinophils ≥300 cells/mcL)

Improvements were also observed for ACQ-7-IA and PAQLQ(S)-IA at Week 24 and were sustained at Week 52. Greater responder rates were observed for ACQ-7-IA and PAQLQ(S)-IA compared to placebo at Week 24. The responder rate was defined as an improvement in score of 0.5 or more (scale range 0-6 for ACQ-7-IA and 1-7 for PAQLQ(S)-IA). In the subgroup of subjects with baseline blood eosinophil count ≥300 cells/mcL, DUPIXENT led to a higher proportion of subjects with a response in ACQ-7-IA (80.6% versus 64.3% for placebo) with an OR of 2.79 (95% CI: 1.43, 5.44), and in PAQLQ(S)-IA (72.8% versus 63.0% for placebo) with an OR of 1.84 (95% CI: 0.92, 3.65) at Week 24.
Chronic Rhinosinusitis with Nasal Polyps
The efficacy of DUPIXENT as an add-on maintenance treatment in adults with inadequately controlled chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps (CRSwNP) was evaluated in two randomized, double-blind, parallel-group, multicenter, placebo-controlled studies (SINUS-24 (NCT02912468) and SINUS-52 (NCT02898454)) in 724 adult subjects 18 years of age and older on background intranasal corticosteroids (INCS). These studies included subjects with CRSwNP despite prior sino-nasal surgery or treatment with, or who were ineligible to receive or were intolerant to, systemic corticosteroids in the past 2 years. Subjects with chronic rhinosinusitis without nasal polyps were not included in these trials. Rescue with systemic corticosteroids or surgery was allowed during the studies at the investigator's discretion. In SINUS-24, a total of 276 subjects were randomized to receive either 300 mg DUPIXENT (N=143) or placebo (N=133) every 2 weeks for 24 weeks. In SINUS-52, 448 subjects were randomized to receive either 300 mg DUPIXENT (N=150) every 2 weeks for 52 weeks, 300 mg DUPIXENT (N=145) every 2 weeks until Week 24 followed by 300 mg DUPIXENT every 4 weeks until Week 52, or placebo (N=153). All subjects had evidence of sinus opacification on the Lund Mackay (LMK) sinus CT scan and 73% to 90% of subjects had opacification of all sinuses. Subjects were stratified based on their histories of prior surgery and co-morbid asthma/nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug exacerbated respiratory disease (NSAID-ERD). A total of 63% of subjects reported previous sinus surgery, with a mean number of 2.0 prior surgeries, 74% used systemic corticosteroids in the previous 2 years with a mean number of 1.6 systemic corticosteroid courses in the previous 2 years, 59% had co-morbid asthma, and 28% had NSAID-ERD.
The co-primary efficacy endpoints were change from baseline to Week 24 in bilateral endoscopic nasal polyps score (NPS; 0-8 scale) as graded by central blinded readers, and change from baseline to Week 24 in nasal congestion/obstruction score averaged over 28 days (NC; 0-3 scale), as determined by subjects using a daily diary. For NPS, polyps on each side of the nose were graded on a categorical scale (0=no polyps; 1=small polyps in the middle meatus not reaching below the inferior border of the middle turbinate; 2=polyps reaching below the lower border of the middle turbinate; 3=large polyps reaching the lower border of the inferior turbinate or polyps medial to the middle turbinate; 4=large polyps causing complete obstruction of the inferior nasal cavity). The total score was the sum of the right and left scores. Nasal congestion was rated daily by the subjects on a 0 to 3 categorical severity scale (0=no symptoms; 1=mild symptoms; 2=moderate symptoms; 3=severe symptoms).
In both studies, key secondary end-points at Week 24 included change from baseline in: LMK sinus CT scan score, daily loss of smell, and 22-item sino-nasal outcome test (SNOT-22). The LMK sinus CT scan score evaluated the opacification of each sinus using a 0 to 2 scale (0=normal; 1=partial opacification; 2=total opacification) deriving a maximum score of 12 per side and a total maximum score of 24 (higher scores indicate more opacification). Loss of smell was scored reflectively by the subject every morning on a 0-3 scale (0=no symptoms, 1=mild symptoms, 2=moderate symptoms, 3=severe symptoms). SNOT-22 includes 22 items assessing symptoms and symptom impact associated with CRSwNP with each item scored from 0 (no problem) to 5 (problem as bad as it can be) with a global score ranging from 0 to 110. SNOT-22 had a 2 week recall period. In the pooled efficacy results, the reduction in the proportion of subjects rescued with systemic corticosteroids and/or sino-nasal surgery (up to Week 52) were evaluated.
The demographics and baseline characteristics of these 2 trials are provided in Table 27 below.
| Parameter | SINUS-24 (N=276) | SINUS-52 (N=448) |
|---|---|---|
| SD = standard deviation; AM = morning; NPS = nasal polyps score; SNOT-22 = 22-item sino-nasal outcome test; NSAID-ERD = asthma/nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug exacerbated respiratory disease | ||
| Mean age (years) (SD) | 50 (13) | 52 (12) |
| % Male | 57 | 62 |
| Mean CRSwNP duration (years) (SD) | 11 (9) | 11 (10) |
| Subjects with ≥1 prior surgery (%) | 72 | 58 |
| Subjects with systemic corticosteroid use in the previous 2 years (%) | 65 | 80 |
| Mean Bilateral endoscopic NPS Higher scores indicate greater disease severity (SD), range 0-8 | 5.8 (1.3) | 6.1 (1.2) |
| Mean Nasal congestion (NC) score(SD), range 0-3 | 2.4 (0.6) | 2.4 (0.6) |
| Mean LMK sinus CT total score(SD), range 0-24 | 19 (4.4) | 18 (3.8) |
| Mean loss of smell score(AM), (SD) range 0-3 | 2.7 (0.5) | 2.8 (0.5) |
| Mean SNOT-22 total score(SD), range 0-110 | 49.4 (20.2) | 51.9 (20.9) |
| Mean blood eosinophils (cells/mcL) (SD) | 440 (330) | 430 (350) |
| Mean total IgE IU/mL (SD) | 212 (276) | 240 (342) |
| Atopic Medical History % Overall | 75 | 82 |
| Asthma (%) | 58 | 60 |
| NSAID-ERD (%) | 30 | 27 |
Clinical Response (SINUS-24 and SINUS-52)
The results for primary endpoints in CRSwNP studies are presented in Table 28.
| SINUS-24 | SINUS-52 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Placebo (n=133) | DUPIXENT 300 mg Q2W (n=143) | LS mean difference vs. Placebo (95% CI) | Placebo (n=153) | DUPIXENT 300 mg Q2W (n=295) | LS mean difference vs. Placebo (95% CI) | |||||
| Primary Endpoints at Week 24 | ||||||||||
| Scores | Baseline mean | LS mean change | Baseline mean | LS mean change | Baseline mean | LS mean change | Baseline mean | LS mean change | ||
| A reduction in score indicates improvement. NPS = nasal polyps score; NC = nasal congestion/obstruction | ||||||||||
| NPS | 5.86 | 0.17 | 5.64 | -1.89 | -2.06 (-2.43, -1.69) | 5.96 | 0.10 | 6.18 | -1.71 | -1.80 (-2.10, -1.51) |
| NC | 2.45 | -0.45 | 2.26 | -1.34 | -0.89 (-1.07, -0.71) | 2.38 | -0.38 | 2.46 | -1.25 | -0.87 (-1.03, -0.71) |
Statistically significant efficacy was observed in SINUS-52 with regard to improvement in bilateral endoscopic NPS score at week 24 and week 52 (see Figure 11 ).
Figure 11: LS Mean Change from Baseline in Bilateral Nasal Polyps Score (NPS) up to Week 52 in Subjects 18 Years of Age and Older with CRSwNP (SINUS-52 - ITT Population)

Similar results were seen in SINUS-24 at Week 24. In the post-treatment period when subjects were off DUPIXENT, the treatment effect diminished over time (see Figure 12 ).
Figure 12: LS Mean Change from Baseline in Bilateral Nasal Polyps Score (NPS) up to Week 48 in Subjects 18 Years of Age and Older with CRSwNP (SINUS-24 - ITT Population)

At Week 52, the LS mean difference for nasal congestion in the DUPIXENT group versus placebo was -0.98 (95% CI -1.17, -0.79). In both studies, significant improvements in nasal congestion were observed as early as the first assessment at Week 4. The LS mean difference for nasal congestion at Week 4 in the DUPIXENT group versus placebo was -0.41 (95% CI: -0.52, -0.30) in SINUS-24 and -0.37 (95% CI: -0.46, -0.27) in SINUS-52.
A significant decrease in the LMK sinus CT scan score was observed. The LS mean difference for LMK sinus CT scan score at Week 24 in the DUPIXENT group versus placebo was -7.44 (95% CI: -8.35, -6.53) in SINUS-24 and -5.13 (95% CI: -5.80, -4.46) in SINUS-52. At Week 52, in SINUS-52 the LS mean difference for LMK sinus CT scan score in the DUPIXENT group versus placebo was -6.94 (95% CI: -7.87, -6.01).
Dupilumab significantly improved the loss of smell compared to placebo. The LS mean difference for loss of smell at Week 24 in the DUPIXENT group versus placebo was -1.12 (95% CI: -1.31, -0.93) in SINUS-24 and -0.98 (95% CI: -1.15, -0.81) in SINUS-52. At Week 52, the LS mean difference for loss of smell in the DUPIXENT group versus placebo was -1.10 (95% CI -1.31, -0.89). In both studies, significant improvements in daily loss of smell severity were observed as early as the first assessment at Week 4.
Dupilumab significantly decreased sino-nasal symptoms as measured by SNOT-22 compared to placebo. The LS mean difference for SNOT-22 at Week 24 in the DUPIXENT group versus placebo was -21.12 (95% CI: -25.17, -17.06) in SINUS-24 and -17.36 (95% CI: -20.87, -13.85) in SINUS-52. At Week 52, the LS mean difference in the DUPIXENT group versus placebo was -20.96 (95% CI -25.03, -16.89).
In the pre-specified multiplicity-adjusted pooled analysis of two studies, treatment with DUPIXENT resulted in significant reduction of systemic corticosteroid use and need for sino-nasal surgery versus placebo (HR of 0.24; 95% CI: 0.17, 0.35) (see Figure 13 ). The proportion of subjects who required systemic corticosteroids was reduced by 74% (HR of 0.26; 95% CI: 0.18, 0.38). The total number of systemic corticosteroid courses per year was reduced by 75% (RR of 0.25; 95% CI: 0.17, 0.37). The proportion of subjects who required surgery was reduced by 83% (HR of 0.17; 95% CI: 0.07, 0.46).
Figure 13: Kaplan Meier Curve for Time to First Systemic Corticosteroid Use and/or Sino-Nasal Surgery During Treatment Period in Subjects 18 Years of Age and Older with CRSwNP (SINUS-24 and SINUS-52 Pooled - ITT Population)

The effects of DUPIXENT on the primary endpoints of NPS and nasal congestion and the key secondary endpoint of LMK sinus CT scan score were consistent in subjects with prior surgery and without prior surgery.
In subjects with co-morbid asthma, improvements in pre-bronchodilator FEV 1 were similar to subjects in the asthma program.
Eosinophilic Esophagitis
Adult and Pediatric Subjects 12 Years of Age and Older with EoE
A single randomized, double-blind, parallel-group, multicenter, placebo-controlled trial, including two 24-week treatment periods (Study EoE-1 Parts A and B) was conducted in adult and pediatric subjects 12 years of age and older, weighing at least 40 kg, with EoE (NCT03633617). In both parts, subjects were randomized to receive 300 mg DUPIXENT every week or placebo. Eligible subjects had ≥15 intraepithelial eosinophils per high-power field (eos/hpf) following a treatment course of a proton pump inhibitor (PPI) either prior to or during the screening period and symptoms of dysphagia as measured by the Dysphagia Symptom Questionnaire (DSQ). At baseline, 43% of subjects in Part A and 37% of subjects in Part B had a history of prior esophageal dilations.
Demographics and baseline characteristics were similar in Parts A and B. A total of 81 subjects (61 adults and 20 pediatric subjects) were enrolled in Part A and 159 subjects (107 adults and 52 pediatric subjects) were enrolled in Part B. The mean age in years was 32 years (range 13 to 62 years) in Part A and 28 years (range 12 to 66 years) in Part B. The majority of subjects were male (60% in Part A and 68% in Part B) and White (96% in Part A and 90% in Part B). The mean baseline DSQ score (SD) was 33.6 (12.4) in Part A and 37.2 (10.7) in Part B.
The coprimary efficacy endpoints in Parts A and B were the (1) proportion of subjects achieving histological remission defined as peak esophageal intraepithelial eosinophil count of ≤6 eos/hpf at Week 24; and (2) the absolute change in the subject-reported DSQ score from baseline to Week 24.
Efficacy results for Parts A and B are presented in Table 29.
| Study EoE-1 Part A | Study EoE-1 Part B | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DUPIXENT 300 mg QW For histological remission, the difference in percentages is estimated using the Cochran Mantel Haenszel method, adjusting for randomization stratification factors. For absolute change in DSQ score, the LS mean changes, standard errors, and differences are estimated using an ANCOVA model with treatment group, randomization stratification factors, and baseline measurement as covariates. | Placebo | Difference vs. Placebo (95% CI) | DUPIXENT 300 mg QW | Placebo | Difference vs. Placebo (95% CI) | |
| N = 42 | N = 39 | N = 80 | N = 79 | |||
| Co-primary Endpoints | ||||||
| Proportion of subjects achieving histological remission (peak esophageal intraepithelial eosinophil count ≤6 eos/hpf), n (%) | 25 (59.5) | 2 (5.1) | 57.0 (40.9, 73.1) | 47 (58.8) | 5 (6.3) | 53.5 (41.2, 65.8) |
| Absolute change from baseline in DSQ score (0-84 Total biweekly DSQ scores range from 0 to 84; higher scores indicate greater frequency and severity of dysphagia ), LS mean (SE) | -21.9 (2.5) | -9.6 (2.8) | -12.3 (-19.1, -5.5) | -23.8 (1.9) | -13.9 (1.9) | -9.9 (-14.8, -5.0) |
In Parts A and B, a greater proportion of subjects randomized to DUPIXENT achieved histological remission (peak esophageal intraepithelial eosinophil count ≤6 eos/hpf) compared to placebo. Treatment with DUPIXENT also resulted in a significant improvement in LS mean change in DSQ score compared to placebo at Week 24. The results of the anchor-based analyses that incorporated the subjects' perspectives indicated that the observed improvement in dysphagia from Parts A and B is representative of a clinically meaningful within-subject improvement.
Pediatric Subjects 1 to 11 Years of Age, Weighing at Least 15 kg, with EoE
The efficacy and safety of DUPIXENT was evaluated in pediatric subjects 1 to 11 years of age, weighing at least 15 kg, with EoE in a randomized, blinded, parallel-group, multicenter trial (Study EoE-2 Parts A and B; NCT04394351). Eligible subjects had ≥15 intraepithelial eosinophils per high-power field (eos/hpf) despite a treatment course of a proton pump inhibitor (PPI) either prior to or during the screening period and a history of EoE signs and symptoms. Part A evaluated weight-based dosing regimens of DUPIXENT, 200 mg Q2W (≥15 to <30 kg) and 300 mg Q2W (≥30 to <60 kg), or placebo in 61 subjects during the 16-week treatment period.
The recommended dosage of 300 mg QW for pediatric subjects 1 to 11 years of age weighing ≥40 kg is based on modeled pharmacokinetic data to provide comparable exposures to the 300 mg QW dosage in adult and pediatric subjects 12 years of age and older weighing ≥40 kg with EoE [see Dosage and Administration (2.6) and Pharmacokinetics (12.3) ] .
Forty-seven subjects who completed Part A were evaluated in the 36-week extended active treatment period (Study EoE-2 Part B). All subjects in Part B were treated with the weight-based dosing regimens of DUPIXENT described for Part A.
Of the total subjects evaluated in Part A, the mean age was 8 years, the median weight was 28 kg, and 75% were male. Seven percent identified as Hispanic or Latino; 85% identified as White, 12% as Black, 2% as Asian, and 2% identified as another racial subgroup.
The primary efficacy endpoint in Part A was the proportion of subjects achieving histological remission defined as peak esophageal intraepithelial eosinophil count of ≤6 eos/hpf at Week 16.
Efficacy results for Part A are presented in Table 30.
| DUPIXENT DUPIXENT was evaluated at tiered dosing regimens based on body weight: ≥15 to <30 kg (200 mg Q2W) and ≥30 to <60 kg (300 mg Q2W). The 300 mg Q2W dosing regimen is lower than the recommended dosage of DUPIXENT in subjects ≥40 kg [see Dosage and Administration (2.6) ] . N=32 | Placebo N=29 | Difference vs Placebo (95% CI) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Proportion of subjects achieving histological remission (peak esophageal intraepithelial eosinophil count ≤6 eos/hpf), n (%) The difference in percentages is estimated using the Mantel-Haenszel method, adjusting for baseline weight group (≥15 to <30 kg and ≥30 to <60 kg). | 21 (65.6) | 1 (3.4) | 62.0 (44.00, 79.95) |
In Part B, histological remission was achieved at Week 52 in 17/32 subjects treated with DUPIXENT in Parts A and B and 8/15 subjects treated with placebo in Part A and DUPIXENT in Part B.
In Study EoE-2 Part A, an observer-reported outcome, the Pediatric EoE Sign/Symptom Questionnaire-Caregiver (PESQ-C), was used to measure signs of EoE. A greater decrease in the proportion of days with 1 or more signs of EoE (based on the PESQ-C) was observed for subjects treated with DUPIXENT compared to placebo after 16 weeks of treatment.
Prurigo Nodularis
The efficacy of DUPIXENT in adults with prurigo nodularis (PN) was evaluated in two 24-week randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicenter, parallel-group trials (PRIME (NCT04183335) and PRIME 2 (NCT04202679)). These trials enrolled 311 adult subjects with pruritus (WI-NRS ≥ 7 on a scale of 0 to 10) and greater than or equal to 20 nodular lesions. PRIME and PRIME 2 assessed the effect of DUPIXENT on pruritus improvement as well as its effect on PN lesions.
In these two trials, subjects received either subcutaneous DUPIXENT 600 mg (two 300 mg injections) on day 1, followed by 300 mg once every 2 weeks (Q2W) for 24 weeks, or matching placebo.
In these trials, the mean age was 49.5 years, the median weight was 71 kg, 65% of subjects were female, 57% were White, 6% were Black, and 34% were Asian. At baseline, the mean Worst Itch-Numeric Rating Scale (WI-NRS) was 8.5, 66% had 20 to 100 nodules (moderate), and 34% had greater than 100 nodules (severe). Eleven percent (11%) of subjects were taking stable doses of antidepressants at baseline and were instructed to continue taking these medications during the trial. Forty-three percent (43%) had a history of atopy (defined as having a medical history of AD, allergic rhinitis/rhinoconjunctivitis, asthma, or food allergy).
The WI-NRS is comprised of a single item, rated on a scale from 0 ("no itch") to 10 ("worst imaginable itch"). Subjects were asked to rate the intensity of their worst pruritus (itch) over the past 24 hours using this scale. The Investigator's Global Assessment for Prurigo Nodularis-Stage (IGA PN-S) is a scale that measures the approximate number of nodules using a 5-point scale from 0 (clear) to 4 (severe).
Efficacy was assessed with the proportion of subjects with improvement (reduction) in WI-NRS by ≥4 points, the proportion of subjects with IGA PN-S 0 or 1 (the equivalent of 0-5 nodules), and the proportion of subjects who achieved a response in both WI-NRS and IGA PN-S per the criteria described above.
The efficacy results for PRIME and PRIME2 are presented in Table 31 and Figures 14, 15, and 16.
| PRIME | PRIME2 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Placebo (N=76) | DUPIXENT 300 mg Q2W (N=75) | Difference (95% CI) for DUPIXENT vs. Placebo | Placebo (N=82) | DUPIXENT 300 mg Q2W (N=78) | Difference (95% CI) for DUPIXENT vs. Placebo | |
| Proportion of subjects with both an improvement (reduction) in WI-NRS by ≥4 points from baseline to Week 24 and an IGA PN-S 0 or 1 at Week 24 Subjects who received rescue treatment earlier or had missing data were considered as non-responders. | 9.2% | 38.7% | 29.6% (16.4, 42.8) | 8.5% | 32.1% | 25.5% (13.1, 37.9) |
| Proportion of subjects with improvement (reduction) in WI-NRS by ≥4 points from baseline at Week 24 | 18.4% | 60.0% | 42.7% (27.8, 57.7) | 19.5% | 57.7% | 42.6% (29.1, 56.1) |
| Proportion of subjects with IGA PN-S 0 or 1 at Week 24 | 18.4% | 48.0% | 28.3% (13.4, 43.2) | 15.9% | 44.9% | 30.8% (16.4, 45.2) |
| Proportion of subjects with improvement (reduction) in WI-NRS by ≥4 points from baseline at Week 12 | 15.8% Not adjusted for multiplicity in PRIME. | 44.0% | 29.2% (14.5, 43.8) | 22.0% | 37.2% | 16.8% (2.3, 31.2) |
Figure 14: Proportion of Adult Subjects with PN with Both WI-NRS ≥4-point Improvement and IGA PN-S 0 or 1 Over Time in PRIME and PRIME2

Figure 15: Proportion of Adult Subjects with PN with WI-NRS ≥4-point Improvement Over Time in PRIME and PRIME2

Figure 16: Proportion of Adult Subjects with IGA PN-S 0 or 1 Over Time in PRIME and PRIME 2

The efficacy data did not show differential treatment effect across demographic subgroups.
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
The efficacy of DUPIXENT as add-on maintenance treatment of adult patients with inadequately controlled COPD and an eosinophilic phenotype was evaluated in two randomized, double-blind, multicenter, parallel-group, placebo-controlled trials (BOREAS [NCT03930732] and NOTUS [NCT04456673]) of 52 weeks duration. The two trials enrolled a total of 1874 adult subjects with COPD.
Both trials enrolled subjects with a diagnosis of COPD with moderate to severe airflow limitation (post-bronchodilator FEV 1 /FVC ratio <0.7 and post-bronchodilator FEV 1 of 30% to 70% predicted) and a minimum blood eosinophil count of 300 cells/mcL at screening. Trial enrollment required an exacerbation history of at least 2 moderate or 1 severe exacerbation(s) in the previous year despite receiving maintenance triple therapy consisting of a long-acting muscarinic antagonist (LAMA), long-acting beta agonist (LABA), and inhaled corticosteroid (ICS), and symptoms of chronic productive cough for at least 3 months in the past year. Greater than or equal to 95% of subjects in each trial had chronic bronchitis. Subjects also had a Medical Research Council (MRC) dyspnea score ≥2 (range 0-4). Exacerbations of COPD were defined as clinically significant worsening of COPD symptoms including increases in dyspnea, wheezing, cough, sputum volume, and/or increase in sputum purulence. Exacerbation severity was further defined as moderate if treatment with systemic corticosteroids and/or antibiotics was required, or severe if they resulted in hospitalization or observation for over 24 hours in an emergency department or urgent care facility.
In both trials, subjects were randomized to receive DUPIXENT 300 mg subcutaneously every 2 weeks (Q2W) or placebo in addition to their background maintenance therapy for 52 weeks.
The demographics and baseline characteristics of BOREAS and NOTUS trial populations are provided in Table 32 below.
| Parameter | BOREAS (N = 939) | NOTUS (N = 935) |
|---|---|---|
| ICS = inhaled corticosteroid; LAMA = long-acting muscarinic antagonist; LABA = long-acting beta agonist; FEV 1 = forced expiratory volume in 1 second; FVC = forced vital capacity | ||
| Mean age (years) (± SD) | 65.1 (8.1) | 65.0 (8.3) |
| Male (%) | 66.0 | 67.6 |
| White, N (%) | 790 (84.1) | 838 (89.6) |
| Asian, N (%) | 134 (14.3) | 10 (1.1) |
| Black, N (%) | 5 (0.5) | 12 (1.3) |
| American Indian or Alaska Native, N (%) | 7 (0.7) | 48 (5.1) |
| Other/Multiple, N (%) | 3 (0.3) | 27 (2.9) |
| Ethnicity Hispanic/Latino, N (%) | 261 (27.8) | 300 (32.1) |
| Mean smoking history (pack-years) (± SD) | 40.5 (23.4) | 40.3 (27.2) |
| Current smokers (%) | 30.0 | 29.5 |
| Chronic Bronchitis (%) | 95.0 | 99.9 |
| Emphysema (%) | 32.6 | 30.4 |
| Mean number of moderate Exacerbations treated with either systemic corticosteroids and/or antibiotics. or severe Exacerbations requiring hospitalization or observation for over 24 hours in an emergency department or urgent care facility. exacerbations in previous year (± SD) | 2.3 (1.0) | 2.1 (0.9) |
| Background COPD medications at randomization: ICS/LAMA/LABA (%) | 97.6 | 98.8 |
| Mean post-bronchodilator FEV 1 /FVC ratio (± SD) | 0.49 (0.12) | 0.50 (0.12) |
| Mean post-bronchodilator FEV 1 (L) (± SD) | 1.40 (0.47) | 1.45 (0.49) |
| Mean percent predicted post-bronchodilator FEV 1 (%) (± SD) | 50.6 (13.1) | 50.1 (12.6) |
| Mean SGRQ total score (± SD) | 48.4 (17.4) | 51.5 (17.0) |
| Mean screening blood eosinophil count Reported screening eosinophil value is the highest values from up to three retests (cells/mcL) (± SD) | 521 (307) | 538 (333) |
| Mean baseline blood eosinophil count Reported baseline eosinophil value was obtained within 4 weeks of screening value (cells/mcL) (± SD) | 401 (298) | 407 (336) |
Exacerbations in Adult Subjects with COPD
The primary endpoint for BOREAS and NOTUS trials was the annualized rate of moderate or severe COPD exacerbations during the 52-week treatment period. In both trials, DUPIXENT demonstrated a significant reduction in the annualized rate of moderate or severe COPD exacerbations compared to placebo when added to background maintenance therapy (see Table 33 ).
| Trial | Treatment (N) | Rate (exacerbations/year) | Rate Ratio vs. Placebo (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|---|
| BOREAS | DUPIXENT 300 mg Q2W (N=468) | 0.78 | 0.71 (0.58, 0.86) |
| Placebo (N=471) | 1.10 | ||
| NOTUS | DUPIXENT 300 mg Q2W (N=470) | 0.86 | 0.66 (0.54, 0.82) |
| Placebo (N=465) | 1.30 |
Treatment with DUPIXENT decreased the risk of a moderate to severe COPD exacerbation as measured by time to first exacerbation when compared with placebo in BOREAS (HR: 0.80; 95% CI: 0.66, 0.98) and NOTUS (HR: 0.71; 95% CI: 0.57, 0.89).
Lung Function in Adult Subjects with COPD
In both trials (BOREAS and NOTUS), DUPIXENT demonstrated numerical improvement in post-bronchodilator FEV 1 at Weeks 12 and 52 compared to placebo when added to background maintenance therapy (see Table 34 and Figure 17 ). Significant improvements of similar magnitude were observed in change from baseline in pre-bronchodilator FEV 1 at Weeks 12 and 52 in subjects treated with DUPIXENT compared to placebo across both trials.
| Trial | Treatment (N) | LS Mean Change from baseline mL | LS Mean Difference vs. placebo mL (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Post-bronchodilator FEV 1 at Week 12 | |||
| BOREAS | DUPIXENT 300 mg Q2W (N=468) | 158 | 74 (31, 117) |
| Placebo (N=471) | 84 | ||
| NOTUS | DUPIXENT 300 mg Q2W (N=470) | 134 | 68 (26, 110) |
| Placebo (N=465) | 67 | ||
| Post-bronchodilator FEV 1 at Week 52 | |||
| BOREAS | DUPIXENT 300 mg Q2W (N=468) | 138 | 79 (34, 124) |
| Placebo (N=471) | 58 | ||
| NOTUS Efficacy results for mean change from baseline in post-bronchodilator FEV 1 at Week 52 are presented for 721 out of 935 subjects who completed the 52-week treatment period or had discontinued the trial at the time of data analysis. | DUPIXENT 300 mg Q2W (N=362) | 127 | 67 (16, 119) |
| Placebo (N=359) | 59 | ||
| Figure 17: LS Mean Change from Baseline in Post-Bronchodilator FEV 1 (mL) Over Time in BOREAS and NOTUS Efficacy results for mean change from baseline in post-bronchodilator FEV 1 over time are presented for 721 out of 935 subjects who completed the 52-week treatment period or had discontinued the trial at the time of data analysis. Trials for COPD | |
|---|---|
| BOREAS | NOTUS |
 | |
Health-Related Quality of Life
In both trials (BOREAS and NOTUS), the St. George's Respiratory Questionnaire (SGRQ) total score responder rate (defined as the proportion of subjects with SGRQ improvement from baseline of at least 4 points) at Week 52 was evaluated. In BOREAS, the responder rate was 51% for subjects treated with DUPIXENT versus 43% for placebo (N=939, odds ratio: 1.44; 95% CI: 1.10, 1.89). In NOTUS, the responder rate was 51% for subjects treated with DUPIXENT versus 47% for placebo (N=721, odds ratio: 1.16; 95% CI: 0.86, 1.58).
Chronic Spontaneous Urticaria
The efficacy of DUPIXENT for the treatment of adult and pediatric patients aged 12 years and older with chronic spontaneous urticaria who remain symptomatic despite H1 antihistamine treatment was evaluated in a master protocol clinical trial (CUPID [NCT04180488]) that included three 24-week, randomized, double-blind, parallel-group, multicenter, placebo-controlled trials (CUPID Study A, Study B, and Study C), followed by 12-week blinded safety follow-up periods. CUPID Study A and Study C included subjects who remained symptomatic despite H1 antihistamine treatment and were anti-IgE treatment naïve, while CUPID Study B included patients who remained symptomatic despite H1 antihistamine and anti-IgE treatments. The efficacy of DUPIXENT was based only on CUPID Study A and Study C; Study B did not meet the primary endpoint.
CUPID Study A and Study C
A total of 284 adult and pediatric patients 12 years of age and older with CSU (Itch Severity Score over 7 days (ISS7) ≥8 on a scale of 0 to 21 and Urticaria Activity Score over 7 days (UAS7) ≥16 on a scale of 0 to 42) who were symptomatic despite the use of H1 antihistamines, but who were anti-IgE treatment naïve, were enrolled in CUPID Study A and Study C. In the DUPIXENT group, adults and pediatric subjects (12 years of age and older) weighing ≥60 kg received a subcutaneous dose of DUPIXENT 600 mg on Day 1, followed by 300 mg every 2 weeks (Q2W), while pediatric subjects (12 years of age and older) weighing 30 kg to less than 60 kg received a subcutaneous dose of DUPIXENT 400 mg on Day 1, followed by 200 mg Q2W. The demographics and baseline characteristics of the efficacy population in CUPID Study A and Study C are provided in Table 35.
| CUPID Study A (N=136) | CUPID Study C (N=148) | |
|---|---|---|
| ISS7 = Itch Severity Score over 7 days; UAS7 = Urticaria Activity Score over 7 days; HSS7 = Hives Severity Score over 7 days; H1AH = H1 antihistamine; Q1 = 1st quartile; Q3 = 3rd quartile | ||
| Mean age (years) (SD) | 42 (15.1) | 46 (16.3) |
| % Female | 66 | 70 |
| % White | 68 | 45 |
| % Asian | 26 | 42 |
| % Black | 2 | 1 |
| % Hispanic or Latino | 18 | 16 |
| Mean body weight (kg) | 77 | 74 |
| Mean ISS7 | 16 | 15.1 |
| Mean UAS7 | 31.4 | 28.2 |
| Mean HSS7 | 15.4 | 13.1 |
| % subjects with UAS7 ≥28 | 70.6 | 58.8 |
| Median total IgE IU/ml (Q1,Q3) | 101 (40.3, 252) | 108 (37, 309) |
The primary endpoint was change from baseline in itch severity score over 7 days (ISS7) at Week 24. The ISS7 score was defined as the sum of the daily itch severity scores (ISS), from 0 to 3, recorded at the same time of the day for a 7-day period, ranging from 0 to 21.
The key secondary endpoint was change from baseline in urticaria activity score over 7 days (UAS7) at Week 24. The UAS7 (range 0 to 42) was a composite of the weekly itch severity score (ISS7, range 0 to 21) and the weekly hive count score (HSS7, range 0 to 21).
The results for primary and secondary endpoints in CUPID Study A and Study C are presented in Table 36.
| CUPID Study A | CUPID Study C | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DUPIXENT (N=68) | Placebo (N=68) | DUPIXENT vs. Placebo (95% CI) | DUPIXENT (N=73) | Placebo (N=75) | DUPIXENT vs. Placebo (95% CI) | |
| Primary Endpoint | ||||||
| Change from baseline in ISS7 at Week 24 Values presented are LS mean change from baseline (SE) for continuous variables and number and percent of responders for binary variables. | -10.44 (0.92) | -6.02 (0.94) | -4.42 (-6.84, -2.01) Values presented are LS mean differences. | -8.50 (1.39) | -6.13 (1.38) | -2.37 (-4.48, -0.27) |
| Secondary Endpoints | ||||||
| Change from baseline in UAS7 at Week 24 | -20.99 (1.77) | -11.95 (1.81) | -9.04 (-13.68, -4.40) | -15.61 (2.62) | -11.27 (2.61) | -4.34 (-8.31, -0.36) |
| Change from baseline in HSS7 at Week 24 | -10.54 (0.91) | -5.85 (0.93) | -4.69 (-7.08, -2.30) | -7.16 (1.30) | -5.15 (1.29) | -2.01 (-3.98, -0.04) |
| Proportion of patients with UAS7 ≤6 at Week 24 | 32 (47.1) | 16 (23.5) | 3.23 (1.43, 7.27) Values presented are odds ratios. | 29 (39.7) | 17 (22.7) | 3.05 (1.32, 7.02) |
| Proportion of patients with UAS7 = 0 at Week 24 | 22 (32.4) | 9 (13.2) | 3.09 (1.24, 7.69) | 22 (30.1) | 13 (17.3) | 2.73 (1.15, 6.50) |
CUPID Study A showed significant improvement in ISS7 and UAS7 from baseline at Week 12 in the DUPIXENT group (LS mean difference DUPIXENT versus placebo of -2.53 [95% CI: (-4.79, -0.27)] for ISS7 and -5.44 [95% CI: (-9.77, -1.11)] for UAS7). The proportion of patients with UAS7 ≤6 at Week 12 in CUPID Study A was 35.3% in the DUPIXENT group and 17.6% in the placebo group (Odds Ratio: 2.79 [95% CI: (1.22, 6.40)]).
Mean changes in ISS7 over time in CUPID Study A and Study C are shown in Figure 18.
| Figure 18: LS Mean Change from Baseline in ISS7 Over 24 Weeks in CUPID Study A and Study C | |
|---|---|
| Study A | Study C |
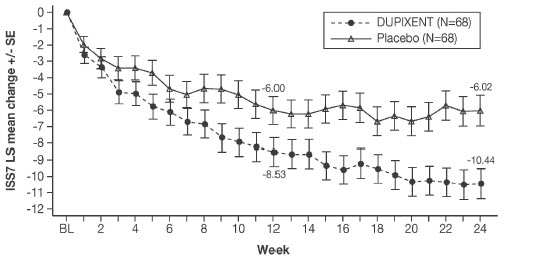 | 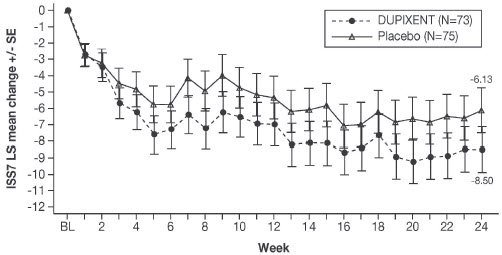 |
Similar changes in UAS7 and HSS7 were observed over 24 weeks.
Improvements in ISS7 and UAS7 at Week 24 were consistent regardless of the patients' baseline IgE level.
CUPID Study B
CUPID Study B enrolled 108 adult and pediatric patients 12 years of age and older with CSU who were inadequate responders (N=104) to H1 antihistamines and anti-IgE treatments or intolerant (N=4) to anti-IgE therapy. At baseline, the mean ISS7 was 16, mean UAS7 score was 31.5 and the mean HSS7 was 15.4. The majority of participants (69.4%) had a UAS7 score of ≥28 at baseline. The median (Q1, Q3) total IgE (IU/mL) at baseline was 77 (20, 204.5). CUPID Study B evaluated efficacy using the same primary and secondary endpoints as CUPID Study A and Study C. The DUPIXENT group in CUPID Study B did not meet statistical significance for reduction in the primary endpoint ISS7 at Week 24.
Bullous Pemphigoid
The efficacy of DUPIXENT in adults with bullous pemphigoid (BP) was evaluated in a 52-week randomized, double-blind, parallel-group, multicenter, placebo-controlled trial (ADEPT; NCT04206553). This trial enrolled 106 adult subjects with a Bullous Pemphigoid Disease Area Index (BPDAI) activity score ≥24 on a scale of 0-360 and a weekly average Peak Pruritus NRS score ≥4 on a scale of 0-10.
In this trial, subjects were randomized to receive either subcutaneous DUPIXENT 600 mg (two 300 mg injections) on Day 1, followed by 300 mg every other week (Q2W), or matching placebo for 52 weeks. All subjects were also initiated on a standard regimen of oral corticosteroids (prednisone or prednisolone; 0.5 or 0.75 mg/kg/day) on Day 1. After achieving control of disease activity for 2 weeks, oral corticosteroids (OCS) were tapered with the objective to taper them off no later than Week 16 as long as the control of disease activity was maintained. Subjects who experienced a loss of control of disease activity (new lesions form and existing lesions cease to heal) during OCS taper, or who relapsed post-taper, or who used rescue medications were considered treatment failures. During the OCS taper, subjects were permitted to increase their OCS once, with any subsequent increases being considered rescue therapy. Subjects could be rescued during the trial with topical or oral corticosteroids, non-steroidal immunosuppressive medications, or immunomodulating biologics. Subjects were allowed to continue trial treatment if rescued with topical or oral corticosteroids.
Demographics and baseline characteristics were similar between the treatment arms. Of the 106 subjects enrolled, the mean age was 71.3 years; 53% were female; 68% were White, 2% were Black or African American, and 15% were Asian; 3% of subjects identified as Hispanic or Latino. At baseline, 63% of subjects had prior systemic corticosteroid use for BP. The mean Peak Pruritus NRS score was 7.5 at baseline.
The primary endpoint was the proportion of subjects achieving sustained remission at Week 36. Sustained remission was defined as the achievement of complete remission and off OCS no later than Week 16, absence of disease relapse from the time of completion of the corticosteroid taper to Week 36, and absence of rescue therapy during the 36-week double-blind treatment period. Secondary endpoints included total cumulative dose of OCS and proportion of subjects with a reduction in itch defined as at least a 4-point improvement (reduction) in the Peak Pruritus NRS.
The efficacy results for ADEPT are presented in Table 37. The proportion of subjects that received rescue therapy during the 36-week treatment period was 53% in the DUPIXENT group and 79% in the placebo group.
| DUPIXENT 300 mg Q2W + OCS (N=53) | Placebo + OCS (N=53) | Difference (95% CI) for DUPIXENT vs. Placebo | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Proportion of subjects achieving sustained remission Sustained remission was defined as the achievement of complete remission and off OCS no later than Week 16, absence of disease relapse from the time of completion of the corticosteroid taper to Week 36, and absence of rescue therapy during the 36-week double-blind treatment period. | 18.3% | 6.1% | 12.2% (-0.8, 26.1) |
| Proportion of subjects with improvement (reduction) of ≥4 points in Peak Pruritus NRS from baseline | 38.3% | 10.5% | 27.8% (11.6, 43.4) |
The median (min, max) cumulative dose of OCS at Week 36 was 2.8 g (1.2, 22.7) in the DUPIXENT group compared to 4.1 g (1.5, 23.3) in the placebo group.
HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
How Supplied
DUPIXENT (dupilumab) Injection is a clear to slightly opalescent, colorless to pale yellow solution, supplied in single-dose pre-filled syringes with needle shield or pre-filled pens.
The pre-filled syringe with needle shield is designed to deliver:
- 300 mg of DUPIXENT in 2 mL solution (NDC 0024-5914-00)
- 200 mg of DUPIXENT in 1.14 mL solution (NDC 0024-5918-00)
The pre-filled pen is designed to deliver:
- 300 mg of DUPIXENT in 2 mL solution (NDC 0024-5915-00)
- 200 mg of DUPIXENT in 1.14 mL solution (NDC 0024-5919-00)
DUPIXENT is available in cartons containing 2 pre-filled syringes with needle shield or 2 pre-filled pens.
| Pack Size | 300 mg/2 mL (150 mg/mL) Pre-filled Syringe with Needle Shield | 200 mg/1.14 mL (175 mg/mL) Pre-filled Syringe with Needle Shield |
|---|---|---|
| Pack of 2 syringes | NDC 0024-5914-01 | NDC 0024-5918-01 |
| Pack Size | 300 mg/2 mL (150 mg/mL) Pre-filled Pen | 200 mg/1.14 mL (175 mg/mL) Pre-filled Pen |
|---|---|---|
| Pack of 2 pens | NDC 0024-5915-02 | NDC 0024-5919-02 |
Storage and Handling
DUPIXENT is sterile and preservative-free. Discard any unused portion.
Store refrigerated at 2°C to 8°C (36°F to 46°F) in the original carton to protect from light.
If necessary, DUPIXENT may be kept at room temperature up to 25°C (77°F) for a maximum of 14 days. Do not store above 25°C (77°F). After removal from the refrigerator, DUPIXENT must be used within 14 days or discarded.
Do not expose DUPIXENT to heat or direct sunlight.
Do NOT freeze. Do NOT shake.
INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE DUPIXENT ® (DU-pix-ent) (dupilumab) injection, for subcutaneous use Single-Dose Pre-filled Syringe with Needle Shield
Read this Instructions for Use before using the DUPIXENT Pre-filled Syringe. Do not inject yourself or someone else until you have been shown how to inject DUPIXENT. Your healthcare provider can show you or your caregiver how to prepare and inject a dose of DUPIXENT before you try to do it yourself the first time. Keep these instructions for future use. Call your healthcare provider if you have any questions.
This device is a Single-Dose Pre-filled Syringe (called "DUPIXENT Syringe" in these instructions). It contains 300 mg of DUPIXENT for injection under the skin (subcutaneous injection).
The parts of the DUPIXENT Syringe are shown below:
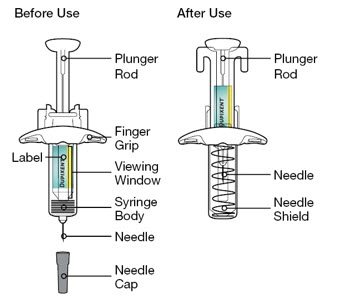
| Important Information | |
|---|---|
|
|
How should I store DUPIXENT?
| |
Step 1: Remove
Remove the DUPIXENT Syringe from the carton by holding the middle of the Syringe Body.
 Do not pull off the Needle Cap until you are ready to inject.
Do not pull off the Needle Cap until you are ready to inject.
 Do not use the DUPIXENT Syringe if it has been dropped on a hard surface or damaged.
Do not use the DUPIXENT Syringe if it has been dropped on a hard surface or damaged.
Step 2: Prepare
Ensure you have the following:
- the DUPIXENT Pre-filled Syringe
- 1 alcohol wipe•
- 1 cotton ball or gauze•
- a sharps disposal container• (See Step 13 )
• Items not included in the carton

Step 3: Check
When you receive your DUPIXENT Syringes, always check to see that:
- you have the correct medicine and dose.
- the expiration date on the Single-Dose Pre-filled Syringe has not passed.
 Do not use the DUPIXENT Syringe if the expiration date has passed.
Do not use the DUPIXENT Syringe if the expiration date has passed.
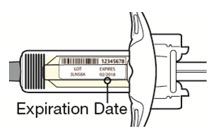
Step 4: Inspect
Look at the medicine through the Viewing Window on the DUPIXENT Syringe:
Check to see if the liquid is clear and colorless to pale yellow.
Note: You may see an air bubble, this is normal.
 Do not use the DUPIXENT Syringe if the liquid is discolored or cloudy, or if it contains visible flakes or particles.
Do not use the DUPIXENT Syringe if the liquid is discolored or cloudy, or if it contains visible flakes or particles.
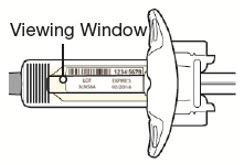
Step 5: Wait 45 minutes
Lay the DUPIXENT Syringe on a flat surface and let it naturally warm to room temperature for at least 45 minutes.
 Do not heat the DUPIXENT Syringe.
Do not heat the DUPIXENT Syringe.
 Do not put the DUPIXENT Syringe into direct sunlight.
Do not put the DUPIXENT Syringe into direct sunlight.
 Do not keep DUPIXENT Syringes at room temperature for more than 14 days. Throw away (dispose of) any DUPIXENT Syringes that have been left at room temperature for longer than 14 days.
Do not keep DUPIXENT Syringes at room temperature for more than 14 days. Throw away (dispose of) any DUPIXENT Syringes that have been left at room temperature for longer than 14 days.
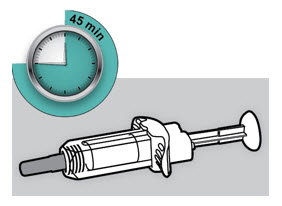
Step 6: Choose your injection site
- You can inject into your thigh or stomach, except for the 2 inches (5 cm) around your belly button (navel).
- If a caregiver injects your dose, they can also use the outer area of the upper arm.
- Choose a different site each time you inject DUPIXENT.
 Do not inject into skin that is tender, damaged, bruised or scarred.
Do not inject into skin that is tender, damaged, bruised or scarred.
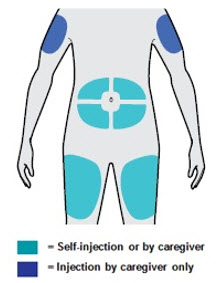
Step 7: Clean
Wash your hands.
Clean the injection site with an alcohol wipe.
Let your skin dry before injecting.
 Do not touch the injection site again or blow on it before the injection.
Do not touch the injection site again or blow on it before the injection.
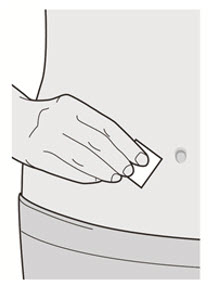
Step 8: Remove Needle Cap
Hold the DUPIXENT Syringe in the middle of the Syringe Body with the Needle pointing away from you and pull off the Needle Cap.
 Do not put the Needle Cap back on.
Do not put the Needle Cap back on.
 Do not touch the Needle.
Do not touch the Needle.
Inject your medicine right away after removing the Needle Cap.
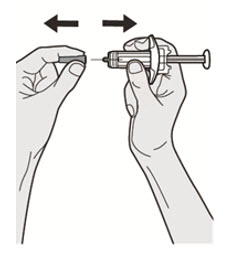
Step 9: Pinch
Pinch a fold of skin at the injection site (thigh or stomach, except 2 inches around your belly button, or outer area of the upper arm if injected by your caregiver). The figure below shows an example of pinching a fold of skin on your stomach.
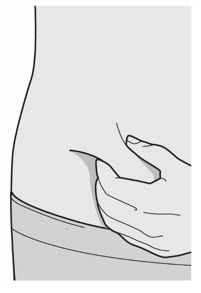
Step 10: Insert
Insert the Needle completely into the fold of the skin at about a 45° angle.
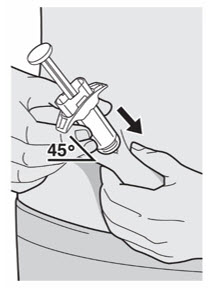
Step 11: Push
Relax the pinch.
Push the Plunger Rod down slowly and steadily as far as it will go until the DUPIXENT Syringe is empty.
Note: You will feel some resistance. This is normal.
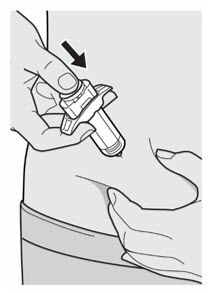
Step 12: Release and Remove
Lift your thumb to release the Plunger Rod until the Needle is covered by the Needle Shield and then remove the Syringe from the injection site.
Lightly press a cotton ball or gauze on the injection site if you see any blood.
 Do not put the Needle Cap back on.
Do not put the Needle Cap back on.
 Do not rub your skin after the injection.
Do not rub your skin after the injection.
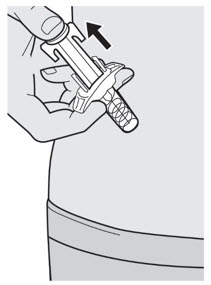
Step 13: Dispose
Put your used Needles, DUPIXENT Syringes, and Needle Caps in a FDA-cleared sharps disposal container right away after use.
 Do not dispose of (throw away) Needles, DUPIXENT Syringes, and Needle Caps in your household trash.
Do not dispose of (throw away) Needles, DUPIXENT Syringes, and Needle Caps in your household trash.
If you do not have a FDA-cleared sharps disposal container, you may use a household container that is:
- made of a heavy-duty plastic,
- can be closed with a tight-fitting, puncture-resistant lid, without sharps being able to come out,
- upright and stable during use,
- leak-resistant, and
- properly labeled to warn of hazardous waste inside the container
When your sharps disposal container is almost full, you will need to follow your community guidelines for the right way to dispose of your sharps disposal container. There may be state or local laws about how you should throw away used Needles and Syringes.
For more information about safe sharps disposal, and for specific information about sharps disposal in the state that you live in, go to the FDA's website at: http://www.fda.gov/safesharpsdisposal
Do not dispose of your used sharps disposal container in your household trash unless your community guidelines permit this. Do not recycle your used sharps disposal container.
 Do not put the Needle Cap back on.
Do not put the Needle Cap back on.
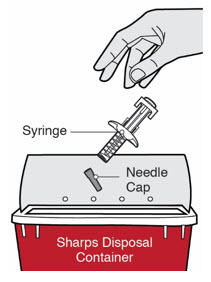

Manufactured by: Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc. Tarrytown, NY 10591 U.S. License No. 1760
Marketed by: sanofi-aventis U.S. LLC (Bridgewater, NJ 08807) and Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc. (Tarrytown, NY 10591) DUPIXENT ® is a registered trademark of Sanofi Biotechnology
© 2023 Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc. / sanofi-aventis U.S. LLC. All rights reserved.
This Instructions for Use has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
Revised: July 2023
Mechanism of Action
Dupilumab is a human monoclonal IgG4 antibody that inhibits interleukin-4 (IL-4) and interleukin-13 (IL-13) signaling by specifically binding to the IL-4Rα subunit shared by the IL-4 and IL-13 receptor complexes. Dupilumab inhibits IL-4 signaling via the Type I receptor and both IL-4 and IL-13 signaling through the Type II receptor.
Inflammation driven by IL-4 and IL-13 is an important component in the pathogenesis of asthma, AD, CRSwNP, EoE, PN, COPD, CSU, and BP. Multiple cell types that express IL-4Rα (e.g., mast cells, basophils, eosinophils, macrophages, lymphocytes, epithelial cells, goblet cells) and inflammatory mediators (e.g., histamine, eicosanoids, leukotrienes, cytokines, chemokines) are involved in inflammation. Blocking IL-4Rα with dupilumab inhibits IL-4 and IL-13 cytokine-induced inflammatory responses, including the release of proinflammatory cytokines, chemokines, nitric oxide, and IgE. The mechanism of dupilumab action has not been definitively established.