Adenosine
Adenosine Prescribing Information
Adenosine, a pharmacologic stress agent, is indicated as an adjunct to thallium-201 myocardial perfusion scintigraphy in patients unable to exercise adequately (
Adenosine, a pharmacologic stress agent, is indicated as an adjunct to thallium-201 myocardial perfusion scintigraphy in patients unable to exercise adequately
Adenosine injection, USP is indicated as an adjunct to thallium-201 myocardial perfusion scintigraphy in patients unable to exercise adequately.
Recommended dose is 0.14 mg/kg/min infused over six minutes as a continuous peripheral intravenous infusion (total dose of 0.84 mg/kg) (
Recommended dose is 0.14 mg/kg/min infused over six minutes as a continuous peripheral intravenous infusion (total dose of 0.84 mg/kg)
The recommended adenosine injection dose is 0.14 mg/kg/min infused over six minutes (total dose of 0.84 mg/kg) (Table 1).
- Administer adenosine injection only as a continuous peripheral intravenous infusion
- Inject Thallium-201 at the midpoint of the adenosine injection infusion (i.e., after the first three minutes of adenosine injection)
- Thallium-201 is physically compatible with adenosine injection and may be injected directly into the adenosine injection infusion set
- Inject Thallium-201 as close to the venous access as possible to prevent an inadvertent increase in the dose of adenosine injection (the contents of the intravenous tubing) being administered
Visually inspect adenosine injection for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration. Do not administer adenosine injection if it contains particulate matter or is discolored.
There are no data on the safety or efficacy of alternative adenosine injection infusion protocols. The safety and efficacy of adenosine injection administered by the intracoronary route have not been established.
Patient Weight (kilograms) | Infusion Rate (mL per minute over 6 minutes for total dose of 0.84 mg/kg) |
| 45 | 2.1 |
| 50 | 2.3 |
| 55 | 2.6 |
| 60 | 2.8 |
| 65 | 3 |
| 70 | 3.3 |
| 75 | 3.5 |
| 80 | 3.8 |
| 85 | 4 |
| 90 | 4.2 |
The nomogram displayed in Table 1 was derived from the following general formula:
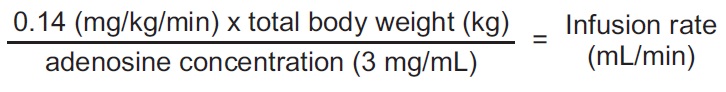
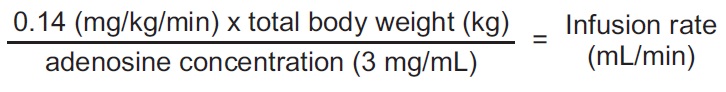
For Injection: 3 mg/mL in single-dose vials (
For Injection: 3 mg/mL in single-dose vials
Adenosine injection, USP is supplied as 20 mL and 30 mL single-dose vials containing a sterile, nonpyrogenic, clear solution of adenosine 3 mg/mL.
- Second- or third-degree AV block (except in patients with a functioning artificial pacemaker) ()
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHSFor Injection: 3 mg/mL in single-dose vials
Adenosine injection, USP is supplied as 20 mL and 30 mL single-dose vials containing a sterile, nonpyrogenic, clear solution of adenosine 3 mg/mL.
- Sinus node disease, such as sick sinus syndrome or symptomatic bradycardia (except in patients with a functioning artificial pacemaker) ()
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHSFor Injection: 3 mg/mL in single-dose vials
Adenosine injection, USP is supplied as 20 mL and 30 mL single-dose vials containing a sterile, nonpyrogenic, clear solution of adenosine 3 mg/mL.
- Known or suspected bronchoconstrictive or bronchospastic lung disease (e.g., asthma) ()
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS- Second- or third-degree AV block (except in patients with a functioning artificial pacemaker)
- Sinus node disease, such as sick sinus syndrome or symptomatic bradycardia (except in patients with a functioning artificial pacemaker)
- Known or suspected bronchoconstrictive or bronchospastic lung disease (e.g., asthma)
- Known hypersensitivity to adenosine injection
Adenosine injection is contraindicated in patients with:
- Second- or third-degree AV block (except in patients with a functioning artificial pacemaker)[see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Sinus node disease, such as sick sinus syndrome or symptomatic bradycardia (except in patients with a functioning artificial pacemaker)[see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Known or suspected bronchoconstrictive or bronchospastic lung disease (e.g., asthma)[see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
- Known hypersensitivity to adenosine[see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)]
- Known hypersensitivity to adenosine injection ()
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS- Second- or third-degree AV block (except in patients with a functioning artificial pacemaker)
- Sinus node disease, such as sick sinus syndrome or symptomatic bradycardia (except in patients with a functioning artificial pacemaker)
- Known or suspected bronchoconstrictive or bronchospastic lung disease (e.g., asthma)
- Known hypersensitivity to adenosine injection
Adenosine injection is contraindicated in patients with:
- Second- or third-degree AV block (except in patients with a functioning artificial pacemaker)[see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Sinus node disease, such as sick sinus syndrome or symptomatic bradycardia (except in patients with a functioning artificial pacemaker)[see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Known or suspected bronchoconstrictive or bronchospastic lung disease (e.g., asthma)[see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
- Known hypersensitivity to adenosine[see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)]
- Cardiac Arrest, Ventricular Arrhythmias, and Myocardial Infarction.Fatal cardiac events have occurred. Avoid use in patients with symptoms or signs of acute myocardial ischemia. Appropriate resuscitative measures should be available ()
5.1 Cardiac Arrest, Ventricular Arrhythmias, and Myocardial InfarctionFatal and nonfatal cardiac arrest, sustained ventricular tachycardia (requiring resuscitation), and myocardial infarction have occurred following adenosine injection infusion. Avoid use in patients with symptoms or signs of acute myocardial ischemia, for example, unstable angina or cardiovascular instability; these patients may be at greater risk of serious cardiovascular reactions to adenosine injection. Appropriate resuscitative measures should be available
[see Overdosage (10)]. - Sinoatrial (SA) and Atrioventricular (AV) Nodal Block.First-, second- or third-degree AV block, or sinus bradycardia can occur. Discontinue adenosine injection if patient develops persistent or symptomatic high-grade AV block ()
5.2 Sinoatrial and Atrioventricular Nodal BlockAdenosine injection exerts a direct depressant effect on the SA and AV nodes and may cause first-, second- or third-degree AV block, or sinus bradycardia. In clinical trials, approximately 6% of patients developed AV block following adenosine injection administration (first-degree heart block developed in 3%, second-degree in 3%, and third-degree in 0.8% of patients)
[see Clinical Trials Experience (6.1)].Use adenosine injection with caution in patients with pre-existing first-degree AV block or bundle branch block. Do not use in patients with high-grade AV block or sinus node dysfunction (except in patients with a functioning artificial pacemaker). Discontinue adenosine injection in any patient who develops persistent or symptomatic high-grade AV block.
- Bronchoconstriction.Can induce dyspnea, bronchoconstriction, and respiratory compromise, especially in patients with obstructive pulmonary disease. Discontinue adenosine injection if patient develops severe respiratory difficulties ()
5.3 BronchoconstrictionAdenosine injection administration can cause dyspnea, bronchoconstriction, and respiratory compromise. Adenosine injection should be used with caution in patients with obstructive lung disease not associated with bronchoconstriction (e.g., emphysema, bronchitis). Do not use in patients with bronchoconstriction or bronchospasm (e.g., asthma). Discontinue adenosine injection in any patient who develops severe respiratory difficulties. Resuscitative measures should be available prior to adenosine injection administration
[see Clinical Trials Experience (6.1), Overdosage (10), and Clinical Pharmacology (12.2)]. - Hypotension.Significant hypotension can occur. Discontinue adenosine injection if patient develops persistent or symptomatic hypotension ()
10 OVERDOSAGEThe half-life of adenosine is less than 10 seconds and adverse reactions of adenosine injection usually resolve quickly when the infusion is discontinued, although delayed or persistent reactions have been observed. Methylxanthines, such as caffeine, aminophylline, and theophylline, are competitive adenosine receptor antagonists and theophylline has been used to terminate persistent adverse reactions. In clinical trials, theophylline (50 to 125 mg slow intravenous injection) was used to attenuate adenosine injection adverse reactions in approximately 2% of patients. Methylxanthine use is not recommended in patients who experience seizures in association with adenosine injection
[see Drug Interactions (7.1)]. - Cerebrovascular Accidents.Hemorrhagic and ischemic cerebrovascular accidents have occurred ()
5.5 Cerebrovascular AccidentHemorrhagic and ischemic cerebrovascular accidents have occurred. Hemodynamic effects of adenosine injection including hypotension or hypertension can be associated with these adverse reactions.
[see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)and ]. - Seizures.New onset or recurrence of convulsive seizures have occurred. Use of methylxanthines (e.g., caffeine, aminophylline and theophylline) is not recommended in patients who experience a seizures in association with adenosine injection ()
5.6 SeizuresNew-onset or recurrence of convulsive seizures has occurred following adenosine injection. Some seizures are prolonged and require emergent anticonvulsive management. Aminophylline may increase the risk of seizures associated with adenosine injection. Methylxanthine use is not recommended in patients who experience seizures in association with adenosine injection administration
[see Overdosage (10)]. - Hypersensitivity.Dyspnea, throat tightness, flushing, erythema, rash, and chest discomfort have occurred. Have personnel and resuscitative equipment immediately available ()
5.7 HypersensitivityDyspnea, throat tightness, flushing, erythema, rash, and chest discomfort have occurred. Symptomatic treatment may be required. Have personnel and appropriate treatment available. Resuscitative measures may be necessary if symptoms progress.
[see Post-Marketing Experience (6.2)]. - Atrial Fibrillation.Reported in patients with or without a history of atrial fibrillation ()
5.8 Atrial FibrillationAdenosine injection can cause atrial fibrillation in patients with or without a history of atrial fibrillation. Atrial fibrillation typically began 1.5 to 3 minutes after initiation of adenosine injection, lasted for 15 seconds to 6 hours, and spontaneously converted to normal sinus rhythm
[see Post-Marketing Experience (6.2)]. - Hypertension.Clinically significant increases in systolic and diastolic pressure have been observed ()
5.9 HypertensionAdenosine injection can induce clinically significant increases in systolic and diastolic blood pressure. Most increases resolved spontaneously within several minutes, but in some cases, hypertension lasted for several hours
[see Clinical Trials Experience (6.1)].