Albuterol
Albuterol Prescribing Information
Albuterol tablets, USP are indicated for the relief of bronchospasm in adults and children 6 years of age and older with reversible obstructive airway disease.
The following dosages of albuterol tablets are expressed in terms of albuterol base.
Albuterol tablets are contraindicated in patients with a history of hypersensitivity to albuterol, or any of its components.
The adverse reactions to albuterol are similar in nature to those of other sympathomimetic agents.
Adverse Event | Percent Incidence |
Central nervous system | |
| Nervousness | 20% |
| Tremor | 20% |
| Headache | 7% |
| Dizziness | 2% |
| Weakness | 2% |
| Sleeplessness | 2% |
| Irritability | <1% |
| Drowsiness | <1% |
| Restlessness | <1% |
Cardiovascular | |
| Palpitations | 5% |
| Tachycardia | 5% |
| Flushing | <1% |
| Chest discomfort | <1% |
Musculoskeletal | |
| Muscle cramps | 3% |
Gastrointestinal | |
| Nausea | 2% |
Genitourinary | |
| Difficulty in micturition | <1% |
Cases of urticaria, angioedema, rash, bronchospasm, oropharyngeal edema and antirhytmias (including atrial fibrillation, supraventricular tachycardia, and extrasystoles) have been reported after the use of albuterol tablets.
In addition to those adverse reactions reported above, albuterol, like other sympathomimetic agents, can cause adverse reactions such as angina, central nervous system stimulation, drying or irritation of the oropharynx, hypertension, unusual taste, and vertigo.
The reactions are generally transient in nature, and it is usually not necessary to discontinue treatment with albuterol tablets. In selected cases, however, dosage may be reduced temporarily; after the reaction has subsided, dosage should be increased in small increments to the optimal dosage.
The concomitant use of albuterol tablets and other oral sympathomimetic agents is not recommended since such combined use may lead to deleterious cardiovascular effects. This recommendation does not preclude the judicious use of an aerosol bronchodilator of the adrenergic stimulant type in patients receiving albuterol tablets. Such concomitant use, however, should be individualized and not given on a routine basis. If regular coadministration is required, then alternative therapy should be considered.
Albuterol tablets, USP contain albuterol sulfate, USP, the racemic form of albuterol and a relatively selective beta2 -adrenergic bronchodilator. Albuterol sulfate has the chemical name α1-[(
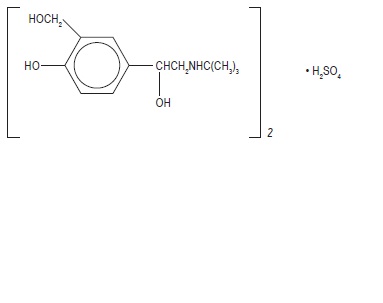
The molecular weight of albuterol sulfate is 576.71, and the molecular formula is (C13H21NO3)2 •H2SO4. Albuterol sulfate, USP is a white or practically white powder. It is freely soluble in water, slightly soluble in alcohol, in chloroform and in ether.
The World Health Organization recommended name for albuterol base is salbutamol.
Each albuterol tablet, USP for oral administration contains 2 mg or 4 mg of albuterol as 2.4 mg or 4.8 mg of albuterol sulfate, USP respectively and following inactive ingredients: colloidal silicon dioxide, lactose monohydrate, magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose, povidone, pregelatinized starch (botanical source: maize) and sodium starch glycolate.
FDA approved dissolution specification differs from the USP dissolution specification.