Amoxapine - Amoxapine tablet prescribing information
Suicidality and Antidepressant Drugs
Antidepressants increased the risk compared to placebo of suicidal thinking and behavior (suicidality) in children, adolescents, and young adults in short-term studies of major depressive disorder (MDD) and other psychiatric disorders. Anyone considering the use of amoxapine or any other antidepressant in a child, adolescent, or young adult must balance this risk with the clinical need. Short-term studies did not show an increase in the risk of suicidality with antidepressants compared to placebo in adults beyond age 24; there was a reduction in risk with antidepressants compared to placebo in adults aged 65 and older. Depression and certain other psychiatric disorders are themselves associated with increases in the risk of suicide. Patients of all ages who are started on antidepressant therapy should be monitored appropriately and observed closely for clinical worsening, suicidality, or unusual changes in behavior. Families and caregivers should be advised of the need for close observation and communication with the prescriber. Amoxapine is not approved for use in pediatric patients. (See Warnings: Clinical Worsening and Suicide Risk , Precautions: Information for Patients , and Precautions: Pediatric Use )
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Amoxapine is indicated for the relief of symptoms of depression in patients with neurotic or reactive depressive disorders as well as endogenous and psychotic depressions. It is indicated for depression accompanied by anxiety or agitation.
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Effective dosage of amoxapine may vary from one patient to another. Usual effective dosage is 200 to 300 mg daily. Three weeks constitutes an adequate period of trial providing dosage has reached 300 mg daily (or lower level of tolerance) for at least two weeks. If no response is seen at 300 mg, dosage may be increased, depending upon tolerance, up to 400 mg daily. Hospitalized patients who have been refractory to antidepressant therapy and who have no history of convulsive seizures may have dosage raised cautiously up to 600 mg daily in divided doses.
Amoxapine may be given in a single daily dose, not to exceed 300 mg, preferably at bedtime. If the total daily dosage exceeds 300 mg, it should be given in divided doses.
Initial Dosage for Adults
Usual starting dosage is 50 mg two or three times daily. Depending upon tolerance, dosage may be increased to 100 mg two or three times daily by the end of the first week. (Initial dosage of 300 mg daily may be given, but notable sedation may occur in some patients during the first few days of therapy at this level.) Increases above 300 mg daily should be made only if 300 mg daily has been ineffective during a trial period of at least two weeks. When effective dosage is established, the drug may be given in a single dose (not to exceed 300 mg) at bedtime.
Elderly Patients
In general, lower dosages are recommended for these patients. Recommended starting dosage of amoxapine is 25 mg two or three times daily. If no intolerance is observed, dosage may be increased by the end of the first week to 50 mg two or three times daily. Although 100 to 150 mg daily may be adequate for many elderly patients, some may require higher dosage. Careful increases up to 300 mg daily are indicated in such cases.
Once an effective dosage is established, amoxapine may conveniently be given in a single bedtime dose, not to exceed 300 mg.
Maintenance
Recommended maintenance dosage of amoxapine is the lowest dose that will maintain remission. If symptoms reappear, dosage should be increased to the earlier level until they are controlled.
For maintenance therapy at dosages of 300 mg or less, a single dose at bedtime is recommended.
CONTRAINDICATIONS
Amoxapine is contraindicated in patients who have shown prior hypersensitivity to dibenzoxazepine compounds. It should not be given concomitantly with monoamine oxidase inhibitors. Hyperpyretic crises, severe convulsions, and deaths have occurred in patients receiving tricyclic antidepressants and monoamine oxidase inhibitors simultaneously. When it is desired to replace a monoamine oxidase inhibitor with amoxapine, a minimum of 14 days should be allowed to elapse after the former is discontinued. Amoxapine should then be initiated cautiously with gradual increase in dosage until optimum response is achieved. The drug is not recommended for use during the acute recovery phase following myocardial infarction.
ADVERSE REACTIONS
Adverse reactions reported in controlled studies in the United States are categorized with respect to incidence below. Following this is a listing of reactions known to occur with other antidepressant drugs of this class.
Incidence Greater Than 1%
The most frequent types of adverse reactions occurring with amoxapine in controlled clinical trials were sedative and anticholinergic: these included drowsiness (14%), dry mouth (14%), constipation (12%), and blurred vision (7%).
Less frequently reported reactions are:
CNS and Neuromuscular: anxiety, insomnia, restlessness, nervousness, palpitations, tremors, confusion, excitement, nightmares, ataxia, alterations in EEG patterns.
Allergic: edema, skin rash.
Endocrine: elevation of prolactin levels.
Gastrointestinal: nausea.
Other: dizziness, headache, fatigue, weakness, excessive appetite, increased perspiration.
Incidence Less Than 1%
Anticholinergic: disturbances of accommodation, mydriasis, delayed micturition, urinary retention, nasal stuffiness.
Cardiovascular: hypotension, hypertension, syncope, tachycardia.
Allergic: drug fever, urticaria, photosensitization, pruritus, vasculitis, hepatitis.
CNS and Neuromuscular: tingling, paresthesias of the extremities, tinnitus, disorientation, seizures, hypomania, numbness, incoordination, disturbed concentration, hyperthermia, extrapyramidal symptoms, including, tardive dyskinesia. Neuroleptic malignant syndrome has been reported. (See WARNINGS .)
Hematologic: leukopenia, agranulocytosis.
Gastrointestinal: epigastric distress, vomiting, flatulence, abdominal pain, peculiar taste, diarrhea.
Endocrine: increased or decreased libido, impotence, menstrual irregularity, breast enlargement and galactorrhea in the female, syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone secretion.
Other: lacrimation, weight gain or loss, altered liver function, painful ejaculation.
Drug Relationship Unknown
The following reactions have been reported rarely, and occurred under uncontrolled circumstances where a drug relationship was difficult to assess. These observations are listed to serve as alerting information to physicians.
Anticholinergic: paralytic ileus.
Cardiovascular: atrial arrhythmias (including atrial fibrillation), myocardial infarction, stroke, heart block.
CNS and Neuromuscular: hallucinations.
Hematologic: thrombocytopenia, eosinophilia, purpura, petechiae.
Gastrointestinal: parotid swelling.
Endocrine: change in blood glucose levels.
Other: pancreatitis, hepatitis, jaundice, urinary frequency, testicular swelling, anorexia, alopecia.
Additional Adverse Reactions
The following reactions have been reported with other antidepressant drugs.
Anticholinergic: sublingual adenitis, dilation of the urinary tract.
CNS and Neuromuscular: delusions.
Gastrointestinal: stomatitis, black tongue.
Endocrine: gynecomastia.
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Teva at 1-888-838-2872 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
Drug Interactions
See CONTRAINDICATIONS about concurrent usage of tricyclic antidepressants and monoamine oxidase inhibitors. Paralytic ileus may occur in patients taking tricyclic antidepressants in combination with anticholinergic drugs. Amoxapine may enhance the response to alcohol and the effects of barbiturates and other CNS depressants. Serum levels of several tricyclic antidepressants have been reported to be significantly increased when cimetidine is administered concurrently. Although such an interaction has not been reported to date with amoxapine, specific interaction studies have not been done, and the possibility should be considered.
Drugs Metabolized by P450 2D6
The biochemical activity of the drug metabolizing isozyme cytochrome P450 2D6 (debrisoquin hydroxylase) is reduced in a subset of the caucasian population (about 7 to 10% of caucasians are so called “poor metabolizers”); reliable estimates of the prevalence of reduced P450 2D6 isozyme activity among Asian, African and other populations are not yet available. Poor metabolizers have higher than expected plasma concentrations of tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs) when given usual doses. Depending on the fraction of drug metabolized by P450 2D6, the increase in plasma concentration may be small, or quite large (8 fold increase in plasma AUC of the TCA).
In addition, certain drugs inhibit the activity of this isozyme and make normal metabolizers resemble poor metabolizers. An individual who is stable on a given dose of TCA may become abruptly toxic when given one of these inhibiting drugs as concomitant therapy. The drugs that inhibit cytochrome P450 2D6 include some that are not metabolized by the enzyme (quinidine, cimetidine) and many that are substrates for P450 2D6 (many other antidepressants, phenothiazines, and the Type 1C antiarrhythmics propafenone and flecainide). While all the selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), e.g., fluoxetine, sertraline, and paroxetine, inhibit P450 2D6, they may vary in the extent of inhibition. The extent to which SSRI-TCA interactions may pose clinical problems will depend on the degree of inhibition and the pharmacokinetics of the SSRI involved. Nevertheless, caution is indicated in the co-administration of TCAs with any of the SSRIs and also in switching from one class to the other. Of particular importance, sufficient time must elapse before initiating TCA treatment in a patient being withdrawn from fluoxetine, given the long half-life of the parent and active metabolite (at least 5 weeks may be necessary).
Concomitant use of tricyclic antidepressants with drugs that can inhibit cytochrome P450 2D6 may require lower doses than usually prescribed for either the tricyclic antidepressant or the other drug. Furthermore, whenever one of these other drugs is withdrawn from co-therapy, an increased dose of tricyclic antidepressant may be required. It is desirable to monitor TCA plasma levels whenever a TCA is going to be co-administered with another drug known to be an inhibitor of P450 2D6.
DESCRIPTION
Amoxapine, USP is an antidepressant of the dibenzoxazepine class, chemically distinct from the dibenzazepines, dibenzocycloheptenes, and dibenzoxepines.
It is designated chemically as 2-Chloro-11-(1-piperazinyl)dibenz[b,f][1,4]oxazepine. The structural formula is represented below:
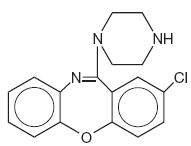
C 17 H 16 CIN 3 O M.W. 313.78
Amoxapine is supplied for oral administration as 25 mg, 50 mg, 100 mg and 150 mg tablets.
Amoxapine tablets USP, 25 mg, 50 mg, 100 mg and 150 mg contain: dibasic calcium phosphate, magnesium stearate, pregelatinized (corn) starch, and stearic acid.
Amoxapine tablets USP, 50 mg and 150 mg also contain: FD&C Yellow No. 6 Aluminum Lake.
Amoxapine tablets USP, 100 mg also contain: FD&C Blue No. 2 Aluminum Lake.
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Amoxapine is an antidepressant with a mild sedative component to its action. The mechanism of its clinical action in man is not well understood. In animals, amoxapine reduced the uptake of norepinephrine and serotonin and blocked the response of dopamine receptors to dopamine. Amoxapine is not a monoamine oxidase inhibitor.
Amoxapine is absorbed rapidly and reaches peak blood levels approximately 90 minutes after ingestion. It is almost completely metabolized. The main route of excretion is the kidney. In vitro tests show that amoxapine binding to human serum is approximately 90%.
In man, amoxapine serum concentration declines with a half-life of eight hours. However, the major metabolite, 8-hydroxy-amoxapine, has a biologic half-life of 30 hours. Metabolites are excreted in the urine in conjugated form as glucuronides.
Clinical studies have demonstrated that amoxapine has a more rapid onset of action than either amitriptyline or imipramine. The initial clinical effect may occur within four to seven days and occurs within two weeks in over 80% of responders.
HOW SUPPLIED
Amoxapine tablets USP, 25 mg are white, round, flat-faced, beveled, bisected tablets debossed with “ DAN 25 ” on one side and “ 5713 ” on the other side, supplied in bottles of 100 (NDC 0591-5713-01).
Amoxapine tablets USP, 50 mg are orange, round, flat-faced, beveled, bisected tablets debossed with “ DAN 50 ” on one side and “ 5714 ” on the other side, supplied in bottles of 100 (NDC 0591-5714-01).
Amoxapine tablets USP, 100 mg are blue, round, flat-faced, beveled, bisected tablets debossed with “ DAN 100 ” on one side and “ 5715 ” on the other side, supplied in bottles of 100 (NDC 0591-5715-01).
Amoxapine tablets USP, 150 mg are orange, round, flat-faced, beveled, bisected tablets debossed with “ DAN 150 ” one side and “ 5716 ” on the other side, supplied in bottles of 30 (NDC 0591-5716-30).
Dispense in a tight container with child-resistant closure.
Store at 20° to 25°C (68° to 77°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature].
Dispense with Medication Guide available at: www.tevausa.com/medguides
Manufactured In India By: Watson Pharma Private Limited Verna, Salcette Goa 403 722 INDIA
Manufactured For: Teva Pharmaceuticals Parsippany, NJ 07054
Rev. A 10/2024