Ampicillin And Sulbactam Prescribing Information
Ampicillin and Sulbactam for Injection, USP is indicated for the treatment of infections due to susceptible strains of the designated microorganisms in the conditions listed below.
NOTE: For information on use in pediatric patients see
* Efficacy for this organism in this organ system was studied in fewer than 10 infections.
While Ampicillin and Sulbactam for Injection, USP is indicated only for the conditions listed above, infections caused by ampicillin-susceptible organisms are also amenable to treatment with Ampicillin and Sulbactam for Injection, USP due to its ampicillin content.
Therefore, mixed infections caused by ampicillin-susceptible organisms and beta-lactamase producing organisms susceptible to Ampicillin and Sulbactam for Injection, USP should not require the addition of another antibacterial.
Appropriate culture and susceptibility tests should be performed before treatment in order to isolate and identify the organisms causing infection and to determine their susceptibility to Ampicillin and Sulbactam for Injection, USP.
Therapy may be instituted prior to obtaining the results from bacteriological and susceptibility studies, when there is reason to believe the infection may involve any of the beta-lactamase producing organisms listed above in the indicated organ systems.
Once the results are known, therapy should be adjusted if appropriate.
To reduce the development of drug-resistant bacteria and maintain the effectiveness of Ampicillin and Sulbactam for Injection, USP and other antibacterial drugs, Ampicillin and Sulbactam for Injection, USP should be used only to treat infections that are proven or strongly suspected to be caused by susceptible bacteria. When culture and susceptibility information are available, they should be considered in selecting or modifying antibacterial therapy. In the absence of such data, local epidemiology and susceptibility patterns may contribute to the empiric selection of therapy.
Ampicillin and Sulbactam for Injection is for preparation of solutions for intravenous infusion only. Ampicillin and Sulbactam for Injection should be administered by slow intravenous injection over at least 10-15 minutes or can also be delivered in greater dilutions with 50-100 mL of a compatible diluent as an intravenous infusion over 15-30 minutes.
The recommended adult dosage of Ampicillin and Sulbactam for Injection is 1.5 g (1 g ampicillin as the sodium salt plus 0.5 g sulbactam as the sodium salt) to 3 g (2 g ampicillin as the sodium salt plus 1 g sulbactam as the sodium salt) every six hours. This 1.5 to 3 g range represents the total of ampicillin content plus the sulbactam content of Ampicillin and Sulbactam for Injection, and corresponds to a range of 1 g ampicillin/0.5 g sulbactam to 2 g ampicillin/1 g sulbactam. The total dose of sulbactam should not exceed 4 grams per day.
The recommended daily dose of Ampicillin and Sulbactam for Injection in pediatric patients is 300 mg per kg of body weight administered via intravenous infusion in equally divided doses every 6 hours. This 300 mg/kg/day dosage represents the total ampicillin content plus the sulbactam content of Ampicillin and Sulbactam for Injection, and corresponds to 200 mg ampicillin/100 mg sulbactam per kg per day. The safety and efficacy of Ampicillin and Sulbactam for Injection administered via intramuscular injection in pediatric patients have not been established. Pediatric patients weighing 40 kg or more should be dosed according to adult recommendations, and the total dose of sulbactam should not exceed 4 grams per day. The course of intravenous therapy should not routinely exceed 14 days. In clinical trials, most children received a course of oral antimicrobials following initial treatment with intravenous Ampicillin and Sulbactam for Injection (see
In patients with impairment of renal function the elimination kinetics of ampicillin and sulbactam are similarly affected, hence the ratio of one to the other will remain constant whatever the renal function. The dose of Ampicillin and Sulbactam for Injection in such patients should be administered less frequently in accordance with the usual practice for ampicillin and according to the following recommendations:
Creatinine Clearance (mL/min/1.73m 2) | Ampicillin/ Sulbactam Half-Life (Hours) | Recommended Ampicillin and Sulbactam for Injection Dosage |
≥ 30 | 1 | 1.5-3 g q 6h-q 8h |
15-29 | 5 | 1.5-3 g q 12h |
5-14 | 9 | 1.5-3 g q 24h |
When only serum creatinine is available, the following formula (based on sex, weight, and age of the patient) may be used to convert this value into creatinine clearance. The serum creatinine should represent a steady state of renal function.
Males | weight (kg) × (140 - age) 72 × serum creatinine |
Females | 0.85 × above value |
The use of ampicillin and sulbactam for injection is contraindicated in individuals with a history of serious hypersensitivity reactions (e.g., anaphylaxis or Stevens-Johnson syndrome) to ampicillin, sulbactam or to other beta-lactam antibacterial drugs (e.g., penicillins and cephalosporins).
Ampicillin and sulbactam for injection is contraindicated in patients with a previous history of cholestatic jaundice/hepatic dysfunction associated with ampicillin and sulbactam for injection.
Ampicillin and sulbactam for injection is generally well tolerated. The following adverse reactions have been reported in clinical trials.
Pain at IV injection site – 3%
Thrombophlebitis – 3%
Phlebitis – 1.2%
The most frequently reported adverse reactions were diarrhea in 3% of the patients and rash in less than 2% of the patients.
Additional systemic reactions reported in less than 1% of the patients were: itching, nausea, vomiting, candidiasis, fatigue, malaise, headache, chest pain, flatulence, abdominal distension, glossitis, urine retention, dysuria, edema, facial swelling, erythema, chills, tightness in throat, substernal pain, epistaxis and mucosal bleeding.
Available safety data for pediatric patients treated with ampicillin and sulbactam for injection demonstrate a similar adverse events profile to those observed in adult patients.
Additionally, atypical lymphocytosis has been observed in one pediatric patient receiving ampicillin and sulbactam for injection.
Adverse laboratory changes without regard to drug relationship that were reported during clinical trials were:
In addition to adverse reactions reported from clinical trials, the following have been identified during post-marketing use of ampicillin and sulbactam for injection or other products containing ampicillin. Because they are reported voluntarily from a population of unknown size, estimates of frequency cannot be made. These events have been chosen for inclusion due to a combination of their seriousness, frequency, or potential causal connection to ampicillin and sulbactam for injection.
Ampicillin and Sulbactam for Injection, USP is a sterile injectable antibacterial combination consisting of the semisynthetic antibacterial ampicillin sodium and the beta-lactamase inhibitor sulbactam sodium for intravenous administration.
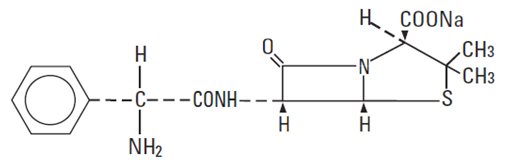
Ampicillin sodium is derived from the penicillin nucleus, 6-aminopenicillanic acid. Chemically, it is monosodium (2S, 5R, 6R)-6-[(R)-2-amino-2-phenylacetamido]-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-4-thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0] heptane-2-carboxylate and has a molecular weight of 371.39. Its chemical formula is C16H18N3NaO4S. The structural formula is:
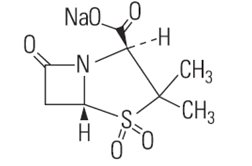
Sulbactam sodium is a derivative of the basic penicillin nucleus. Chemically, sulbactam sodium is sodium penicillinate sulfone; sodium (2S, 5R)-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-4-thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylate 4,4-dioxide.
Its chemical formula is C8H10NNaO5S with a molecular weight of 255.22. The structural formula is:
Ampicillin and Sulbactam for Injection, USP is available as a white to off-white dry powder for reconstitution. Ampicillin and Sulbactam for Injection, USP dry powder is freely soluble in aqueous diluents to yield pale yellow to yellow solutions containing ampicillin sodium and sulbactam sodium equivalent to 250 mg ampicillin per mL and 125 mg sulbactam per mL. The pH of the solutions is between 8 and 10.
Dilute solutions (up to 30 mg ampicillin and 15 mg sulbactam per mL) are essentially colorless to pale yellow. The pH of dilute solutions remains the same.
Each sterile Pharmacy Bulk Package contains 15 g Ampicillin and Sulbactam for Injection, USP (10 g ampicillin as the sodium salt and 5 g sulbactam as the sodium salt). The sodium content is 1150 mg (50 mEq) sodium per 15 gram Pharmacy Bulk Package bottle. Ampicillin and Sulbactam for Injection, USP Pharmacy Bulk Package is a bottle containing a sterile preparation of ampicillin sodium and sulbactam sodium for intravenous use that contains many single doses. The Pharmacy Bulk Package is for use in a pharmacy admixture setting; it provides many single doses of Ampicillin and Sulbactam for Injection, USP for addition to suitable parenteral fluids in the preparation of admixtures for intravenous infusion. (See