Atorvastatin Calcium
Atorvastatin Calcium Prescribing Information
Atorvastatin calcium tablets are indicated:
- To reduce the risk of:
- Myocardial infarction (MI), stroke, revascularization procedures, and angina in adults with multiple risk factors for coronary heart disease (CHD) but without clinically evident CHD
- MI and stroke in adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus with multiple risk factors for CHD but without clinically evident CHD
- Non-fatal MI, fatal and non-fatal stroke, revascularization procedures, hospitalization for congestive heart failure, and angina in adults with clinically evident CHD
- As an adjunct to diet to reduce low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) in:
- Adults with primary hyperlipidemia.
- Adults and pediatric patients aged 10 years and older with heterozygous familial hypercholesterolemia (HeFH).
- As an adjunct to other LDL-C-lowering therapies, or alone if such treatments are unavailable, to reduce LDL-C in adults and pediatric patients aged 10 years and older with homozygous familial hypercholesterolemia (HoFH).
- As an adjunct to diet for the treatment of adults with:
- Primary dysbetalipoproteinemia
- Hypertriglyceridemia
Atorvastatin calcium tablets, USP:
- 10 mg of atorvastatin: White to off white, oval shaped, film coated tablet, debossed with "TV" on one side and "5056" on the other side of the tablet.
- 20 mg of atorvastatin: White to off white, oval shaped, film coated tablet, debossed with "TV" on one side and "5059" on the other side of the tablet.
- 40 mg of atorvastatin: White to off white, oval shaped, film coated tablet, debossed with "TV" on one side and "5058" on the other side of the tablet.
- 80 mg of atorvastatin: White to off white, oval shaped, film coated tablet, debossed with "TV" on one side and "5057" on the other side of the tablet.
- Acute liver failure or decompensated cirrhosis [see Warnings and Precautions ]
- Hypersensitivity to atorvastatin or any excipients in atorvastatin calcium tablets. Hypersensitivity reactions, including anaphylaxis, angioneurotic edema, erythema multiforme, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, and toxic epidermal necrolysis, have been reported [see Adverse Reactions ].
The following adverse reactions have been identified during post-approval use of atorvastatin calcium. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Atorvastatin is an inhibitor of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A (HMG-CoA) reductase.
Atorvastatin calcium, USP is (3
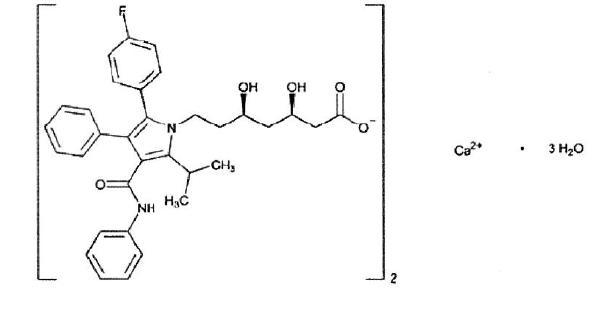
C66H68CaF2N4O10•3H2O M.W. 1209.42
Atorvastatin calcium trihydrate (Form I) is a white to off-white powder that is insoluble in aqueous solutions of pH 4.5 and below. Atorvastatin calcium, USP is very slightly soluble in distilled water, pH 7.8 phosphate buffer, and acetonitrile; slightly soluble in ethanol; and freely soluble in methanol.
Atorvastatin calcium tablets, USP for oral administration contain 10 mg, 20 mg, 40 mg, or 80 mg of atorvastatin and the following inactive ingredients: calcium carbonate, croscarmellose sodium, hydroxypropyl cellulose, hypromellose, lactose monohydrate, magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose, polyethylene glycol, polysorbate, talc and titanium dioxide.
Atorvastatin calcium is a selective, competitive inhibitor of HMG-CoA reductase, the rate-limiting enzyme that converts 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A to mevalonate, a precursor of sterols, including cholesterol. In animal models, atorvastatin calcium lowers plasma cholesterol and lipoprotein levels by inhibiting HMG-CoA reductase and cholesterol synthesis in the liver and by increasing the number of hepatic LDL receptors on the cell surface to enhance uptake and catabolism of LDL; atorvastatin calcium also reduces LDL production and the number of LDL particles.