Aviane Prescribing Information
Combination oral contraceptives should not be used in women with any of the following conditions:
- Thrombophlebitis or thromboembolic disorders
- A history of deep-vein thrombophlebitis or thromboembolic disorders
- Cerebrovascular or coronary artery disease (current or past history)
- Valvular heart disease with thrombogenic complications
- Thrombogenic rhythm disorders
- Hereditary or acquired thrombophilias
- Prolonged immobilization (especially with major surgery)
- Diabetes with vascular involvement
- Headaches with focal neurological symptoms or migraine with aura
- Women with migraine who are 35 years or older
- Uncontrolled hypertension
- Known or suspected carcinoma of the breast or personal history of breast cancer
- Known or suspected estrogen- or progesterone sensitive malignancy
- Undiagnosed abnormal vaginal bleeding
- Cholestatic jaundice of pregnancy or jaundice with prior pill use
- Hepatic adenomas or carcinomas, or active liver disease
Women who are receiving Hepatitis C drug combinations containing ombitasvir/paritaprevir/ritonavir, with or without dasabuvir, due to the potential for alanine aminotransferase (ALT) elevations (see
The use of oral contraceptives is associated with increased risks of several serious conditions including venous and arterial thrombotic and thromboembolic events (such as myocardial infarction, thromboembolism, and stroke), hepatic neoplasia, gallbladder disease, and hypertension, although the risk of serious morbidity or mortality is very small in healthy women without underlying risk factors. The risk of morbidity and mortality increases significantly in the presence of other underlying risk factors such as certain inherited or acquired thrombophilias, hypertension, hyperlipidemias, obesity, diabetes, and surgery or trauma with increased risk of thrombosis (see CONTRAINDICATIONS).
Practitioners prescribing oral contraceptives should be familiar with the following information relating to these risks.
The information contained in this package insert is principally based on studies carried out in patients who used oral contraceptives with higher doses of estrogens and progestogens than those in common use today. The effect of long-term use of the oral contraceptives with lower doses of both estrogens and progestogens remains to be determined.
Throughout this labeling, epidemiological studies reported are of two types: retrospective or case control studies and prospective or cohort studies. Case control studies provide a measure of the relative risk of disease, namely, a ratio of the incidence of a disease among oral-contraceptive users to that among nonusers. The relative risk does not provide information on the actual clinical occurrence of a disease. Cohort studies provide a measure of attributable risk, which is the difference in the incidence of disease between oral-contraceptive users and nonusers. The attributable risk does provide information about the actual occurrence of a disease in the population. For further information, the reader is referred to a text on epidemiological methods.
Cardiovascular and Cerebrovascular Events
Use of CHCs increases the risk of cardiovascular events and cerebrovascular events, such as myocardial infarction and stroke. The risk of these events with CHC use is greater in females with concomitant risk factors: age 35 years and older, smoking, hypertension, dyslipidemia, diabetes, or obesity. The risk increases with increasing age and with increasing number of cigarettes smoked.
Venous Thromboembolism
Use of CHCs also increases the risk of VTE, such as deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism. The rate of VTE in females using COCs has been estimated to be 3 to 9 cases per 10,000 woman-years. The VTE risk should be considered in the context of relevant subpopulations of females of reproductive potential who are not taking CHCs (
Risk factors for VTE with CHC use include smoking, obesity, family history of VTE, and prolonged immobilization, in addition to other factors that contraindicate use of CHCs (see
The risk of VTE is increased during the first six weeks postpartum. The risk is highest up to four weeks postpartum but remains higher than baseline until at least six weeks postpartum. The presence of multiple risk factors for VTE may further increase the risk. Obstetric complications may extend the elevated risk up to 12 weeks postpartum
Breast Cancer
Aviane is contraindicated in females who currently have or have had breast cancer because breast cancer may be hormonally sensitive (see
Cervical Cancer
Some studies suggest that oral contraceptive use has been associated with an increase in the risk of cervical intraepithelial neoplasia or invasive cervical cancer in some populations of women. However, there continues to be controversy about the extent to which such findings may be due to differences in sexual behavior and other factors.
Benign hepatic adenomas are associated with oral-contraceptive use, although the incidence of these benign tumors is rare in the United States. Indirect calculations have estimated the attributable risk to be in the range of 3.3 cases/100,000 for users, a risk that increases after four or more years of use. Rupture of rare, benign, hepatic adenomas may cause death through intra-abdominal hemorrhage.
Studies from Britain have shown an increased risk of developing hepatocellular carcinoma in long-term (>8 years) oral-contraceptive users. However, these cancers are extremely rare in the U.S. and the attributable risk (the excess incidence) of liver cancers in oral-contraceptive users approaches less than one per million users.
During clinical trials with the Hepatitis C combination drug regimen that contains ombitasvir/paritaprevir/ritonavir, with or without dasabuvir, ALT elevations greater than 5 times the upper limit of normal (ULN), including some cases greater than 20 times the ULN, were significantly more frequent in women using ethinyl estradiol-containing medications such as COCs. Discontinue Aviane prior to starting therapy with the combination drug regimen ombitasvir/paritaprevir/ritonavir, with or without dasabuvir (see CONTRAINDICATIONS). Aviane can be restarted approximately 2 weeks following completion of treatment with the combination drug regimen.
There have been clinical case reports of retinal thrombosis associated with the use of oral contraceptives that may lead to partial or complete loss of vision. Oral contraceptives should be discontinued if there is unexplained partial or complete loss of vision; onset of proptosis or diplopia; papilledema; or retinal vascular lesions. Appropriate diagnostic and therapeutic measures should be undertaken immediately.
Extensive epidemiological studies have revealed no increased risk of birth defects in infants born to women who have used oral contraceptives prior to pregnancy. Studies also do not suggest a teratogenic effect, particularly insofar as cardiac anomalies and limb-reduction defects are concerned, when taken inadvertently during early pregnancy (see CONTRAINDICATIONS).
It is recommended that for any patient who has missed two consecutive periods, pregnancy should be ruled out. If the patient has not adhered to the prescribed schedule, the possibility of pregnancy should be considered at the time of the first missed period. Oral-contraceptive use should be discontinued if pregnancy is confirmed.
Combination oral contraceptives may worsen existing gallbladder disease and may accelerate the development of this disease in previously asymptomatic women. Earlier studies have reported an increased lifetime relative risk of gallbladder surgery in users of oral contraceptives and estrogens. More recent studies, however, have shown that the relative risk of developing gallbladder disease among oral-contraceptive users may be minimal. The recent findings of minimal risk may be related to the use of oral-contraceptive formulations containing lower hormonal doses of estrogens and progestogens. A past history of COC-related cholestasis predicts an increased risk with subsequent COC use. Women with a history of pregnancy-related cholestasis may be at an increased risk for COC related cholestasis.
Oral contraceptives have been shown to cause glucose intolerance in a significant percentage of users. Carefully monitor females with prediabetes and diabetes who are using Aviane. Aviane may decrease glucose tolerance.
A small proportion of women will have persistent hypertriglyceridemia while on COCs. As discussed earlier (see
Aviane is contraindicated in women with uncontrolled hypertension or hypertension with vascular disease (see
An increase in blood pressure has been reported in females using CHCs, and this increase is more likely in older women with extended duration of use. The effect of CHCs on blood pressure may vary according to the progestin in the CHC.
Aviane is contraindicated in females who have headaches with focal neurological symptoms or have migraine headaches with aura, and in women over age 35 years who have migraine head aches with or without aura.
The onset or exacerbation of migraine or development of headache with a new pattern that is recurrent, persistent, or severe requires discontinuation of oral contraceptives and evaluation of the cause. Consider discontinuation of Aviane if there is an increased frequency or severity of migraines during CHC use (which may be prodromal of a cerebrovascular event; see
Unscheduled bleeding and spotting are sometimes encountered in patients on oral contraceptives, especially during the first three months of use. The type and dose of progestogen may be important. If bleeding persists or recurs, nonhormonal causes should be considered and adequate diagnostic measures taken to rule out malignancy or pregnancy in the event of unscheduled bleeding, as in the case of any abnormal vaginal bleeding. If pathology has been excluded, time or a change to another formulation may solve the problem. In the event of amenorrhea, pregnancy should be ruled out.
Some women may encounter post-pill amenorrhea or oligomenorrhea (possibly with anovulation), especially when such a condition was preexistent.
In the clinical trial with levonorgestrel 0.1 mg and ethinyl estradiol 0.02 mg tablets, unscheduled bleeding was defined as bleeding or spotting that occurred:
- During cycle 1 on pill-pack Days 4 to 21, inclusive of a 28-day cycle.
- In subsequent cycles, on Days 5 to 21 inclusive or on pill-pack Days 1 to 4 inclusive if preceded by 2 consecutive days without bleeding or spotting.
Based on subject diaries, the proportion of subjects reporting unscheduled bleeding or spotting per 28-day cycle decreased over time: 30.5% at Cycle 1 versus 18.2% at Cycle 12.
Hereditary Angioedema
In women with hereditary angioedema, exogenous estrogens may induce or exacerbate symptoms of angioedema.
Chloasma
Chloasma may occur, especially in women with a history of chloasma gravidarum. Advise women with a history of chloasma to avoid exposure to the sun or ultraviolet radiation while taking Aviane.
Effect on Binding Globulins
The estrogen component of COCs may raise the serum concentrations of thyroxine-binding globulin, sex hormone-binding globulin, and cortisol-binding globulin. Monitor thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) levels for females receiving Aviane and thyroid hormone replacement therapy concomitantly. Follow the recommendation for the thyroid hormone in accordance with its Prescribing Information.
Aviane (levonorgestrel and ethinyl estradiol tablets) is indicated for use by females of reproductive potential to prevent pregnancy.
In a clinical trial with Aviane (levonorgestrel and ethinyl estradiol tablets), 1,477 subjects had 7,720 cycles of use and a total of 5 pregnancies were reported. This represents an overall pregnancy rate of 0.84 per 100 woman-years. This rate includes patients who did not take the drug correctly. One or more pills were missed during 1,479 (18.8%) of the 7,870 cycles; thus all tablets were taken during 6,391 (81.2%) of the 7,870 cycles. Of the total 7,870 cycles, a total of 150 cycles were excluded from the calculation of the Pearl index due to the use of backup contraception and/or missing 3 or more consecutive pills.
The mean BMI of the study population was 24 kg/m2. Females with a BMI greater than 30 kg/m2 accounted for 12.1% (n=179) of the study population. Females with a BMI over 35 kg/m2 accounted for 4.3% (n=63) of the study population.
To achieve maximum contraceptive effectiveness, Aviane (levonorgestrel and ethinyl estradiol tablets) must be taken exactly as directed and at intervals not exceeding 24 hours. The dosage of Aviane-28 is one orange tablet daily for 21 consecutive days, followed by one light-green inert tablet daily for 7 consecutive days, according to the prescribed schedule. It is recommended that Aviane-28 tablets be taken at the same time each day.
The dispenser should be kept in the wallet supplied to avoid possible fading of the pills. If the pills fade, patients should continue to take them as directed.
The possibility of ovulation and conception prior to initiation of medication should be considered. The patient should be instructed to begin taking Aviane on either the first Sunday after the onset of menstruation (Sunday Start) or on Day 1 of menstruation (Day 1 Start).
The patient is instructed to begin taking Aviane-28 on the first Sunday after the onset of menstruation. If menstruation begins on a Sunday, the first tablet (orange) is taken that day. One orange tablet should be taken daily for 21 consecutive days, followed by one light-green inert tablet daily for 7 consecutive days. Withdrawal bleeding should usually occur within 3 days following discontinuation of orange tablets and may not have finished before the next pack is started. During the first cycle, contraceptive reliance should not be placed on Aviane-28 until an orange tablet has been taken daily for 7 consecutive days, and a nonhormonal back-up method of birth control should be used during those 7 days.
During the first cycle of medication, the patient is instructed to begin taking Aviane-28 during the first 24 hours of her period (day one of her menstrual cycle). One orange tablet should be taken daily for 21 consecutive days, followed by one light-green inert tablet daily for 7 consecutive days. Withdrawal bleeding should usually occur within 3 days following discontinuation of orange tablets and may not have finished before the next pack is started. If medication is begun on day one of the menstrual cycle, no back-up contraception is necessary. If Aviane-28 tablets are started later than day one of the first menstrual cycle or postpartum, contraceptive reliance should not be placed on Aviane-28 tablets until after the first 7 consecutive days of administration, and a nonhormonal back-up method of birth control should be used during those 7 days.
The patient begins her next and all subsequent courses of tablets on the day after taking her last light-green tablet. She should follow the same dosing schedule: 21 days on orange tablets followed by 7 days on light-green tablets. If in any cycle the patient starts tablets later than the proper day, she should protect herself against pregnancy by using a nonhormonal back-up method of birth control until she has taken an orange tablet daily for 7 consecutive days.
When the patient is switching from a 21-day regimen of tablets, she should wait 7 days after her last tablet before she starts Aviane. She will probably experience withdrawal bleeding during that week. She should be sure that no more than 7 days pass after her previous 21-day regimen. When the patient is switching from a 28-day regimen of tablets, she should start her first pack of Aviane on the day after her last tablet. She should not wait any days between packs. The patient may switch any day from a progestin-only pill and should begin Aviane the next day. If switching from an implant or injection, the patient should start Aviane on the day of implant removal or, if using an injection, the day the next injection would be due. In switching from a progestin-only pill, injection, implant, or intrauterine system (IUS), the patient should be advised to use additional nonhormonal contraception (such as condoms) until active tablets have been taken for 7 consecutive days of the first pack.
If spotting or breakthrough bleeding occur, the patient is instructed to continue on the same regimen. This type of bleeding is usually transient and without significance; however, if the bleeding is persistent or prolonged, the patient is advised to consult her physician.
While there is little likelihood of ovulation occurring if only one or two orange tablets are missed, the possibility of ovulation increases with each successive day that scheduled orange tablets are missed. Although the occurrence of pregnancy is unlikely if Aviane is taken according to directions, if withdrawal bleeding does not occur, the possibility of pregnancy must be considered. If the patient has not adhered to the prescribed schedule (missed one or more tablets or started taking them on a day later than she should have), the probability of pregnancy should be considered at the time of the first missed period and appropriate diagnostic measures taken. If the patient has adhered to the prescribed regimen and misses two consecutive periods, pregnancy should be ruled out.
The risk of pregnancy increases with each active (orange) tablet missed. For additional patient instructions regarding missed tablets, see the
Aviane may be initiated no earlier than day 28 postpartum in the nonlactating mother or after a second trimester abortion due to the increased risk for thromboembolism (see
Aviane may be initiated immediately after a first trimester abortion or miscarriage. Instruct the patient to use additional nonhormonal contraception (such as condoms) until active tablets have been taken for 7 consecutive days, unless starting Aviane on the day of surgical abortion.
Combination oral contraceptives should not be used in women with any of the following conditions:
- Thrombophlebitis or thromboembolic disorders
- A history of deep-vein thrombophlebitis or thromboembolic disorders
- Cerebrovascular or coronary artery disease (current or past history)
- Valvular heart disease with thrombogenic complications
- Thrombogenic rhythm disorders
- Hereditary or acquired thrombophilias
- Prolonged immobilization (especially with major surgery)
- Diabetes with vascular involvement
- Headaches with focal neurological symptoms or migraine with aura
- Women with migraine who are 35 years or older
- Uncontrolled hypertension
- Known or suspected carcinoma of the breast or personal history of breast cancer
- Known or suspected estrogen- or progesterone sensitive malignancy
- Undiagnosed abnormal vaginal bleeding
- Cholestatic jaundice of pregnancy or jaundice with prior pill use
- Hepatic adenomas or carcinomas, or active liver disease
Women who are receiving Hepatitis C drug combinations containing ombitasvir/paritaprevir/ritonavir, with or without dasabuvir, due to the potential for alanine aminotransferase (ALT) elevations (see
An increased risk of the following serious adverse reactions (see WARNINGS section for additional information) has been associated with the use of oral contraceptives:
Thromboembolic and thrombotic disorders and other vascular problems (including thrombophlebitis and venous thrombosis with or without pulmonary embolism, mesenteric thrombosis, arterial thromboembolism, myocardial infarction, cerebral hemorrhage, cerebral thrombosis), carcinoma of the reproductive organs and breasts, hepatic neoplasia (including hepatic adenomas or benign liver tumors), ocular lesions (including retinal vascular thrombosis), gallbladder disease, carbohydrate and lipid effects, elevated blood pressure, and headache including migraine.
Five studies that compared breast cancer risk between ever-users (current or past use) of COCs and never-users of COCs reported no association between ever use of COCs and breast cancer risk, with effect estimates ranging from 0.90 - 1.12 (Figure 2).
Three studies compared breast cancer risk between current or recent COC users (<6 months since last use) and never users of COCs (Figure 2). One of these studies reported no association between breast cancer risk and COC use. The other two studies found an increased relative risk of 1.19 - 1.33 with current or recent use. Both of these studies found an increased risk of breast cancer with current use of longer duration, with relative risks ranging from 1.03 with less than one year of COC use to approximately 1.4 with more than 8-10 years of COC use.
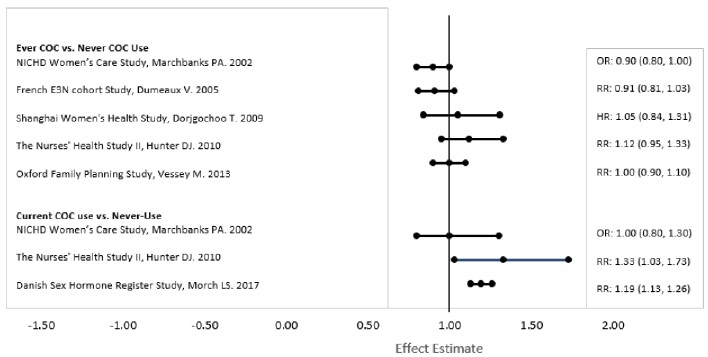
RR = relative risk; OR = odds ratio; HR = hazard ratio. “ever COC” are females with current or past COC use; “never COC use” are females that never used COCs.
The following adverse reactions associated with the use of oral CHCs were identified in clinical studies or postmarketing reports. Because some of these reactions were reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure. Common adverse reactions associated with oral CHCs are headache, abdominal pain, nausea, metrorrhagia, vaginal moniliasis and pain, acne, and vaginitis.
Additional adverse reactions that have been reported include the following:
21 orange active tablets each containing 0.10 mg of levonorgestrel, USP (-)-13-Ethyl-17-hydroxy-18,19-dinor-17α-pregn-4-en-20-yn-3-one, a totally synthetic progestogen, and 0.02 mg of ethinyl estradiol, USP, (19-Nor-17α-pregna-1,3,5(10)-trien-20-yne-3,17-diol). The inactive ingredients present are: FD&C yellow no. 6 aluminum lake, hypromellose, lactose monohydrate, magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose, polyethylene glycol, pregelatinized corn starch, sodium starch glycolate and titanium dioxide.
7 light-green, inert tablets each containing: D&C yellow no. 10 aluminum lake, FD&C blue no. 1 aluminum lake, FD&C yellow no. 6 aluminum lake, lactose monohydrate, magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose and pregelatinized corn starch.
Levonorgestrel, USP
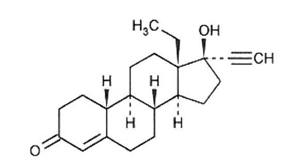
C21H28O2 M.W. 312.45
Ethinyl Estradiol, USP
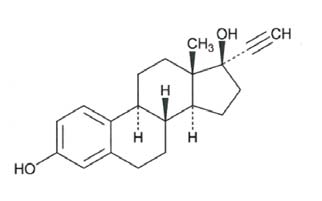
C20H24O2 M.W. 296.40