Azacitidine
Azacitidine Prescribing Information
Azacitidine for injection is supplied as lyophilized powder in 100 mg single-dose vials
The following adverse reactions are described in other labelingsections:
- Anemia, Neutropenia and Thrombocytopenia [see Warnings and Precautions ()]5.2Anemia, Neutropenia and Thrombocytopenia
Azacitidine for injection causes anemia, neutropenia and thrombocytopenia in adult patients with MDS. Monitor complete blood counts frequently for response and/or toxicity, at a minimum, prior to each dosing cycle.
In adult patients with MDS, after administration of the recommended dosage for the first cycle, adjust dosage for subsequent cycles based on nadir counts and hematologic response
[see Dosage and Administration ].Pediatric use information is approved for Celgene Corporation's Vidaza (azacitidine for injection). However, due to Celgene Corporation's marketing exclusivity rights, this drug product is not labeled with that information. - Hepatotoxicity in Patients with Severe Pre-existing Hepatic Impairment [see Warnings and Precautions ()]5.3 Hepatotoxicity in Patients with Severe Pre-existing Hepatic Impairment
Because azacitidine is potentially hepatotoxic in patients with severe pre-existing hepatic impairment, caution is needed in patients with liver disease. Patients with extensive tumor burden due to metastatic disease have been reported to experience progressive hepatic coma and death during azacitidine treatment, especially in such patients with baseline albumin <30 g/L. Azacitidine is contraindicated in patients with advanced malignant hepatic tumors
[see Contraindications ]. Monitor liver chemistries prior to initiation of therapy and with each cycle.Safety and effectiveness of azacitidine for injection in patients with MDS and hepatic impairment have not been studied as these patients were excluded from the clinical trials.
Pediatric use information is approved for Celgene Corporation's Vidaza (azacitidine for injection). However, due to Celgene Corporation's marketing exclusivity rights, this drug product is not labeled with that information. - Renal Toxicity[see Warnings and Precautions ()]5.4 Renal Toxicity
Renal toxicity ranging from elevated serum creatinine to renal failure and death have been reported in patients treated with intravenous azacitidine in combination with other chemotherapeutic agents for non-MDS conditions. In addition, renal tubular acidosis, defined as a fall in serum bicarbonate to <20 mEq/L in association with an alkaline urine and hypokalemia (serum potassium <3 mEq/L) developed in 5 patients with CML treated with azacitidine and etoposide. Monitor serum creatinine and electrolytes prior to initiation of therapy and with each cycle. If unexplained reductions in serum bicarbonate <20 mEq/L or elevations of BUN or serum creatinine occur, reduce or hold the dose
[see Dosage and Administration ].Patients with renal impairment may be at increased risk for renal toxicity. Also, azacitidine and its metabolites are primarily excreted by the kidney. Therefore, monitor these patients closelyfor toxicity
[see Dosage and Administration]. Patients with MDS and renal impairment were excluded from the clinical studies.Pediatric use information is approved for Celgene Corporation's Vidaza (azacitidine for injection). However, due to Celgene Corporation's marketing exclusivity rights, this drug product is not labeled with that information. - Tumor Lysis Syndrome[see Warnings and Precautions ()]5.5 Tumor Lysis Syndrome
Azacitidine for injection may cause fatal or serious tumor lysis syndrome, including in patients with MDS. Tumor lysis syndrome may occur despite concomitant use of allopurinol. Assess baseline risk and monitor and treat as appropriate.
Azacitidine for injection contains azacitidine, which is a nucleoside metabolic inhibitor. Azacitidine is 4-amino-1-β-D-ribofuranosyl-1,3,5-triazin-2(1H)-one. The structural formula is as follows:
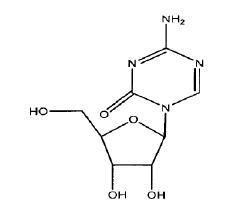
The empirical formula is C8H12N4O5. The molecular weight is 244.20. Azacitidine is a white to off- white powder. Azacitidine was found to be soluble in dimethyl sulphoxide, sparingly soluble in water and insoluble in acetone and ethanol.
The finished product is supplied in a sterile form for reconstitution as a suspension for subcutaneous injection or reconstitution as a solution with further dilution for intravenous infusion. Vials of azacitidine for injection contain 100 mg of azacitidine and 100 mg mannitol as a sterile lyophilized powder.
Azacitidine for injection is supplied as a lyophilized powder in 100 mg single-dose vials packaged in cartons of 1 vial (NDC 75907-225-11).
Store unreconstituted vials at 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F); (See USP Controlled Room Temperature).
Azacitidine for injection is a hazardous drug. Follow applicable special handling and disposal procedures.1
Azacitidine for injection is a pyrimidine nucleoside analog of cytidine. Azacitidine for injection is believed to exert its antineoplastic effects by causing hypomethylation of DNA and direct cytotoxicity on abnormal hematopoietic cells in the bone marrow. The concentration of azacitidine required for maximum inhibition of DNA methylation in vitro does not cause major suppression of DNA synthesis.
Hypomethylation may restore normal function to genes that are critical for differentiation and proliferation. The cytotoxic effects of azacitidine cause the death of rapidly dividing cells, including cancer cells that are no longer responsive to normal growth control mechanisms.Non-proliferating cells are relatively insensitive to azacitidine.