Azmiro
(Testosterone Cypionate)Azmiro Prescribing Information
Warnings and Precautions, Venous Thromboembolism (
There have been postmarketing reports of venous thromboembolic events, including deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and pulmonary embolism (PE), in patients using testosterone replacement products, such as AZMIRO.
In the Testosterone Replacement therapy for Assessment of long-term Vascular Events and efficacy ResponSE in hypogonadal men (TRAVERSE) Study, a randomized, double-blind, placebo controlled, cardiovascular (CV) outcomes study, compared to placebo, topical testosterone gel was associated with a numerically higher incidence of VTE (1.7% vs 1.2%) which included DVT (0.6% vs 0.5%) and PE events (0.9% vs 0.5%)
Evaluate patients who report symptoms of pain, edema, warmth and erythema in the lower extremity for DVT and those who present with acute shortness of breath for PE. If a venous thromboembolic event is suspected, discontinue treatment with AZMIRO and initiate appropriate workup and management
Warnings and Precautions, Blood Pressure Increases (
Testosterone products, such as AZMIRO, can increase blood pressure. Blood pressure increases can increase cardiovascular (CV) risk over time.
The CV risk associated with topical testosterone gel was evaluated in TRAVERSE, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, CV outcomes study in men with a history of CV disease or multiple CV risk factors. In TRAVERSE, topical testosterone gel increased mean systolic blood pressure by 1.0 mm Hg from baseline to 36 months, whereas a mean decrease from baseline of 0.5 mm Hg was observed in the placebo group at this timepoint, for a mean between-group difference of 1.5 mm Hg. However, the incidences of major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE), including cardiovascular death, non-fatal myocardial infarction [MI] and non-fatal stroke, were similar between treatment groups (7% for topical testosterone gel vs 7.3% for placebo)
Monitor blood pressure periodically in men using AZMIRO, especially men with hypertension. AZMIRO is not recommended for use in patients with uncontrolled hypertension.
Warnings and Precautions, Cardiovascular Risk (5.2) Removed 07/2025
AZMIRO is indicated for testosterone replacement therapy in males in conditions associated with a deficiency or absence of endogenous testosterone:
• Primary hypogonadism (congenital or acquired): testicular failure due to conditions such as cryptorchidism, bilateral torsion, orchitis, vanishing testis syndrome; or orchiectomy, Klinefelter’s syndrome, or toxic damage from alcohol or heavy metals, chemotherapy, or toxic damage from alcohol or heavy metals. These men usually have low serum testosterone concentrations and gonadotropins (follicle stimulating hormone (FSH), luteinizing hormone (LH)) above the normal range [
Prior to initiating AZMIRO, confirm the diagnosis of hypogonadism by ensuring that serum testosterone concentrations have been measured in the morning on at least two separate days and that these serum testosterone concentrations are below the normal range.
• Hypogonadotropic hypogonadism (congenital or acquired): gonadotropin or luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone (LHRH) deficiency, or pituitary-hypothalamic injury from tumors, trauma, or radiation. These men have low testosterone serum concentrations but have gonadotropins in the normal or low range [
• Safety and efficacy of AZMIRO in men with “age- related hypogonadism” (also referred to as “late-onset hypogonadism”) have not been established.
• Safety and efficacy of AZMIRO in pediatric patients below the age of 12 years have not been established [
Improper use may result in acceleration of bone age and premature closure of epiphyses. The effect on bone maturation should be monitored by assessing bone age of the wrist and hand every 6 months. In children, androgen treatment may accelerate bone maturation without producing compensatory gain in linear growth. This adverse effect may result in compromised adult stature. The younger the child the greater the risk of compromising final mature height. Precocious puberty has also been reported with use of testosterone.
The safety and effectiveness of AZMIRO have not been established in pediatric patients young than 12 years of age.
• Injectable testosterone products may have different doses, strengths, or administration instructions and they are not substitutable on a milligram-per-milligram basis. Administer AZMIRO by deep gluteal intramuscular injection only (
• Injectable testosterone products may have different doses, strengths, or administration instructions and they are not substitutable on a milligram-per-milligram basis.
• Administer AZMIRO by deep gluteal intramuscular injection only.
• Prior to initiating AZMIRO, confirm the diagnosis of hypogonadism by ensuring that serum testosterone concentrations have been measured in the morning on at least two separate days and that these serum concentrations are below the normal range (
Prior to initiating AZMIRO, confirm the diagnosis of hypogonadism by ensuring that serum testosterone concentrations have been measured in the morning on at least two separate days and that these serum testosterone concentrations are below the normal range.
• Recommended dosage is 50 mg to 400 mg administered every two to four weeks as a deep intramuscular injection in the gluteal muscle.
Individualize the dose and schedule based on the patient’s age, diagnosis, response to treatment, and the appearance of adverse reactions (
The recommended dosage of AZMIRO is 50 mg to 400 mg administered every two to four weeks as a deep intramuscular injection in the gluteal muscle.
Individualize the dose and schedule of AZMIRO based on the patient’s age, diagnosis, response to treatment, and the appearance of adverse reactions.
• The prefilled syringe should be administered as an intramuscular injection by a healthcare professional only.
Injection:
• 200 mg/mL available as 1 mL of clear colorless to pale yellow solution filled in a single-dose glass vial.
• 200 mg/mL available as 1 mL of clear colorless to pale yellow solution filled in a single-dose glass prefilled syringe.
Geriatric Patients: Geriatric patients treated with androgens may also be at risk for worsening of signs and symptoms of BPH and prostatic carcinoma (
Geriatric patients treated with androgens may be at an increased risk of developing BPH and prostatic carcinoma [see Warnings and Precautions ].
AZMIRO is contraindicated in:
• Known hypersensitivity to AZMIRO or to any of its components [see Description (
AZMIRO (testosterone cypionate) injection for intramuscular injection, contains testosterone cypionate which is the oil-soluble 17 (beta)-cyclopentylpropionate ester of the androgenic hormone testosterone.
Testosterone cypionate is a white or creamy white crystalline powder, odorless or nearly so and stable in air. It is insoluble in water, freely soluble in alcohol, chloroform, dioxane, ether, and soluble in vegetable oils.
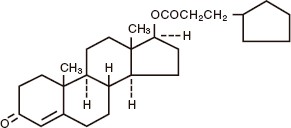
The chemical name for testosterone cypionate is androst-4-en-3-one, 17-(3-cyclopentyl-1-oxopropoxy)-, (17ß)-. Its molecular formula is C27H40O3, and the molecular weight 412.61. The structural formula is shown in the following figure:
AZMIRO (testosterone cypionate) injection is provided as sterile, clear colorless to pale yellow solution containing 200 mg/mL testosterone cypionate in vials and prefilled syringes.
Each mL of solution contains:
Testosterone cypionate………………………………………..200 mg
Benzyl alcohol………………………………………………….20 mg
Benzyl benzoate……………………………………………….0.2 mL
Cottonseed oil…………………………………………………542 mg

The following adverse reactions associated with the use of testosterone were identified in clinical studies or postmarketing reports. Because some of these reactions were reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
• Men with carcinoma of the breast or known or suspected carcinoma of the prostate gland [
• Patients with BPH treated with androgens are at an increased risk for worsening of signs and symptoms of BPH. Monitor patients with BPH for worsening signs and symptoms.
• Patients treated with androgens may be at increased risk for prostate cancer. Evaluate patients for prostate cancer prior to initiating and during treatment with androgens [
• Women who are pregnant. Testosterone can cause virilization of the female fetus when administered to a pregnant woman [
AZMIRO is contraindicated in pregnant women and not indicated for use in females [see Contraindications ]. Testosterone is teratogenic and may cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman based on data from animal studies (
In developmental studies conducted in rats, rabbits, pigs, sheep and rhesus monkeys, pregnant animals received intramuscular injection of testosterone during the period of organogenesis. Testosterone treatment at doses that were comparable to those used for testosterone replacement therapy resulted in structural impairments in both female and male offspring. Structural impairments observed in females included increased anogenital distance, phallus development, empty scrotum, no external vagina, intrauterine growth retardation, reduced ovarian reserve, and increased ovarian follicular recruitment. Structural impairments seen in male offspring included increased testicular weight, larger seminal tubular lumen diameter, and higher frequency of occluded tubule lumen. Increased pituitary weight was seen in both sexes.
Testosterone exposure in utero also resulted in hormonal and behavioral changes in offspring. Hypertension was observed in pregnant females and offspring in rats exposed to doses approximately twice those used for testosterone replacement therapy.