Betamethasone Valerate - Betamethasone Valerate aerosol, Foam
(Betamethasone Valerate)Betamethasone Valerate - Betamethasone Valerate aerosol, Foam Prescribing Information
Betamethasone valerate foam, 0.12% is a medium potency topical corticosteroid indicated for relief of the inflammatory and pruritic manifestations of corticosteroid-responsive dermatoses of the scalp.
Note: For proper dispensing of foam, can must be inverted.
For application to the scalp invert can and dispense a small amount of betamethasone valerate foam, 0.12% onto a saucer or other cool surface. Do not dispense directly onto hands as foam will begin to melt immediately upon contact with warm skin. Pick up small amounts of foam with fingers and gently massage into affected area until foam disappears. Repeat until entire affected scalp area is treated. Apply twice daily, once in the morning and once at night.
As with other corticosteroids, therapy should be discontinued when control is achieved. If no improvement is seen within 2 weeks, reassessment of the diagnosis may be necessary.
Betamethasone valerate foam, 0.12% should not be used with occlusive dressings unless directed by a physician.
Betamethasone valerate foam, 0.12% is contraindicated in patients who are hypersensitive to betamethasone valerate, to other corticosteroids, or to any ingredient in this preparation.
The most frequent adverse event was burning/itching/stinging at the application site; the incidence and severity of this event were as follows:
| Incidence and severity of burning/itching/stinging | ||||
| Product | Total incidence | Maximum severity | ||
| Mild | Moderate | Severe | ||
| Betamethasone Valerate Foam n = 63 | 34 (54%) | 28 (44%) | 5 (8%) | 1 (2%) |
| Betamethasone Valerate Lotion n = 63 | 33 (52%) | 26 (41%) | 6 (10%) | 1 (2%) |
| Placebo Foam n = 32 | 24 (75%) | 13 (41%) | 7 (22%) | 4 (12%) |
| Placebo Lotion n=30 | 20 (67%) | 12 (40%) | 5 (17%) | 3 (10%) |
Other adverse events which were considered to be possibly, probably, or definitely related to betamethasone valerate foam occurred in 1 patient each; these were paresthesia, pruritus, acne, alopecia, and conjunctivitis.
The following additional local adverse reactions have been reported with topical corticosteroids, and they may occur more frequently with the use of occlusive dressings. These reactions are listed in an approximately decreasing order of occurrence: irritation; dryness; folliculitis; acneiform eruptions; hypopigmentation; perioral dermatitis; allergic contact dermatitis; secondary infection; skin atrophy; striae; and miliaria.
Systemic absorption of topical corticosteroids has produced reversible hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis suppression, manifestations of Cushing's syndrome, hyperglycemia, and glucosuria in some patients.
Betamethasone valerate foam, 0.12% contains betamethasone valerate, a synthetic corticosteroid, for topical dermatologic use. The corticosteroids constitute a class of primarily synthetic steroids used topically as anti-inflammatory agents.
Betamethasone valerate is 9α-fluoro-11ß,17,21-trihydroxy-16ß-methylpregna-1,4-diene-3,20-dione-17-valerate, with the empirical formula C27H37FO6, a molecular weight of 476.58. The following is the chemical structure:
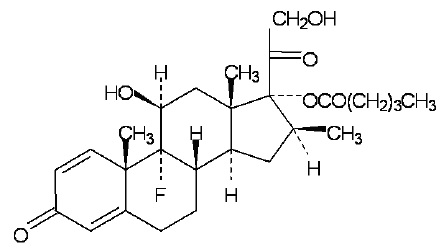
Betamethasone valerate, USP is a white to almost-white, crystalline powder, and is practically insoluble in water, freely soluble in acetone and in chloroform, soluble in alcohol, and slightly soluble in benzene and in ether.
Betamethasone valerate foam, 0.12%, contains 1.2 mg betamethasone valerate, USP, per gram in a thermolabile hydroethanolic foam vehicle consisting of cetyl alcohol, citric acid, ethanol (60.4%), polysorbate 60, potassium citrate, propylene glycol, purified water, and stearyl alcohol pressurized with a hydrocarbon (propane/butane) propellant.
Like other topical corticosteroids, betamethasone valerate foam has anti-inflammatory, antipruritic, and vasoconstrictive properties. The mechanism of the anti-inflammatory activity of the topical steroids, in general, is unclear. However, corticosteroids are thought to act by the induction of phospholipase A2 inhibitory proteins, collectively called lipocortins. It is postulated that these proteins control the biosynthesis of potent mediators of inflammation such as prostaglandins and leukotrienes by inhibiting the release of their common precursor arachidonic acid. Arachidonic acid is released from membrane phospholipids by phospholipase A2.
Topical corticosteroids can be absorbed from intact healthy skin. The extent of percutaneous absorption of topical corticosteroids is determined by many factors, including the vehicle and the integrity of the epidermal barrier. Occlusion, inflammation and/or other disease processes in the skin may also increase percutaneous absorption.
The use of pharmacodynamic endpoints for assessing the systemic exposure of topical corticosteroids is necessary due to the fact that circulating levels are well below the level of detection. Once absorbed through the skin, topical corticosteroids are handled through pharmacokinetic pathways similar to systemically administered corticosteroids. They are metabolized, primarily in the liver, and are then excreted by the kidneys. In addition, some corticosteroids and their metabolites are also excreted in the bile.