Bethanechol Chloride
Bethanechol Chloride Prescribing Information
Bethanechol chloride is indicated for the treatment of acute postoperative and postpartum nonobstructive (functional) urinary retention and for neurogenic atony of the urinary bladder with retention.
Dosage must be individualized, depending on the type and severity of the condition to be treated.
Preferably give the drug when the stomach is empty. If taken soon after eating, nausea and vomiting may occur.
The usual adult oral dose ranges from 10 to 50 mg three or four times a day. The minimum effective dose is determined by giving 5 to 10 mg initially and repeating the same amount at hourly intervals until satisfactory response occurs, or until a maximum of 50 mg has been given. The effects of the drug sometimes appear within 30 minutes and are usually maximal within 60 to 90 minutes. The drug's effects persist for about one hour.
If necessary, the effects of the drug can be abolished promptly by atropine (see OVERDOSAGE).
Hypersensitivity to bethanechol chloride tablets, hyperthyroidism, peptic ulcer, latent or active bronchial asthma, pronounced bradycardia or hypotension, vasomotor instability, coronary artery disease, epilepsy and parkinsonism.
Bethanechol chloride should not be employed when the strength or integrity of the gastrointestinal or bladder wall is in question, or in the presence of mechanical obstruction; when increased muscular activity of the gastrointestinal tract or urinary bladder might prove harmful, as following recent urinary bladder surgery, gastrointestinal resection and anastomosis, or when there is possible gastrointestinal obstruction; in bladder neck obstruction, spastic gastrointestinal disturbances, acute inflammatory lesions of the gastrointestinal tract, or peritonitis; or in marked vagotonia.
Adverse reactions are rare following oral administration of bethanechol, but are more common following subcutaneous injection. Adverse reactions are more likely to occur when dosage is increased.
The following adverse reactions have been observed: Body as a Whole. malaise; Digestive: abdominal cramps or discomfort, colicky pain, nausea and belching, diarrhea, borborygmi, salivation; Renal: urinary urgency; Nervous System: headache; Cardiovascular: a fall in blood pressure with reflex tachycardia, vasomotor response; Skin: flushing producing a feeling of warmth, sensation of heat about the face, sweating; Respiratory: bronchial constriction, asthmatic attacks; Special Senses: lacrimation, miosis.
Causal Relationship Unknown
The following adverse reactions have been reported, and a causal relationship to therapy with bethanechol has not been established: Body as a Whole: malaise; Nervous System: seizures.
Drug Interactions
Special care is required if this drug is given to patients receiving ganglion blocking compounds because a critical fall in blood pressure may occur. Usually, severe abdominal symptoms appear before there is such a fall in the blood pressure.
Bethanechol chloride, a cholinergic agent, is a synthetic ester which is structurally and pharma-cologically related to acetylcholine.
It is designated chemically as 2-[(aminocarbonyl)oxy]-N, N, N-trimethyl-1-propanaminium chloride. Its molecular formula is C7H17ClN2O2 and its structural formula is:
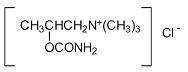
It is a white, hygroscopic crystalline powder having a slight amine-like odor, freely soluble in water, and has a molecular weight of 196.68.
Each tablet for oral administration contains 5 mg, 10 mg, 25 mg or 50 mg bethanechol chloride, USP. Tablets also contain the following inactive ingredients: anhydrous lactose, colloidal silicon dioxide, magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose, sodium starch glycolate, (10 mg) FD&C Red # 40 and (25 mg and 50 mg) D&C Yellow # 10 and FD&C Yellow # 6.