Buspirone Hydrochloride
Buspirone Hydrochloride Prescribing Information
Buspirone hydrochloride capsules are indicated for the management of anxiety disorders or the short-term relief of the symptoms of anxiety. Anxiety or tension associated with the stress of everyday life usually does not require treatment with an anxiolytic.
Generalized, persistent anxiety (of at least 1 month continual duration), manifested by symptoms from three of the four following categories:
The effectiveness of buspirone hydrochloride in long-term use, that is, for more than 3 to 4 weeks, has not been demonstrated in controlled trials. There is no body of evidence available that systematically addresses the appropriate duration of treatment for GAD. However, in a study of long-term use, 264 patients were treated with buspirone hydrochloride for 1 year without ill effect. Therefore, the physician who elects to use buspirone hydrochloride for extended periods should periodically reassess the usefulness of the drug for the individual patient.
The recommended initial dose is 15 mg daily (7.5 mg two times per day.). To achieve an optimal therapeutic response, at intervals of 2 to 3 days the dosage may be increased 5 mg per day, as needed. The maximum daily dosage should not exceed 60 mg per day. In clinical trials allowing dose titration, divided doses of 20 to 30 mg per day were commonly employed.
The bioavailability of buspirone is increased when given with food as compared to the fasted state (see
After single or multiple doses in adults, no significant differences in buspirone pharmacokinetics (AUC and Cmax) were observed between elderly and younger subjects or between men and women.
After multiple-dose administration of buspirone to patients with hepatic impairment, steady-state AUC of buspirone increased 13-fold compared with healthy subjects (see
After multiple-dose administration of buspirone to renally impaired (Clcr= 10-70 mL/min/1.73 m2) patients, steady-state AUC of buspirone increased 4-fold compared with healthy (Clcr≥80 mL/min/1.73 m2) subjects (see
The effects of race on the pharmacokinetics of buspirone have not been studied.
For patients who have difficulty swallowing capsules, buspirone hydrochloride capsules can be opened and the contents sprinkled on a small amount (about 1-2 tablespoons) of applesauce. The drug-applesauce mixture should be swallowed immediately.
When buspirone is to be given with a potent inhibitor of CYP3A4, the dosage recommendations described in the
Buspirone has been shown
At least 14 days should elapse between discontinuation of an MAOI intended to treat depression and initiation of therapy with buspirone hydrochloride. Conversely, at least 14 days should be allowed after stopping buspirone hydrochloride before starting an MAOI antidepressant (see
Buspirone hydrochloride capsules are contraindicated in patients hypersensitive to buspirone hydrochloride.
The use of monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs) intended to treat depression with buspirone or within 14 days of stopping treatment with buspirone is contraindicated because of an increased risk of serotonin syndrome and/or elevated blood pressure. The use of buspirone within 14 days of stopping an MAOI intended to treat depression is also contraindicated.
Starting buspirone in a patient who is being treated with reversible MAOIs such as linezolid or intravenous methylene blue is also contraindicated because of an increased risk of serotonin syndrome. (see
Buspirone has been shown
Do not start buspirone hydrochloride capsules in a patient who is being treated with a reversible MAOI such as linezolid or intravenous methylene blue because there is an increased risk of serotonin syndrome. In a patient who requires more urgent treatment of a psychiatric condition, non-pharmacological interventions, including hospitalization, should be considered (see
Buspirone hydrochloride capsules are contraindicated in patients hypersensitive to buspirone hydrochloride.
The use of monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs) intended to treat depression with buspirone or within 14 days of stopping treatment with buspirone is contraindicated because of an increased risk of serotonin syndrome and/or elevated blood pressure. The use of buspirone within 14 days of stopping an MAOI intended to treat depression is also contraindicated.
Starting buspirone in a patient who is being treated with reversible MAOIs such as linezolid or intravenous methylene blue is also contraindicated because of an increased risk of serotonin syndrome. (see
Buspirone has been shown
In some cases, a patient already receiving therapy with buspirone hydrochloride capsules may require urgent treatment with linezolid or intravenous methylene blue. If acceptable alternatives to linezolid or intravenous methylene blue treatment are not available and the potential benefits of linezolid or intravenous methylene blue treatment are judged to outweigh the risks of serotonin syndrome in a particular patient, buspirone hydrochloride capsules should be stopped promptly, and linezolid or intravenous methylene blue can be administered. The patient should be monitored for symptoms of serotonin syndrome for 2 weeks or until 24 hours after the last dose of linezolid or intravenous methylene blue, whichever comes first. Therapy with buspirone hydrochloride capsules may be resumed 24 hours after the last dose of linezolid or intravenous methylene blue (see
The development of a potentially life-threatening serotonin syndrome has been reported with SNRIs SSRIs, and other serotonergic drugs, including buspirone, alone but particularly with concomitant use of other serotonergic drugs (including triptans), with drugs that impair metabolism of serotonin (in particular, MAOIs, including reversible MAOIs such as linezolid and intravenous methylene blue), or with antipsychotics or other dopamine antagonists.
Serotonin syndrome symptoms may include mental status changes (e.g., agitation, hallucinations, delirium, and coma), autonomic instability (e.g., tachycardia, labile blood pressure, dizziness, diaphoresis, flushing, hyperthermia), neuromuscular changes (e.g., tremor, rigidity, myoclonus, hyperreflexia, incoordination), seizures, and/or gastrointestinal symptoms (e.g., nausea, vomiting, diarrhea). Patients should be monitored for emergence of serotonin syndrome.
The concomitant use of buspirone with MAOIs intended to treat depression is contraindicated. Buspirone should also not be started in a patient who is being treated with reversible MAOIs such as linezolid or intravenous methylene blue. All reports with methylene blue that provided information on the route of administration involved intravenous administration in the dose range of 1 mg/kg to 8 mg/kg. There have been no reports involving the administration of methylene blue by other routes (such as oral tablets or local tissue injection) or at lower doses. There may be circumstances when it is necessary to initiate treatment with a reversible MAOI such as linezolid or intravenous methylene blue in a patient taking buspirone. Buspirone should be discontinued before initiating treatment with the reversible MAOI [see
If concomitant use of buspirone with a 5-hydroxytryptmine receptor agonist (triptan) is clinically warranted, careful observation of the patient is advised, particularly during treatment initiation and dose increases.
The concomitant use of buspirone with serotonin precursors (such as tryptophan) is not recommended.
Treatment with buspirone and any concomitant serotonergic or antidopaminergic agents, including antipsychotics, should be discontinued immediately if the above events occur and supportive symptomatic treatment should be initiated.
Because buspirone hydrochloride capsules has no established antipsychotic activity, it should not be employed in lieu of appropriate antipsychotic treatment.
The risk of administering methylene blue by non-intravenous routes (such as oral tablets or by local injection) or in intravenous doses much lower than 1 mg per kg with buspirone hydrochloride capsules are unclear. The clinician should, nevertheless, be aware of the possibility of emergent symptoms of serotonin syndrome with such use (see
Buspirone hydrochloride capsules are contraindicated in patients hypersensitive to buspirone hydrochloride.
The use of monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs) intended to treat depression with buspirone or within 14 days of stopping treatment with buspirone is contraindicated because of an increased risk of serotonin syndrome and/or elevated blood pressure. The use of buspirone within 14 days of stopping an MAOI intended to treat depression is also contraindicated.
Starting buspirone in a patient who is being treated with reversible MAOIs such as linezolid or intravenous methylene blue is also contraindicated because of an increased risk of serotonin syndrome. (see
The development of a potentially life-threatening serotonin syndrome has been reported with SNRIs SSRIs, and other serotonergic drugs, including buspirone, alone but particularly with concomitant use of other serotonergic drugs (including triptans), with drugs that impair metabolism of serotonin (in particular, MAOIs, including reversible MAOIs such as linezolid and intravenous methylene blue), or with antipsychotics or other dopamine antagonists.
Serotonin syndrome symptoms may include mental status changes (e.g., agitation, hallucinations, delirium, and coma), autonomic instability (e.g., tachycardia, labile blood pressure, dizziness, diaphoresis, flushing, hyperthermia), neuromuscular changes (e.g., tremor, rigidity, myoclonus, hyperreflexia, incoordination), seizures, and/or gastrointestinal symptoms (e.g., nausea, vomiting, diarrhea). Patients should be monitored for emergence of serotonin syndrome.
The concomitant use of buspirone with MAOIs intended to treat depression is contraindicated. Buspirone should also not be started in a patient who is being treated with reversible MAOIs such as linezolid or intravenous methylene blue. All reports with methylene blue that provided information on the route of administration involved intravenous administration in the dose range of 1 mg/kg to 8 mg/kg. There have been no reports involving the administration of methylene blue by other routes (such as oral tablets or local tissue injection) or at lower doses. There may be circumstances when it is necessary to initiate treatment with a reversible MAOI such as linezolid or intravenous methylene blue in a patient taking buspirone. Buspirone should be discontinued before initiating treatment with the reversible MAOI [see
If concomitant use of buspirone with a 5-hydroxytryptmine receptor agonist (triptan) is clinically warranted, careful observation of the patient is advised, particularly during treatment initiation and dose increases.
The concomitant use of buspirone with serotonin precursors (such as tryptophan) is not recommended.
Treatment with buspirone and any concomitant serotonergic or antidopaminergic agents, including antipsychotics, should be discontinued immediately if the above events occur and supportive symptomatic treatment should be initiated.
Because buspirone hydrochloride capsules has no established antipsychotic activity, it should not be employed in lieu of appropriate antipsychotic treatment.
Buspirone has been shown
Buspirone hydrochloride capsules are contraindicated in patients hypersensitive to buspirone hydrochloride.
The use of monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs) intended to treat depression with buspirone or within 14 days of stopping treatment with buspirone is contraindicated because of an increased risk of serotonin syndrome and/or elevated blood pressure. The use of buspirone within 14 days of stopping an MAOI intended to treat depression is also contraindicated.
Starting buspirone in a patient who is being treated with reversible MAOIs such as linezolid or intravenous methylene blue is also contraindicated because of an increased risk of serotonin syndrome. (see
The development of a potentially life-threatening serotonin syndrome has been reported with SNRIs SSRIs, and other serotonergic drugs, including buspirone, alone but particularly with concomitant use of other serotonergic drugs (including triptans), with drugs that impair metabolism of serotonin (in particular, MAOIs, including reversible MAOIs such as linezolid and intravenous methylene blue), or with antipsychotics or other dopamine antagonists.
Serotonin syndrome symptoms may include mental status changes (e.g., agitation, hallucinations, delirium, and coma), autonomic instability (e.g., tachycardia, labile blood pressure, dizziness, diaphoresis, flushing, hyperthermia), neuromuscular changes (e.g., tremor, rigidity, myoclonus, hyperreflexia, incoordination), seizures, and/or gastrointestinal symptoms (e.g., nausea, vomiting, diarrhea). Patients should be monitored for emergence of serotonin syndrome.
The concomitant use of buspirone with MAOIs intended to treat depression is contraindicated. Buspirone should also not be started in a patient who is being treated with reversible MAOIs such as linezolid or intravenous methylene blue. All reports with methylene blue that provided information on the route of administration involved intravenous administration in the dose range of 1 mg/kg to 8 mg/kg. There have been no reports involving the administration of methylene blue by other routes (such as oral tablets or local tissue injection) or at lower doses. There may be circumstances when it is necessary to initiate treatment with a reversible MAOI such as linezolid or intravenous methylene blue in a patient taking buspirone. Buspirone should be discontinued before initiating treatment with the reversible MAOI [see
If concomitant use of buspirone with a 5-hydroxytryptmine receptor agonist (triptan) is clinically warranted, careful observation of the patient is advised, particularly during treatment initiation and dose increases.
The concomitant use of buspirone with serotonin precursors (such as tryptophan) is not recommended.
Treatment with buspirone and any concomitant serotonergic or antidopaminergic agents, including antipsychotics, should be discontinued immediately if the above events occur and supportive symptomatic treatment should be initiated.
Because buspirone hydrochloride capsules has no established antipsychotic activity, it should not be employed in lieu of appropriate antipsychotic treatment.
The recommended initial dose is 15 mg daily (7.5 mg two times per day.). To achieve an optimal therapeutic response, at intervals of 2 to 3 days the dosage may be increased 5 mg per day, as needed. The maximum daily dosage should not exceed 60 mg per day. In clinical trials allowing dose titration, divided doses of 20 to 30 mg per day were commonly employed.
The bioavailability of buspirone is increased when given with food as compared to the fasted state (see
For patients who have difficulty swallowing capsules, buspirone hydrochloride capsules can be opened and the contents sprinkled on a small amount (about 1-2 tablespoons) of applesauce. The drug-applesauce mixture should be swallowed immediately.
When buspirone is to be given with a potent inhibitor of CYP3A4, the dosage recommendations described in the
At least 14 days should elapse between discontinuation of an MAOI intended to treat depression and initiation of therapy with buspirone hydrochloride. Conversely, at least 14 days should be allowed after stopping buspirone hydrochloride before starting an MAOI antidepressant (see
Do not start buspirone hydrochloride capsules in a patient who is being treated with a reversible MAOI such as linezolid or intravenous methylene blue because there is an increased risk of serotonin syndrome. In a patient who requires more urgent treatment of a psychiatric condition, non-pharmacological interventions, including hospitalization, should be considered (see
In some cases, a patient already receiving therapy with buspirone hydrochloride capsules may require urgent treatment with linezolid or intravenous methylene blue. If acceptable alternatives to linezolid or intravenous methylene blue treatment are not available and the potential benefits of linezolid or intravenous methylene blue treatment are judged to outweigh the risks of serotonin syndrome in a particular patient, buspirone hydrochloride capsules should be stopped promptly, and linezolid or intravenous methylene blue can be administered. The patient should be monitored for symptoms of serotonin syndrome for 2 weeks or until 24 hours after the last dose of linezolid or intravenous methylene blue, whichever comes first. Therapy with buspirone hydrochloride capsules may be resumed 24 hours after the last dose of linezolid or intravenous methylene blue (see
The risk of administering methylene blue by non-intravenous routes (such as oral tablets or by local injection) or in intravenous doses much lower than 1 mg per kg with buspirone hydrochloride capsules are unclear. The clinician should, nevertheless, be aware of the possibility of emergent symptoms of serotonin syndrome with such use (see
Buspirone has been shown
The more commonly observed untoward events associated with the use of buspirone hydrochloride capsules not seen at an equivalent incidence among placebo-treated patients include dizziness, nausea, headache, nervousness, lightheadedness, and excitement.
Starting buspirone in a patient who is being treated with reversible MAOIs such as linezolid or intravenous methylene blue is also contraindicated because of an increased risk of serotonin syndrome. (see
The development of a potentially life-threatening serotonin syndrome has been reported with SNRIs SSRIs, and other serotonergic drugs, including buspirone, alone but particularly with concomitant use of other serotonergic drugs (including triptans), with drugs that impair metabolism of serotonin (in particular, MAOIs, including reversible MAOIs such as linezolid and intravenous methylene blue), or with antipsychotics or other dopamine antagonists.
Serotonin syndrome symptoms may include mental status changes (e.g., agitation, hallucinations, delirium, and coma), autonomic instability (e.g., tachycardia, labile blood pressure, dizziness, diaphoresis, flushing, hyperthermia), neuromuscular changes (e.g., tremor, rigidity, myoclonus, hyperreflexia, incoordination), seizures, and/or gastrointestinal symptoms (e.g., nausea, vomiting, diarrhea). Patients should be monitored for emergence of serotonin syndrome.
The concomitant use of buspirone with MAOIs intended to treat depression is contraindicated. Buspirone should also not be started in a patient who is being treated with reversible MAOIs such as linezolid or intravenous methylene blue. All reports with methylene blue that provided information on the route of administration involved intravenous administration in the dose range of 1 mg/kg to 8 mg/kg. There have been no reports involving the administration of methylene blue by other routes (such as oral tablets or local tissue injection) or at lower doses. There may be circumstances when it is necessary to initiate treatment with a reversible MAOI such as linezolid or intravenous methylene blue in a patient taking buspirone. Buspirone should be discontinued before initiating treatment with the reversible MAOI [see
If concomitant use of buspirone with a 5-hydroxytryptmine receptor agonist (triptan) is clinically warranted, careful observation of the patient is advised, particularly during treatment initiation and dose increases.
The concomitant use of buspirone with serotonin precursors (such as tryptophan) is not recommended.
Treatment with buspirone and any concomitant serotonergic or antidopaminergic agents, including antipsychotics, should be discontinued immediately if the above events occur and supportive symptomatic treatment should be initiated.
Because buspirone hydrochloride capsules has no established antipsychotic activity, it should not be employed in lieu of appropriate antipsychotic treatment.
The recommended initial dose is 15 mg daily (7.5 mg two times per day.). To achieve an optimal therapeutic response, at intervals of 2 to 3 days the dosage may be increased 5 mg per day, as needed. The maximum daily dosage should not exceed 60 mg per day. In clinical trials allowing dose titration, divided doses of 20 to 30 mg per day were commonly employed.
The bioavailability of buspirone is increased when given with food as compared to the fasted state (see
For patients who have difficulty swallowing capsules, buspirone hydrochloride capsules can be opened and the contents sprinkled on a small amount (about 1-2 tablespoons) of applesauce. The drug-applesauce mixture should be swallowed immediately.
When buspirone is to be given with a potent inhibitor of CYP3A4, the dosage recommendations described in the
At least 14 days should elapse between discontinuation of an MAOI intended to treat depression and initiation of therapy with buspirone hydrochloride. Conversely, at least 14 days should be allowed after stopping buspirone hydrochloride before starting an MAOI antidepressant (see
Do not start buspirone hydrochloride capsules in a patient who is being treated with a reversible MAOI such as linezolid or intravenous methylene blue because there is an increased risk of serotonin syndrome. In a patient who requires more urgent treatment of a psychiatric condition, non-pharmacological interventions, including hospitalization, should be considered (see
In some cases, a patient already receiving therapy with buspirone hydrochloride capsules may require urgent treatment with linezolid or intravenous methylene blue. If acceptable alternatives to linezolid or intravenous methylene blue treatment are not available and the potential benefits of linezolid or intravenous methylene blue treatment are judged to outweigh the risks of serotonin syndrome in a particular patient, buspirone hydrochloride capsules should be stopped promptly, and linezolid or intravenous methylene blue can be administered. The patient should be monitored for symptoms of serotonin syndrome for 2 weeks or until 24 hours after the last dose of linezolid or intravenous methylene blue, whichever comes first. Therapy with buspirone hydrochloride capsules may be resumed 24 hours after the last dose of linezolid or intravenous methylene blue (see
The risk of administering methylene blue by non-intravenous routes (such as oral tablets or by local injection) or in intravenous doses much lower than 1 mg per kg with buspirone hydrochloride capsules are unclear. The clinician should, nevertheless, be aware of the possibility of emergent symptoms of serotonin syndrome with such use (see
Starting buspirone in a patient who is being treated with reversible MAOIs such as linezolid or intravenous methylene blue is also contraindicated because of an increased risk of serotonin syndrome. (see
Buspirone has been shown
Therapeutic levels of aspirin, desipramine, diazepam, flurazepam, ibuprofen, propranolol, thioridazine, and tolbutamide had only a limited effect on the extent of binding of buspirone to plasma proteins (see
Buspirone has been shown
Buspirone hydrochloride capsules are antianxiety agents that are not chemically or pharmacologically related to the benzodiazepines, barbiturates, or other sedative/anxiolytic drugs.
Buspirone hydrochloride is a white crystalline, water soluble compound with a molecular weight of 422.0. Chemically, buspirone hydrochloride is 8-[4-[4-(2- pyrimidinyl)- 1-piperazinyl]butyl]-8-azaspiro[4.5]decane-7,9- dione monohydrochloride. The empirical formula C21H31N502 ∙ HCl is represented by the following structural formula: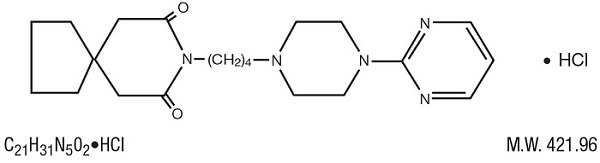
Buspirone hydrochloride capsules are supplied as capsules for oral administration. Buspirone hydrochloride capsules contains 7.5 mg, 10 mg, or 15 mg of buspirone hydrochloride, USP (equivalent to 6.8 mg, 9.1 mg, and 13.7 mg of buspirone free base, respectively) in a hard gelatin shell. Each capsule also contains the following inactive ingredients: colloidal silicon dioxide, lactose anhydrous, magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose and sodium starch glycolate. The shell consists of black ink, gelatin, titanium dioxide, fd&c blue no. 1 (7.5 mg, 10 mg, and 15 mg), and black iron oxide (10 mg) and is imprinted with edible ink.