Calcitriol
Calcitriol Prescribing Information
Calcitriol injection is indicated in the management of hypocalcemia in patients undergoing chronic renal dialysis. It has been shown to significantly reduce elevated parathyroid hormone levels. Reduction of PTH has been shown to result in an improvement in renal osteodystrophy.
Calcitriol injection is for intravenous injection only.
The optimal dose of calcitriol injection must be carefully determined for each patient.
The effectiveness of calcitriol injection therapy is predicated on the assumption that each patient is receiving an adequate and appropriate daily intake of calcium. The RDA for calcium in adults is 800 mg. To ensure that each patient receives an adequate daily intake of calcium, the physician should either prescribe a calcium supplement or instruct the patient in proper dietary measures.
The recommended initial dose of Calcitriol Injection, depending on the severity of the hypocalcemia and/or secondary hyperparathyroidism, is 1 mcg (0.02 mcg/kg) to 2 mcg administered intravenously three times weekly, approximately every other day. Doses as small as 0.5 mcg and as large as 4 mcg three times weekly have been used as an initial dose. If a satisfactory response is not observed, the dose may be increased by 0.5 to 1 mcg at two to four week intervals. During this titration period, serum calcium and phosphorus levels should be obtained at least twice weekly. If hypercalcemia or a serum calcium times phosphate product greater than 70 is noted, the drug should be immediately discontinued until these parameters are appropriate. Then, the calcitriol injection dose should be reinitiated at a lower dose. Doses may need to be reduced as the PTH levels decrease in response to the therapy. Thus, incremental dosing must be individualized and commensurate with PTH, serum calcium and phosphorus levels. The following is a suggested approach in dose titration:
PTH Levels | Calcitriol Injection Dose |
| the same or increasing | increase |
| decreasing by < 30% | increase |
| decreasing by > 30%, < 60% | maintain |
| decreasing by > 60% | decrease |
| one and one-half to three times the upper limit of normal | maintain |
Parenteral drug products should be inspected visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration, whenever solution and container permit.
Discard unused portion.
Calcitriol injection should not be given to patients with hypercalcemia or evidence of vitamin D toxicity.
Calcitriol injection is contraindicated in patients with previous hypersensitivity to calcitriol or any of its excipients.
Adverse effects of calcitriol injection are, in general, similar to those encountered with excessive vitamin D intake. The early and late signs and symptoms of vitamin D intoxication associated with hypercalcemia include:
Concomitant use of magnesium-containing preparations should be used with caution or avoided since such use may lead to the development of hypermagnesemia.
Corticosteroids with glucocorticoid activity may counteract the bone and mineral metabolism effects of vitamin D analogues.
Cytochrome P450 enzyme-inducing anticonvulsants such as carbamazepine, phenobarbital and phenytoin may reduce the effects of vitamin D because they increase vitamin D catabolism.
Calcitriol injection is synthetically manufactured calcitriol and is available as a sterile, isotonic, clear, colorless to yellow, aqueous solution for intravenous injection. Calcitriol Injection, USP is available in 1 mL vials. Each 1 mL contains: Active: Calcitriol, 1 mcg. Inactives: Polysorbate 20, 4 mg; Dibasic Sodium Phosphate, Anhydrous 7.6 mg; Edetate Disodium, Dihydrate 1.1 mg; Monobasic Sodium Phosphate, Monohydrate 1.8 mg; Butylated hydroxyltoluene 0.02 mg; Butylated hydroxyl anisole 0.003 mg; Sodium Chloride 1.5 mg; pH Range is from 6.5 to 8.0 and Water for Injection.
Calcitriol is a crystalline compound which occurs naturally in humans. It is soluble in organic solvents but relatively insoluble in water. Calcitriol is chemically designated (5Z,7E)-9,10 secocholesta-5,7,10(19)-triene-1α,3β,25-triol and has the following structural formula:
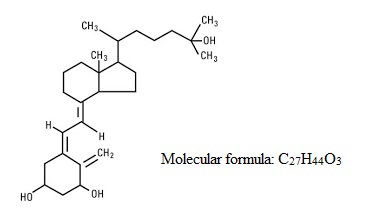
The other names frequently used for calcitriol are 1α,25-dihydroxycholecalciferol,1α,25- dihydroxyvitamin D3,1,25-DHCC,1,25(OH)2D3 and 1,25-diOHC.