Carbidopa And Levodopa
Carbidopa And Levodopa Prescribing Information
Carbidopa and levodopa tablets, USP are indicated in the treatment of Parkinson's disease, post-encephalitic parkinsonism, and symptomatic parkinsonism that may follow carbon monoxide intoxication or manganese intoxication.
Carbidopa allows patients treated for Parkinson's disease to use much lower doses of levodopa. Some patients who responded poorly to levodopa have improved on carbidopa and levodopa tablets. This is most likely due to decreased peripheral decarboxylation of levodopa caused by administration of carbidopa rather than by a primary effect of carbidopa on the nervous system. Carbidopa has not been shown to enhance the intrinsic efficacy of levodopa.
Carbidopa may also reduce nausea and vomiting and permit more rapid titration of levodopa.
The optimum daily dosage of carbidopa and levodopa tablets must be determined by careful titration in each patient. Carbidopa and levodopa tablets are available in a 1:4 ratio of carbidopa to levodopa (25 mg/100 mg) as well as 1:10 ratio (25 mg/250 mg and 10 mg/100 mg). Tablets of the two ratios may be given separately or combined as needed to provide the optimum dosage.
Studies show that peripheral dopa decarboxylase is saturated by carbidopa at approximately 70 to 100 mg a day. Patients receiving less than this amount of carbidopa are more likely to experience nausea and vomiting.
Nonselective monoamine oxidase (MAO) inhibitors are contraindicated for use with carbidopa and levodopa tablets. These inhibitors must be discontinued at least two weeks prior to initiating therapy with carbidopa and levodopa tablets. Carbidopa and levodopa tablets may be administered concomitantly with the manufacturer's recommended dose of an MAO inhibitor with selectivity for MAO type B (e.g., selegiline HCl) (see
Symptomatic postural hypotension occurred when carbidopa and levodopa tablets was added to the treatment of a patient receiving antihypertensive drugs. Therefore, when therapy with carbidopa and levodopa tablets is started, dosage adjustment of the antihypertensive drug may be required.
For patients receiving MAO inhibitors (Type A or B), see CONTRAINDICATIONS. Concomitant therapy with selegiline and carbidopa and levodopa may be associated with severe orthostatic hypotension not attributable to carbidopa and levodopa alone (see CONTRAINDICATIONS).
There have been rare reports of adverse reactions, including hypertension and dyskinesia, resulting from the concomitant use of tricyclic antidepressants and carbidopa and levodopa tablets.
Dopamine D2receptor antagonists (e.g., phenothiazines, butyrophenones, risperidone) and isoniazid may reduce the therapeutic effects of levodopa. In addition, the beneficial effects of levodopa in Parkinson's disease have been reported to be reversed by phenytoin and papaverine. Patients taking these drugs with carbidopa and levodopa tablets should be carefully observed for loss of therapeutic response.
Use of carbidopa and levodopa tablets with dopamine-depleting agents (e.g., reserpine and tetrabenazine) or other drugs known to deplete monoamine stores is not recommended.
Carbidopa and levodopa tablets and iron salts or multivitamins containing iron salts should be coadministered with caution. Iron salts can form chelates with levodopa and carbidopa and consequently reduce the bioavailability of carbidopa and levodopa.
Although metoclopramide may increase the bioavailability of levodopa by increasing gastric emptying, metoclopramide may also adversely affect disease control by its dopamine receptor antagonistic properties.
Carbidopa and levodopa tablets are contraindicated in patients with known hypersensitivity to any component of this drug, and in patients with narrow-angle glaucoma.
The most common adverse reactions reported with carbidopa and levodopa tablets have included dyskinesias, such as choreiform, dystonic, and other involuntary movements, and nausea.
The following other adverse reactions have been reported with carbidopa and levodopa tablets:
Other adverse reactions that have been reported with levodopa alone and with various carbidopa and levodopa formulations, and may occur with carbidopa and levodopa tablets are:
Symptomatic postural hypotension occurred when carbidopa and levodopa tablets was added to the treatment of a patient receiving antihypertensive drugs. Therefore, when therapy with carbidopa and levodopa tablets is started, dosage adjustment of the antihypertensive drug may be required.
For patients receiving MAO inhibitors (Type A or B), see
Nonselective monoamine oxidase (MAO) inhibitors are contraindicated for use with carbidopa and levodopa tablets. These inhibitors must be discontinued at least two weeks prior to initiating therapy with carbidopa and levodopa tablets. Carbidopa and levodopa tablets may be administered concomitantly with the manufacturer's recommended dose of an MAO inhibitor with selectivity for MAO type B (e.g., selegiline HCl) (see PRECAUTIONS, Drug Interactions).
Carbidopa and levodopa tablets are contraindicated in patients with known hypersensitivity to any component of this drug, and in patients with narrow-angle glaucoma.
Nonselective monoamine oxidase (MAO) inhibitors are contraindicated for use with carbidopa and levodopa tablets. These inhibitors must be discontinued at least two weeks prior to initiating therapy with carbidopa and levodopa tablets. Carbidopa and levodopa tablets may be administered concomitantly with the manufacturer's recommended dose of an MAO inhibitor with selectivity for MAO type B (e.g., selegiline HCl) (see PRECAUTIONS, Drug Interactions).
Carbidopa and levodopa tablets are contraindicated in patients with known hypersensitivity to any component of this drug, and in patients with narrow-angle glaucoma.
There have been rare reports of adverse reactions, including hypertension and dyskinesia, resulting from the concomitant use of tricyclic antidepressants and carbidopa and levodopa tablets.
Dopamine D2 receptor antagonists (e.g., phenothiazines, butyrophenones, risperidone) and isoniazid may reduce the therapeutic effects of levodopa. In addition, the beneficial effects of levodopa in Parkinson's disease have been reported to be reversed by phenytoin and papaverine. Patients taking these drugs with carbidopa and levodopa tablets should be carefully observed for loss of therapeutic response.
Use of carbidopa and levodopa tablets with dopamine-depleting agents (e.g., reserpine and tetrabenazine) or other drugs known to deplete monoamine stores is not recommended.
Carbidopa and levodopa tablets and iron salts or multivitamins containing iron salts should be coadministered with caution. Iron salts can form chelates with levodopa and carbidopa and consequently reduce the bioavailability of carbidopa and levodopa.
Although metoclopramide may increase the bioavailability of levodopa by increasing gastric emptying, metoclopramide may also adversely affect disease control by its dopamine receptor antagonistic properties.
Carbidopa and levodopa tablets are a combination product for the treatment of Parkinson's disease and syndrome.
Carbidopa, USP an inhibitor of aromatic amino acid decarboxylation, is a white, crystalline compound, slightly soluble in water, with a molecular weight of 244.3.. It is designated chemically as (-)-L-α-hydrazino-α-methyl-β-(3,4-dihydroxybenzene) propanoic acid monohydrate. Its empirical formula is C10H14N2O4.H2O, and its structural formula is:
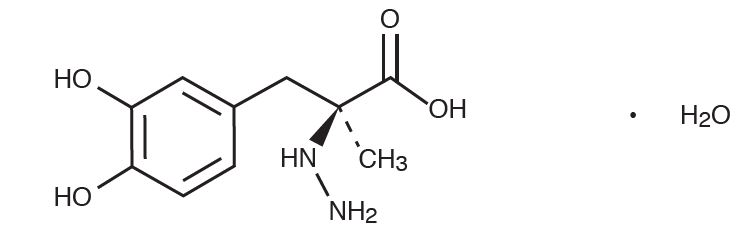
Tablet content is expressed in terms of anhydrous carbidopa which has a molecular weight of 226.23.
Levodopa, USP an aromatic amino acid, is a white, crystalline compound, slightly soluble in water with a molecular weight of 197.19. It is designated chemically as (-)-L-α-amino-β-(3,4-dihydroxybenzene) propanoic acid. Its empirical formula is C9H11NO4, and its structural formula is:
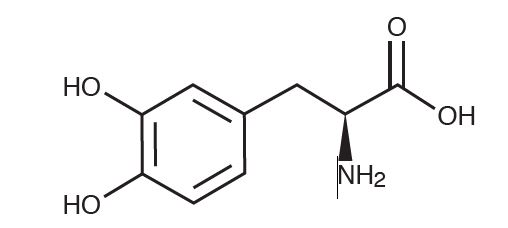
Carbidopa and levodopa tablets, USP for oral administration, are supplied in three strengths:
10 mg/100 mg, containing 10 mg of carbidopa and 100 mg of levodopa.
25 mg/100 mg, containing 25 mg of carbidopa and 100 mg of levodopa.
25 mg/250 mg, containing 25 mg of carbidopa and 250 mg of levodopa.
In addition, each tablet contains the following inactive ingredients:
| 10 mg/100 mg — | Corn starch, FD&C blue #2 aluminum lake, magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose, and pregelatinized starch (maize). |
| 25 mg/100 mg — | Corn starch, D&C yellow #10 aluminum lake, FD&C yellow #6 aluminum lake (sunset yellow lake), magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose, and pregelatinized starch (maize). |
| 25 mg/250 mg — | Corn starch, FD&C blue #2 aluminum lake, magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose, and pregelatinized starch (maize). |