Cefazolin
Cefazolin Prescribing Information
Cefazolin for Injection, USP is indicated in the treatment of the following serious infections due to susceptible organisms:
Injectable benzathine penicillin is considered to be the drug of choice in treatment and prevention of streptococcal infections, including the prophylaxis of rheumatic fever.
Cefazolin for Injection, USP is effective in the eradication of streptococci from the nasopharynx; however, data establishing the efficacy of Cefazolin for Injection, USP in the subsequent prevention of rheumatic fever are not available at present.
The perioperative use of Cefazolin for Injection, USP may also be effective in surgical patients in whom infection at the operative site would present a serious risk (e.g., during open-heart surgery and prosthetic arthroplasty).
The prophylactic administration of Cefazolin for Injection, USP should usually be discontinued within a 24 hour period after the surgical procedure. In surgery where the occurrence of infection may be particularly devastating (e.g., open-heart surgery and prosthetic arthroplasty), the prophylactic administration of Cefazolin for Injection, USP may be continued for 3 to 5 days following the completion of surgery.
If there are signs of infection, specimens for cultures should be obtained for the identification of the causative organism so that appropriate therapy may be instituted. (See
Type of Infection | Dose | Frequency |
|---|---|---|
Moderate to severe infections | 500 mg to 1 gram | every 6 to 8 hrs. |
Mild infections caused by susceptible gram-positive cocci | 250 mg to 500 mg | every 8 hours |
Acute, uncomplicated urinary tract infections | 1 gram | every 12 hours |
Pneumococcal pneumonia | 500 mg | every 12 hours |
Severe, life-threatening infections (e.g., endocarditis, septicemia)In rare instances, doses of up to 12 grams of Cefazolin for injection per day have been used. | 1 gram to 1.5 grams | every 6 hours |
a. 1 gram IV administered1/2hour to 1 hour prior to the start of surgery.
b. For lengthy operative procedures (e.g., 2 hours or more), 500 mg to 1 gram IV during surgery (administration modified depending on the duration of the operative procedure).
c. 500 mg to 1 gram IV every 6 to 8 hours for 24 hours postoperatively.
It is important that (1) the preoperative dose be given just (1/2to 1 hour) prior to the start of surgery so that adequate antibiotic levels are present in the serum and tissues at the time of initial surgical incision; and (2) Cefazolin for Injection be administered, if necessary, at appropriate intervals during surgery to provide sufficient levels of the antibiotic at the anticipated moments of greatest exposure to infective organisms.
In surgery where the occurrence of infection may be particularly devastating (e.g., open-heart surgery and prosthetic arthroplasty), the prophylactic administration of Cefazolin for Injection may be continued for 3 to 5 days following the completion of surgery.
Pediatric Dosage Guide | |||||
Weight | 25 mg/kg/day Divided into 3 Doses | 25 mg/kg/day Divided into 4 Doses | |||
Lbs | Kg | Approximate Single Dose mg/q8h | Vol. (mL) needed with dilution of 125 mg/mL | Approximate Single Dose mg/q6h | Vol. (mL) needed with dilution of 125 mg/mL |
10 | 4.5 | 40 mg | 0.35 mL | 30 mg | 0.25 mL |
20 | 9.0 | 75 mg | 0.60 mL | 55 mg | 0.45 mL |
30 | 13.6 | 115 mg | 0.90 mL | 85 mg | 0.70 mL |
40 | 18.1 | 150 mg | 1.20 mL | 115 mg | 0.90 mL |
50 | 22.7 | 190 mg | 1.50 mL | 140 mg | 1.10 mL |
Weight | 50 mg/kg/day Divided into 3 Doses | 50 mg/kg/day Divided into 4 Doses | |||
Lbs | Kg | Approximate | Vol. (mL) needed with dilution of 225 mg/mL | Approximate Single Dose mg/q6h | Vol. (mL) needed with dilution of 225 mg/mL |
10 | 4.5 | 75 mg | 0.35 mL | 55 mg | 0.25 mL |
20 | 9.0 | 150 mg | 0.70 mL | 110 mg | 0.50 mL |
30 | 13.6 | 225 mg | 1.00 mL | 170 mg | 0.75 mL |
40 | 18.1 | 300 mg | 1.35 mL | 225 mg | 1.00 mL |
50 | 22.7 | 375 mg | 1.70 mL | 285 mg | 1.25 mL |
In pediatric patients with mild to moderate renal impairment (creatinine clearance of 70 to 40 mL/min.), 60 percent of the normal daily dose given in equally divided doses every 12 hours should be sufficient. In patients with moderate impairment (creatinine clearance of 40 to 20 mL/min.), 25 percent of the normal daily dose given in equally divided doses every 12 hours should be adequate. Pediatric patients with severe renal impairment (creatinine clearance of 20 to 5 mL/min.) may be given 10 percent of the normal daily dose every 24 hours. All dosage recommendations apply after an initial loading dose.
To reduce the development of drug-resistant bacteria and maintain the effectiveness of Cefazolin for Injection, USP and other antibacterial drugs, Cefazolin for Injection, USP should be used only to treat or prevent infections that are proven or strongly suspected to be caused by susceptible bacteria. When culture and susceptibility information are available, they should be considered in selecting or modifying antibacterial therapy. In the absence of such data, local epidemiology and susceptibility patterns may contribute to the empiric selection of therapy.
Type of Infection | Dose | Frequency |
|---|---|---|
Moderate to severe infections | 500 mg to 1 gram | every 6 to 8 hrs. |
Mild infections caused by susceptible gram-positive cocci | 250 mg to 500 mg | every 8 hours |
Acute, uncomplicated urinary tract infections | 1 gram | every 12 hours |
Pneumococcal pneumonia | 500 mg | every 12 hours |
Severe, life-threatening infections (e.g., endocarditis, septicemia) | 1 gram to 1.5 grams | every 6 hours |
a. 1 gram IV administered
1/
2hour to 1 hour prior to the start of surgery.
b. For lengthy operative procedures (e.g., 2 hours or more), 500 mg to 1 gram IV during surgery (administration modified depending on the duration of the operative procedure).
c. 500 mg to 1 gram IV every 6 to 8 hours for 24 hours postoperatively.
It is important that (1) the preoperative dose be given just (
1/
2to 1 hour) prior to the start of surgery so that adequate antibiotic levels are present in the serum and tissues at the time of initial surgical incision; and (2) Cefazolin for Injection be administered, if necessary, at appropriate intervals during surgery to provide sufficient levels of the antibiotic at the anticipated moments of greatest exposure to infective organisms.
In surgery where the occurrence of infection may be particularly devastating (e.g., open-heart surgery and prosthetic arthroplasty), the prophylactic administration of Cefazolin for Injection may be continued for 3 to 5 days following the completion of surgery.
1/
2the usual dose every 12 hours. Patients with creatinine clearance rates of 10 mL/min. or less or serum creatinine of 4.6 mg % or greater should be given
1/
2the usual dose every 18 to 24 hours. All reduced dosage recommendations apply after an initial loading dose appropriate to the severity of the infection. Patients undergoing peritoneal dialysis: See
After intramuscular administration of Cefazolin for Injection to normal volunteers, the mean serum concentrations were 37 mcg/mL at 1 hour and 3 mcg/mL at 8 hours following a 500-mg dose, and 64 mcg/mL at 1 hour and 7 mcg/mL at 8 hours following a 1-gram dose.
Studies have shown that following intravenous administration of Cefazolin for Injection to normal volunteers, mean serum concentrations peaked at approximately 185 mcg/mL and were approximately 4 mcg/mL at 8 hours for a 1-gram dose.
The serum half-life for Cefazolin for Injection is approximately 1.8 hours following IV administration.
In a study (using normal volunteers) of constant intravenous infusion with dosages of 3.5 mg/kg for 1 hour (approximately 250 mg) and 1.5 mg/kg the next 2 hours (approximately 100 mg), Cefazolin produced a steady serum level at the third hour of approximately 28 mcg/mL.
Studies in patients hospitalized with infections indicate that Cefazolin produces mean peak serum levels approximately equivalent to those seen in normal volunteers.
Bile levels in patients without obstructive biliary disease can reach or exceed serum levels by up to 5 times; however, in patients with obstructive biliary disease, bile levels of Cefazolin for Injection are considerably lower than serum levels (< 1 mcg/mL).
In synovial fluid, the level of Cefazolin for Injection becomes comparable to that reached in serum at about 4 hours after drug administration.
Studies of cord blood show prompt transfer of Cefazolin across the placenta. Cefazolin for Injection is present in very low concentrations in the milk of nursing mothers.
Cefazolin for Injection is excreted unchanged in the urine. In the first 6 hours approximately 60% of the drug is excreted in the urine and this increases to 70% to 80% within 24 hours.
Cefazolin for Injection achieves peak urine concentrations of approximately 2,400 mcg/mL and 4,000 mcg/mL respectively following 500-mg and 1-gram intramuscular doses.
In patients undergoing peritoneal dialysis (2 L/hr.), Cefazolin for Injection produced mean serum levels of approximately 10 and 30 mcg/mL after 24 hours’ instillation of a dialyzing solution containing 50 mg/L and 150 mg/L, respectively. Mean peak levels were 29 mcg/mL (range 13 to 44 mcg/mL) with 50 mg/L (3 patients), and 72 mcg/mL (range 26 to 142 mcg/mL) with 150 mg/L (6 patients). Intraperitoneal administration of Cefazolin is usually well tolerated.
Controlled studies on adult normal volunteers, receiving 1 gram 4 times a day for 10 days, monitoring CBC, SGOT, SGPT, bilirubin, alkaline phosphatase, BUN, creatinine and urinalysis, indicated no clinically significant changes attributed to Cefazolin.
Cefazolin is a bactericidal agent that acts by inhibition of bacterial cell wall synthesis.
Predominant mechanisms of bacterial resistance to cephalosporins include the presence of extended-spectrum beta-lactamases and enzymatic hydrolysis.
Cefazolin has been shown to be active against most isolates of the following microorganisms, both
Gram-Positive Bacteria
Methicillin-resistant staphylococci are uniformly resistant to cefazolin.
Gram-Negative Bacteria
Most isolates of indole positive Proteus (
For specific information regarding susceptibility test interpretive criteria and associated test methods and quality control standards recognized by FDA for this drug, please see: https://www.fda.gov/STIC.
Pediatric Dosage Guide | |||||
Weight | 25 mg/kg/day Divided into 3 Doses | 25 mg/kg/day Divided into 4 Doses | |||
Lbs | Kg | Approximate Single Dose mg/q8h | Vol. (mL) needed with dilution of 125 mg/mL | Approximate Single Dose mg/q6h | Vol. (mL) needed with dilution of 125 mg/mL |
10 | 4.5 | 40 mg | 0.35 mL | 30 mg | 0.25 mL |
20 | 9.0 | 75 mg | 0.60 mL | 55 mg | 0.45 mL |
30 | 13.6 | 115 mg | 0.90 mL | 85 mg | 0.70 mL |
40 | 18.1 | 150 mg | 1.20 mL | 115 mg | 0.90 mL |
50 | 22.7 | 190 mg | 1.50 mL | 140 mg | 1.10 mL |
Weight | 50 mg/kg/day Divided into 3 Doses | 50 mg/kg/day Divided into 4 Doses | |||
Lbs | Kg | Approximate | Vol. (mL) needed with dilution of 225 mg/mL | Approximate Single Dose mg/q6h | Vol. (mL) needed with dilution of 225 mg/mL |
10 | 4.5 | 75 mg | 0.35 mL | 55 mg | 0.25 mL |
20 | 9.0 | 150 mg | 0.70 mL | 110 mg | 0.50 mL |
30 | 13.6 | 225 mg | 1.00 mL | 170 mg | 0.75 mL |
40 | 18.1 | 300 mg | 1.35 mL | 225 mg | 1.00 mL |
50 | 22.7 | 375 mg | 1.70 mL | 285 mg | 1.25 mL |
In pediatric patients with mild to moderate renal impairment (creatinine clearance of 70 to 40 mL/min.), 60 percent of the normal daily dose given in equally divided doses every 12 hours should be sufficient. In patients with moderate impairment (creatinine clearance of 40 to 20 mL/min.), 25 percent of the normal daily dose given in equally divided doses every 12 hours should be adequate. Pediatric patients with severe renal impairment (creatinine clearance of 20 to 5 mL/min.) may be given 10 percent of the normal daily dose every 24 hours. All dosage recommendations apply after an initial loading dose.
CEFAZOLIN FOR INJECTION IS CONTRAINDICATED IN PATIENTS WITH KNOWN ALLERGY TO THE CEPHALOSPORIN GROUP OF ANTIBIOTICS.
The following reactions have been reported:
BEFORE THERAPY WITH CEFAZOLIN FOR INJECTION USP IS INSTITUTED, CAREFUL INQUIRY SHOULD BE MADE TO DETERMINE WHETHER THE PATIENT HAS HAD PREVIOUS HYPERSENSITIVITY REACTIONS TO CEFAZOLIN, CEPHALOSPORINS, PENICILLINS, OR OTHER DRUGS. IF THIS PRODUCT IS GIVEN TO PENICILLIN-SENSITIVE PATIENTS, CAUTION SHOULD BE EXERCISED BECAUSE CROSS-HYPERSENSITIVITY AMONG BETA-LACTAM ANTIBIOTICS HAS BEEN CLEARLY DOCUMENTED AND MAY OCCUR IN UP TO 10% OF PATIENTS WITH A HISTORY OF PENICILLIN ALLERGY. IF AN ALLERGIC REACTION TO CEFAZOLIN FOR INJECTION USP OCCURS, DISCONTINUE TREATMENT WITH THE DRUG. SERIOUS ACUTE HYPERSENSITIVITY REACTIONS MAY REQUIRE TREATMENT WITH EPINEPHRINE AND OTHER EMERGENCY MEASURES, INCLUDING OXYGEN, IV FLUIDS, IV ANTIHISTAMINES, CORTICOSTEROIDS, PRESSOR AMINES, AND AIRWAY MANAGEMENT, AS CLINICALLY INDICATED.
Treatment with antibacterial agents alters the normal flora of the colon and may permit overgrowth of clostridia. Studies indicate that a toxin produced by
After the diagnosis of pseudomembranous colitis has been established, therapeutic measures should be initiated. Mild cases of pseudomembranous colitis usually respond to drug discontinuation alone. In moderate to severe cases, consideration should be given to management with fluids and electrolytes, protein supplementation, and treatment with an oral antibacterial drug clinically effective against
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE EVENTS, contact FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov.
Cefazolin for Injection, USP is a semi-synthetic cephalosporin for parenteral administration. It is the sodium salt of (6
14H
13N
8NaO
4S
3and molecular weight is 476.49.
Structural Formula:
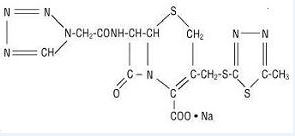
Each vial contains 48 mg (2 mEq) of sodium/1 gram of cefazolin. Cefazolin for Injection, USP is white or off-white powder or crystalline powder.
Cefazolin for Injection, USP is supplied in 10 grams Pharmacy Bulk Packages. Each Pharmacy Bulk Package contains cefazolin sodium equivalent to 10 grams of cefazolin. After reconstitution with either 45 mL or 96 mL of diluent the concentration is 1 gram cefazolin per 5 mL or 1 gram cefazolin per 10 mL, respectively. The pH of the reconstituted solution is between 4.0 and 6.0.
A pharmacy bulk package is a container of a sterile preparation for parenteral use that contains many single doses. The contents of this pharmacy bulk package are intended for use by a pharmacy admixture service for addition to suitable parenteral fluids in the preparation of admixtures for intravenous infusion (See
Type of Infection | Dose | Frequency |
|---|---|---|
Moderate to severe infections | 500 mg to 1 gram | every 6 to 8 hrs. |
Mild infections caused by susceptible gram-positive cocci | 250 mg to 500 mg | every 8 hours |
Acute, uncomplicated urinary tract infections | 1 gram | every 12 hours |
Pneumococcal pneumonia | 500 mg | every 12 hours |
Severe, life-threatening infections (e.g., endocarditis, septicemia)In rare instances, doses of up to 12 grams of Cefazolin for injection per day have been used. | 1 gram to 1.5 grams | every 6 hours |
a. 1 gram IV administered1/2hour to 1 hour prior to the start of surgery.
b. For lengthy operative procedures (e.g., 2 hours or more), 500 mg to 1 gram IV during surgery (administration modified depending on the duration of the operative procedure).
c. 500 mg to 1 gram IV every 6 to 8 hours for 24 hours postoperatively.
It is important that (1) the preoperative dose be given just (1/2to 1 hour) prior to the start of surgery so that adequate antibiotic levels are present in the serum and tissues at the time of initial surgical incision; and (2) Cefazolin for Injection be administered, if necessary, at appropriate intervals during surgery to provide sufficient levels of the antibiotic at the anticipated moments of greatest exposure to infective organisms.
In surgery where the occurrence of infection may be particularly devastating (e.g., open-heart surgery and prosthetic arthroplasty), the prophylactic administration of Cefazolin for Injection may be continued for 3 to 5 days following the completion of surgery.
Pediatric Dosage Guide | |||||
Weight | 25 mg/kg/day Divided into 3 Doses | 25 mg/kg/day Divided into 4 Doses | |||
Lbs | Kg | Approximate Single Dose mg/q8h | Vol. (mL) needed with dilution of 125 mg/mL | Approximate Single Dose mg/q6h | Vol. (mL) needed with dilution of 125 mg/mL |
10 | 4.5 | 40 mg | 0.35 mL | 30 mg | 0.25 mL |
20 | 9.0 | 75 mg | 0.60 mL | 55 mg | 0.45 mL |
30 | 13.6 | 115 mg | 0.90 mL | 85 mg | 0.70 mL |
40 | 18.1 | 150 mg | 1.20 mL | 115 mg | 0.90 mL |
50 | 22.7 | 190 mg | 1.50 mL | 140 mg | 1.10 mL |
Weight | 50 mg/kg/day Divided into 3 Doses | 50 mg/kg/day Divided into 4 Doses | |||
Lbs | Kg | Approximate | Vol. (mL) needed with dilution of 225 mg/mL | Approximate Single Dose mg/q6h | Vol. (mL) needed with dilution of 225 mg/mL |
10 | 4.5 | 75 mg | 0.35 mL | 55 mg | 0.25 mL |
20 | 9.0 | 150 mg | 0.70 mL | 110 mg | 0.50 mL |
30 | 13.6 | 225 mg | 1.00 mL | 170 mg | 0.75 mL |
40 | 18.1 | 300 mg | 1.35 mL | 225 mg | 1.00 mL |
50 | 22.7 | 375 mg | 1.70 mL | 285 mg | 1.25 mL |
In pediatric patients with mild to moderate renal impairment (creatinine clearance of 70 to 40 mL/min.), 60 percent of the normal daily dose given in equally divided doses every 12 hours should be sufficient. In patients with moderate impairment (creatinine clearance of 40 to 20 mL/min.), 25 percent of the normal daily dose given in equally divided doses every 12 hours should be adequate. Pediatric patients with severe renal impairment (creatinine clearance of 20 to 5 mL/min.) may be given 10 percent of the normal daily dose every 24 hours. All dosage recommendations apply after an initial loading dose.
After intramuscular administration of Cefazolin for Injection to normal volunteers, the mean serum concentrations were 37 mcg/mL at 1 hour and 3 mcg/mL at 8 hours following a 500-mg dose, and 64 mcg/mL at 1 hour and 7 mcg/mL at 8 hours following a 1-gram dose.
Studies have shown that following intravenous administration of Cefazolin for Injection to normal volunteers, mean serum concentrations peaked at approximately 185 mcg/mL and were approximately 4 mcg/mL at 8 hours for a 1-gram dose.
The serum half-life for Cefazolin for Injection is approximately 1.8 hours following IV administration.
In a study (using normal volunteers) of constant intravenous infusion with dosages of 3.5 mg/kg for 1 hour (approximately 250 mg) and 1.5 mg/kg the next 2 hours (approximately 100 mg), Cefazolin produced a steady serum level at the third hour of approximately 28 mcg/mL.
Studies in patients hospitalized with infections indicate that Cefazolin produces mean peak serum levels approximately equivalent to those seen in normal volunteers.
Bile levels in patients without obstructive biliary disease can reach or exceed serum levels by up to 5 times; however, in patients with obstructive biliary disease, bile levels of Cefazolin for Injection are considerably lower than serum levels (< 1 mcg/mL).
In synovial fluid, the level of Cefazolin for Injection becomes comparable to that reached in serum at about 4 hours after drug administration.
Studies of cord blood show prompt transfer of Cefazolin across the placenta. Cefazolin for Injection is present in very low concentrations in the milk of nursing mothers.
Cefazolin for Injection is excreted unchanged in the urine. In the first 6 hours approximately 60% of the drug is excreted in the urine and this increases to 70% to 80% within 24 hours.
Cefazolin for Injection achieves peak urine concentrations of approximately 2,400 mcg/mL and 4,000 mcg/mL respectively following 500-mg and 1-gram intramuscular doses.
In patients undergoing peritoneal dialysis (2 L/hr.), Cefazolin for Injection produced mean serum levels of approximately 10 and 30 mcg/mL after 24 hours’ instillation of a dialyzing solution containing 50 mg/L and 150 mg/L, respectively. Mean peak levels were 29 mcg/mL (range 13 to 44 mcg/mL) with 50 mg/L (3 patients), and 72 mcg/mL (range 26 to 142 mcg/mL) with 150 mg/L (6 patients). Intraperitoneal administration of Cefazolin is usually well tolerated.
Controlled studies on adult normal volunteers, receiving 1 gram 4 times a day for 10 days, monitoring CBC, SGOT, SGPT, bilirubin, alkaline phosphatase, BUN, creatinine and urinalysis, indicated no clinically significant changes attributed to Cefazolin.
Cefazolin is a bactericidal agent that acts by inhibition of bacterial cell wall synthesis.
Predominant mechanisms of bacterial resistance to cephalosporins include the presence of extended-spectrum beta-lactamases and enzymatic hydrolysis.
Cefazolin has been shown to be active against most isolates of the following microorganisms, both
Cefazolin for Injection, USP is indicated in the treatment of the following serious infections due to susceptible organisms:
Injectable benzathine penicillin is considered to be the drug of choice in treatment and prevention of streptococcal infections, including the prophylaxis of rheumatic fever.
Cefazolin for Injection, USP is effective in the eradication of streptococci from the nasopharynx; however, data establishing the efficacy of Cefazolin for Injection, USP in the subsequent prevention of rheumatic fever are not available at present.
The perioperative use of Cefazolin for Injection, USP may also be effective in surgical patients in whom infection at the operative site would present a serious risk (e.g., during open-heart surgery and prosthetic arthroplasty).
The prophylactic administration of Cefazolin for Injection, USP should usually be discontinued within a 24 hour period after the surgical procedure. In surgery where the occurrence of infection may be particularly devastating (e.g., open-heart surgery and prosthetic arthroplasty), the prophylactic administration of Cefazolin for Injection, USP may be continued for 3 to 5 days following the completion of surgery.
If there are signs of infection, specimens for cultures should be obtained for the identification of the causative organism so that appropriate therapy may be instituted. (See DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION.)
To reduce the development of drug-resistant bacteria and maintain the effectiveness of Cefazolin for Injection, USP and other antibacterial drugs, Cefazolin for Injection, USP should be used only to treat or prevent infections that are proven or strongly suspected to be caused by susceptible bacteria. When culture and susceptibility information are available, they should be considered in selecting or modifying antibacterial therapy. In the absence of such data, local epidemiology and susceptibility patterns may contribute to the empiric selection of therapy.
Gram-Positive Bacteria
Methicillin-resistant staphylococci are uniformly resistant to cefazolin.
Gram-Negative Bacteria
Most isolates of indole positive Proteus (
For specific information regarding susceptibility test interpretive criteria and associated test methods and quality control standards recognized by FDA for this drug, please see: https://www.fda.gov/STIC.