Cefdinir
Cefdinir Prescribing Information
To reduce the development of drug-resistant bacteria and maintain the effectiveness of cefdinir for oral suspension and other antibacterial drugs, cefdinir for oral suspension should be used only to treat or prevent infections that are proven or strongly suspected to be caused by susceptible bacteria. When culture and susceptibility information are available, they should be considered in selecting or modifying antibacterial therapy. In the absence of such data, local epidemiology and susceptibility patterns may contribute to the empiric selection of therapy.
Cefdinir for oral suspension is indicated for the treatment of patients with mild to moderate infections caused by susceptible strains of the designated microorganisms in the conditions listed below.
(see
To reduce the development of drug-resistant bacteria and maintain the effectiveness of cefdinir for oral suspension and other antibacterial drugs, cefdinir for oral suspension should be used only to treat or prevent infections that are proven or strongly suspected to be caused by susceptible bacteria. When culture and susceptibility information are available, they should be considered in selecting or modifying antibacterial therapy. In the absence of such data, local epidemiology and susceptibility patterns may contribute to the empiric selection of therapy.
Cefdinir for oral suspension is indicated for the treatment of patients with mild to moderate infections caused by susceptible strains of the designated microorganisms in the conditions listed below.
Caused by
Caused by
Caused by
Only intramuscular penicillin has been demonstrated to be effective for the prevention of rheumatic fever.
Caused by
Caused by
Only intramuscular penicillin has been demonstrated to be effective for the prevention of rheumatic fever.
Caused by
The recommended dosage and duration of treatment for infections in pediatric patients are described in the following chart; the total daily dose for all infections is 14 mg/kg, up to a maximum dose of 600 mg per day. Once-daily dosing for 10 days is as effective as BID dosing. Once-daily dosing has not been studied in skin infections; therefore, cefdinir for oral suspension should be administered twice daily in this infection. Cefdinir for oral suspension may be administered without regard to meals.
Header$Type of Infection | Dosage | Duration |
| Acute Bacterial Otitis Media | 7 mg/kg q12h or | 5 to 10 days |
| 14 mg/kg q24h | 10 days | |
| Acute Maxillary Sinusitis | 7 mg/kg q12h or | 10 days |
| 14 mg/kg q24h | 10 days | |
| Pharyngitis/Tonsillitis | 7 mg/kg q12h or | 5 to 10 days |
| 14 mg/kg q24h | 10 days | |
| Uncomplicated Skin and Skin Structure Infections | 7 mg/kg q12h | 10 days |
a Pediatric patients who weight ≥43 kg should receive the maximum daily dose of 600 mg. | ||
Header$Weight | 125 mg/5 mL | 250 mg/5 mL |
| 9 kg/20 lbs | 2.5 mL q12h or 5 mL q24h | Use 125 mg/5 mL product |
| 18 kg/40 lbs | 5 mL q12h or 10 mL q24h | 2.5 mL q12h or 5 mL q24h |
| 27 kg/60 lbs | 7.5 mL q12h or 15 mL q24h | 3.75 mL q12h or 7.5 mL q24h |
| 36 kg/80 lbs | 10 mL q12h or 20 mL q24h | 5 mL q12h or 10 mL q24h |
| ≥43 kga/95 lbs | 12 mL q12h or 24 mL q24h | 6 mL q12h or 12 mL q24h |
Cefdinir is contraindicated in patients with known allergy to the cephalosporin class of antibiotics.
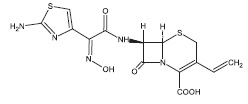
Cefdinir for oral suspension contain the active ingredient cefdinir, an extended-spectrum, semisynthetic cephalosporin, for oral administration. Chemically, cefdinir is [6R-[6α,7β(Z)]]-7-[[(2-amino-4-thiazolyl)(hydroxyimino)acetyl]amino]-3-ethenyl-8-oxo-5-thia-1-azabicyclo[4.2.0]oct-2-ene-2-carboxylic acid. Cefdinir is a white to slightly brownish-yellow solid. It is slightly soluble in dilute hydrochloric acid and sparingly soluble in 0.1 M pH 7.0 phosphate buffer. The molecular formula is C14H13N5O5S2 and the molecular weight is 395.42. Cefdinir has the structural formula shown below:
Cefdinir for oral suspension, after reconstitution, contains 125 mg cefdinir per 5 mL or 250 mg cefdinir per 5 mL and the following inactive ingredients: anhydrous citric acid; colloidal silicon dioxide; guar gum; anhydrous sodium citrate; sodium benzoate; strawberry flavour; sucrose; and xanthan gum.
Dose | Cmax ( mcg / mL ) | tmax ( hr ) | AUC ( mcg . hr / mL ) |
| 7 mg/kg | 2.30(0.65) | 2.2(0.6) | 8.31(2.50) |
| 14 mg/kg | 3.86(0.62) | 1.8(0.4) | 13.4(2.64) |
In a controlled, double-blind study in adults and adolescents conducted in the US, cefdinir BID was compared with cefaclor 500 mg TID. Using strict evaluability and microbiologic/clinical response criteria 6 to 14 days posttherapy, the following clinical cure rates, presumptive microbiologic eradication rates, and statistical outcomes were obtained:
Cefdinir BID | Cefaclor TID | Outcome | |
Clinical Cure Rates | 150/187 (80%) | 147/186 (79%) | Cefdinir equivalent to control |
Eradication Rates | |||
| Overall | 177/195 (91%) | 184/200 (92%) | Cefdinir equivalent to control |
S . pneumoniae | 31/31 (100%) | 35/35 (100%) | |
H . influenzae | 55/65 (85%) | 60/72 (83%) | |
M . catarrhalis | 10/10 (100%) | 11/11 (100%) | |
H . parainfluenzae | 81/89 (91%) | 78/82 (95%) |
In a second controlled, investigator-blind study in adults and adolescents conducted primarily in Europe, cefdinir BID was compared with amoxicillin/clavulanate 500/125 mg TID. Using strict evaluability and clinical response criteria 6 to 14 days posttherapy, the following clinical cure rates, presumptive microbiologic eradication rates, and statistical outcomes were obtained:
Cefdinir BID | Amoxicillin / Clavulanate TID | Outcome | |
Clinical Cure Rates | 83/104 (80%) | 86/97 (89%) | Cefdinir not equivalent to control |
Eradication Rates | |||
| Overall | 85/96 (89%) | 84/90 (93%) | Cefdinir equivalent to control |
S . pneumoniae | 42/44 (95%) | 43/44 (98%) | |
H . influenzae | 26/35 (74%) | 21/26 (81%) | |
M . catarrhalis | 6/6 (100%) | 8/8 (100%) | |
H . parainfluenzae | 11/11 (100%) | 12/12 (100%) |