Cefprozil - Cefprozil tablet, Film Coated
(Cefprozil)Cefprozil - Cefprozil tablet, Film Coated Prescribing Information
To reduce the development of drug-resistant bacteria and maintain the effectiveness of cefprozil and other antibacterial drugs, cefprozil should be used only to treat or prevent infections that are proven or strongly suspected to be caused by susceptible bacteria. When culture and susceptibility information are available, they should be considered in selecting or modifying antibacterial therapy. In the absence of such data, local epidemiology and susceptibility patterns may contribute to the empiric selection of therapy.
Cefprozil tablets are indicated for the treatment of patients with mild to moderate infections caused by susceptible strains of the designated microorganisms in the conditions listed below:
UPPER RESPIRATORY TRACT
Pharyngitis/tonsillitis
NOTE: The usual drug of choice in the treatment and prevention of streptococcal infections, including the prophylaxis of rheumatic fever, is penicillin given by the intramuscular route. Cefprozil is generally effective in the eradication of
Otitis Media
In a controlled clinical study of
EFFICACY: | ||
Pathogen | % of Cases with Pathogen (n=155) | Outcome |
S. pneumoniae | 48.4% | cefprozil success rate 5% better than control |
H. influenzae | 35.5% | cefprozil success rate 17% less than control |
M. catarrhalis | 13.5% | cefprozil success rate 12% less than control |
S. pyogenes | 2.6% | cefprozil equivalent to control |
| Overall | 100.0% | cefprozil success rate 5% less than control |
The incidences of adverse events, primarily diarrhea and rash*, were clinically and statistically significantly higher in the control arm versus the cefprozil arm.
| Age Group | Cefprozil | Control |
|---|---|---|
| *The majority of these involved the diaper area in young children. | ||
| 6 months to 2 years | 21% | 41% |
| 3 to 12 years | 10% | 19% |
In a controlled clinical study of
EFFICACY: | ||
Pathogen | % of Cases with Pathogen (n=47) | Outcome |
S. pneumoniae | 51.0% | cefprozil equivalent to control |
H. influenzae | 29.8% | cefprozil equivalent to control |
M. catarrhalis | 6.4% | cefprozil equivalent to control |
S. pyogenes | 12.8% | cefprozil equivalent to control |
| Overall | 100.0% | cefprozil equivalent to control |
The incidence of adverse events in the cefprozil arm was comparable to the incidence of adverse events in the control arm (agent that contained a specific β-lactamase inhibitor).
Distributed by:
East Windsor, NJ 08520
Manufactured by:
Revised: 10/2021
NOTE: In the treatment of otitis media due to β-lactamase producing organisms, cefprozil had bacteriologic eradication rates somewhat lower than those observed with a product containing a specific β-lactamase inhibitor. In considering the use of cefprozil, lower overall eradication rates should be balanced against the susceptibility patterns of the common microbes in a given geographic area and the increased potential for toxicity with products containing β-lactamase inhibitors.
Acute Sinusitis
LOWER RESPIRATORY TRACT
SKIN AND SKIN STRUCTURE
Uncomplicated Skin and Skin-Structure Infections
Cefprozil tablets are administered orally.
| Population/Infection | Dosage (mg) | Duration (days) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| a In the treatment of infections due to Streptococcus pyogenes , cefprozil should be administered for at least 10 days.b Not to exceed recommended adult doses. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ADULTS (13 years and older) | | | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| UPPER RESPIRATORY TRACT | | | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pharyngitis/Tonsillitis | 500 q24h | 10a | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Acute Sinusitis (For moderate to severe infections, the higher dose should be used) | 250 q12h or 500 q12h | 10 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LOWER RESPIRATORY TRACT | | | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Acute Bacterial Exacerbation of Chronic Bronchitis | 500 q12h | 10 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SKIN AND SKIN STRUCTURE | | | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Uncomplicated Skin and Skin Structure Infections | 250 q12h or 500 q24h or 500 q12h | 10 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CHILDREN (2 years to 12 years) | | | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| UPPER RESPIRATORY TRACTb | | | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pharyngitis/Tonsillitis | 7.5 mg/kg q12h | 10a | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SKIN AND SKIN STRUCTURE | | | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Uncomplicated Skin and Skin Structure Infections | 20 mg/kg q24h | 10 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| INFANTS & CHILDREN (6 months to 12 years) | | | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| UPPER RESPIRATORY TRACTb | | | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Otitis Media (See To reduce the development of drug-resistant bacteria and maintain the effectiveness of cefprozil and other antibacterial drugs, cefprozil should be used only to treat or prevent infections that are proven or strongly suspected to be caused by susceptible bacteria. When culture and susceptibility information are available, they should be considered in selecting or modifying antibacterial therapy. In the absence of such data, local epidemiology and susceptibility patterns may contribute to the empiric selection of therapy. Pharyngitis/tonsillitis Streptococcus pyogenes .NOTE: The usual drug of choice in the treatment and prevention of streptococcal infections, including the prophylaxis of rheumatic fever, is penicillin given by the intramuscular route. Cefprozil is generally effective in the eradication of Streptococcus pyogenes from the nasopharynx; however, substantial data establishing the efficacy of cefprozil in the subsequent prevention of rheumatic fever are not available at present.Otitis Media Streptococcus pneumoniae ,Haemophilus influenzae (including β-lactamase-producing strains), andMoraxella (Branhamella) catarrhalis (including β-lactamase-producing strains). (See CLINICAL STUDIES .)NOTE: In the treatment of otitis media due to β-lactamase producing organisms, cefprozil had bacteriologic eradication rates somewhat lower than those observed with a product containing a specific β-lactamase inhibitor. In considering the use of cefprozil, lower overall eradication rates should be balanced against the susceptibility patterns of the common microbes in a given geographic area and the increased potential for toxicity with products containing β-lactamase inhibitors. Acute Sinusitis Streptococcus pneumoniae ,Haemophilus influenzae (including β-lactamase-producing strains), andMoraxella (Branhamella) catarrhalis (including β-lactamase-producing strains).LOWER RESPIRATORY TRACT Acute Bacterial Exacerbation of Chronic Bronchitis caused byStreptococcus pneumoniae ,Haemophilus influenzae (including β-lactamase-producing strains), andMoraxella (Branhamella) catarrhalis (including β-lactamase-producing strains).SKIN AND SKIN STRUCTURE Uncomplicated Skin and Skin-Structure Infections Staphylococcus aureus (including penicillinase-producing strains) andStreptococcus pyogenes . Abscesses usually require surgical drainage.In a controlled clinical study of acute otitis media performed in the United States where significant rates of β-lactamase-producing organisms were found, cefprozil was compared to an oral antimicrobial agent that contained a specific β-lactamase inhibitor. In this study, using very strict evaluability criteria and microbiologic and clinical response criteria at the 10 to 16 days post-therapy follow-up, the following presumptive bacterial eradication/clinical cure outcomes i.e., clinical success) and safety results were obtained:
SAFETY: The incidences of adverse events, primarily diarrhea and rash*, were clinically and statistically significantly higher in the control arm versus the cefprozil arm.
In a controlled clinical study of acute otitis media performed in Europe, cefprozil was compared to an oral antimicrobial agent that contained a specific β-lactamase inhibitor. As expected in a European population, this study population had a lower incidence of β-lactamase-producing organisms than usually seen in U.S. trials. In this study, using very strict evaluability criteria and microbiologic and clinical response criteria at the 10 to 16 days post-therapy follow-up, the following presumptive bacterial eradication/clinical cure outcomes (i.e., clinical success) were obtained:
SAFETY: The incidence of adverse events in the cefprozil arm was comparable to the incidence of adverse events in the control arm (agent that contained a specific β-lactamase inhibitor). Distributed by: Aurobindo Pharma USA, Inc. 279 Princeton-Hightstown RoadEast Windsor, NJ 08520 Manufactured by: Aurobindo Pharma Limited Hyderabad-500 032, IndiaRevised: 10/2021 | 15 mg/kg q12h | 10 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Acute Sinusitis (For moderate to severe infections, the higher dose should be used) | 7.5 mg/kg q12h or 15 mg/kg q12h | 10 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Cefprozil tablets are contraindicated in patients with known allergy to the cephalosporin class of antibiotics.
The adverse reactions to cefprozil are similar to those observed with other orally administered cephalosporins. Cefprozil was usually well tolerated in controlled clinical trials. Approximately 2% of patients discontinued cefprozil therapy due to adverse events.
The most common adverse effects observed in patients treated with cefprozil are:
Gastrointestinal:
Hepatobiliary:
Hypersensitivity:
CNS:
Hematopoietic:
Renal:
Other:
The following adverse events, regardless of established causal relationship to cefprozil tablets, have been rarely reported during postmarketing surveillance: anaphylaxis, angioedema, colitis (including pseudomembranous colitis), erythema multiforme, fever, serum-sickness like reactions, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, and thrombocytopenia.
Nephrotoxicity has been reported following concomitant administration of aminoglycoside antibiotics and cephalosporin antibiotics. Concomitant administration of probenecid doubled the AUC for cefprozil.
The bioavailability of the capsule formulation of cefprozil was not affected when administered 5 minutes following an antacid.
Cefprozil is a semi-synthetic broad-spectrum cephalosporin antibiotic.
Cefprozil is a cis and trans isomeric mixture (≥90% cis). The chemical name for the monohydrate is (6
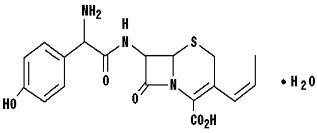
Cefprozil USP is a white to yellowish powder with a molecular formula for the monohydrate of C18H19N3O5S•H2O and a molecular weight of 407.45.
Cefprozil tablets USP are intended for oral administration.
Cefprozil tablets USP contain cefprozil USP equivalent to 250 mg or 500 mg of anhydrous cefprozil. In addition, each tablet contains the following inactive ingredients: microcrystalline cellulose, sodium starch glycolate, magnesium stearate, hypromellose, polyethylene glycol, polysorbate 80, and titanium dioxide. The 250 mg tablets also contain FD&C Yellow #6 aluminum lake. The tablets are imprinted with edible ink containing shellac glaze, black iron oxide, propylene glycol and ammonium hydroxide.