Celontin
(Methsuximide)Celontin Prescribing Information
Celontin is indicated for the control of absence (petit mal) seizures that are refractory to other drugs.
Optimum dosage of Celontin must be determined by trial. A suggested dosage schedule is 300 mg per day for the first week. If required, dosage may be increased thereafter at weekly intervals by 300 mg per day for the three weeks following to a daily dosage of 1.2 g. Because therapeutic effect and tolerance vary among patients, therapy with Celontin must be individualized according to the response of each patient. Optimal dosage is that amount of Celontin which is barely sufficient to control seizures so that side effects may be kept to a minimum.
Celontin may be administered in combination with other anticonvulsants when other forms of epilepsy coexist with absence (petit mal).
Methsuximide should not be used in patients with a history of hypersensitivity to succinimides.
Since Celontin (methsuximide) may interact with concurrently administered antiepileptic drugs, periodic serum level determinations of these drugs may be necessary (eg, methsuximide may increase the plasma concentrations of phenytoin and phenobarbital).
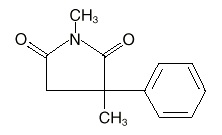
Celontin (methsuximide) is an anticonvulsant succinimide, chemically designated as N,2-Dimethyl-2-phenylsuccinimide, with the following structural formula:
Each Celontin capsule contains 300 mg methsuximide, USP. Also contains starch, NF. The capsule contains colloidal silicon dioxide, NF; D&C yellow No. 10; FD&C yellow No. 6; gelatin, NF; and sodium lauryl sulfate, NF.