Cetirizine Hydrochloride
Cetirizine Hydrochloride Prescribing Information
Cetirizine hydrochloride oral solution, USP is indicated for the treatment of the uncomplicated skin manifestations of chronic idiopathic urticaria in adults and children 6 months to 5 years of age. It significantly reduces the occurrence, severity, and duration of hives and significantly reduces pruritus.
The recommended dose of cetirizine hydrochloride oral solution, USP in children 6 months to 23 months of age is 2.5 mg (½ teaspoonful) once daily. The dose in children 12 to 23 months of age can be increased to a maximum dose of 5 mg per day, given as ½ teaspoonful (2.5 mg) every 12 hours.
Cetirizine hydrochloride oral solution, USP is contraindicated in those patients with a known hypersensitivity to it or any of its ingredients or hydroxyzine.
Pediatric studies were conducted with cetirizine hydrochloride. More than 1300 pediatric patients aged 6 to 11 years with more than 900 treated with cetirizine hydrochloride at doses of 1.25 to 10 mg per day were included in controlled and uncontrolled clinical trials conducted in the United States. The duration of treatment ranged from 2 to 12 weeks. Placebo-controlled trials up to 4 weeks duration included 168 pediatric patients aged 2 to 5 years who received cetirizine, the majority of whom received single daily doses of 5 mg.
A placebo-controlled trial 18 months in duration included 399 patients aged 12 to 24 months treated with cetirizine (0.25 mg/kg bid), and another placebo-controlled trial of 7 days duration included 42 patients aged 6 to 11 months who were treated with cetirizine (0.25 mg/kg bid).
The majority of adverse reactions reported in pediatric patients aged 2 to 11 years with cetirizine hydrochloride were mild or moderate. In placebo-controlled trials, the incidence of discontinuations due to adverse reactions in pediatric patients receiving up to 10 mg of cetirizine hydrochloride was uncommon (0.4% on cetirizine hydrochloride vs. 1.0% on placebo).
Table 1 lists adverse experiences which were reported for cetirizine hydrochloride 5 and 10 mg in pediatric patients aged 6 to 11 years in placebo-controlled clinical trials in the United States and were more common with cetirizine hydrochloride than placebo. Of these, abdominal pain was considered treatment-related and somnolence appeared to be dose-related, 1.3% in placebo, 1.9% at 5 mg and 4.2% at 10 mg. The adverse experiences reported in pediatric patients aged 2 to 5 years in placebo-controlled trials were qualitatively similar in nature and generally similar in frequency to those reported in trials with children aged 6 to 11 years.
In the placebo-controlled trials of pediatric patients 6 to 24 months of age, the incidences of adverse experiences, were similar in the cetirizine and placebo treatment groups in each study. Somnolence occurred with essentially the same frequency in patients who received cetirizine and patients who received placebo. In a study of 1 week duration in children 6 to 11 months of age, patients who received cetirizine exhibited greater irritability/fussiness than patients on placebo. In a study of 18 months duration in patients 12 months and older, insomnia occurred more frequently in patients who received cetirizine compared to patients who received placebo (9.0% v. 5.3%). In those patients who received 5 mg or more per day of cetirizine as compared to patients who received placebo, fatigue (3.6% v. 1.3%) and malaise (3.6% v. 1.8%) occurred more frequently.
| Adverse Experiences | Cetirizine Hydrochloride | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Placebo (N = 309) | 5 mg (N = 161) | 10 mg (N = 215) | |
| Headache | 12.3% | 11.0% | 14.0% |
| Pharyngitis | 2.9% | 6.2% | 2.8% |
| Abdominal pain | 1.9% | 4.4% | 5.6% |
| Coughing | 3.9% | 4.4% | 2.8% |
| Somnolence | 1.3% | 1.9% | 4.2% |
| Diarrhea | 1.3% | 3.1% | 1.9% |
| Epistaxis | 2.9% | 3.7% | 1.9% |
| Bronchospasm | 1.9% | 3.1% | 1.9% |
| Nausea | 1.9% | 1.9% | 2.8% |
| Vomiting | 1.0% | 2.5% | 2.3% |
The following events were observed infrequently (less than 2%), in either 3982 adults and children 12 years and older or in 659 pediatric patients aged 6 to 11 years who received cetirizine hydrochloride in U.S. trials, including an open adult study of six months duration. A causal relationship of these infrequent events with cetirizine hydrochloride administration has not been established.
No clinically significant drug interactions have been found with theophylline at a low dose, azithromycin, pseudoephedrine, ketoconazole, or erythromycin. There was a small decrease in the clearance of cetirizine caused by a 400 mg dose of theophylline; it is possible that larger theophylline doses could have a greater effect.
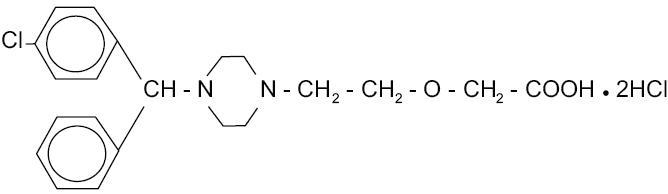
Cetirizine hydrochloride, USP is an orally active and selective H
1-receptor antagonist. The chemical name is (±) - [2- [4- [ (4-chlorophenyl)phenylmethyl] -1- piperazinyl] ethoxy]acetic acid, dihydrochloride. Cetirizine hydrochloride is a racemic compound with a molecular formula of C
21H
25ClN
2O
3•2HCl. The molecular weight is 461.82 and the chemical structure is shown below:
Cetirizine hydrochloride, USP is a white, crystalline powder and is water soluble.
Cetirizine hydrochloride oral solution, USP is a colorless to slightly yellow oral solution containing cetirizine hydrochloride at a concentration of 1 mg/mL (5 mg/5 mL) for oral administration. The pH is between 4 and 5. The inactive ingredients of the oral solution are: glacial acetic acid, glycerin, grape flavor, methylparaben, propylene glycol, propylparaben, purified water, sodium acetate, and sucrose.