Cevimeline Hydrochloride
Cevimeline Hydrochloride Prescribing Information
Cevimeline is indicated for the treatment of symptoms of dry mouth in patients with SjÖgren's Syndrome.
The recommended dose of cevimeline hydrochloride is 30 mg taken three times a day. There is insufficient safety information to support doses greater than 30 mg tid. There is also insufficient evidence for additional efficacy of cevimeline hydrochloride at doses greater than 30 mg tid.
Cevimeline is contraindicated in patients with uncontrolled asthma, known hypersensitivity to cevimeline, and when miosis is undesirable, e.g., in acute iritis and in narrow-angle (angle-closure) glaucoma.
Cevimeline was administered to 1777 patients during clinical trials worldwide, including SjÖgren's patients and patients with other conditions. In placebo-controlled SjÖgren's studies in the U.S., 320 patients received cevimeline doses ranging from 15 mg tid to 60 mg tid, of whom 93% were women and 7% were men. Demographic distribution was 90% Caucasian, 5% Hispanic, 3% Black and 2% of other origin. In these studies, 14.6% of patients discontinued treatment with cevimeline due to adverse events.
The following adverse events associated with muscarinic agonism were observed in the clinical trials of cevimeline in SjÖgren's syndrome patients:
*n is the total number of patients exposed to the dose at any time during the study. | ||
Adverse Event | Cevimeline 30 mg (tid) n *= 533 | Placebo (tid) n = 164 |
| Excessive Sweating | 18.7% | 2.4% |
| Nausea | 13.8% | 7.9% |
| Rhinitis | 11.2% | 5.4% |
| Diarrhea | 10.3% | 10.3% |
| Excessive Salivation | 2.2% | 0.6% |
| Urinary Frequency | 0.9% | 1.8% |
| Asthenia | 0.5% | 0.0% |
| Flushing | 0.3% | 0.6% |
| Polyuria | 0.1% | 0.6% |
In addition, the following adverse events (≥3% incidence) were reported in the SjÖgren's clinical trials:
*n is the total number of patients exposed to the dose at any time during the study. | ||
Adverse Event | Cevimeline 30 mg (tid) n *= 533 | Placebo (tid) n = 164 |
| Headache | 14.4% | 20.1% |
| Sinusitis | 12.3% | 10.9% |
| Upper Respiratory | 11.4% | 9.1% |
| Tract Infection | ||
| Dyspepsia | 7.8% | 8.5% |
| Abdominal Pain | 7.6% | 6.7% |
| Urinary Tract Infection | 6.1% | 3.0% |
| Coughing | 6.1% | 3.0% |
| Pharyngitis | 5.2% | 5.4% |
| Vomiting | 4.6% | 2.4% |
| Injury | 4.5% | 2.4% |
| Back Pain | 4.5% | 4.2% |
| Rash | 4.3% | 6.0% |
| Conjunctivitis | 4.3% | 3.6% |
| Dizziness | 4.1% | 7.3% |
| Bronchitis | 4.1% | 1.2% |
| Arthralgia | 3.7% | 1.8% |
| Surgical Intervention | 3.3% | 3.0% |
| Fatigue | 3.3% | 1.2% |
| Pain | 3.3% | 3.0% |
| Skeletal Pain | 2.8% | 1.8% |
| Insomnia | 2.4% | 1.2% |
| Hot Flushes | 2.4% | 0.0% |
| Rigors | 1.3% | 1.2% |
| Anxiety | 1.3% | 1.2% |
The following events were reported in SjÖgren's patients at incidences of <3% and ≥1%: constipation, tremor, abnormal vision, hypertonia, peripheral edema, chest pain, myalgia, fever, anorexia, eye pain, earache, dry mouth, vertigo, salivary gland pain, pruritus, influenza-like symptoms, eye infection, post-operative pain, vaginitis, skin disorder, depression, hiccup, hyporeflexia, infection, fungal infection, sialoadenitis, otitis media, erythematous rash, pneumonia, edema, salivary gland enlargement, allergy, gastroesophageal reflux, eye abnormality, migraine, tooth disorder, epistaxis, flatulence, toothache, ulcerative stomatitis, anemia, hypoesthesia, cystitis, leg cramps, abscess, eructation, moniliasis, palpitation, increased amylase, xerophthalmia, allergic reaction.
The following events were reported rarely in treated SjÖgren's patients (<1%): Causal relation is unknown:
In one subject with lupus erythematosus receiving concomitant multiple drug therapy, a highly elevated ALT level was noted after the fourth week of cevimeline therapy. In two other subjects receiving cevimeline in the clinical trials, very high AST levels were noted. The significance of these findings is unknown.
Additional adverse events (relationship unknown) which occurred in other clinical studies (patient population different from SjÖgren's patients) are as follows:
cholinergic syndrome, blood pressure fluctuation, cardiomegaly, postural hypotension, aphasia, convulsions, abnormal gait, hyperesthesia, paralysis, abnormal sexual function, enlarged abdomen, change in bowel habits, gum hyperplasia, intestinal obstruction, bundle branch block, increased creatine phosphokinase, electrolyte abnormality, glycosuria, gout, hyperkalemia, hyperproteinemia, increased lactic dehydrogenase (LDH), increased alkaline phosphatase, failure to thrive, abnormal platelets, aggressive reaction, amnesia, apathy, delirium, delusion, dementia, illusion, impotence, neurosis, paranoid reaction, personality disorder, hyperhemoglobinemia, apnea, atelectasis, yawning, oliguria, urinary retention, distended vein, lymphocytosis.
The following adverse reaction has been identified during post-approval use of Cevimeline Hydrochloride Capsules. Because post-marketing adverse reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Cevimeline should be administered with caution to patients taking beta adrenergic antagonists, because of the possibility of conduction disturbances. Drugs with parasympathomimetic effects administered concurrently with cevimeline can be expected to have additive effects. Cevimeline might interfere with desirable antimuscarinic effects of drugs used concomitantly.
Drugs which inhibit CYP2D6 and CYP3A3/4 also inhibit the metabolism of cevimeline. Cevimeline should be used with caution in individuals known or suspected to be deficient in CYP2D6 activity, based on previous experience, as they may be at a higher risk of adverse events. In an
Cevimeline is cis-2'-methylspiro {1-azabicyclo [2.2.2] octane-3, 5'-[1,3] oxathiolane} hydrochloride, hydrate (2:1). Its empirical formula is C10H17NOS.HCl.1/2 H2O, and its structural formula is:
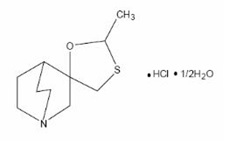
Cevimeline has a molecular weight of 244.79. It is a white to off white crystalline powder with a melting point range of 201 to 203°C. It is freely soluble in alcohol and chloroform, very soluble in water, and virtually insoluble in ether. The pH of a 1% solution ranges from 4.6 to 5.6. Inactive ingredients include lactose monohydrate, hydroxypropyl cellulose, and magnesium stearate; a hard gelatin capsule which contains D&C Yellow #10, FD&C Red #40, FD&C Yellow #6, titanium dioxide and gelatin; and an imprinting ink which contains shellac, iron oxide black, isopropyl alcohol, butyl alcohol, propylene glycol and ammonium hydroxide.