Chlordiazepoxide Hydrochloride And Clidinium Bromide Prescribing Information
Concomitant use of benzodiazepines, including chlordiazepoxide hydrochloride and clidinium bromide capsules, and opioids may result in profound sedation, respiratory depression, coma, and death. Because of these risks, reserve concomitant prescribing of these drugs for use in patients for whom alternative treatment options are inadequate.
Observational studies have demonstrated that concomitant use of opioid analgesics and benzodiazepines increases the risk of drug-related mortality compared to use of opioids alone. If a decision is made to prescribe chlordiazepoxide hydrochloride and clidinium bromide capsules concomitantly with opioids, prescribe the lowest effective dosages and minimum durations of concomitant use, and follow patients closely for signs and symptoms of respiratory depression and sedation.
Advise both patients and caregivers about the risks of respiratory depression and sedation when chlordiazepoxide hydrochloride and clidinium bromide capsules is used with opioids (see
As in the case of other preparations containing CNS-acting drugs, patients receiving chlordiazepoxide hydrochloride and clidinium bromide capsules should be cautioned about possible combined effects with opioids, alcohol and other CNS depressants. For the same reason, they should be cautioned against hazardous occupations requiring complete mental alertness, such as operating machinery or driving a motor vehicle.
An increased risk of congenital malformations associated with the use of minor tranquilizers (chlordiazepoxide, diazepam and meprobamate) during the first trimester of pregnancy has been suggested in several studies. Because use of these drugs is rarely a matter of urgency, their use during this period should almost always be avoided. The possibility that a woman of childbearing potential may be pregnant at the time of institution of therapy should be considered. Patients should be advised that if they become pregnant during therapy or intend to become pregnant they should communicate with their physicians about the desirability of discontinuing the drug.
As with all anticholinergic drugs, an inhibiting effect on lactation may occur (see
In debilitated patients, it is recommended that the dosage be limited to the smallest effective amount to preclude the development of ataxia, oversedation or confusion (not more than 2 Chlordiazepoxide Hydrochloride/Clidinium Bromide capsules per day initially, to be increased gradually as needed and tolerated). In general, the concomitant administration of chlordiazepoxide hydrochloride and clidinium bromide capsules and other psychotropic agents is not recommended. If such combination therapy seems indicated, careful consideration should be given to the pharmacology of the agents to be employed - particularly when the known potentiating compounds such as the MAO inhibitors and phenothiazines are to be used. The usual precautions in treating patients with impaired renal or hepatic function should be observed.
Paradoxical reactions to chlordiazepoxide hydrochloride, e.g., excitement, stimulation and acute rage, have been reported in psychiatric patients and should be watched for during chlordiazepoxide hydrochloride and clidinium bromide capsules therapy. The usual precautions are indicated when chlordiazepoxide hydrochloride is used in the treatment of anxiety states where there is any evidence of impending depression; it should be borne in mind that suicidal tendencies may be present and protective measures may be necessary. Although clinical studies have not established a cause and effect relationship, physicians should be aware that variable effects on blood coagulation have been reported very rarely in patients receiving oral anticoagulants and chlordiazepoxide hydrochloride.
Inform patients and caregivers that potentially fatal additive effects may occur if chlordiazepoxide hydrochloride and clidinium bromide capsules is used with opioids or other CNS depressants, including alcohol, and not to use these concomitantly unless supervised by a health care provider (see
To assure the safe and effective use of benzodiazepines, patients should be informed that, since benzodiazepines may produce psychological and physical dependence, it is advisable that they consult with their physician before either increasing the dose or abruptly discontinuing this drug.
The concomitant use of benzodiazepines and opioids increases the risk of respiratory depression because of actions at different receptor sites in the CNS that control respiration. Benzodiazepines interact at GABAA sites and opioids interact primarily at mu receptors. When benzodiazepines and opioids are combined, the potential for benzodiazepines to significantly worsen opioid-related respiratory depression exists. Limit dosage and duration of concomitant use of benzodiazepines and opioids, and follow patients closely for respiratory depression and sedation.
Safety and effectiveness in pediatric patients have not been established.
Geriatric subjects may be particularly prone to experiencing drowsiness, ataxia and confusion while receiving chlordiazepoxide hydrochloride and clidinium bromide capsules. These effects can usually be avoided with proper dosage adjustment, although they have occasionally been observed even at the lower dosage ranges. Dosing in geriatric subjects should be initiated cautiously (no more than 2 capsules per day) and increased gradually if needed and tolerated (see
- Reserve concomitant prescribing of these drugs for use in patients for whom alternative treatment options are inadequate.
- Limit dosages and durations to the minimum required.
- Follow patients for signs and symptoms of respiratory depression and sedation.
Chlordiazepoxide hydrochloride and clidinium bromide capsules are indicated to control emotional and somatic factors in gastrointestinal disorders. Chlordiazepoxide hydrochloride and clidinium bromide capsules may also be used as adjunctive therapy in the treatment of peptic ulcer and in the treatment of the irritable bowel syndrome (irritable colon, spastic colon, mucous colitis) and acute enterocolitis.
Because of the varied individual responses to tranquilizers and anticholinergics, the optimum dosage of chlordiazepoxide hydrochloride and clidinium bromide capsules varies with the diagnosis and response of the individual patient. The dosage, therefore, should be individualized for maximum beneficial effects. The usual maintenance dose is 1 or 2 capsules, 3 or 4 times a day administered before meals and at bedtime.
Dosage should be limited to the smallest effective amount to preclude the development of ataxia, oversedation or confusion. The initial dose should not exceed 2 chlordiazepoxide hydrochloride and clidinium bromide capsules per day, to be increased gradually as needed and tolerated.
Chlordiazepoxide hydrochloride and clidinium bromide capsules are contraindicated in the presence of glaucoma (since the anticholinergic component may produce some degree of mydriasis) and in patients with prostatic hypertrophy and benign bladder neck obstruction. It is contraindicated in patients with known hypersensitivity to chlordiazepoxide hydrochloride and/or clidinium bromide.
No side effects or manifestation not seen with either compound alone have been reported with the administration of chlordiazepoxide hydrochloride and clidinium bromide capsules. However, since the chlordiazepoxide hydrochloride and clidinium bromide capsules contain chlordiazepoxide hydrochloride and clidinium bromide, the possibility of untoward effects which may be seen with either of these two compounds cannot be excluded.
When chlordiazepoxide hydrochloride has been used alone the necessity of discontinuing therapy because of undesirable effects has been rare. Drowsiness, ataxia and confusion have been reported in some patients – particularly the elderly and debilitated. While these effects can be avoided in almost all instances by proper dosage adjustment, they have occasionally been observed at the lower dosage ranges. In a few instances syncope has been reported.
Other adverse reactions reported during therapy with chlordiazepoxide hydrochloride include isolated instances of skin eruptions, edema, minor menstrual irregularities, nausea and constipation, extrapyramidal symptoms, as well as increased and decreased libido. Such side effects have been infrequent and are generally controlled with reduction of dosage. Changes in EEG patterns (low-voltage fast activity) have been observed in patients during and after chlordiazepoxide hydrochloride treatment.
Blood dyscrasias, including agranulocytosis, jaundice and hepatic dysfunction have occasionally been reported during therapy with chlordiazepoxide hydrochloride. When chlordiazepoxide hydrochloride treatment is protracted, periodic blood counts and liver function tests are advisable.
Adverse effects reported with use of chlordiazepoxide hydrochloride and clidinium bromide capsules are those typical of anticholinergic agents, i.e., dryness of the mouth, blurring of vision, urinary hesitancy and constipation. Constipation has occurred most often when Chlordiazepoxide Hydrochloride/Clidinium Bromide therapy has been combined with other spasmolytic agents and/or low residue diet.
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Chartwell RX, LLC at 1-845-232-1683 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
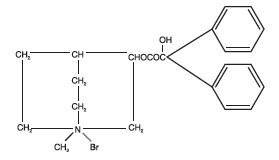
Chlordiazepoxide hydrochloride and clidinium bromide capsules USP, 5 mg/2.5 mg combines in a single capsule formulation the antianxiety action of chlordiazepoxide hydrochloride and the anticholinergic/spasmolytic effects of clidinium bromide.
Each chlordiazepoxide hydrochloride and clidinium bromide capsules USP, 5 mg/2.5 mg contains the active ingredients 5 mg chlordiazepoxide hydrochloride and 2.5 mg clidinium bromide. Each capsule also contains the inactive ingredients corn starch, lactose monohydrate, talc, sodium lauryl sulfate, D&C Yellow No. 10, FD&C Green No. 3, titanium dioxide, and gelatin. The imprinting ink contains ammonia solution, black iron oxide, potassium hydroxide, propylene glycol, and shellac.
Chlordiazepoxide hydrochloride is a versatile, therapeutic agent of proven value for the relief of anxiety and tension. It is indicated when anxiety, tension or apprehension are significant components of the clinical profile. It is among the safer of the effective psychopharmacologic compounds.
Chlordiazepoxide hydrochloride is 7-chloro-2-(methylamino)-5-phenyl-3H-1,4-benzodiazepine 2-oxide monohydrochloride. A white to slightly yellow, crystalline powder, it is soluble in water. It is unstable in solution and the powder must be protected from light. The molecular weight is 336.2. The structural formula of chlordiazepoxide hydrochloride is as follows:
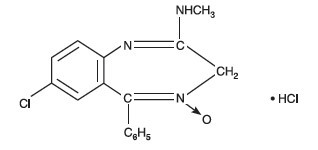
Clidinium bromide is a synthetic anticholinergic agent which has been shown in experimental and clinical studies to have a pronounced antispasmodic and antisecretory effect on the gastrointestinal tract. Structurally clidinium bromide is: