Chlorzoxazone
Chlorzoxazone Prescribing Information
Chlorzoxazone is indicated as an adjunct to rest, physical therapy, and other measures for the relief of discomfort associated with acute, painful musculoskeletal conditions. The mode of action of this drug has not been clearly identified, but may be related to its sedative properties. Chlorzoxazone does not directly relax tense skeletal muscles in man.
One tablet three or four times daily. If adequate response is not obtained with this dose, it may be increased to one and one-half tablets (750 mg) three or four times daily. As improvement occurs dosage can usually be reduced.
Chlorzoxazone is contraindicated in patients with known intolerance to the drug.
Chlorzoxazone containing products are usually well tolerated. It is possible in rare instances that chlorzoxazone may have been associated with gastrointestinal bleeding. Drowsiness, dizziness, lightheadedness, malaise, or over-stimulation may be noted by an occasional patient. Rarely, allergic-type skin rashes, petechiae, or ecchymoses may develop during treatment. Angioneurotic edema or anaphylactic reactions are extremely rare. There is no evidence that the drug will cause renal damage. Rarely, a patient may note discoloration of the urine resulting from a phenolic metabolite of chlorzoxazone. This finding is of no known clinical significance.
Chlorzoxazone, USP is a centrally-acting skeletal muscle relaxant, available as tablets of 500 mg for oral administration. Its chemical name is 5-Chloro-2-benzoxazolinone, and its structural formula is:
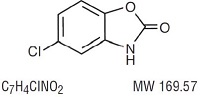
Chlorzoxazone, USP is a white or practically white, practically odorless, crystalline powder. Chlorzoxazone, USP is slightly soluble in water; sparingly soluble in alcohol, in isopropyl alcohol, and in methanol; soluble in solutions of alkali hydroxides and ammonia.
Chlorzoxazone Tablets, USP contain the inactive ingredients docusate sodium, lactose monohydrate, magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellullose, pregelatinized starch, sodium benzoate, and sodium starch glycolate.
Chlorzoxazone is a centrally-acting agent for painful musculoskeletal conditions. Data available from animal experiments as well as human study indicate that chlorzoxazone acts primarily at the level of the spinal cord and subcortical areas of the brain where it inhibits multisynaptic reflex arcs involved in producing and maintaining skeletal muscle spasm of varied etiology. The clinical result is a reduction of the skeletal muscle spasm with relief of pain and increased mobility of the involved muscles. Blood levels of chlorzoxazone can be detected in people during the first 30 minutes and peak levels may be reached, in the majority of the subjects, in about 1 to 2 hours after oral administration of chlorzoxazone. Chlorzoxazone is rapidly metabolized and is excreted in the urine, primarily in a conjugated form as the glucuronide. Less than one percent of a dose of chlorzoxazone is excreted unchanged in the urine in 24 hours.