Cisplatin Prescribing Information
- Nephrotoxicity: Cisplatin Injection can cause severe renal toxicity, including acute renal failure. Severe renal toxicities are dose-related and cumulative. Ensure adequate hydration and monitor renal function and electrolytes. Consider dose reductions or alternative treatments in patients with renal impairment[see Dosageand Administration () and Warnings and Precautions (
2.1 Hydration and Anti-Emetic TreatmentPatients treated with Cisplatin Injection must receive appropriate pre-treatment hydration. Maintain adequate hydration and urinary output for 24 hours after Cisplatin Injection administration
[see Warnings and Precautions ]. Administer pre-treatment and post-treatment antiemetics as appropriate[see Warnings and Precautions ].)].5.1 NephrotoxicityCisplatin Injection can cause dose-related nephrotoxicity, including acute renal failure that becomes more prolonged and severe with repeated courses of the drug. Renal toxicity typically begins during the second week after a dose of Cisplatin Injection. Patients with baseline renal impairment, geriatric patients, patients who are taking other nephrotoxic drugs, or patients who are not well hydrated may be more susceptible to nephrotoxicity
[see Use in Specific Populations ].Ensure adequate hydration before, during, and after Cisplatin Injection administration
[see Dosage and Administration ].Measure serum creatinine, blood urea nitrogen, creatinine clearance, and serum electrolytes including magnesium prior to initiating therapy, and as clinically indicated. Consider magnesium supplementation as clinically needed.Consider alternative treatments or reduce the dose of Cisplatin Injection for patients with baseline renal impairment or who develop significant reductions in creatinine clearance during treatment with Cisplatin Injection according to clinical treatment guidelines
[see Dosage and Administration ]. - Nausea and Vomiting: Cisplatin Injection can cause severe nausea and vomiting. Use highly effective antiemetic premedication[see Dosage and Administration ()
2.1 Hydration and Anti-Emetic TreatmentPatients treated with Cisplatin Injection must receive appropriate pre-treatment hydration. Maintain adequate hydration and urinary output for 24 hours after Cisplatin Injection administration
[see Warnings and Precautions ]. Administer pre-treatment and post-treatment antiemetics as appropriate[see Warnings and Precautions ].and Warnings and Precautions ()].5.3 Nausea and VomitingCisplatin Injection is a highly emetogenic antineoplastic agent. Premedicate with anti-emetic agents
[see Dosage and Administration ]. Without antiemetic therapy, marked nausea and vomiting occur in almost all patients treated with Cisplatin Injection and may be so severe that the drug must be discontinued. Nausea and vomiting may begin within 1 to 4 hours after treatment and last up to 72 hours. Maximal intensity occurs 48 to 72 hours after administration.Various degrees of vomiting, nausea, and/or anorexia may persist for up to 1 week after treatment. Delayed nausea and vomiting (begins or persists 24 hours or more after chemotherapy) has occurred in patients attaining complete emetic control on the day of Cisplatin Injection therapy. Consider the use of additional anti-emetics following infusion.
- Myelosuppression: Cisplatin Injection can cause severe myelosuppression with fatalities due to infections. Monitor blood counts accordingly. Interruption of therapy may be required[see Warnings and Precautions ()].
5.4 MyelosuppressionMyelosuppression suppression occurs in 25% to 30% of patients treated with Cisplatin Injection. Fever and infection have been reported in patients with neutropenia. Potential fatalities due to infection (secondary to myelosuppression) have been reported. Geriatric patients may be more susceptible to myelosuppression
[see Use in Specific Populations ].Perform standard hematologic tests before initiating Cisplatin Injection, before each subsequent course, and as clinically indicated. Closely monitor patients for the development of signs and symptoms of infection during and after treatment with Cisplatin Injection. For patients who develop severe myelosuppression during treatment with Cisplatin Injection, consider dose modifications and manage according to clinical treatment guidelines.
Cisplatin Injection, is a clear, light-yellow, sterile aqueous solution, for intravenous use, available in sterile multiple-dose vials containing
- 50 mg/50 mL (1 mg/mL)
- 100 mg/100 mL (1 mg/mL)
Cisplatin Injection is contraindicated in patients with severe hypersensitivity to cisplatin
Myelosuppression suppression occurs in 25% to 30% of patients treated with Cisplatin Injection. Fever and infection have been reported in patients with neutropenia. Potential fatalities due to infection (secondary to myelosuppression) have been reported. Geriatric patients may be more susceptible to myelosuppression
Perform standard hematologic tests before initiating Cisplatin Injection, before each subsequent course, and as clinically indicated. Closely monitor patients for the development of signs and symptoms of infection during and after treatment with Cisplatin Injection. For patients who develop severe myelosuppression during treatment with Cisplatin Injection, consider dose modifications and manage according to clinical treatment guidelines.
The following adverse reactions are described in greater detail, in other sections:
- Nephrotoxicity [see Warnings and Precautions ()]
5.1 NephrotoxicityCisplatin Injection can cause dose-related nephrotoxicity, including acute renal failure that becomes more prolonged and severe with repeated courses of the drug. Renal toxicity typically begins during the second week after a dose of Cisplatin Injection. Patients with baseline renal impairment, geriatric patients, patients who are taking other nephrotoxic drugs, or patients who are not well hydrated may be more susceptible to nephrotoxicity
[see Use in Specific Populations ].Ensure adequate hydration before, during, and after Cisplatin Injection administration
[see Dosage and Administration ].Measure serum creatinine, blood urea nitrogen, creatinine clearance, and serum electrolytes including magnesium prior to initiating therapy, and as clinically indicated. Consider magnesium supplementation as clinically needed.Consider alternative treatments or reduce the dose of Cisplatin Injection for patients with baseline renal impairment or who develop significant reductions in creatinine clearance during treatment with Cisplatin Injection according to clinical treatment guidelines
[see Dosage and Administration ]. - Nausea and vomiting [see Warnings and Precautions ()]
5.3 Nausea and VomitingCisplatin Injection is a highly emetogenic antineoplastic agent. Premedicate with anti-emetic agents
[see Dosage and Administration ]. Without antiemetic therapy, marked nausea and vomiting occur in almost all patients treated with Cisplatin Injection and may be so severe that the drug must be discontinued. Nausea and vomiting may begin within 1 to 4 hours after treatment and last up to 72 hours. Maximal intensity occurs 48 to 72 hours after administration.Various degrees of vomiting, nausea, and/or anorexia may persist for up to 1 week after treatment. Delayed nausea and vomiting (begins or persists 24 hours or more after chemotherapy) has occurred in patients attaining complete emetic control on the day of Cisplatin Injection therapy. Consider the use of additional anti-emetics following infusion.
- Myelosuppression [see Warnings and Precautions ()]
5.4 MyelosuppressionMyelosuppression suppression occurs in 25% to 30% of patients treated with Cisplatin Injection. Fever and infection have been reported in patients with neutropenia. Potential fatalities due to infection (secondary to myelosuppression) have been reported. Geriatric patients may be more susceptible to myelosuppression
[see Use in Specific Populations ].Perform standard hematologic tests before initiating Cisplatin Injection, before each subsequent course, and as clinically indicated. Closely monitor patients for the development of signs and symptoms of infection during and after treatment with Cisplatin Injection. For patients who develop severe myelosuppression during treatment with Cisplatin Injection, consider dose modifications and manage according to clinical treatment guidelines.
- Hypersensitivity reactions [see Warnings and Precautions ()]
5.5 Hypersensitivity ReactionsCisplatin Injection can cause severe hypersensitivity reactions, including anaphylaxis and death. Manifestations have included facial edema, wheezing, tachycardia, and hypotension. Hypersensitivity reactions have occurred within minutes of administration to patients with prior exposure to Cisplatin Injection.
Monitor patients receiving Cisplatin Injection for possible hypersensitivity reactions. Ensure supportive equipment and medications are available to treat severe hypersensitivity reactions. Severe hypersensitivity reactions require immediate discontinuation of Cisplatin Injection and aggressive therapy. Patients with a history of severe hypersensitivity reactions should not be rechallenged with Cisplatin Injection
[see Contraindications ]. Cross-reactivity between platinum-based antineoplastic agents has been reported. Cases of severe hypersensitivity reactions have recurred after rechallenging patients with a different platinum agent. - Ototoxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (]
5.6 OtotoxicityCisplatin Injection can cause ototoxicity, which is cumulative and may be severe. Consider audiometric and vestibular function monitoring.
Ototoxicity is manifested by tinnitus, hearing loss in the high frequency range (4,000 to 8,000 Hz) and/or decreased ability to hear normal conversational tones. Ototoxicity can occur during or after treatment and can be unilateral or bilateral. Deafness after the initial dose of Cisplatin Injection has been reported. Vestibular toxicity has also been reported.
Ototoxic effects can be more severe and detrimental in pediatric patients, particularly in patients less than 5 years of age. The prevalence of hearing loss in pediatric patients is estimated to be 40-60%. Additional risk factors for ototoxicity include simultaneous cranial irradiation, treatment with other ototoxic drugs and renal impairment. Consider audiometric and vestibular testing in all pediatric patients receiving cisplatin
[see Use in Specific Populations ].Genetic factors (e.g. variants in the thiopurine S-methyltransferase [TPMT] gene) may also contribute to the cisplatin-induced ototoxicity; although this association has not been consistent across populations and study designs.
- Ocular toxicity [see Warnings and Precautions ()]
5.7 Ocular ToxicityOptic neuritis, papilledema, and cortical blindness have been reported in patients receiving standard recommended doses of Cisplatin Injection. Blurred vision and altered color perception have been reported after the use of regimens with higher doses and dose frequencies of Cisplatin Injection. The altered color perception manifests as a loss of color discrimination, particularly in the blue-yellow axis and irregular retinal pigmentation of the macular area on fundoscopic exam. Improvement and/or total recovery usually occurs after discontinuing Cisplatin Injection but can be delayed.
- Secondary malignancies [see Warnings and Precautions ()]
5.8 Secondary MalignanciesThe development of acute leukemia secondary to the use of Cisplatin Injection has been reported. In these reports, Cisplatin Injection was generally given in combination with other leukemogenic agents.
- Injection site reactions [see Warnings and Precautions ()]
5.10 Injection Site ReactionsInjection site reactions can occur during the administration of Cisplatin Injection. Local soft tissue toxicity has been reported following extravasation of Cisplatin Injection. Severity of the local tissue toxicity appears to be related to the concentration of the Cisplatin Injection solution. Infusion of solutions with a Cisplatin Injection concentration greater than 0.5 mg/mL may result in tissue cellulitis, fibrosis, necrosis, pain, edema, and erythema.
Because of the possibility of extravasation, closely monitor the infusion site during drug administration.
Common adverse reactions are nephrotoxicity, peripheral neuropathy, nausea and vomiting myelosuppression, and ototoxicity. The following adverse reactions have been identified from clinical trials or post-marketing surveillance.
The following drug interactions are described in other sections:
- Nephrotoxic drugs [see Warnings and Precautions ()]
5.1 NephrotoxicityCisplatin Injection can cause dose-related nephrotoxicity, including acute renal failure that becomes more prolonged and severe with repeated courses of the drug. Renal toxicity typically begins during the second week after a dose of Cisplatin Injection. Patients with baseline renal impairment, geriatric patients, patients who are taking other nephrotoxic drugs, or patients who are not well hydrated may be more susceptible to nephrotoxicity
[see Use in Specific Populations ].Ensure adequate hydration before, during, and after Cisplatin Injection administration
[see Dosage and Administration ].Measure serum creatinine, blood urea nitrogen, creatinine clearance, and serum electrolytes including magnesium prior to initiating therapy, and as clinically indicated. Consider magnesium supplementation as clinically needed.Consider alternative treatments or reduce the dose of Cisplatin Injection for patients with baseline renal impairment or who develop significant reductions in creatinine clearance during treatment with Cisplatin Injection according to clinical treatment guidelines
[see Dosage and Administration ].Genetic factors (e.g. variants in the thiopurine S-methyltransferase [TPMT] gene) may also contribute to the cisplatin-induced ototoxicity; although this association has not been consistent across populations and study designs.
Cisplatin Injection, a platinum-based drug for intravenous use, is a clear, light yellow sterile aqueous solution. Each mL of Cisplatin Injection contains: 1 mg cisplatin USP, 9 mg sodium chloride, hydrochloric acid and/or sodium hydroxide to adjust pH, and Water for Injection to a final volume of 50 mL or 100 mL. The pH range of Cisplatin Injection is 3.2 to 4.4.
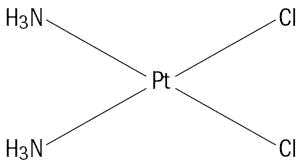
Cisplatin USP, the active ingredient in Cisplatin Injection, is an orange-yellow crystalline powder with the molecular formula Cl2H6N2Pt and a molecular weight of 300.05. Cisplatin, USP is a heavy metal complex containing a central atom of platinum surrounded by two chloride atoms and two ammonia molecules in the cis position. It is soluble in water or saline at 1 mg/mL and in dimethylformamide at 24 mg/mL. It has a melting point of 207°C.
The structural formula is: