Clariscan Prescribing Information
WARNING: RISK ASSOCIATED WITH INTRATHECAL USE and NEPHROGENIC SYSTEMIC FIBROSIS
- Intrathecal administration of gadolinium-based contrast agents (GBCAs) can cause serious adverse reactions including death, coma, encephalopathy, and seizures. Clariscan is not approved for intrathecal use. ()
5.1 Risk Associated with Intrathecal UseIntrathecal administration of GBCAs can cause serious adverse reactions including death, coma, encephalopathy, and seizures. The safety and effectiveness of Clariscan have not been established with intrathecal use. Clariscan is not approved for intrathecal use
[see Dosage and Administration (2.1)]. - GBCAs increase the risk for nephrogenic systemic fibrosis (NSF) among patients with impaired elimination of the drugs. Avoid use of Clariscan in these patients unless the diagnostic information is essential and not available with non-contrasted MRI or other modalities. The risk for NSF appears highest among patients with:
- Chronic, severe kidney disease (GFR < 30 mL/min/1.73 m2), or
- Acute kidney injury.
Screen patients for acute kidney injury and other conditions that may reduce renal function. For patients at risk for chronically reduced renal function (for example, age > 60 years, hypertension or diabetes), estimate the glomerular filtration rate (GFR) through laboratory testing ().5.2 Nephrogenic Systemic FibrosisGBCAs increase the risk for nephrogenic systemic fibrosis (NSF) among patients with impaired elimination of the drugs. Avoid use of Clariscan among these patients unless the diagnostic information is essential and not available with non-contrast MRI or other modalities. The GBCA-associated NSF risk appears highest for patients with chronic, severe kidney disease (GFR < 30 mL/min/1.73 m2) as well as patients with acute kidney injury. The risk appears lower for patients with chronic, moderate kidney disease (GFR 30 to 59 mL/min/1.73 m2) and little, if any, for patients with chronic, mild kidney disease (GFR 60 to 89 mL/min/1.73 m2). NSF may result in fatal or debilitating fibrosis affecting the skin, muscle, and internal organs. Report any diagnosis of NSF following Clariscan administration to GE HealthCare at (1-800-654-0118) or FDA at (1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch).
Screen patients for acute kidney injury and other conditions that may reduce renal function. Features of acute kidney injury consist of rapid (over hours to days), and usually reversible, decrease in kidney function, commonly in the setting of surgery, severe infection, injury or drug-induced kidney toxicity. Serum creatinine levels and estimated GFR may not reliably assess renal function in the setting of acute kidney injury. For patients at risk for chronically reduced renal function (e.g., age > 60 years, diabetes mellitus or chronic hypertension), estimate the GFR through laboratory testing.
The factors that may increase the risk for NSF are repeated or higher than recommended doses of a GBCA, and the degree of renal impairment at the time of exposure. Record the specific GBCA and the dose administered to a patient. For patients at highest risk for NSF, do not exceed the recommended Clariscan dose and allow a sufficient period of time for elimination of the drug prior to re-administration. For patients receiving hemodialysis, physicians may consider the prompt initiation of hemodialysis following the administration of a GBCA in order to enhance the contrast agent's elimination. The usefulness of hemodialysis in the prevention of NSF is unknown
[see Dosage and Administration (2)and Clinical Pharmacology (12)].
Clariscan is a gadolinium-based contrast agent indicated for intravenous use with magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) in brain (intracranial), spine and associated tissues in adult and pediatric patients (including term neonates) to detect and visualize areas with disruption of the blood brain barrier (BBB) and/or abnormal vascularity.
Adult and pediatric patients: The recommended dose of Clariscan is 0.2 mL/kg (0.1 mmol/kg) body weight administered as an intravenous bolus injection at a flow rate of approximately 2 mL/second for adults and 1 to 2 mL/second for pediatric patients (including term neonates). The dose is delivered by manual or power injection. (
Adult and pediatric patients: The recommended dose of Clariscan is 0.2 mL/kg (0.1 mmol/kg) body weight administered as an intravenous bolus injection at a flow rate of approximately 2 mL/second for adults and 1 to 2 mL/second for pediatric patients (including term neonates). The dose is delivered by manual or power injection.
For adult and pediatric patients (including term neonates), the recommended dose of Clariscan is 0.2 mL/kg (0.1 mmol/kg) body weight administered as an intravenous bolus injection, manually or by power injector, at a flow rate of approximately 2 mL/second for adults and 1 to 2 mL/second for pediatric patients. Table 1 provides weight-adjusted dose volumes.
| Body Weight | Volume | |
|---|---|---|
| Pounds (lb) | Kilograms (kg) | Milliliters (mL) |
| 5.5 | 2.5 | 0.5 |
| 11 | 5 | 1 |
| 22 | 10 | 2 |
| 44 | 20 | 4 |
| 66 | 30 | 6 |
| 88 | 40 | 8 |
| 110 | 50 | 10 |
| 132 | 60 | 12 |
| 154 | 70 | 14 |
| 176 | 80 | 16 |
| 198 | 90 | 18 |
| 220 | 100 | 20 |
| 242 | 110 | 22 |
| 264 | 120 | 24 |
| 286 | 130 | 26 |
| 308 | 140 | 28 |
| 330 | 150 | 30 |
To ensure complete injection of Clariscan, the injection may be followed by normal saline flush. Contrast MRI can begin immediately following Clariscan injection.
- Visually inspect Clariscan for particulate matter prior to administration. Do not use the solution if particulate matter is present or if the container appears damaged. Clariscan should be a clear, colorless to yellow solution.
- Do not mix with other drugs or parenteral nutrition.
- Discard any unused portions of the drug.
Aseptically draw up the contrast medium into a disposable syringe and use immediately.
Plastic pre-filled syringe:
1) Holding the syringe vertically so the tip cap is pointed upward, aseptically remove the tip cap from the tip of the syringe and attach either a sterile, disposable needle or compatible needleless luer lock tubing set using a push- twist action. At this point, the tubing set is not attached to a patient's intravenous connection.- If using a needleless luer lock tubing set, check the connection between the syringe and the tubing as the fluid flows. Ensure that the connection is successful before administration of Clariscan Injection.
- If using a needle, hold the syringe vertically and push plunger forward until all of the air is evacuated and fluid either appears at the tip of the needle or the tubing is filled. Following the usual venous blood aspiration procedure, complete the Clariscan injection.
2) To ensure complete delivery of the contrast medium, the injection may be followed by a normal saline flush.3) Properly dispose of the syringe and any other materials used.
Plastic pre-filled syringe
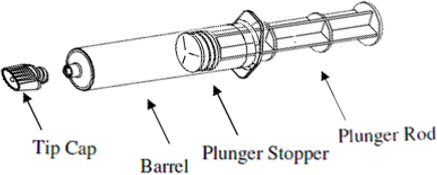

Clariscan 0.5 mmol/mL is a sterile, clear, colorless to yellow, aqueous solution for intravenous injection containing 376.9 mg/mL gadoterate meglumine and is available in vials and pre-filled syringes.
Pregnancy: Use only if imaging is essential during pregnancy and cannot be delayed. (
GBCAs cross the human placenta and result in fetal exposure and gadolinium retention. The human data on the association between GBCAs and adverse fetal outcomes are limited and inconclusive
The estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population(s) are unknown. All pregnancies have a background risk of birth defect, loss, or other adverse outcomes. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2 to 4% and 15 to 20%, respectively.
Human Data
Contrast enhancement is visualized in the placenta and fetal tissues after maternal GBCA administration.
Cohort studies and case reports on exposure to GBCAs during pregnancy have not reported a clear association between GBCAs and adverse effects in the exposed neonates. However, a retrospective cohort study, comparing pregnant women who had a GBCA MRI to pregnant women who did not have an MRI, reported a higher occurrence of stillbirths and neonatal deaths in the group receiving GBCA MRI. Limitations of this study include a lack of comparison with non-contrast MRI and lack of information about the material indication for MRI. Overall, these data preclude a reliable evaluation of the potential risk of adverse fetal outcomes with the use of GBCAs in pregnancy.
Animal Data
GBCAs administered to pregnant non-human primates (0.1 mmol/kg on gestational days 85 and 135) result in measurable gadolinium concentration in the offspring in bone, brain, skin, liver, kidney, and spleen for at least 7 months. GBCAs administered to pregnant mice (2 mmol/kg daily on gestational days 16 through 19) result in measurable gadolinium concentrations in the pups in bone, brain, kidney, liver, blood, muscle, and spleen at one-month postnatal age.
Gadoterate meglumine was administered in intravenous doses of 0, 2, 4 and 10 mmol/kg/day [3, 7 and 16 times the recommended human dose (RHD) based on body surface area (BSA)] to female rats for 14 days before mating, throughout the mating period and until gestation day (GD) 17. Pregnant rabbits were administered gadoterate meglumine in intravenous doses of 0, 1, 3 and 7 mmol/kg/day (3, 10 and 23 times the RHD based on BSA) from GD6 to GD19. No effects on embryo-fetal development were observed at doses up to 10 mmol/kg/day in rats and 3 mmol/kg/day in rabbits. Maternal toxicity was observed in rats at 10 mmol/kg/day and in rabbits at 7 mmol/kg/day. This maternal toxicity was characterized in rats by a slightly lower litter size and gravid uterus weight compared to the control group, and in rabbits by a reduction in body weight and food consumption.
History of clinically important hypersensitivity reactions to Clariscan
Anaphylactic and anaphylactoid reactions have been reported with gadoterate meglumine, involving cardiovascular, respiratory, and/or cutaneous manifestations. Some patients experienced circulatory collapse and died. In most cases, initial symptoms occurred within minutes of gadoterate meglumine administration and resolved with prompt emergency treatment
- Before Clariscan administration, assess all patients for any history of a reaction to contrast media, bronchial asthma and/or allergic disorders. These patients may have an increased risk for a hypersensitivity reaction to Clariscan.
- Administer Clariscan only in situations where trained personnel and therapies are promptly available for the treatment of hypersensitivity reactions, including personnel trained in resuscitation.
- During and following Clariscan administration, observe patients for signs and symptoms of hypersensitivity reactions.